 ), 李超凡1
), 李超凡1 1. 北京外国语大学国际商学院, 北京 100089
2. 对外经济贸易大学国际商学院, 北京 100029
收稿日期:2018-12-23出版日期:2019-09-15发布日期:2019-07-24通讯作者:龚诗阳E-mail:gongshiyang@uibe.edu.cn基金资助:国家自然科学基金青年项目(71702010);国家自然科学基金青年项目(71602033);北京外国语大学中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金项目(2015QD010);和一流学科建设项目(2018YY033);对外经济贸易大学惠园优秀青年****项目资助(18YQ05)The impact of team cultural diversity on team innovation
LI Qian1, GONG Shiyang2( ), LI Chaofan1
), LI Chaofan1 1. International Business School, Beijing Foreign Studies University, Beijing 100089, China
2. Business School, University of International Business and Economics, Beijing 100029, China
Received:2018-12-23Online:2019-09-15Published:2019-07-24Contact:GONG Shiyang E-mail:gongshiyang@uibe.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 随着经济全球化和跨国企业的迅速发展, 越来越多的企业中开始出现具有多样性文化背景的团队。企业管理者期待具有不同文化背景的员工能在团队工作中贡献新的观点和视角, 从而促进团队创新。因此, 探讨团队文化多样性与团队创新之间的影响关系已成为近年来学术界和企业界共同关注的焦点问题。所以, 采用社会分类-信息加工的理论视角, 首先厘清团队文化多样性的理论框架, 并进一步检验团队文化多样性与团队创新之间的影响关系及内在机制; 并且, 分别从团队内部和团队外部因素出发, 探讨团队文化多样性与团队创新影响关系中的边界条件。在实践上, 研究结论也将为企业有效管理跨文化团队, 推动企业创新提供一定的理论指导。
图/表 5
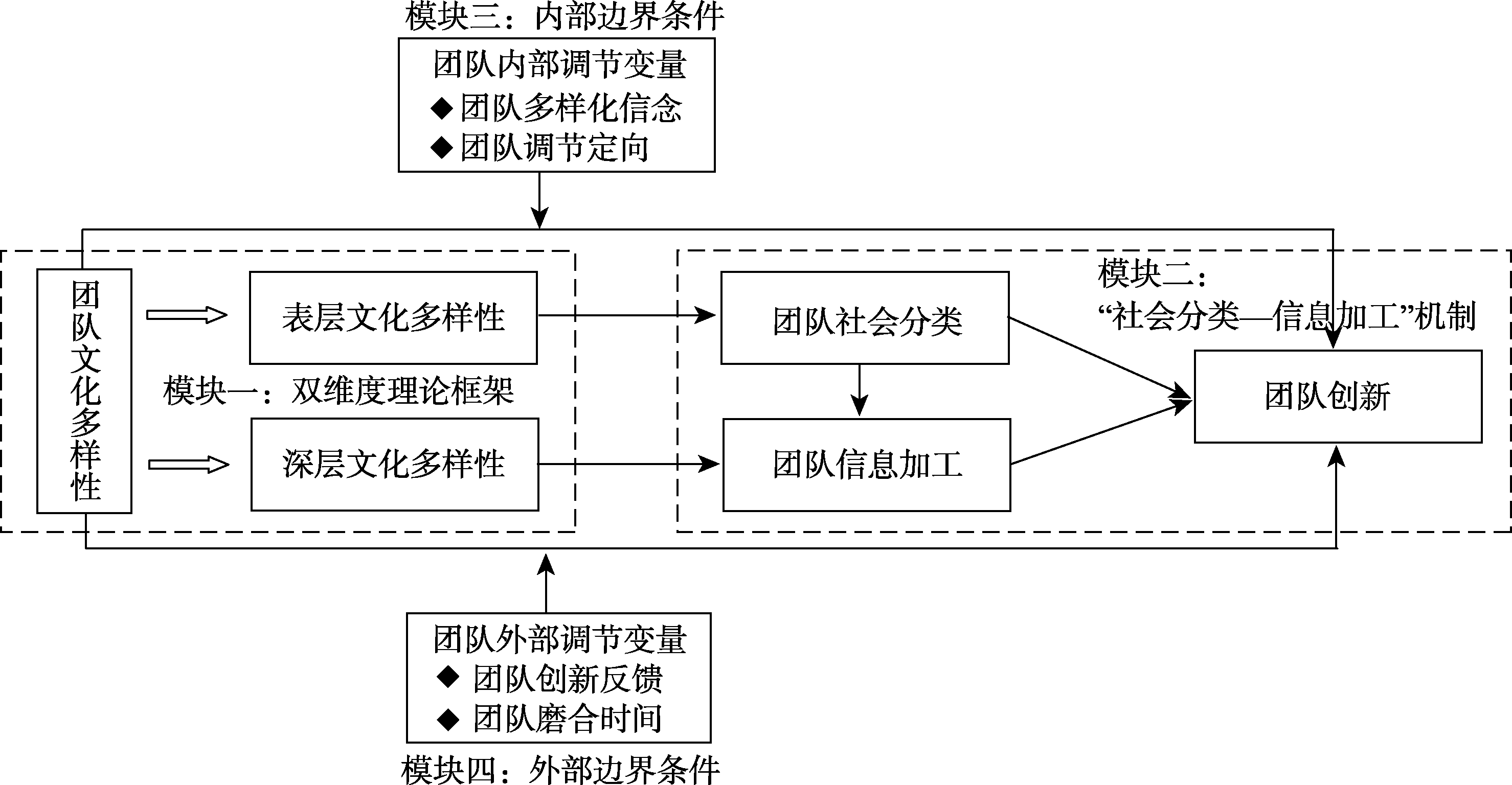
图1理论研究框架
 图1理论研究框架
图1理论研究框架
图2研究模块一:团队文化多样性的双维度理论
 图2研究模块一:团队文化多样性的双维度理论
图2研究模块一:团队文化多样性的双维度理论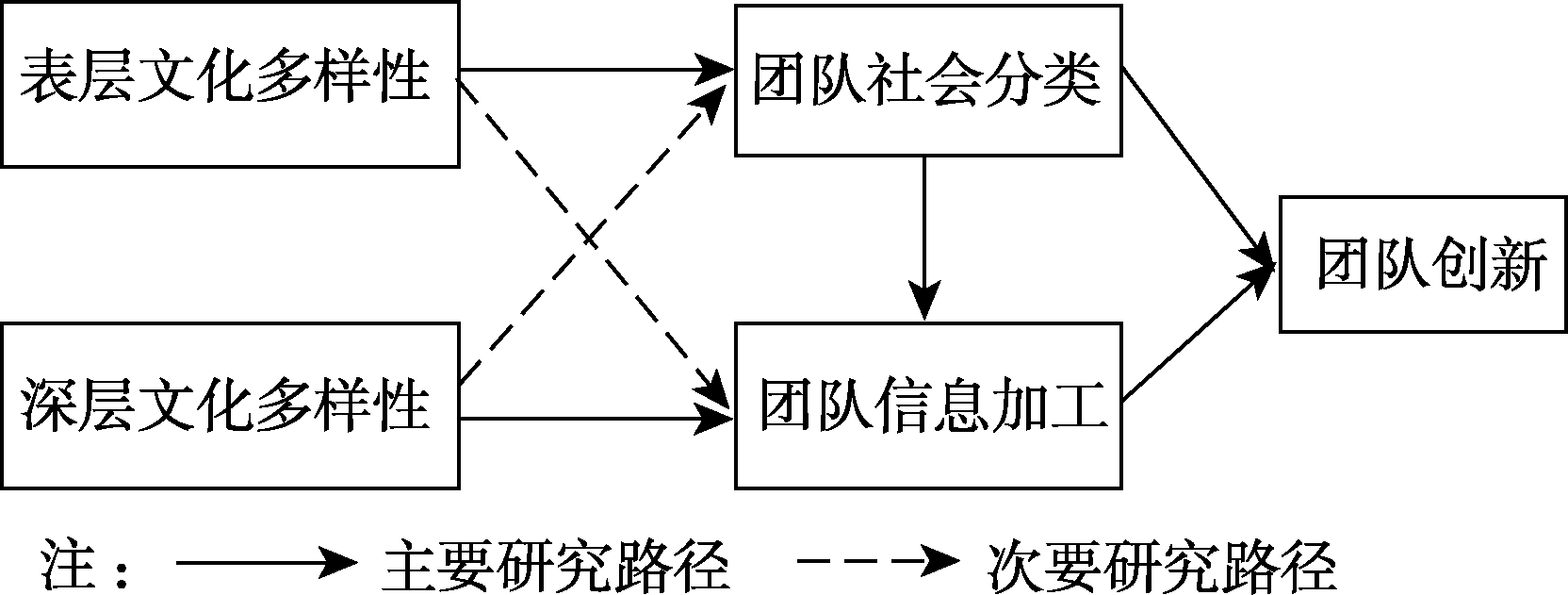
图3研究模块二:“社会分类-信息加工”影响机制
 图3研究模块二:“社会分类-信息加工”影响机制
图3研究模块二:“社会分类-信息加工”影响机制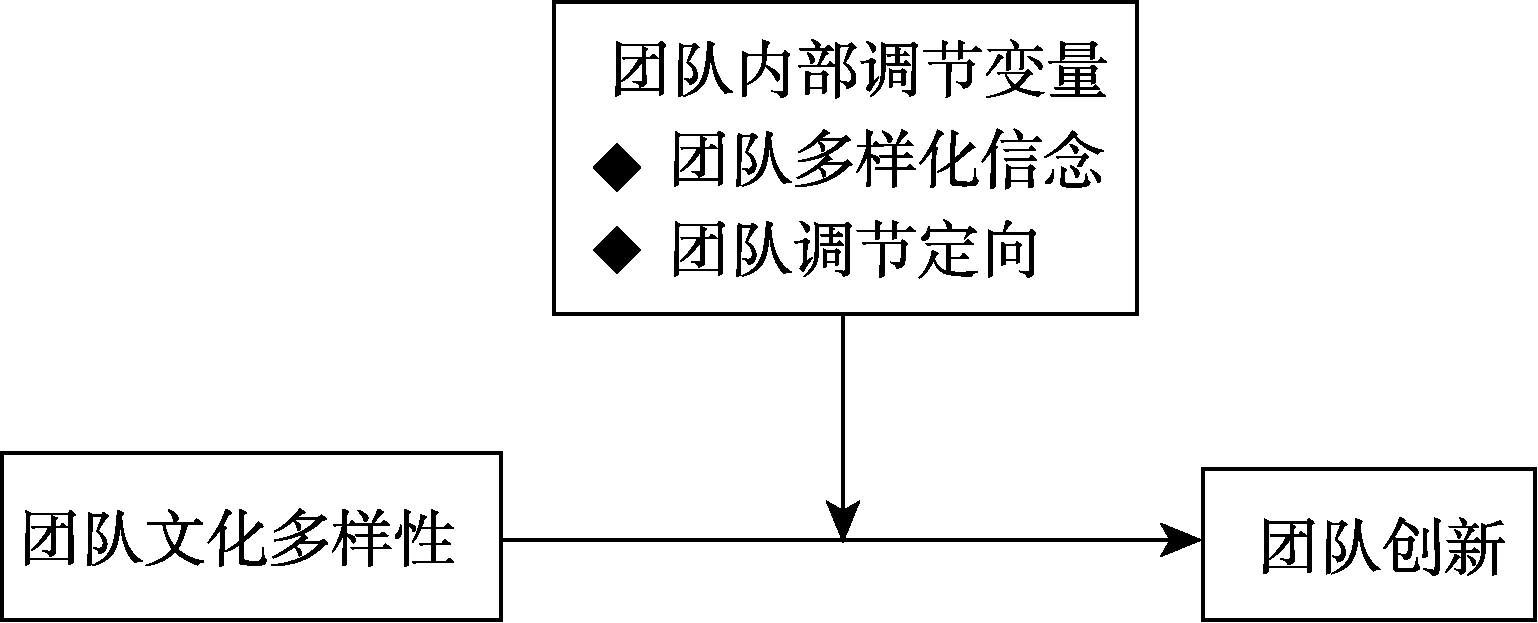
图4研究模块三:团队文化多样性对团队创新影响的内部边界条件
 图4研究模块三:团队文化多样性对团队创新影响的内部边界条件
图4研究模块三:团队文化多样性对团队创新影响的内部边界条件
图5研究模块四:团队文化多样性对团队创新影响的外部边界条件
 图5研究模块四:团队文化多样性对团队创新影响的外部边界条件
图5研究模块四:团队文化多样性对团队创新影响的外部边界条件参考文献 89
| 1 | 陈晓萍 . (2009). 跨文化管理. 北京: 清华大学出版社. |
| 2 | 姜秀珍, 顾琴轩, 王莉红, 金思宇 . ( 2011). 错误中学习与研发团队创新: 基于人力资本与社会资本视角. 管理世界, (12), 178-181. |
| 3 | 刘小禹, 刘军 . ( 2012). 团队情绪氛围对团队创新绩效的影响机制. 心理学报, 44(4), 546-557. |
| 4 | 刘小禹, 刘军 . ( 2013). 公平与领导理论视角的团队创新绩效研究. 科研管理, 34(12), 100-109. |
| 5 | 彭伟, 周晗鹭, 符正平 . ( 2013). 团队内部社会网络对团队创新绩效的影响机制——以企业R&D团队为样本的实证研究. 科研管理, 34(12), 135-142. |
| 6 | 秦伟平, 赵曙明, 周路路, 张子源 . ( 2015). 企业人力资源管理实践对跨功能团队创造力的跨层影响. 管理学报, 12(1), 88-95. |
| 7 | 隋杨, 陈云云, 王辉 . ( 2012). 创新氛围、创新效能感与团队创新: 团队领导的调节作用. 心理学报, 44(2), 237-248. |
| 8 | 汤超颖, 艾树, 龚增良 . ( 2011). 积极情绪的社会功能及其对团队创造力的影响: 隐性知识共享的中介作用. 南开管理评论, 14(4), 129-137. |
| 9 | 徐建中, 朱晓亚 . ( 2016). 员工前摄行为对团队创新绩效的影响——一个跨层次研究. 科学学与科学技术管理, 37(11), 104-116. |
| 10 | 杨皎平, 侯楠, 邓雪 . ( 2014). 基于团队认同对学习空间调节作用的成员异质性对团队创新绩效的影响研究. 管理学报, 11(7), 1021-1028. |
| 11 | 袁庆宏, 张华磊, 王震, 黄勇 . ( 2015). 研发团队跨界活动对团队创新绩效的“双刃剑”效应——团队反思的中介作用和授权领导的调节作用. 南开管理评论, 18(3), 13-23. |
| 12 | 赵志裕, 康萤仪 . (2011). 文化社会心理学 (刘爽译). 北京: 中国人民大学出版社. |
