 ), 孔祥祯3, Eric-Jan Wagenmakers4, Alexander Ly4,5, 彭凯平1(
), 孔祥祯3, Eric-Jan Wagenmakers4, Alexander Ly4,5, 彭凯平1( )
) 1 清华大学心理学系, 北京 100084
2 Neuroimaging Center, Johannes Gutenberg University Medical Center, 55131 Mainz, Germany
3 Language and Genetics Department, Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics, 6500 AH Nijmegen, The Netherlands
4 Department of Psychological Methods, University of Amsterdam, 1018 VZ Amsterdam, The Netherlands
5 Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica, 1090 GB Amsterdam, The Netherlands
收稿日期:2017-10-10出版日期:2018-06-10发布日期:2018-04-28通讯作者:胡传鹏,彭凯平E-mail:hcp4715@hotmail.com;pengkp@mail.tsinghua.edu.cnThe Bayes factor and its implementation in JASP: A practical primer
HU Chuan-Peng1,2( ), KONG Xiang-Zhen3, Eric-Jan WAGENMAKERS4, Alexander LY4,5, PENG Kaiping1(
), KONG Xiang-Zhen3, Eric-Jan WAGENMAKERS4, Alexander LY4,5, PENG Kaiping1( )
) 1 Department of Psychology, School of Social Science, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2 Neuroimaging Center, Johannes Gutenberg University Medical Center, 55131 Mainz, Germany
3 Language and Genetics Department, Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics, 6500 AH Nijmegen, The Netherlands
4 Department of Psychological Methods, University of Amsterdam, 1018 VZ Amsterdam, The Netherlands
5 Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica, 1090 GB Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Received:2017-10-10Online:2018-06-10Published:2018-04-28Contact:HU Chuan-Peng,PENG Kaiping E-mail:hcp4715@hotmail.com;pengkp@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 统计推断在科学研究中起到关键作用, 然而当前科研中最常用的经典统计方法——零假设检验(Null hypothesis significance test, NHST)却因难以理解而被部分研究者误用或滥用。有研究者提出使用贝叶斯因子(Bayes factor)作为一种替代和(或)补充的统计方法。贝叶斯因子是贝叶斯统计中用来进行模型比较和假设检验的重要方法, 其可以解读为对零假设H0或者备择假设H1的支持程度。其与NHST相比有如下优势:同时考虑H0和H1并可以用来支持H0、不“严重”地倾向于反对H0、可以监控证据强度的变化以及不受抽样计划的影响。目前, 贝叶斯因子能够很便捷地通过开放的统计软件JASP实现, 本文以贝叶斯t检验进行示范。贝叶斯因子的使用对心理学研究者来说具有重要的意义, 但使用时需要注意先验分布选择的合理性以及保持数据分析过程的透明与公开。
图/表 6
表1假设检验中贝叶斯推断与传统NHST推断的比较
| 假设检验中的问题 | 贝叶斯因子 | 传统推理 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 同时考虑H0和H1的支持证据 | √ | × | 10, 11 |
| 2. 可以用来支持H0 | √ | × | 12, 13 |
| 3. 不“严重”地倾向于反对H0 | √ | × | 14, 15, 16 |
| 4. 可以随着数据累积来监控证据的强度 | √ | × | 17, 18 |
| 5. 不依赖于未知的或者不存在的抽样计划 | √ | × | 19, 20 |
表1假设检验中贝叶斯推断与传统NHST推断的比较
| 假设检验中的问题 | 贝叶斯因子 | 传统推理 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 同时考虑H0和H1的支持证据 | √ | × | 10, 11 |
| 2. 可以用来支持H0 | √ | × | 12, 13 |
| 3. 不“严重”地倾向于反对H0 | √ | × | 14, 15, 16 |
| 4. 可以随着数据累积来监控证据的强度 | √ | × | 17, 18 |
| 5. 不依赖于未知的或者不存在的抽样计划 | √ | × | 19, 20 |
表2贝叶斯因子决策标准
| 贝叶斯因子, BF10 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| > 100 | 极强的证据支持H1 |
| 30 ~ 100 | 非常强的证据支持H1 |
| 10 ~ 30 | 较强的证据支持H1 |
| 3 ~ 10 | 中等程度的证据支持H1 |
| 1 ~ 3 | 较弱的证据支持H1 |
| 1 | 没有证据 |
| 1/3 ~ 1 | 较弱的证据支持H0 |
| 1/10 ~ 1/3 | 中等程度的证据支持H0 |
| 1/30 ~ 1/10 | 较强的证据支持H0 |
| 1/100 ~ 1/30 | 非常强的证据支持H0 |
| < 1/100 | 极强的证据支持H0 |
表2贝叶斯因子决策标准
| 贝叶斯因子, BF10 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| > 100 | 极强的证据支持H1 |
| 30 ~ 100 | 非常强的证据支持H1 |
| 10 ~ 30 | 较强的证据支持H1 |
| 3 ~ 10 | 中等程度的证据支持H1 |
| 1 ~ 3 | 较弱的证据支持H1 |
| 1 | 没有证据 |
| 1/3 ~ 1 | 较弱的证据支持H0 |
