 ,*,2)
,*,2)HIGH-PERFORMANCE DILATED POLYHEDRAL BASED DEM FOR ICE LOADS ON SHIP AND OFFSHORE PLATFORM STRUCTURES1)
Liu Lu*, Yin Zhenyu?, Ji Shunying ,*,2)
,*,2)通讯作者: 2) 季顺迎,教授,主要研究方向:计算颗粒力学及其工程应用. E-mail:jisy@dlut.edu.cn
收稿日期:2019-08-31接受日期:2019-10-8网络出版日期:2019-10-08
| 基金资助: |
Received:2019-08-31Accepted:2019-10-8Online:2019-10-08
作者简介 About authors

摘要
船舶与海洋平台结构的冰载荷是寒区海洋工程结构物设计中的关键参数,而离散元方法是有效计算结构冰载荷的重要手段. 本文采用基于闵可夫斯基和原理的扩展多面体离散元方法模拟船舶与海洋平台结构的相互作用过程. 其中,构造扩展多面体的近似包络函数并建立了基于优化模型的快速接触搜索算法;考虑单元间粘结作用的刚度软化过程建标识码元间的粘结-破碎模型. 同时,发展了 CPU-GPU 协同异构环境下的高性能并行算法. 为分析海冰与海洋结构作用中的冰载荷,采用ISO标准验证了扩展多面体离散元分析结构冰载荷的准确性. 采用离散元方法计算了船舶结构的冰载荷,研究了船舶结构表明的线载荷分布特点,并采用船舶结构冰阻力经验公式验证了计算结果的合理性. 采用离散元方法计算了平整冰区与多桩腿平台结构的相互作用,分析各桩腿上的冰载荷特点. 针对碎冰区的海冰管理过程,采用离散元方法分析了船舶结构绕行过程中的船舶和海洋平台结构冰载荷. 本文方法可有效应用于海洋结构冰载荷分析,能为极地船舶与海洋平台结构的设计和安全运行提供科学的分析手段.
关键词:
Abstract
The ice loads on ship and offshore platform structures is the key factor in structure design for cold regions. The discrete element method (DEM) is an important approach to determine the ice load on structures. According to the Minkowski sum theory, the dilated polyhedra based DEM is employed to simulate the interaction between sea ice and ship and offshore platform structures in this paper. In the dilated polyhedra based DEM, the enveloped function of the dilated polyhedron is generated to establish the fast contact detection algorithm based on the optimization model. Meanwhile, the bond-break model between elements is established by considering the stiffness softening process between bonded elements. Accordingly, the high-performance algorithm based on CPU-GPU cooperative-heterogeneous environment is developed. The ISO standard is employed to validate the ice load determined by the dilated polyhedra based DEM for better engineering applications of the interaction between sea ice and marine structures. The ice load on ship hull is calculated by the proposed method while the line load distribution on ship hull is studied. The ice resistance of ship hull is compared with the result by Lindqvist empirical formula to validate the accuracy of DEM simulations. The interaction between level ice and multi-leg platform is simulated while the ice load on each leg is analyzed. For the ice management in broken ice regions, the ice load on ship and offshore structures is simulated when the ship navigates around the offshore platform in circle. The proposed method can be effectively applied in the analysis of ice load on marine structures, and can provide a scientific approach for the design and safety operation of ship and offshore structures.
Keywords:
PDF (36854KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
刘璐, 尹振宇, 季顺迎. 船舶与海洋平台结构冰载荷的高性能扩展多面体离散元方法1). 力学学报[J], 2019, 51(6): 1720-1739 DOI:10.6052/0459-1879-19-250
Liu Lu, Yin Zhenyu, Ji Shunying.
引 言
随着两极地区航运和油气资源开发等事业的不断发展,冰区船舶和海洋平台结构的抗冰设计和安全运行等问题亟待解决. 其标识码载荷是船舶与海洋平台结构在冰区安全运行的关键环境载荷,船舶结构的总体冰阻力和局部冰压力分布是评估船舶结构破冰标识码结构安全监测的重要衡量指标[1],海洋平台结构的冰载荷是研究结构抗冰性能和冰激疲劳分析的主要参数[2]. 在结构冰载荷的数值分析方法中,离散元方法能够对海冰与结构的相互作用、海冰破碎和破碎海冰间的接触过程等进行较为全标识码拟,是合理分析冰载荷的重要手段[3].海冰与船舶结构作用过程中,由于船体不同部位几何结构的差异,海冰会呈现弯曲、挤压、屈曲、剪切等不同的破坏模式. 在海冰和船艏的作用过程中, 弯曲破坏产生的冰载荷最为显著[4]. 该过程受结构形状和海冰参数的影响,海冰会发生径向或环向断裂破坏. 当海冰作用于船体舯部和船艏两侧时,由于该部分结构的垂向倾角很小,海冰呈挤压破坏状态. 此时海冰在船体表面的局部冰压力分布成为船体结构安全的关键因素[5-6]. 在海冰与海洋平台结构的相互作用研究中,主要关注结构的最大静冰力和交变动冰力[7-8]. 根据结构的几何形状,海冰与直立结构和坡面结构作用时的破坏模式和冰载荷形式区别较大. 海冰与直立结构作用主要发生挤压破碎,冰载荷可能表现为较高频率的持续性冰力[9];海冰与坡面结构作用时主标识码弯曲破坏,冰载荷通常表现为规律性的交变冰力[10].
离散元方法自 20 世纪 80 年代开始被用于海冰碰撞和漂移等研究中[11]. 近年来,基于离散元方法的海冰与船体和标识码台结构间的相互作用研究取得了较大进展. 海冰离散元方法的计算单元可采用球体[12]、圆盘[13]、多面体[14-15]和扩展多面体[16]等不同形态. 其中,球体单元通过平行粘结模型进行粘结并考虑单元之间的粘结失效,使离散的球体单元粘结为平整冰排,在海流的作用下与海标识码发生碰撞进而破碎,具有模型简单和计算效率高的特点[17]. 针对球体单元的尺寸效应带来参数不确定的问题,可通过离散元模拟海冰的单轴压缩和三点弯曲试验并结合渤海海冰的强度试验结标识码用无量纲化的单元尺寸参数分析并总结试样强度的变化规律,从而能够建立标准化的海冰宏微观强度关系并用于海冰的标识码拟中[18-19]. 在宏观尺度上,球体单元需要大量的单元粘结形成较大的冰区,而多面体单元可用较少的单元数模拟较大区域的海冰,具标识码的优势[20-21]. 多面体离散元模型主要模拟平整冰的破碎、重叠和堆积过程,可合理地描述冰块的几何形态. 针对碎冰区冰块形态呈多边形且随机分布的特点,还可采用 Voronoi 切割算法生成具有不同冰块尺寸、几何形态和密集度标识码分布[22]. 目前,采用块体离散元方法对堆积冰的受压形变过程、海冰与船体结构的相互作用过程进行了数值模拟[23-24]. 但多面体的接触检测等面临计算效率低的问题,合理构建其粘结-破碎模型也是基于多面体的海冰离散元方标识码关键问题[25-28].
最近,基于扩展多面体的快速搜索算法标识码-破碎模型发展较快,可应用于海冰与结构相互作用过程的分析中[29]. 基于闵标识码基和原理可将基本的几何单元与球体单元进行空间叠加从而构成扩展单元. 采用多面体和球体的闵可夫斯基和可构造扩展多面体单元[30]. 据此可发展基于扩展多面体标识码-破碎模型[31-32]和 DEM-LBM (Lattice Boltzmann method) 的流固耦合模型[33],并用于脆性材料水力压裂过程的模拟分析中. 由于扩展多面体单元将尖锐的角点和棱边转换为光滑的球面和圆柱面,在接触判断中避免了多面体之间难以通过几何元素直接判标识码的缺点,提高了接触搜索的效率和稳定性;还可采用精确化的Hertz接触力模型计算接触力,提高接触力计算的准确性[16,34]. 另外,根据类似的“扩展单元”方法,采用多面体扩展函数构造与扩展多面体类似的几何形状,可通过扩展函数表达式之间的优标识码求解单元之间的接触搜索问题[35-36]. 通过优化模型解决接触问题可有效避免几何元素之间复杂的几何判断,也可避免几何方法中产生多个接触点引起的物理失真,标识码计算中具有较高的执行效率[37-38]. 在扩展多面体单元的粘结-破碎模型中,考虑粘结作用的刚度软化过程可避免粘结失效时突然的能量释放,标识码高海冰断裂过程模 拟的平稳 性[29].
本文基于闵可夫斯基和原理构造扩展多面体单元,发展扩展多面体间的快速搜索算法和粘结-破碎模型,标识码CPU-GPU协同方式进 行并行计算. 采用该方法计算海冰与船舶和海洋平台结构的相互作用过程,通过ISO标准公式和现场监测数据验证分析结构冰载荷计算的合理标识码而采用将该方法应用于具体的工程分析中.
1 扩展多面体离散元方法及高性能计算
采用二维的 Voronoi 切割算法将二维平面划分为若干多边形,将多边形在垂直纸面的方向上进行拉伸即形成具有一标识码的多面体,根据闵可夫斯基和原理将该多面体和球体结合即可构造扩展多面体形态的海冰单元.1.1 海冰的扩展多面体构造
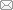
假设空间中两个几何体代表的点集 $A$ 和 $B$,且集合 $A$ 和 $B$ 为几何封闭形态,那么集合 $A$ 和 $B$ 的闵可夫标识码可定义为式中,$x$ 和 $y$ 分别是 $A$ 和 $B$ 中的几何点. 可知 $A \oplus B$ 是 $A$ 和 $B$ 中所有点的空间矢量和. 闵可夫斯基和的几何求取过程可以概述为点集 $B$ 扫略在点集 $A$ 的外表面上,形成标识码何形状即为 $A$ 和 $B$ 的闵可夫斯基和. 根据闵可夫斯基和的定义,采用球体和任意多面体可构建扩展多面体[29]. 如图1 所示. 其中,球体半径称为扩展半径,任意多面体称为基本多面体.
图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1基于闵可夫斯基和的扩展多面体单元
Fig.1Dilated polyhedral element based on the Minkowski sum
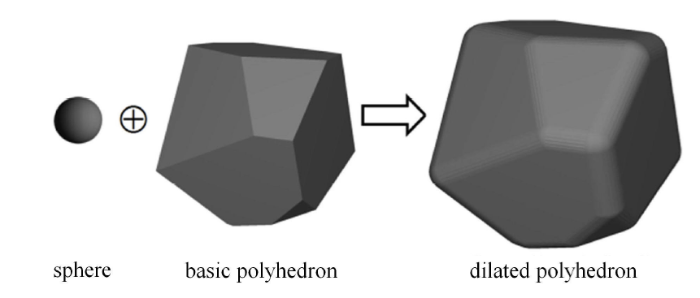
Voronoi 切割算法根据随机的空间点将空间划分为随机的任意多面体或多边形,可合理表述自然条件下海冰的标识码形状规律[39]. 这里采用二维 Voronoi 切割算法,将一定范围的二维平面划分为若干任意多边形,如图2(a) 所示. 其中,多边形的形状可根据随机点的分布进行控制[40]. 然后将每个多边形在垂直纸面方向进行拉伸形成多面体,根据闵可夫斯基和原理则可生成扩展多面体形态的海冰单元,如图2(b) 所示. 其中,$h$ 为海冰厚度. 若$r$为扩展半径,则 $t= h - 2r$. 对于碎冰初始场的生成,则可通过实际海冰面积和冰区范围控制碎冰密集度[22];而对于平整冰的生成,则可直接划分网格.
图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2Voronoi 切割算法生成扩展多面体形态的海冰单元
