 ), 王爱君3, 唐晓雨1,2(
), 王爱君3, 唐晓雨1,2( )
) 1. 辽宁师范大学心理学院
2. 辽宁省儿童青少年健康人格评定与培养协同创新中心, 大连 116029
3. 苏州大学教育学院心理学系, 苏州 215123
收稿日期:2017-10-26出版日期:2018-12-15发布日期:2018-10-30通讯作者:任桂琴,唐晓雨E-mail:ajwang@suda.edu.cn;2006@163.com基金资助:*国家自然科学基金项目(31600882);国家自然科学基金项目(31700939);国家自然科学基金项目(31471075);中国博士后基金面上项目赞助(2017M611888)The interaction between exogenous attention and multisensory integration
PENG Xing1, CHANG Ruosong1,2, REN Guiqin1( ), WANG Aijun3, TANG Xiaoyu1,2(
), WANG Aijun3, TANG Xiaoyu1,2( )
) 1. School of Psychology, Liaoning Normal University
2. Liaoning Collaborative Innovation Center of Children and Adolescents Healthy Personality Assessment and Cultivation, Dalian 116029, China
3. Department of Psychology, Research Center for Psychology and Behavioral Sciences, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, China
Received:2017-10-26Online:2018-12-15Published:2018-10-30Contact:REN Guiqin,TANG Xiaoyu E-mail:ajwang@suda.edu.cn;2006@163.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 外源性注意与多感觉整合的交互关系是一个复杂且具有争议的研究领域, 一直以来备受研究者们关注。为了解释两者间的交互作用机制, 本文基于已有研究成果从两方面综述了外源性注意与多感觉整合的交互关系:(1)外源性注意可以通过自下而上的方式调节多感觉整合, 包括空间不确定性、感知觉敏感度和感觉通道间信号强度差异三种理论假说; (2)多感觉整合可以调节外源性注意。一方面, 来自多感觉通道的刺激能够以自下而上的方式自动整合, 整合后的多感觉通道刺激比单通道刺激具有更大的凸显性从而有效地吸引注意。另一方面, 整合后的多感觉通道刺激能够作为多感觉信号模板存储于大脑之中, 从而在任务中实现自上而下地调节注意捕获。
图/表 3
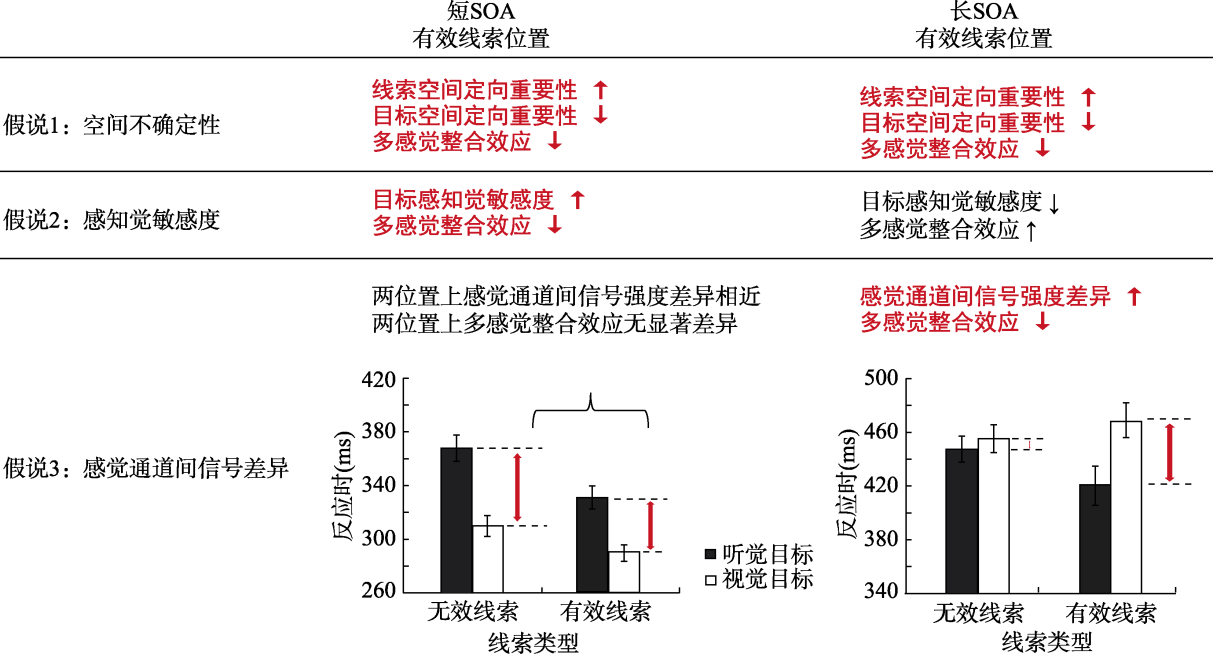
图1外源性注意调节多感觉整合的三种理论假说注:图中分别表示三种理论假说(空间不确定性假说, 感知觉敏感度假说, 感觉通道间信号强度差异假说)在不同SOA条件下(短SOA vs长 SOA)的结果。其中, 加粗红色字体代表基于已有研究数据得到的结果, 黑色字体代表假定结果。假说3结果分别引自Van der Stoep等(2015实验1, 2016)。
 图1外源性注意调节多感觉整合的三种理论假说注:图中分别表示三种理论假说(空间不确定性假说, 感知觉敏感度假说, 感觉通道间信号强度差异假说)在不同SOA条件下(短SOA vs长 SOA)的结果。其中, 加粗红色字体代表基于已有研究数据得到的结果, 黑色字体代表假定结果。假说3结果分别引自Van der Stoep等(2015实验1, 2016)。
图1外源性注意调节多感觉整合的三种理论假说注:图中分别表示三种理论假说(空间不确定性假说, 感知觉敏感度假说, 感觉通道间信号强度差异假说)在不同SOA条件下(短SOA vs长 SOA)的结果。其中, 加粗红色字体代表基于已有研究数据得到的结果, 黑色字体代表假定结果。假说3结果分别引自Van der Stoep等(2015实验1, 2016)。
图2Talsma等(2005)研究的实验流程与结果图 注:内源性注意调节多感觉整合的实验流程及其结果。实验中要求被试注意屏幕中的一侧(左/右侧), 并对该空间位置上的所有目标刺激(视觉、听觉和视听觉)进行检测反应(左图)。结果显示, 内源性注意位置上的多感觉整合效应更大(右图)。
 图2Talsma等(2005)研究的实验流程与结果图 注:内源性注意调节多感觉整合的实验流程及其结果。实验中要求被试注意屏幕中的一侧(左/右侧), 并对该空间位置上的所有目标刺激(视觉、听觉和视听觉)进行检测反应(左图)。结果显示, 内源性注意位置上的多感觉整合效应更大(右图)。
图2Talsma等(2005)研究的实验流程与结果图 注:内源性注意调节多感觉整合的实验流程及其结果。实验中要求被试注意屏幕中的一侧(左/右侧), 并对该空间位置上的所有目标刺激(视觉、听觉和视听觉)进行检测反应(左图)。结果显示, 内源性注意位置上的多感觉整合效应更大(右图)。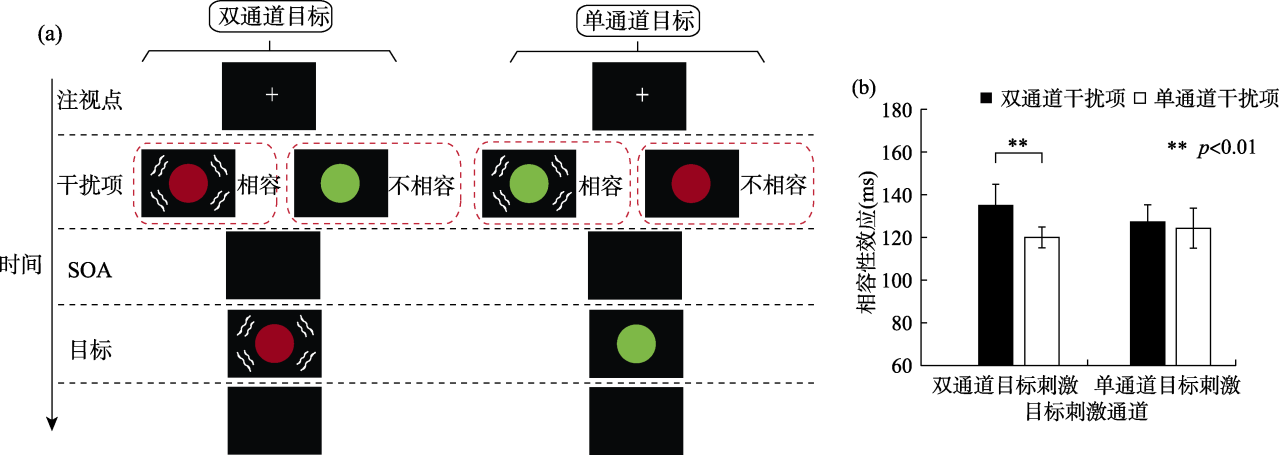
图3Mast等(2015, 实验1b)研究的实验流程与结果图 注:(a)任务和实验流程。图中分别表示在双通道目标(左图)和单通道目标条件(右图)下的实验流程。双通道目标由视觉刺激(红色圆形)与触觉振动刺激(图上用波浪线表示)组合而成。单通道目标只有视觉目标(绿色圆形), 从不伴随触觉振动刺激。同样, 启动项也分为双通道与单通道条件。实验中要求被试忽略启动项颜色特征, 既快又准地对目标刺激的颜色特征进行反应。(b)行为学结果。纵坐标代表相容性效应, 结果显示只有在双通道目标条件下发现双通道启动项比单通道启动项有更大的相容性效应。(引并改自Mast等(2015), copyright (2015)The Psychonomic Society.)
 图3Mast等(2015, 实验1b)研究的实验流程与结果图 注:(a)任务和实验流程。图中分别表示在双通道目标(左图)和单通道目标条件(右图)下的实验流程。双通道目标由视觉刺激(红色圆形)与触觉振动刺激(图上用波浪线表示)组合而成。单通道目标只有视觉目标(绿色圆形), 从不伴随触觉振动刺激。同样, 启动项也分为双通道与单通道条件。实验中要求被试忽略启动项颜色特征, 既快又准地对目标刺激的颜色特征进行反应。(b)行为学结果。纵坐标代表相容性效应, 结果显示只有在双通道目标条件下发现双通道启动项比单通道启动项有更大的相容性效应。(引并改自Mast等(2015), copyright (2015)The Psychonomic Society.)
图3Mast等(2015, 实验1b)研究的实验流程与结果图 注:(a)任务和实验流程。图中分别表示在双通道目标(左图)和单通道目标条件(右图)下的实验流程。双通道目标由视觉刺激(红色圆形)与触觉振动刺激(图上用波浪线表示)组合而成。单通道目标只有视觉目标(绿色圆形), 从不伴随触觉振动刺激。同样, 启动项也分为双通道与单通道条件。实验中要求被试忽略启动项颜色特征, 既快又准地对目标刺激的颜色特征进行反应。(b)行为学结果。纵坐标代表相容性效应, 结果显示只有在双通道目标条件下发现双通道启动项比单通道启动项有更大的相容性效应。(引并改自Mast等(2015), copyright (2015)The Psychonomic Society.)参考文献 82
