 )
) 辽宁师范大学心理学院, 大连 116029
收稿日期:2020-06-09出版日期:2021-01-15发布日期:2020-11-23通讯作者:隋雪E-mail:suixue88@163.com基金资助:* 辽宁省教育厅自然科学基金青年项目(L201783637);教育部人文社会科学规划基金项目(19YJA190005);国家自然科学基金面上项目(31971036);本研究是博士后部分研究工作(243514)Semantic association effect and its neural mechanism from the perspective of lexical co-occurrence frequency
LI Yutong, SUI Xue( )
) Department of psychology, Liaoning Normal University, Dalian 116029, China
Received:2020-06-09Online:2021-01-15Published:2020-11-23Contact:SUI Xue E-mail:suixue88@163.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 词汇识别与记忆受到词汇之间语义联想关系的影响。鉴于自由联想方法建立词汇语义联想关系的局限性, 研究者们提出用共现联想法建立词汇之间的语义联想关系。本文对词汇共现频率视角下的语义联想效应及其神经机制的研究进行分析发现, 语义联想的丰富程度和关联程度影响词汇的加工; 与少语义联想词相比, 多语义联想词导致P200波幅增大和N400波幅减小; 语义联想加工涉及的脑区主要是额上回和左内侧颞叶区域。未来研究需要探讨自由联想法和共现联想法建立语义联想关系的差异, 基于共现联想法进一步地探究语义联想的行为规律和神经机制, 并从共现联想的角度开展汉语语义联想效应及神经机制的研究。
图/表 1
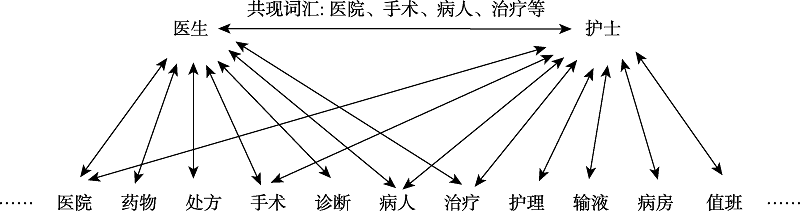
图1词汇之间的语义联想关系(数据来源于莱比锡语料库(见2.3节))
 图1词汇之间的语义联想关系(数据来源于莱比锡语料库(见2.3节))
图1词汇之间的语义联想关系(数据来源于莱比锡语料库(见2.3节))参考文献 69
| [1] | Baror, S., & Bar, M. (2016). Associative activation and its relation to exploration and exploitation in the brain. Psychological Science, 27(6), 776-789. doi: 10.1177/0956797616634487URLpmid: 27122295 |
| [2] | Bentin, S., McCarthy, G., & Wood, C. C. (1985). Event- related potentials, lexical decision and semantic priming. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 60(4), 343-355. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(85)90008-2URLpmid: 2579801 |
| [3] | Biemann, C., & Riedl, M. (2013). Text: Now in 2D! A framework for lexical expansion with contextual similarity. Journal of Language Modelling, 1(1), 55-95. doi: 10.15398/jlm.v1i1.60URL |
| [4] | Braun, M., Jacobs, A. M., Hahne, A., Ricker, B., Hofmann, M. J., & Hutzler, F. (2006). Model-generated lexical activity predicts graded ERP amplitudes in lexical decision. Brain Research, 1073-1074, 431-439. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.12.078URLpmid: 16464440 |
| [5] | Braun, M., Jacobs, A. M., Richlan, F., Hawelka, S., Hutzler, F., & Kronbichler, M. (2015). Many neighbors are not silent. fMRI evidence for global lexical activity in visual word recognition. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 423-423. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00423URLpmid: 26257634 |
| [6] | Braun, M., Kronbichler, M., Richlan, F., Hawelka, S., Hutzler, F., & Jacobs, A. M. (2019). A model-guided dissociation between subcortical and cortical contributions to word recognition. Scientific Reports, 9, 4506. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41011-9URLpmid: 30872701 |
| [7] | Coane, J. H., McBride, D. M., Termonen, M. -L., & Cutting, J. C. (2016). Categorical and associative relations increase false memory relative to purely associative relations. Memory & cognition, 44(1), 37-49. doi: 10.3758/s13421-015-0543-1URLpmid: 26250805 |
| [8] | Coltheart, M., Rastle, K., Perry, C., Langdon, R., & Ziegler, J. (2001). DRC: A dual route cascaded model of visual word recognition and reading aloud. Psychological Review, 108(1), 204-256. doi: 10.1037/0033-295x.108.1.204URLpmid: 11212628 |
| [9] | Dambacher, M., Kliegl, R., Hofmann, M. J., & Jacobs, A. M. (2006). Frequency and predictability effects on event-related potentials during reading. Brain Research, 1084(1), 89-103. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.02.010URLpmid: 16545344 |
| [10] | Deese, J. (1959). On the prediction of occurrence of particular verbal intrusions in immediate recall. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 58(1), 17-22. doi: 10.1037/h0046671URLpmid: 13664879 |
| [11] | Diana, R. A., Yonelinas, A. P., & Ranganath, C. (2007). Imaging recollection and familiarity in the medial temporal lobe: A three-component model. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 11(9), 379-386. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2007.08.001URL |
| [12] | Dunning, T. (1993). Accurate methods for the statistics of surprise and coincidence. Computational Linguistics, 19(1), 61-74. |
