全文HTML
--> --> --> 厌氧氨氧化反应是厌氧氨氧化菌在厌氧或缺氧条件下,利用CO2或H2CO3等无机碳源,以与所有污水处理工艺一样,厌氧氨氧化属于复杂的生化反应过程,具有非线性、时变性和大时滞的特点[5],难以建立精确的数学模型。目前,用于水质预测的数学模型主要有多元线性回归模型、灰色预测模型、支持向量机、神经网络模型等。多元线性回归模型因其算法精度低、智能化程度弱,达不到很好的预测效果[6];灰色预测模型因其不考虑系统的内在机理,在作较长时间预测时往往精度不高[7];虽然支持向量机模型算法在处理小样本预测方面较有优势,但基于小样本的学习随机性较强,易忽略数据样本的关键信息,且模型运行时间较神经网络长[8]。有研究[9-11]表明,BP神经网络是解决非线性、大时变系统的分析、预测及建模问题的有效工具,具有智能化程度高、仿真能力强的优势,但也存在易收敛至局部极值点的缺陷,须辅助其他优化模型以改善其性能。常用的解决方法是对神经网络模型各层之间的权重和阈值进行优化,如BAGHERI等[12]利用遗传算法(genetic algorithm,GA)优化人工神经网络,对神经网络的权值、阈值所组成的种群随机搜索并进行选择、交叉、变异等数值计算,成功实现了对活性污泥膨胀的预测。但GA计算复杂,容易陷入“早熟”,近年来,粒子群算法(particle swarm optimization,PSO)因其算法简单、参数少、求解速度快、通用性强等优点而备受人们关注。粒子群中的每一个粒子都代表一个问题的可能解,通过粒子个体的简单行为、群体内的信息交互可实现问题的求解,常用于智能系统模型的优化。但PSO也存在着搜索精度较低、后期迭代效率不高等不足[13]。
