 )
) 西华师范大学教育学院, 四川 南充 637002
收稿日期:2020-03-17出版日期:2021-02-15发布日期:2020-12-29通讯作者:曹晓君E-mail:cxj841118@aliyun.comSibling conflict and its resolution: The effects of family subsystem
QU Guoliang, CAO Xiaojun( )
) School of Education, China West Normal University, Nanchong 637002, China
Received:2020-03-17Online:2021-02-15Published:2020-12-29Contact:CAO Xiaojun E-mail:cxj841118@aliyun.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 同胞冲突是指在一个完整的家庭中, 具有相同生身父母的两个或多个人在行为、目标或活动上所表达出的不相容, 其通常表现为争吵和敌对情绪以及相互间的攻击行为。父母干预同胞冲突的方式分为孩子中心策略、控制策略和不干预策略。家庭系统理论指出, 家庭是一个有等级结构的、动态的系统, 这个系统中的子系统(包括父母婚姻关系、亲子关系和同胞关系)是相互联系、相互影响的。基于这一理论, 探讨家庭子系统对同胞冲突的影响, 整合建构同胞冲突的理论假设模型, 以便从多路径的角度去分析同胞冲突的产生机制。未来的研究需要对同胞冲突及其相关概念进行区分或整合, 关注父母干预同胞冲突的方式的影响因素, 并且以发展的眼光去看待同胞冲突。
图/表 3
表1调解四步曲
| 步骤 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 第一步 | 调解人制定基本规则和行为准则, 以减少冲突升级和敌对的可能性。 |
| 第二步 | 调解人在调解过程中发现冲突的问题。只有明确问题, 集中讨论, 才能让冲突双方在解决问题上取得进展。 |
| 第三步 | 调解人试图促进相互理解并在冲突的双方之间建立移情。 |
| 第四步 | 调解人鼓励冲突的双方提出可能的解决方案, 并从中选择双方都能接受和实现的解决方案。 |
表1调解四步曲
| 步骤 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 第一步 | 调解人制定基本规则和行为准则, 以减少冲突升级和敌对的可能性。 |
| 第二步 | 调解人在调解过程中发现冲突的问题。只有明确问题, 集中讨论, 才能让冲突双方在解决问题上取得进展。 |
| 第三步 | 调解人试图促进相互理解并在冲突的双方之间建立移情。 |
| 第四步 | 调解人鼓励冲突的双方提出可能的解决方案, 并从中选择双方都能接受和实现的解决方案。 |
表2儿童早期亲密同胞关系的基本能力列表
| 能力 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 积极参与 | 玩耍、交谈、共同的兴趣、享乐和乐趣。确定一些适合所有同胞不同发展水平的活动。 |
| 凝聚力 | 认可并重视一系列相互帮助、支持、保护、合作、忠诚、信任、自豪的实例。 |
| 建立支持型的共同经验 | 欣赏同胞对彼此和家庭的独特认识, 以加强联系, 同时避免利用这些认识损害同胞的利益。重视共同的和独立的利益。 |
| 社会和情绪理解(换位思考) | 去中心化; 学会评估和尊重同胞的独特观点、需要、目标和兴趣。 |
| 情绪调节 | 在情绪上面临挑战和挫折的情况下识别和管控情绪。 |
| 行为控制 | 避免做一些同胞不喜欢的行为(如专横、调侃、使在朋友面前尴尬、不尊重个人界限和空间、过度活跃、胡闹)。 |
| 形成中立或积极的归因 | 在情况不明的处境下, 孩子们可能会对同胞的行为意图形成敌对的归因; 孩子们必须学会检查或纠正错误的归因。家庭成员应帮助澄清意图, 并就他人行为的影响进行交流。 |
| 冲突管理、问题解决 | 冲突是可以解决的社会问题, 但儿童需要明确地学习这些方法。父母有效的冲突管理策略的运用和构建(例如, 协作解决问题、调解)对儿童学习至关重要。 |
| 评价父母的差别对待行为 | 讨论父母差别对待的影响, 调整父母的行为以满足儿童的独特需要。 |
表2儿童早期亲密同胞关系的基本能力列表
| 能力 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 积极参与 | 玩耍、交谈、共同的兴趣、享乐和乐趣。确定一些适合所有同胞不同发展水平的活动。 |
| 凝聚力 | 认可并重视一系列相互帮助、支持、保护、合作、忠诚、信任、自豪的实例。 |
| 建立支持型的共同经验 | 欣赏同胞对彼此和家庭的独特认识, 以加强联系, 同时避免利用这些认识损害同胞的利益。重视共同的和独立的利益。 |
| 社会和情绪理解(换位思考) | 去中心化; 学会评估和尊重同胞的独特观点、需要、目标和兴趣。 |
| 情绪调节 | 在情绪上面临挑战和挫折的情况下识别和管控情绪。 |
| 行为控制 | 避免做一些同胞不喜欢的行为(如专横、调侃、使在朋友面前尴尬、不尊重个人界限和空间、过度活跃、胡闹)。 |
| 形成中立或积极的归因 | 在情况不明的处境下, 孩子们可能会对同胞的行为意图形成敌对的归因; 孩子们必须学会检查或纠正错误的归因。家庭成员应帮助澄清意图, 并就他人行为的影响进行交流。 |
| 冲突管理、问题解决 | 冲突是可以解决的社会问题, 但儿童需要明确地学习这些方法。父母有效的冲突管理策略的运用和构建(例如, 协作解决问题、调解)对儿童学习至关重要。 |
| 评价父母的差别对待行为 | 讨论父母差别对待的影响, 调整父母的行为以满足儿童的独特需要。 |
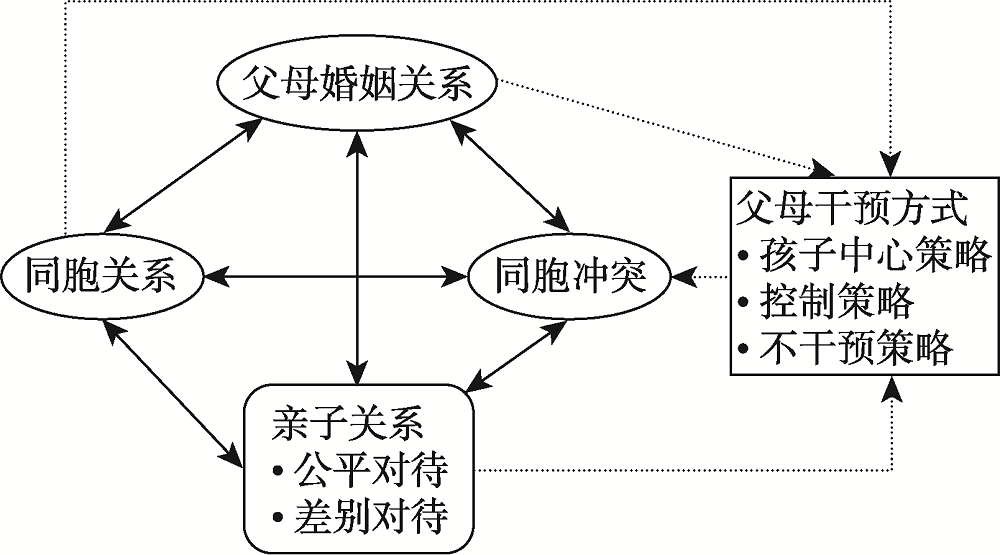
图1家庭子系统对同胞冲突的影响路径 注:实线为双向作用, 虚线为单向作用。
 图1家庭子系统对同胞冲突的影响路径 注:实线为双向作用, 虚线为单向作用。
图1家庭子系统对同胞冲突的影响路径 注:实线为双向作用, 虚线为单向作用。参考文献 78
| [1] | 陈斌斌, 施泽艺. (2017). 二胎家庭的父母养育. 心理科学进展, 25(7), 1172-1181. |
| [2] | 陈斌斌, 王燕, 梁霁, 童连. (2016). 二胎进行时: 头胎儿童在向同胞关系过渡时的生理和心理变化及其影响因素. 心理科学进展, 24(6), 863-873. |
| [3] | 陈斌斌, 赵语, 韩雯, 王逸辰, 吴嘉雯, 岳新宇, 吴英挺. (2017). 手足之情: 同胞关系的类型、影响因素及对儿童发展的作用机制. 心理科学进展, 25(12), 2168-2178. |
| [4] | 张潮, 柴亚星, 刘赛芳, 刘金蕙, 赵若晨. (2020). 初中生同胞冲突对其攻击行为的影响机制. 中国健康心理学杂志, 28(1), 119-124. |
| [5] | 张荣臻, 曹晓君, 冉光明, 夏云川. (2019). 同胞关系质量对头胎幼儿共情的影响. 学前教育研究, (8), 52-63. |
| [6] | 赵凤青, 俞国良. (2017). 同胞关系及其与儿童青少年社会性发展的关系. 心理科学进展, 25(5), 825-836. |
