 )
) 1南京师范大学心理学院, 南京 210097
2河北中医学院, 石家庄 050000
收稿日期:2018-05-19出版日期:2019-02-15发布日期:2018-12-25通讯作者:李晶E-mail:lij@njnu.edu.cn基金资助:* 江苏省高校自然科学基金, 南京师范大学“青蓝工程”资助(17KJD19002)The cognitive aging effect of route knowledge acquisition
ZHANG Aizhen1, WANG Yao1,2, LI Jing1( )
) 1 School of Psychology, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210097, China
2 Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050000, China
Received:2018-05-19Online:2019-02-15Published:2018-12-25Contact:LI Jing E-mail:lij@njnu.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 年龄与路径知识习得的关系是空间与认知老化两大领域研究的重要议题。老年人在面对不同的路径学习环境时呈现出不同的认知老化表现。以往与年龄相关的路径知识习得能力变化的研究, 主要支持了认知老化衰退理论。然而近来发现随着年龄增长, 老年人保留了一种空间认知补偿能力。由此, 在对前人文献进行回顾和反思的基础上, 整合路径知识习得的认知老化表现及机制以探究缓解空间认知老化可能的内部因素和外部有效措施。
图/表 2
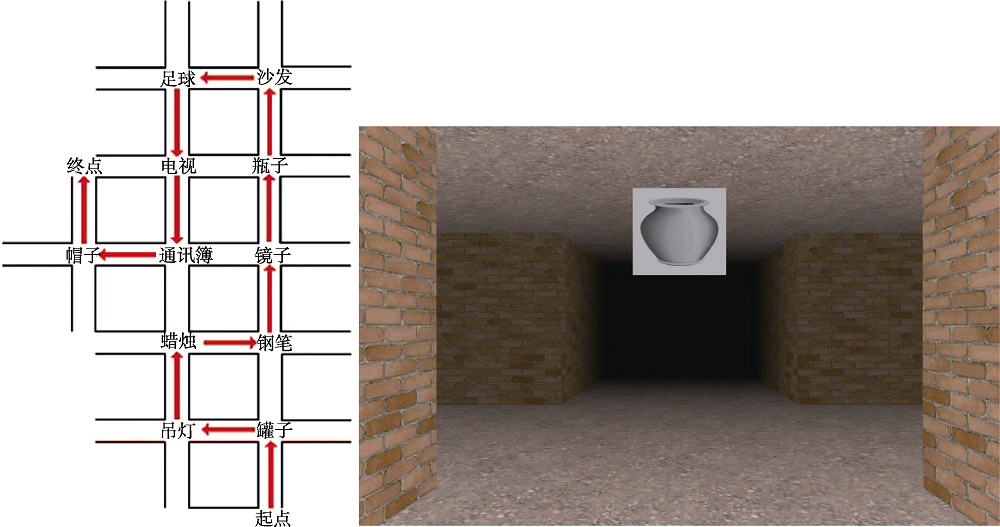
图1左:由11个交叉点组成的路径追踪路线示意图。右:一个十字路口的视觉呈现图
 图1左:由11个交叉点组成的路径追踪路线示意图。右:一个十字路口的视觉呈现图
图1左:由11个交叉点组成的路径追踪路线示意图。右:一个十字路口的视觉呈现图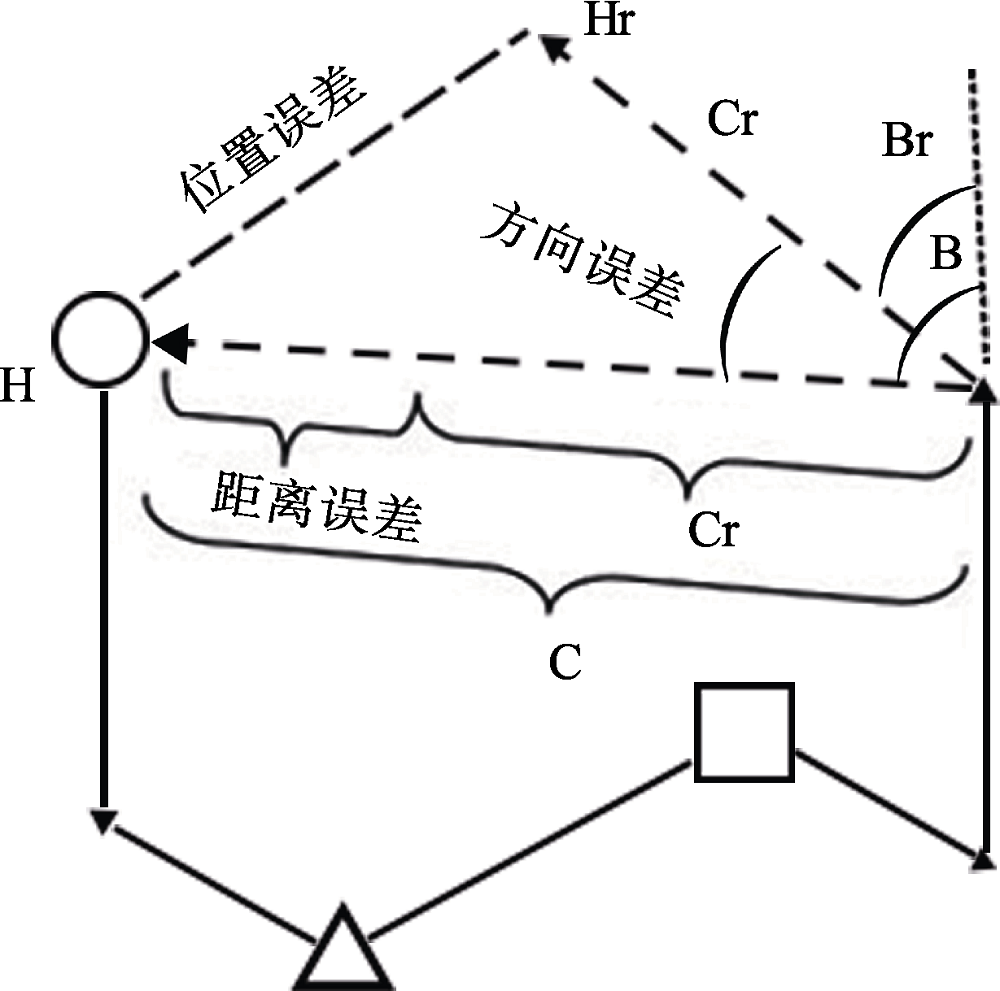
图2路径完成任务示意图。被试从H出发, 穿过五条外出路径到达A, 要求直接返回H。返回H的正确方式是先自转一个角度?, 再前进一个距离C。被试实际可能做出的反应是, 转过角度?r再前进一个距离Cr, 到达一个新的位置Hr。通过评估位置误差、角度误差与距离误差来判断被试在路径完成任务中的表现。
 图2路径完成任务示意图。被试从H出发, 穿过五条外出路径到达A, 要求直接返回H。返回H的正确方式是先自转一个角度?, 再前进一个距离C。被试实际可能做出的反应是, 转过角度?r再前进一个距离Cr, 到达一个新的位置Hr。通过评估位置误差、角度误差与距离误差来判断被试在路径完成任务中的表现。
图2路径完成任务示意图。被试从H出发, 穿过五条外出路径到达A, 要求直接返回H。返回H的正确方式是先自转一个角度?, 再前进一个距离C。被试实际可能做出的反应是, 转过角度?r再前进一个距离Cr, 到达一个新的位置Hr。通过评估位置误差、角度误差与距离误差来判断被试在路径完成任务中的表现。参考文献 53
| 1 | 何承林, 陈传锋 . ( 2013). 活动参与在认知损害中的延缓作用.心理科学进展, 21( 3), 506-516. |
| 2 | 宛小昂 . ( 2016). 人类路径整合的现象与机制. 杭州: 浙江大学出版社. |
| 3 | Adler J., Beutel M. E., Knebel A., Berti S., Unterrainer J., & Michal M . ( 2014). Altered orientation of spatial attention in depersonalization disorder.Psychiatry Research, 216( 2), 230-235. |
| 4 | Aisenberg D., Sapir A., d'Avossa G., & Henik A . ( 2014). Long trial durations normalise the interference effect and sequential updating during healthy aging. Acta Psychologica, 153, 169-178. |
| 5 | Allison S. & Head, D. ( 2017). Route repetition and route reversal: Effects of age and encoding method.Psychology & Aging, 32( 3), 220-231. |
| 6 | Ashendorf L. & McCaffrey, R.J . ( 2008). Exploring age-related decline on the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test.The Clinical Neuropsychologist, 22( 2), 262-272. |
| 7 | Bates, S.L., & Wolbers, T. ( 2014). How cognitive aging affects multisensory integration of navigational cues.Neurobiology of Aging, 35( 12), 2761-2769. |
| 8 | Borella E., Meneghetti C., Ronconi L., & De Beni R . ( 2014). Spatial abilities across the adult life Span.Developmental Psychology, 50( 2), 384-392. |
