 ), 孙秀丽2, 郝喜玲3
), 孙秀丽2, 郝喜玲3 1 天津财经大学商学院, 天津 300222
2 北京大学光华管理学院, 北京 100871
3 安徽财经大学工商管理学院, 蚌埠 233030
收稿日期:2018-11-27出版日期:2020-02-15发布日期:2019-12-25通讯作者:郑方E-mail:zhengfang@tjufe.edu.cn基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金青年项目(71702124);国家自然科学基金青年项目(71802146);国家自然科学基金青年项目(71602001);教育部人文社会科学研究青年基金项目(16YJC630176);中国博士后科学基金特别资助项目(2018T110196)The dynamic process and reciprocal effect of employee social capital cross-level fit
ZHENG Fang1( ), SUN Xiuli2, HAO Xiling3
), SUN Xiuli2, HAO Xiling3 1 School of Business, Tianjin University of Finance and Economics, Tianjin 300222, China
2 Guanghua School of Management, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
3 School of Business Administration, Anhui University of Finance and Economics, Bengbu 233030, China
Received:2018-11-27Online:2020-02-15Published:2019-12-25Contact:ZHENG Fang E-mail:zhengfang@tjufe.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 员工社会资本向企业社会资本的转化是拓展员工价值、获取外部资源的有效途径, 为阐释这一多层次主体互动现象, 提出社会资本跨层次契合的构念, 运用跨层次追踪研究设计, 对其动态演化过程和双向作用机制进行剖析。首先, 探索员工社会资本跨层次契合的维度结构, 并基于此开发跨层次契合量表; 其次, 对社会资本跨层次契合进行过程解构, 探讨员工心理与行为、企业能力与情境在动态演化过程中的作用; 再次, 构建自上而下和自下而上的嵌入与涌现机制理论模型, 将影响员工社会资本跨层次契合的多层次因素整合到同一个理论框架, 并以纵向追踪数据进行实证检验, 厘清作用路径和作用边界。在此基础上, 运用追踪跨案例研究方法, 探讨社会资本跨层次契合的战略选择, 研究结论能为激发员工角色外行为, 有效利用社会资本的管理实践提供启示。
图/表 4
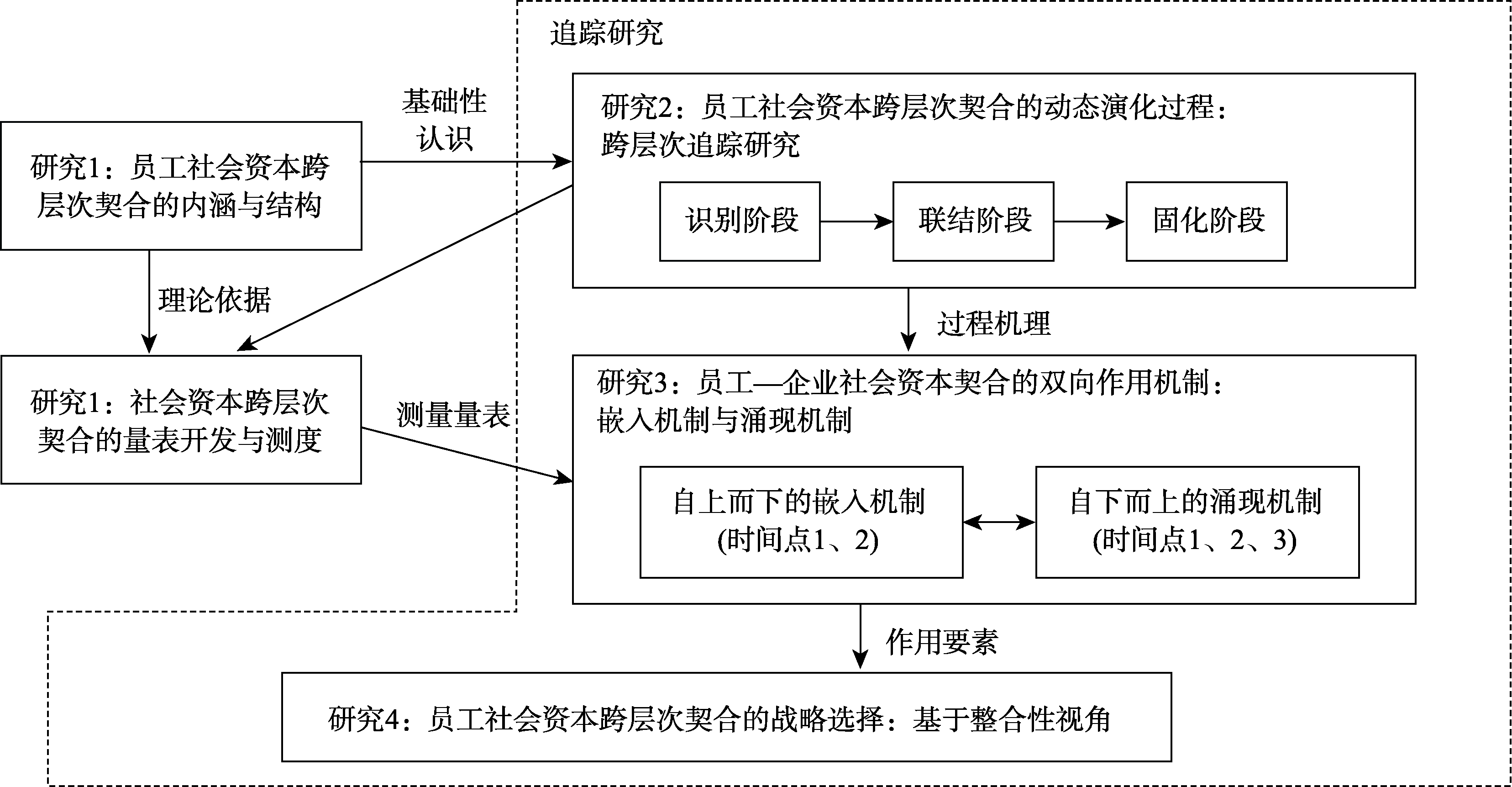
图1本研究内容框架
 图1本研究内容框架
图1本研究内容框架
图2员工社会资本跨层次契合的动态演化过程 注:e表示企业; i表示员工; o表示联结对象。
 图2员工社会资本跨层次契合的动态演化过程 注:e表示企业; i表示员工; o表示联结对象。
图2员工社会资本跨层次契合的动态演化过程 注:e表示企业; i表示员工; o表示联结对象。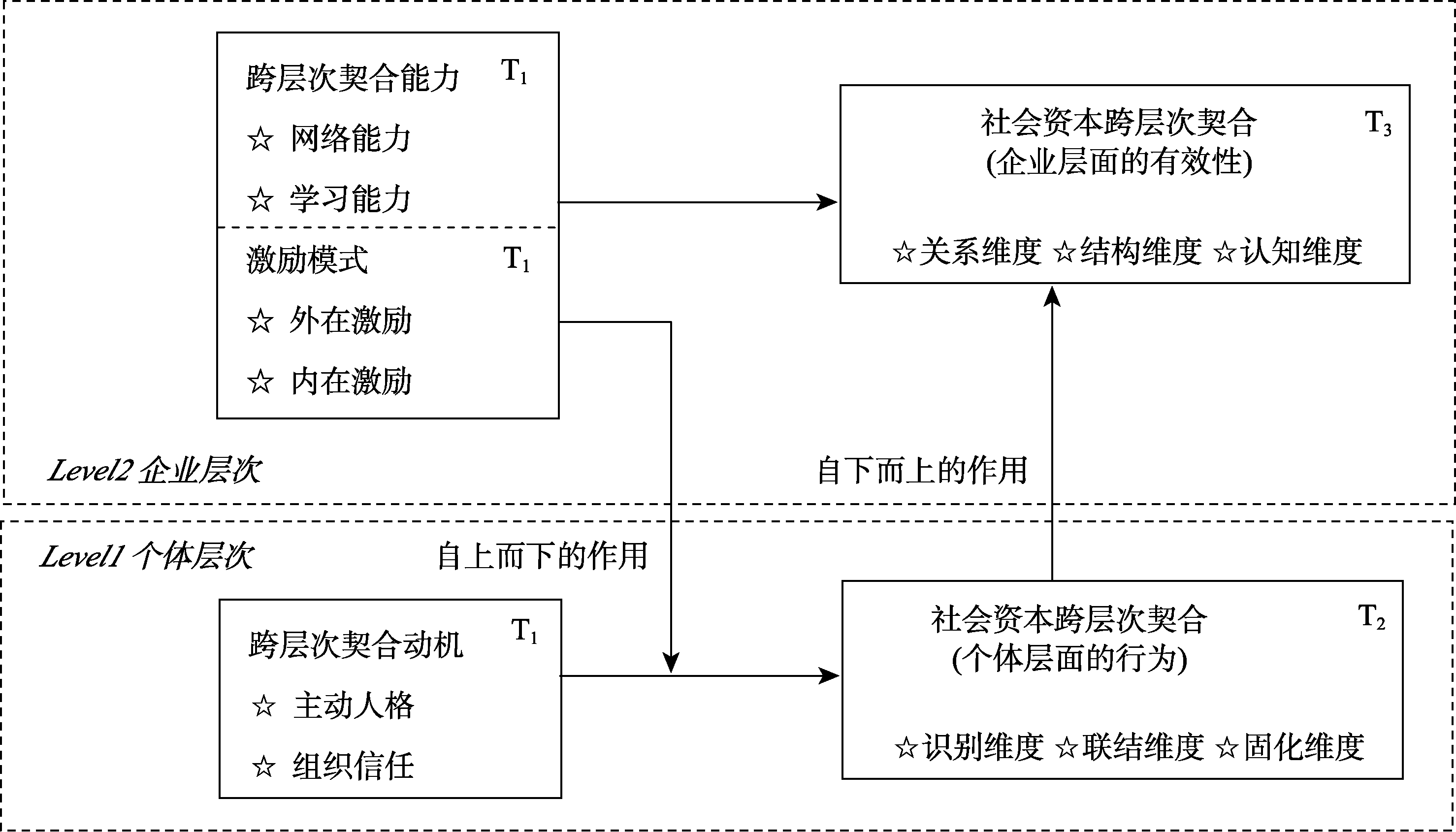
图3员工社会资本跨层次契合的双向作用机制 注:上方虚线框内是企业层次的构念, 下方虚线框内是个体层次的构念; T1、T2、T3表示数据收集的时间节点。
 图3员工社会资本跨层次契合的双向作用机制 注:上方虚线框内是企业层次的构念, 下方虚线框内是个体层次的构念; T1、T2、T3表示数据收集的时间节点。
图3员工社会资本跨层次契合的双向作用机制 注:上方虚线框内是企业层次的构念, 下方虚线框内是个体层次的构念; T1、T2、T3表示数据收集的时间节点。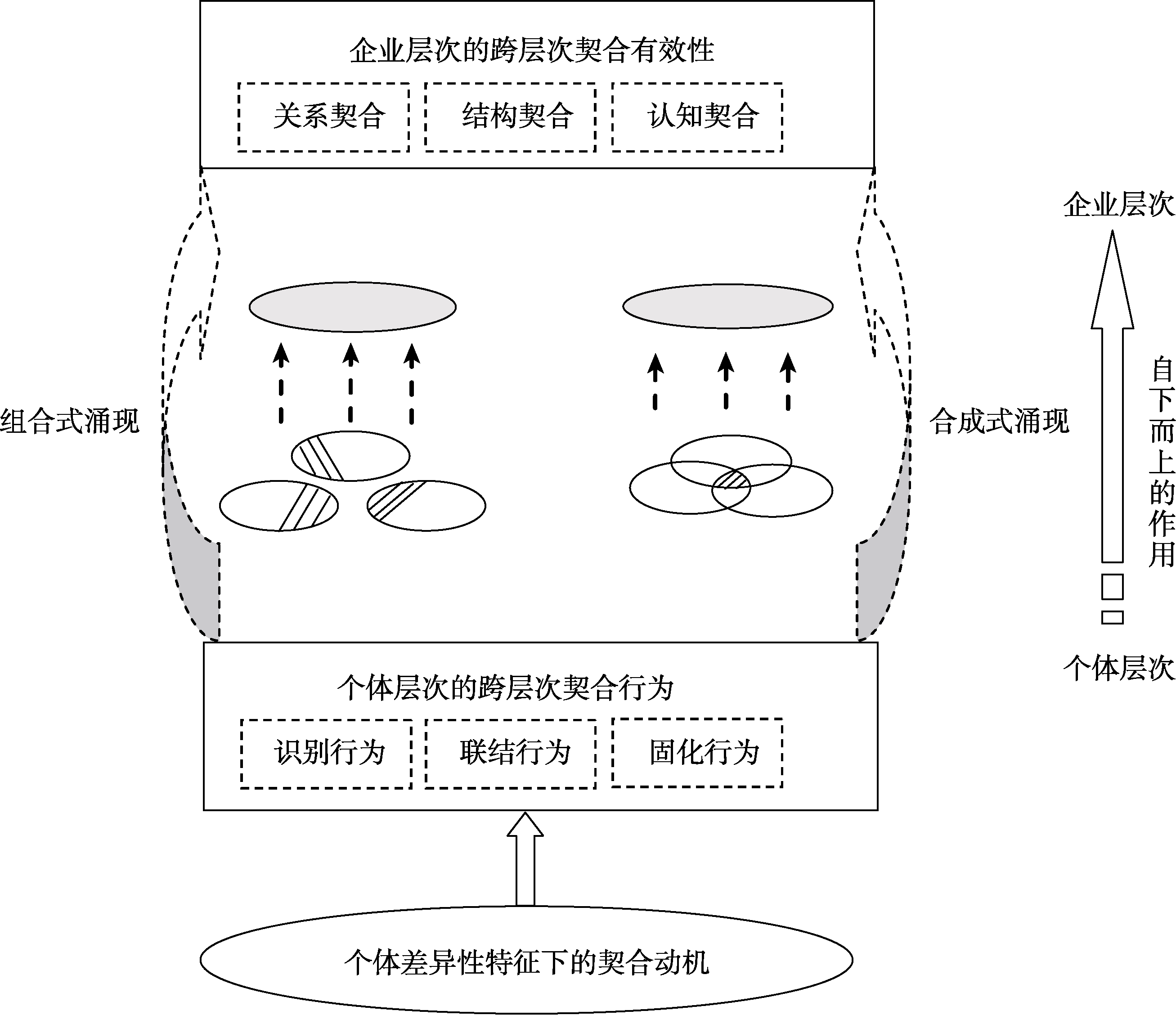
