 )
) 1南京师范大学心理学院
2南京师范大学音乐学院, 南京 210097
收稿日期:2019-09-03出版日期:2020-06-15发布日期:2020-04-22通讯作者:陈庆荣E-mail:jscqr80@sina.com基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金青年项目(31800914);江苏省社会科学基金项目研究成果(19YYC003);国家社会科学基金重点项目(18AYY010);江苏省高校自然科学研究面上项目(18KJD190003)The cognitive mechanism of music syntactic processing and the influence of music structure on its processing
ZHANG Jingjing1, LIANG Xiaoyue2, CHEN Yidi2, CHEN Qingrong1( )
) 1 School of Psychology, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210097, China
2 Conservatory of Music, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210097, China
Received:2019-09-03Online:2020-06-15Published:2020-04-22Contact:CHEN Qingrong E-mail:jscqr80@sina.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 音乐和语言是人类最重要的两种交流系统。与语言一样, 音符的排列和组织也是建立在一定的句法规则之上。尽管现有研究发现听众具有感知音乐句法的能力, 音乐句法加工的认知机制以及影响因素仍不清楚。基于此, 拟深入探究预期和整合在音乐音高句法加工中的作用, 以及音乐层级结构和时间结构对音高句法加工的影响。以期进一步揭示音乐句法加工的本质, 为音乐和语言的比较以及探索人类更一般的交流机制提供实证依据。
图/表 1
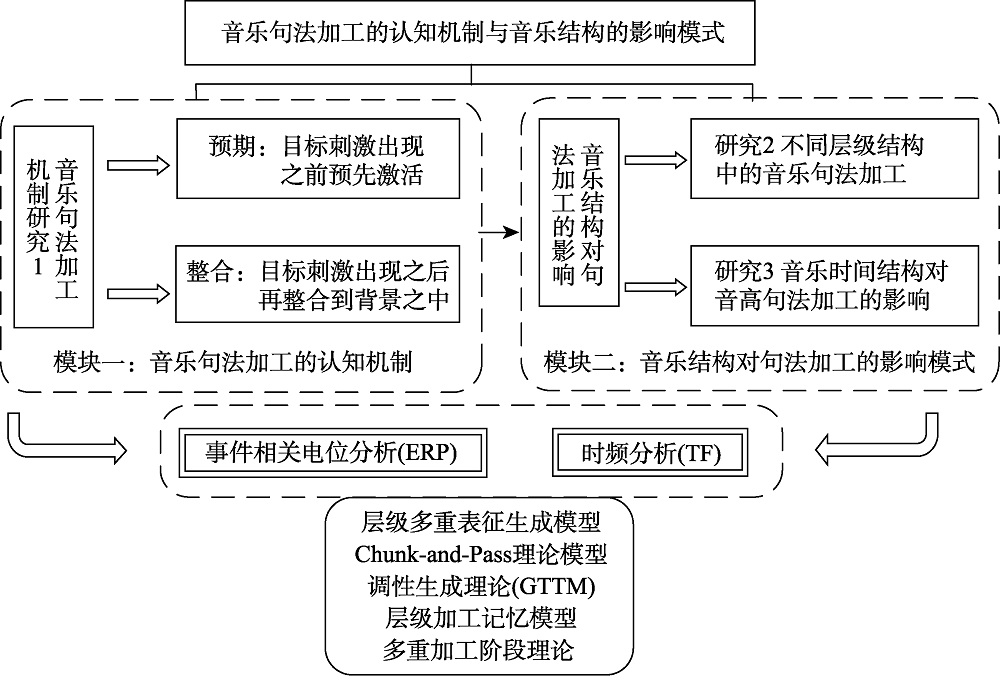
图1理论研究框架
 图1理论研究框架
图1理论研究框架参考文献 77
| [1] | 江俊, 王梓梦, 万璇, 蒋存梅 . (2014). 音乐时间加工的影响因素. 心理科学进展, 22(4), 650-658. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00650URL |
| [2] | 马谐, 杨玉芳, 张秋月 . (2016). 音乐句法的加工. 科学通报, 61(10), 1099-1111. |
| [3] | 叶铮, 周晓林 . (2006). 音乐之脑. 心理科学进展, 14(5), 641-647. |
| [4] | 张晶晶, 杨玉芳 . (2017). 音乐句法加工的影响因素. 心理科学进展, 25(11), 1823-1830. |
| [5] | 周临舒, 蒋存梅, 杨玉芳 . (2012). 音乐和语言句法认知的比较. 科学通报, 57(28), 2674-2685. |
| [6] | Arai, M., & Keller, F . (2013). The use of verb-specific information for prediction in sentence processing. Language and Cognitive Processes, 28(4), 525-560. doi: 10.1080/01690965.2012.658072URL |
| [7] | Bengtsson, S. L., & Ullén, F . (2006). Dissociation between melodic and rhythmic processing during piano performance from musical scores. NeuroImage, 30(1), 272-284. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.09.019URL |
| [8] | Bharucha, J. J., & Stoeckig, K . (1987). Priming of chords: Spreading activation or overlapping frequency spectra? Perception & Psychophysics, 41(6), 519-524. |
| [9] | Bigand, E., & Pineau, M . (1997). Global context effects on musical expectancy. Perception & Psychophysics, 59(7), 1098-1107. |
| [10] | Bigand, E., Tillmann, B., Poulin, B., D'Adamo, D. A., & Madurell, F . (2001). The effect of harmonic context on phoneme monitoring in vocal music. Cognition, 81(1), B11-B20. |
| [11] | Brown, R. M., Chen, J. L., Hollinger, A., Penhune, V. B., Palmer, C., & Zatorre, R. J . (2013). Repetition suppression in auditory-motor regions to pitch and temporal structure in music. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 25(2), 313-328. |
| [12] | Carey, D., Rosen, S., Krishnan, S., Pearce, M. T., Shepherd, A., Aydelott, J., & Dick, F . (2015). Generality and specificity in the effects of musical expertise on perception and cognition. Cognition, 137, 81-105. |
| [13] | Chen, Q., Zhang, J., Xu, X., Scheepers, C., Yang, Y., & Tanenhaus, M. K . (2016). Prosodic expectations in silent reading: ERP evidence from rhyme scheme and semantic congruence in classic Chinese poems. Cognition, 154, 11-21. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2016.05.007URL |
| [14] | Christiansen, M. H., & Chater, N . (2016). The now-or-never bottleneck: A fundamental constraint on language. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 39, 1-72. |
| [15] | DeLong, K. A., Urbach, T. P., & Kutas, M . (2005). Probabilistic word pre-activation during language comprehension inferred from electrical brain activity. Nature Neuroscience, 8(8), 1117-1121. doi: 10.1038/nn1504URL |
| [16] | Du, Y., & Zatorre, R. J . (2017). Musical training sharpens and bonds ears and tongue to hear speech better. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(51), 13579-13584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1712223114URL |