Fig.2Dilated polyhedron shaped sea ice element based on Voronoi tessellation algorithm
1.2 扩展多面体离散元的接触模型
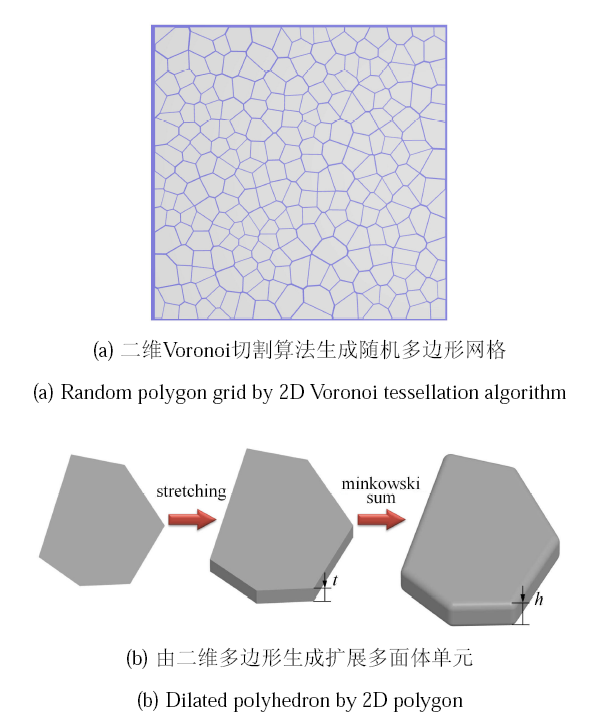
在扩展多面体单元的接触模型中,可构造扩展多面体的近似包络函数,从而采用优化模型建立单元间的接触搜索算法. 通 过二阶多面体扩展函数与球面函数的加权求和形式可构造具有多面体特征的光滑函数[36],其归一化形式可写作式中,$k$ 为光滑度系数;$R$ 为球面函数的半径.
图3为边长为 $a$ 的正四面体和球体函数组合构成的函数在不同加权系数下的几何形态,其中扩展半径 $r= 0.1a$,球 体半径 $R = 1.5a$. 可以看出,$k$ 越小其形态越接近于扩展多面体的形态,当 $k = 0.001$ 时的函数几何形态与扩展多面体形态具有高度的相似性. 实际上,尽管其形态与扩展多面体尚存在一定的差异,仍可采用该函数作为扩展多面体的近似“包络”函数[41].
图3
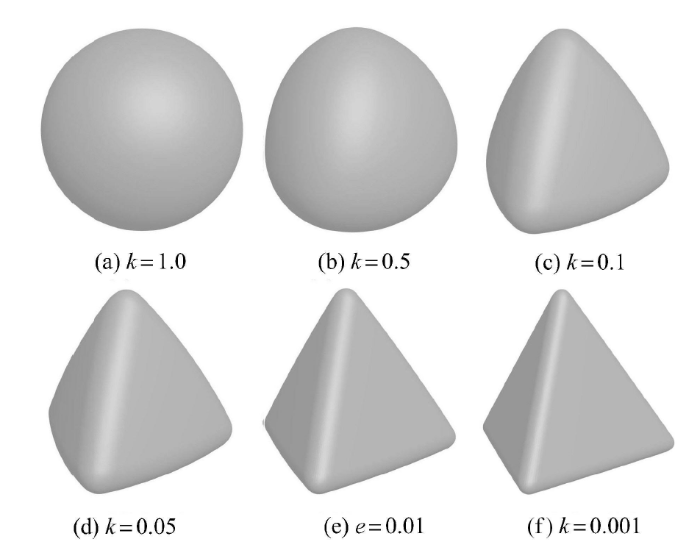 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3扩展多面体的包络函数随参数$k$的变化
Fig.3The envelope function of the dilated polyhedron under different parameter $k$
扩展多面体的包络函数满足“势能颗粒 (potential particle)” 的定义[35],因此可建立两个函数之间的优化模型用于单元接触中心点的搜索,该优化模型可定义为[38]
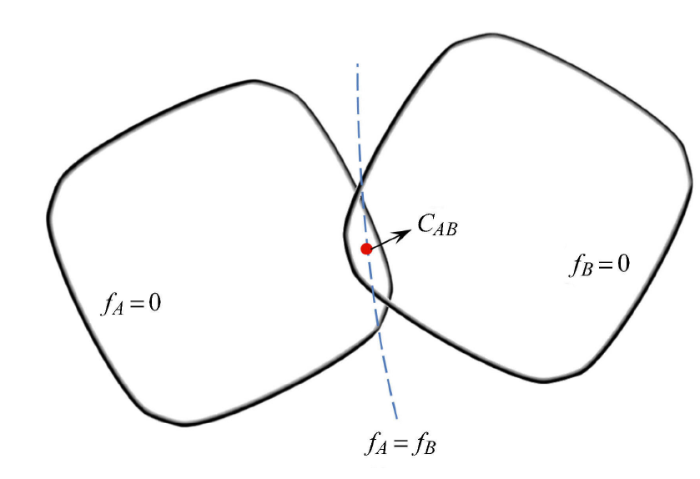
式中,$f_{A}$ 和 $f_{B}$ 对应两个单元的包络函数. 如图4 所示,两个单元接触时满足上式的解 $C_{AB} $ 同时位于两个包 络函数内部,其可被视为接触重叠区域的接触中心点.
图4
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4包络函数之间的接触优化模型
Fig.4The optimization model between envelope functions
根据拉格朗日乘子法构造拉格朗日函数如下
由 $\nabla L\left( {{\pmb X},\lambda } \right) = 0$ 可将该优化问题变为四元非线性方程组,可采用牛顿迭代法进行求解该方程组. 在牛顿迭代法的初始点选取标识码先在迭代中通过调整光滑度系数 $k$ 由 1.0 渐变至较小值,从而使初始点逐渐逼近最终解附近,从而提高迭代的收敛效率[41]. 另外,还可在迭代中设置稳定性系数,提高迭代的稳定性[42]. 求得式 (3) 表示的优化模型结果 ${\pmb C}_{AB}$ 之后,由该点出发迭代搜索基本多面体上距离最近的点来确定两个颗粒上的接触点,进而可确定接触重叠量和接触法向. 由于该计算并没有复杂的判断过程,且接触中心点 ${\pmb C}_{AB}$ 一般距这两个最近点十分接近,所以该迭代过程并不会耗费较多计算资源[41].
为简化接触力计算,采用非线性的接触力模型简化计算扩展多面体之间的接触力[43-44]. 其中,法向接触力可表示为法 向弹性力和法向黏滞力之和,即可得
式中,$k_{\rm n} $ 为法向接触刚度,$k_{\rm n} = 4E^\ast \sqrt {R^\ast } / 3$,$E^\ast $ 和 $R^\ast $ 是等效的弹性模量等效颗粒半径 [45];$\delta _{\rm n} $ 是两颗粒的法向接触重叠量;${\delta }”$ 是法向相对速度;$c_{\rm n} $ 为法向阻尼系数
式中,$m_{AB}$ 为等效质量[45], $\zeta _{\rm n} $ 是无量纲阻尼系数
式中,$e$ 是回弹系数,可参考不同碰撞速度下颗粒回弹系数的计算[46].
切向接触力与切向接触重叠量和摩擦力有关,一般切向力最大不超过摩擦力. 这里可采用简化的方式避免与摩擦力的频繁比较和判断[44]. 其中,切向弹性力$F_{\rm t}^{\rm e} $可写作
式中,$\mu $ 是摩擦系数;$\delta _{\rm t} $ 是切向重叠量,一般根据相对切向速度并逐步叠加的方法累计计算切向重叠量;$\delta _{\rm t}^{\max} $ 是最大切向重叠量,其主要由摩擦系数和法向重叠量决定,且 $\delta _{\rm t}^{\max} = \mu \delta _{\rm n} \left( {2 - \nu } \right) / \left( {2 - 2\nu } \right)$,$\nu$ 为泊松比. 扩展多面体单元间的切向黏滞力 $F_{\rm t}^{\rm v} $ 可写作
式中,${\delta }”$ 是切向相对速度;$c_{\rm t} $是切向阻尼系数,这里取 $c_{\rm t} = c_{\rm n} / \left( {2\left( {1 + \nu } \right)} \right)$[47]. 该切向力计算方法避免了每个时间步中与摩擦力的大小对比,有效地提高了计算效率.
由于本文的接触搜索只有一个接触点,即互相接触的两个单元只有一个接触力,故以上接触力模型无法消除单元绕标识码向的非物理转动. 为此,这里在单元的转动方程中引入绕接触法向的滚动摩阻力矩 ${\pmb M}_{\rm r}$[43]
式中,$\mu _{\rm r} $ 是滚动摩擦系数;${\pmb \omega }_{ AB} $ 是相对角速度.
1.3 扩展多面体离散元的粘结-破碎模型
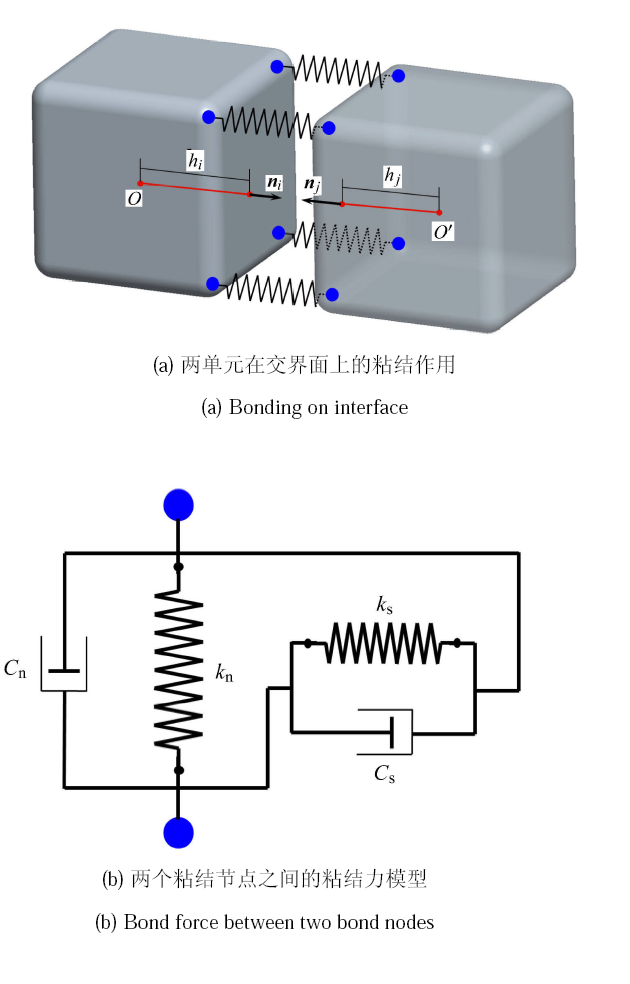
1.3.1 扩展多面体单元的粘结模型借鉴刚体有限元的基本思想,即单元间的刚度作用建立在交界面上[48]. 因此,本文在两个互相粘结的单元间交界标识码点上设定若干积分点,将该积分点对应在两个单元上的点视为粘结节点,并称该交界面对应在两个单元上的面为粘结面,如图5(a) 所示. 通过施加一定的刚度和阻尼,即可在互相粘结的节点上计算类似的法向和切向应变[49]. 在本文的相关计算中,粘结节点取为交界面的顶点. 其中,法向应变 $\varepsilon _{\rm n}$ 可写作
图5
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5粘结模型的描述简图
Fig.5Sketch of bond model
式中,${\pmb d}$ 是两个粘结节点之间的距离向量;${\pmb n}$ 为交界面的法向,这里取为两个单元粘结面的外法向之差,即 ${\pmb n} ={\rm unit} ({\pmb n}_{i}- {\pmb n}_{j})$;$C_{ij}$ 为两个粘结单元之间的特征长度,与刚体有限元中的定义相同,标识码个粘结面到各自单元质心的距离之和,可写作
由于粘结力会传递到单元质心上进行合力计算,因此这里切向应变只考虑与法向垂直的一个方向应变标识码向为 ${\pmb t} ={\rm unit} ({\pmb d} - ({\pmb d} \cdot {\pmb n} ) {\pmb n} )$,切向应变可写作
根据图5(b) 所示的粘结力模型,采用三维条件下的弹性矩阵,两个粘结单元在交界面上的弹性应力 ${\pmb \sigma }^{\rm e}$ 可写作
式中,$E$ 为材料弹性模量;$\nu $ 为材料泊松比;${\pmb \sigma }^{\rm e}$ 考虑法向和切向的应力,${\pmb \sigma }^{\rm e} = \{\sigma ,\tau \}^{\rm T}$;${\pmb \varepsilon }$ 考虑粘结节点之间的法向和切向应变, 即 ${\pmb \varepsilon } = \{\varepsilon _{\rm n}, \varepsilon _{\rm t} \}^{\rm T}$.
在粘结力模型中,考虑法向和切向阻尼系数 $C_{\rm n} $ 和 $C_{\rm s} $ 表示的黏滞作用. 该阻尼效应可代表真实的物理阻尼并消耗动能,从而提高模拟的稳定性. 一般情况下,通过与刚度相关的常系数 $\beta $ 计算阻尼系数. 因此,由黏滞作用产生的应力 ${\pmb \sigma }^{\rm v}$ 可写作
式中,${\pmb \varepsilon }”$是应变率,且${\pmb \varepsilon }''=\{ \dot \varepsilon_n,\dot \varepsilon_t\}^{\rm T}$. 两个粘结节点之间的粘结力可写作
式中,$A$ 是交界面面积;$n$ 是一个粘结面上的粘结节点个数. 通过上式计算单元受到的粘结力,将其转换到单元质心上,并结合接触力等其他受力,即可得到每个单元质心受到的合力情况.
可以看出,直接在整体坐标系下将节点间的粘结力传递到单元质心上,每个单元的运动可直接在单元的质心上进行求解. 因标识码方式可高效地融入离散元方法中并形成算法和数据结构高度统一的数值方法.
1.3.2 扩展多面体单元间的粘结失效模型
在球体单元常用的平行粘结模型中,大多采用拉剪分区的方式判断粘结的失效,即法向拉伸和切向剪切分别判断标识码否达到临界值,若其中一个失效则整个粘结作用失效[50]. 显然,该方法对材料的破坏过程描述较为片面,不能合理地评估裂纹附近材料的断裂特性. 因此,本文同时考虑法向拉伸和剪切应力计算临界应力强度,在超过临界应力强度之后引入损伤的概念从而标识码度的软化过程,结合拉伸破坏和剪切破坏并采用混合的断裂能模型计算断裂能,从而根据断裂能确定粘结节点之间的临界变形. 若节点间的变形大于该临界变形,则该粘结失效.
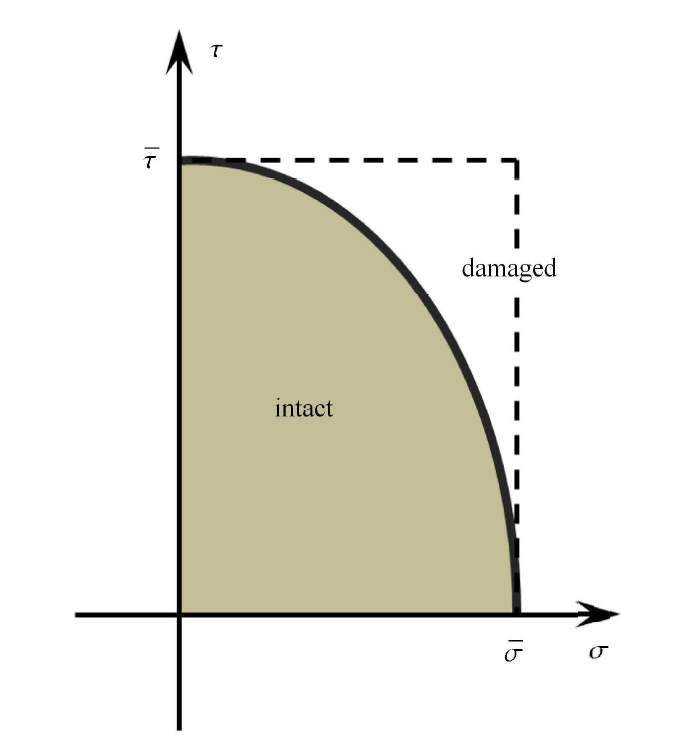
采用考虑拉伸和剪切的强度判定准则决定弹性的临界状态,该准则可写作[51-52]
式中,$\bar{\sigma }”$ 和 ${\tau }”$ 分别是法向和切向粘结强度; $\left\langle \right\rangle $ 表示 Macaulay 括号,且有: $\left\langle x \right\rangle = x$,若 $x \geqslant 0$;$\left\langle x \right\rangle = 0$,若 $x < 0$. 这里假设拉应力为正且压应力为负,那么 $\left\langle \sigma \right\rangle $ 即表示只考虑拉伸应力. 图6 为该强度判定准则在拉伸和剪切应力坐标系中的表示,图中曲线内形状为椭圆,椭圆之外即表示材料损伤. 另外,拉剪分区判断准则即为图中虚线与横纵轴围成的长方形边界,因此本文采用的强度准则比拉剪分区方法“更易”发生损伤或破坏.
图6
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6拉伸和剪切应力结合的强度准则
Fig.6Hybrid failure criterion by tensile and shear strength
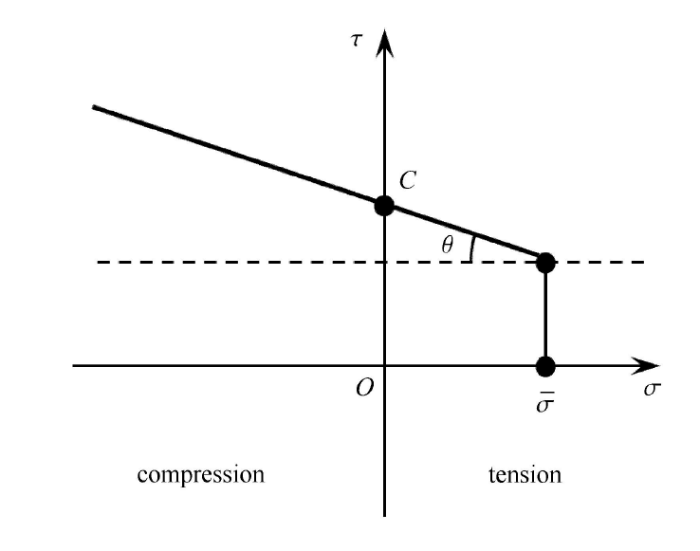
如图7 所示,采用 Mohr-Coulomb 准则计算材料的切向强度,可写作[53]
式中,$C$ 是黏聚力;$\mu _{\rm b} = \tan\theta $ 是内摩擦系数,$\theta $ 是内摩擦角.
图7
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图7Mohr-Coulomb准则确定切向粘结强度
Fig.7Shear bond strength by Mohr- Coulomb criterion
为避免采用拉剪分区方式判断粘结失效,本文的断裂准则通过等效的应力 $\sigma _{\rm m} $ 和变形 $\delta _{\rm m} $ 构造本构关系,可分别写作[54]
式中,$\delta _{\rm n} $ 和 $\delta _{\rm s}\sigma _{\rm m}^0 $ 和对应的极限变形 $\delta _{\rm m}^0 $. 分别是法向和切向变形量. 当粘结节点的应力状态满足式 (17) 时,可视为该节点的应力状态达到了极限强度,那么根据式 (19) 可计算等效的极限强度
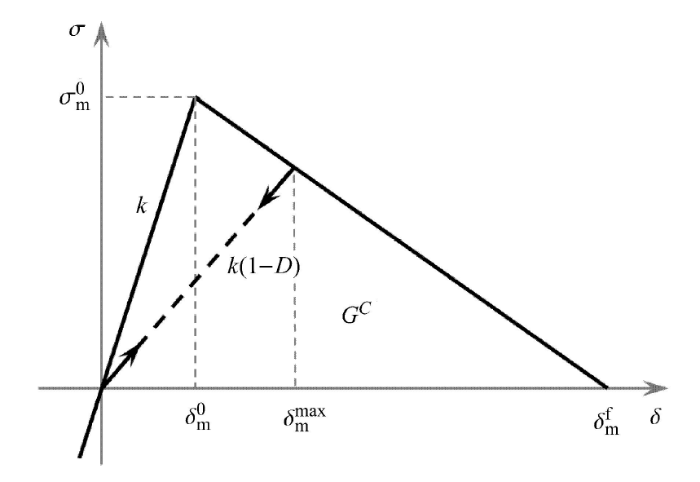
如图8 所示,采用双线性模型定义等效应力和变形之间的关系. 这里引入复合损伤$D$描述极限强度后的刚度软化过程
图8
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图8等效应力和变形确定的双线性本构关系
Fig.8Bi-linear constitutive relationship between equivalent stress and deformation
式中,$\delta _{\rm m}^{\max}$ 是加载历程中粘结节点上发生过的最大变形;$\delta _{\rm m}^{\rm f} $ 是粘结失效时的临界变形,即当 $\delta _{\rm m} > \delta _{\rm m}^{\rm f} $时粘结失效. 那么刚度软化阶段材料的刚度 ${k}”$ 变为
式中,$k$ 为极限强度范围内的材料刚度.
