 ), 赵源1
), 赵源1 1 河海大学公共管理学院暨应用心理研究所, 南京 211100
2 河海大学商学院, 南京 211100
3 荷兰莱顿大学社会与行为科学学部, 莱顿, 2333 AK
收稿日期:2017-06-28出版日期:2018-10-15发布日期:2018-08-27通讯作者:沈汪兵E-mail:wbshenhhu@126.com基金资助:*国家自然科学基金(31500870);中央高校基本科研业务费项目(2017B14514);中国博士后基金(2017M6216 03);国家留学基金(201706715037);江苏高校哲学社会科学基金的阶段性成果(2017SJB0649)The effect of ZEN on creative thinking
SHU Chenye1, SHEN Wangbing1,2,3( ), ZHAO Yuan1
), ZHAO Yuan1 1 School of Public Administration and Institute of Applied Psychology, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100, China
2 Business School, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100, China
3 Faculty of Social and Behavioural Sciences, Leiden University, 2333 AK Leiden, The Netherlands
Received:2017-06-28Online:2018-10-15Published:2018-08-27Contact:SHEN Wangbing E-mail:wbshenhhu@126.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 禅修是一种能够对人类心理有广泛影响的训练工具。作为两种重要、相似但又不同的禅修方式, 冥想和正念对创造性思维中的发散思维和聚合思维产生了不同影响。在发散思维方面, 冥想主要通过对注意调控和无意识激活影响以及对解题动机和情绪的有效调控两方面显著增强了发散思维, 尤其是认知灵活性; 在聚合思维方面, 正念和冥想的影响相当复杂, 主要是通过聚合思维所需的执行功能和可能涉及表征重构来促进定势转移或功能固着的消除。就机制而言, 禅修对创造性思维的影响总体上不仅得益于走神时的无意识关联加工, 而且受禅修中诱发的情绪效应的调节。基于这些, 对未来研究的趋势进行了展望。
图/表 2
表1不同禅修方式对创造性思维的影响方式 (↑为正向作用, ↓为负向作用)
| 类型 | 发散思维 | 聚合思维 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 效果 | 机制 | 效果 | 机制 | |
| 冥想 | 促进 | 注意瞬脱↓( | 促进 | 内省机制↑( |
| 注意分配↑( | 深度加工↑( | |||
| 自上而下加工↓( | 认知重构↑( | |||
| 发散思维独特性↑( | 元认知↑( | |||
| 表征转换↑( | 注意、警觉↑( | |||
| 认知灵活性↑( | 无意识的关联处理↑( | |||
| 积极情绪↑( | 积极情绪↑( | |||
| 注意切换↑( | 损害 | 认知策略↓( | ||
| 弥散注意↑( | ||||
| 酝酿效应↑( | ||||
| 正念 | 促进 | 惯性思维↓( | 促进 | 知觉↑( |
| 功能固着↓( | 元认知↑( | |||
| 流体智力↑( | 线索搜索↑( | |||
| 类别转换↑( | 认知重构↑( | |||
| 兴趣↑( | 注意监控↑( | |||
| 坚持性↑( | 工作记忆↑( | |||
| 注意控制↑( | 思维僵局↓( | |||
| 积极情绪↑( | “啊哈”时刻↑( | |||
| 认知敏感↑( | 不确定 | 积极情绪↑( | ||
| 思维工作效率↑( | ||||
表1不同禅修方式对创造性思维的影响方式 (↑为正向作用, ↓为负向作用)
| 类型 | 发散思维 | 聚合思维 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 效果 | 机制 | 效果 | 机制 | |
| 冥想 | 促进 | 注意瞬脱↓( | 促进 | 内省机制↑( |
| 注意分配↑( | 深度加工↑( | |||
| 自上而下加工↓( | 认知重构↑( | |||
| 发散思维独特性↑( | 元认知↑( | |||
| 表征转换↑( | 注意、警觉↑( | |||
| 认知灵活性↑( | 无意识的关联处理↑( | |||
| 积极情绪↑( | 积极情绪↑( | |||
| 注意切换↑( | 损害 | 认知策略↓( | ||
| 弥散注意↑( | ||||
| 酝酿效应↑( | ||||
| 正念 | 促进 | 惯性思维↓( | 促进 | 知觉↑( |
| 功能固着↓( | 元认知↑( | |||
| 流体智力↑( | 线索搜索↑( | |||
| 类别转换↑( | 认知重构↑( | |||
| 兴趣↑( | 注意监控↑( | |||
| 坚持性↑( | 工作记忆↑( | |||
| 注意控制↑( | 思维僵局↓( | |||
| 积极情绪↑( | “啊哈”时刻↑( | |||
| 认知敏感↑( | 不确定 | 积极情绪↑( | ||
| 思维工作效率↑( | ||||
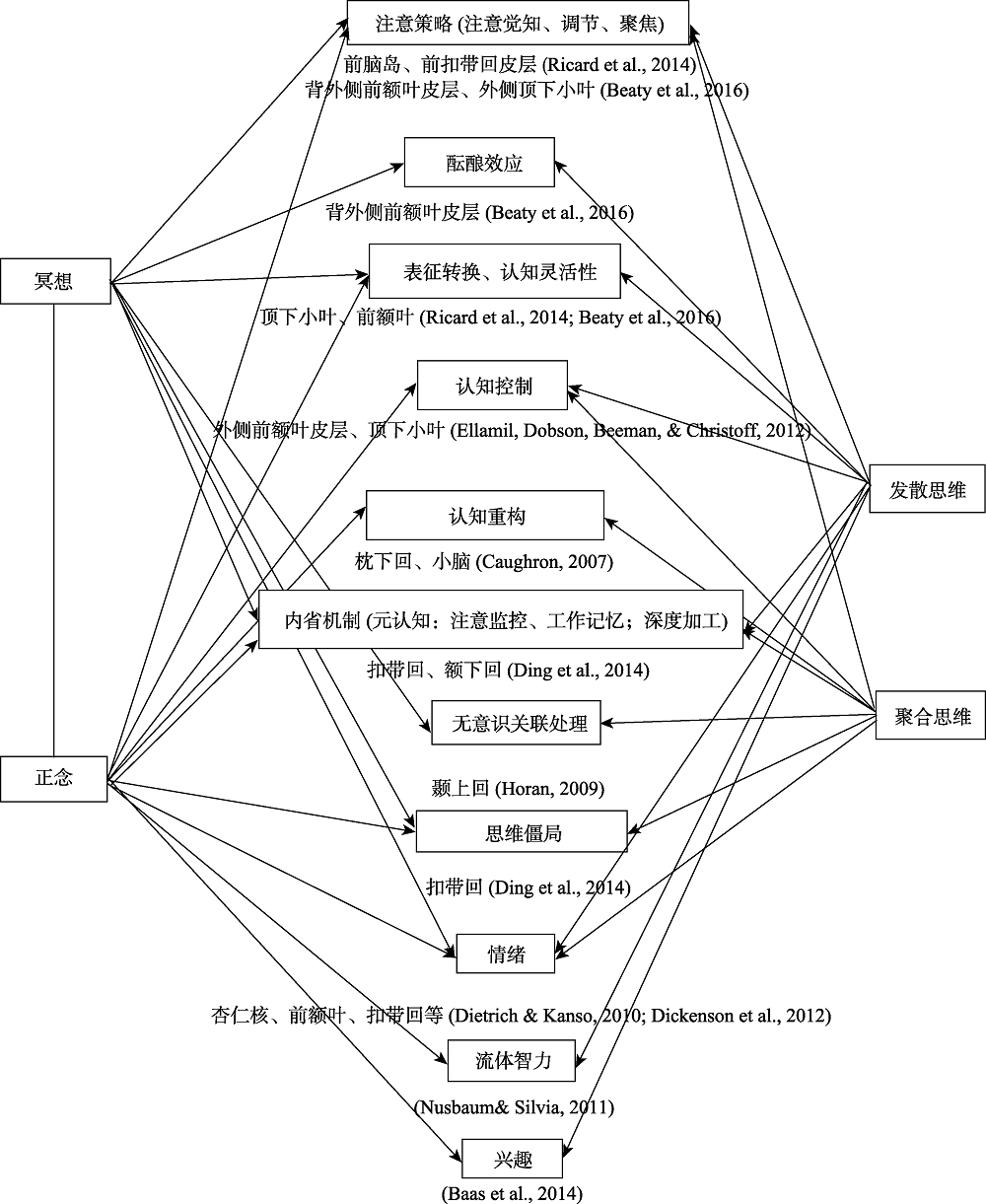
图1禅修影响创造性思维的潜在机制图注:箭头代表作用的方向
 图1禅修影响创造性思维的潜在机制图注:箭头代表作用的方向
图1禅修影响创造性思维的潜在机制图注:箭头代表作用的方向参考文献 68
| 1 | 段文杰 . ( 2014). 正念研究的分歧: 概念与测量. 心理科学进展, 22( 10), 1616-1627. |
| 2 | 任俊, 黄璐, 张振新 . ( 2010). 基于心理学视域的冥想研究. 心理科学进展, 18( 5), 857-864. |
| 3 | 沈汪兵, 刘昌, 陈晶晶 . ( 2010). 创造力的脑结构与脑功能基础. 心理科学进展, 18( 9), 1420-1429. |
| 4 | 沈汪兵, 刘昌, 施春华, 袁媛 . ( 2015). 创造性思维的性别差异. 心理科学进展, 23( 8), 1380-1389. |
| 5 | 沈汪兵, 袁媛 . ( 2015). 创造性思维的社会文化基础. 心理科学进展, 23( 7), 1169-1180. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2015.01169URL |
| 6 | 宋晓兰, 王晓, 唐孝威 . ( 2010). 心智游移: 现象、机制及意义. 心理科学进展, 19( 4), 499-509. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2011.00499URL |