| [13] | Eichenbaum, H., Yonelinas, A. P., & Ranganath, C. (2007). The medial temporal lobe and recognition memory. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 30(1), 123-152. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.30.051606.094328URL |
| [14] | Ellis, N. C., Frey, E., & Jalkanen, I. (2009). The psycholinguistic reality of collocation and semantic prosody (1): Lexical access. In U. R?mer, & R. Schulze (Eds.), Studies in Corpus Linguistics, Exploring the Lexis-Grammar Interface(pp. 89-114). Amsterdam, Holand: John Benjamins. |
| [15] | Franke, N., Roelke, A., Radach, R. R., & Hofmann, M. J. (2017, July). After braking comes hasting: reversed effects of indirect associations in 2nd and 4th graders. Paper presented at the meeting of the Cognitive Science Society, London, England. |
| [16] | Gallo, D. A. (2010). False memories and fantastic beliefs: 15 years of the DRM illusion. Memory & Cognition, 38(7), 833-848. doi: 10.3758/MC.38.7.833URLpmid: 20921097 |
| [17] | Geng, H., Qi, Y., Li, Y., Fan, S., Wu, Y., & Zhu, Y. (2007). Neurophysiological correlates of memory illusion in both encoding and retrieval phases. Brain Research, 1136, 154-168. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.12.027URLpmid: 17239833 |
| [18] | Grainger, J., & Jacobs, A. M. (1994). A dual read-out model of word context effects in letter perception: Further investigations of the word superiority effect. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 20(6), 1158-1176. doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.20.6.1158URL |
| [19] | Goldhahn, D., Eckart, T., Quasthoff, U. (2012). Building large monolingual dictionaries at the Leipzig Corpora Collection_ From 100 to 200 Languages. In N. Calzolari, K. Choukri, T. Declerck, M. Ugur Dogan, B. Maegaard, J. Mariani, J. Odijk, & S. Piperidis (Eds.), Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-2012) (pp. 3196-3200). European Language Resources Association (ELRA). |
| [20] | Grainger, J., & Jacobs, A. M. (1996). Orthographic processing in visual word recognition: A multiple read-out model. Psychological Review, 103(3), 518-565. doi: 10.1037/0033-295x.103.3.518URLpmid: 8759046 |
| [21] | Hawelka, S., Schuster, S., Gagl, B., & Hutzler, F. (2013). Beyond single syllables: The effect of first syllable frequency and orthographic similarity on eye movements during silent reading. Language and Cognitive Processes, 28(8), 1134-1153. doi: 10.1080/01690965.2012.696665URL |
| [22] | Hebb, D. O. (Eds). (1949). The organization of behavior: a neuropsychological theory. New York: Wiley. |
| [23] | Hofmann, M. J., Biemann, C., Westbury, C., Murusidze, M., Conrad, M., & Jacobs, A. M. (2018). Simple co-occurrence statistics reproducibly predict association ratings. Cognitive Science, 42(7), 2287-2312. doi: 10.1111/cogs.12662URLpmid: 30098213 |
| [24] | Hofmann, M. J., & Jacobs, A. M. (2014). Interactive activation and competition models and semantic context: From behavioral to brain data. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 46, 85-104. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.06.011URLpmid: 24992217 |
| [25] | Hofmann, M. J., Kuchinke, L., Biemann, C., Tamm, S., & Jacobs, A. M. (2011). Remembering words in context as predicted by an associative read-out model. Frontiers in Psychology, 2, 11. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00011URLpmid: 21713185 |
| [26] | Hofmann, M. J., Kuchinke, L., Tamm, S., V?, M. L. H., & Jacobs, A. M. (2009). Affective processing within 1/10th of a second: High arousal is necessary for early facilitative processing of negative but not positive words. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 9(4), 389-397. |
| [27] | Jared, D., Jouravlev, O., & Joanisse, M. F. (2017). The effect of semantic transparency on the processing of morphologically derived words: Evidence from decision latencies and event- related potentials. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition, 43(3), 422-450. doi: 10.1037/xlm0000316URL |