| 1/10 ~ 1/3 | 中等程度的证据支持H0 |
| 1/30 ~ 1/10 | 较强的证据支持H0 |
| 1/100 ~ 1/30 | 非常强的证据支持H0 |
| < 1/100 | 极强的证据支持H0 |
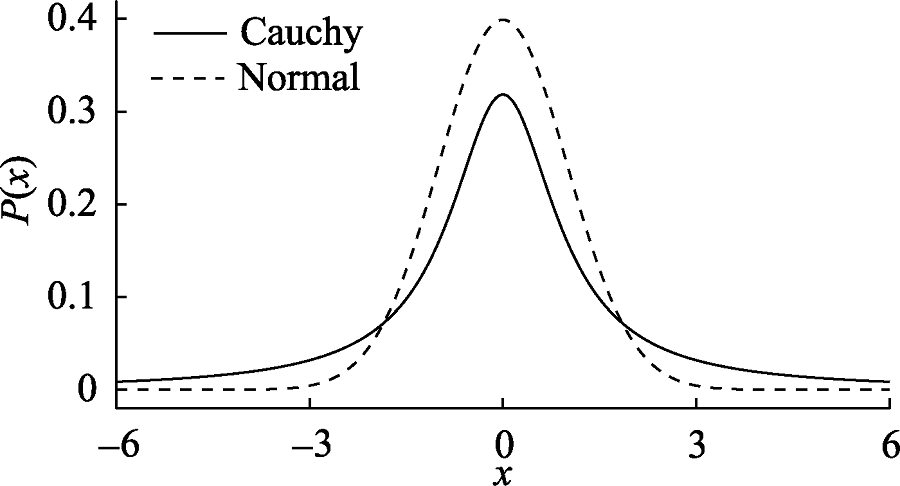
图1柯西分布与正态分布的对比
 图1柯西分布与正态分布的对比
图1柯西分布与正态分布的对比
图2使用JASP进行贝叶斯独立样本t检验时的操作截屏。软件左侧是数据; 中间为数据分析选项; 右侧为结果输出。
 图2使用JASP进行贝叶斯独立样本t检验时的操作截屏。软件左侧是数据; 中间为数据分析选项; 右侧为结果输出。
图2使用JASP进行贝叶斯独立样本t检验时的操作截屏。软件左侧是数据; 中间为数据分析选项; 右侧为结果输出。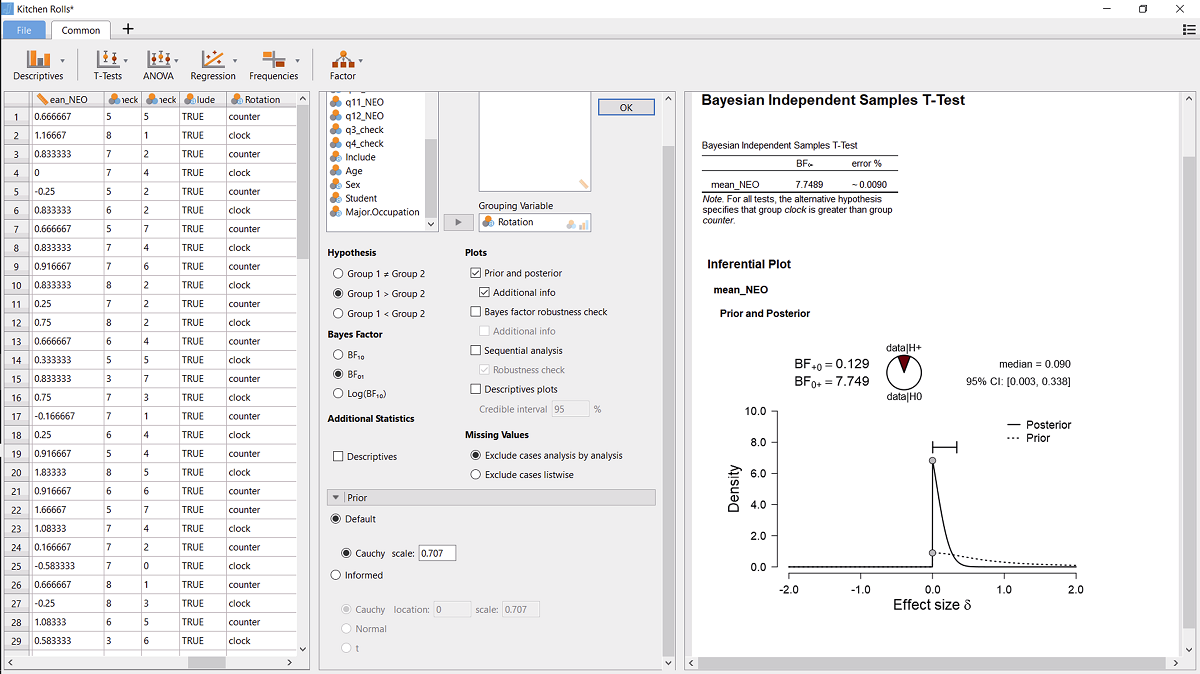
图3使用JASP对Wagenmakers等人(2015)数据进行贝叶斯单侧独立样本t检验的示意图。左侧是数据, 中间为操作过程, 右侧为结果输出。细节见文中的描述。
 图3使用JASP对Wagenmakers等人(2015)数据进行贝叶斯单侧独立样本t检验的示意图。左侧是数据, 中间为操作过程, 右侧为结果输出。细节见文中的描述。
图3使用JASP对Wagenmakers等人(2015)数据进行贝叶斯单侧独立样本t检验的示意图。左侧是数据, 中间为操作过程, 右侧为结果输出。细节见文中的描述。
图4使用JASP进行贝叶斯因子的稳健性分析
 图4使用JASP进行贝叶斯因子的稳健性分析
图4使用JASP进行贝叶斯因子的稳健性分析参考文献 98
| [1] | 胡传鹏, 王非, 过继成思, 宋梦迪, 隋洁, 彭凯平 . ( 2016). 心理学研究中的可重复性问题: 从危机到契机. 心理科学进展, 24( 9), 1504-1518. |
| [2] | 骆大森 . ( 2017). 心理学可重复性危机两种根源的评估. 心理与行为研究, 15( 5), 577-586. |
| [3] | 钟建军, Dienes, Z., 陈中永 . ( 2017). 心理研究中引入贝叶斯统计推断的必要性、应用思路与领域. 心理科学, 40( 6), 1477-1482. |
| [4] | Bahadur,R. R., &Bickel, P. J . ( 2009). An optimality property of Bayes' test statistics. Lecture Notes-Monograph Series, 57, 18-30. doi: 10.2307/30250033URL |
| [5] | Baker, M.(2016). 1,500 scientists lift the lid on reproducibility. Nature, 533, 452-454. doi: 10.1038/533452aURLpmid: 27225100 |
| [6] | Begley,C. G., & Ellis, L. M . ( 2012). Drug development: Raise standards for preclinical cancer research. Nature, 483( 7391), 531-533. doi: 10.1038/483531aURL |
| [7] | Bem,D. J . ( 2011). Feeling the future: Experimental evidence for anomalous retroactive influences on cognition and affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 100( 3), 407-425. doi: 10.1037/a0021524URLpmid: 21280961 |
| [8] | Bem D. J., Utts J., & Johnson W. O . ( 2011). Must psychologists change the way they analyze their data? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 101( 4), 716-719. doi: 10.1037/a0024777URLpmid: 21928916 |
| [9] | Benjamin D. J., Berger J. O., Johannesson M., Nosek B. A., Wagenmakers E.-J., Berk R., … Johnson V. E . ( 2018). Redefine statistical significance. Nature Human Behaviour, 2( 1), 6-10. doi: 10.1038/s41562-017-0189-zURL |
| [10] | Berger,J. O., & Berry, D. A . ( 1988). Statistical analysis and the illusion of objectivity. American Scientist, 76( 2), 159-165. doi: 10.1016/S0730-725X(97)00243-9URL |
| [11] | Berger,J. O., & Delampady, M.(1987). Testing precise hypotheses. Statistical Science, 2( 3), 317-335. doi: 10.1214/ss/1177013238URL |
| [12] | Berger,J. O., & Wolpert, R. L . ( 1988). The likelihood principle (2nd ed.). Hayward (CA): Institute of Mathematical Statistics. |
| [13] | Carpenter B., Gelman A., Hoffman M. D., Lee D., Goodrich B., Betancourt M., … Riddell A . ( 2017). Stan: A probabilistic programming language. Journal of Statistical Software, 76( 1), 1-32. doi: 10.18637/jss.v076.i01URL |
| [14] | Chambers C. D., Feredoes E., Muthukumaraswamy S. D., & Etchells P. J . ( 2014). Instead of “playing the game” it is time to change the rules: Registered Reports at AIMS Neuroscience and beyond. AIMS Neuroscience, 1( 1), 4-17. |