图4从个体层次到企业层次自下而上的涌现机制 注:组合式和合成式涌现图示中箭头下方代表不同个体的社会资本, 箭头上方代表跨层次生成的企业社会资本。
 图4从个体层次到企业层次自下而上的涌现机制 注:组合式和合成式涌现图示中箭头下方代表不同个体的社会资本, 箭头上方代表跨层次生成的企业社会资本。
图4从个体层次到企业层次自下而上的涌现机制 注:组合式和合成式涌现图示中箭头下方代表不同个体的社会资本, 箭头上方代表跨层次生成的企业社会资本。参考文献 79
| [1] | 边燕杰, 丘海雄 . ( 2000). 企业的社会资本及其功效. 中国社会科学, ( 2), 87-99. |
| [2] | 蔡莉, 汤淑琴, 马艳丽, 高祥 . ( 2014). 创业学习、创业能力与新企业绩效的关系研究. 科学学研究, 32( 8), 1189-1197. |
| [3] | 韩炜, 彭正银 . ( 2016). 关系视角下创业网络的形成过程研究. 中国软科学, ( 2), 89-104. |
| [4] | 侯楠, 杨皎平, 戴万亮 . ( 2016). 团队异质性、外部社会资本对团队成员创新绩效影响的跨层次研究. 管理学报, 13( 2), 212-220. |
| [5] | 李超平, 苏琴, 宋照礼 . ( 2014). 互动视角的组织社会化动态跟踪研究. 心理科学进展, 22( 3), 409-417. |
| [6] | 李海舰, 朱芳芳 . ( 2017). 重新定义员工——从员工1.0到员工4.0的演进. 中国工业经济, ( 10), 156-173. |
| [7] | 李新春, 梁强, 宋丽红 . ( 2010). 外部关系-内部能力平衡与新创企业成长——基于创业者行为视角的实证研究. 中国工业经济, ( 12), 97-107. |
| [8] | 李雪灵, 马文杰, 白晓晓, 任海波 . ( 2011). 转型经济背景下的新创企业关系网络研究前沿探析与未来展望. 外国经济与管理, 33( 5), 9-16. |
| [9] | 刘红云, 张雷 . (2005). 追踪数据分析方法及其应用. 北京: 教育科学出版社. |
| [10] | 石军伟 . ( 2017). 企业社会资本的动态演化及其管理策略. 学海, ( 1), 184-191. |
| [11] | 王凤彬, 刘松博 . ( 2007). 企业社会资本生成问题的跨层次分析. 浙江社会科学, ( 4), 87-132. |
| [12] | 王雁飞, 朱瑜 . ( 2012). 组织社会化与员工行为绩效——基于个人-组织匹配视角的纵向实证研究. 管理世界, ( 5), 109-124. |
| [13] | 魏江, 邬爱其, 彭雪蓉 . ( 2014). 中国战略管理研究: 情境问题与理论前沿. 管理世界, ( 12), 167-171. |
| [14] | 谢洪涛, 赖应良, 孙玉梅 . ( 2016). 科研团队社会资本、个体动机对个体知识共享行为的影响——基于多层线性模型的跨层次分析. 技术经济, 35( 1), 30-35. |
| [15] | 张宝建, 孙国强, 裴梦丹, 齐捧虎 . ( 2015). 网络能力、网络结构与创业绩效——基于中国孵化产业的实证研究. 南开管理评论, 18( 2), 39-50. |
| [16] | 张俊瑞, 王良辉, 汪方军 . ( 2018). 管理层任职网络会影响高管薪酬吗?——一项基于社会资本的实证研究. 管理评论, 30( 6), 136-148. |
| [17] | 张颖, 杨付 . ( 2017). 主动性人格: 机制与未来走向. 心理科学进展, 25( 9), 1544-1551. |
| [18] | 赵晨, 高中华 . ( 2017). 组织社会化交互视角下新员工政治自我效能的动态演化及作用机制. 心理科学进展, 25( 9), 1456-1468. |
| [19] | 赵晶, 张书博, 祝丽敏, 王明 .( 2014). 个人社会资本与组织社会资本契合度对企业实际控制权的影响——基于国美电器和雷士照明的对比. 中国工业经济, ( 3), 121-133. |
| [20] | 赵延东, 罗家德 . ( 2005). 如何测量社会资本: 一个经验研究综述. 国外社会科学, ( 2), 18-24. |