| [7] | Abuhatoum, S., & Howe, N. (2013). Power in sibling conflict during early and middle childhood. Social Development, 22(4), 738-754. |
| [8] | Abuhatoum, S., Howe, N., Porta, S. D., & DeHart, G. (2018). A dyadic analysis of power in sibling and friend conflict in early childhood. Infant and Child Development, 27(4), e2085. |
| [9] | Bank, L., Burraston, B., & Snyder, J. (2004). Sibling conflict and ineffective parenting as predictors of adolescent boys’ antisocial behavior and peer difficulties: Additive and interactional effects. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 14(1), 99-125. |
| [10] | Bekkhus, M., Staton, S., Borge, A. I. H., & Thorpe, K. (2011). Conflict, closeness and comfort: The inter-twin relationship as a risk factor for behavioral difficulties. Twin Research and Human Genetics, 14(5), 444-451. URLpmid: 21962137 |
| [11] | Bouchard, G., Plamondon, A., & Lachance-Grzela, M. (2018). Parental intervention style and adult sibling conflicts: The mediating role of involvement in sibling bullying. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 36(8), 2585-2602. |
| [12] | Breitenstein, R. S., Doane, L. D., Clifford, S., & Lemery-Chalfant, K. (2018). Children’s sleep and daytime functioning: Increasing heritability and environmental associations with sibling conflict. Social Development, 27(4), 967-983. doi: 10.1111/sode.12302URLpmid: 30686863 |
| [13] | Brody, G. H., Stoneman, Z., & Gauger, K. (1996). Parent-child relationships, family problem-solving behavior, and sibling relationship quality: The moderating role of sibling temperaments. Child Development, 67(3), 1289-1300. URLpmid: 8706522 |
| [14] | Buist, K. L., Dekovi?, M., & Prinzie, P. (2013). Sibling relationship quality and psychopathology of children and adolescents: A meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 33(1), 97-106. URLpmid: 23159327 |
| [15] | Carvalho, J., Fernandes, O. M., & Relva, I. C. (2017). Family functioning and its relation to parental discipline. Child and Adolescent Social Work Journal, 35(1), 31-44. |
| [16] | Chen, B.-B. (2019). Chinese adolescents’ sibling conflicts: Links with maternal involvement in sibling relationships and coparenting. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 29(3), 752-762. doi: 10.1111/jora.12413URLpmid: 29911742 |
| [17] | Cox, M. J. (2010). Family systems and sibling relationships. Child Development Perspectives, 4(2), 95-96. |
| [18] | Cox, M. J., & Paley, B. (1997). Families as systems. Annual Review of Psychology, 48(1), 243-267. |
| [19] | Cox, M. J., & Paley, B. (2003). Understanding families as systems. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 12(5), 193-196. |
| [20] | Davies, P. T., Parry, L. Q., Bascoe, S. M., Martin, M. J., & Cummings, E. M. (2019). Children’s vulnerability to interparental conflict: The protective role of sibling relationship quality. Child Development, 90(6), 2118-2134. doi: 10.1111/cdev.13078URLpmid: 29916198 |
| [21] | Dawson, A., Pike, A., & Bird, L. (2015). Parental division of household labour and sibling relationship quality: Family relationship mediators. Infant and Child Development, 24(4), 379-393. |