| 1 | 刘强, 胡中华, 赵光, 陶维东, 张庆林, 孙弘进 . ( 2010). 通道估计可靠性先验知识在早期的知觉加工阶段影响多感觉信息整合. 心理学报, 42( 2), 227-234. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2010.00227URL |
| 2 | 王慧媛, 隋洁, 张明 . ( 2016). 线索靶子关联和搜索策略对注意捕获的作用——来自意义线索的证据. 心理学报, 48( 7), 783-793. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.00783URL |
| 3 | 王慧媛, 张明, 隋洁 . ( 2014). 线索靶子关联和搜索策略对注意捕获的作用. 心理学报, 46( 2), 185-195. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.00185URL |
| 4 | Ansorge, U., &Becker, S.I . ( 2013). Contingent capture in cueing: The role of color search templates and cue-target color relations. Psychological Research, 78( 2), 209-221. doi: 10.1007/s00426-013-0497-5URLpmid: 23807453 |
| 5 | Atchley P., Jones S. E., & Hoffman L . ( 2003). Visual marking: A convergence of goal- and stimulus-driven processes during visual search. Perception & Psychophysics, 65( 5), 667-677. doi: 10.3758/BF03194805URLpmid: 12956576 |
| 6 | Barrett, D. J.K., &Katrin, K . ( 2012). Evidence for multisensory integration in the elicitation of prior entry by bimodal cues. Experimental Brain Research, 222( 1-2), 11-20. doi: 10.1007/s00221-012-3191-8URLpmid: 22975896 |
| 7 | Busse L., Katzner S., & Treue S . ( 2008). Temporal dynamics of neuronal modulation during exogenous and endogenous shifts of visual attention in macaque area MT. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105( 42), 16380-16385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707369105URLpmid: 18922778 |
| 8 | Callan A., Callan D., & Ando H . ( 2015). An fMRI study of the ventriloquism effect. Cerebral Cortex, 25( 11), 4248-4258. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhu306URLpmid: 4816779 |
| 9 | Calvert, G.A., &Thesen, T . ( 2004). Multisensory integration: Methodological approaches and emerging principles in the human brain. Journal of Physiology-Paris, 98( 1-3), 191-205. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2004.03.018URLpmid: 15477032 |
| 10 | Carrasco, M. ( 2011). Visual attention: The past 25 years. Vision Research, 51( 13), 1484-1525. |
| 11 | Chamberland C., Hodgetts H. M., Vallières B. R., Vachon F., & Tremblay S . ( 2016). Pip and pop: When auditory alarms facilitate visual change detection in dynamic settings. Human Factors & Ergonomics Society Meeting , 60( 1), 284-288. doi: 10.1177/1541931213601065URL |
| 12 | Chen K., Zhou B., Chen S., He S., & Zhou W . ( 2013). Olfaction spontaneously highlights visual saliency map. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 280( 1768), 20131729. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.1729URLpmid: 23945694 |
| 13 | Chica A. B., Bartolomeo P., & LupiÁñez J . ( 2013). Two cognitive and neural systems for endogenous and exogenous spatial attention. Behavioural Brain Research, 237( 1), 107-123. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2012.09.027URLpmid: 23000534 |
| 14 | Chica, A.B., &LupiÁñez, J . ( 2009). Effects of endogenous and exogenous attention on visual processing: An inhibition of return study. Brain Research, 1278, 75-85. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.04.011URLpmid: 19374885 |