厌氧氨氧化工艺的优势在于其较高的脱氮效率,总氮去除率是评判工艺水平和运行水平的重要指标之一[14]。为确定厌氧氨氧化工艺工程应用的关键运行控制参数,本研究以SBBR单级自养脱氮厌氧氨氧化工艺系统为研究对象,以出水总氮去除率为目标,建立了基于BP神经网络的多级预测模型。其中:一级模型通过灰色关联度分析,对影响出水总氮去除率的关键性指标进行了预测;二级模型在基于一级模型上增加数据维度,并通过改进粒子群算法优化人工神经网络、借鉴遗传算法变异的思想扩大搜索范围,提高出水总氮去除率的预测精度。通过模型预测和结果分析,明确了厌氧氨化工艺系统运行的关键控制参数,为工艺过程的优化与进一步工程应用提供参考。
1.1. 实验装置
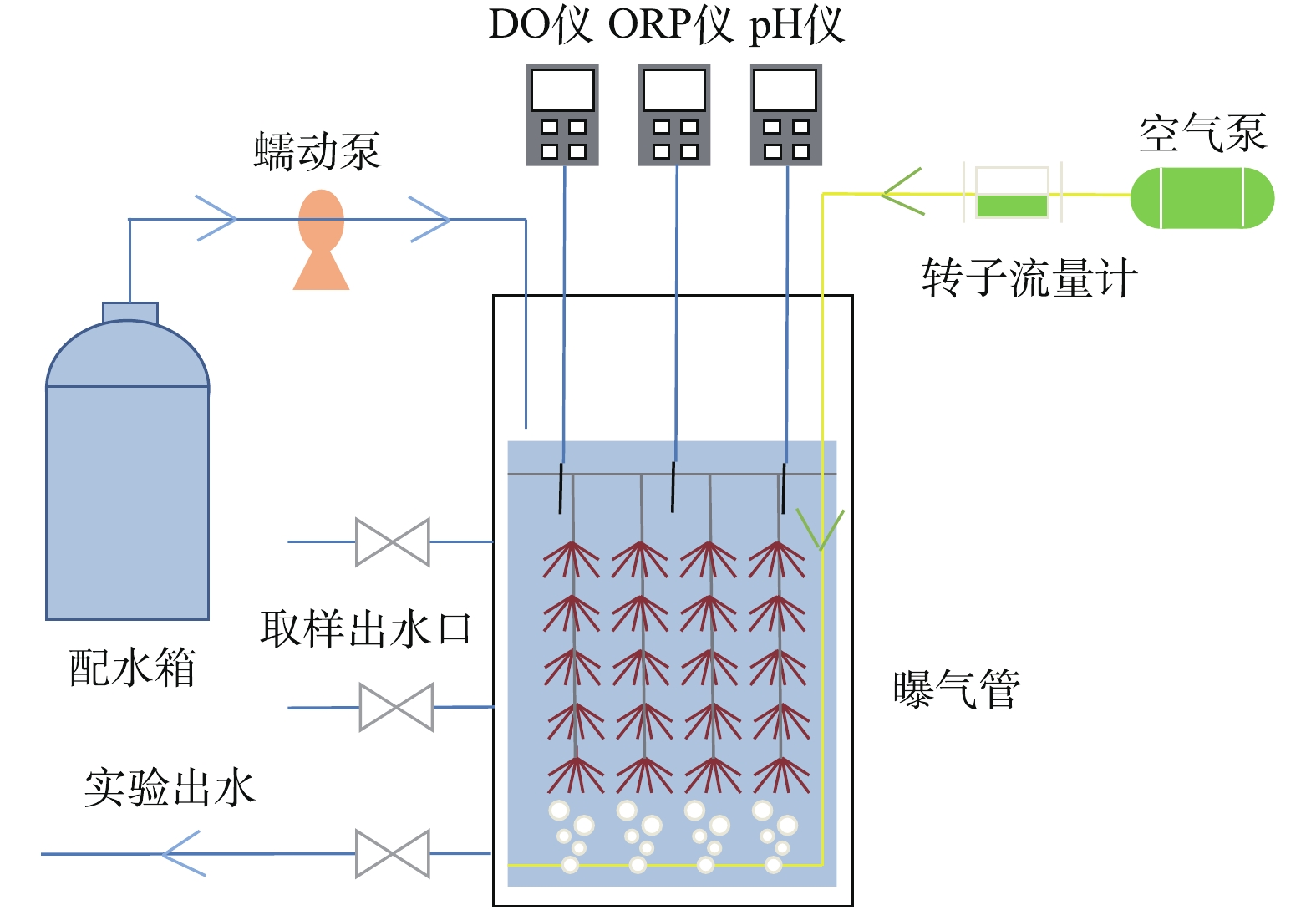
实验采用的工艺装置由SBBR及其附属的水箱、蠕动泵、空气泵、转子流量计及在线检测仪表组成,如图1所示。其中,SBBR是由树脂不透光材料制成的圆柱形反应器,内径 20 cm、高度50 cm,有效容积为10 L,内填充组合材料,以适应微生物的附着和生长,填充比为50%。1.2. 人工合成污水
实验采用人工合成污水,通过向自来水中投加适量NH4HCO3以配制不同氨氮浓度的进水。水中其他组分如下:葡萄糖适量;KH2PO4为25 mg·L?1;FeSO4为6.25 mg·L?1;MgSO4·7H2O为100 mg·L?1;CaCl2为150 mg·L?1;EDTA为25 mg·L?1;pH为7.8±0.2。考虑到微生物生长需要,配水中添加了微量元素。1.3. 实验方法及构建过程
接种污泥采用污水厂脱水剩余污泥,通过设置不同的换水比 0.5、0.25、0.12,实现反应器在不同进水氮负荷(分别为 0.2、0.1、0.05 kg·(m3·d)?1)条件下的构建与运行。反应器通过蠕动泵控制进水,电磁阀控制出水,通过空气泵及转子流量计调节系统中的溶解氧含量,并配备加热棒以维持反应器温度。反应周期为12 h,采用序批式运行方式,具体运行工况为进水→曝气→排水。实验过程中,每天收集反应器进、出水水样,并测定水质指标。反应器配备DO仪、pH仪及ORP仪,随时监测运行状况。