| 13 | Balkundi, P., & Harrison D. A . ( 2006). Ties, leaders, and time in teams: Strong inference about network structure’s effects on team viability and performance. Academy of Management Journal, 49(1), 49-68. |
| 14 | Bell S. T., Villado A. J., Lukasik M. A., Belau L., & Briggs A. L . ( 2011). Getting specific about demographic diversity variable and team performance relationships: A meta-analysis. Journal of Management. 37(3), 709-743. |
| 15 | Belschak, F.D., & Den Hartog D.N., . ( 2009). Consequences of positive and negative feedback: The impact on emotions and extra‐role behaviors. Applied Psychology, 58(2), 274-303. |
| 16 | Billig, M. , & Tajfel, H. ( 1973). Social categorization and similarity in intergroup behaviour. European Journal of Social Psychology, 3(1), 27-52. |
| 17 | Blau P. M. (1977). Inequality and heterogeneity: A primitive theory of social structure. New York: Free Press. |
| 18 | Bock G. W., Zmud R. W., Kim Y. G., & Lee J. N . ( 2005). Behavioral intention formation in knowledge sharing: Examining the roles of extrinsic motivators, social- psychological forces, and organizational climate. MIS Quarterly, 29(1), 87-111. |
| 19 | Carton, A.M., & Cummings J.N, . ( 2012). A theory of subgroups in work teams. Academy of Management Review, 37(3), 441-470. |
| 20 | Chatman, J. A., & Flynn, F.J . ( 2001). The influence of demographic heterogeneity on the emergence and consequences of cooperative norms in work teams. Academy of Management Journal, 44(5), 956-974. |
| 21 | Chirumbolo A., Mannetti L., Pierro A., Areni A., & Kruglanski A. W . ( 2005). Motivated closed-mindedness and creativity in small groups. Small Group Research, 36(1), 59-82. |
| 22 | Chua, R. Y. J . ( 2013). The costs of ambient cultural disharmony: Indirect intercultural conflicts in social environment undermine creativity. Academy of Management Journal, 56(6), 1545-1577. |
| 23 | Chua, R. Y. J . ( 2018). Innovating at cultural crossroads: How multicultural social networks promote idea flow and creativity. Journal of Management, 44(3), 1119-1146. |
| 24 | Chung Y., Liao H., Jackson S. E., Subramony M., Colakoglu S., & Jiang Y . ( 2015). Cracking but not Breaking: Joint effects of faultline strength and diversity climate on loyal behavior. Academy of Management Journal, 58(5), 1495-1515. |
| 25 | Cox, T. (1994). Cultural diversity in organizations: Theory, research and practice. San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler Publishers. |
| 26 | Dahlin K. B., Weingart L. R., & Hinds P. J . ( 2005). Team diversity and information use. Academy of Management Journal, 48(6), 1107-1123. |