| 15 | De Meo R., Murray M. M., Clarke S., & Matusz P. J . ( 2015). Top-down control and early multisensory processes: Chicken vs. egg. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 9( 17). doi: 10.3389/fnint.2015.00017URLpmid: 4347447 |
| 16 | Degerman A., Rinne T., Salmi J., Salonen O., & Alho K . ( 2006). Selective attention to sound location or pitch studied with fMRI. Brain Research, 1077( 1), 123-134. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.01.025URLpmid: 16515772 |
| 17 | Donohue S. E., Green J. J., & Woldorff M. G . ( 2015). The effects of attention on the temporal integration of multisensory stimuli. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 9, 32. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2015.00032URLpmid: 4407588 |
| 18 | Fairhall, &Macaluso . ( 2009). Spatial attention can modulate audiovisual integration at multiple cortical and subcortical sites. European Journal of Neuroscience, 29( 6), 1247-1257. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06688.xURLpmid: 19302160 |
| 19 | Fetsch C. R., Pouget A., Deangelis G. C., & Angelaki D. E . ( 2011). Neural correlates of reliability-based cue weighting during multisensory integration. Nature Neuroscience, 15( 1), 146-154. doi: 10.1038/nn.2983URLpmid: 22101645 |
| 20 | Folk C., Berenato A., & Wyble B . ( 2014). Semantic priming produces contingent attentional capture by conceptual content. Journal of Vision, 14( 10), 318. |
| 21 | Folk, C.L., &Remington, R . ( 1998). Selectivity in distraction by irrelevant featural singletons: Evidence for two forms of attentional capture. Journal of Experimental Psychology Human Perception & Performance, 24( 3), 847-858. doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.24.3.847URLpmid: 9627420 |
| 22 | Gao Y. L., Li Q., Yang W. P., Yang J. J., Tang X. Y., & Wu J. L . ( 2014). Effects of ipsilateral and bilateral auditory stimuli on audiovisual integration: A behavioral and event-related potential study. Neuroreport, 25( 9), 668-675. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000155URLpmid: 24780895 |
| 23 | Giard, M., &Peronnet, F . ( 1999). Auditory-visual integration during multimodal object recognition in humans: A behavioral and electrophysiological study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 11( 5), 473-490. |
| 24 | Goller, F., &Ansorge, U . ( 2015). There is more to trial history than priming in attentional capture experiments. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 77( 5), 1574-1584. doi: 10.3758/s13414-015-0896-3URLpmid: 25832193 |
| 25 | Goodhew S. C., Kendall W., Ferber S., & Pratt J . ( 2014). Setting semantics: Conceptual set can determine the physical properties that capture attention. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 76( 6), 1577-1589. doi: 10.3758/s13414-014-0686-3URLpmid: 24824982 |
| 26 | Henderickx D., Maetens K., & Soetens E . ( 2012). The involvement of bottom-up saliency processing in endogenous inhibition of return. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 74( 2), 285-299. doi: 10.3758/s13414-011-0234-3URLpmid: 22038667 |