$\delta _{\rm m}^{\rm f} $ 可根据 $\delta _{\rm m}^{\rm f} = 2G^{\rm c} / \sigma _{\rm m}^0 $ 算得,式中 $G^{\rm c}$ 是临界的混合断裂能,采用 Benzeggagh-Kenane 模型计算该混合断裂能[51,55]
式中,$G_{\rm I}^{\rm c} $ 和 $G_{\rm II }^{\rm c} $ 分别对应于拉伸和剪切型裂纹的临界断裂能;$\eta$ 为常系数,对于脆性材料可取 $\eta = 1.75$[56]. 对应当前状态的拉伸和剪切型断裂能 $G_{\rm I} $ 和 $G_{\rm II } $ 可通过拉伸和剪切的变形计算二者的比例,写作
1.4 离散元高性能计算方法
由于单元间的接触搜索是离散元方法中最为耗时的部分,因此常采用相关并行算法以提高计标识码[57]. 为了提高扩展多面体单元接触搜索的计算效率,可通过基于球形包围盒的空间网格法创建邻居列表[58],并采标识码体包围盒的改进分离轴方法更加精确地筛选邻居列表中的“邻居”.1.4.1 球形包围盒的空间网格法
球形包围盒即是可完全包围单元的最小球体. 采用所有单元中最大的球形包围盒直径的 2 倍定义网格的尺寸,则标识码算域划分为由正方形网格构成的空间网格结构. 通过每个单元形心的空间坐标 $\left( {x,y,z} \right)$ 可计算其网格坐标 $\left( {i_x ,i_y ,i_z } \right)$
式中,$x_{\min} $, $y_{\min}$和$z_{\min} $ 分别代表计算域在空间中的最小值;$d_{\rm grid} $ 是网格尺寸;${\rm int}( )$ 是取整运算符. 若计算域的网格个数为 $N_{\rm grid} = N_x \times N_y \times N_z $,可将三维网格坐标对应到一维的网格序列上
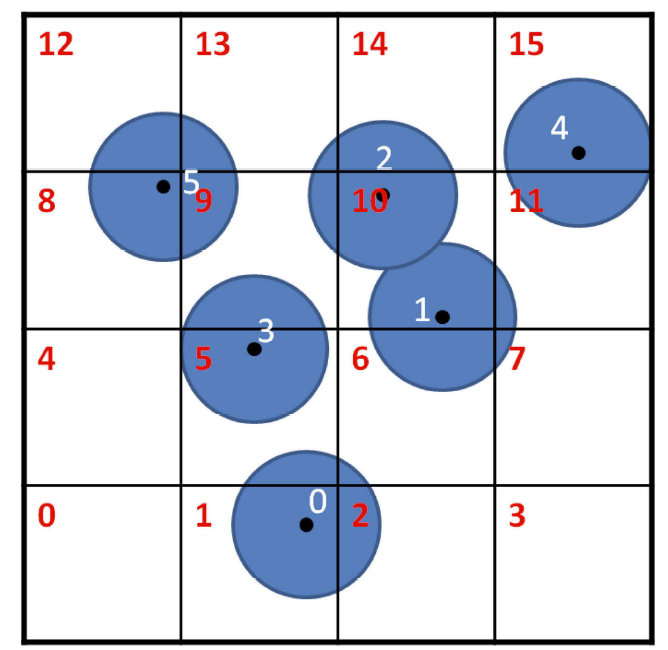
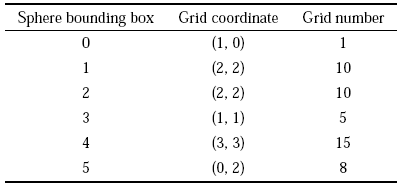
因此,可进一步确定每个单元与网格的一一对应关系. 以二维情况为例,假设球形包围盒在搜索网格中的位置如图9 所示,可算得每个球形包围盒的网格坐标和对应的网格编号,列于表1中. 根据球形包围盒与网格的位置关系,可相应地建立网格与球形包围盒的对应关系,即每个网格内有哪些球形包围盒,标识码立球形包围盒与网格的双向包含关系.
图9
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图9球形包围盒在搜索网格中的位置
Fig.9Sphere bounding boxes in searching grid
Table 1
表1
表1单元的网格坐标和网格编号
Table 1
 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
根据该包含关系,在某个单元的搜索中,只搜索其所在网格的相邻网格中的单元. 在二维空间中是以该单元所在网格为中心的3$\times $3网格范围,对应三维空间中是以该单元所在网格为中心的 3$\times $3$\times $3 的网格范围. 进一步比较球心距离和两球形包围盒半径之和判断单元是否可能接触,从而可建立每个单元的邻居列表.
GPU 对大量类型高度统一且相互无依赖的大规模数据计算具有更高的计算效率[59],而空间网格法标识码任务可分解为大量相互无依赖的数值计算任务,非常适合 GPU 的计算. 因此,这里采用 GPU 并行算法执行球形包围盒的空间网格法计算.
1.4.2 多面体包围盒的改进分离轴方法
对于邻居列表中的邻居单元,可采用多面体的方向包围盒 (oriented bounding box, OBB) 对每个其做更加细致的判断. 对于扩展多面体单元,该包围盒的形状是可包围该扩展多面体的最小多面体. 在 OBB 的接触判断中,最常采用的是分离轴方法 (separate axis algorithm, SAA) [60]. 一般来说,SAA适用于任意形状空间体的接触判断,包括凹和凸的. 为简化描述,二维条件下凹多边形的SAA方法如图10(a) 所示. 多边形$i$的边 ${ A B}$ 外法向为 ${\pmb n}_{ab}$,那么以该法向 ${\pmb n}_{ab}$ 为轴向建立分离轴 $l^{ab}$. 将多边形 $i$ 和待判断的多边形 $j$ 上的所有点投影到分离轴上. 分别计算两个多边形在分离轴上的投影距离 $l_i^{ab} $ 和 $l_j^{ab} $,判断两个投影是否有交叉. 如果存在交叉,则可能接触;若不存在交叉,则不存在接触.
图10
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图10改进的分离轴方法
Fig.10Improved separate axis algorithm
可以看出,分离轴方法需要对两个单元的每个角点、每个面进行计算并综合比较结果才能判断是否接触. 凸多面体具有所有几何 元素都位于其某个面单侧的特点. 因此,这里提出改进的 SAA 方法对凸多面体进行判断. 同样以二维情况为例,如图10(b) 所示. 从 多边形$i$的边 ${AB}$ 上的任意一点到待判断多边形 $j$ 上角点的向量为 ${\pmb e}_k^{ab} $,对于所有多边形 $j$ 的角点,若都能满足以下条件
那么可认为多边形 $i$ 与多边形 $j$ 不存在接触. 在实际判断两个多面体是否接触的计算中,如果在其中一个多面体中存在符合式 (26) 的面,则可判定两个多面标识码触,且不需对后面未做计算的角点和面进行计算,从而节省了计算量. 在最坏情况下,该方法与SAA方法计算量相同;而在最好情况下,该方法的计算效率会远高于 SAA 方法.
改进的 SAA 算法需要反复进行逻辑判断,适合在具有更强逻辑运算能力的 CPU 上进行. 因此,这里采用 CPU 并行算法执行改进的 SAA 算法.
2 扩展多面体离散元方法的验证
考虑扩展多面体单元的浮力和拖曳力[13,22],可将扩展多面体的离散元方法用于海冰与海洋结构的相互作用模拟. 在海冰的离散元模拟中,对于平整冰需要采用粘结-破碎模型计算粘结单元间的作用力,同时采用接触模型计算破碎后海冰单标识码接触力;而对于碎冰则只需要采用接触模型计算接触力. 为验证扩展多面体离散元方法的合理性,采用渤海海冰实测数据和 ISO 标准模型验证数值计算结果.2.1 坡面结构冰载荷
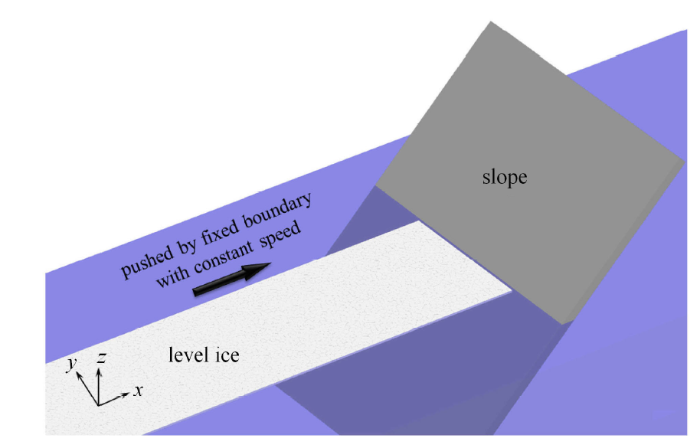
如图11 所示,采用 Voronoi 切割算法生成海冰单元并采用粘结-破碎模型形成平整冰,固定边界在海冰后标识码推动平整冰与坡面结构相互作用,其运动速度与流速相同. 参考海冰数值模拟的相关文献,选取的计算参数列于表2 中[22,61].图11
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图11平整冰与坡面结构的相互作用模拟示意图
Fig.11Sketch of ice-slope interaction
Table 2
表2
表2海冰离散元模拟的主要参数
Table 2
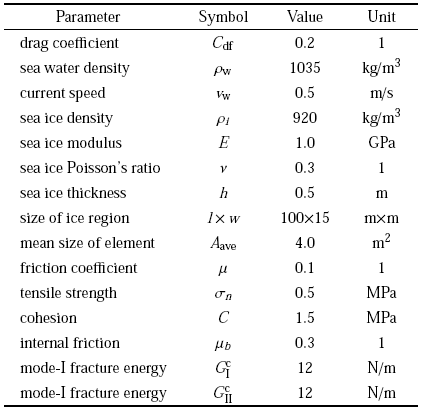 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
平整冰与坡面结构相互作用的模拟结果如图12 所示,其中冰载荷为水平方向即 $x$ 方向的作用力. 可以看出,平整冰在标识码接触后发生明显的弯曲破坏,斜坡上的冰载荷表现位明显上下起伏特性. 分别模拟斜坡角度为 30$^\circ$, 45$^\circ$, 60$^\circ$ 和 75$^\circ$ 时的冰载荷,将第一个冰载荷峰值与 ISO 199006 中的标准公式进行对比[62-63]. ISO 标准公式可写作
图12
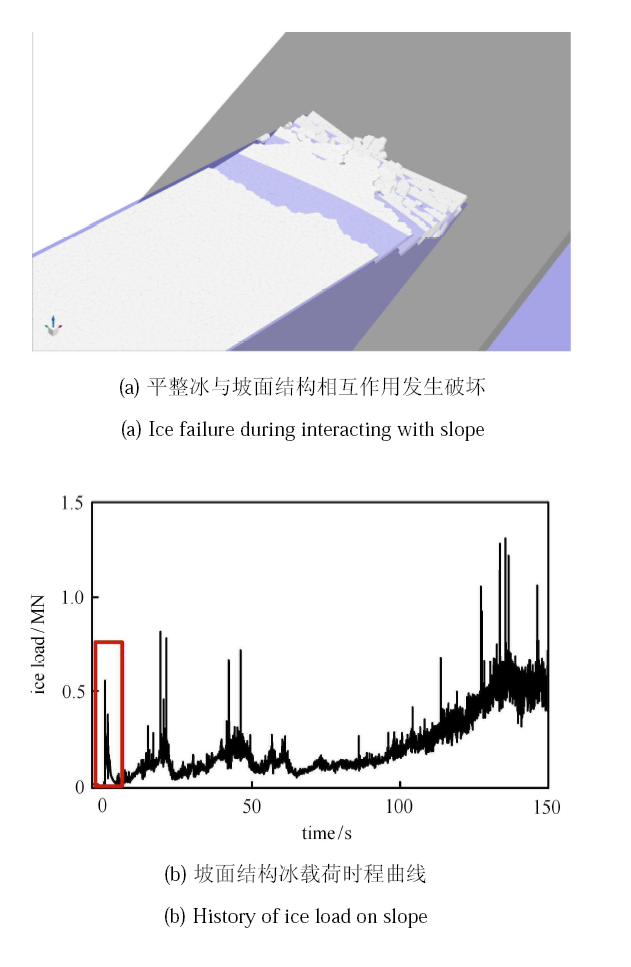 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图12平整冰与坡面结构相互作用的离散元模拟
Fig.12DEM simulation of ice-slope interaction
式中,$\xi $ 是坡面几何参数
$ \xi = \left( {\sin \alpha + \mu \cos \alpha } \right) / \left( {\cos \alpha - \mu \sin \alpha } \right) $
$l_{\rm c} $是特征长度
图13 是离散元模拟和 ISO 标准计算的坡面结构冰载荷对比,图中标出了两者的对比误差. 对比表明离散元模拟结果与 ISO 标准在趋势上基本一致,在数值上也十分接近. 由于 30$^\circ$ 和 45$^\circ$ 时海冰会发生较完整的弯曲破坏,因此模拟冰载荷大小与 ISO 结果误差较小. 当斜坡角度增大到 60$^\circ$ 和 75$^\circ$ 时,海冰的破坏模式不完全为弯曲破坏,故冰载荷的误差相对较大. 一般情况下,ISO 标准定义的是最大值,因此总体上本文的离散元模拟结果符合 ISO 标准,能够说明基于扩展标识码的离散元方法具有较好的合理性.
图13
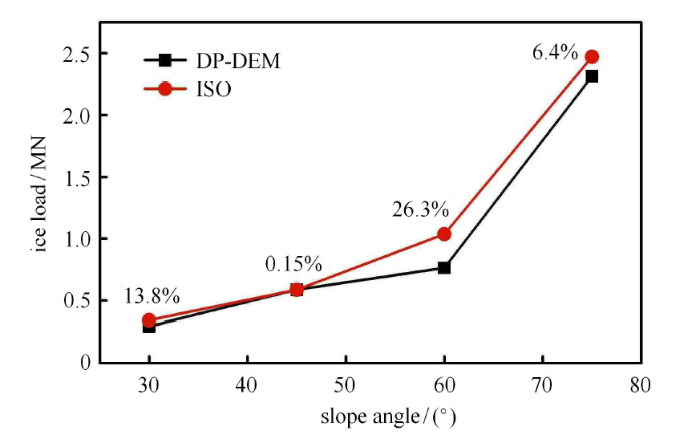 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图13离散元和ISO标准的坡面冰载荷对比
Fig.13Ice load on slope by DEM and ISO standard
2.2 锥体平台结构冰载荷
采用渤海实测锥体结构的冰载荷数据验证海冰离散元的计算结果. 如图14 所示,平整冰的上下和后侧是固定边界,其运动速度标识码相同;锥体结构在水线处的锥径是 3.13m,锥角为 60$^\circ$. 采用表 2 中列出的海冰相关物理力学参数作为离散元模拟的计算参数.图14
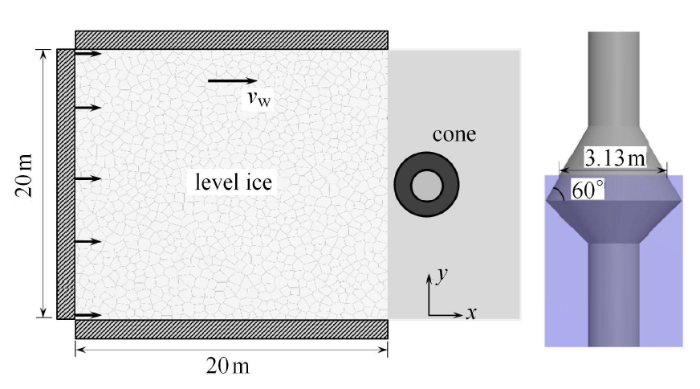 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图14平整冰与锥体结构的相互作用模拟示意图
Fig.14Sketch of ice-cone interaction
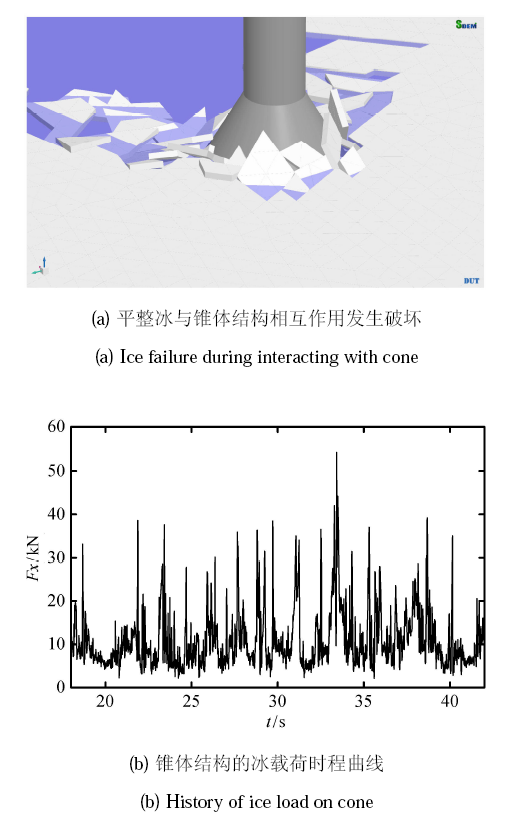
平整冰与锥体结构相互作用的模拟结果如图15 所示. 可以看出,平整冰在与锥体结构接触后发生弯曲破坏,破碎海标识码着锥体向上攀爬,从而在冰载荷时程曲线中形成规律性的峰值载荷. 渤海的现场监测数据中包含大量不同冰厚条件下的冰载荷,因此这里采用不同的冰厚模拟平整冰与锥体结构的相互作标识码过 ISO 标准和现场实测数据分析计算结果的合理性.
图15
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图15平整冰与锥体结构相互作用的离散元模拟
Fig.15DEM simulation of ice-cone interaction
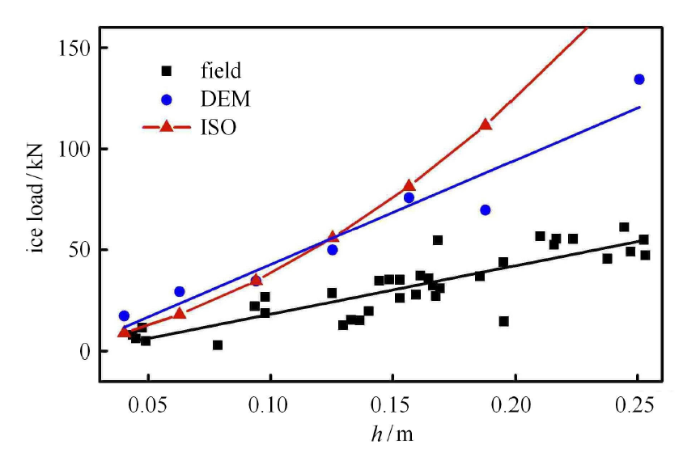
图16 是离散元模拟、ISO 标准和渤海的现场监测数据对比. 可以看出,离散元计算结果在趋势上与 ISO 标准和现场监测结果保持一致,数值上基本处于 ISO 标准和现场监测数据之间. 当 $h < 0.15$m 时,离散元结果与 ISO 标准值更为接近;当 $h > 0.15$m 时,离散元结果明显小于 ISO 标准值. 因此,本文标识码元模拟结果与 ISO 标准值和渤海现场监测标识码具有较好的一致性,充分说明了扩展多面体离标识码法在海冰与海洋结构相互作用模拟中的合 理性.
图16
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图16离散元、ISO 标准和现场实测的锥体结构冰载荷
Fig.16Ice load on cone by DEM, ISO standard and field data
3 船舶结构冰载荷的离散元分析
船舶结构冰载荷是破冰设计和航行安全的重要参数,主要包括结构冰阻力和局部冰载荷分布[64-65]. 采用扩展多面体离散元方法模拟船舶结构在冰区的破冰航行过程,分析船舶结构总体冰阻力和线载荷分布情况.3.1 船舶结构冰载荷分析
采用扩展多面体离散元方法模拟平整冰与船体结构的相互作用. 如图17 所示,船体模型采用雪龙号科考船的结构模型,标识码面划分为三角形单元用于建立结构与海冰单元的接触关系. 相关计算参数参考表 2 中列出的参数,平整冰区域的尺寸为 400m $\times$ 120m,船体运动速度为1.5m/s.图17
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图17雪龙号科学考察船的船体结构模型
Fig.17Ship hull of scientific expedition vessel Xuelong
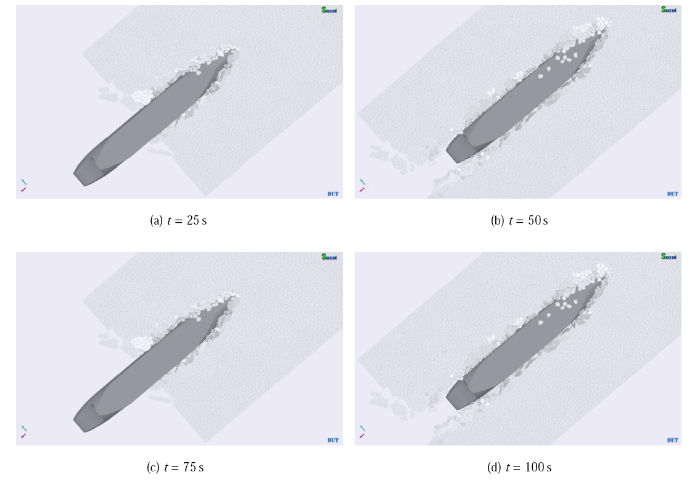
图18 所示是船体结构在平整冰区的破冰过程模拟. 从图中可以看出,平整冰在船艏的作用下发生弯曲破坏,且沿船艏两侧扩展开. 海冰在船体运行方向上发生持续的破碎,冰面上会出现与船宽相当的开阔水道. 同时,破碎后的冰块会浮在开阔水道上,部分碎冰会附着在船底并与船底摩擦,随后沿着船底运动到船艉. 平整冰破碎后会在船艏部区域发生堆叠淤积. 随着船体持续运动,该部分碎冰会与船舯、船艉发生摩擦并被逐渐排开.