| 27 | DeShon R. P., Kozlowski S. W. J., Schmidt A. M., Milner K. R., & Wiechmann D . ( 2004). A multiple-goal, multilevel model of feedback effects on the regulation of individual and team performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89(6), 1035-1056. |
| 28 | DeVellis, R.F . ( 2016). Scale development: Theory and applications (fourth ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA, US: Sage Publications, Inc. |
| 29 | Earley, C. P., & Mosakowski, E.. ( 2000). Creating hybrid team cultures: An empirical test of transnational team functioning. Academy of Management Journal, 43(1), 26-49. |
| 30 | Ely, R. J., & Thomas, D.A . ( 2001). Cultural diversity at work: The effects of diversity perspectives on work group processes and outcomes. Administrative Science Quarterly, 46(2), 229-273. |
| 31 | Florack, A., & Hartmann J. , (2007). Regulatory focus and investment decisions in small groups. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 43(4), 626-632. |
| 32 | F?rster, J.,& Dannenberg, L. ( 2010). GLOMO sys: A systems account of global versus local processing . Psychological Inquiry, 21(3), 175-197. |
| 33 | Geister S., Konradt U., & Hertel G . ( 2006). Effects of process feedback on motivation, satisfaction, and performance in virtual teams. Small Group Research, 37(5), 459-489. |
| 34 | Gertsen, M. C., & S?derberg, A.M . ( 2011). Intercultural collaboration stories: On narrative inquiry and analysis as tools for research in international business. Journal of International Business Studies, 42(6), 787-804. |
| 35 | Giambatista, R. C., & Bhappu, A.D . ( 2010). Diversity’s harvest: Interactions of diversity sources and communication technology on creative group performance. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 111(2), 116-126. |
| 36 | Gilson, L.L., & Shalley, C.E . ( 2004). A little creativity goes a long way: An examination of teams’ engagement in creative processes. Journal of Management, 30 (4), 453-470. |
| 37 | Gino F., Argote L., Miron-Spektor E., & Todorova G . ( 2010). First, get your feet wet: The effects of learning from direct and indirect experience on team creativity. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 111(2), 102-115. |
| 38 | Harrison D. A., Mohammed S., McGrath J. E., Florey A. T., & Vanderstoep S. W . ( 2003). Time matters in team performance: Effects of member familiarity, entrainment, and task discontinuity on speed and quality. Personnel Psychology, 56(3), 633-669. |