在系统构建过程中,前5~7 d为适应期,污泥中的微生物逐渐恢复活性;之后系统内出现亚氮积累现象,氨氮去除率上升,而总氮去除率保持稳定,即系统发生了短程硝化作用;通过调节曝气量控制出水,60 d后,亚氮积累现象消失,出水亚氮浓度明显下降,总氮去除率升高,推测此时系统内总氮的损失原因在于厌氧氨氧化菌的富集;68 d后,系统出水趋于稳定,硝氮为主要的出水氮形态;90 d后,系统稳定运行。研究采用16S rRNA序列分析测试方法对所构建的系统中微生物群落特征进行了探讨分析。16S rRNA分析测试按样品的选取、Illumina平台测序、样品的检测分析3个步骤进行,分析结果显示,在属水平上样品中存在优势微生物主要包括:Anaerolineaceae_uncultured、Haliangium、Bacillus、Bdellovibrio、Caldilineaceae_uncultured、Ignavibacterium、Lactococcus、Nitrosomonas、TK10_norank、Candidatus Brocadia,分别占样品总序列数的7.4%、0.4%、0.6%、0.2%、1.0%、4.3%、3.6%、5.2%、3.2%和22.3%。系统中Nitrosomonas属于亚硝化菌,负责将氨氮转化为亚氮供厌氧氨氧化菌等利用;分析表明,厌氧氨氧化菌Candidatus Brocadia属在系统中占绝对优势,表明系统构建成功。2.1. 数据采集与处理
实验装置构建完成后,反应器稳定运行。通过改变进水条件进行实验和数据采集,每组数据包含温度、溶解氧、进水氨氮、出水氨氮、出水亚氮、出水硝氮等6个参数,并计算总氮去除率。剔除异常数据后部分实验数据如表1所示。为避免各维数据之间数量级差异带来的误差,数据采集完成后需要对实验数据进行归一化处理。2.2. 一级预测模型
