 ), 戴月娥, 聂思源, 姚奕, 韩施
), 戴月娥, 聂思源, 姚奕, 韩施 华中师范大学心理学院$\centerdot$社会心理研究中心, 青少年网络心理与行为教育部重点实验室, 武汉 430079
收稿日期:2020-10-10出版日期:2021-11-15发布日期:2021-09-23通讯作者:佐斌E-mail:zuobin@ccnu.edu.cn基金资助:国家社会科学基金后期资助项目(20FSHB003);国家社会科学基金重大项目(18ZDA331);中央高校基本科研业务费(CCNU19ZN021)Implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP): Measuring principle and applications
WEN Fangfang, KE Wenlin, ZUO Bin( ), DAI Yuee, NIE Siyuan, YAO Yi, HAN Shi
), DAI Yuee, NIE Siyuan, YAO Yi, HAN Shi School of Psychology, Research Center of Social Psychology, Central China Normal University, Key Laboratory of Adolescent Cyberpsychology and Behavior, Ministry of Education, Wuhan 430079, China
Received:2020-10-10Online:2021-11-15Published:2021-09-23Contact:ZUO Bin E-mail:zuobin@ccnu.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 内隐关系评估程序(Implicit Relational Assessment Procedure, 简称IRAP)是基于关系结构理论直接测量社会认知、信念或态度的新内隐测量方法, 具备一定的可靠性和有效性, 并与其它相关测量方法的适用性存在一定差异。不同的理论模型为IRAP的不同效应提供了解释。IRAP最初应用于临床诊断性研究, 新近已扩展到自我、社会认知、群体和态度等研究领域。进一步验证不同形式IRAP的信效度、探究IRAP的心理机制及产生的心理效应、在不同领域发挥IRAP的方法优势等将是未来研究的重要方向。
图/表 4

图1典型IRAP和自然语言I RAP试次对比(源自:Kavanagh et al., 2016)
 图1典型IRAP和自然语言I RAP试次对比(源自:Kavanagh et al., 2016)
图1典型IRAP和自然语言I RAP试次对比(源自:Kavanagh et al., 2016)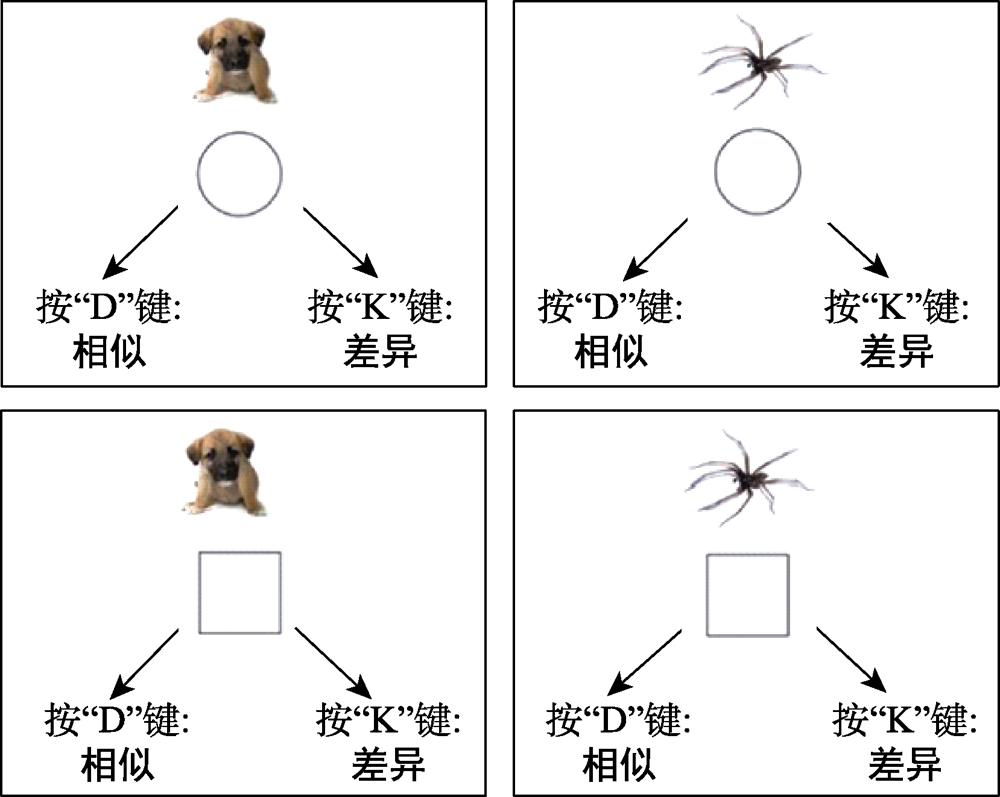
图2四种类型的训练IRAP试次(源自:Leech et al., 2018)
 图2四种类型的训练IRAP试次(源自:Leech et al., 2018)
图2四种类型的训练IRAP试次(源自:Leech et al., 2018)
图3四种类型的改变事项IRAP试次(源自:Inoue et al., 2020)
 图3四种类型的改变事项IRAP试次(源自:Inoue et al., 2020)
图3四种类型的改变事项IRAP试次(源自:Inoue et al., 2020)
图4基于复杂性和衍生性的关系反应类型(源自:Hughes et al., 2012)
 图4基于复杂性和衍生性的关系反应类型(源自:Hughes et al., 2012)
图4基于复杂性和衍生性的关系反应类型(源自:Hughes et al., 2012)参考文献 57
| [1] | 蔡华俭. (2003). Greenwald提出的内隐联想测验介绍. 心理科学进展, 11(3), 339-344. |
| [2] | 陈志霞, 陈剑峰. (2007). 矛盾态度的概念、测量及其相关因素. 心理科学进展, 15(6), 962-967. |
| [3] | 刘伟, 贾玉雪. (2015). 大学生对农民工的内隐矛盾态度. 安顺学院学报, 17(1), 73-75. |
| [4] | 刘文, 毛晶晶, 俞睿玮, 李凤杰. (2014). 青少年恋爱关系内隐倾向发展特点及其与依恋的关系. 心理科学, 37(3), 593-600. |
| [5] | 王沛, 王凯. (2009). 内隐关系评估程序: 内隐态度测量的新方法. 心理科学, 32(3), 669-671. |
| [6] | 温芳芳, 佐斌. (2007). 评价单一态度对象的内隐社会认知测验方法. 心理科学进展, 15(5), 828-833. |
| [7] | 薛曼曼, 郭瞻予. (2017). 测量观点采择的一种新方法: 内隐关系评估程序. 重庆文理学院学报(社会科学版), 36(5), 97-101. |
| [8] | Barbero-Rubio, A., López-López, J. C., Luciano, C., & Eisenbeck, N. (2016). Perspective-taking measured by implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP). Psychological Record, 66(2), 243-252. doi: 10.1007/s40732-016-0166-3URL |
| [9] | Barnes-Holmes, D., Barnes-Holmes, Y., Hayden, E., Milne, R., & Stewart, I. (2006). Do you really know what you believe? Developing the implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP) as a direct measure of implicit beliefs. Holmes, 32. |
| [10] | Barnes-Holmes, D., Barnes-Holmes, Y., Hussey, I., & Luciano, C. (2016). Relational frame theory:Finding its historical and intellectual roots and reflecting upon its future development. In R. Zettle, S. C. Hayes, D. Barnes-Holmes, & T. Biglan (Eds.), Handbook of contextual behavioral science (pp.117-128). Chichester, England: Wiley-Blackwell. |
| [11] | Barnes-Holmes, D., Barnes-Holmes, Y., Luciano, C., & McEnteggart, C. (2017). From the IRAP and REC model to a multi-dimensional multi-level framework for analyzing the dynamics of arbitrarily applicable relational responding. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 6(4), 434-445. doi: 10.1016/j.jcbs.2017.08.001URL |
| [12] | Barnes-Holmes, D., Barnes-Holmes, Y., Stewart, I., & Boles, S. (2010). A sketch of the implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP) and the relational elaboration and coherence (REC) model. Psychological Record, 60(3), 527-541. doi: 10.1007/BF03395726URL |
