 )
) 南开大学周恩来政府管理学院社会心理学系, 天津 300350
收稿日期:2019-09-20出版日期:2020-04-26发布日期:2020-03-27通讯作者:汪新建E-mail:wangxj@nankai.edu.cn基金资助:* 教育部哲学社会科学研究重大课题攻关项目“医患信任关系建设的社会心理机制研究”(15JZD030);天津市社会科学规划项目“天津市心理健康服务体系的实务模式探索”(TJJX18-001);南开大学博士研究生科研创新基金资助The cognitive neural network model of trust
CHEN Ying, XU Minxia, WANG Xinjian( )
) Zhou Enlai School of Government, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
Received:2019-09-20Online:2020-04-26Published:2020-03-27Contact:WANG Xinjian E-mail:wangxj@nankai.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 信任是指一方在基于对另一方行为期望的基础上愿意冒一定的风险, 以期在将来得到积极结果的心理过程。近年, 认知神经取向的研究对信任行为引起的特定脑区激活进行了考察, 却忽略了大规模脑网络在信任过程中的整体作用。在总结前人研究的基础上提出信任的认知神经网络模型, 并从认知神经网络视角对信任行为进行解释和整合。在模型中, 信任行为是动力系统、情感系统和认知系统相互作用的结果, 并分别与奖励网络、显著网络、中央执行网络和默认网络等神经网络激活有关。此外, 模型还强调信任行为的反馈机制, 以此构成完整的建构模型。模型阐明了心理系统与中枢神经网络之间的对应关系, 从认知神经角度解释了信任行为发生的心理机制和神经基础。
图/表 3

图1简化信任博弈游戏示意图 注:括号中数字分别为委托人和受托人的收益
 图1简化信任博弈游戏示意图 注:括号中数字分别为委托人和受托人的收益
图1简化信任博弈游戏示意图 注:括号中数字分别为委托人和受托人的收益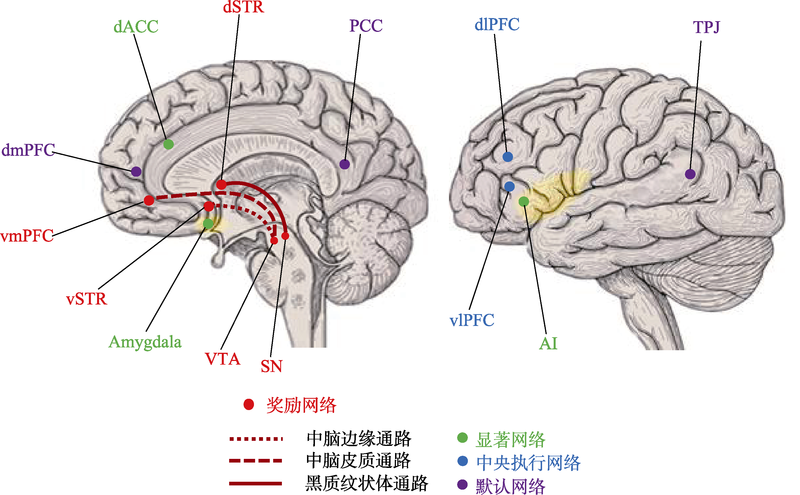
图2信任的认知神经网络 注:奖励网络包括中脑边缘通路、中脑皮质通路和黑质纹状体通路, 涉及的脑区有中脑腹侧被盖区(VTA)、腹侧纹状体(vSTR)、腹内侧前额皮层(vmPFC)、黑质(SN)和背侧纹状体(dSTR)等; 显著网络涉及的脑区有杏仁核(Amygdala)、前脑岛(AI)和背侧前扣带回(dACC)等; 中央执行网络涉及的脑区有背外侧前额皮层(dlPFC)和腹外侧前额皮层(vlPFC)等; 默认网络涉及的脑区有颞顶联合区(TPJ)、后扣带皮层(PCC)以及背内侧前额皮层(dmPFC)等。
 图2信任的认知神经网络 注:奖励网络包括中脑边缘通路、中脑皮质通路和黑质纹状体通路, 涉及的脑区有中脑腹侧被盖区(VTA)、腹侧纹状体(vSTR)、腹内侧前额皮层(vmPFC)、黑质(SN)和背侧纹状体(dSTR)等; 显著网络涉及的脑区有杏仁核(Amygdala)、前脑岛(AI)和背侧前扣带回(dACC)等; 中央执行网络涉及的脑区有背外侧前额皮层(dlPFC)和腹外侧前额皮层(vlPFC)等; 默认网络涉及的脑区有颞顶联合区(TPJ)、后扣带皮层(PCC)以及背内侧前额皮层(dmPFC)等。
图2信任的认知神经网络 注:奖励网络包括中脑边缘通路、中脑皮质通路和黑质纹状体通路, 涉及的脑区有中脑腹侧被盖区(VTA)、腹侧纹状体(vSTR)、腹内侧前额皮层(vmPFC)、黑质(SN)和背侧纹状体(dSTR)等; 显著网络涉及的脑区有杏仁核(Amygdala)、前脑岛(AI)和背侧前扣带回(dACC)等; 中央执行网络涉及的脑区有背外侧前额皮层(dlPFC)和腹外侧前额皮层(vlPFC)等; 默认网络涉及的脑区有颞顶联合区(TPJ)、后扣带皮层(PCC)以及背内侧前额皮层(dmPFC)等。
图3信任的认知神经网络模型
 图3信任的认知神经网络模型
图3信任的认知神经网络模型参考文献 48
| 1 | 张宁, 张雨青, 吴坎坎 . ( 2011). 信任的心理和神经生理机制. 心理科学, 34( 5), 1137-1143. |
| 2 | 张蔚, 张振, 高宇, 段华平, 吴兴南 . ( 2016). 经济决策中人际信任博弈的理论模型与脑机制. 心理科学进展, 24( 11), 1780-1791. |
| 3 | Amodio D. M., &Frith C. D . ( 2006). Meeting of minds: The medial frontal cortex and social cognition. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 7( 4), 268-277. |
| 4 | Anderhub V., Engelmann D., & Güth W . ( 2002). An experimental study of the repeated trust game with incomplete information. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization, 48( 2), 197-216. |
| 5 | Arrow K.J . ( 1972). Gifts and exchanges. Philosophy and Public Affairs, 1( 4), 343-362. |
| 6 | Belfi A. M., Koscik T. R., & Tranel D . ( 2015). Damage to the insula is associated with abnormal interpersonal trust. Neuropsychologia, 71, 165-172. |
| 7 | Bellucci G., Chernyak S. V., Goodyear K., Eickhoff S. B., & Krueger F . ( 2017). Neural signatures of trust in reciprocity: A coordinate-based meta-analysis. Human Brain Mapping, 38( 3), 1233-1248. |
| 8 | Bellucci G., Hahn T., Deshpande G., Krueger F . ( 2019). Functional connectivity of specific resting-state networks predicts trust and reciprocity in the trust game. Cognitive, Affective, and Behavioral Neuroscience, 19( 1), 165-176. |
