 ), 符植煜1
), 符植煜1 1 北京师范大学心理学部
2 应用实验心理北京市重点实验室, 北京 100875
收稿日期:2017-08-10出版日期:2018-07-15发布日期:2018-05-29基金资助:* 北京市教育科学“十二五”规划青年专项课题资助(CBA15048)Using game log-file to predict students' reasoning ability and mathematical achievement: An application of machine learning
SUN Xin1, LI Jian1,2( ), FU Zhiyu1
), FU Zhiyu1 1 Faculty of Psychology, Beijing Normal University
2 Beijing Key Lab of Applied Experimental Psychology, Beijing 100875, China
Received:2017-08-10Online:2018-07-15Published:2018-05-29摘要/Abstract
摘要: 以360名初中生为被试, 使用推箱子游戏, 结合游戏日志文件(log-file)和机器学习技术预测学生的推理能力和数学成绩。预测变量是从推箱子的过程数据中提取的一系列特征指标, 结果变量是瑞文推理测验成绩和数学成绩, 且均以25%为高低分组的临界值转换为二分变量。结果发现, 训练的模型预测推理能力最高能获得76.11%的查准率、65.72%的精确率、63.10%的查全率以及65.01%的F1得分; 预测数学成绩最高能获得83.07%的查准率、73.70%的精确率、73.33%的查全率以及75.57%的F1得分。研究结果说明, 机器学习建立的区分模型具有较好的预测效果, 利用log-file所记录的游戏过程数据可以对个体的能力进行有效预测。
图/表 6
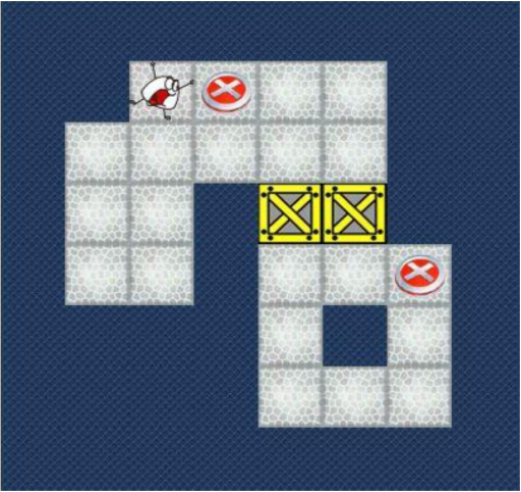
图1推箱子游戏界面截图
 图1推箱子游戏界面截图
图1推箱子游戏界面截图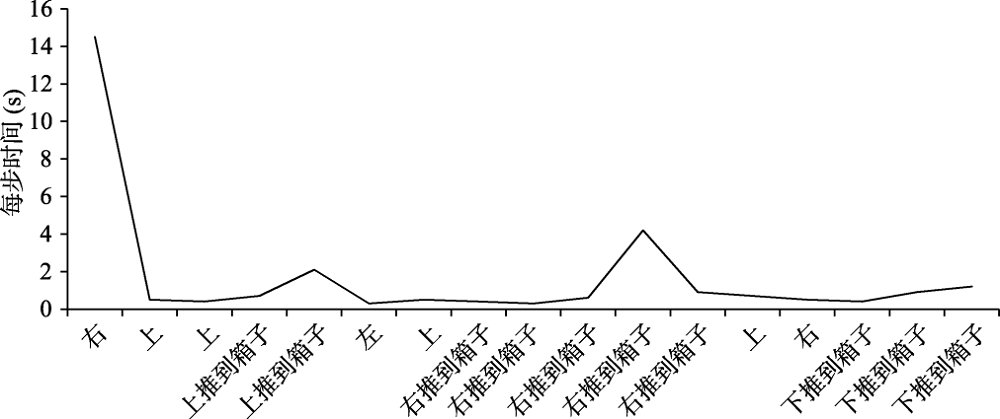
图2一个典型的行动过程
 图2一个典型的行动过程
图2一个典型的行动过程表1特征的描述统计结果
| 特征 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 最小值 | 最大值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 失败组 | ||||
| 第一步用时/平均执行时间 | 22.71 | 24.26 | 2.52 | 198.34 |
| ln (第一步用时/平均执行时间) | 2.31 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 4.97 |
| 完成箱子的比例 | 0.33 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.57 |
| 第一步用时/总时间 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.76 |
| ln (第一步用时/总时间) | -1.92 | 0.60 | -3.31 | -0.29 |
| 思考步数占比 | -2.39 | 0.23 | -3.04 | -1.69 |
| 平均执行时间 | 0.64 | 0.15 | 0.37 | 1.33 |
| 执行间波动 | 2.15 | 1.20 | 0.35 | 10.52 |
| 重复步数占比 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.20 |
| 与最优步数相差 | -5.75 | 9.45 | -23.36 | 65.78 |
| 与最优路径重合步数占比 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.32 |
| 成功组 | ||||
| 第一步用时/平均执行时间 | 24.36 | 23.81 | 2.65 | 168.97 |
| ln (第一步用时/平均执行时间) | 2.49 | 0.78 | 0.92 | 4.95 |
| 第一步用时/总时间 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.77 |
| ln (第一步用时/总时间) | -1.77 | 0.61 | -3.18 | -0.27 |
| 思考步数占比 | -2.61 | 0.27 | -3.53 | -1.64 |
| 平均执行时间 | 0.48 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 1.18 |
| 执行间波动 | 1.17 | 0.76 | 0.20 | 5.43 |
| 重复步数占比 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.16 |
| 与最优步数相差 | 7.65 | 5.45 | 0.00 | 52.67 |
| 与最优路径重合步数占比 | 0.71 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 1.06 |
表1特征的描述统计结果
| 特征 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 最小值 | 最大值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 失败组 | ||||
| 第一步用时/平均执行时间 | 22.71 | 24.26 | 2.52 | 198.34 |
| ln (第一步用时/平均执行时间) | 2.31 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 4.97 |
| 完成箱子的比例 | 0.33 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.57 |
| 第一步用时/总时间 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.76 |
| ln (第一步用时/总时间) | -1.92 | 0.60 | -3.31 | -0.29 |
| 思考步数占比 | -2.39 | 0.23 | -3.04 | -1.69 |
| 平均执行时间 | 0.64 | 0.15 | 0.37 | 1.33 |