| [13] | Barnes-Holmes, D., Hayes, S. C., Dymond, S., & O’Hora, D. (2001). Multiple stimulus relations and the transformation of stimulus functions. In S. C. Hayes, D. Barnes-Holmes, & B. Roche (Eds.), Relational frame theory: A post- Skinnerian account of human language and cognition (pp.51-72). New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers. |
| [14] | Barnes-Holmes, D., Murphy, A., Barnes-Holmes, Y., & Stewart, I. (2010). The implicit relational assessment procedure: Exploring the impact of private versus public contexts and the response latency criterion on pro-white and anti-black stereotyping among white Irish individuals. The Psychological Record, 60(1), 57-79. doi: 10.1007/BF03395694URL |
| [15] | Bast, D. F., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2014). A first test of the implicit relational assessment procedure as a measure of forgiveness of self and others. Psychological Record, 64(2), 253-260. doi: 10.1007/s40732-014-0022-2URL |
| [16] | Bast, D. F., Barnes-Holmes, Y., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2015). Developing an individualized implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP) as a potential measure of self-forgiveness related to negative and positive behavior. Psychological Record, 65(4), 717-730. doi: 10.1007/s40732-015-0141-4URL |
| [17] | Cagney, S., Harte, C., Barnes-Holmes, D., Barnes-Holmes, Y., & Mcenteggart, C. (2017). Response biases on the IRAP for adults and adolescents with respect to smokers and nonsmokers: The impact of parental smoking status. Psychological Record, 67(4), 473-483. doi: 10.1007/s40732-017-0249-9URL |
| [18] | Cullen, C., Barnes-Holmes, D., Barnes-Holmes, Y., & Stewart, I. (2009). The implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP) and the malleability of ageist attitudes. Psychological Record, 59(4), 591-620. doi: 10.1007/BF03395683URL |
| [19] | de Houwer, J. (2002). The implicit association test as a tool for studying dysfunctional associations in psychopathology: Strengths and limitations. Journal of Behavior Therapy & Experimental Psychiatry, 33(2), 115-133. |
| [20] | de Houwer, J. (2014). A propositional perspective on context effects in human associative learning. Behavioural Processes, 104(18), 20-25. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2014.02.002URL |
| [21] | de Houwer, J., Heider, N., Spruyt, A., Roets, A., & Hughes, S. (2015). The relational responding task: Toward a new implicit measure of beliefs. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 319-327. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00319pmid: 25852624 |
| [22] | Dodds, P. S., Clark, E. M., Desu, S., Frank, M. R., Reagan, A. J., Williams, J. R., ... Danforth, C. M. (2015). Human language reveals a universal positivity bias. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(8), 2389-2394. |
| [23] | Drake, C. E., Primeaux, S., & Thomas, J. (2017). Comparing implicit gender stereotypes between women and men with the implicit relational assessment procedure. Gender Issues, 35(1), 3-20. doi: 10.1007/s12147-017-9189-6URL |
| [24] | Errasti, J., Martinez, H., Rodriguez, C., Marquez, J., Maldonado, A., & Menendez, A. (2019). Social context in a collective IRAP application about gender stereotypes: Mixed versus single gender groups. The Psychological Record, 69(1), 39-48. doi: 10.1007/s40732-018-0320-1URL |
| [25] | Farrell, L., & McHugh, L. (2020). Exploring the relationship between implicit and explicit gender-STEM bias and behavior among STEM students using the implicit relational assessment procedure. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 15, 142-152. doi: 10.1016/j.jcbs.2019.12.008URL |