| [28] | Jou, J., Arredondo, M. L., Li, C., Escamilla, E. E., & Zuniga, R. (2017). The effects of increasing semantic-associate list length on the Deese-Roediger-McDermott false recognition memory: Dual false-memory process in retrieval from sub- and supraspan lists. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 70(10), 2076-2093. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2016.1222446URLpmid: 27606720 |
| [29] | Jou, J., Escamilla, E. E., Arredondo, M. L., Pena, L., Zuniga, R., Perez, M., & Garcia, C. (2018). The role of decision criterion in the Deese-Roediger-McDermott (DRM) false recognition memory: False memory falls and rises as a function of restriction on criterion setting. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 71(2), 499-521. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2016.1256416URLpmid: 27808007 |
| [30] | Kuchinke, L., Fritzemeier, S., Hofmann, M. J., & Jacobs, A. M. (2013). Neural correlates of episodic memory: Associative memory and confidence drive hippocampus activations. Behavioural Brain Research, 254, 92-101. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.04.035URL |
| [31] | Li, B. B., Taylor, J. R., Wang, W., Gao, C. J., & Guo, C. Y. (2017). Electrophysiological signals associated with fluency of different levels of processing reveal multiple contributions to recognition memory. Consciousness and Cognition, 53, 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2017.05.001URLpmid: 28558307 |
| [32] | Lothane, H. Z. (2018). Free association as the foundation of the psychoanalytic method and psychoanalysis as a historical science. Psychoanalytic Inquiry, 38(6), 416-434. doi: 10.1080/07351690.2018.1480225URL |
| [33] | Lucas, M. (2000). Semantic priming without association: A meta-analytic review. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 7(4), 618-630. doi: 10.3758/bf03212999URLpmid: 11206202 |
| [34] | Mandera, P., Keuleers, E., & Brysbaert, M. (2017). Explaining human performance in psycholinguistic tasks with models of semantic similarity based on prediction and counting: A review and empirical validation. Journal of Memory and Language, 92, 57-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2016.04.001URL |
| [35] | Mcclelland, J. L., & Rumelhart, D. E. (1981). An interactive activation model of context effects in letter perception, part I: An account of basic findings. Psychological Review, 88(88), 580-596. |
| [36] | Meade, G., Grainger, J., & Holcomb, P. J. (2019). Task modulates ERP effects of orthographic neighborhood for pseudowords but not words. Neuropsychologia, 129, 385-396. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2019.02.014URLpmid: 30797831 |
| [37] | Meade, G., Midgley, K. J., Dijkstra, T., & Holcomb, P. J. (2018). Cross-language neighborhood effects in learners indicative of an integrated lexicon. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 30(1), 70-85. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01184URLpmid: 28880767 |
| [38] | Midgley, K. J., Holcomb, P. J., & Grainger, J. (2009). Masked repetition and translation priming in second language learners: A window on the time-course of form and meaning activation using ERPs. Psychophysiology, 46(3), 551-565. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2009.00784.xURLpmid: 19298629 |
| [39] | Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., & Dean, J. (2013, May). Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. Paper presented at the meeting of the international conference on learning representations, Scottsdale, USA. |
| [40] | Molinaro, N., Conrad, M., Barber, H. A., & Carreiras, M. (2010). On the functional nature of the N400: Contrasting effects related to visual word recognition and contextual semantic integration. Cognitive Neuroscience, 1(1), 1-7. doi: 10.1080/17588920903373952URLpmid: 24168241 |