| [21] | 郑方 . ( 2011). 治理与战略的双重嵌入性——基于连锁董事网络的研究. 中国工业经济, ( 9), 108-118. |
| [22] | 周小虎, 陈传明 . ( 2004). 企业社会资本与持续竞争优势. 中国工业经济, ( 5), 90-96. |
| [23] | 庄玉梅 . ( 2014). 组织社会资本的跨层次衍生研究. 山东大学学报(哲学社会科学版), ( 5), 123-131. |
| [24] | Acton, B. P., Foti, R. J., Lord, R. G., & Gladfelter, J. A . ( 2019). Putting emergence back in leadership emergence: A dynamic, multilevel, process-oriented framework. The Leadership Quarterly, 30( 1), 145-164. |
| [25] | Adler, P. S., & Kwon, S.-W . ( 2002). Social capital: Prospects for a new concept. Academy of Management Review, 27( 1), 17-40. |
| [26] | Atuahene-Gima, K., & Murray, J. Y . ( 2007). Exploratory and exploitative learning in new product development: A social capital perspective on new technology ventures in China. Journal of International Marketing, 15( 2), 1-29. |
| [27] | Brown, T. F. (1997). Theoretical perspectives on social capital. working paper from |
| [28] | Campbell, A . ( 2014). Signaling in social network and social capital formation. Econ Theory, 57 (2), 303-337. |
| [29] | Cappelli, P., & Sherer, P. D . ( 1991). The missing role of context in OB: The need for a meso-level approach. Research in Organizaional Behavior, 13( 1), 55-110. |
| [30] | Carter, N. T., Carter, D. R., & DeChurch, L. A . ( 2018). Implications of observability for the theory and measurement of emergent team phenomena. Journal of Management, 44( 4), 1398-1425. |
| [31] | Chen, X.-P., Pillutla, M. M., & Yao, X . ( 2009). Unintended consequences of cooperation inducing and maintaining mechanisms in public goods dilemmas: Sanctions and moral appeals. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations, 12( 2), 241-255. |
| [32] | Chuang, A., Hsu, R. S., Wang, A.-C. & Judge, T. A . ( 2015), Does west “fit” with east? In search of a Chinese model of person-environment fit. Academy of Management Journal, 58( 2), 480-510. |