1)预测变量的选取。为确定预测变量,首先计算各影响因素对出水总氮去除率的灰色关联度[18]。灰色关联度分析方法根据序列曲线几何形状的相似度来判断其关联程度的大小,曲线越相似,相应序列的关联度就越大,反之则越小。首先,对数据进行处理,设处理后的参考序列X0={x0(k),k=1,2,···,n},比较序列Xi={xi(k),k=1,2,···,n},一般选择因变量为参考序列,自变量为比较序列;按式(1)计算X0与Xi在k点的关联系数值。式中:ηi(k)为比较序列与参考序列在k点的关联系数值;ρ为分辨系数,ρ越小,分辨力越大,本研究取值为0.2;
最后,通过求比较序列与参考序列的关联系数的均值,来定量描述两者的关联度,如式(2)所示。
式中:λi为比较序列与参考序列之间的关联度值,n为影响因素数量。
比较序列与参考序列的关联度计算结果如下:进水氨氮为0.356 5,溶解氧为0.474 9,温度为0.472 9,出水氨氮为0.434 4,出水硝氮为0.477 0,出水亚氮为0.477 8。出水亚氮浓度是关联度最大的因素,是厌氧氨氧化反应的关键性指标。如果预测模型存在易被忽略的环境因素将使得模型存在系统性误差。出水亚氮浓度带有反应过程环境因素的影响成分[19],将出其作为出水总氮去除率预测模型的输入变量可避免此类误差的产生。
DECANETE等[20]和LACKNER等[21]的研究结果也表明,亚氮是厌氧氨氧化工艺必要的底物,但其过高的浓度也会对反应产生消极影响。为此,研究将出水亚氮浓度作为一级预测模型的预测变量。
2) BP神经网络模型。BP神经网络是一种多层前馈网络,由输入层、隐含层和输出层组成。BP神经网络的主要特点是信号前向传递,误差反向传播,并以均方误差最小化为目标,通过不断修改网络的权值和阈值达到拟合非线性、不确定性数学模型的目的,被证明是解决非线性、大时变系统的分析、预测、控制与建模问题的有效工具。本研究设计的一级预测模型拓扑结构为3-11-1。其输入变量为进水氨氮、溶解氧、温度,输出变量为出水亚氮浓度。通过试凑法确定隐含层神经元个数为11。
