 ,?,3), 叶红玲*, 铁军***
,?,3), 叶红玲*, 铁军*** †
**
RECIPROCAL PROGRAMMING THEORY AND ITS APPLICATION TO ESTABLISH A REASONABLE MODEL OF STRUCTURAL TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION 1)
Sui Yunkang*, Peng Xirong ,?,3), Ye Hongling*, Tie Jun***
,?,3), Ye Hongling*, Tie Jun*** †
**
通讯作者: 3) 彭细荣,教授,主要研究方向:结构优化.E-mail:pxr568@163.com
收稿日期:2019-09-12接受日期:2019-11-5网络出版日期:2019-11-07
| 基金资助: |
Received:2019-09-12Accepted:2019-11-5Online:2019-11-07
作者简介 About authors
2)隋允康,教授,主要研究方向:结构优化.E-mail:ysui@bjut.edu.cn

摘要
在数学规划的领域里定义了互逆规划——各自目标函数与约束条件位置相互交换的一对规划. 接着指出,尽管互逆规划与对 偶规划在表面上似乎类似,但是二者存在 5 点不同:(1) 是否为同一个问题的不同;(2) 存在``对偶间隙''与否的不同;(3) 设计变量数目的不同;(4) 是否单目标与多目标问题的不同;(5) 问题合理与否的不同. 然后,基于互逆规划的定义,用以审视结 构拓扑优化模型,给出如下结果:(1) 从这个角度洞悉,在结构优化中,确实有不合理的模型一直被沿用着;(2) 找到了修正不 合理模型使之合理化的方法;(3) 对于给定体积下的柔顺度最小化 (MCVC) 模型,指出了其不合理的原因;(4) MCVC 模型实际是互 逆规划的 m 方,由此建立起其对应的 s 方, 即给出了多个柔顺度约束的体积最小化 (MVCC) 模型;(5)给出了MVCC模型中的结构 柔顺度约束的物理解释和算法,论证了 ICM (independent continuous and mapping) 方法以往关于全局化应力约束的概念和方法;(6)数值算例表明了 MCVC 与 MVCC 模型作为互逆规划的差异,且印证了 MVCC 模型的合理性.MCVC 模型在不同体积约束及多工况下不同的权系数时,得到最优拓扑不同;但 MVCC 模型在多工况柔顺度约束下可得到唯一的最优拓扑.
关键词:
Abstract
Based on mathematical programming theory, the reciprocal programming is defined as a pair of programming which objective and constraint functions are changed each other. After that, it is pointed out that reciprocal programming and dual programming seem similar but there are five differences between them: (1) the difference in whether they are the same problem or not; (2) the difference in whether there exists a dual gap or not; (3) the difference in the number of design variables; (4) the difference between single-objective and multi-objective problems; (5) the difference between reasonable and unreasonable problems. Finally, based on the definition of the reciprocal programming, the structural topology optimization model is examined; and following results are obtained: (1) from this perspective, it is clear that there exists indeed unreasonable models that have been used in structural optimization; (2) a way to correct the unreasonable model and make it reasonable is put forward; (3) the reasons that the minimizing compliance model with volume constraint (MCVC for short) is unreasonable are presented; (4) according to the theory presented in this paper, the MCVC model is actually the m-aspect of reciprocal programming, so its corresponding s-aspect is established, that is, the minimizing volume model with multiple compliance constraints (MVCC for short); (5) the physical interpretation and algorithm of structural compliance constraints in the MVCC model are presented; and the concepts and methods of global stress constraint in the ICM (Independent continuous and mapping ) method are demonstrated; (6) numerical examples show the differences between the MCVC and MVCC model as a pair of reciprocal programming and verify the rationality of the MVCC model. Different optimized topologies are obtained for the MCVC model with different volume constraints and different weighting coefficients for multiple load cases. But a unique optimized topology can be achieved by the MVCC model with compliance constraints under multiple load case.
Keywords:
PDF (1369KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
隋允康, 彭细荣, 叶红玲, 铁军. 互逆规划理论及其用于建立结构拓扑优化的合理模型 1). 力学学报[J], 2019, 51(6): 1940-1948 DOI:10.6052/0459-1879-19-259
Sui Yunkang, Peng Xirong, Ye Hongling, Tie Jun.