| 9 | Berg J., Dickhaut J., & McCabe K . ( 1995). Trust, reciprocity, and social history. Games and Economic Behavior, 10( 1), 122-142. |
| 10 | Bosch O. G., Eisenegger C., Gertsch J., von Rotz R., Dornbierer D., Gachet M. S., … Quednow B. B . ( 2015). Gamma-hydroxybutyrate enhances mood and prosocial behavior without affecting plasma oxytocin and testosterone. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 62, 1-10. |
| 11 | Bressler S. L., &Menon V. , ( 2010). Large-scale brain networks in cognition: Emerging methods and principles. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14( 6), 277-290. |
| 12 | Bush G., Luu P., & Posner M. I . ( 2000). Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4( 6), 215-222. |
| 13 | Clark A. K., &Eisenstein M. A . ( 2013). Interpersonal trust: An age-period-cohort analysis revisited. Social Science Research, 42( 2), 361-375. |
| 14 | Davidenko O., Bonny J.-M., Morrot G., Jean B., Claise B., Benmoussa A., … Darcel N . ( 2018). Differences in BOLD responses in brain reward network reflect the tendency to assimilate a surprising flavor stimulus to an expected stimulus. NeuroImage, 183, 37-46. |
| 15 | Declerck C. H., Boone C., & Emonds G . ( 2013). When do people cooperate? The neuroeconomics of prosocial decision making. Brain and Cognition, 81( 1), 95-117. |
| 16 | Delgado M. R., Frank R. H., & Phelps E. A . ( 2005). Perceptions of moral character modulate the neural systems of reward during the trust game. Nature Neuroscience, 8( 11), 1611-1618. |
| 17 | Engell A. D., Haxby J. V., & Todorov A . ( 2007). Implicit trustworthiness decisions: automatic coding of face properties in the human amygdala. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19( 9), 1508-1519. |
| 18 | Engle-Warnick J. &Slonim R. L . ( 2004). The evolution of strategies in a repeated trust game. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization, 55( 4), 553-573. |
| 19 | Etkin A., Egner T., & Kalisch R . ( 2011). Emotional processing in anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15( 2), 85-93. |
| 20 | Fang C. &Wu B. , ( 2019). Socially-maximal nash equilibrium distributions in large distributional games. Economics Letters, 175, 40-42. |
| 21 | Fett A.-K. J., Gromann P. M., Giampietro V., Shergill S. S., & Krabbendam L . ( 2012). Default distrust? An fMRI investigation of the neural development of trust and cooperation. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 9( 4), 395-402. |
| 22 | Fett A.-K. J., Shergill S. S., Gromann P. M., Dumontheil I., Blakemore S.-J., Yakub F., & Krabbendam L . ( 2014). Trust and social reciprocity in adolescence-a matter of perspective-taking. Journal of Adolescence, 37( 2), 175-184. |
| 23 | Greene J. D., Sommerville R. B., Nystrom L. E., Darley J. M., & Cohen J. D . ( 2001). An fMRI investigation of emotional engagement in moral judgment. Science, 293( 5537), 2105-2108. |
| 24 | Hahn T., Notebaert K., Anderl C., Teckentrup V., Ka?ecker A., & Windmann S . ( 2014). How to trust a perfect stranger: Predicting initial trust behavior from resting-state brain-electrical connectivity. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 10( 6), 809-813. |