| [17] | Eitan, Z., & Granot, R. Y . (2008). Growing oranges on Mozart's apple tree: "Inner form" and aesthetic judgment. Music Perception, 25(5), 397-418. doi: 10.1525/mp.2008.25.issue-5URL |
| [18] | Farbood, M. M., Heeger, D. J., Marcus, G., Hasson, U., & Lerner, Y . (2015). The neural processing of hierarchical structure in music and speech at different timescales. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 9, 157. |
| [19] | Fitch, W. T . (2013). Rhythmic cognition in humans and animals: Distinguishing meter and pulse perception. Frontiers in systems neuroscience, 7, 68. |
| [20] | Friston, K., & Buzsáki, G . (2016). The functional anatomy of time: What and when in the brain. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20(7), 500-511. |
| [21] | Geiser, E., Ziegler, E., Jancke, L., & Meyer, M . (2009). Early electrophysiological correlates of meter and rhythm processing in music perception. Cortex, 45(1), 93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2007.09.010URL |
| [22] | Granot, R. Y., & Jacoby, N . (2011). Musically puzzling I: Sensitivity to overall structure in the sonata form? Musicae Scientiae, 15(3), 365-386. doi: 10.1177/1029864911409508URL |
| [23] | Hasson, U., Chen, J., & Honey, C. J . (2015). Hierarchical process memory: Memory as an integral component of information processing. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 19(6), 304-313. |
| [24] | Huron, D. B . (2006). Sweet anticipation: Music and the psychology of expectation. Cambridge, MA: MIT press. |
| [25] | Ito, A., Corley, M., Pickering, M. J., Martin, A. E., & Nieuwland, M. S . (2016). Predicting form and meaning: Evidence from brain potentials. Journal of Memory and Language, 86, 157-171. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2015.10.007URL |
| [26] | Ito, A., Pickering, M. J., & Corley, M . (2018). Investigating the time-course of phonological prediction in native and non-native speakers of English: A visual world eye-t racking study. Journal of Memory and Language, 98, 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2017.09.002URL |
| [27] | Jentschke, S., Friederici, A. D., & Koelsch, S . (2014). Neural correlates of music-syntactic processing in two-year old children. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 9, 200-208. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2014.04.005URL |
| [28] | Jones, M. R., & Boltz, M . (1989). Dynamic attending and responses to time. Psychological Review, 96(3), 459-491. |
| [29] | Jones, M. R., Moynihan, H., MacKenzie, N., & Puente, J . (2002). Temporal aspects of stimulus-driven attending in dynamic arrays. Psychological Science, 13(4), 313-319. |
| [30] | Kamide, Y . (2012). Learning individual talkers’ structural preferences. Cognition, 124(1), 66-71. |
| [31] | Kintsch, W . (1988). The role of knowledge in discourse comprehension: A construction-integration model. Psychological Review, 95(2), 163-182. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.95.2.163URL |
| [32] | Koelsch, S . (2014). Brain correlates of music-evoked emotions. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 15(3), 170-180. doi: 10.1038/nrn3666URL |
| [33] | Koelsch, S., Gunter, T., Friederici, A. D., & Schröger, E . (2000). Brain indices of music processing: “nonmusicians” are musical. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 12(3), 520-541. doi: 10.1162/089892900562183URL |
| [34] | Koelsch, S., Jentschke, S., Sammler, D., & Mietchen, D . (2007). Untangling syntactic and sensory processing: An ERP study of music perception. Psychophysiology, 44(3), 476-490. doi: 10.1111/psyp.2007.44.issue-3URL |