引言
对偶规划是数学规划领域里极为重要的概念之一,具体可以细分为线性规划的对偶规划、非线性规划的对偶规划和正定几何规划的对偶规划等等[1-3].对偶理论作为一个重要的方法论,能将大规模的原规划问题转换为一个规模小得多的对偶规划问题求解,从而可以极大减少计算量,提高算法效率,在优化领域中得到广泛应用.1979 年,Fleury 将对偶规划引到结构优化领域,进行建立模型和求解算法的研究[4-6].1984 年,钱令希团队用对偶序列二次规划算法求解结构优化问题[7].结构优化中经典的优化求解算法如 CONLIN (convex linearizationmethod)[8] 及 MMA (method of movingasymptotes)[9] 均基于对偶算法.文献[10,11,12] 等也是此方面的研究.隋允康等[13-14]结合累积迭代信息策略,研究了对偶算法在结构优化中的方法和应用.
在连续体结构拓扑优化中,设计变量数量通常是极大的,对一个工程实际问题,设计变量数量达到上百万都有可能.对大规模的优化模型,如果直接对原问题进行求解,其计算量将是无法接受的.因而,结构拓扑优化 ICM 方法一直特别重视应用对偶求解算法[1-3].
论及结构拓扑优化方法,应当追溯到 1988 年Bendsoe 与 Kikuchi[15] 提出的均匀化方法.从那时起,连续体结构拓扑优化首次被提出并且得到了快速发展,涌现的许多方法中,包含 SIMP (solid isotropic material withpenalization) 方法[16]、拓扑导数方法 [17-18]、ESO (evolutionarystructuraloptimization) 方法[19]、水平集方法[20]、相场法[21]、MMC(moving morphable components) 方法[22] 等等.对各类方法的综述可参阅 Rozvany[23] 和 Sigmund 等[24]的文献.
各种方法基本上集中在建模途径和求解效率上,而对于优化模型是否合理性则缺乏注意.为此,可以考察一下连续体结构拓扑 优化的第一篇论文[15],文中取体积约束下柔顺度最小化为研究模型,为方便叙述,称其为 MCVC(minimum compliances with a volume constraint) 模型.实际上,不少方法在目标函数和约束条件的选取上,都因循了 MCVC 模型的做法.
客观地说,MCVC 模型模型存在一些不合理之处,应当予以指出[25-26]:(1)需要事先指定一个体积约束值,其实这是事先难以确定的,而且指定不同的体积约束值,所得到的结构拓扑构型的差别很大;(2)多工况情况下,多个柔顺度目标函数需要加权组合成单目标函数,而权系数的指定亦没有科学的依据,且结构拓扑构型依赖于权系数的选择.
或许因为先入为主的思维定势,桎梏了研究者思考MCVC模型是否合理的头脑.或许是由于该模型易于显式化,又只有一个体积约束,导致模型易于建立和求解,在连续体拓扑优化的早期发展中,避免了显式建模与高效求解这两大困难,有利于研究者把精力集中在探求不同的方法上,因而MCVC模型起了很好的、不可替代的作用,直到现在仍在起作用.
模型中目标函数和约束条件的设置是否合理?历经三十多年来的发展,到了需要明确揭示的时候了,也亟待需要予以解决.为此,隋 允康等曾经将MCVC模型同 MVDC (minimum volume withdisplacementconstraints) 模型进行了比较研究[25-26],说明 MCVC 模型的不合理性.然而,MCVC 模型与 MVDC 模型不具有完全的对应性,已经发表的两篇文章的说理性还不够充分.
为了彻底解决如何建立合理的结构优化模型问题,本文旨在纯数学角度的思考,类比对偶规划,在数学规划的领域里,首次提出互逆规划的概念,进行了相关的研究.接着,用新概念和方法洞察连续体结构拓扑优化模型,建立了与 MCVC 模型互逆的 MVCC (minimum volume with compliance constraints),即柔顺度约束下体积极小化模型.
在 MVCC 模型中,存在柔顺度约束条件,本文对于柔顺度约束的物理意义进行了探讨,其中包含在 ICM 方法中冠名应力全局化的一种形式[2-3,27-28].本文的算例验证了 MVCC 模型的合理性,从而印证了建立互逆规划概念和方法的意义.