| 7 | 汪芬, 黄宇霞 . ( 2011). 正念的心理和脑机制. 心理科学进展, 19( 11), 1635-1644. |
| 8 | Beaty R. E., Benedek M., Silvia P. J., & Schacter D. L . ( 2016). Creative cognition and brain network dynamics. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20( 2), 87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2015.10.004URLpmid: 26553223 |
| 9 | Baas M., Nevicka B ., & Ten Velden, F. S.( 2014). Specific mindfulness skills differentially predict creative performance. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 40( 9), 1092-1106. doi: 10.1177/0146167214535813URLpmid: 24857851 |
| 10 | Baird B., Smallwood J., Mrazek M. D., Kam J. W. Y., Franklin M. S., & Schooler J. W . ( 2012). Inspired by distraction: Mind wandering facilitates creative incubation. Psychological Science, 23( 10), 1117-1122. doi: 10.1177/0956797612446024URL |
| 11 | Brefczynski-Lewis J. A., Lutz A., Schaefer H. S., Levinson D. B., & Davidson R. J . ( 2007). Neural correlates of attentional expertise in long-term meditation practitioners. Proceedings of the national Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104( 27), 11483-11488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606552104URLpmid: 17596341 |
| 12 | Cahn B. R., & Polich, J. ( 2006). Meditation states and traits: eeg, erp, and neuroimaging studies. Psychological Bulletin, 132(2), 180-211. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.132.2.180URLpmid: 16536641 |
| 13 | Cropley A., ( 2006). In praise of convergent thinking. Creativity Research Journal, 18( 3), 391-404. doi: 10.1207/s15326934crj1803_13URL |
| 14 | Cowger, E. L . ( 1974). The effects of meditation (zazen) upon selected dimensions of personality development. Dissertation Abstracts International, 34, 4734. |
| 15 | Cayoun, B. A . ( 2011). Operationalization of mindfulness. In Mindfulness-integrated CBT: Principles and practice( pp. 11-20). United Kingdom: John Wiley & Sons. |
| 16 | Capurso V., Fabbro F., & Crescentini C . ( 2013). Mindful creativity: The influence of mindfulness meditation on creative thinking. Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 1020. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.01020URLpmid: 24454303 |
| 17 | Christoff K., Irving Z. C., Fox K. C. R., Spreng R. N., & Andrews-Hanna J. R . ( 2016). Mind-wandering as spontaneous thought: A dynamic framework. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 17( 11), 718-731. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.113URLpmid: 27654862 |
| 18 | Chiesa A., & Malinowsk, P. ( 2011). Mindfulness-based approaches: Are they all the same?. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 67( 4), 404-424. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20776URLpmid: 21254062 |
| 19 | Colzato L. S., Szapora A., & Hommel B . ( 2012). Meditate to create: The impact of focused-attention and open- monitoring training on convergent and divergent thinking. Frontiers in Psychology, 3, 116. |
| 20 | Colzato L. S., Szapora A., Lippelt D., & Hommel B . ( 2014). Prior meditation practice modulates performance and strategy use in convergent- and divergent-thinking problems. Mindfulness, 8( 1), 10-16. |