| 27 | Ho C., Santangelo V., & Spence C . ( 2009). Multisensory warning signals: When spatial correspondence matters. Experimental Brain Research. 195( 2), 261-272. doi: 10.1007/s00221-009-1778-5URLpmid: 19381621 |
| 28 | Hopfinger, J.B., &West, V.M . ( 2006). Interactions between endogenous and exogenous attention on cortical visual processing. NeuroImage, 31( 2), 774-789. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.12.049URLpmid: 16490366 |
| 29 | Koelewijn T., Bronkhorst A., & Theeuwes J . ( 2010). Attention and the multiple stages of multisensory integration: A review of audiovisual studies. Acta Psychologica, 134( 3), 372-384. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2010.03.010URLpmid: 20427031 |
| 30 | Kok P., Jehee J. F. M ., & de Lange, F. P. ( 2012). Less is more: Expectation sharpens representations in the primary visual cortex. Neuron, 75( 2), 265-270. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.04.034URLpmid: 22841311 |
| 31 | Krause H., Schneider T. R., Engel A. K., & Senkowski D . ( 2012). Capture of visual attention interferes with multisensory speech processing. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 6, 67. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2012.00067URLpmid: 23325222 |
| 32 | Lamy, D.F., &Árni, K . ( 2013). Is goal-directed attentional guidance just intertrial priming? A review. Journal of Vision, 13( 3), 14-14. doi: 10.1167/13.3.14URLpmid: 23818660 |
| 33 | Lavie, N. ( 2005). Distracted and confused? Selective attention under load. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9( 2), 75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2004.12.004URLpmid: 15668100 |
| 34 | Li Q., Wu J., & Touge T . ( 2010). Audiovisual interaction enhances auditory detection in late stage: An event-related potential study. Neuroreport, 21( 3), 173-178. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e3283345f08URLpmid: 20065887 |
| 35 | Li Q., Yang H., Sun F., & Wu J . ( 2015). Spatiotemporal relationships among audiovisual stimuli modulate auditory facilitation of visual target discrimination. Perception, 44( 3), 232-242. doi: 10.1068/p7846URLpmid: 26562250 |
| 36 | Li Q., Yu H., Wu Y., & Gao N . ( 2016). The spatial reliability of task-irrelevant sounds modulates bimodal audiovisual integration: An event-related potential study. Neuroscience Letters, 629, 149-154. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.07.003URLpmid: 27392755 |
| 37 | Luck, S.J., &Hillyard, S.A . ( 1994). Spatial filtering during visual search: Evidence from human electrophysiology. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 20( 5), 1000-1014. doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.20.5.1000URLpmid: 7964526 |
| 38 | Macaluso E., Noppeney U., Talsma D., Vercillo T., Hartcher-O’Brien J., & Adam R . ( 2016). The curious incident of attention in multisensory integration: Bottom- up vs. top-down. Multisensory Research, 29( 6), 557-583. |
| 39 | Mahoney J. R., Verghese J., Dumas K., Wang C., & Holtzer R . ( 2012). The effect of multisensory cues on attention in aging. Brain Research, 1472, 63-73. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.07.014URLpmid: 3592377 |