| [26] | Finn, M., Barnes-Holmes, D., & Mcenteggart, C. (2018). Exploring the single-trial-type-dominance-effect in the IRAP: Developing a differential arbitrarily applicable relational responding effects (DAARRE) model. Psychological Record, 68(1), 11-25. doi: 10.1007/s40732-017-0262-zURL |
| [27] | Finn, M., Barnes-Holmes, D., Hussey, I., & Graddy, J. (2016). Exploring the behavioral dynamics of the implicit relational assessment procedure: The impact of three types of introductory rules. Psychological Record, 66(2), 309- 321. doi: 10.1007/s40732-016-0173-4URL |
| [28] | Fleming, K., Foody, M., & Murphy, C. (2020). Using the implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP) to examine implicit gender stereotypes in science, technology, engineering and maths (STEM). Psychological Record, 70(3), 459-469. doi: 10.1007/s40732-020-00401-6URL |
| [29] | Hayes, S. C., Barnes-Holmes, D., & Roche, B. (2001). Relational frame theory:A précis. In S. C. Hayes, D., Barnes-Holmes, & B. Roche (Eds.), Relational frame theory: A post-Skinnerian account of human language and cognition (pp.141-154). New York: Kluwer Academic/ Plenum. |
| [30] | Hughes, S., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2011). On the formation and persistence of implicit attitudes: New evidence from the implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP). The Psychological Record, 61(3), 391-410. doi: 10.1007/BF03395768URL |
| [31] | Hughes, S., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2013). Associative concept learning, stimulus equivalence, and relational frame theory: Working out the similarities and differences between human and nonhuman behavior. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 101(1), 156-160. doi: 10.1002/jeab.v101.1URL |
| [32] | Hughes, S., Barnes-Holmes, D., & Vahey, N. (2012). Holding on to our functional roots when exploring new intellectual islands: A voyage through implicit cognition research. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 1(1-2), 17-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jcbs.2012.09.004URL |
| [33] | Hughes, S., Hussey, I., Corrigan, B., Jolie, K., Murphy, C., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2016). Faking revisited: exerting strategic control over performance on the implicit relational assessment procedure. European Journal of Social Psychology, 46(5), 632-648. doi: 10.1002/ejsp.v46.5URL |
| [34] | Hussey, I., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2012). The implicit relational assessment procedure as a measure of implicit depression and the role of psychological flexibility. Cognitive and Behavioral Practice, 19(4), 573-582. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpra.2012.03.002URL |
| [35] | Hussey, I., Barnes-Holmes, D., & Barnes-Holmes, Y. (2015). From relational frame theory to implicit attitudes and back again: Clarifying the link between RFT and IRAP research. Current Opinion in Psychology, 2, 11-15. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2014.12.009URL |
| [36] | Hussey, I., Mhaoileoin, D. N., Barnes-Holmes, D., Ohtsuki, T., Kishita, N., Hughes, S., & Murphy, C. (2016). The IRAP is nonrelative but not acontextual: Changes to the contrast category influence men’s dehumanization of women. Psychological Record, 66(2), 291-299. doi: 10.1007/s40732-016-0171-6URL |