| 21 | Domino G., ( 1977). Transcendental meditation and creativity: An empirical investigation. Journal of Applied Psychology, 62( 3), 358-362. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.62.3.358URLpmid: 324968 |
| 22 | Dickenson J., Berkman E. T., Arch J., & Lieberman M. D . ( 2013). Neural correlates of focused attention during a brief mindfulness induction. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 8( 1), 40-47. doi: 10.1093/scan/nss030URLpmid: 22383804 |
| 23 | Davidson R. J., & Lutz, A. ( 2008). Buddha's brain: Neuroplasticity and meditation. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 25( 1), 176. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2008.4431873URLpmid: 2944261 |
| 24 | Ding X. Q., Li S., & Tang Y. Y . ( 2011). Short-term meditation improves creativity. Second World Congr Positive Psychol Poster Abstr, 167. |
| 25 | Ding X. Q., Tang Y. Y., Tang R. X., & Posner M. I . ( 2014). Improving creativity performance by short-term meditation. Behavioral and Brain Functions, 10, 9. doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-10-9URLpmid: 24645871 |
| 26 | Ding X. Q., Tang Y. Y., Cao C., Deng Y. Q., Wang Y., Xin X., & Posner M. I . ( 2015). Short-term meditation modulates brain activity of insight evoked with solution cue. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 10( 1), 43-49. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsu032URL |
| 27 | Ding X. Q., Tang Y. Y., Deng Y. Q., Tang R. X., & Posner M. I . ( 2015). Mood and personality predict improvement in creativity due to meditation training. Learning and Individual Differences, 37, 217-221. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2014.11.019URL |
| 28 | Edenfield T. M., & Saeed, S. A . ( 2012). An update on mindfulness meditation as a self-help treatment for anxiety and depression. Psychology Research & Behavior Management, 5, 131-141. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S34937URLpmid: 3500142 |
| 29 | Fresco D. M., Segal Z. V., Buis T., & Kennedy S . ( 2007). Relationship of posttreatment decentering and cognitive reactivity to relapse in major depression. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 75( 3), 447-455. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.75.3.447URL |
| 30 | Frewen P. A., Evans E. M., Maraj N., Dozois D. J. A., & Partridge K . ( 2008). Letting go: Mindfulness and negative automatic thinking. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 32( 6), 758-774. doi: 10.1007/s10608-007-9142-1URL |
| 31 | Guglietti C. L., Daskalakis Z. J., Radhu N., Fitzgerald P. B., & Ritvo P . ( 2013). Meditation-related increases in gabab modulated cortical inhibition. Brain Stimulation, 6(3), 397-402. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2012.08.005URLpmid: 23022436 |
| 32 | Greenberg J., Reiner K., & Meiran N . ( 2012). “mind the trap”: mindfulness practice reduces cognitive rigidity. Plos One, 7(5), e36206. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036206URLpmid: 22615758 |