| 40 | Martín-ArÉvalo E., Chica A. B., & LupiÁñez J . ( 2015). No single electrophysiological marker for facilitation and inhibition of return: A review. Behavioural Brain Research, 300, 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.11.030URLpmid: 26643119 |
| 41 | Mast F., Frings C., & Spence C . ( 2015). Multisensory top-down sets: Evidence for contingent crossmodal capture. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 77( 6), 1970-1985. doi: 10.3758/s13414-015-0915-4URL |
| 42 | Mast F., Frings C., & Spence C . ( 2017). Crossmodal attentional control sets between vision and audition. Acta Psychologica, 178, 41-47. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2017.05.011URLpmid: 28575705 |
| 43 | Matusz, P.J., &Eimer, M . ( 2011). Multisensory enhancement of attentional capture in visual search. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 18( 5), 904-909. doi: 10.3758/s13423-011-0131-8URLpmid: 21748418 |
| 44 | Matusz, P.J., &Eimer, M . ( 2013). Top-down control of audiovisual search by bimodal search templates. Psychophysiology, 50( 10), 996-1009. doi: 10.1111/psyp.12086URLpmid: 23834379 |
| 45 | Meredith M. A., Nemitz J. W., & Stein B. E . ( 1987). Determinants of multisensory integration in superior colliculus neurons. I. Temporal factors. Journal of Neuroscience, 7( 10), 3215-3229. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199808000-00008URLpmid: 3668625 |
| 46 | Miller, J. ( 2016). Statistical facilitation and the redundant signals effect: What are race and coactivation models? Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 78( 2), 516-519. doi: 10.3758/s13414-015-1017-zURLpmid: 26555650 |
| 47 | Mishler, A Neider, M., . ( 2016). Evidence for the redundant signals effect in detection of categorical targets Journal of Vision, 16( 12), 1024. |
| 48 | Mozolic J. L., Hugenschmidt C. E., Peiffer A. M., & Laurienti P. J . ( 2008). Modality-specific selective attention attenuates multisensory integration. Experimental Brain Research, 184( 1), 39-52. doi: 10.1007/s00221-007-1080-3URLpmid: 17684735 |
| 49 | Murray M. M., Thelen A., Thut G., Romei V., Martuzzi R., & Matusz P. J . ( 2016). The multisensory function of the human primary visual cortex. Neuropsychologia, 83, 161-169. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.08.011URLpmid: 26275965 |
| 50 | Ngo, M.K., &Spence, C . ( 2012). Facilitating masked visual target identification with auditory oddball stimuli. Experimental Brain Research, 221( 2), 129-136. doi: 10.1007/s00221-012-3153-1URLpmid: 22760584 |
| 51 | Otto T. U., Dassy B., & Mamassian P . ( 2013). Principles of multisensory behavior. Journal of Neuroscience, 33( 17), 7463-7474. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4678-12.2013URLpmid: 23616552 |
| 52 | Pluta S. R., Rowland B. A., Stanford T. R., & Stein B. E . ( 2011). Alterations to multisensory and unisensory integration by stimulus competition. Journal of Neurophysiology, 106( 6), 3091-3101. doi: 10.1152/jn.00509.2011URL |
| 53 | Posner, M.I., &Cohen, Y . ( 1984). Components of visual orienting. Attention and Performance X: Control of Language Processes, 32, 531-556. |