| [22] | Dix, T., Ruble, D. N., & Zambarano, R. J. (1989). Mothers’ implicit theories of discipline: Child effects, parent effects, and the attribution process. Child Development, 60(6), 1373-1391. |
| [23] | Eriksen, S., & Jensen, V. (2006). All in the family? Family environment factors in sibling violence. Journal of Family Violence, 21(8), 497-507. |
| [24] | Eriksen, S., & Jensen, V. (2009). A push or a punch: Distinguishing the severity of sibling violence. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 24(1), 183-208. URLpmid: 18417730 |
| [25] | Faith, M. A., Elledge, L. C., Newgent, R. A., & Cavell, T. A. (2015). Conflict and dominance between siblings as predictors of children’s peer victimization. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 24(12), 3623-3635. |
| [26] | Feinberg, M. E., Solmeyer, A. R., & McHale, S. M. (2012). The third rail of family systems: Sibling relationships, mental and behavioral health, and preventive intervention in childhood and adolescence. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 15(1), 43-57. URLpmid: 22105663 |
| [27] | Finzi-Dottan, R., & Cohen, O. (2010). Young adult sibling relations: The effects of perceived parental favoritism and narcissism. The Journal of Psychology, 145(1), 1-22. URLpmid: 21290927 |
| [28] | Hakvoort, E. M., Bos, H. M. W., Balen, F. V., & Hermanns, J. M. A. (2010). Family relationships and the psychosocial adjustment of school-aged children in intact families. The Journal of Genetic Psychology, 171(2), 182-201. URLpmid: 20486403 |
| [29] | Hoffman, K. L., Kiecolt, K. J., & Edwards, J. N. (2005). Physical violence between siblings A theoretical and empirical analysis. Journal of Family Issues, 26(8), 1103-1130. |
| [30] | Howe, N., & Recchia, H. (2014). Sibling relationships as a context for learning and development. Early Education and Development, 25(2), 155-159. |
| [31] | Iturralde, E., Margolin, G., & Shapiro, L. A. S. (2013). Positive and negative interactions observed between siblings: Moderating effects for children exposed to parents’ conflict. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 23(4), 716-729. |
| [32] | Kendrick, C., & Dunn, J. (1983). Sibling quarrels and maternal responses. Developmental Psychology, 19(1), 62-70. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.19.1.62URL |
| [33] | Kim, J.-Y., McHale, S. M., Osgood, D. W., & Crouter, A. C. (2006). Longitudinal course and family correlates of sibling relationships from childhood through adolescence. Child Development, 77(6), 1746-1761. URLpmid: 17107458 |
| [34] | Kramer, L. (2010). The essential ingredients of successful sibling relationships: An emerging framework for advancing theory and practice. Child Development Perspectives, 4(2), 80-86. |
| [35] | Kramer, L., Perozynski, L. A., & Chung, T. (1999). Parental responses to sibling conflict: The effects of development and parent gender. Child Development, 70(6), 1401-1414. URLpmid: 10621963 |
| [36] | Krienert, J. L., & Walsh, J. A. (2011). My brother’s keeper: A contemporary examination of reported sibling violence using national level data, 2000-2005. Journal of Family Violence, 26(5), 331-342. |