| [15] | Chen X., Lu B., & Yan C.-G . ( 2018). Reproducibility of R-fMRI metrics on the impact of different strategies for multiple comparison correction and sample sizes. Human Brain Mapping, 39( 1), 300-318. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23843URLpmid: 29024299 |
| [16] | Cumming, G.(2014). The new statistics: Why and how. Psychological Science, 25( 1), 7-29. doi: 10.1177/0956797613504966URL |
| [17] | Depaoli, S.,& van de Schoot, R.(2017). Improving transparency and replication in Bayesian statistics: The WAMBS-Checklist. Psychological Methods, 22( 2), 240-261. doi: 10.1037/met0000065URLpmid: 26690773 |
| [18] | Dienes, Z.(2008). Understanding psychology as a science: An introduction to scientific and statistical inference. London, UK: Palgrave Macmillan. |
| [19] | Dienes, Z.(2011). Bayesian versus orthodox statistics: Which side are you on? Perspectives on Psychological Science, 6( 3), 274-290. doi: 10.1177/1745691611406920URLpmid: 26168518 |
| [20] | Dienes, Z.(2014). Using Bayes to get the most out of non-significant results. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 781. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00781URLpmid: 4114196 |
| [21] | Ebersole C. R., Atherton O. E., Belanger A. L., Skulborstad H. M., Allen J. M., Banks J. B., .. Nosek B. A . ( 2016). Many Labs 3: Evaluating participant pool quality across the academic semester via replication. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 67, 68-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2015.10.012URL |
| [22] | Edwards, W.(1965). Tactical note on the relation between scientific and statistical hypotheses. Psychological Bulletin, 63( 6), 400-402. doi: 10.1037/h0021967URLpmid: 14314074 |
| [23] | Edwards W., Lindman H., & Savage L. J . ( 1963). Bayesian statistical inference for psychological research. Psychological Review, 70( 3), 193-242. doi: 10.1037/h0044139URL |
| [24] | Etz A .(in press). Introduction to the concept of likelihood and its applications.Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science. doi: 10.1177/2515245917744314URL |
| [25] | Francis, G.(2013). Replication, statistical consistency, and publication bias. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 57( 5), 153-169. doi: 10.1016/j.jmp.2013.02.003URL |
| [26] | Gallistel,C. R . ( 2009). The importance of proving the null. Psychological Review, 116( 2), 439-453. doi: 10.1037/a0015251URLpmid: 2859953 |
| [27] | Gigerenzer, G.(2004). Mindless statistics. The Journal of Socio-Economics, 33( 5), 587-606. doi: 10.1016/j.socec.2004.09.033URL |
| [28] | Greenland S., Senn S. J., Rothman K. J., Carlin J. B., Poole C., Goodman S. N., … Altman D. G . ( 2016). Statistical tests, P values, confidence intervals, and power: A guide to misinterpretations. European Journal of Epidemiology, 31( 4), 337-350. doi: 10.1007/s10654-016-0149-3URL |
| [29] | Gronau,Q. F., & Wagenmakers, E.-J.(2017). Bayesian evidence accumulation in experimental mathematics: A case study of four irrational numbers. Experimental Mathematics, 1-10. doi: 10.1080/10586458.2016.1256006URL |
| [30] | Halsey L. G., Curran-Everett D., Vowler S. L., & Drummond G. B . ( 2015). The fickle P value generates irreproducible results. Nature Methods, 12( 3), 179-185. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3288URLpmid: 25719825 |