| 54 | Santangelo V., Fagioli S., & Macaluso E . ( 2010). The costs of monitoring simultaneously two sensory modalities decrease when dividing attention in space. NeuroImage, 49( 3), 2717-2727. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.10.061URLpmid: 19878728 |
| 55 | Santangelo, V., &Spence, C . ( 2007). Multisensory cues capture spatial attention regardless of perceptual load. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 33( 6), 1311-1321. doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.33.6.1311URLpmid: 18085945 |
| 56 | Santangelo V., Van der Lubbe, R. H., Belardinelli M. O., & Postma A . ( 2006). Spatial attention triggered by unimodal, crossmodal, and bimodal exogenous cues: A comparison of reflexive orienting mechanisms. Experimental Brain Research, 173( 1), 40-48. doi: 10.1007/s00221-006-0361-6URLpmid: 16489435 |
| 57 | Santangelo V., Van der Lubbe, R. H., Belardinelli M. O., & Postma A . ( 2008). Multisensory integration affects ERP components elicited by exogenous cues. Experimental Brain Research, 185( 2), 269-277. doi: 10.1007/s00221-007-1151-5URLpmid: 17909764 |
| 58 | Senkowski D., Saint-Amour D., Gruber T., & Foxe J. J . ( 2008). Look who's talking: The deployment of visuo- spatial attention during multisensory speech processing under noisy environmental conditions. NeuroImage, 43( 2), 379-387. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.06.046URLpmid: 18678262 |
| 59 | Senkowski D., Saint-Amour D., Höfle M., & Foxe J. J . ( 2011). Multisensory interactions in early evoked brain activity follow the principle of inverse effectiveness. NeuroImage, 56( 4), 2200-2208. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.03.075URLpmid: 21497200 |
| 60 | Slagter H. A., Prinssen S., Reteig L. C., & Mazaheri A . ( 2016). Facilitation and inhibition in attention: Functional dissociation of pre-stimulus alpha activity, P1, and N1 components. NeuroImage, 125( 6), 25-35. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.09.058URLpmid: 26436713 |
| 61 | Soto-Faraco S., Navarra J., & Alsius A . ( 2004). Assessing automaticity in audiovisual speech integration: Evidence from the speeded classification task. Cognition, 92( 3), B13-B23. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2003.10.005URLpmid: 15019556 |
| 62 | Spence, C. ( 2010). Crossmodal spatial attention. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1191( 1), 182-200. |
| 63 | Spence, C. ( 2013). Just how important is spatial coincidence to multisensory integration? Evaluating the spatial rule. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1296( 1), 31-49. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12121URLpmid: 23710729 |
| 64 | Spence, C., &Santangelo, V . ( 2009). Capturing spatial attention with multisensory cues: A review. Hearing research, 258( 1-2), 134-142. doi: 10.3758/PBR.15.2.398URLpmid: 18488658 |
| 65 | Stein, B.E., &Stanford, T.R . ( 2008). Multisensory integration: Current issues from the perspective of the single neuron. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9( 4), 255-266. doi: 10.1006/jsvi.1999.2508URLpmid: 18354398 |