| 执行间波动 | 2.15 | 1.20 | 0.35 | 10.52 |
| 重复步数占比 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.20 |
| 与最优步数相差 | -5.75 | 9.45 | -23.36 | 65.78 |
| 与最优路径重合步数占比 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.32 |
| 成功组 | ||||
| 第一步用时/平均执行时间 | 24.36 | 23.81 | 2.65 | 168.97 |
| ln (第一步用时/平均执行时间) | 2.49 | 0.78 | 0.92 | 4.95 |
| 第一步用时/总时间 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.77 |
| ln (第一步用时/总时间) | -1.77 | 0.61 | -3.18 | -0.27 |
| 思考步数占比 | -2.61 | 0.27 | -3.53 | -1.64 |
| 平均执行时间 | 0.48 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 1.18 |
| 执行间波动 | 1.17 | 0.76 | 0.20 | 5.43 |
| 重复步数占比 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.16 |
| 与最优步数相差 | 7.65 | 5.45 | 0.00 | 52.67 |
| 与最优路径重合步数占比 | 0.71 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 1.06 |
表2分类表现评估表
| 表现类型 | 预测为阳性 | 预测为阴性 |
|---|---|---|
| 实际为阳性 | TP | FN |
| 实际为阴性 | FP | TN |
表2分类表现评估表
| 表现类型 | 预测为阳性 | 预测为阴性 |
|---|---|---|
| 实际为阳性 | TP | FN |
| 实际为阴性 | FP | TN |
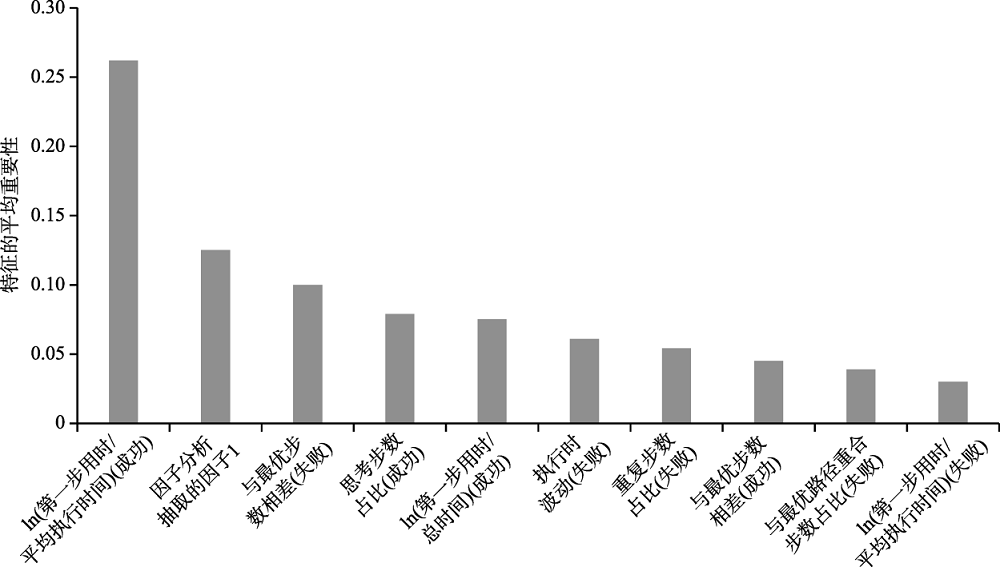
图3数学成绩预测模型中平均重要性排列前十位的特征
 图3数学成绩预测模型中平均重要性排列前十位的特征
图3数学成绩预测模型中平均重要性排列前十位的特征表3模型预测结果
| 最优化目标 | F1 | 查准率 | 查全率 | 精确率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 推理能力 | ||||
| F1优先 | 68.83% | 74.40% | 61.19% | 63.46% |
| 查准率优先 | 63.72% | 75.51% | 59.17% | 65.03% |
| 查全率优先 | 65.01% | 74.91% | 63.10% | 64.21% |
| 精确率优先 | 64.22% | 76.11% | 59.05% | 65.72% |
| 数学成绩 | ||||
| F1优先 | 71.14% | 79.35% | 71.11% | 68.02% |
| 查准率优先 | 75.57% | 83.07% | 73.33% | 73.70% |
| 查全率优先 | 73.09% | 81.06% | 71.78% | 70.62% |
| 精确率优先 | 71.65% | 80.19% | 69.67% | 69.44% |
表3模型预测结果
| 最优化目标 | F1 | 查准率 | 查全率 | 精确率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 推理能力 | ||||
| F1优先 | 68.83% | 74.40% | 61.19% | 63.46% |
| 查准率优先 | 63.72% | 75.51% | 59.17% | 65.03% |
| 查全率优先 | 65.01% | 74.91% | 63.10% | 64.21% |
| 精确率优先 | 64.22% | 76.11% | 59.05% | 65.72% |
| 数学成绩 | ||||
| F1优先 | 71.14% | 79.35% | 71.11% | 68.02% |
| 查准率优先 | 75.57% | 83.07% | 73.33% | 73.70% |
| 查全率优先 | 73.09% | 81.06% | 71.78% | 70.62% |
| 精确率优先 | 71.65% | 80.19% | 69.67% | 69.44% |
参考文献 35
| [1] | Baumert A., Schlösser T., & Schmitt M . ( 2014). Economic games: A performance-based assessment of fairness and altruism. European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 30( 3), 178-192. doi: 10.1027/1015-5759/a000183URL |
| [2] | Berg, W.K., &Byrd D.L . ( 2002). The Tower of London spatial problem-solving task: Enhancing clinical and research implementation. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 24( 5), 586-604. doi: 10.1076/jcen.24.5.586.1006URLpmid: 12187443 |
| [3] | Bors, D.A., &Vigneau F. , ( 2003). The effect of practice on Raven's Advanced Progressive Matrices. Learning and Individual Differences, 13( 4), 291-312. doi: 10.1016/S1041-6080(03)00015-3URL |
| [4] | Breiman, L. ( 2001). Random forests. Machine Learning, 45( 1), 5-32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324URL |