| [33] | Coleman, J. S . ( 1988). Social capital in the creation of human capital. American Journal of Sociology, 94( Suppl.), S95-S120. |
| [34] | Cope, J . ( 2011). Entrepreneurial learning from failure: An interpretative phenomenological analysis. Journal of Business Venturing, 26( 6), 604-623. |
| [35] | Crossan, M. M., Lane, H. W., & White, R. E . ( 1999). An Organizational learning framework: From intuition to institution. Academy of Management Review, 24( 3), 522-537. |
| [36] | Farh, C. I. C., Lanaj, K., & Ilies, R . ( 2017). Resource-based contingencies of when team-member exchange helps member performance in teams. Academy of Management Journal, 60( 3), 1117-1137. |
| [37] | Fulkerson, G. M., & Thompson, G. H . ( 2008). The evolution of a contested concept: A meta-analysis of social capital definitions and trends (1988-2006). Sociological Inquiry, 78( 4), 536-557. |
| [38] | Gambeta, E., Koka, B. R., & Hoskisson, R. E . ( 2019). Being too good for your own good: A stakeholder perspective on the differential effect of firm-employee relationships on innovation search. Strategic Management Journal, 40( 1), 108-126. |
| [39] | Gao, J. L., Wang, J., Yu, D. L, Dai, J. M., Zhu, Y. K., & Fu, H . ( 2018). Associations between psychosocial work environments and social capital: A multilevel analysis study in a Chinese context. BMC Public Health, 18( 1), 976. |
| [40] | Granovetter, M . ( 1985). Economic action and social structure: The problem of embeddedness. American Journal of Sociology, 91( 3), 481-510. |
| [41] | Guo, C., & Miller, J. K . ( 2010). Guanxi dynamics and entrepreneurial firm creation and development in China. Management and Organization Review, 6( 2), 267-291. |
| [42] | Guzman, F. A., & Espejo, A . ( 2019). Introducing changes at work: How voice behavior relates to management innovation. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 40( 1), 73-90. |