| 9 | Byrne P., Becker S., & Burgess N . ( 2007). Remembering the past and imagining the future: A neural model of spatial memory and imagery.Psychological Review, 114( 2), 340-375. |
| 10 | Campbell K. L., Al-Aidroos N., Fatt R., Pratt J., & Hasher L . ( 2010). The effects of multisensory targets on saccadic trajectory deviations: Eliminating age differences.Experimental Brain Research, 201( 3), 385-392. |
| 11 | Chen X. L., McNamara T. P., Kelly J. W., & Wolbers T . ( 2017). Cue combination in human spatial navigation.Cognitive Psychology, 95, 105-144. |
| 12 | Cushman L. A., Stein K., & Duffy C. J . ( 2008). Detecting navigational deficits in cognitive aging and Alzheimer disease using virtual reality. Neurology, 71( 12), 888-895. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000326262.67613.feURLpmid: 18794491 |
| 13 | Davis S. W., Kragel J. E., Madden D. J., & Cabeza R . ( 2012). The architecture of cross-hemispheric communication in the aging brain: Linking behavior to functional and structural connectivity. Cerebral Cortex, 22( 1), 232-242. |
| 14 | Devlin, A.L., & Wilson, P.H . ( 2010). Adult age differences in the ability to mentally transform object and body stimuli.Aging, Neuropsychology and Cognition, 17( 6), 709-729. |
| 15 | Diaconescu A. O., Hasher L., & McIntosh A. R . ( 2013). Visual dominance and multisensory integration changes with age. Neuroimage, 65, 152-166. |
| 16 | Gamboz N., Borella E., & Brandimonte M. A . ( 2009). The role of switching, inhibition and working memory in older adults' performance in the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test.Aging, Neuropsychology and Cognition, 16( 3), 260-284. |
| 17 | Gazes Y. L., Rakitin B. C., Habeck C., Steffener J., & Stern Y . ( 2012). Age differences of multivariate network expressions during task-switching and their associations with behavior.Neuropsychologia, 50( 14), 3509-3518. |
| 18 | Grady C. L., Protzner A. B., Kovacevic N., Strother S. C., Afshin-Pour B., Wojtowicz M., .. McIntosh A. R . ( 2010). A multivariate analysis of age-related differences in default mode and task-positive networks across multiple cognitive domains.Cerebral Cortex, 20( 6), 1432-1447. |
| 19 | Grewe P., Lahr D., Kohsik A., Dyck E., Markowitsch H. J., Bien C. G., .. Piefke M . ( 2014). Real-life memory and spatial navigation in patients with focal epilepsy: Ecological validity of a virtual reality supermarket task.Epilepsy & Behavior, 31, 57-66. |