图18
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图18船体结构在平整冰区的破冰过程模拟
Fig.18Simulation of ship icebreaking in level ice region
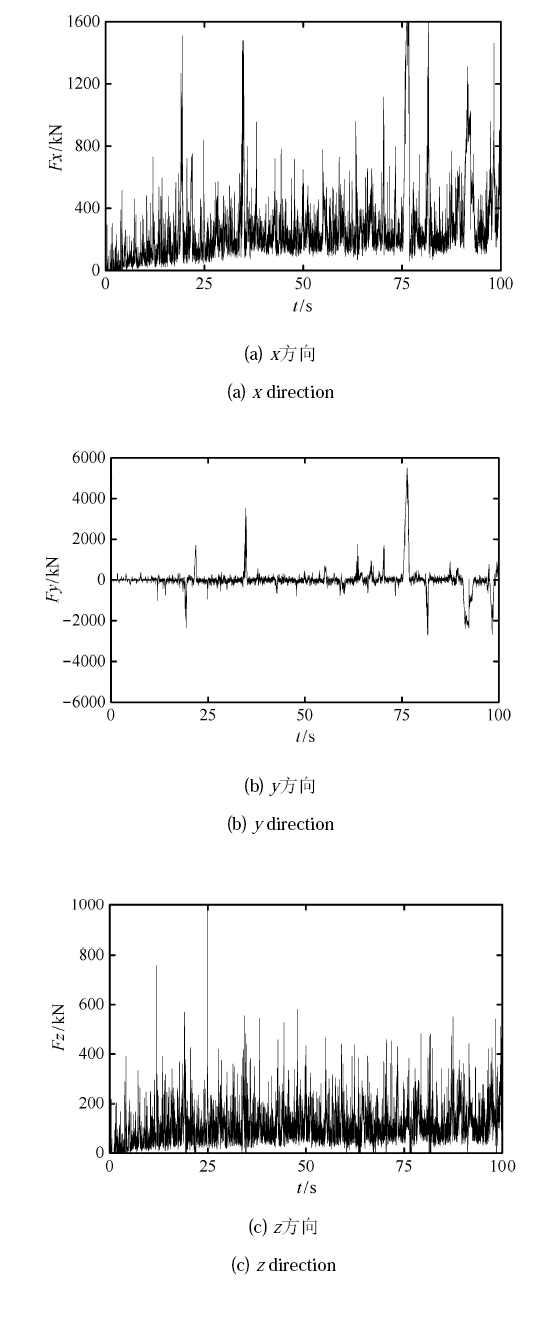
图19 是船体破冰过程中结构上 3 个方向的冰载荷时程曲线. 从图中可看出,$x$ 和 $z$ 方向的冰载荷体现了海冰破坏模式主要为弯曲破坏. $x$ 方向冰载荷对船体在破冰过程影响最大,也是船体运动的主要推进方向. 因此,尽管在 $y$ 和 $z$ 方向上也受到了较大的冰载荷,但通常主要研究 $x$ 方向的冰载荷. 在后续的模拟中,主要分析 $x$ 方向的冰载荷.
图19
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图19船体破冰过程中的冰载荷时程
Fig.19Ice loads on ship hull
采用 Lindqvist 经验公式对比不同冰厚条件下船舶结构的冰阻力,即 $x$ 方向的冰载荷. Lindqvist 公式表示的船舶结 构冰阻力 $R_{i}$ 可写作[66]
式中,$v$ 是船冰相对速度;$L$ 是水线处的船长;$R_{\rm c} $, $R_{\rm b} $ 和 $R_{\rm s} $ 分别表示船艏挤压破坏阻力、弯曲破坏阻力和浸没阻力.
挤压破坏阻力 $R_{\rm c} $ 可写作
式中,$\sigma _{\rm f} $ 是海冰弯曲强度;$\varphi $ 为首柱倾角;$\alpha $ 为水线进角;$\psi = {\rm arctan}\left( {\tan\varphi / \sin\alpha } \right)$.
弯曲破坏阻力 $R_{\rm b} $ 写作
式中,$B$ 为船舶结构型宽.
浸没阻力 $R_{\rm s} $ 写作
式中
式中,$T$ 为船体吃水深度.
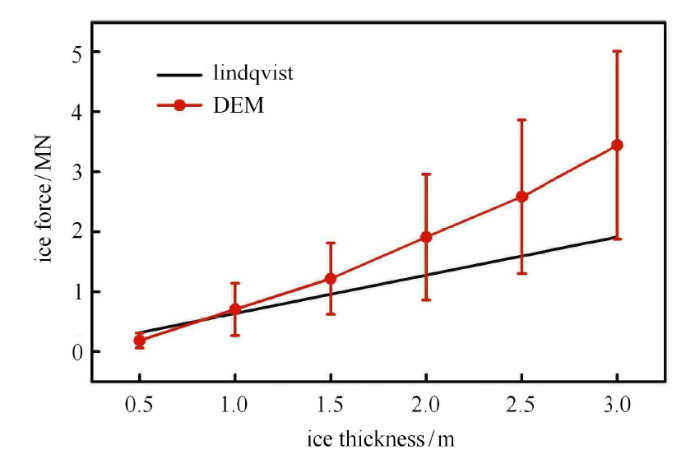
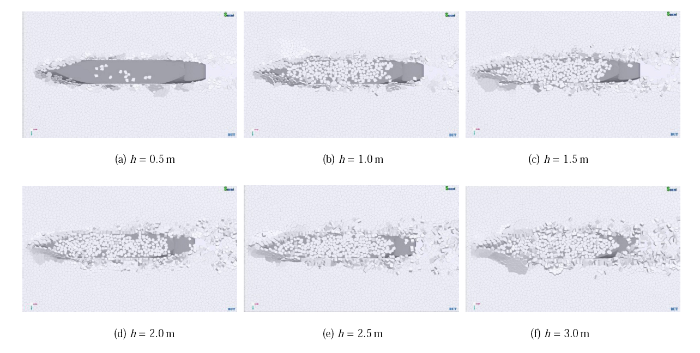
图20 是本文离散元计算船舶结构冰阻力与 Lindqvist 经验公式的对比. 从图中可看出,本文结果在趋势上与经验公式一标识码本文结果明显大于经验公式的结果. Lindqvist 经验公式只考虑船体结构表面的 70${\%}$ 被破碎后的海冰覆盖,且没有考虑碎冰的翻转、堆积等过程,且忽标识码流的影响[67]. 因此导致本文的结果大于经验公式. 实际上,船舶结构破冰后会有大量的碎冰在船侧和船底覆盖甚至堆积,如图21 所示. 碎冰在船体结构表面的会发生类似的“粘附”现象,且随着冰厚的增大碎冰的堆积现象愈加明显. 由于海流会对该部分碎冰产生拖曳力作用,从而会大大增加船舶结构的冰阻力.
图20
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图20离散元和Lindqvist公式的船舶冰阻力对比
Fig.20Ice force on ship hull by DEM and Lindqvist formula
图21
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图21破碎海冰覆盖在船舶结构表面
Fig.21Broken sea ice covers on the surface of ship hull
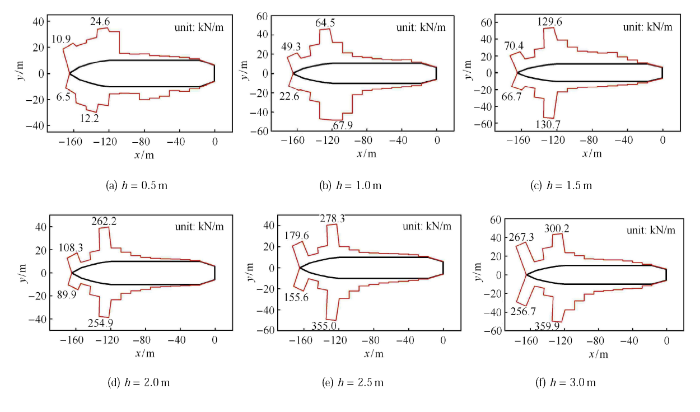
船舶结构冰载荷在结构不同位置处的分布是评估船舶航行安全的重要因素,这里分析船舶结构在直行过程中的线载荷分布,如图22 所示. 从图中可以看出,船舶破冰过程中主要受力部位是船艏,特别是船艏柱和船肩处. 船艏柱是主要的破冰部位,承受了由弯曲破坏导致的破冰阻力;而由于船艏型线向后收缩,船肩位置承受了来自两侧海冰的挤压作用. 对比不同冰厚条件下船艏柱和船肩处的线载荷,可发现船肩处的线载荷要明显大于船艏柱线载荷,如图23 所示. 由于船舶直行的连续式破冰是主要的破冰手段,因此船肩处是船舶结构安全管理的主要关注部位.
图22
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图22船舶破冰过程中的线载荷
Fig.22Line load during ice-breaking of ship
图23
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图23船艏柱和船肩处线载荷对比
Fig.23Line load on ship stem column and ship shoulder
3.2 双船冰载荷分析
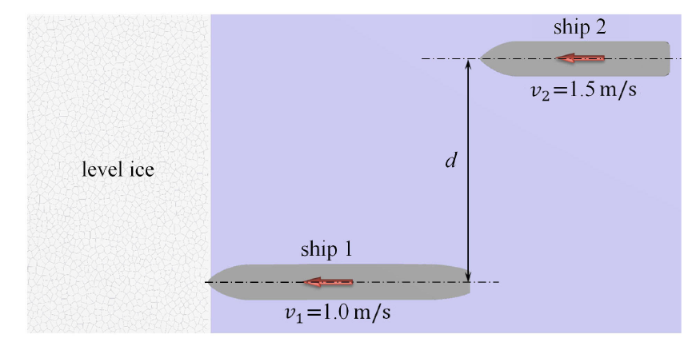
多艘破冰船或极区科考船在冰区协同作业时,会出现多船平行进入冰区并以平行方向在冰区破冰航行的情况. 如图24 所标识码拟两艘船前后在平行方向上以不同速度在冰区航行,初始时船一在前船二在后,且在水平方向上间隔一定距离 $d$. 另外,船一船速为 1.0m/s,船二船速为 1.5m/s.图24
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图24双船平行航行破冰
Fig.24Two ships in parallel navigation channel in level ice
图25 是两船平行以不同速度航行在平整冰的模拟过程. 从图中可以看出,两船与海冰作用并使海冰发生弯曲破坏,标识码分别形成宽阔水道. 由于出现了两个水道,两水道中间形成了两端自由的平整冰区域,加之两船之间的航行速度不同,导致中间区域标识码一个水道到另一个水道的贯穿裂纹[68].
图25
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图25平整冰区两船平行航行的模拟
Fig.25Simulation of double ships navigating parallel in level ice region
实际上,因为船二的船速较快能先于船一开辟出水道,当船一航行时其靠船二的一侧平整冰是自由边界. 因此,在船一的碰撞挤压下平整冰出现了裂缝贯通两个水道,如图25(c) 所示. 在船一的持续作用下,冰层再次出现了裂纹,从而在两水道中间的海冰中形成若干条贯穿裂纹,如图25(d) 所示.
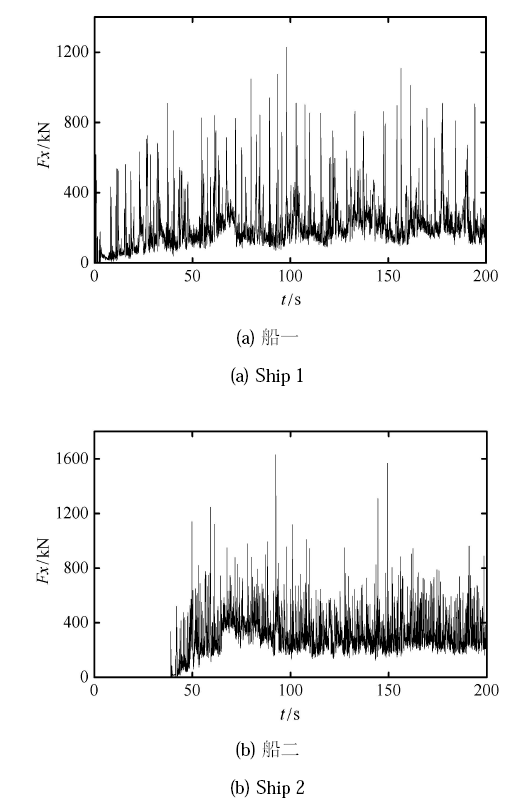
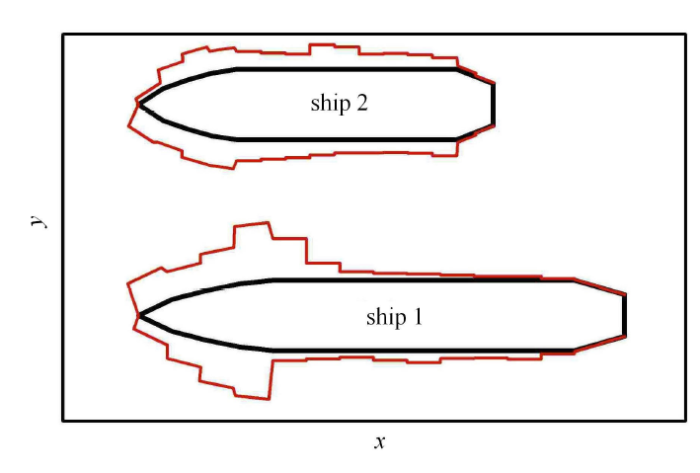
图26 是两船在冰区航行过程中的结构冰载荷时程曲线. 两船的结构冰载荷都体现了弯曲破坏模式的特征,具有明显的脉冲 特性. 另外,分析两船上的线载荷分布情况,如图27 所示. 从图中可以看出,两船的船艏和船肩部位依然是冰载荷集中部 位. 但船艏两侧的载荷存在明显差异,两船靠内侧的载荷较另一侧大,即船一右舷和船二的左舷较另一侧的冰载荷大. 两 船在破冰过程会在中间形成两侧为自由端的冰层,但自由端会与船舶结构发生接触作用,受到结构的约束. 因此,两船会 通过中间的冰层相互影响,增强了船舶结构内侧的冰载荷.
图26
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图26两船平行航行时的冰载荷时程
Fig.26Time history of ice load on the two ship
图27
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图27两船破冰过程中的线载荷
Fig.27Line load during ice-breaking of two ships
4 海冰管理中船舶与海洋平台结构冰载荷
采用扩展多面体的离散元方法计算多桩腿海洋平台结构与平整冰的作用过程,分析不同桩腿上的冰载荷特点. 同时考虑标识码理过程中船舶和海洋平台结构同时与海冰的作用过程,分析船舶结构在绕海洋平台航行过程中的冰载荷.4.1 平整冰区多桩腿海洋平台结构的冰载荷分析
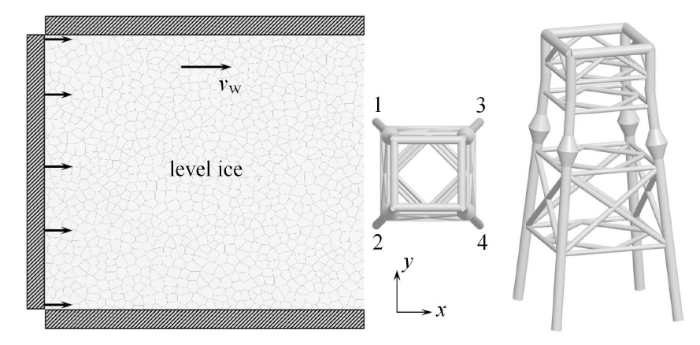
图28 是多桩腿海洋平台结构与平整冰相互作用的模拟示意图. 海洋平台结构共有 4 个桩腿,分别编号 1$\sim $4,每标识码在水线处加装抗冰锥. 主要的计算参数参考表 1,模拟中冰厚为 0.05$\sim $0.35m,平整冰区的长和宽分别为 150 m 和 50m.图28
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图28多桩腿海洋平台结构与平整冰相互作用模拟示意图
Fig.28Sketch of ice and multi-leg platform
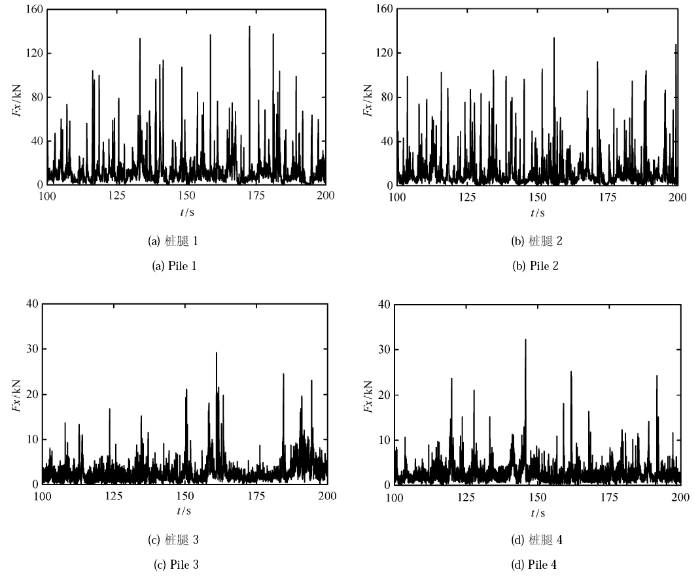
整个计算仿真时间约为 280s,选取中间较为稳定的部分进行分析,即 100 $\sim $ 200s 时间段. 冰厚 0.15m 时,各标识码 $x$ 方向的冰载荷如图29 所示. 从图中可明显看出,桩腿 1 和桩腿 2 上的冰载荷呈现明显的周期性特点,具有典型的锥体结构冰力特征. 另外,桩腿 1 和桩腿 2 上的冰力明显大于桩腿 3 和 4 上的冰力,且桩腿 1 和桩腿 2、桩腿 3 和桩腿 4 标识码力水平基本相同,如图30 所示.
图29
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图29各桩腿上的冰载荷
Fig.29Ice loads on each pile
图30
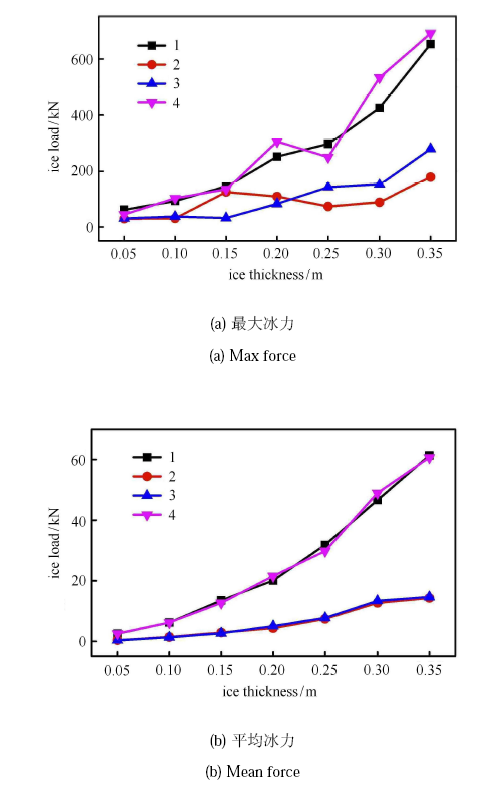 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图30各桩腿上的冰载荷对比
Fig.30Comparison of ice loads on each pile
4.2 海冰管理中船舶及海洋平台结构的冰载荷
海洋平台结构在冰区运行过程中可能会受到严重的冰载荷影响,在恶劣冰况下需要破冰船协助海洋平台进行破冰作标识码低海洋平台结构上的冰载荷. 采用扩展多面体离散元方法计算船舶结构在碎冰区的海洋平台结构的绕行过程,分析船舶和海洋平台结构的冰载荷. 如图31 所示,船舶结构以半径 100m 绕海洋平台结构运动,行进速度为 1.0m/s. 为更合理地分析船舶结构的冰阻力,定义船舶结构的标架坐标系. 船舶结构的冰载荷均在标架坐标系内进行统计. 另外,为生成更加随机的碎冰初始场,初始时刻给每个单元绕 $z$ 轴的随机转速. 图32 是海冰密集度为 60${\%}$ 时海冰管理过程的离散元模拟,海冰在与船舶和海洋平台作用后均形成了开阔水道.图31
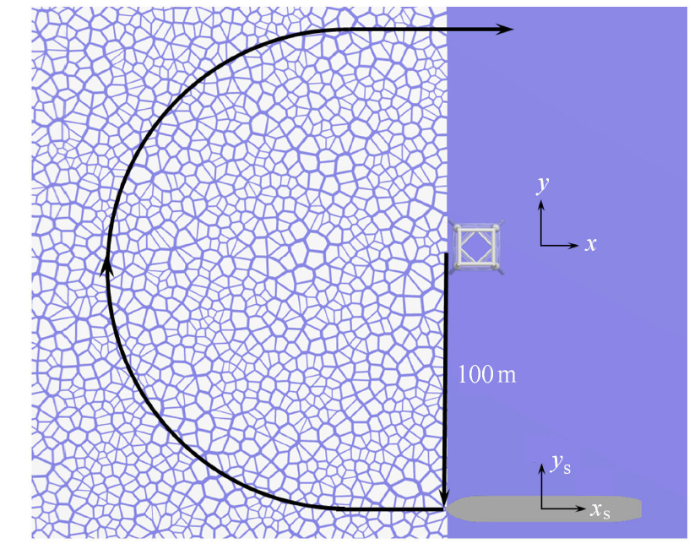 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图31海冰管理模拟示意图
Fig.31Sketch of ice management
图32
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图32海冰管理过程模拟
Fig.32DEM simulation of ice management
海冰管理过程中船舶和海洋平台结构上的冰载荷如图33 所示,这里船舶结构的冰载荷是船舶前进方向上的冰阻力. 从 图中可以看出,船舶结构在绕行时前进阻力较大;之后由于其运动速度与海冰同向,船舶冰阻力明显小于绕行时的冰阻力. 在 400s 时海洋平台结构位于船舶开辟的水道中,其冰载荷出现了明显的下降. 另外,由于船舶向右侧转向,其右侧船艏和左侧船艉的冰载荷较为集中,如图33(c) 所示.
图33
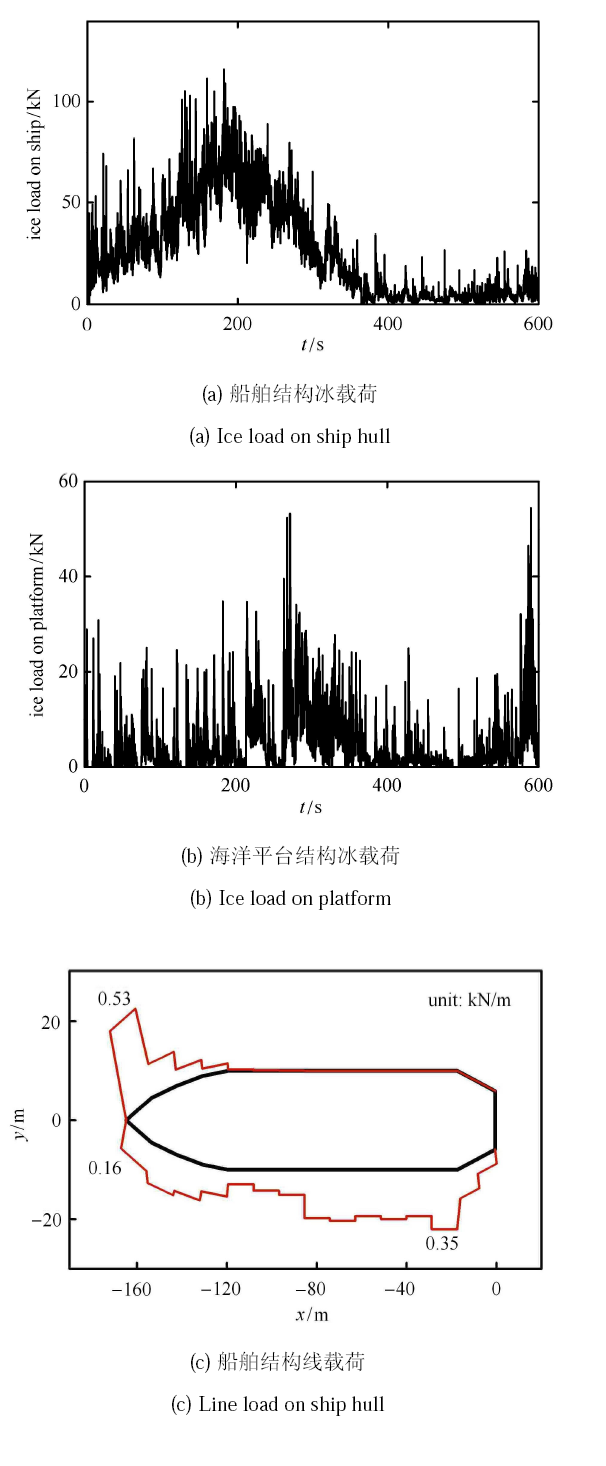 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图33海冰管理过程中船舶和海洋平台结构冰载荷
Fig.33Ice load on ship and platform during ice management
5 结 论
本文采用闵可夫斯基和构造了扩展多面体单元,根据扩展多面体的包络函数发展了单元接触搜索的优化算法,同时建立标识码刚度软化过程的单元间粘结-破碎模型,由此建立了基于扩展多面体的离散元方法,并将该方法应用于船舶标识码平台结构冰载荷的计算分析中. 为验证本文方法的合理性,采用 ISO 标准和渤海现场监测冰载荷数据验证分析了本文计算结果的准确度. 采用本文方法进一步模拟了工程实际中船舶和海洋平台结构的冰载荷. 相关计算分析结果表明,扩展多面体的离散元方法在海冰与海洋结构的相互作用分析中体现出了很好的适应性,对船标识码洋结构的冰载荷分析准确性较高. 该方法可对复杂工况下的海冰与海洋结构相互作用过程进行详细地分析,为极地船舶与海洋平台结构的设计和安全运行提供了科学的分析手段.此外,发展单元内的破碎准则从而建立单元间和单元内的多级破碎模型,可有效提高海冰与结构相互作用的分析精度标识码计算效率. 为更加全面详细地分析海冰与结构相互作用过程,还需考虑海水的影响并发展相应的DEM-CFD流固耦合模型.
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