| [41] | Müller, O., Du?abeitia, J. A., & Carreiras, M. (2010). Orthographic and associative neighborhood density effects: What is shared, what is different? Psychophysiology, 47(3), 455-466. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2009.00960.xURLpmid: 20102534 |
| [42] | Namaziandost, E., Shafiee, S., & Rasooyar, H. (2018). Paradigmatic relations and syntagmatic relations: Are they useful in learning grammatical structures? Journal of Applied Linguistics and Language Research, 5(5), 20-34. |
| [43] | Otgaar, H., Moldoveanu, G., Wang, J. Q., & Howe, M. L. (2017). Exploring the consequences of nonbelieved memories in the DRM paradigm. Memory, 25(7), 922-933. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2016.1272701URLpmid: 28029065 |
| [44] | Otgaar, H., Muris, P., Howe, M. L., & Merckelbach, H. (2017). What drives false memories in psychopathology? A case for associative activation. Clinical Psychological Science, 5(6), 1048-1069. doi: 10.1177/2167702617724424URLpmid: 29170722 |
| [45] | Park, J. L., & Donaldson, D. I. (2016). Investigating the relationship between implicit and explicit memory: Evidence that masked repetition priming speeds the onset of recollection. NeuroImage, 139, 8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.06.013URL |
| [46] | Perry, C., Ziegler, J. C., & Zorzi, M. (2007). Nested incremental modeling in the development of computational theories: The CDP+ model of reading aloud. Psychological Review, 114(2), 273-315. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.114.2.273URLpmid: 17500628 |
| [47] | Perry, C., Ziegler, J. C., & Zorzi, M. (2010). Beyond single syllables: Large-scale modeling of reading aloud with the connectionist dual process (CDP++) model. Cognitive Psychology, 61(2), 106-151. doi: 10.1016/j.cogpsych.2010.04.001URL |
| [48] | Pleger, B., & Timmann, D. (2018). The role of the human cerebellum in linguistic prediction, word generation and verbal working memory: Evidence from brain imaging, non-invasive cerebellar stimulation and lesion studies. Neuropsychologia, 115, 204-210. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.03.012URLpmid: 29530801 |
| [49] | Qu, Q. Q., Zhang, Q. F., & Damian, M. F. (2016). Tracking the time course of lexical access in orthographic production: An event-related potential study of word frequency effects in written picture naming. Brain and Language, 159, 118-126. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2016.06.008URLpmid: 27393929 |
| [50] | Rapp, R. (2002, September). The computation of word associations: comparing syntagmatic and paradigmatic approaches. Paper presented at the meeting of the 19th international conference on Computational linguistics, Taipei, China. |
| [51] | Roediger, H. L., & McDermott, K. B. (1995). Creating false memories: Remembering words not presented in lists. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 21(4), 803-814. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.21.4.803URL |
| [52] | Roelke, A., Franke, N., Biemann, C., Radach, R., Jacobs, A. M., & Hofmann, M. J. (2018). A novel co-occurrence-based approach to predict pure associative and semantic priming. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 25(4), 1488-1493. doi: 10.3758/s13423-018-1453-6URLpmid: 29546666 |
| [53] | Ross, D. A., Sadil, P., Wilson, D. M., & Cowell, R. A. (2017). Hippocampal engagement during recall depends on memory content. Cerebral Cortex, 28(8), 2685-2698. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhx147URLpmid: 28666344 |
| [54] | Schachter, J. (2018). Free association: From Freud to current use—the effects of training analysis on the use of free association. Psychoanalytic Inquiry, 38(6), 457-467. doi: 10.1080/07351690.2018.1480231URL |
| [55] | Shin, J. -E., Suh, E. M., Eom, K., & Kim, H. S. (2018). What does “happiness” prompt in your mind? Culture, word choice, and experienced happiness. Journal of Happiness Studies, 19(3), 649-662. doi: 10.1007/s10902-016-9836-8URL |