| [5] | Cassady, J.C., &Johnson R.E . ( 2002). Cognitive test anxiety and academic performance. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 27( 2), 270-295. doi: 10.1006/ceps.2001.1094URL |
| [6] | Csapó B., Ainley J., Bennett R. E., Latour T., & Law N . ( 2012). Technological issues for computer-based assessment. In P. Griffin, B. McGaw, & E. Care (Eds.), Assessment and teaching of 21st century skills( pp. 143-230). Dordrecht: Springer. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-2324-5_4URL |
| [7] | DiCerbo, K.E ., & Behrens, J. T .( 2012). Implications of the digital ocean on current and future assessment. In R. W. Lissitz & H. Jiao (Eds.), Computers and their impact on state assessments: Recent history and predictions for the future (pp. 143-306). Charlotte, NC: Information Age Publishing. |
| [8] | Di Giunta L., Alessandri G., Gerbino M., Kanacri P. L., Zuffiano A., & Caprara G. V . ( 2013). The determinants of scholastic achievement: The contribution of personality traits, self-esteem, and academic self-efficacy. Learning and Individual Differences, 27, 102-108. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2013.07.006URL |
| [9] | Duncan G. J., Dowsett C. J., Claessens A., Magnuson K., Huston A. C., Klebanov P., .. Japel C . ( 2007). School readiness and later achievement. Developmental Psychology, 43( 6), 1428-1446. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.43.6.1428URLpmid: 18020822 |
| [10] | Greiff S., Wüstenberg S., & Avvisati F . ( 2015). Computer-generated log-file analyses as a window into students' minds? A showcase study based on the PISA 2012 assessment of problem solving. Computers & Education, 91, 92-105. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2015.10.018URL |
| [11] | Harrington, P . ( 2013). Machine learning in action (R. Li, P. Li, Y. D. Qu, & B. Wang, Trans.). Beijing, China: Posts & Telecom Press. |
| [ Harrington,P. ( 2013). 机器学习实战 (李锐, 李鹏, 曲亚东, 王斌译). 北京: 人民邮电出版社.] | |
| [12] | Hausknecht J. P., Halpert J. A., Di Paolo N. T., & Moriarty Gerrard, M. O. ( 2007). Retesting in selection: A meta- analysis of coaching and practice effects for tests of cognitive ability. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92( 2), 373-385. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.92.2.373URLpmid: 17371085 |
| [13] | Heinzen T. E., Landrum R. E., Gurung R. A.R., & Dunn, D. S. ( 2015). Game-based assessment:The mash-up we've been waiting for. In T. Reiners & L. C. Wood (Eds.), Gamification in education and business (pp. 201-217). Switzerland: Springer International Publishing. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10208-5_11URL |
| [14] | Hembree, R ( 1988). Correlates, causes, effects, and treatment of test anxiety. Review of Educational Research, 58( 1), 47-77. doi: 10.3102/00346543058001047URL |