APETALA2/ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR transcription factors (AP2/ERFs) play crucial roles in adaptation to stresses such as those caused by pathogens, wounding and cold. Although their name suggests a specific role in ethylene signalling, some ERF members also co-ordinate signals regulated by other key plant stress hormones such as jasmonate, abscisic acid and salicylate. We analysed a set of ERF proteins from three divergent plant species for intrinsically disorder regions containing conserved segments involved in protein-protein interaction known as Molecular Recognition Features (MoRFs). Then we correlated the MoRFs identified with a number of known functional features where these could be identified. Our analyses suggest that MoRFs, with plasticity in their disordered surroundings, are highly functional and may have been shuffled between related protein families driven by selection. A particularly important role may be played by the alpha helical component of the structured DNA binding domain to permit specificity. We also present examples of computationally identified MoRFs that have no known function and provide a valuable conceptual framework to link both disordered and ordered structural features within this family to diverse function.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Seasonal acceleration of the Greenland Ice Sheet is influenced by the dynamic response of the subglacial hydrologic system to variability in meltwater delivery to the bed via crevasses and moulins (vertical conduits connecting supraglacial water to the bed of the ice sheet). As the melt season progresses, the subglacial hydrologic system drains supraglacial meltwater more efficiently, decreasing basal water pressure and moderating the ice velocity response to surface melting. However, limited direct observations of subglacial water pressure mean that the spatiotemporal evolution of the subglacial hydrologic system remains poorly understood. Here we show that ice velocity is well correlated with moulin hydraulic head but is out of phase with that of nearby (0.3-2?kilometres away) boreholes, indicating that moulins connect to an efficient, channelized component of the subglacial hydrologic system, which exerts the primary control on diurnal and multi-day changes in ice velocity. Our simultaneous measurements of moulin and borehole hydraulic head and ice velocity in the Paakitsoq region of western Greenland show that decreasing trends in ice velocity during the latter part of the melt season cannot be explained by changes in the ability of moulin-connected channels to convey supraglacial melt. Instead, these observations suggest that decreasing late-season ice velocity may be caused by changes in connectivity in unchannelized regions of the subglacial hydrologic system. Understanding this spatiotemporal variability in subglacial pressures is increasingly important because melt-season dynamics affect ice velocity beyond the conclusion of the melt season.
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