| 20 | Grieves, R.M., & Jeffery, K.J . ( 2017). The representation of space in the brain.Behavioural Processes, 135, 113-131. |
| 21 | Gyselinck V., Meneghetti C., Bormetti M., Orriols E., Piolino P., & De Beni R . ( 2013). Considering spatial ability in virtual route learning in early aging.Cognitive Processing, 14, 309-316. |
| 22 | Hakun J. G., Zhu Z. D., Johnson N. F., & Gold B. T . ( 2015). Evidence for reduced efficiency and successful compensation in older adults during task switching.Cortex, 64, 352-362. |
| 23 | Hara Y., Rapp P. R., & Morrison J. H . ( 2012). Neuronal and morphological bases of cognitive decline in aged rhesus monkeys.Age, 34( 5), 1051-1073. |
| 24 | Harris M. A., Wiener J. M., & Wolbers T . ( 2012). Aging specifically impairs switching to an allocentric navigational strategy. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 4, 29. |
| 25 | Harris, M.A., & Wolbers, T. ( 2012). Aging effects on path integration and landmark navigation.Hippocampus, 22( 8), 1770-1780. |
| 26 | Harris, M.A., & Wolbers, T. ( 2014). How age-related strategy switching deficits affect wayfinding in complex environments.Neurobiology of Aging, 35( 5), 1095-1102. |
| 27 | Head D. & Isom, M. ( 2010). Age effects on wayfinding and route learning skills.Behavioural Brain Research, 209( 1), 49-58. |
| 28 | Iaria G., Palermo L., Committeri G., & Barton, J. J. S .( 2009). Age differences in the formation and use of cognitive maps. Behavioural Brain Research, 196( 2), 187-191. |
| 29 | Jansen P., Schmelter A., & Heil M . ( 2010). Spatial knowledge acquisition in younger and elderly adults: A study in a virtual environment.Experimental Psychology, 57( 1), 54-60. |
| 30 | Kessels R. P. C., Meulenbroek O., Fernandez G., & Olde Rikkert, M. G. M . ( 2010). Spatial working memory in aging and mild cognitive impairment: Effects of task load and contextual cueing.Aging, Neuropsychology and Cognition, 17( 5), 556-574. |
| 31 | Laurienti P. J., Burdette J. H., Maldjian J. A., & Wallace M. T . ( 2006). Enhanced multisensory integration in older adults. Neurobiology of Aging, 27( 8), 1155-1163. |
| 32 | Mahmood O., Adamo D., Briceno E., & Moffat S. D . ( 2009). Age differences in visual path integration. Behavioural Brain Research, 205( 1), 88-95. |
| 33 | Mahoney J. R., Li P. C. C., Oh-Park M., Verghese J., & Holtzer R . ( 2011). Multisensory integration across the senses in young and old adults.Brain Research, 1426, 43-53. |
| 34 | Meneghetti C., Pazzaglia F., & Beni R . ( 2015). Mental representations derived from spatial descriptions: The influence of orientation specificity and visuospatial abilities.Psychological Research, 79( 2), 289-307. |