| [37] | McGuire, S., & Shanahan, L. (2010). Sibling experiences in diverse family contexts. Child Development Perspectives, 4(2), 72-79. |
| [38] | McHale, S. M., Updegraff, K. A., Jackson-Newsom, J., Tucker, C. J., & Crouter, A. C. (2000). When does parents’ differential treatment have negative implications for siblings? Social Development, 9(2), 149-172. |
| [39] | McHale, S. M., Updegraff, K. A., Tucker, C. J., & Crouter, A. C. (2000). Step in or stay out? Parents’ roles in adolescent siblings’ relationships. Journal of Marriage and Family, 62(3), 746-760. |
| [40] | Noller, P. (2005). Sibling relationships in adolescence: Learning and growing together. Personal Relationships, 12(1), 1-22. doi: 10.1111/pere.2005.12.issue-1URL |
| [41] | Perlman, M., Garfinkel, D. A., & Turrell, S. L. (2007). Parent and sibling influences on the quality of children’s conflict behaviours across the preschool period. Social Development, 16(4), 619-641. |
| [42] | Perozynski, L., & Kramer, L. (1999). Parental beliefs about managing sibling conflict. Developmental Psychology, 35(2), 489-499. URLpmid: 10082019 |
| [43] | Persram, R. J., Howe, N., Porta, S. D., & Ross, H. S. (2017). Family members’ helping behavior: Alliance formations during naturalistic polyadic conflicts. Infant and Child Development, 26(4), 1-15. |
| [44] | Phillips, K. E., & Schrodt, P. (2015). Sibling antagonism and shared family identity as mediators of differential parental treatment and relational outcomes in the sibling relationship. Western Journal of Communication, 79(5), 634-654. |
| [45] | Pickering, J. A., & Sanders, M. R. (2017). Integrating parents’ views on sibling relationships to tailor an evidence-based parenting intervention for sibling conflict. Family Process, 56(1), 105-125. URLpmid: 26333041 |
| [46] | Pike, A., Coldwell, J., & Dunn, J. F. (2005). Sibling relationships in early/middle childhood: Links with individual adjustment. Journal of Family Psychology, 19(4), 523-532. doi: 10.1037/0893-3200.19.4.523URLpmid: 16402867 |
| [47] | Poortman, A.-R., & Voorpostel, M. (2009). Parental divorce and sibling relationships: A research note. Journal of Family Issues, 30(1), 74-91. |
| [48] | Porta, S. D., & Howe, N. (2017). Siblings’ power and influence in polyadic family conflict during early childhood. In N. Campione-Barr (Ed.), Power, control, and influence in sibling relationships across development. New directions for child and adolescent development (pp.15-31). Jossey-Bass San Francisco |
| [49] | Raffaelli, M. (1997). Young adolescents’ conflicts with siblings and friends. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 26(5), 539-558. |
| [50] | Recchia, H. E., & Howe, N. (2009). Sibling relationship quality moderates the associations between parental interventions and siblings’ independent conflict strategies and outcomes. Journal of Family Psychology, 23(4), 551-561. URLpmid: 19685990 |
| [51] | Recchia, H. E., Rajput, A., & Peccia, S. (2015). Children’s interpretations of ambiguous provocation from their siblings: Comparisons with peers and links to relationship quality. Social Development, 24(4), 782-797. |
