1 暨南大学管理学院, 广州 510632
2 首都经济贸易大学工商管理学院, 北京 100071
3 广东外语外贸大学商学院, 广州 510420
收稿日期:2019-03-25出版日期:2019-10-31发布日期:2019-09-23通讯作者:李爱梅基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金项目(71801109,71571087);第64批中国博士后科学基金面上项目(2018M640879);广东省自然科学基金项目(2017A030308013)Constant connectivity attenuates autonomy: Mechanism and consequences
WANG Haixia1, JIA Huiyuan2, SUN Hailong3, LI Aimei11 Management School, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 College of Business Administration, Capital University of Economics and Business, Beijing 100071, China
3 School of Business, Guangdong University of Foreign Studies, Guangzhou 510420, China
Received:2019-03-25Online:2019-10-31Published:2019-09-23Contact:LI Aimei 摘要/Abstract
摘要: 万物可互联了, 时间却稀缺了, 情感也耗竭了。把这三种现实工作中的趋势关联起来的关键概念是自主性:员工不能自主控制工作时间引发时间稀缺和情感耗竭。过往研究认为, 在一般情景中, 互联网连接性会增加自主性。但是, 当处于一种不对称的权力依赖关系中时, 互联网连接性反而会降低自主性。借助权力依赖理论, 相对依赖性和家长式领导监控氛围是逆转互联网连接性增强自主性的关键条件。通过引入权力依赖理论, 从一个新颖的视角探讨互联网连接性降低自主性的作用机制及其后效, 所构建的理论模型挑战了以往文献中互联网连接性增加自主性的主流理论观点, 也为互联网连接性环境下的自主性问题构建了一个新的理论基础。
图/表 2
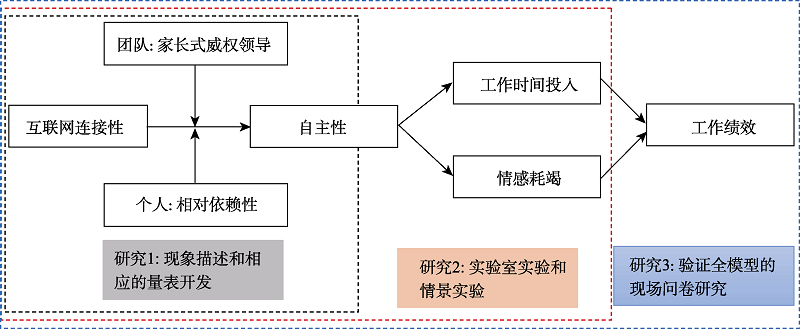
图1研究框架
 图1研究框架
图1研究框架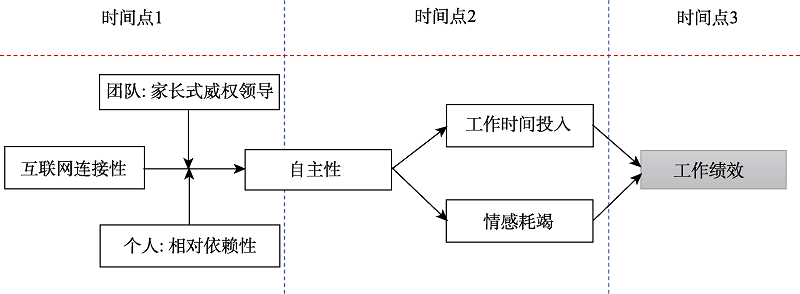
图2研究3采用多源、多时点和多层次的现场问卷研究(工作绩效为上司评价)
 图2研究3采用多源、多时点和多层次的现场问卷研究(工作绩效为上司评价)
图2研究3采用多源、多时点和多层次的现场问卷研究(工作绩效为上司评价)参考文献 48
| 1 | 樊景立, 鄭伯壎 . ( 2000). 華人組織的家長式領導: 一項文化觀點的分析. 本土心理學研究, ( 13), 126-180. |
| 2 | 范皑皑, 丁小浩 . ( 2007). 教育, 工作自主性与工作满意度. 清华大学教育研究, 28( 6), 40-47. |
| 3 | 哈佛商业评论. ( 2018). 工作时间越来越长, 咋就停不下来?. 2019-03-21 取自 |
| 4 | 胡进梅, 沈勇 . ( 2014). 工作自主性和研发人员的创新绩效: 基于任务互依性的调节效应模型. 中国人力资源开发, ( 17), 30-35. |
| 5 | 刘燕, 范巍 . ( 2005). 知识员工团队工作自主性与效能的关系研究. 应用心理学, 11( 4), 313-317. |
| 6 | 潘陆山, 符健春, 黄逸群, 李远 . ( 2010). 工作自主性对前瞻性人格-工作绩效的缓冲作用研究. 人类工效学, 16( 4), 36-39. |
| 7 | 王益富, 秦启文, 张建人 . ( 2012). 生产型企业的工作自主性: 概念, 测量与相关研究. 心理科学进展, 20( 7), 1062-1067. |
| 8 | 徐世勇, 朱金强 . ( 2017). 道德领导与亲社会违规行为: 双中介模型. 心理学报, 49( 1), 106-115. |
| 9 | 周浩, 龙立荣 . ( 2005). 恩威并施, 以德服人——家长式领导研究述评. 心理科学进展, 13( 2), 227-238. |
| 10 | Abramson L. Y., Seligman M. E., & Teasdale J. D . ( 1978). Learned helplessness in humans: Critique and reformulation. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 87( 1), 49-74. |
| 11 | Attewell, P. . ( 1987). The deskilling controversy. Work and Occupations, 14( 3), 323-346. |
| 12 | Bakker,A. B . ( 2011). An evidence-based model of work engagement. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 20( 4), 265-269. doi: 10.1177/0963721411414534 |
| 13 | Bakker A. B., Albrecht S. L., & Leiter M. P . ( 2011). Key questions regarding work engagement. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 20( 1), 4-28. doi: 10.1080/1359432X.2010.485352 |
| 14 | Boekhorst J. A., Singh P., & Burke R . ( 2017). Work intensity, emotional exhaustion and life satisfaction: The moderating role of psychological detachment. Personnel Review, 46( 5), 891-907. |
| 15 | Burawoy, M. . ( 1979). The anthropology of industrial work. Annual Review of Anthropology, 8( 1), 231-266. |
| 16 | Deci E. L., Olafsen A. H., & Ryan R. M . ( 2017). Self-determination theory in work organizations: The state of a science. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 4( 1), 19-43. |