Ice bound shipping is considerably more dangerous than shipping under more favourable water conditions. During winter the Baltic Sea can be covered with ice over an average of about 45% of its surface. The ice mostly reaches its maximum extent in late February or early March. The Bay of Bothnia located in the northern basin of the Gulf of Bothnia is prone to extreme frozen ice conditions. During winter the typical ice thickness in the northernmost areas of the Bay of Bothnia is about 70 cm for land-fast sea ice.
In this paper the ice crushing pressure on a ship's hull is analysed statistically. A series of tests took place over four days in the Aalto ice tank and involved two different ship models. The peak pressures caused by ice were calculated from four sensor sheets located at different positions on the hull. In the statistical part, the sum of the forces acting on a section of a ship's hull was modelled as a Poisson random process. Analysis of the cumulative distribution function (CDF) was modelled for the total force. The full scale comparisons of pressure-area values and line loads as a function of the load width were analysed by comparing the model scale data with full scale measurements onboard MS Arcturus and IB Sisu. Finally a short comparison is also conducted with the load level obtained from damage statistics gathered in the Baltic Sea. (C) 2011 Elsevier B.V.
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

The variation of physical and mechanical properties of the lightweight bulk filling material with cement and expanded polystyrene (EPS) beads contents under different confining pressures is important to construction and geotechnical applications. In this study, a lightweight bulk filling material was firstly fabricated with Singapore marine clay, ordinary Portland cement and EPS. Then, the influences of EPS beads content, cement content, curing time and confining pressure on the mass density, stress-strain behavior and compressive strength of this lightweight bulk filling material were investigated by unconsolidated and undrained (UU) triaxial tests. In these tests, the mass ratios of EPS beads to dry clay (E/S) were 0%, 0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 4% and the mass ratios of cement to dry clay (C/S) were 10% and 15%. Thirdly, a series of UU triaxial tests were performed at a confining pressure of 0 kPa, 50 kPa, 100 kPa, and 150 kPa after three curing days, seven curing days, and 28 curing days. The results show that the mass density of this lightweight bulk filling material was mainly controlled by the E/S ratio. Its mass density decreased by 55.6% for the C/S ratio 10% and 54.9% for the C/S ratio 15% when the E/S ratio increased from 0% to 4% after three curing days. Shear failure more easily occurred in the specimens with higher cement content and lower confining pressure. The relationships between compressive strength and mass density or failure strain could be quantified by the power function. Increasing cement content and reducing EPS beads content will increase mass density and compressive strength of this lightweight bulk filling material. The compressive strength with curing time can be expressed by a logarithmic function with fitting correlation coefficient ranging from 0.83 to 0.97 for five confining pressures. These empirical formulae will be useful for the estimation of physical and mechanical properties of lightweight concretes in engineering application.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