| 39 | Harrison D. A., Price K. H., & Bell M. P . ( 1998). Beyond relational demography: Time and the effects of surface- and deep-level diversity on work group cohesion. Academy of Management Journal, 41(1), 96-107. |
| 40 | Harrison, L. E . ( 2002). Culture matters: How values shape human progress. NY: Basic books. |
| 41 | Harvey, S. (2013). A different perspective: The multiple effects of deep level diversity on group creativity. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 49(5), 822-832. |
| 42 | Higgins, E. T . ( 1997). Beyond pleasure and pain. American Psychologist, 52(12), 1280-1300. |
| 43 | Higgins, E. T . ( 2000). Making a good decision: Value from fit. American Psychologist, 55(11), 1217-1230. |
| 44 | Hinsz V. B., Tindale R. S., & Vollrath D. A . ( 1997). The emerging conceptualization of groups as information processors. Psychological Bulletin, 121(1), 43-64. |
| 45 | Hoever I. J., van Knippenberg D., van Ginkel W. P., & Barkema H. G . ( 2012). Fostering team creativity: Perspective taking as key to unlocking diversity’s potential. Journal of Applied Psychology, 97 (5), 982-996. |
| 46 | Hollenbeck J. R., Ilgen D. R., LePine J. A., Colquitt J. A., & Hedlund J . ( 1998). Extending the multilevel theory of team decision making: Effects of feedback and experience in hierarchical teams. Academy of Management Journal, 41(3), 269-282. |
| 47 | Homan A. C., van Knippenberg D., van Kleef G. A& de Dreu, C. K. W. (2007). Bridging faultlines by valuing diversity: Diversity beliefs, information elaboration, and performance in diverse work groups. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92 (5), 1189-1199. |
| 48 | Hülsheger U. R., Anderson N., & Salgado J. F . ( 2009). Team-level predictors of innovation at work: A comprehensive meta-analysis spanning three decades of research. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(5), 1128-1145. |
| 49 | Jackson S. E., Joshi A., & Erhardt N. L . ( 2003). Recent research on team and organizational diversity: SWOT analysis and implications. Journal of Management, 29(6), 801-830. |
| 50 | Kearney, E. & Gebert, D. ( 2009). Managing diversity and enhancing team outcomes: The promise of transformational leadership. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(1), 77-89. |
| 51 | Kearney E., Gebert D., & Voelpel S. C . ( 2009). When and how diversity benefits teams: The importance of team members’ need for cognition. Academy of Management Journal, 52(3), 581-598. |