| [56] | Siew, C. S. Q., & Vitevitch, M. S. (2016). Spoken word recognition and serial recall of words from components in the phonological network. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition, 42(3), 394-410. doi: 10.1037/xlm0000139URL |
| [57] | Smith, C. N., Wixted, J. T., & Squire, L. R. (2011). The hippocampus supports both recollection and familiarity when memories are strong. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(44), 15693-15702. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3438-11.2011URLpmid: 22049412 |
| [58] | Stoodley, C. J., & Schmahmann, J. D. (2009). Functional topography in the human cerebellum: A meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neuroimage, 44(2), 489-501. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.08.039URL |
| [59] | Strozak, P., Abedzadeh, D., & Curran, T. (2016). Separating the FN400 and N400 potentials across recognition memory experiments. Brain Research, 1635, 41-60. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.01.015URLpmid: 26776478 |
| [60] | Stuellein, N., Radach, R. R., Jacobs, A. M., & Hofmann, M. J. (2016). No one way ticket from orthography to semantics in recognition memory: N400 and P200 effects of associations. Brain Research, 1639, 88-98. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.02.029URLpmid: 26921776 |
| [61] | Trevor, A. H. (Eds).(2008). The psychology of language, from data to theory. Hove and New York: Psychology Press. |
| [62] | Voss, J. L., & Federmeier, K. D. (2011). FN400 potentials are functionally identical to N400 potentials and reflect semantic processing during recognition testing. Psychophysiology, 48(4), 532-546. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2010.01085.xURL |
| [63] | Wagenmakers, E. -J., Ratcliff, R., Gomez, P., & Mckoon, G. (2008). A diffusion model account of criterion shifts in the lexical decision task. Journal of Memory and Language, 58(1), 140-159. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2007.04.006URL |
| [64] | Wang, J. Q., Otgaar, H., Howe, M. L., & Zhou, C. (2019). A self-reference false memory effect in the DRM paradigm: Evidence from eastern and western samples. Memory & Cognition, 47(1), 76-86. doi: 10.3758/s13421-018-0851-3URLpmid: 30141171 |
| [65] | Wixted, J. T., Goldinger, S. D., Squire, L. R., Kuhn, J. R., Papesh, M. H., Smith, K. A., ... Steinmetz, P. N. (2018). Coding of episodic memory in the human hippocampus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(5), 1093-1098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1716443115URL |
| [66] | Wixted, J. T., & Squire, L. R. (2010). The role of the human hippocampus in familiarity-based and recollection-based recognition memory. Behavioural Brain Research, 215, 197-208. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.04.020URLpmid: 20412819 |
| [67] | Woods, J. A., & Dewhurst, S. A. (2019). Putting false memories into context: The effects of odour contexts on correct and false recall. Memory, 27(3), 379-386. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2018.1512632URLpmid: 30139301 |
| [68] | Zannino, G. D., Perri, R., Teghil, A., Caltagirone, C., & Carlesimo, G. A. (2018). Associative agreement as a predictor of naming ability in alzheimer's disease: A case for the semantic nature of associative links. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 11(261), 1-11. |
| [69] | Zhang, W. W., Gross, J., & Hayne, H. (2017). The effect of mood on false memory for emotional DRM word lists. Cognition and Emotion, 31(3), 526-537. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2016.1138930URLpmid: 26823096 |
相关文章 4
| [1] | 滑慧敏, 顾俊娟, 林楠, 李兴珊. 视觉词汇识别中的字符位置编码[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(7): 1132-1138. |
| [2] | 白学军;张慢慢;臧传丽;李馨;陈璐;闫国利. 词边界信息在中文词汇学习与识别中的作用:眼动研究的证据[J]. 心理科学进展, 2014, 22(1): 1-8. |
| [3] | 任桂琴;韩玉昌;刘颖. 句子语境中汉语词汇识别的即时加工过程[J]. 心理科学进展, 2012, 20(4): 493-503. |
| [4] | 李馨;白学军;闫国利;臧传丽;梁菲菲. 空格在文本阅读中的作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2010, 18(9): 1377-1385. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=5298