| 25 | Hare T. A., Camerer C. F., & Rangel A . ( 2009). Self-control in decision-making involves modulation of the vmPFC valuation system. Science, 324( 5927), 646-648. |
| 26 | Ikemoto, S. ( 2010). Brain reward circuitry beyond the mesolimbic dopamine system: A neurobiological theory. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 35( 2), 129-150. |
| 27 | Irwin K., Edwards K., & Tamburello J. A . ( 2015). Gender, trust and cooperation in environmental social dilemmas. Social Science Research, 50, 328-342. |
| 28 | Joel D. &Weiner I. , ( 2000). Striatal contention scheduling and the split circuit scheme of basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuitry: From anatomy to behaviour. Brain Dynamics and the Striatal Complex, 12, 209-236. |
| 29 | Knoch D. &Fehr E. , ( 2007). Resisting the power of temptations: The right prefrontal cortex and self-control. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1104( 1), 123-134. |
| 30 | Koscik T. R., &Tranel D. , ( 2011). The human amygdala is necessary for developing and expressing normal interpersonal trust. Neuropsychologia, 49( 4), 602-611. |
| 31 | Krueger F., McCabe K., Moll J., Kriegeskorte N., Zahn R., Strenziok M., … Grafman J . ( 2007). Neural correlates of trust. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104, 20084-20089. |
| 32 | Krueger F. &Meyer-Lindenberg A. , ( 2018). Toward a model of interpersonal trust drawn from neuroscience, psychology, and economics. Trends in Neurosciences, 42( 2), 92-101. |
| 33 | Levy B. J., &Wagner A. D . ( 2011). Cognitive control and right ventrolateral prefrontal cortex: Reflexive reorienting, motor inhibition, and action updating. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1224( 1), 40-62. |
| 34 | McCabe K., Houser D., Ryan L., Smith V., & Trouard T . ( 2001). A functional imaging study of cooperation in two-person reciprocal exchange. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 98( 20), 11832-11835. |
| 35 | Menon V. . (2015). Salience network. In A. W. Toga (Ed.), Brain mapping (pp. 597-611). Waltham: Academic Press. |
| 36 | Miller E. K., &Cohen J. D . ( 2001). An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 24( 1), 167-202. |
| 37 | Moretto G., Sellitto M., & di Pellegrino G . ( 2013). Investment and repayment in a trust game after ventromedial prefrontal damage. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 593. |
| 38 | Namkung H., Kim S.-H., & Sawa A . ( 2017). The insula: an underestimated brain area in clinical neuroscience, psychiatry, and neurology. Trends in Neurosciences, 40( 4), 200-207. |
| 39 | Raichle M. E., MacLeod A. M., Snyder A. Z., Powers W. J., Gusnard D. A., & Shulman G. L . ( 2001). A default mode of brain function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 98( 2), 676-682. |
| 40 | Rothstein B. &Uslaner E. M . ( 2005). All for all: Equality, corruption, and social trust. World Politics, 58( 1), 41-72. |