| 17 | Demerouti E., Bakker A. B., Nachreiner F., & Schaufeli W. B . ( 2001). The job demands-resources model of burnout. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86( 3), 499-512. |
| 18 | Emerson,R. M . ( 1962). Power-dependence relations. American Sociological Review, 27( 1), 31-41. |
| 19 | Gaines, J., &Jermier,J. M . ( 1983). Emotional exhaustion in a high stress organization. Academy of Management Journal, 26( 4), 567-586. |
| 20 | Galinsky A. D., Rucker D. D., & Magee J. C . ( 2016). Power and perspective-taking: A critical examination. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 67, 91-92. |
| 21 | Guinote, A. . ( 2007). Power and goal pursuit. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 33( 8), 1076-1087. |
| 22 | Hackman,J. R., &Oldham,G. R . ( 1976). Motivation through the design of work: Test of a theory. Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 16( 2), 250-279. |
| 23 | Haushofer, J., &Fehr E. 2014). On the psychology of poverty. Science, 344( 6186), 862-867. |
| 24 | Hinkin,T. R . ( 1998). A brief tutorial on the development of measures for use in survey questionnaires. Organizational Research Methods, 1( 1), 104-121. |
| 25 | Karasek,R. A .,Jr. . ( 1979). Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: Implications for job redesign. Administrative Science Quarterly, 24( 2), 285-308. |
| 26 | Kubicek B., Pa?kvan M., & Bunner J . ( 2017). The bright and dark sides of job autonomy. In Job demands in a changing world of work(pp. 45-63). Cham: Springer. |
| 27 | Levine,L. J., &Edelstein,R. S . ( 2009). Emotion and memory narrowing: A review and goal-relevance approach. Cognition & Emotion, 23( 5), 833-875. |
| 28 | Malhotra, D., &Gino F. 2011). The pursuit of power corrupts: How investing in outside options motivates opportunism in relationships. Administrative Science Quarterly, 56( 4), 559-592. doi: 10.1177/0001839212441350 |
| 29 | Mani A., Mullainathan S., Shafir E., & Zhao J . ( 2013). Poverty impedes cognitive function. Science, 341( 6149), 976-980. doi: 10.1126/science.1238041 |
| 30 | Mathieu J. E., Wolfson M. A., & Park S . ( 2018). The evolution of work team research since Hawthorne. American Psychologist, 73( 4), 308-321. |
| 31 | Mazmanian, M. . ( 2013). Avoiding the trap of constant connectivity: When congruent frames allow for heterogeneous practices. Academy of Management Journal, 56( 5), 1225-1250. |
| 32 | Mazmanian M., Orlikowski W. J., & Yates J . ( 2013). The autonomy paradox: The implications of mobile email devices for knowledge professionals. Organization Science, 24( 5), 1337-1357. |
| 33 | Molm,L. D . ( 1991). Affect and social exchange: Satisfaction in power-dependence relations. American Sociological Review, 56( 4), 475-493. |
| 34 | Morgeson,F. P., &Humphrey,S. E . ( 2006). The work design questionnaire (WDQ): Developing and validating a comprehensive measure for assessing job design and the nature of work. Journal of Applied Psychology, 91( 6), 1321-1339. |