| 33 | Grossman P., & van Dam N.T, . ( 2011). Mindfulness, by any other name…: Trials and tribulations of sati in western psychology and science. Contemporary Buddhism, 12( 1), 219-239. |
| 34 | Hodgins H. S., & Adair, K. C . ( 2010). Attentional processes and meditation. Consciousness and Cognition, 19( 4), 872-878. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2010.04.002URL |
| 35 | Horan R., ( 2009). The neuropsychological connection between creativity and meditation. Creativity Research Journal, 21( 2-3), 199-222. doi: 10.1080/10400410902858691URL |
| 36 | Jha A. P., Krompinger J., & Baime M. J . ( 2007). Mindfulness training modifies subsystems of attention. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci, 7(2), 109-119. doi: 10.3758/CABN.7.2.109URLpmid: 17672382 |
| 37 | Kudesia R. S. ( 2015). Mindfulness and creativity in the workplace. In Mindfulness in organizations: Foundations, research, and applications (pp. 190-212). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| 38 | Lippelt D. P., Hommel B., & Colzato L. S . ( 2014). Focused attention, open monitoring and loving kindness meditation: Effects on attention, conflict monitoring, and creativity-A review. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 1083. |
| 39 | Lyubomirsky S., King L., & Diener E . ( 2005). The benefits of frequent positive affect: Does happiness lead to success?. Psychological Bulletin, 131( 6), 803-855. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.131.6.803URLpmid: 16351326 |
| 40 | Lutz A., Slagter H. A., Dunne J. D., & Davidson R. J . ( 2008). Attention regulation and monitoring in meditation. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 12( 4), 163-169. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2008.01.005URL |
| 41 | Lebuda I., Zabelina D. L., & Karwowski M . ( 2016). Mind full of ideas: A meta-analysis of the mindfulness-creativity link. Personality & Individual Differences, 93, 22-26. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2015.09.040URL |
| 42 | Moore A., & Malinowsk, P. ( 2009). Meditation, mindfulness and cognitive flexibility. Consciousness and Cognition, 18( 1), 176-186. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2008.12.008URL |
| 43 | Müller B. C., Gerasimova A., & Ritter S. M . ( 2016). Concentrative meditation influences creativity by increasing cognitive flexibility. Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts, 10( 3), 278-286. doi: 10.1037/a0040335URL |
| 44 | Mrazek M. D., Franklin M. S., Phillips D. T., Baird B., & Schooler J. W . ( 2013). Mindfulness training improves working memory capacity and GRE performance while reducing mind wandering. Psychological Science, 24( 5), 776-781. doi: 10.1177/0956797612459659URL |
| 45 | McMillan, R. L, Kaufman, S. B., & Singer, J. L . ( 2013). Ode to positive constructive daydreaming. Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 626. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00626URLpmid: 24065936 |
| 46 | Nusbaum E. C., & Silvia, P. J . ( 2011). Are intelligence and creativity really so different?: Fluid intelligence, executive processes, and strategy use in divergent thinking. Intelligence, 39( 1), 36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.intell.2010.11.002URL |