1 从对偶规划到互逆规划
在线性规划、非线性规划乃至在具有高度非线性性质的几何规划里,先后建立了各自的对偶理论.尽管这些不同的对偶理论各 具个性,但是它们也具有共性.对偶理论已经成为相关问题的重要理论基础和有效求解途径.线性规划的原规划
线性规划的对偶规划
两者的关系是:$P({\pmb x}^\ast ) = D(\lambda ^\ast )$,问题 (1a) 与问题 (1b) 的最优解相等,即原-对偶问题的对偶间隙为零.
非线性规划的原规划
非线性规划的对偶规划
其中,对偶目标函数可以借助增广的 Lagrange 函数表达为
在非线性规划理论中,上述是 Falk 形式的原-对偶规划.对于凸规划,原问题 (2a) 与其对偶问题 (2b) 的对偶间隙为零.
正项几何规划或正定几何规划的原-对偶关系远比上述复杂得多,原因是它针对高度非线性的幂函数正项多项式,借助于 Cauchy 不等式进行推导,得到的对偶规划属于线性规划的一种,其对偶规划可以用线性规划的单纯形算法求解.
线性规划和非线性规划的对偶变量源于 Lagrange 乘子,对应于每一个约束条件,或者说,对偶变量的数值表达了每一个约束对于最优解的贡献大小.正项几何规划中,对偶变量对应于原规划的目标函数和约束条件的每一项,或者说,对偶变量的数值表达了每一项对于最优解的贡献大小.也就是说,在正项几何规划中,对偶变量关注到更为细致的层次,这一特点与对偶规划可用线性规划求解的特点在一起,导致正项几何规划受到了青睐.
尽管如此,但是正项几何规划的求解范围有局限性:不仅只适用于幂函数形式的函数,而且要求函数的每一项都是正项,对于含有负项的函数不得不进行近似处理.鉴于它不具有普遍性,此处就不列出相关的原-对偶规划的数学形式了.
由于线性规划和非线性规划的对偶理论均具有普遍性,值得深入思考.虽然它们有各自的个性,例如非线性程度不同、显式与隐式的差别等等,但是它们具有共性:
(1)原-对偶问题表达的是同一个最优化问题的两个方面.
(2)当对偶间隙等于零时,可以先求解对偶问题,然后求出原问题的解.
对偶理论在结构优化中颇有应用价值.结构优化中最常见的问题大多是隐式的式 (2a),需要采用数学和力学的方法建立近似显式模型.由于设计变量数 $N$ 通常比约束数$M$大得许多,通过求解一个小得多的对偶问题式(2b),可以极大提高求解原问题的效率.在连续体结构拓扑优化中,因 $N$ 更是远大于 $M$,效率的提高更为明显.因之,ICM 方法一直采用对偶序列二次规划算法求解所建立的结构拓扑优化模型[1-3].
尽管对偶理论的应用十分有效,然而不少研究者在建模中,实际运用了同对偶规划类似的另一种规划,本文称之为互逆规划,具体作如下构造.
互逆规划的 s (single objective function,单目标) 方
互逆规划的 m (multiple objective functions,多目标) 方
表面上,互逆规划类似与原-对偶规划,实则不然,互逆规划的两方具有目标函数与约束条件相互交换位置的对应关系,故又称互逆规划为对应规划.不难看出:式 (2a) 与式 (4a) 是完全相同的.
将互逆规划同对偶规划相比较,可以列出5点不同:
(1)互逆规划是目标函数与约束条件地位相反对应的两个规划,对偶规划则是同一个问题不同表达的一对规划;
(2)相互互逆的一对规划之间没有``对偶间隙''的概念,相互对偶的一对规划之间有``对偶间隙''的概念;
(3)一对互逆规划的设计变量数目是相同的,一对对偶规划的原设计变量和对偶设计变量的数目经常会相差极为悬殊;
(4)在一对互逆规划中,通常是一个单目标问题,另一个是多目标问题;而一对对偶规划通常都是单目标问题;
(5)互逆规划的 m 方与 s 方,通常分别是不合理与合理的问题;而一对对偶规划则都是合理的问题.
至于一些研究者在结构拓扑优化的建模中,如何不自觉地运用了互逆规划的 m 方,下一节将给出详细的阐述.
2 从 MCVC 模型到 MVCC 模型
基于互逆规划的定义及其同对偶规划的比较,去审视结构优化模型,就可以做到两点:(1)表明在研究的结构优化中,确实有不合理的模型一直被沿用;
(2)找到修正不合理的模型使之合理化的方法.