2.3. 二级预测模型
二级预测模型仍采用BP神经网络,输入变量升维为4个,即进水氨氮、溶解氧含量、温度以及一级预测模型的输出变量出水亚氮,输出变量为出水总氮去除率。同样采用试凑法确定隐含层神经元个数为11个,构成拓扑结构为4-11-1的神经网络。多级神经网络模型结构如图2所示。由于二级预测模型是对系统总氮去除率进行预测,提高预测精度是二级预测模型设计应考虑的关键要素。为避免BP网络易收敛至局部极值造成的预测误差,研究了采用改进的PSO算法改善网络的性能。
1) PSO算法及改进。假设在一个Z维的搜索空间中,有n个粒子组成的种群X=(X1,X2,···,Xn),其中第i个粒子在Z维搜索空间中的位置表示为一个Z维的向量Xi=[xi1,xi2,···,xiZ]T,同时也是问题的一个潜在解;速度表示为Vi=[Vi1,Vi2,···,ViZ]T,决定了粒子的搜索距离和方向。根据目标函数可计算出每个粒子的位置Xi对应的适应度值,其个体极值为Pi=[Pi1,Pi2,···,PiZ]T,种群的全局极值为Pg=[Pg1,Pg2,···,PgZ]T。
PSO算法[22]在每一次迭代过程中,粒子通过个体极值和全局极值更新自身的速度和位置,如式(3)和式(4)所示。
式中:ω为惯性权重;c1和c2为非负的常数,称为学习因子;r1和r2为分布于[0,1]之间的随机数;Vizk为迭代k次时粒子的速度;Xizk为迭代k次时粒子的位置。为了防止盲目搜索,一般建议限制其位置和速度分别在[?Xmax, Xmax]、[?Vmax, Vmax]区间内。
有研究[22]发现,通过不断更新PSO算法的惯性权重因子、学习因子,以确定其合理值,这样有助于促进粒子的收敛性。为了平衡PSO算法的全局搜索能力和局部改良能力,本研究采用非线性的动态惯性权重,如式(5)所示。