| [31] | Hoijtink, H.(2011). Informative hypotheses: Theory and practice for behavioral and social scientists. Boca Raton, FL: Chapman & Hall/CRC. |
| [32] | Hoijtink H., van Kooten P., & Hulsker K . ( 2016). Why Bayesian psychologists should change the way they use the Bayes factor. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 51( 1), 2-10. doi: 10.1080/00273171.2014.969364URLpmid: 26881951 |
| [33] | JASP Team. ( 2017). JASP (Version 0.8.2) [Computer software]. |
| [34] | Jeffreys, H.(1935). Some tests of significance, treated by the theory of probability. Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 31( 2), 203-222. doi: 10.1017/S030500410001330XURL |
| [35] | Jeffreys, H.(1938). Significance tests when several degrees of freedom arise simultaneously. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 165( 921), 161-198. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1938.0052URL |
| [36] | Jeffreys, H. (1961). Theory of probability (3rd ed.). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. |
| [37] | Johnson,V. E . ( 2013). Revised standards for statistical evidence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110( 48), 19313-19317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1313476110URL |
| [38] | Kerr,N. L . ( 1998). HARKing: Hypothesizing after the results are known. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 2( 3), 196-217. doi: 10.1207/s15327957pspr0203_4URLpmid: 15647155 |
| [39] | Klein R. A., Ratliff K. A., Vianello M., Adams R. B., Jr., Bahník ?., Bernstein M. J., … Nosek B. A . ( 2014). Investigating variation in replicability: A “many labs” replication project. Social Psychology, 45( 3), 142-152. doi: 10.1027/1864-9335/a000178URL |
| [40] | Klugkist I., Laudy O., & Hoijtink H . ( 2005). Inequality constrained analysis of variance: A Bayesian approach. Psychological Methods, 10( 4), 477-493. doi: 10.1037/1082-989X.10.4.477URLpmid: 16393001 |
| [41] | Kruschke J. K. (2014). Doing Bayesian data analysis: A tutorial with R, JAGS, and stan (2nd ed.). San Diego, CA: Academic Press/Elsevier. |
| [42] | Kruschke,J. K., & Liddell, T. M . ( 2017a). Bayesian data analysis for newcomers. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 1-23. doi: 10.3758/s13423-017-1272-1URLpmid: 28405907 |
| [43] | Kruschke,J. K., & Liddell, T. M . ( 2017 b). The Bayesian New Statistics: Hypothesis testing, estimation, meta-analysis, and power analysis from a Bayesian perspective. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 1-29. |
| [44] | Lakens, D.(2017). Equivalence tests: A practical primer for t-Tests, correlations, and meta-analyses. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 8( 4), 355-362. doi: 10.1177/1948550617697177URL |
| [45] | Lindley,D. V . ( 1993). The analysis of experimental data: The appreciation of tea and wine. Teaching Statistics, 15( 1), 22-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9639.1993.tb00252.xURL |
| [46] | Lindsay,D. S . ( 2015). Replication in psychological science. Psychological Science, 26( 12), 1827-1832. doi: 10.1177/0956797615616374URL |