| [43] | Håkansson, H., & Ford, D . ( 2002). How should companies interact in business networks? Journal of Business Research, 55( 2), 133-139. |
| [44] | Hanifan, L. J . ( 1916). The rural school community center. The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, 67( 1), 130-138. |
| [45] | Han, S . ( 2016). The association of self-esteem with individual and contextual levels of social capital: Evidence from a multilevel analysis. Social Science Quarterly, 97( 5), 1315-1329. |
| [46] | Holcomb, T. R., Ireland, R. D., Holmes, R. M., & Hitt, M. A . ( 2009). Architecture of entrepreneurial learning: Exploring the link among heuristics, knowledge, and action. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 33( 1), 167-192. |
| [47] | Hollenbeck, J. R., & Jamieson, B. B . ( 2015). Human capital, social capital, and social network analysis: Implications for strategic human resource management. Academy of Management Perspectives, 29( 3), 370-385. |
| [48] | Inkpen, A. C., & Tsang, E. W. K . ( 2005). Social capital, networks, and knowledge transfer. Academy of Management Review, 30( 1), 146-165. |
| [49] | Jia, L. D., Shaw, J. D., Tsui, A. S., & Park, T.-Y . ( 2014). A social-structural perspective on employee-organization relationships and team creativity. Academy of Management Journal, 57( 3), 869-891. |
| [50] | Kaasa, A . ( 2009). Effects of different dimensions of social capital on innovative activity: Evidence from Europe at the regional level. Technovation, 29( 3), 218-233. |
| [51] | Kammeyer-Mueller, J. D., Livingston, B. A., & Liao, H . ( 2011). Perceived similarity, proactive adjustment, and organizational socialization. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 78( 2), 225-236. |