| [37] | Inoue, K., Shima, T., Takahashi, M., Lee, S. K., Ohtsuki, T., & Kumano, H. (2020). Reliability and validity of the implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP) as a measure of change agenda. The Psychological Record, 70(3), 499-513. doi: 10.1007/s40732-020-00416-zURL |
| [38] | Kavanagh, D., Barnes-Holmes, Y., Barnes-Holmes, D., Mcenteggart, C., & Finn, M. (2018). Exploring differential trial-type effects and the impact of a read-aloud procedure on deictic relational responding on the IRAP. Psychological Record, 68(2), 163-176. doi: 10.1007/s40732-018-0276-1URL |
| [39] | Kavanagh, D., Hussey, I., Mcenteggart, C., Barnes-Holmes, Y., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2016). Using the IRAP to explore natural language statements. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 5(4), 247-251. doi: 10.1016/j.jcbs.2016.10.001URL |
| [40] | Leech, A., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2020). Training and testing for a transformation of fear and avoidance functions via combinatorial entailment using the implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP): Further exploratory analyses. Behavioural Processes, 172. |
| [41] | Leech, A., Bouyrden, J., Bruijsten, N., Barnes-Holmes, D., & McEnteggart, C. (2018). Training and testing for a transformation of fear and avoidance functions using the implicit relational assessment procedure: The first study. Behavioural Processes, 157, 24-35. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2018.08.012URL |
| [42] | Lynn, F., & Louise, M. (2017). Examining gender-STEM bias among STEM and non-STEM students using the implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP). Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 6(1), 80-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jcbs.2017.02.001URL |
| [43] | Maloney, E., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2016). Exploring the behavioral dynamics of the implicit relational assessment procedure: The role of relational contextual cues versus relational coherence indicators as response options. The Psychological Record, 66(3), 395-403. doi: 10.1007/s40732-016-0180-5URL |
| [44] | Maloney, E., Foody, M., & Murphy, C. (2020). Do response options in the implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP) matter? A comparison of contextual relations versus relational coherent Indicators. The Psychological Record, 70(6), 205-214. doi: 10.1007/s40732-019-00360-7URL |
| [45] | Mckenna, I. M., Barnes-Holmes, D., Barnes-Holmes, Y., & Stewart, I. (2007). Testing the fake-ability of the implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP): The first study. International Journal of Psychology and Psychological Therapy, 7, 253-268. |
| [46] | Munnelly, A., Farrell, L., O’connor, M., & Mchugh, L. (2018). Adolescents' implicit and explicit attitudes toward cyberbullying: An exploratory study using the implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP) and self-report measures. The Psychological Record, 68(1), 1-10. doi: 10.1007/s40732-017-0261-0URL |
| [47] | Murphy, C., Maccarthaigh, S., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2014). Implicit relational assessment procedure and attractiveness bias: Directionality of bias and influence of gender of participants. International Journal of Psychology & Psychological Therapy, 14(3), 333-351. |
| [48] | O’hora, D., Pelaez, M., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2005). Derived relational responding and performance on verbal subtests of the wais-iii. Psychological Record, 55(1), 155-175. doi: 10.1007/BF03395504URL |