| 41 | Sherman L. E., Rudie J. D., Pfeifer J. H., Masten C. L., McNealy K., & Dapretto M . ( 2014). Development of the default mode and central executive networks across early adolescence: A longitudinal study. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 10, 148-159. |
| 42 | Smith A. &Skinner A. S . ( 2000). The wealth of nations: Books IV-V. London: Penguin Classics. |
| 43 | Souza M. J., Donohue S. E., & Bunge S. A . ( 2009). Controlled retrieval and selection of action-relevant knowledge mediated by partially overlapping regions in left ventrolateral prefrontal cortex. NeuroImage, 46( 1), 299-307. |
| 44 | Stets J. E., &Fares P. , ( 2019). The effects of race/ethnicity and racial/ethnic identification on general trust. Social Science Research, 80, 1-14. |
| 45 | Tzieropoulos, H. ( 2013). The trust game in neuroscience: A short review. Social Neuroscience, 8( 5), 407-416. |
| 46 | Uddin L.Q . ( 2015). Salience processing and insular cortical function and dysfunction. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 16( 1), 55-61. |
| 47 | Unoka Z., Seres I., áspán N., Bódi N., & Kéri S . ( 2009). Trust game reveals restricted interpersonal transactions in patients with borderline personality disorder. Journal of Personality Disorders, 23( 4), 399-409. |
| 48 | van Overwalle , F. ( 2009). Social cognition and the brain: A meta-analysis. Human Brain Mapping, 30( 3), 829-858. |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 贡喆, 唐玉洁, 刘昌. 信任博弈范式真的能测量信任吗?[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 19-30. |
| [2] | 高青林, 周媛. 计算模型视角下信任形成的心理和神经机制——基于信任博弈中投资者的角度[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 178-189. |
| [3] | 黄崇蓉, 胡瑜. 组织内信任与创造力的关系:元分析的证据[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7): 1118-1132. |
| [4] | 颜爱民, 李亚丽, 谢菊兰, 李莹. 员工对企业社会责任的差异化反应:基于归因理论的阐释[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(6): 1004-1014. |
| [5] | 李庆功, 王震炎, 孙捷元, 师妍. 网约车场景中声誉和面孔可信度对女性信任判断的影响以及直觉性思维的调节作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(5): 746-751. |
| [6] | 廖嘉俊, 李红, 吴寅. 睾酮与人类决策行为[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(9): 1607-1621. |
| [7] | 孙连荣, 王沛. 和谐医患关系的心理机制及其促进技术[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(6): 951-964. |
| [8] | 辛自强. 市场化与人际信任变迁[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(12): 1951-1966. |
| [9] | 张旭凯, 尹航, 李鹏, 李红. 催产素对社会决策行为的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(8): 1438-1449. |
| [10] | 董妍, 于晓琪, 李哲能. 信任的遗传基础:来自基因的证据[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(7): 1204-1212. |
| [11] | 刘效广, 王志浩. 情与理对立视角下管理者亲社会违规 对员工行为的影响机理:一项跨层次追踪研究[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(2): 191-203. |
| [12] | 程南华, 李占星, 朱莉琪. 儿童的社会权力认知及其与社会行为的关系[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(2): 283-293. |
| [13] | 王新野, 李苑, 常明, 游旭群. 自动化信任和依赖对航空安全的危害及其改进[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(9): 1614-1622. |
| [14] | 袁博, 董悦, 李伟强. 道歉在信任修复中的作用:来自元分析的证据[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(7): 1103-1113. |
| [15] | 贡喆;刘昌;沈汪兵;王贤;石荣. 信任对创造力的影响:激发、抑制以及倒U假设[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(3): 463-474. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=5040