| [52] | Recchia, H. E., & Witwit, M. (2017). Family perspectives on siblings’ conflict goals in middle childhood: Links to hierarchical and affective features of sibling relationships. In N. Campione-Barr (Ed.), Power, control, and influence in sibling relationships across development. New directions for child and adolescent development (pp.33-48). Jossey-Bass San Francisco |
| [53] | Relva, I. C., Alarc?o, M., Fernandes, O. M., Carvalho, J., & Fauchier, A. (2019). Sibling conflict and parental discipline: The mediating role of family communication in Portuguese adolescents. Child and Adolescent Social Work Journal, 36(3), 295-304. |
| [54] | Relva, I. C., Alarc?o, M., Fernandes, O. M., & Graham-Bermann, S. (2019). Quality of sibling relationship and parental differential treatment in a sample of Portuguese adolescents. Análise Psicológica, 37(3), 341-353. |
| [55] | Rinaldi, C., & Howe, N. (1998). Siblings’ reports of conflict and the quality of their relationships. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 44(3), 404-422. |
| [56] | Ross, H. S., & Lazinski, M. J. (2014). Parent mediation empowers sibling conflict resolution. Early Education and Development, 25(2), 259-275. doi: 10.1080/10409289.2013.788425URL |
| [57] | Ruff, S. C., Durtschi, J. A., & Day, R. D. (2018). Family subsystems predicting adolescents’ perceptions of sibling relationship quality over time. Journal of Marital and Family Therapy, 44(3), 527-542. URLpmid: 28869765 |
| [58] | Shanahan, L., Mchale, S. M., Crouter, A. C., & Osgood, D. W. (2008). Linkages between parents’ differential treatment, youth depressive symptoms, and sibling relationships. Journal of Marriage and Family, 70(2), 480-494. |
| [59] | Shebloski, B., Conger, K. J., & Widaman, K. F. (2005). Reciprocal links among differential parenting, perceived partiality, and self-worth: A three-wave longitudinal study. Journal of Family Psychology, 19(4), 633-642. doi: 10.1037/0893-3200.19.4.633URLpmid: 16402879 |
| [60] | Siddiqui, A., & Ross, H. (2004). Mediation as a method of parent intervention in children’s disputes. Journal of Family Psychology, 18(1), 147-159. doi: 10.1037/0893-3200.18.1.147URLpmid: 14992617 |
| [61] | Smith, J., & Ross, H. (2007). Training parents to mediate sibling disputes affects children’s negotiation and conflict understanding. Child Development, 78(3), 790-805. URLpmid: 17517005 |
| [62] | Song, J. H., Volling, B. L., Lane, J. D., & Wellman, H. M. (2016). Aggression, sibling antagonism, and theory of mind during the first year of siblinghood: A developmental cascade model. Child Development, 87(4), 1250-1263. doi: 10.1111/cdev.12530URLpmid: 27096923 |
| [63] | Stocker, C. M., Lanthier, R. P., & Furman, W. (1997). Sibling relationships in early adulthood. Journal of Family Psychology, 11(2), 210-221. doi: 10.1037/0893-3200.11.2.210URL |
| [64] | Stocker, C. M., & Youngblade, L. (1999). Marital conflict and parental hostility: Links with children’s sibling and peer relationships. Journal of Family Psychology, 13(4), 598-609. |
| [65] | Suitor, J. J., Sechrist, J., Plikuhn, M., Pardo, S. T., Gilligan, M., & Pillemer, K. (2009). The role of perceived maternal favoritism in sibling relations in midlife. Journal of Marriage and Family, 71(4), 1026-1038. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-3737.2009.00650.xURLpmid: 20104251 |