| [15] | Ikeda M., Iwanaga M., & Seiwa H . ( 1996). Test anxiety and working memory system. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 82( 3), 1223-1231. doi: 10.2466/pms.1996.82.3c.1223URLpmid: 8823887 |
| [16] | Judd L. L., Schettler P. J., & Rush A. J . ( 2016). A brief clinical tool to estimate individual patients’ risk of depressive relapse following remission: Proof of concept. American Journal of Psychiatry, 173( 11), 1140-1146. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2016.15111462URLpmid: 27418380 |
| [17] | Keogh, E ., &French C.C . ( 2001). Test anxiety, evaluative stress, and susceptibility to distraction from threat. European Journal of Personality, 15( 2), 123-141. doi: 10.1002/per.400URL |
| [18] | Kinnunen, R., &Vauras M. , ( 1995). Comprehension monitoring and the level of comprehension in high-and low-achieving primary school children's reading. Learning and Instruction, 5( 2), 143-165. doi: 10.1016/0959-4752(95)00009-RURL |
| [19] | Köstering L., Schmidt C. S. M., Egger K., Amtage F., Peter J., Klöppel S., ..Kaller C. P . ( 2015). Assessment of planning performance in clinical samples: Reliability and validity of the Tower of London task (TOL-F). Neuropsychologia, 75, 646-655. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.07.017URLpmid: 26197091 |
| [20] | Li J., Zhang B., Du H., Zhu Z., & Li Y. M . ( 2015). Metacognitive planning: Development and validation of an online measure. Psychological Assessment, 27( 1), 260-271. doi: 10.1037/pas0000019URLpmid: 25222433 |
| [21] | Moharil B., Gokhale C., Ghadge V., Tambvekar P., Pundlik S., & Rai G . ( 2014). Real time generalized log file management and analysis using pattern matching and dynamic clustering. International Journal of Computer Applications, 91( 16), 1-6. doi: 10.5120/15962-5320URL |
| [22] | Neisser, U. ( 1997). Rising scores on intelligence tests: Test scores are certainly going up all over the world, but whether intelligence itself has risen remains controversial. American Scientist, 85( 5), 440-447. |
| [23] | Pedregosa F., Varoquaux G., Gramfort A., Michel V., Thirion B., Grisel O., .. Duchesnay é . ( 2011). Scikit-learn: Machine learning in python. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12, 2825-2830. |
| [24] | Pressley, M., &Afflerbach P. , ( 1995). Verbal protocols of reading: The nature of constructively responsive reading. Hillsdale, N.J.: Erlbaum. |
| [25] | Raven, J. ( 1989). The raven progressive matrices: A review of national norming studies and ethnic and socioeconomic variation within the united-states. Journal of Educational Measurement, 26( 1), 1-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-3984.1989.tb00314.xURL |
| [26] | Schmidt, F.L . ( 2002). The role of general cognitive ability and job performance: Why there cannot be a debate. Human Performance, 15( 1-2), 187-210. doi: 10.1080/08959285.2002.9668091URL |