| 52 | Kirkman, B. L., & Shapiro, D. L . ( 2001). The impact of cultural values on job satisfaction and organizational commitment in self-managing work teams: The mediating role of employee resistance. Academy of Management Journal, 44(3), 557-569. |
| 53 | Konradt U., Schippers M. C., Garbers Y., & Steenfatt C . ( 2015). Effects of guided reflexivity and team feedback on team performance improvement: The role of team regulatory processes and cognitive emergent states. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 24(5), 777-795. |
| 54 | Leslie, L.M . ( 2017). A status-based multilevel model of ethnic diversity and work unit performance. Journal of Management, 43(2), 426-454. |
| 55 | Leung, A. K. Y., & Chiu, C.Y . ( 2010). Multicultural experience, idea receptiveness, and creativity. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 41(5-6), 723-741. |
| 56 | Leung, K., & Wang, J. ( 2015). Social processes and team creativity in multicultural teams: A socio-technical framework. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 36(7), 1008-1025. |
| 57 | Levine J. M., Higgins E. T., & Choi H. S . ( 2000). Development of strategic norms in groups. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 82(1), 88-101. |
| 58 | Lipman-Blumen, J., & Leavitt, H. J . ( 1999). Hot groups “with attitude”: A new organizational state of mind. Organizational Dynamics, 27(4), 63-73. |
| 59 | Meyer B., Shemla M., & Schermuly C. C . ( 2011). Social category salience moderates the effect of diversity faultlines on information elaboration. Small Group Research, 42(3), 257-282. |
| 60 | Nederveen Pieterse A., van Knippenberg D., & van Dierendonck D . ( 2013). Cultural diversity and team performance: The role of team member goal orientation. Academy of Management Journal, 56(3), 782-804. |
| 61 | Niebuhr, A. (2010). Migration and innovation: Does cultural diversity matter for regional R&D activity? Papers in Regional Science, 89(3), 563-585. |
| 62 | Nouri R., Erez M., Rockstuhl T., Ang S., Leshem-Calif L., & Rafaeli A . ( 2013). Taking the bite out of culture: The impact of task structure and task type on overcoming impediments to cross-cultural team performance. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 34(6), 739-763. |
| 63 | ?stergaard C. R., Timmermans B., & Kristinsson K . (2011). Does a different view create something new? The effect of employee diversity on innovation. Research Policy, 40(3), 500-509. |
| 64 | Pe?arroja V., Orengo V., Zornoza A., Sánchez J., & Ripoll P . ( 2015). How team feedback and team trust influence information processing and learning in virtual teams: A moderated mediation model. Computers in Human Behavior, 48, 9-16. |