| [52] | Kempster, S., & Cope, J . ( 2010). Learning to lead in the entrepreneurial context. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research, 16( 1), 5-34. |
| [53] | Klein, K. J., & Kozlowski, S. W. J . ( 2000). Multilevel theory, research, and methods in organizations: Foundations, extensions, and new directions. SanFrancisco: Josssy-Boss. |
| [54] | Kozlowski, S. W. J., & Klein, K. J . ( 2000). A multilevel approach to theory and research in organizations: Contextual, temporal, and emergent processes. In K. J. Klein & S. W. J. Kozlowski (Eds.), Multilevel theory, research, and methods in organizations: Foundations, extensions, and new directions (pp. 3-90). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. |
| [55] | Kuvaas, B., Buch, R., Weibel, A., Dysvik, A., & Nerstad, C. G. L .( 2017). Do intrinsic and extrinsic motivation relate differently to employee outcomes? Journal of Economic Psychology, 61( 8), 244-258. |
| [56] | Kwon, S., & Adler, P. S . ( 2014). Social capital: Maturation of a field of research. Academy of Management Review, 39( 4), 412-422. |
| [57] | Lans, T., Blok, V., & Gulikers, J . ( 2015). Show me your network and I'll tell you who you are: Social competence and social capital of early-stage entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurship & Regional Development, 27( 7-8), 458-473. |
| [58] | Leana, C. R., & van Buren, H. J . ( 1999). Organizational social capital and employment practices. The Academy of Management Review, 24( 3), 538-555. |
| [59] | Lee, T . ( 1999). Using qualitative methods in organizational research. Los Angeles: Sage Publications. |
| [60] | Lepper, M. R., David, G., & Nisbett, R. E . ( 1973). Undermining children’s intrinsic interest with extrinsic reward: A test of the “overjustification” hypothesis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 28( 1), 129-137. |