| [27] | Sonnleitner P., Brunner M., Greiff S., Funke J., Keller U., Martin R., .. Latour T . ( 2012). The Genetics Lab: Acceptance and psychometric characteristics of a computer- based microworld assessing complex problem solving. Psychological Test and Assessment Modeling, 54( 1), 54-72. |
| [28] | Tan P. N., Steinbach M., & Kumar V . ( 2006). Introduction to data mining . India:Pearson Education. |
| [29] | Tenorio Delgado M., Arango Uribe P., Aparicio Alonso A., & Rosas Díaz R . ( 2016). TENI: A comprehensive battery for cognitive assessment based on games and technology. Child Neuropsychology, 22( 3), 276-291. doi: 10.1080/09297049.2014.977241URLpmid: 25396766 |
| [30] | Veenman M. V. J., Wilhelm P., & Beishuizen J. J . ( 2004). The relation between intellectual and metacognitive skills from a developmental perspective. Learning and Instruction, 14( 1), 89-109. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2003.10.004URL |
| [31] | Veenman M. V. J., Bavelaar L., De Wolf L., &van Haaren, M. G. P. ( 2014). The on-line assessment of metacognitive skills in a computerized learning environment. Learning and Individual Differences, 29, 123-130. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2013.01.003URL |
| [32] | Ventura, M., &Shute V ., ( 2013). The validity of a game-based assessment of persistence. Computers in Human Behavior, 29( 6), 2568-2572. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2013.06.033URL |
| [33] | Wu Y. Y., Kosinski M., & Stillwell D . ( 2015). Computer- based personality judgments are more accurate than those made by humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112( 4), 1036-1040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1418680112URLpmid: 25583507 |
| [34] | Zhang B., Li J., Xu C., & Li Y. M . ( 2014). The developmental differences of problem solving ability between intellectually- gifted and intellectually-average children aged from 11-14 years old. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 46, 1823-1834. |
| [ 张博, 黎坚, 徐楚, 李一茗 . ( 2014). 11~14岁超常儿童与普通儿童问题解决能力的发展比较. 心理学报, 46, 1823-1834.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.01823URL | |
| [35] | Zhang Z., Song Y. F., Cui L. Q., Liu X. Q., & Zhu T. S . ( 2016). Emotion recognition based on customized smart bracelet with built-in accelerometer. PeerJ, 4, e2258. doi: 10.7717/peerj.2258URLpmid: 27547564 |
相关文章 5
| [1] | 章文佩, 沈群伦, 宋锦涛, 周仁来. 基于事件相关电位(ERPs)和机器学习的考试焦虑诊断[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(10): 1116-1127. |
| [2] | 张博;黎坚;徐楚;李一茗. 11~14岁超常儿童与普通儿童问题解决能力的发展比较[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(12): 1823-1834. |
| [3] | 郭晓丽,江光荣,朱旭. 暴力电子游戏的短期脱敏效应:两种接触方式比较[J]. 心理学报, 2009, 41(03): 259-266. |
| [4] | 王有智, 欧阳仑. 汉、回、维、哈、藏、白和锡伯族中学生人格特征与推理能力、学业成就的关系[J]. 心理学报, 2003, 35(增刊): 85-92. |
| [5] | 孙长华,吴振云,吴志平. 瑞文作业的年龄差异及其与“位置法”记忆训练的关系[J]. 心理学报, 1994, 26(1): 59-63. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4220