| [47] | Lunn D., Spiegelhalter D., Thomas A., & Best N . ( 2009). The BUGS project: Evolution, critique and future directions. Statistics in Medicine, 28( 25), 3049-3067. doi: 10.1002/sim.3680URLpmid: 19630097 |
| [48] | Ly A., Etz A., Marsman M., & Wagenmakers E.-J . ( 2017). Replication Bayes factors from evidence updating. PsyArXiv. Retrieved from |
| [49] | Ly A., Marsman M., & Wagenmakers E.-J . ( 2018). Analytic posteriors for Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Statistica Neerlandica, 72, 4-13. doi: 10.1111/stan.12111URL |
| [50] | Ly A., Verhagen J., & Wagenmakers E.-J . (2016a). An evaluation of alternative methods for testing hypotheses, from the perspective of Harold Jeffreys. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 72, 43-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jmp.2016.01.003URL |
| [51] | Ly A., Verhagen J., & Wagenmakers E.-J . (2016b). Harold Jeffreys’s default Bayes factor hypothesis tests: Explanation, extension, and application in psychology. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 72, 19-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jmp.2015.06.004URL |
| [52] | Marsman, M.,& Wagenmakers, E.-J.(2017 a). Bayesian benefits with JASP. European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 14( 5), 545-555. doi: 10.1080/17405629.2016.1259614URL |
| [53] | Marsman, M.,& Wagenmakers, E.-J.(2017 b). Three insights from a bayesian interpretation of the one-sided P value. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 77( 3), 529-539. doi: 10.1177/0013164416669201URL |
| [54] | Masson,M. E. J . ( 2011). A tutorial on a practical Bayesian alternative to null-hypothesis significance testing. Behavior Research Methods, 43( 3), 679-690. doi: 10.3758/s13428-010-0049-5URLpmid: 21302025 |
| [55] | Matzke D., Nieuwenhuis S., van Rijn H., Slagter H. A., van der Molen, M. W., & Wagenmakers E.-J . ( 2015). The effect of horizontal eye movements on free recall: A preregistered adversarial collaboration. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 144( 1), e1-e15. doi: 10.1037/xge0000038URLpmid: 25621378 |
| [56] | Miller, G.(2011). ESP paper rekindles discussion about statistics. Science, 331( 6015), 272-273. doi: 10.1126/science.331.6015.272URLpmid: 21252321 |
| [57] | Morey R. D., Hoekstra R., Rouder J. N., Lee M. D., & Wagenmakers E.-J . ( 2016). The fallacy of placing confidence in confidence intervals. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 23( 1), 103-123. doi: 10.3758/s13423-015-0947-8URLpmid: 26450628 |
| [58] | Morey,R. D., & Rouder, J. N . ( 2011). Bayes factor approaches for testing interval null hypotheses. Psychological Methods, 16( 4), 406-419. doi: 10.1037/a0024377URLpmid: 21787084 |
| [59] | Mulder J., Klugkist I., van de Schoot R., Meeus W. H. J., Selfhout M., & Hoijtink H . ( 2009). Bayesian model selection of informative hypotheses for repeated measurements. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 53( 6), 530-546. doi: 10.1016/j.jmp.2009.09.003URL |
| [60] | Munafò M. R., Nosek B. A., Bishop D. V. M., Button K. S., Chambers C. D., Percie du Sert N., … Ioannidis, J. P. A.(2017). A manifesto for reproducible science. Nature Human Behaviour, 1( 1), 0021. doi: 10.1038/s41562-016-0021URL |