式中:ωmax、ωmin分别为惯性权重因子ω的最大值和最小值;θ为粒子的当前适应度值;θmin为当前所有粒子的适应度最小值,即此刻的全局最优值;θa为当前所有粒子的适应度平均值。
在优化过程中,采用异步变化的方式确定学习因子。在优化初始阶段,通过参数设定,使得粒子具有较大的自我学习能力和较小的社会学习能力,加强全局搜索能力;在优化后期,粒子具有较大的社会学习能力和较小的自我学习能力,有利于收敛至全局最优解,其更新公式如式(6)和式(7)所示。
式中:c1,ini、c2,ini分别为c1、c2的初始值,分别设定为2.5、0.5;c1,fin、c2,fin分别为c1、c2的迭代终值,分别设定为0.5、2.5;t为当前迭代次数;tmax为最大迭代次数。
标准的PSO算法收敛快,具有很强的通用性,但也存在易早熟收敛、搜索精度较低、后期迭代效率不高等缺点。为此,本研究借鉴遗传算法变异的思想,在标准PSO算法中,引入自适应变异操作,即在每一次迭代过程中对某些变量以一定的概率重新初始化,既保证粒子有一定的变异率,又使得其搜索范围不局限于逐渐变小的搜索空间内。
在每一次迭代寻优过程中,都需要计算粒子的适应度值,其适应度函数如式(8)所示。
式中:θ(i)为粒子的适应度值;yjk(i)为训练输出期望值;ojk(i)为训练输出值。
2)改进的PSO-BP预测模型。首先,随机初始化BP神经网络的输入层与隐含层连接权值、隐含层神经元阈值、隐含层与输出层连接权值以及输出层神经元阈值,构成PSO算法中各微粒的位置和速度。其次,采用改进的PSO算法优化微粒的位置和速度,并将满足适应度函数要求的粒子作为最优解输出,从而确定出一个结构、权值、阈值确定的神经网络。然后,运用测量的历史数据训练神经网络,使其误差达到性能要求。训练误差函数如式(9)所示。
式中:Emse为模型训练误差;ui为出水总氮去除率预测值;vi为出水总氮去除率期望值;N为训练样本数量。
最后,将一级预测模型的预测结果与进水氨氮、溶解氧浓度及温度共3个输入变量一同导入改进型PSO-BP神经网络进行计算。多级神经网络预测算法流程图如图3所示。