| 66 | Stevenson R. A., Fister J. K., Barnett Z. P., Nidiffer A. R., & Wallace M. T . ( 2012). Interactions between the spatial and temporal stimulus factors that influence multisensory integration in human performance. Experimental Brain Research, 219( 1), 121-137. doi: 10.1007/s00221-012-3072-1URLpmid: 3526341 |
| 67 | Talsma D., Doty T. J., & Woldorff M. G . ( 2007). Selective attention and audiovisual integration: Is attending to both modalities a prerequisite for early integration? Cerebral cortex, 17( 3), 679-690. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhk016URLpmid: 16707740 |
| 68 | Talsma D., Senkowski D., Soto-Faraco S., & Woldorff M. G . ( 2010). The multifaceted interplay between attention and multisensory integration. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14( 9), 400-410. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2010.06.008URLpmid: 20675182 |
| 69 | Talsma, D., &Woldorff, M . ( 2005). Selective attention and multisensory integration: Multiple phases of effects on the evoked brain activity. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 17( 7), 1098-1114. doi: 10.1162/0898929054475172URLpmid: 16102239 |
| 70 | Tang X. Y., Wu J. L., & Shen Y . ( 2016). The interactions of multisensory integration with endogenous and exogenous attention. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 61, 208-224. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.11.002URLpmid: 26546734 |
| 71 | Tiippana, K. ( 2014). What is the McGurk effect? Frontiers in Psychology, 5( 4), 725. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00725URLpmid: 25071686 |
| 72 | Van der Burg E., Olivers C. N. L., Bronkhorst A. W., & Theeuwes J . ( 2008 b). Audiovisual events capture attention: Evidence from temporal order judgments. Journal of Vision, 8( 5), 1-10. |
| 73 | Van der Burg E., Olivers C. N. L., Bronkhorst A. W., & Theeuwes J . ( 2008 a). Pip and pop: Nonspatial auditory signals improve spatial visual search. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 34( 5), 1053-1065. doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.34.5.1053URLpmid: 18823194 |
| 74 | Van der Burg E., Olivers C. N. L., Bronkhorst A. W., & Theeuwes J . ( 2009). Poke and pop: Tactile-visual synchrony increases visual saliency. Neuroscience Letters, 450( 1), 60-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.11.002URLpmid: 19013216 |
| 75 | Van Der Burg E., Olivers C. N. L., & Theeuwes J . ( 2012). The attentional window modulates capture by audiovisual events. PloS One, 7( 7), e39137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039137URLpmid: 3393717 |
| 76 | Van der Burg E., Talsma D., Olivers C. N. L., Hickey C., & Theeuwes J . ( 2011). Early multisensory interactions affect the competition among multiple visual objects. NeuroImage, 55( 3), 1208-1218. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.12.068URLpmid: 21195781 |
| 77 | Van der Stoep N., Spence C., Nijboer T. C. W ., & Van der Stigchel, S. ( 2015). On the relative contributions of multisensory integration and crossmodal exogenous spatial attention to multisensory response enhancement. Acta Psychologica, 162, 20-28. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2015.09.010URLpmid: 26436587 |