| 65 | Perry-Smith, J. E., & Shalley, C. E . ( 2003). The social side of creativity: A static and dynamic social network perspective. Academy of Management Review, 28(1), 89-106. |
| 66 | Rietzschel, E. F . ( 2011). Collective regulatory focus predicts specific aspects of team innovation. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations, 14(3), 337-345. |
| 67 | Sacco, J. M., & Schmitt, N. (2005). A dynamic multilevel model of demographic diversity and misfit effects. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90(2), 203-231. |
| 68 | Sarala, R. M., & Vaara, E. (2010). Cultural differences, convergence, and crossvergence as explanations of knowledge transfer in international acquisitions. Journal of International Business Studies, 41(8), 1365-1390. |
| 69 | Schippers M. C., Homan A. C., & van Knippenberg D . (2013). To reflect or not to reflect: Prior team performance as a boundary condition of the effects of reflexivity on learning and final team performance. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 34(1), 6-23. |
| 70 | Shin S. J., Kim T. Y., Lee J. Y., & Bian L . (2012). Cognitive team diversity and individual team member creativity: A cross-level interaction. Academy of Management Journal, 55(1), 197-212. |
| 71 | Shin, S. J., & Zhou, J. (2007). When is educational specialization heterogeneity related to creativity in research and development teams? Transformational leadership as a moderator. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92(6), 1709-1721. |
| 72 | Stahl G. K., Maznevski M. L., Voigt A., & Jonsen K . ( 2010). Unraveling the effects of cultural diversity in teams: A meta-analysis of research on multicultural work groups. Journal of International Business Studies, 41(4), 690-709. |
| 73 | Tadmor C. T., Satterstrom P., Jang S., & Polzer J. T . ( 2012). Beyond individual creativity: The superadditive benefits of multicultural experience for collective creativity in culturally diverse teams. Journal of Cross- Cultural Psychology, 43(3), 384-392. |
| 74 | Taggar, S. (2002). Individual creativity and group ability to utilize individual creative resources: A multilevel model. Academy of Management Journal, 45(2), 315-330. |
| 75 | Tajfel, H., & Turner,J. C. ( 1986). The social identity theory of intergroup behavior. In Worchel, S., & Austin, W. G.(Eds.), Psychology of intergroup relation (pp. 7-24). Chicago, US: Hall Publishers. |