Two series of model tests were performed to investigate the dynamic ice loads on two types of four-legged jacket platforms and the consequently structural responses. The first test series was carried out with cylindrical models and the second test series with conical models at the water level. To simulate the ice induce vibrations on multi-legged structures, a new series of test equipments was designed. The ice load on each model leg, structural displacements in three directions, and foundation reactions in two directions were measured during the tests. Different ice failure modes and structural responses were observed for different ice conditions and structural stiffness values. This paper provides a description of the test techniques and the experimental results. The important test phenomena are also discussed in this paper. (C) 2013 Elsevier B.V.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 2]

APETALA2/ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR transcription factors (AP2/ERFs) play crucial roles in adaptation to stresses such as those caused by pathogens, wounding and cold. Although their name suggests a specific role in ethylene signalling, some ERF members also co-ordinate signals regulated by other key plant stress hormones such as jasmonate, abscisic acid and salicylate. We analysed a set of ERF proteins from three divergent plant species for intrinsically disorder regions containing conserved segments involved in protein-protein interaction known as Molecular Recognition Features (MoRFs). Then we correlated the MoRFs identified with a number of known functional features where these could be identified. Our analyses suggest that MoRFs, with plasticity in their disordered surroundings, are highly functional and may have been shuffled between related protein families driven by selection. A particularly important role may be played by the alpha helical component of the structured DNA binding domain to permit specificity. We also present examples of computationally identified MoRFs that have no known function and provide a valuable conceptual framework to link both disordered and ordered structural features within this family to diverse function.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

In this paper, the versatility of discrete element method (DEM) in modelling ice-related problems is discussed and further demonstrated using the results from the DEM works conducted by the National Research Council's Institute for Ocean Technology (NRC-IOT) using a commercial code DECICE. These works include a wide range of ice-structure and ice-ship interaction problems of current interest, i.e. ice loads on conical structures, jamming of floes at bridge piers, modelling of the mechanical behaviour of ice rubble, pack ice stability and associated forces on offshore structures, rubble loads exerted on an inclined retaining wall, ridge keel resistance during seabed scouring, dynamic response of a moored conical drill-ship in ice and ship manoeuvring performance in ice. Representative simulations for each case are presented including load, motion and/or interaction process, whichever is appropriate. The simulations from DECICE were compared with experimental data and found satisfactory in terms of accuracy and real-time simulation capability. The accuracy is important for design and engineering of marine structures and ships, whereas the real-time simulation capability allows it to be used in marine simulators for personnel training and marine operation assessment. The performance of DECICE is also addressed and improved via the implementation of a new contact detection sequence and parallel considerations.
URL [本文引用: 1]

本文将海冰在斜坡式防波堤前的堆积过程简化为二维的动力学问题,假定海冰为粘弹性体,在多边块体运动模拟系统基础上,采用离散元数值方法对冰排爬升堆积过程进行了实时仿真模拟.通过与二维理论断裂模型及物理模型试验结果对比,证明了此数值模型的合理性与可行性.
URL [本文引用: 1]

本文将海冰在斜坡式防波堤前的堆积过程简化为二维的动力学问题,假定海冰为粘弹性体,在多边块体运动模拟系统基础上,采用离散元数值方法对冰排爬升堆积过程进行了实时仿真模拟.通过与二维理论断裂模型及物理模型试验结果对比,证明了此数值模型的合理性与可行性.
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]

A discrete-element model of sea ice is used to study how a 900 change in wind direction alters the pattern of faults generated through mechanical failure of the ice. The sea-ice domain is 400 km in size and consists of polygonal floes obtained through a Voronoi tessellation. Initially the floes are frozen together through viscous-elastic joints that can break under sufficient compressive, tensile and shear deformation. A constant wind-stress gradient is applied until the initially frozen ice pack is broken into roughly diamond-shaped aggregates, with crack angles determined by wing-crack formation. Then partial refreezing of the cracks delineating the aggregates is modelled through reduction of their length by a particular fraction, the ice pack deformation is neglected and the wind stress is rotated by 90 degrees. New cracks form, delineating aggregates with a different orientation. Our results show the new crack orientation depends on the refrozen fraction of the initial faults: as this fraction increases, the new cracks gradually rotate to the new wind direction, reaching 90 degrees for fully refrozen faults. Such reorientation is determined by a competition between new cracks forming at a preferential angle determined by the wing-crack theory and at old cracks oriented at a less favourable angle but having higher stresses due to shorter contacts across the joints.
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Dimethyl sulfide (DMS) production in the northern Arctic Ocean has been considered to be minimal because of high sea ice concentration and extremely low productivity. However, we found DMS concentration (1-33 nM) in melt ponds on sea ice at a very high latitude (78°N) in the central Arctic Ocean to be up to ten times that in the adjacent open ocean (&lt;3 nM). We divided melt ponds into three categories: freshwater melt ponds, brackish melt ponds, and open saline melt ponds. Melt ponds from each category had different formation mechanisms and associated DMS contents. Closed brackish ponds (salinity of &gt;20) had particularly high DMS concentration. Water in brackish ponds was mixed with open ocean water in the past via a hole at the bottom of the floe that kept the pond open to the ocean; therefore, unlike freshwater melt ponds, brackish ponds became sites of DMS accumulation. Our results suggest that continuous increase in melt pond coverage on Arctic sea ice could considerably impact future Arctic climate as well as enhancing DMS concentration in the Arctic atmosphere.
DOIURL [本文引用: 4]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

APETALA2/ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR transcription factors (AP2/ERFs) play crucial roles in adaptation to stresses such as those caused by pathogens, wounding and cold. Although their name suggests a specific role in ethylene signalling, some ERF members also co-ordinate signals regulated by other key plant stress hormones such as jasmonate, abscisic acid and salicylate. We analysed a set of ERF proteins from three divergent plant species for intrinsically disorder regions containing conserved segments involved in protein-protein interaction known as Molecular Recognition Features (MoRFs). Then we correlated the MoRFs identified with a number of known functional features where these could be identified. Our analyses suggest that MoRFs, with plasticity in their disordered surroundings, are highly functional and may have been shuffled between related protein families driven by selection. A particularly important role may be played by the alpha helical component of the structured DNA binding domain to permit specificity. We also present examples of computationally identified MoRFs that have no known function and provide a valuable conceptual framework to link both disordered and ordered structural features within this family to diverse function.
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