| 35 | Miller M. & Eilam, D. ( 2011). Decision making at a crossroad: Why to go straight ahead, retrace a path, or turn sideways? Animal Cognition, 14( 1), 11-20. |
| 36 | Montefinese M., Sulpizio V., Galati G., & Committeri G . ( 2015). Age-related effects on spatial memory across viewpoint changes relative to different reference frames.Psychological Research, 79( 4), 687-697. |
| 37 | Mokrisova I., Laczo J., Andel R., Gazova I., Vyhnalek M., Nedelska Z., .. Hort J . ( 2016). Real-space path integration is impaired in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment.Behavioural Brain Research, 307, 150-158. |
| 38 | Moffat, S.D . ( 2009). Aging and spatial navigation: What do we know and where do we go? Neuropsychology Review, 19( 4), 478-489. |
| 39 | Moffat S. D., Elkins W., & Resnick S. M . ( 2006). Age differences in the neural systems supporting human allocentric spatial navigation.Neurobiology of Aging, 27( 7), 965-972. |
| 40 | Muffato V., Meneghetti C., & De Beni. R . ( 2016). Not all is lost in older adults' route learning: The role of visuo- spatial abilities and type of task.Journal of Environmental Psychology, 47, 230-241. |
| 41 | Muffato V., Meneghetti C., Di Ruocco V., & De Beni R . ( 2017). When young and older adults learn a map: The influence of individual visuo-spatial factors.Learning and Individual Differences, 53, 114-121. |
| 42 | Park, D. C., & Reuter-Lorenz, P. ( 2009). The adaptive brain: Aging and neurocognitive scaffolding.Annual Review of Psychology, 60, 173-196. |
| 43 | Peiffer A. M., Mozolic J. L., Hugenschmidt C. E., & Laurienti P. J . ( 2007). Age-related multisensory enhancement in a simple audiovisual detection task . Neuroreport: For Rapid Communication of Neuroscience Research, 18( 10), 1077-1081. |
| 44 | Phillips, H., & Andres, P. ( 2010). The cognitive neuroscience of aging: New findings on compensation and connectivity.Cortex, 46( 4), 421-424. |
| 45 | Resnick S. M., Pham D. L., Kraut M. A., Zonderman A. B., & Davatzikos C . ( 2003). Longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging studies of older adults: A shrinking brain.The Journal of Neuroscience, 23( 8), 3295-3301. |
| 46 | Reuter-Lorenz, P. A., & Cappell, K.A . ( 2008). Neurocognitive aging and the compensation hypothesis.Current Directions in Psychological Science, 17( 3), 177-182. |
| 47 | Spence I. & Feng, J. ( 2010). Video games and spatial cognition.Review of General Psychology, 14( 2), 92-104. |