| 76 | Tr?ster C., Mehra A., & van Knippenberg D . ( 2014). Structuring for team success: The interactive effects of network structure and cultural diversity on team potency and performance. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 124(2), 245-255. |
| 77 | Tsai W. C., Chi N. W., Grandey A. A., & Fung S. C . ( 2012). Positive group affective tone and team creativity: Negative group affective tone and team trust as boundary conditions. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 33(5), 638-656. |
| 78 | van der Vegt, G. S., & Janssen, O. ( 2003). Joint impact of interdependence and group diversity on innovation. Journal of Management, 29(5), 729-751. |
| 79 | van Dick R., van Knippenberg D., H?gele S., Guillaume Y. R. F., & Brodbeck F. C . ( 2008). Group diversity and group identification: The moderating role of diversity beliefs. Human Relations, 61(10), 1463-1492. |
| 80 | van Dijk D., & Kluger, A. N . (2011). Task type as a moderator of positive/negative feedback effects on motivation and performance: A regulatory focus perspective. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 32(8), 1084-1105. |
| 81 | van Knippenberg D., de Dreu, C. K. W., & Homan A. C . ( 2004). Work group diversity and group performance: An integrative model and research agenda. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89(6), 1008-1022. |
| 82 | van Knippenberg, D., & Haslam, S. A . (2003). Realizing the diversity dividend: Exploring the subtle interplay between identity, ideology, and reality. In Haslam, S. A., Van Knippenberg, D., Platow, M. J., & Ellemers, N. (Eds.). Social identity at work: Developing theory for organizational practice (pp. 61-77). New York: Psychology Press. |
| 83 | van Knippenberg D., Haslam S. A., & Platow M. J . ( 2007). Unity through diversity: Value-in-diversity beliefs, work group diversity, and group identification. Group Dynamics: Theory, Research, and Practice, 11(3), 207-222. |
| 84 | van Knippenberg D., van Ginkel W. P., & Homan A. C . ( 2013). Diversity mindsets and the performance of diverse teams. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 121(2), 183-193. |
| 85 | Weiss, H. M., & Cropanzano, R. ( 1996). Affective events theory: A theoretical discussion of the structure, causes and consequences of affective experiences at work. Research in Organizational Behavior: An annual series of analytical essays and critical reviews, 18, 1-74. |
| 86 | Williams, K. Y., & O’Reilly III, C. A . ( 1998). Demography and diversity in organizations: A review of 40 years of research. Research in Organizational Behavior, 20, 77-140. |