| [35] | Koelsch, S., Rohrmeier, M., Torrecuso, R., & Jentschke, S . (2013). Processing of hierarchical syntactic structure in music. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(38), 15443-15448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300272110URL |
| [36] | Koelsch, S., Schmidt, B.-H., & Kansok, J . (2002). Effects of musical expertise on the early right anterior negativity: An event-related brain potential study. Psychophysiology, 39(5), 657-663. doi: 10.1111/psyp.2002.39.issue-5URL |
| [37] | Koelsch, S., Vuust, P., & Friston, K . (2019). Predictive processes and the peculiar case of music. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 23(1), 63-77. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2018.10.006URL |
| [38] | Kuperberg, G. R., & Jaeger, T. F . (2016). What do we mean by prediction in language comprehension? Language, Cognition and Neuroscience, 31(1), 32-59. doi: 10.1080/23273798.2015.1102299URL |
| [39] | Lagrois, M.-é., Peretz, I., & Zendel, B. R . (2018). Neurophysiological and behavioral differences between older and younger adults when processing violations of tonal structure in music. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 12, 54. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00054URL |
| [40] | Lau, E., Stroud, C., Plesch, S., & Phillips, C . (2006). The role of structural prediction in rapid syntactic analysis. Brain and language, 98(1), 74-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2006.02.003URL |
| [41] | Lebrun-Guillaud, G., Tillmann, B., & Justus, T . (2008). Perception of tonal and temporal structures in chord sequences by patients with cerebellar damage. Music Perception, 25(4), 271-283. doi: 10.1525/mp.2008.25.4.271URL |
| [42] | Lerdahl, F., & Jackendoff, R. S . (1983). A generative theory of tonal music. Cambridge, MA: MIT press. |
| [43] | Lerner, Y., Honey, C. J., Silbert, L. J., & Hasson, U . (2011). Topographic mapping of a hierarchy of temporal receptive windows using a narrated story. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(8), 2906-2915. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3684-10.2011URL |
| [44] | Li, X., Zhang, Y., Xia, J., & Swaab, T. Y . (2017). Internal mechanisms underlying anticipatory language processing: Evidence from event-related-potentials and neural oscillations. Neuropsychologia, 102, 70-81. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.05.017URL |
| [45] | Ma, X., Ding, N., Tao, Y., & Yang, Y. F . (2018a). Differences in neurocognitive mechanisms underlying the processing of center-embedded and non-embedded musical structures. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 12, 425. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00425URL |
| [46] | Ma, X., Ding, N., Tao, Y., & Yang, Y. F . (2018b). Syntactic complexity and musical proficiency modulate neural processing of non-native music. Neuropsychologia, 121, 164-174. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.10.005URL |
| [47] | Maess, B., Koelsch, S., Gunter, T. C., & Friederici, A. D . (2001). Musical syntax is processed in Broca's area: An MEG study. Nature Neuroscience, 4(5), 540-545. doi: 10.1038/87502URL |
| [48] | Maess, B., Mamashli, F., Obleser, J., Helle, L., & Friederici, A. D . (2016). Prediction signatures in the brain: Semantic pre-activation during language comprehension. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 10, 591. |
| [49] | Margulis, E. H . (2005). A model of melodic expectation. Music Perception, 22(4), 663-714. doi: 10.1525/mp.2005.22.4.663URL |
| [50] | Meyer, L. B. (2008). Emotion and meaning in music. Chicago, IL: University of chicago Press. |