| [61] | Major, B. C., Le Nguyen, K. D., Lundberg, K. B., & Fredrickson, B. L . ( 2018). Well-being correlates of perceived positivity resonance: Evidence from trait and episode-level assessments. Personality & Social Psychology Bulletin, 44( 12), 1631-1647. |
| [62] | Miles, J. A . ( 2012). Management and organization theory. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc. |
| [63] | Nahapiet, J., & Ghoshal, S . ( 1998). Social capital, intellectual capital, and the organizational advantage. The Academy of Management Review, 23( 2), 242-266. |
| [64] | Oh, H., Labianca, G., & Chung, M.-H . ( 2006). A multilevel model of group social capital. Academy of Management Review, 31( 3), 569-582. |
| [65] | O'Reilly, C. A., Chatman, J., & Caldwell, D. F . ( 1991). People and organizational culture: A profile comparison approach to assessing person-organization fit. Academy of Management Journal, 34( 3), 487-516. |
| [66] | Oswick, C., Fleming, P., & Hanlon, G . ( 2011). From borrowing to blending: Rethinking the processes of organizational theory building. Academy of Management Review, 36( 2), 318-337. |
| [67] | Payne, G. T., Moore, C. B., Griffis, S. E., & Autry, C. W . ( 2011). Multilevel challenges and opportunities in social capital research. Journal of Management, 37( 2), 491-520. |
| [68] | Peng, M. W., & Luo, Y. D . ( 2000). Managerial ties and firm performance in a transition economy: The nature of a micro-macro link. Academy of Management Journal, 43( 3), 486-501. |
| [69] | Portes, A . ( 1998). Social capital: Its origins and applications in modern sociology. Annual Review of Sociology, 24(1):1-24. |
| [70] | Putnam, R . ( 1993). The prosperous community: Social capital and public life. The American Prospect,(13), 35-42. |