| 87 | Winkler, V. A., & Bouncken, R. B . ( 2011). How does cultural diversity in global innovation teams affect the innovation process? Engineering Management Journal, 23(4), 24-35. |
| 88 | Zhan S., Bendapudi N., & Hong Y. Y . ( 2015). Re- examining diversity as a double-edged sword for innovation process. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 36(7), 1026-1049. |
| 89 | Zhou J. & Shalley, C. E.. ( 2003). Research on employee creativity: A critical review and directions for future research. In Buckley, M., Halbesleben, J., & Wheeler, A. R. (Series Eds.). Research in personnel and human resources management (Vol. 22, pp.165-217). Oxford, England: Emerald Group Publishing Limited. |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 张凯丽, 尹奎, 唐宁玉. 在什么情况下员工会汇报差错?基于秘密分享视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(7): 1149-1162. |
| [2] | 尹奎, 赵景, 李璨, 王宏蕾, 王崇锋. 领导授权行为的形成机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(6): 1097-1110. |
| [3] | 林琳. 职场变革情境下的工作与工余塑造: 基于自我认同理论的双路径模型[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(5): 773-786. |
| [4] | 吴论文, 杨付, 田薏欣, 裴玉蓉. 工作嵌入的影响结果及其理论解释[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(5): 906-920. |
| [5] | 詹思群, 严瑜. 工作场所不文明行为与职场排斥间的螺旋效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 560-570. |
| [6] | 尹奎, 彭坚, 张君. 潜在剖面分析在组织行为领域中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7): 1056-1070. |
| [7] | 倪渊, 李翠. 内隐创业领导与多层次积极追随力的互动机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(5): 711-730. |
| [8] | 李精精, 张剑, 田慧荣, Jeffrey B.Vancouver. 动态计算模型在组织行为学研究中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(2): 368-380. |
| [9] | 王婷, 杨付. 领导幽默的影响效果及其理论解释[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(9): 1631-1642. |
| [10] | 胥彦, 李超平. 领导风格与敬业度关系的元分析[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(8): 1363-1383. |
| [11] | 王弘钰, 崔智淞, 邹纯龙, 于佳利, 赵迪. 忠诚还是叛逆?中国组织情境下的员工越轨创新行为[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(6): 975-989. |
| [12] | 程垦, 林英晖. 动机视角下的亲组织不道德行为[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(6): 1111-1122. |
| [13] | 刘玉新, 陈晨, 朱楠, 季正. 多维范式下神经组织行为学的哲学基础、理论框架和研究方法[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(6): 1093-1110. |
| [14] | 赵君, 鄢苗, 肖素芳, 张永军. 组织公民行为与反生产行为的互动关系:一个基于情绪与认知整合框架的阐释[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(5): 871-883. |
| [15] | 李海虹, 邓州, 何欣, 申劭婧, 邹雅雯, 朱敏帆, 王芸, 谢晓非. 源于“反常”终于“常理”的禀赋效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(3): 394-405. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4780