| [51] | Müller, M., Höfel, L., Brattico, E., & Jacobsen, T . (2010). Aesthetic judgments of music in experts and laypersons— An ERP study. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 76(1), 40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2010.02.002URL |
| [52] | Nan, Y., Liu, L., Geiser, E., Shu, H., Gong, C. C., Dong, Q., ... & Desimone, R . (2018). Piano training enhances the neural processing of pitch and improves speech perception in Mandarin-speaking children. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(28), E6630-E6639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1808412115URL |
| [53] | Otten, M., Nieuwland, M. S., & van Berkum, J. J . (2007). Great expectations: Specific lexical anticipation influences the processing of spoken language. BMC neuroscience, 8(1), 89. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-8-89URL |
| [54] | Otten, M., & van Berkum, J. J . (2008). Discourse-based word anticipation during language processing: Prediction or priming? Discourse Processes, 45(6), 464-496. doi: 10.1080/01638530802356463URL |
| [55] | Palmer, C., & Krumhansl, C. L . (1987). Independent temporal and pitch structures in determination of musical phrases. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 13(1), 116-126. doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.13.1.116URL |
| [56] | Patel, A. D . (2010). Music, language, and the brain. Oxford: Oxford university press. |
| [57] | Patel, A. D., Gibson, E., Ratner, J., Besson, M., & Holcomb, P. J . (1998). Processing syntactic relations in language and music: An event-related potential study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 10(6), 717-733. |
| [58] | Peretz, I . (1990). Processing of local and global musical information by unilateral brain-damaged patients. Brain, 113(4), 1185-1205. |
| [59] | Peretz, I . (1996). Can we lose memory for music? A case of music agnosia in a nonmusician. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 8(6), 481-496. |
| [60] | Peretz, I., & Coltheart, M . (2003). Modularity of music processing. Nature Neuroscience, 6(7), 688-691. doi: 10.1038/nn1083URL |
| [61] | Peretz, I., & Kolinsky, R . (1993). Boundaries of separability between melody and rhythm in music discrimination: A neuropsychological perspective. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 46(2), 301-325. |
| [62] | Poulin-Charronnat, B., Bigand, E., & Koelsch, S . (2006). Processing of musical syntax tonic versus subdominant: An event-related potential study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 18(9), 1545-1554. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2006.18.9.1545URL |
| [63] | Ruiz, M. H., Koelsch, S., & Bhattacharya, J . (2009). Decrease in early right alpha band phase synchronization and late gamma band oscillations in processing syntax in music. Human Brain Mapping, 30(4), 1207-1225. |
| [64] | Schmuckler, M. A., & Boltz, M. G . (1994). Harmonic and rhythmic influences on musical expectancy. Perception & Psychophysics, 56(3), 313-325. |
| [65] | Sun, L., Liu, F., Zhou, L., & Jiang, C . (2018). Musical training modulates the early but not the late stage of rhythmic syntactic processing. Psychophysiology, 55(2), e12983. doi: 10.1111/psyp.2018.55.issue-2URL |
| [66] | Tanenhaus, M. K., Spivey-Knowlton, M. J., Eberhard, K. M., & Sedivy, J. C . (1995). Integration of visual and linguistic information in spoken language comprehension. Science, 268(5217), 1632-1634. doi: 10.1126/science.7777863URL |
| [67] | Tillmann, B., & Bigand, E . (1998). Influence of global structure on musical target detection and recognition. International Journal of Psychology, 33(2), 107-122. |
| [68] | Tillmann, B., Bigand, E., & Pineau, M . (1998). Effects of global and local contexts on harmonic expectancy. Music Perception, 16(1), 99-117. doi: 10.2307/40285780URL |