| 35 | Mullainathan, S., &Shafir E. 2013). Scarcity: Why having too little means so much (1st ed.). New York: Times Books, Henry Holt and Company. |
| 36 | Nijp H. H., Beckers D. G., Geurts S. A., Tucker P., & Kompier M. A . ( 2012). Systematic review on the association between employee worktime control and work- non-work balance, health and well-being, and job-related outcomes. Scandinavian Journal of Work Environment & Health, 38( 4), 298-313. |
| 37 | Pellegrini,E. K., &Scandura,T. A . ( 2008). Paternalistic leadership: A review and agenda for future research. Journal of Management, 34( 3), 566-593. |
| 38 | Podsakoff P. M., MacKenzie S. B., & Podsakoff N. P . ( 2012). Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annual Review of Psychology, 63( 1), 539-569. |
| 39 | Putnam L. L., Myers K. K., & Gailliard B. M . ( 2014). Examining the tensions in workplace flexibility and exploring options for new directions. Human Relations, 67( 4), 413-440. doi: 10.1177/0018726713495704 |
| 40 | Rucker,D. D., &Galinsky,A. D . ( 2017). Social power and social class: Conceptualization, consequences, and current challenges. Current Opinion in Psychology, 18 26-30. |
| 41 | Seligman,M. E . ( 1972). Learned helplessness. Annual Review of Medicine, 23( 1), 407-412. |
| 42 | Sturm,R. E., &Antonakis J. 2014). Interpersonal power: A review, critique, and research agenda. Journal of Management, 41( 1), 136-163. |
| 43 | Tepper B. J., Carr J. C., Breaux D. M., Geider S., Hu C., & Hua W . ( 2009). Abusive supervision, intentions to quit, and employees’ workplace deviance: A power/dependence analysis. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 109( 2), 156-167. |
| 44 | von Nordenflycht A. 2010). What is a professional service firm? Toward a theory and taxonomy of knowledge- intensive firms. Academy of Management Review, 35( 1), 155-174. |
| 45 | Warr, P. . ( 1990). The measurement of well-being and other aspects of mental health. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 63( 3), 193-210. |
| 46 | Warr, P. . ( 1994). A conceptual framework for the study of work and mental health. Work & Stress, 8( 2), 84-97. |
| 47 | Wee E. X. M., Liao H., Liu D., & Liu J . ( 2017). Moving from abuse to reconciliation: A power-dependence perspective on when and how a follower can break the spiral of abuse. Academy of Management Journal, 60( 6), 2352-2380. |
| 48 | Wilson K. S., Sin H-P., & Conlon D. E . ( 2010). What about the leader in leader-member exchange? The impact of resource exchanges and substitutability on the leader. Academy of Management Review, 35( 3), 358-372. |
相关文章 5
| [1] | 尹奎, 赵景, 李璨, 王宏蕾, 王崇锋. 领导授权行为的形成机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(6): 1097-1110. |
| [2] | 杨 莹;寇 彧. 亲社会互动中的幸福感:自主性的作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(7): 1226-1235. |
| [3] | 李琬予;寇彧. 孝道信念的形成与发展:不同文化下亲子互动的视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(7): 1069-1075. |
| [4] | 李锋;王二平. 团队作业特征研究现状与展望[J]. 心理科学进展, 2008, 16(5): 753-759. |
| [5] | 张秀春,邹晓燕. 青少年的个人事务自主观念研究述评[J]. 心理科学进展, 2004, 12(6): 883-883~890. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4853