3.1. 模拟过程
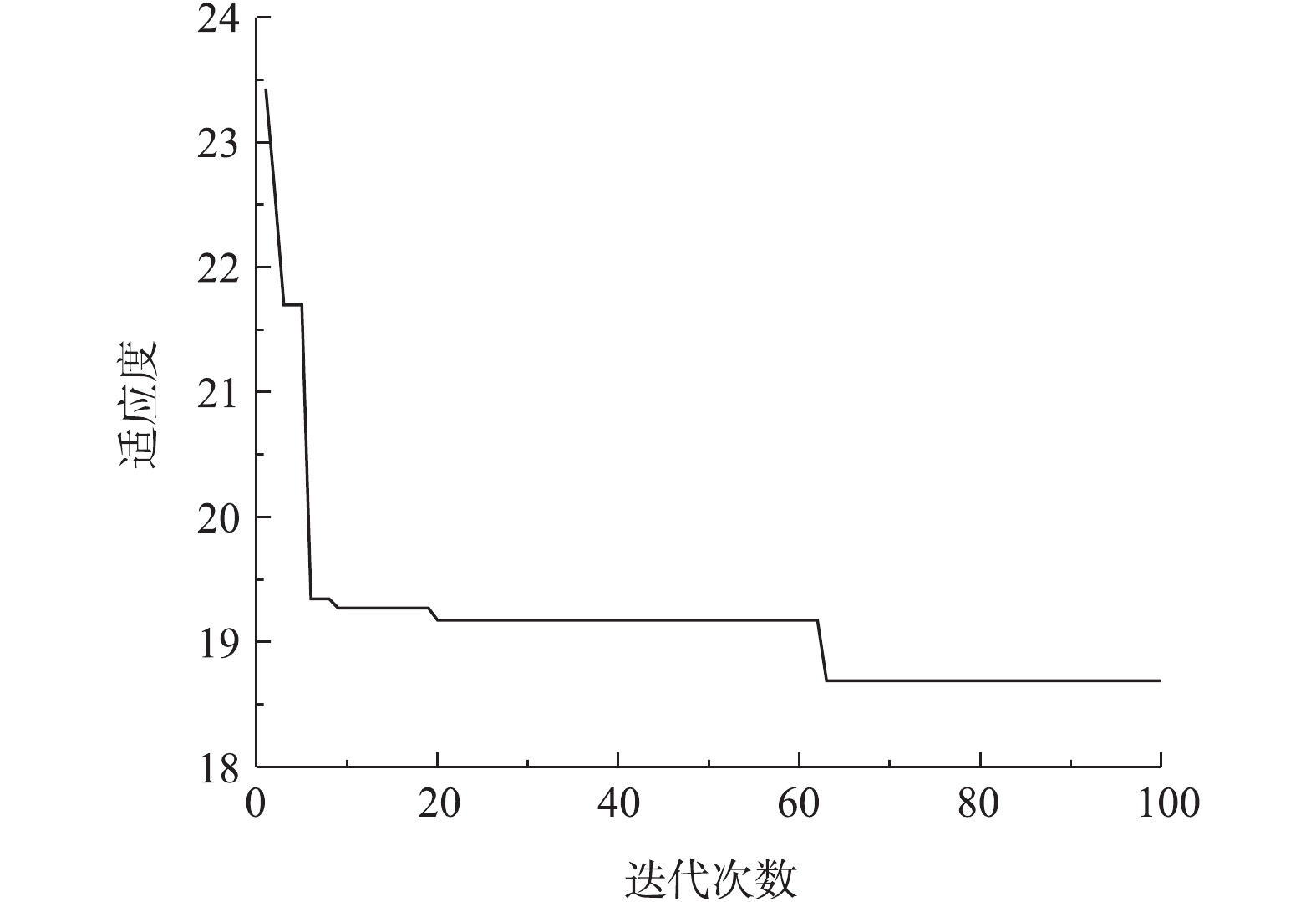
选取实验过程获取的100组数据中的85组用于模型训练,另外15组进行模型预测。模拟平台基于Matlab 2017a,训练误差为0.000 1。二级预测模型中人工神经网络的权值及阈值通过粒子群算法确定,种群粒子数为40,每个粒子的维度为67,算法迭代进化次数为100。改进的PSO算法粒子最优适应度曲线如图4所示,由图4可知,改进算法收敛速度较快,优化精度高。网络性能评价函数包括平均绝对百分比误差Emape、均方根误差Ermse、最大绝对百分比误差Ere,具体计算方法如式(10)、式(11)和式(12)所示。
3.2. 结果与讨论
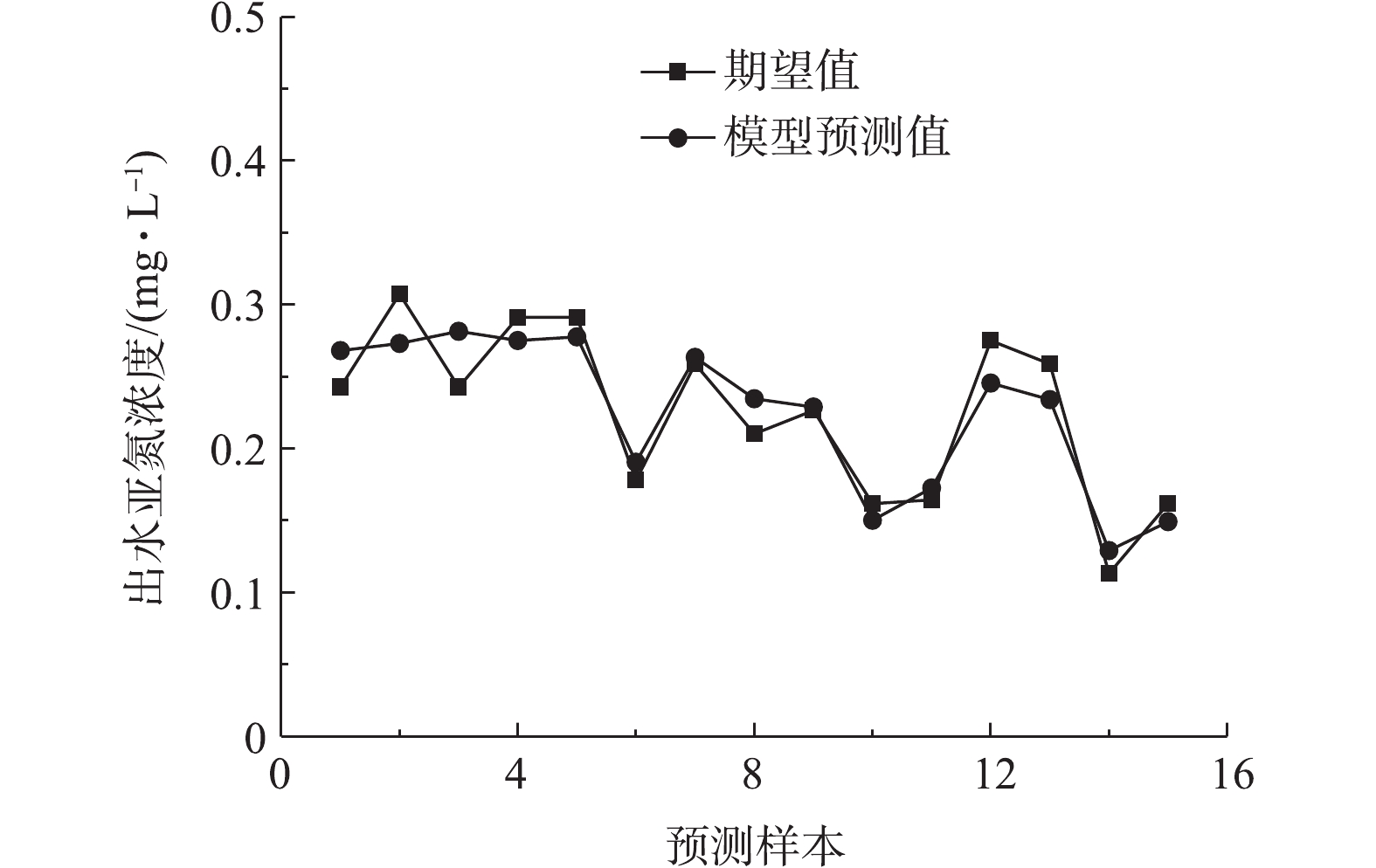
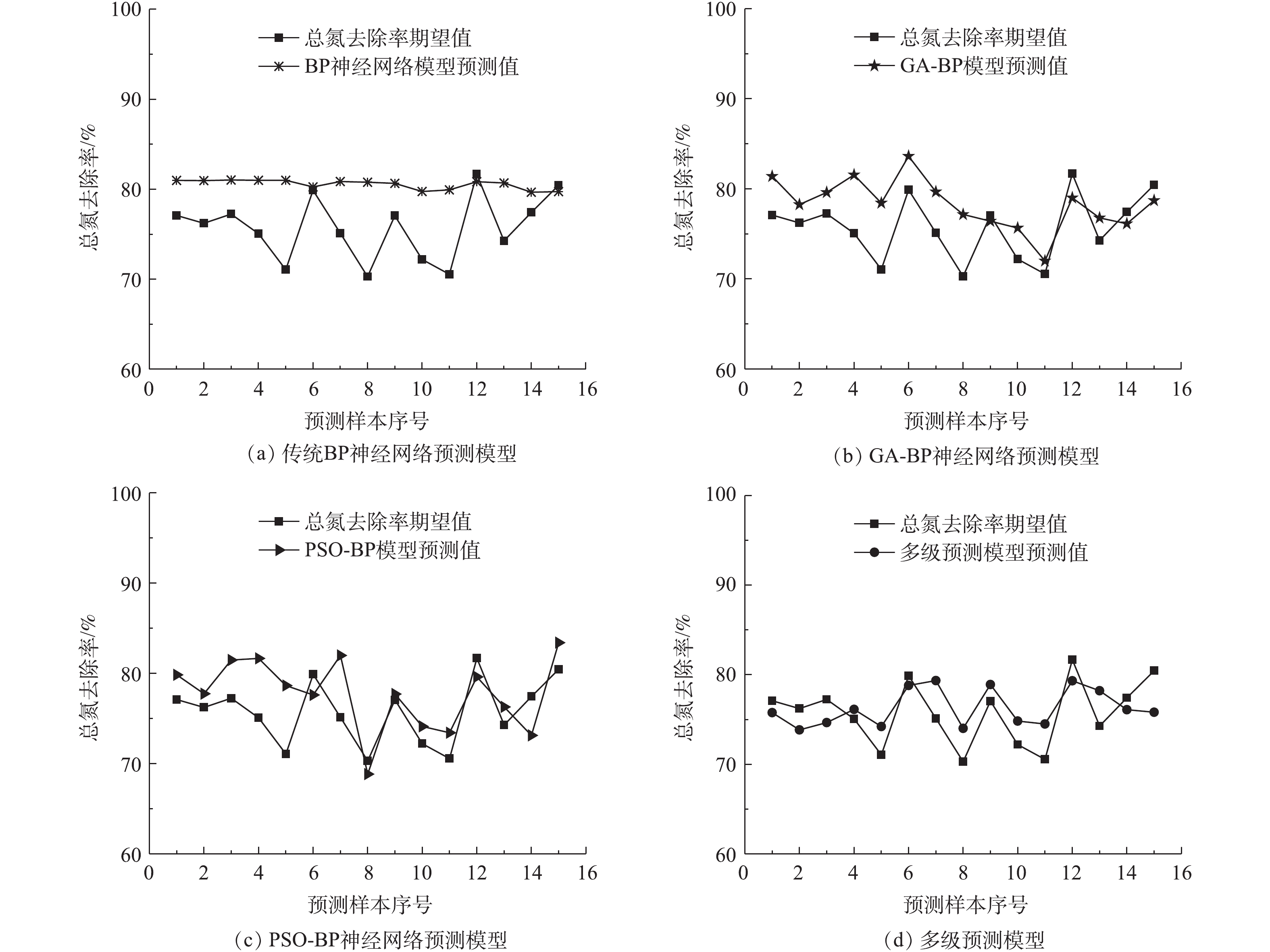
将进水氨氮浓度、溶解氧浓度、温度3个指标导入一级网络模型,得到出水亚氮的预测结果(如图5所示)。最大绝对误差为0.039 mg·L?1,最大相对误差为15.99%,平均相对误差为8.24%。将一级模型预测的出水亚氮浓度同进水氨氮、溶解氧浓度及温度3个参数导入第2级预测模型,对出水总氮去除率进行预测。为验证所提出的多级预测模型精度,本研究将其预测结果与采用传统BP神经网络、遗传算法优化的BP神经网络(GA-BP)以及用标准粒子群算法优化的BP神经网络(PSO-BP)等3个模型的预测结果进行了对比,结果如图6所示。
模型的预测性能误差按式(8)和式(9)计算,得到各模型的性能误差计算结果(如表2所示)。由表2可知,多级预测模型出水总氮去除率的平均相对误差为0.54%,比传统BP神经网络模型、GA-BP模型、PSO-BP模型分别提高6.33%、4.06%和3.89%;预测出水总氮去除率的相对误差为5.76%,均方根误差为1.132?1。预测数据基本与实际值相匹配,说明该模型具有较优的预测精度。