| [49] | O'Shea, B., Watson, D. G., & Brown, G. D. (2016). Measuring implicit attitudes: A positive framing bias flaw in the Implicit Relational Assessment Procedure (IRAP). Psychological Assessment, 28(2), 158-170. doi: 10.1037/pas0000172pmid: 26075407 |
| [50] | Power, P. M., Harte, C., Barnes-Holmes, D., & Barnes- Holmes, Y. (2017). Combining the implicit relational assessment procedure and the recording of event related potentials in the analysis of racial bias: A preliminary study. Psychological Record, 67(4), 499-506. doi: 10.1007/s40732-017-0252-1URL |
| [51] | Remue, J., de Houwer, J., Barnes-Holmes, D., Vanderhasselt, M. A., & de Raedt, R. (2013). Self-esteem revisited: Performance on the implicit relational assessment procedure as a measure of self-versus ideal self-related cognitions in dysphoria. Cognition & Emotion, 27(8), 1441-1449. |
| [52] | Remue, J., Hughes, S., de Houwer, J., & de Raedt, R. (2014). To be or want to be: disentangling the role of actual versus ideal self in implicit self-esteem. Plos One, 9(9), e108837. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108837URL |
| [53] | Scanlon, G., & Barnes-Holmes, Y. (2013). Changing attitudes: Supporting teachers in effectively including students with emotional and behavioural difficulties in mainstream education. Emotional and Behavioural Difficulties, 18(4), 374-395. doi: 10.1080/13632752.2013.769710URL |
| [54] | Stewart, I., Barnes-Holmes, D., & Roche, B. (2004). A functional-analytic model of analogy using the relational evaluation procedure. Psychological Record, 54(4), 531-552. doi: 10.1007/BF03395491URL |
| [55] | Vahey, N. A., Barnes-Holmes, D., Barnes-Holmes, Y., & Stewart, I. (2009). A first test of the implicit relational assessment procedure as a measure of self-esteem: Irish prisoner groups and university students. Psychological Record, 59(3), 371-387. doi: 10.1007/BF03395670URL |
| [56] | Vahey, N. A., Boles, S., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2010). Measuring adolescents? Smoking-related social identity preferences with the implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP) for the first time: A starting point that explains later IRAP evolutions. International Journal of Psychology and Psychological Therapy, 10(3), 453-474. |
| [57] | Vahey, N. A., Nicholson, E., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2015). A meta-analysis of criterion effects for the implicit relational assessment procedure (IRAP) in the clinical domain. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 48, 59-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jbtep.2015.01.004URL |
相关文章 12
| [1] | 贾磊;祝书荣;张常洁;张庆林. 外显与内隐刻板印象的分布式表征及其激活过程——基于认知神经科学视角的探索[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(10): 1519-1533. |
| [2] | 杨紫嫣;刘云芝;余震坤;蔡华俭. 内隐联系测验的应用:国内外研究现状[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(11): 1966-1980. |
| [3] | 潘孝富;王昭静;高飞;徐莹. 辛苦所得与意外所得的非理性消费偏差:基于IAT检测和ERP证据[J]. 心理科学进展, 2014, 22(4): 596-605. |
| [4] | 柏阳;彭凯平;喻丰. 中国人的内隐辩证自我:基于内隐联想测验(IAT)的测量[J]. 心理科学进展, 2014, 22(3): 418-421. |
| [5] | 郝洪达;王詠. 内隐联想测验与消费心理[J]. 心理科学进展, 2013, 21(10): 1865-1873. |
| [6] | 王晓刚;尹天子;黄希庭. 心理疾病内隐污名述评[J]. 心理科学进展, 2012, 20(3): 384-393. |
| [7] | 李西营;王晓丽;赵玉焕;徐青林. 内隐联想测验新变式述评:基于规范性分析框架[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(5): 749-754. |
| [8] | 晋争. 内隐联系测验的修正—— 简式内隐联系测验[J]. 心理科学进展, 2010, 18(10): 1554-1558. |
| [9] | 温芳芳;佐斌. 评价单一态度对象的内隐社会认知测验方法[J]. 心理科学进展, 2007, 15(5): 828-833. |
| [10] | 杜建政;李明. 内隐动机测量的新方法[J]. 心理科学进展, 2007, 15(3): 458-463. |
| [11] | 侯珂,邹泓,张秋凌. 内隐联想测验:信度、效度及原理[J]. 心理科学进展, 2004, 12(2): 223-230. |
| [12] | 蔡华俭. Greenwald提出的内隐联想测验介绍[J]. 心理科学进展, 2003, 11(3): 339-344. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=5615