| 47 | Otis, L. S . ( 1974). The facts about transcendental meditation, Part 3. If well-integrated but anxious, try TM. Psychology Today, 7, 45-46. |
| 48 | Orme-Johnson, D. W., & Granieri, B.( 1977). The effects of the age of enlightenment governor training courses on field independence, creativity, intelligence, and behavioral flexibility. In Scientific research on maharishi’s transcendental meditation and TM-Sidhi program (Vol. 1, pp. 713-718).New York: MERU Press. |
| 49 | Ostafin B. D., & Kassman, K. T . ( 2012). Stepping out of history: Mindfulness improves insight problem solving. Consciousness and Cognition, 21( 2), 1031-1036. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2012.02.014URLpmid: 22483682 |
| 50 | Ostafin B. D., Robinson M. D., & Meier B. P . ( 2015). Handbook of mindfulness and self-regulation. New York: Springer. |
| 51 | Ovington L. A., Saliba A. J., & Goldring J . ( 2017). Dispositions toward flow and mindfulness predict dispositional insight. Mindfulness, 8, 1-12. doi: 10.1007/s12671-016-0654-1URL |
| 52 | Puryear, J. S . ( 2015). Metacognition as a moderator of creative ideation and creative production. Creativity Research Journal, 27( 4), 334-341. doi: 10.1080/10400419.2015.1087270URL |
| 53 | Ren J., Huang Z. H., Luo J., Wei G. X., Ying X. P., Ding Z. G., .. Luo F . ( 2011). Meditation promotes insightful problem-solving by keeping people in a mindful and alert conscious state. Science China Life Sciences, 54( 10), 961-965. doi: 10.1007/s11427-011-4233-3URL |
| 54 | Rowe G., Hirsh J. B., & Anderson A. K . ( 2007). Positive affect increases the breadth of attentional selection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104( 1), 383-388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605198104URLpmid: 17182749 |
| 55 | Ricard M., Lutz A., & Davidson R. J . ( 2014). Mind of the meditator. Scientific American, 311( 5), 38-45. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1114-38URLpmid: 25464661 |
| 56 | Salvi C., & Bowden, E. M . ( 2016). Looking for Creativity: Where do we look when we look for new ideas?. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 161. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00161URLpmid: 4753696 |
| 57 | Sedlmeier P., Eberth J., Schwarz M., Zimmermann D., Haarig F., Jaeger S., & Kunze S . ( 2012). The psychological effects of meditation: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 138( 6), 1139-1171. doi: 10.1037/a0028168URLpmid: 22582738 |
| 58 | Subramaniam K., Kounios J., Parrish T. B., & Jung- Beeman M . ( 2009). A brain mechanism for facilitation of insight by positive affect. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21( 3), 415-432. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2009.21057URLpmid: 18578603 |
| 59 | Sternberg R. J., & Lubart, T. I . ( 1996). Investing in creativity. American Psychologist, 51( 7), 677-688. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.51.7.677URL |