| [66] | Suitor, J. J., Sechrist, J., Plikuhn, M., Pardo, S. T., & Pillemer, K. (2008). Within-family differences in parent-child relations across the life course. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 17(5), 334-338. |
| [67] | Tippett, N., & Wolke, D. (2015). Aggression between siblings: Associations with the home environment and peer bullying. Aggressive Behavior, 41(1), 14-24. doi: 10.1002/ab.21557URLpmid: 25187483 |
| [68] | Tompsett, C. J., Mahoney, A., & Lackey, J. (2016). Sibling aggression among clinic-referred children and adolescents. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 47(6), 1-13. |
| [69] | Tucker, C. J., & Finkelhor, D. (2015). The state of interventions for sibling conflict and aggression: A systematic review. Trauma, Violence, & Abuse, 18(4), 396-406. URLpmid: 26681173 |
| [70] | Tucker, C. J., Finkelhor, D., Shattuck, A. M., & Turner, H. (2013). Prevalence and correlates of sibling victimization types. Child Abuse & Neglect, 37(4), 213-223. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2013.01.006URLpmid: 23428164 |
| [71] | Tucker, C. J., & Kazura, K. (2013). Parental responses to school-aged children’s sibling conflict. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 22(5), 737-745. |
| [72] | Tucker, C. J., Updegraff, K., & Baril, M. E. (2010). Who’s the boss? Patterns of control in adolescents’ sibling relationships. Family Relations, 59(5), 520-532. URLpmid: 21857761 |
| [73] | Volling, B. L., & Elins, J. L. (1998). Family relationships and children’s emotional adjustment as correlates of maternal and paternal differential treatment: A replication with toddler and preschool siblings. Child Development, 69(6), 1640-1656. URLpmid: 9914644 |
| [74] | Vuchinich, S., Emery, R. E., & Cassidy, J. (1988). Family members as third parties in dyadic family conflict: Strategies, alliances, and outcomes. Child Development, 59(5), 1293-1302. URLpmid: 3168641 |
| [75] | Whiteman, S. D., McHale, S. M., & Soli, A. (2011). Theoretical perspectives on sibling relationships. Journal of Family Theory & Review, 3(2), 124-139. URLpmid: 21731581 |
| [76] | Wolke, D., Tippett, N., & Dantchev, S. (2015). Bullying in the family: Sibling bullying. The Lancet Psychiatry, 2(10), 917-929. URLpmid: 26462226 |
| [77] | Yin, X., Li, Z., Li, J., & Liu, X. (2019). Sibling relationship quality and young children’s mental health in Chinese two-child families. Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal, 47(6), 1-9. |
| [78] | Yu, J. J., & Gamble, W. C. (2008). Pathways of influence: Marital relationships and their association with parenting styles and sibling relationship quality. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 17(6), 757-778. |
相关文章 3
| [1] | 陈斌斌, 施泽艺. 二胎家庭的父母养育[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(7): 1172-1181. |
| [2] | 赵凤青;俞国良. 同胞关系及其与儿童青少年社会性发展的关系[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(5): 825-836. |
| [3] | 陈斌斌, 赵语, 韩雯, 王逸辰, 吴嘉雯, 岳新宇, 吴英挺. 手足之情:同胞关系的类型、影响因素及对儿童发展的作用机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(12): 2168-2178. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=5336