| 78 | Van der Stoep N., Van der Stigchel S ., & Nijboer, T. C. W. ( 2015). Erratum to: Exogenous spatial attention decreases audiovisual integration. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 77( 2), 464-482. |
| 79 | Van der Stoep N., Van der Stigchel S., Nijboer T. C., & Spence C . ( 2016). Visually induced inhibition of return affects the integration of auditory and visual Information. Perception, 46( 1), 6-17. doi: 10.1177/0301006616661934URLpmid: 27484341 |
| 80 | Vroomen J., Bertelson P., & De Gelder B . ( 2001). The ventriloquist effect does not depend on the direction of automatic visual attention. Perception & Psychophysics, 63( 4), 651-659. |
| 81 | Wu J. L., Li Q., Bai O., & Touge T . ( 2009). Multisensory interactions elicited by audiovisual stimuli presented peripherally in a visual attention task: A behavioral and event-related potential study in humans. Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology, 26( 6), 407-413. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e3181c298b1URLpmid: 19952565 |
| 82 | Wu J. L., Yang J. J., Yu Y. H., Li Q., Nakamura N., Shen Y., .. Abe K . ( 2012). Delayed audiovisual integration of patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease compared with normal aged controls. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 32( 2), 317-328. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-111070URLpmid: 3746512 |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 曹思琪, 刘勋, 伍海燕. 共情可控?以自上而下视角考察共情的可调节性[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(8): 1420-1429. |
| [2] | 杨晓梦, 王福兴, 王燕青, 赵婷婷, 高春颍, 胡祥恩. 瞳孔是心灵的窗口吗?——瞳孔在心理学研究中的应用及测量[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7): 1029-1041. |
| [3] | 杨伟平, 李胜楠, 李子默, 郭敖, 任艳娜. 老年人视听觉整合的影响因素及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(5): 790-799. |
| [4] | 王爱君, 黄杰, 陆菲菲, 何嘉滢, 唐晓雨, 张明. 多感觉整合中的声音诱发闪光错觉效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(10): 1662-1677. |
| [5] | 赵佩琼, 陈巍, 张静, 平贤洁. 橡胶手错觉:拥有感研究的实验范式及其应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(1): 37-50. |
| [6] | 潘莉, 黄希庭. 时序知觉影响因素与思考[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(4): 614-624. |
| [7] | 罗霄骁, 康冠兰, 周晓林. McGurk效应的影响因素与神经基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(11): 1935-1951. |
| [8] | 王昊, 杨志刚. 面孔空想性错视及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(11): 1952-1960. |
| [9] | 陈一凡, 于洋澜, 刘莹. 外源性注意与视觉意识的关系[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(suppl.): 39-39. |
| [10] | 张燕, 曹慧敏, 郑元杰, 任衍具. 自上而下的目标调节奖赏联结干扰项的注意定向和脱离[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(suppl.): 52-52. |
| [11] | 宋娟;吕勇. 自上而下的因素对掩蔽启动中自动加工过程的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(5): 766-773. |
| [12] | 周爱保;张彦驰;刘沛汝;尹玉龙;张 奋. 我是谁?——人际间多感觉刺激下的识脸错觉[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(2): 159-167. |
| [13] | 袁祥勇;黄希庭. 多感觉整合的时间再校准[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(5): 692-700. |
| [14] | 刘建刚;田捷;Kang Lee. 基于fMRI的自上而下字母加工神经机制的研究[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(2): 159-165. |
| [15] | 吴燕;隋光远;曹晓华. 内源性注意和外源性注意的ERP研究[J]. 心理科学进展, 2007, 15(1): 71-77. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4517