分析发现,本多级神经网络预测模型除采用改进的PSO算法和遗传算法变异的思想以提高第2级神经网络的算法精度外,预测精度得以提高的另一个关键因素在于第1级预测模型对亚氮浓度的预测。对于单级自养脱氮系统的自动控制系统设计而言,一方面对出水亚氮浓度的控制需要通过对曝气量的控制来实现,从氨氮到亚氮的过程,须包含曝气的短程硝化过程,故出水亚氮浓度很大程度上取决于系统曝气量的控制[23];另一方面,系统中的溶解氧浓度影响厌氧氨氧化菌的生长[21],曝气量是此系统实现厌氧氨氧化工艺自动控制的关键控制参数。因此,通过控制工艺系统的曝气量调节系统的出水亚氮浓度,进而保证工艺反应的稳定进行,是实现厌氧氨氧化工艺工程应用的有效控制方式。
2)二级预测模型采用改进的PSO算法,通过不断更新PSO算法的惯性权重因子、学习因子优化神经网络以提高算法的精度,并借鉴遗传算法中变异的思想扩大搜索范围。预测结果显示,多级预测模型预测总氮去除率平均相对误差为0.54%,比传统BP神经网络模型、GA-BP模型、PSO-BP模型分别提高6.33%、4.06%和3.89%;相对误差为5.76%,均方根误差为1.132?1。预测数据基本上与实际值相匹配,说明多级预测模型具有较优的预测精度。
3) 控制反应过程中亚氮浓度是提高厌氧氨氧化工艺总氮去除率的关键因素之一,曝气量是厌氧氨氧化工艺的关键控制参数。因此通过控制工艺系统的曝气量调节出水亚氮浓度,是保证工艺反应的稳定和实现厌氧氨氧化工艺工程应用的有效控制方式。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 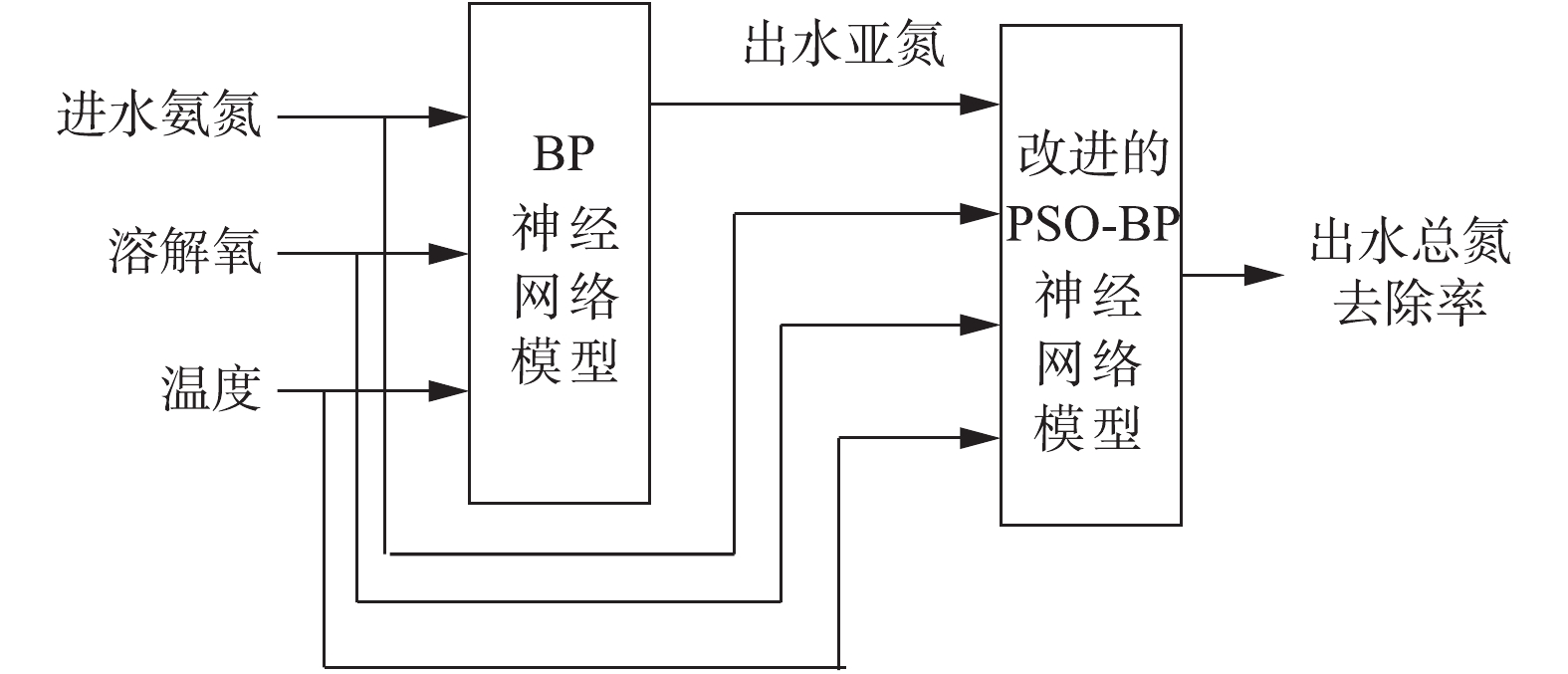

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图