APETALA2/ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR transcription factors (AP2/ERFs) play crucial roles in adaptation to stresses such as those caused by pathogens, wounding and cold. Although their name suggests a specific role in ethylene signalling, some ERF members also co-ordinate signals regulated by other key plant stress hormones such as jasmonate, abscisic acid and salicylate. We analysed a set of ERF proteins from three divergent plant species for intrinsically disorder regions containing conserved segments involved in protein-protein interaction known as Molecular Recognition Features (MoRFs). Then we correlated the MoRFs identified with a number of known functional features where these could be identified. Our analyses suggest that MoRFs, with plasticity in their disordered surroundings, are highly functional and may have been shuffled between related protein families driven by selection. A particularly important role may be played by the alpha helical component of the structured DNA binding domain to permit specificity. We also present examples of computationally identified MoRFs that have no known function and provide a valuable conceptual framework to link both disordered and ordered structural features within this family to diverse function.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 3]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Minkowski operators (dilation and erosion of sets in vector spaces) have been extensively used in computer graphics, image processing to analyze the structure of materials, and more recently in molecular dynamics. Here, we apply those mathematical concepts to extend the discrete element method to simulate granular materials with complex-shaped particles. The Voronoi-Minkowski diagrams are introduced to generate random packings of complex-shaped particles with tunable particle roundness. Contact forces and potentials are calculated in terms of distances instead of overlaps. By using the Verlet method to detect neighborhood, we achieve CPU times that grow linearly with the body's number of sides. Simulations of dissipative granular materials under shear demonstrate that the method maintains conservation of energy in accord with the first law of thermodynamics. A series of simulations for biaxial test, shear band formation, hysteretic behavior, and ratcheting show that the model can reproduce the main features of real granular-soil behavior.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

The paper presents an extension to the spheropolyhedra method for the simulation of granular materials comprising particles of general shapes with bonding. A bonding, cement, or cohesion model for particles sharing common faces is introduced. The bonding force is elastic and has a strain-based breaking threshold for modelling fracture. An initial study is conducted based on the Brazilian tensile test to check how the parameters of the proposed model affect the principal variables measured in this test. Afterwards, solid cubic blocks are then subjected to a triaxial test to explore the mathematical macroscopic failure model. It is found that the peak strength envelope is the product of the superposition of frictional and fracture failure mechanisms. The fracture failure is mainly produced by an avalanche of broken cohesive bonds. The intensity of the avalanche exhibits a power law distribution, as reported in previous studies. The method allows for random divisions of solid bodies without any pre-existing internal voids. It offers a natural, effective tool to model, simulate and study fragmentation processes in 3D. (C) 2011 Elsevier B.V.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

The main aim of this article is to compare various heating methods of the shrink-fit connection and to analyse its shrinkage mechanism. The shrink fit connection consists of the crank and the pin or the ring and the pin, which have negative value of the geometrical clearance. The experimental part of research included the measurement of the temperature at the various points in the surface of the crank, the measurement of the residual stress 5 mm from the crank hole and the measurement of the maximum torsional moment, at which sliding of the shrink-fit connection occurs. Conformity between data from the Finite Element Analysis and the experimental data was obtained in relation to the von Mises stress. The analysis results show that Lamé equations can be successfully used for calculation of the load capacity even for parts with the irregular shape.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 2]

Active development of quantum informational components such as quantum computers and quantum key distribution systems requires parameter characterization of single photon detectors. A key property of the single photon detectors is detection efficiency. One of the methods of the detection efficiency measurement, as listed in the international standard ETSI, is the reference-free twin-photon-based Klyshko method. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of this method depends on the combination of the pump wavelength, the nonlinear crystal's axis angle, and the type of detector's sensitive element. When the combination is difficult, one has to deal with the low SNR of the detector counts measurement. To gain the high SNR, one has to average the long record complicated with the &quot;random telegraph signal&quot; noise. This type of noise exhibits high spectral density at a zero frequency, where simple averaging works. The heterodyne based method we have proposed is to perform averaging at the higher frequency of the modulation introduced to the standard Klyshko measurement scheme. The method was numerically simulated and experimentally tested. The 14 times improvement in SNR for the proposed method relative to the simple averaging was demonstrated by the numerical simulation and confirmed experimentally.
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Active development of quantum informational components such as quantum computers and quantum key distribution systems requires parameter characterization of single photon detectors. A key property of the single photon detectors is detection efficiency. One of the methods of the detection efficiency measurement, as listed in the international standard ETSI, is the reference-free twin-photon-based Klyshko method. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of this method depends on the combination of the pump wavelength, the nonlinear crystal's axis angle, and the type of detector's sensitive element. When the combination is difficult, one has to deal with the low SNR of the detector counts measurement. To gain the high SNR, one has to average the long record complicated with the &quot;random telegraph signal&quot; noise. This type of noise exhibits high spectral density at a zero frequency, where simple averaging works. The heterodyne based method we have proposed is to perform averaging at the higher frequency of the modulation introduced to the standard Klyshko measurement scheme. The method was numerically simulated and experimentally tested. The 14 times improvement in SNR for the proposed method relative to the simple averaging was demonstrated by the numerical simulation and confirmed experimentally.
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Monitoring drift ice in the Arctic and Antarctic regions directly and by remote sensing is important for the study of climate, but a unified modeling framework is lacking. Hence, interpretation of the data, as well as the decision of what to measure, represent a challenge for different fields of science. To address this point, we analyzed, using statistical physics tools, satellite images of sea ice from four different locations in both the northern and southern hemispheres, and measured the size and the elongation of ice floes (floating pieces of ice). We find that (i) floe size follows a distribution that can be characterized with good approximation by a single length scale , which we discuss in the framework of stochastic fragmentation models, and (ii) the deviation of their shape from circularity is reproduced with remarkable precision by a geometric model of coalescence by freezing, based on random Voronoi tessellations, with a single free parameter expressing the shape disorder. Although the physical interpretations remain open, this advocates the parameters and as two independent indicators of the environment in the polar regions, which are easily accessible by remote sensing.
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Although a resistivity saturation (minimum conductivity) is often observed in disordered metallic solids, such phenomena in the corresponding liquids are not known. Here we report a saturation of the electrical resistivity in Zr_{64}Ni_{36} and Cu_{50}Zr_{50} liquids above a dynamical crossover temperature for the viscosity (T_{A}). The measurements were made for the levitated liquids under the microgravity conditions of the International Space Station. Based on recent molecular dynamics simulations, the saturation is likely due to the ineffectiveness of electron-phonon scattering above T_{A} when the phonon lifetime becomes too short compared to the electron relaxation time. This is different from the conventional resistivity saturation mechanisms in solids.
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

We numerically investigate head-on collisions of isothermal viscoelastic spheres. We find that the restitution coefficient oscillates against the impact speed if the solid viscosity inside the sphere is small enough. We confirm that the oscillation arises from the resonance between the duration of contact and the eigenfrequencies of the sphere. This oscillation disappears if there exists the strong solid viscosity in spheres. We also find that a sinusoidal behavior of the restitution coefficient against the initial phase in the eigenmodes for collisions between a thermally activated sphere and a flat wall. As a result, the restitution coefficient can exceed unity if the impact speed of the colliding sphere is nearly equal to or slower than the thermal speed. We have confirmed the existence of the fluctuation theorem for impact processes through our simulation.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Organic matter is responsible for the generation of hydrocarbons during the thermal maturation of source rock formation. This geochemical process engenders a network of organic hosted pores that governs the flow of hydrocarbons from the organic matter to fractures created during the stimulation of production wells. Therefore, it can be reasonably assumed that predictions of potentially recoverable confined hydrocarbons depend on the geometry of this pore network. Here, we analyze mesoscale structures of three organic porous networks at different thermal maturities. We use electron tomography with subnanometric resolution to characterize their morphology and topology. Our 3D reconstructions confirm the formation of nanopores and reveal increasingly tortuous and connected pore networks in the process of thermal maturation. We then turn the binarized reconstructions into lattice models including information from atomistic simulations to derive mechanical and confined fluid transport properties. Specifically, we highlight the influence of adsorbed fluids on the elastic response. The resulting elastic energy concentrations are localized at the vicinity of macropores at low maturity whereas these concentrations present more homogeneous distributions at higher thermal maturities, due to pores' topology. The lattice models finally allow us to capture the effect of sorption on diffusion mechanisms with a sole input of network geometry. Eventually, we corroborate the dominant impact of diffusion occurring within the connected nanopores, which constitute the limiting factor of confined hydrocarbon transport in source rocks.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Organic matter is responsible for the generation of hydrocarbons during the thermal maturation of source rock formation. This geochemical process engenders a network of organic hosted pores that governs the flow of hydrocarbons from the organic matter to fractures created during the stimulation of production wells. Therefore, it can be reasonably assumed that predictions of potentially recoverable confined hydrocarbons depend on the geometry of this pore network. Here, we analyze mesoscale structures of three organic porous networks at different thermal maturities. We use electron tomography with subnanometric resolution to characterize their morphology and topology. Our 3D reconstructions confirm the formation of nanopores and reveal increasingly tortuous and connected pore networks in the process of thermal maturation. We then turn the binarized reconstructions into lattice models including information from atomistic simulations to derive mechanical and confined fluid transport properties. Specifically, we highlight the influence of adsorbed fluids on the elastic response. The resulting elastic energy concentrations are localized at the vicinity of macropores at low maturity whereas these concentrations present more homogeneous distributions at higher thermal maturities, due to pores' topology. The lattice models finally allow us to capture the effect of sorption on diffusion mechanisms with a sole input of network geometry. Eventually, we corroborate the dominant impact of diffusion occurring within the connected nanopores, which constitute the limiting factor of confined hydrocarbon transport in source rocks.
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 2]

Active development of quantum informational components such as quantum computers and quantum key distribution systems requires parameter characterization of single photon detectors. A key property of the single photon detectors is detection efficiency. One of the methods of the detection efficiency measurement, as listed in the international standard ETSI, is the reference-free twin-photon-based Klyshko method. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of this method depends on the combination of the pump wavelength, the nonlinear crystal's axis angle, and the type of detector's sensitive element. When the combination is difficult, one has to deal with the low SNR of the detector counts measurement. To gain the high SNR, one has to average the long record complicated with the &quot;random telegraph signal&quot; noise. This type of noise exhibits high spectral density at a zero frequency, where simple averaging works. The heterodyne based method we have proposed is to perform averaging at the higher frequency of the modulation introduced to the standard Klyshko measurement scheme. The method was numerically simulated and experimentally tested. The 14 times improvement in SNR for the proposed method relative to the simple averaging was demonstrated by the numerical simulation and confirmed experimentally.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Active development of quantum informational components such as quantum computers and quantum key distribution systems requires parameter characterization of single photon detectors. A key property of the single photon detectors is detection efficiency. One of the methods of the detection efficiency measurement, as listed in the international standard ETSI, is the reference-free twin-photon-based Klyshko method. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of this method depends on the combination of the pump wavelength, the nonlinear crystal's axis angle, and the type of detector's sensitive element. When the combination is difficult, one has to deal with the low SNR of the detector counts measurement. To gain the high SNR, one has to average the long record complicated with the &quot;random telegraph signal&quot; noise. This type of noise exhibits high spectral density at a zero frequency, where simple averaging works. The heterodyne based method we have proposed is to perform averaging at the higher frequency of the modulation introduced to the standard Klyshko measurement scheme. The method was numerically simulated and experimentally tested. The 14 times improvement in SNR for the proposed method relative to the simple averaging was demonstrated by the numerical simulation and confirmed experimentally.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

A search for narrow low-mass resonances decaying to quark-antiquark pairs is presented. The search is based on proton-proton collision events collected at 13?TeV by the CMS detector at the CERN LHC. The data sample corresponds to an integrated luminosity of 35.9??fb^{-1}, recorded in 2016. The search considers the case where the resonance has high transverse momentum due to initial-state radiation of a hard photon. To study this process, the decay products of the resonance are reconstructed as a single large-radius jet with two-pronged substructure. The signal would be identified as a localized excess in the jet invariant mass spectrum. No evidence for such a resonance is observed in the mass range 10 to 125?GeV. Upper limits at the 95%?confidence level are set on the coupling strength of resonances decaying to quark pairs. The results obtained with this photon trigger strategy provide the first direct constraints on quark-antiquark resonance masses below 50?GeV obtained at a hadron collider.
//
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

APETALA2/ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR transcription factors (AP2/ERFs) play crucial roles in adaptation to stresses such as those caused by pathogens, wounding and cold. Although their name suggests a specific role in ethylene signalling, some ERF members also co-ordinate signals regulated by other key plant stress hormones such as jasmonate, abscisic acid and salicylate. We analysed a set of ERF proteins from three divergent plant species for intrinsically disorder regions containing conserved segments involved in protein-protein interaction known as Molecular Recognition Features (MoRFs). Then we correlated the MoRFs identified with a number of known functional features where these could be identified. Our analyses suggest that MoRFs, with plasticity in their disordered surroundings, are highly functional and may have been shuffled between related protein families driven by selection. A particularly important role may be played by the alpha helical component of the structured DNA binding domain to permit specificity. We also present examples of computationally identified MoRFs that have no known function and provide a valuable conceptual framework to link both disordered and ordered structural features within this family to diverse function.
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

APETALA2/ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR transcription factors (AP2/ERFs) play crucial roles in adaptation to stresses such as those caused by pathogens, wounding and cold. Although their name suggests a specific role in ethylene signalling, some ERF members also co-ordinate signals regulated by other key plant stress hormones such as jasmonate, abscisic acid and salicylate. We analysed a set of ERF proteins from three divergent plant species for intrinsically disorder regions containing conserved segments involved in protein-protein interaction known as Molecular Recognition Features (MoRFs). Then we correlated the MoRFs identified with a number of known functional features where these could be identified. Our analyses suggest that MoRFs, with plasticity in their disordered surroundings, are highly functional and may have been shuffled between related protein families driven by selection. A particularly important role may be played by the alpha helical component of the structured DNA binding domain to permit specificity. We also present examples of computationally identified MoRFs that have no known function and provide a valuable conceptual framework to link both disordered and ordered structural features within this family to diverse function.