| 48 | Stranahan, A.M., & Mattson, M.P . ( 2010). Selective vulnerability of neurons in layer II of the Entorhinal cortex during aging and Alzheimer's disease.Neural Plasticity, 2010, 1-8. |
| 49 | Tanaka S., Young J. W., Gresack J. E., Geyer M. A., & Risbrough V. B . ( 2011). Factor analysis of attentional set-shifting performance in young and aged mice.Behavioral and Brain Functions, 7, 33. |
| 50 | Wan X., Wang R. F., & Crowell J. A . ( 2012). The effect of landmarks in human path integration.Acta Psychologica, 140( 1), 7-12. |
| 51 | Wiener J. M., Kmecova H., & de Condappa O . ( 2012). Route repetition and route retracing: Effects of cognitive aging. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 4, 1-7. |
| 52 | Zancada-Menendez C., Sampedro-Piquero P., Meneghetti C., Labate E., Begega A., & Lopez L . ( 2015). Age differences in path learning: The role of interference in updating spatial information.Learning and Individual Differences, 38, 83-89. |
| 53 | Zou Z., Chau B. K. H., Ting K. H., & Chan, C. C. H . ( 2017). Aging effect on audiovisual integrative processing in spatial discrimination task.Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 9, 374. |
相关文章 13
| [1] | 赵鑫, 郑巧萍. 童年贫困与晚年认知老化:加速还是延缓?[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 160-166. |
| [2] | 程士静, 何文广. 语义认知的习得、发展和老化及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7): 1156-1163. |
| [3] | 霍丽娟, 郑志伟, 李瑾, 李娟. 老年人的脑可塑性:来自认知训练的证据[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(5): 846-858. |
| [4] | 何文广. 语言认知老化机制及其神经基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(9): 1479-1491. |
| [5] | 何燕;余林;闫志民:赵宇晗. 认知储备的测量及其在认知老化中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(3): 430-438. |
| [6] | 李丹;杨昭宁. 空间导航:路标学习和路径整合的关系[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(10): 1755-1762. |
| [7] | 何承林;陈传锋. 活动参与在认知损害中的延缓作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2013, 21(3): 506-516. |
| [8] | 亓胜辉;余林;马建苓. 人格特质对认知老化的影响及其机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2013, 21(1): 96-107. |
| [9] | 彭华茂;王大华. 基本心理能力老化的认知机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2012, 20(8): 1251-1258. |
| [10] | 于平;徐晖;尹文娟;魏曙光;于萍. 网格细胞在空间记忆中的作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2009, 17(6): 1228-1233. |
| [11] | 付艳;王大华. 认知老化与脑:HAROLD模型之争[J]. 心理科学进展, 2009, 17(1): 86-91. |
| [12] | 赵民涛 . 物体位置与空间关系的心理表征[J]. 心理科学进展, 2006, 14(3): 321-327. |
| [13] | 卜翠萍,奚耕思. 线粒体与认知老化[J]. 心理科学进展, 2005, 13(3): 341-347. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4590