| [61] | Nosek B. A., Alter G., Banks G. C., Borsboom D., Bowman S. D., Breckler S. J., … Yarkoni T . ( 2015). Promoting an open research culture. Science, 348( 6242), 1422-1425. doi: 10.1126/science.aab2374URL |
| [62] | Nosek B. A., Spies J. R., & Motyl M . ( 2012). Scientific Utopia: II. Restructuring incentives and practices to promote truth over publishability. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 7( 6), 615-631. doi: 10.1177/1745691612459058URL |
| [63] | Open Science Collaboration. ( 2015). Estimating the reproducibility of psychological science. Science, 349(6251), aac4716. |
| [64] | Plummer, M.(2003). JAGS: A program for analysis of Bayesian graphical models using Gibbs sampling. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Distributed Statistical Computing (DSC 2003). |
| [65] | Poldrack R. A., Baker C. I., Durnez J., Gorgolewski K. J., Matthews P. M., Munafò M. R., … Yarkoni T . ( 2017). Scanning the horizon: Towards transparent and reproducible neuroimaging research. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 18( 2), 115-126. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.167URLpmid: 28053326 |
| [66] | Poldrack,R. A., & Gorgolewski, K. J . ( 2017). OpenfMRI: Open sharing of task fMRI data. NeuroImage, 144, 259-261. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.05.073URLpmid: 4669234 |
| [67] | Rouder,J. N . ( 2014). Optional stopping: No problem for Bayesians. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 21( 2), 301-308. doi: 10.3758/s13423-014-0595-4URLpmid: 24659049 |
| [68] | Rouder,J. N., & Morey, R. D . ( 2011). A Bayes factor meta-analysis of Bem’s ESP claim. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 18( 4), 682-689. doi: 10.3758/s13423-011-0088-7URLpmid: 21573926 |
| [69] | Rouder J. N., Morey R. D., Speckman P. L., & Province J. M . ( 2012). Default Bayes factors for ANOVA designs. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 56( 5), 356-374. doi: 10.1016/j.jmp.2012.08.001URL |
| [70] | Rouder J. N., Morey R. D., Verhagen J., Swagman A. R., & Wagenmakers E.-J . ( 2017). Bayesian analysis of factorial designs. Psychological Methods, 22( 2), 304-321. doi: 10.1037/met0000057URLpmid: 27280448 |
| [71] | Rouder J. N., Speckman P. L., Sun D. C., Morey R. D., & Iverson G . ( 2009). Bayesian t tests for accepting and rejecting the null hypothesis. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 16( 2), 225-237. |
| [72] | Salsburg, D.(2001). The lady tasting tea: How statistics revolutionized science in the twentieth century. New York, NY: W. H. Freeman and Company. |
| [73] | Salvatier J., Wiecki T. V., & Fonnesbeck C . ( 2016). Probabilistic programming in Python using PyMC3. Peer J Computer Science, 2, e55. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.55URL |
| [74] | Schervish,M. J . ( 1996). P values: What they are and what they are not. The American Statistician, 50( 3), 203-206. doi: 10.2307/2684655URL |
| [75] | Schlaifer, R.,& Raiffa, H.(1961). Applied statistical decision theory. Boston: Harvard University. |