| [69] | Tillmann, B., Janata, P., & Bharucha, J. J . (2003). Activation of the inferior frontal cortex in musical priming. Cognitive Brain Research, 16(2), 145-161. doi: 10.1016/S0926-6410(02)00245-8URL |
| [70] | Tillmann, B., & Lebrun-Guillaud, G . (2006). Influence of tonal and temporal expectations on chord processing and on completion judgments of chord sequences. Psychological Research, 70(5), 345-358. doi: 10.1007/s00426-005-0222-0URL |
| [71] | Treisman, A. M., & Gelade, G . (1980). A feature-integration theory of attention. Cognitive Psychology, 12(1), 97-136. |
| [72] | van Berkum,, J. J. A., Brown, C. M., Zwitserlood, P., Kooijman, V., & Hagoort, P . (2005). Anticipating upcoming words in discourse: Evidence from ERPs and reading times. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 31(3), 443-467. |
| [73] | van Petten, C., & Luka, B. J . (2012). Prediction during language comprehension: Benefits, costs, and ERP components. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 83(2), 176-190. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2011.09.015URL |
| [74] | Zhang, J., Che, X., & Yang, Y . (2019). Event-related brain potentials suggest a late interaction of pitch and time in music perception. Neuropsychologia, 132, 107118. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2019.107118URL |
| [75] | Zhang, J., Jiang, C., Zhou, L., & Yang, Y . (2016). Perception of hierarchical boundaries in music and its modulation by expertise. Neuropsychologia, 91, 490-498. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2016.09.013URL |
| [76] | Zhang, J., Zhou, X., Chang, R., & Yang, Y . (2018). Effects of global and local contexts on chord processing: An ERP study. Neuropsychologia, 109, 149-154. |
| [77] | Zhou, L., Liu, F., Jiang, J., Jiang, H., & Jiang, C . (2019). Abnormal neural responses to harmonic syntactic structures in congenital amusia. Psychophysiology, e13394. |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 王琳, 王志丹, 王泓婧. 孤独症儿童动作发展障碍的神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(7): 1239-1250. |
| [2] | 隋雪, 史汉文, 李雨桐. 语言加工过程中的观点采择及其认知机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(6): 990-999. |
| [3] | 张照, 张力为, 龚然. 视觉工作记忆的过滤效能[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 635-651. |
| [4] | 周爱保, 胡砚冰, 周滢鑫, 李玉, 李文一, 张号博, 郭彦麟, 胡国庆. 听而不“闻”?人声失认症的神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 414-424. |
| [5] | 赵小红, 童薇, 陈桃林, 吴冬梅, 张蕾, 陈正举, 方晓义, 龚启勇, 唐小蓉. 敬畏的心理模型及其认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 520-530. |
| [6] | 魏真瑜, 邓湘树, 赵治瀛. 亲社会行为中的从众效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 531-539. |
| [7] | 岳童, 黄希庭, 傅安国. 人们何以能够“舍生取义”?基于保护性价值观认知神经机制的解释[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 540-548. |
| [8] | 王葛彤, 席洁, 陈霓虹, 黄昌兵. 双眼视差的神经机制与知觉学习效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 56-69. |
| [9] | 郭滢, 龚先旻, 王大华. 错误记忆产生的认知与神经机制:信息加工视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 79-92. |
| [10] | 刘启鹏, 赵小云, 王翠艳, 徐艺雅, 王淑燕. 反刍思维与注意脱离损坏的关系及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 102-111. |
| [11] | 翁纯纯, 王宁. 时距知觉的动物研究范式及相关神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(9): 1478-1492. |
| [12] | 杨晓梦, 王福兴, 王燕青, 赵婷婷, 高春颍, 胡祥恩. 瞳孔是心灵的窗口吗?——瞳孔在心理学研究中的应用及测量[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7): 1029-1041. |
| [13] | 程士静, 何文广. 语义认知的习得、发展和老化及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7): 1156-1163. |
| [14] | 杨国春, 伍海燕, 齐玥, 刘勋. 人类性别加工的认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(12): 2008-2017. |
| [15] | 李灵, 侯晓旭, 张亚, 隋雪. 食物线索注意偏向及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(12): 2040-2051. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=5050