| 60 | Slagter H. A., Lutz A., Greischar L. L., Francis A. D., Nieuwenhuis S., Davis J. M., & Davidson R. J . ( 2007). Mental training affects distribution of limited brain resources. Plos Biology, 5(6), e138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050138URL |
| 61 | Shen W. B., Yuan Y., Liu C., & Luo J . ( 2016). In search of the 'Aha!' experience: Elucidating the emotionality of insight problem-solving. British Journal of Psychology, 107( 2), 281-298. doi: 10.1111/bjop.2016.107.issue-2URL |
| 62 | Tang Y. Y., Hölzel B. K., & Posner M. I . ( 2015). Traits and states in mindfulness meditation. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 17, 59. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46322-3_4URLpmid: 26631928 |
| 63 | Wenk-Sormaz H., ( 2005). Meditation can reduce habitual responding. Alternative Therapies, 11( 2), 42-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.01.006URLpmid: 15819448 |
| 64 | Wiggins G. A., & Bhattacharya, J. ( 2014). Mind the gap: An attempt to bridge computational and neuroscientific approaches to study creativity. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 540. |
| 65 | Zarrabian E., ( 2010). The usefulness of meditation in the alleviation of self-reported depressive symptoms among women (Unpublished doctorial dissertation). Saybrook University. |
| 66 | Zeidan F., Gordon N. S., Merchant J., & Goolkasian P . ( 2010). The effects of brief mindfulness meditation training on experimentally induced pain. The Journal of Pain, 11( 3), 199-209. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2009.07.015URLpmid: 19853530 |
| 67 | Zeng X. L., Oei T. P. S., Ye Y. Q., & Liu X. P . ( 2015). A critical analysis of the concepts and measurement of awareness and equanimity in Goenka's Vipassana meditation. Journal of Religion and Health, 54( 2), 399-412. doi: 10.1007/s10943-013-9796-9URL |
| 68 | Zedelius C. M., & Schooler, J. W . ( 2015). Mind wandering “Ahas” versus mindful reasoning: Alternative routes to creative solutions. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 834. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00834URLpmid: 4469818 |
相关文章 11
| [1] | 徐富明;李燕;邓颖;史燕伟;刘程浩. 正念禅修与成瘾行为[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(6): 985-994. |
| [2] | 贡喆;刘昌;沈汪兵. 有关创造力测量的一些思考[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(1): 31-45. |
| [3] | 沈汪兵;刘昌;施春华;袁媛. 创造性思维的性别差异[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(8): 1380-1389. |
| [4] | 沈汪兵;袁媛. 创造性思维的社会文化基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(7): 1169-1180. |
| [5] | 詹慧佳;刘昌;沈汪兵. 创造性思维四阶段的神经基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(2): 213-224. |
| [6] | 刘春雷;王敏;张庆林. 创造性思维的脑机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2009, 17(1): 106-111. |
| [7] | 宋晓辉;施建农. 创造力测量手段——同感评估技术(CAT)简介[J]. 心理科学进展, 2005, 13(6): 739-744. |
| [8] | 徐展;张庆林. 关于创造性的研究述评[J]. 心理科学进展, 2001, 9(1): 36-40. |
| [9] | 施建农;查子秀;周林. 智力超常与常态学生技术创造性思维的比较研究[J]. 心理科学进展, 1995, 3(1): 51-56. |
| [10] | 李亦菲. 广告创作中的心理因素及莫应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 1994, 2(1): 21-284. |
| [11] | 李自璋;. “发散思维”概念之我见[J]. 心理科学进展, 1992, 0(1): 42-43. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4478