| [71] | Rai, A., Ghosh, P., Chauhan, R., & Singh, R . ( 2018). Improving in-role and extra-role performances with rewards and recognition. Management Research Review, 41( 8), 902-919. |
| [72] | Rotich, K. J . ( 2015). History, evolution and development of human resource management: A contemporary perspective. Global Journal of Human Resource Management, 3( 3), 58-73. |
| [73] | Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L . ( 2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist, 55( 1), 68-83. |
| [74] | Salvato, C., & Vassolo, R . ( 2018). The sources of dynamism in dynamic capabilities. Strategic Management Journal, 39( 6), 1728-1752. |
| [75] | Sauerwald, S., Lin, Z., & Peng, M. W . ( 2016). Board social capital and excess CEO returns. Strategic Management Journal, 37( 3), 498-520. |
| [76] | Shipilov, A., Gulati, R., Kilduff, M., Li, S., & Tsai, W . ( 2014). Relational pluralism within and between organizations. Academy of Management Journal, 57( 2), 449-459. |
| [77] | Sozen, H. C., Varoglu, D., Yeloglu, H. O., & Basim, H. N . ( 2016). Human or social resources management: Which conditions force HR departments to select the right employees for organizational social capital?. European Management Review, 13( 1), 3-18. |
| [78] | Tsai, W., & Ghoshal, S . ( 1998). Social capital and value creation: The role of intrafirm networks. Academy of Management Journal, 41( 4), 464-476. |
| [79] | Zaheer, S., Albert, S., & Zaheer, A . ( 1999). Time scales and organizational theory. Academy of Management Review, 24( 4), 725-741. |
相关文章 3
| [1] | 葛红宁;周宗奎;牛更枫;陈武. 社交网站使用能带来社会资本吗?[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(3): 454-463. |
| [2] | 李宏利,张雷. 家庭社会资本及其相关因素[J]. 心理科学进展, 2005, 13(3): 283-289. |
| [3] | 武欣,吴志明,张德. 组织公民行为研究的新视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2005, 13(2): 211-218. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4942