| [76] | Sch?nbrodt F. D., Wagenmakers E.-J., Zehetleitner M., & Perugini M . ( 2017). Sequential hypothesis testing with Bayes factors: Efficiently testing mean differences. Psychological Methods, 22( 2), 322-339. doi: 10.1037/met0000061URLpmid: 26651986 |
| [77] | Scott,J. G., & Berger, J. O . ( 2006). An exploration of aspects of Bayesian multiple testing. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 136( 7), 2144-2162. doi: 10.1016/j.jspi.2005.08.031URL |
| [78] | Scott,J. G., & Berger, J. O . ( 2010). Bayes and empirical- Bayes multiplicity adjustment in the variable-selection problem. The Annals of Statististics, 38( 5), 2587-2619. doi: 10.1214/10-AOS792URL |
| [79] | Sellke T., Bayarri M. J., & Berger J. O . ( 2001). Calibration of ρ values for testing precise null hypotheses. The American Statistician, 55( 1), 62-71. doi: 10.1198/000313001300339950URL |
| [80] | Stephens, M.,& Balding, D. J . ( 2009). Bayesian statistical methods for genetic association studies. Nature Reviews Genetics, 10( 10), 681-690. doi: 10.1038/nrg2615URLpmid: 1976315119763151 |
| [81] | Stulp G., Buunk A. P., Verhulst S., & Pollet T. V . ( 2013). Tall claims? Sense and nonsense about the importance of height of US presidents. The Leadership Quarterly, 24( 1), 159-171. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2012.09.002URL |
| [82] | Topolinski, S.,& Sparenberg, P.(2012). Turning the hands of time. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 3( 3), 308-314. doi: 10.1177/1948550611419266URL |
| [83] | van de Schoot R., Winter S., Ryan O., Zondervan- Zwijnenburg M., & Depaoli S . ( 2017). A systematic review of Bayesian papers in psychology: The last 25 years. Psychological Methods, 22( 2), 217-239. doi: 10.1037/met0000100URLpmid: 28594224 |
| [84] | Vanpaemel, W.(2010). Prior sensitivity in theory testing: An apologia for the Bayes factor. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 54( 6), 491-498. doi: 10.1016/j.jmp.2010.07.003URL |
| [85] | Wagenmakers, E.-J.(2007). A practical solution to the pervasive problems of p values. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 14( 5), 779-804. doi: 10.3758/BF03194105URLpmid: 18087943 |
| [86] | Wagenmakers E.-J., Beek T. F., Rotteveel M., Gierholz A., Matzke D., Steingroever H., … Pinto Y . ( 2015). Turning the hands of time again: A purely confirmatory replication study and a Bayesian analysis. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 494. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00494URLpmid: 25964771 |
| [87] | Wagenmakers E.-J., Lodewyckx T., Kuriyal H., & Grasman R . ( 2010). Bayesian hypothesis testing for psychologists: A tutorial on the Savage-Dickey method. Cognitive Psychology, 60( 3), 158-189. doi: 10.1016/j.cogpsych.2009.12.001URLpmid: 20064637 |
| [88] | Wagenmakers E.-J., Love J., Marsman M., Jamil T., Ly A., Verhagen J., … van Doorn J . ( 2017). Bayesian inference for psychology. Part II: Example applications with JASP. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 1-19. doi: 10.3758/s13423-017-1323-7URLpmid: 28685272 |
| [89] | Wagenmakers E.-J., Marsman M., Jamil T., Ly A., Verhagen J., Love J., … Morey R. D . ( 2017). Bayesian inference for psychology. Part I: Theoretical advantages and practical ramifications. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 1-23. doi: 10.3758/s13423-017-1343-3URL |
| [90] | Wagenmakers E.-J., Verhagen J., Ly A., Matzke D., Steingroever H., Rouder J. N., & Morey R. D . ( 2017). The need for Bayesian hypothesis testing in psychological science. In S. O. Lilienfeld & I. D. Waldman (Eds.), Psychological science under scrutiny(pp. 123-138). Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. doi: 10.1002/9781119095910.ch8URL |
| [91] | Wagenmakers E.-J., Wetzels R., Borsboom D., & van der Maas, H. L. J.(2011). Why psychologists must change the way they analyze their data: The case of psi: Comment on Bem (2011). Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 100( 3), 426-432. doi: 10.1037/a0022790URLpmid: 212809651 |
| [92] | Wagenmakers E.-J., Wetzels R., Borsboom D., van der Maas, H. L. J., & Kievit R. A . ( 2012). An agenda for purely confirmatory research. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 7( 6), 632-638. doi: 10.1177/1745691612463078URLpmid: 26168122 |
| [93] | Wasserstein,R. L., & Lazar, N. A . ( 2016). The ASA's statement on p-values: Context, process, and purpose. The American Statistician, 70( 2), 129-133. |
| [94] | Wetzels R., Matzke D., Lee M. D., Rouder J. N., Iverson G. J., & Wagenmakers E.-J . ( 2011). Statistical evidence in experimental psychology: An empirical comparison ssing 855 t tests. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 6( 3), 291-298. doi: 10.1177/1745691611406923URL |
| [95] | Zhu J., Chen J. F., Hu W. B., & Zhang B . ( 2017). Big Learning with Bayesian methods. National Science Review, 4( 4), 627-651. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwx044URL |
| [96] | Ziliak S. T., & McCloskey, D. N.( 2008) . The cult of statistical significance. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. |
| [97] | Zuo X.-N., Anderson J. S., Bellec P., Birn R. M., Biswal B. B., Blautzik J., … Milham M. P . ( 2014). An open science resource for establishing reliability and reproducibility in functional connectomics. Nature Scientific Data, 1, 140049. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2014.49URLpmid: 25977800 |
| [98] | Zuo, X.-N.,&Xing, X.-X.(2014). Test-retest reliabilities of resting-state FMRI measurements in human brain functional connectomics: A systems neuroscience perspective. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 45, 100-118. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.05.009URLpmid: 24875392 |
相关文章 5
| [1] | 王珺, 宋琼雅, 许岳培, 贾彬彬, 陆春雷, 陈曦, 戴紫旭, 黄之玥, 李振江, 林景希, 罗婉莹, 施赛男, 张莹莹, 臧玉峰, 左西年, 胡传鹏. 解读不显著结果:基于500个实证研究的量化分析[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 381-393. |
| [2] | 王阳, 温忠麟, 付媛姝. 等效性检验——结构方程模型评价和测量不变性分析的新视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(11): 1961-1969. |
| [3] | 仲晓波. 关于假设检验的争议:问题的澄清与解决[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(10): 1670-1676. |
| [4] | 李富洪;曹云飞;曹碧华;蔡雪丽;李红. 假设形成与检验的神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2012, 20(2): 191-196. |
| [5] | Lyndsey Nickels. 认知损伤的评估[J]. 心理科学进展, 2008, 16(1): 10-13. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4333