以连续体结构刚度拓扑优化问题为例,被广泛研究的是 MCVC 模型,如式 (5) 所示
其中,${\pmb x}$ 为设计变量向量,$C_j $,${\pmb F}_j $ 和 ${\pmb U}_j $ 分别为第$j$号载荷工况的结构柔顺度、总载荷向量和总位移向量,$ v_i $ 为单元$i$ 的体积,$V$为结构总体积,$\overline V $ 为指定的体积上限约束.
多载荷工况下的 MCVC 模型需要处理后方能求解,通常采用权系数方式将多目标转化为单目标模型
其中,$M$ 为载荷工况数,$\alpha _j $ 为各载荷工况权重系数.
各载荷工况的权重依据经验设计. 通常采用的一种方案是取某载荷工况的载荷大小与各载荷工况的总载荷大小的比值作为权重,即
式中$P_j $ 为各载荷工况中所有载荷大小的总和.
比选取权重系数更合理的处理是把式 (5) 转化为极大极小化 (min-max) 模型
尽管 min-max 问题有各种解法例如K-S函数方法[1-3],但是求解的难度比权重系数方法更难了.
顺便指出,因式 (4b)、式 (5)、式 (6a) 和式 (7) 中均只有一个约束条件,故都转化为等式约束.
直到当下,相当多的****没有意识到,长期以来,沿用的 MCVC 模型乃是一个不合理的模型,原因在于 MCVC 模型存在 3 个不足:
(1) 追求柔顺度最小化的目标缺乏工程背景;
(2)结构体积限制数值作为优化模型中先验的参数,无论给出它的任何值,都是没有根据的;
(3) 在多载荷工况下,该模型成为难以求解的多目标函数问题.
第一个不足:使结构拓扑优化出现结构截面、结构形状等层次优化从来未曾有的目标函数——柔顺度,从而使得各层次原本一致的优化提法首次感到不再协调而扭曲了. 本质上是因为把原本的成本目标改成 工程中并不需验证的柔顺度目标.
第二个不足:优化前就给定结构体积,即给定了结构的最优构型值,剩下的工作只是在基结构的各个位置上分配体积的多少而已.好比给出一坨橡皮泥捏出一个小动物,本来总体和各部分用多少橡皮泥都是需要设计的,总体决定是捏出大象还是老鼠,各部分则是该动物的胖或瘦,而现在总体却给定了:给定了最优目标值,寻优工作降格为调配设计变量向量.可能出现很大的老鼠和很小的大象的怪现象.显然,这是先验论的导致的结果.
寻优算法有两种. 第一种是同时寻找出最优设计变量和最优目标值.第二种是首先得到了最优目标值,然后求出最优设计变量,例如:在对偶间隙为零的非线性规划求解中,先解得对偶规划的最优目标和最优设计变量向量,然后借助原-对偶变量的显式关系,得到最优原设计变量向量;正项几何规划的对偶解法虽然类似,但是从对偶最优变量求出最优原变量,不存在显式关系,只得求解复杂一点的线性方程组.
预先给定结构体积的 MCVC 模型同上述两种寻优途径皆不同,它既不是同时寻找最优目标函数值和最优设计变量向量,也不是先寻找最优目标函数值、再调配出最优设计变量向量,而是本质上对目标函数先指定出数值、然后寻找出设计变量向量.岂不令人质疑!
可见,第二个不足是严重的. 其实如下第三个不足也是严重的.
第三个不足是多目标函数求解困难的解决,现有的对策是在MCVC模型本身着手,真正的解决问题,应当是在模型之外,另辟蹊径,建立单目标函数的模型.
公正地讲,MCVC 模型对于结构拓扑优化发展的功绩是不容否定的,尤其在连续体结构拓扑优化的早期,该模型避开了建立显式的困难. 然而当今,应是走到克服MCVC模型存在的不合理特性的时候了.
如何开辟 MCVC 模型之外的合理建模路径?根据刚刚提出的新概念,MCVC模型实际是取某一对互逆规划中的 m 方,完全可以找到它对应的 s 方,给出柔顺度约束下体积最小化的 MVCC 模型
在多载荷工况下,MVCC 也不是多目标模型,仅需要对各个载荷工况下分别指定对应的结构柔顺度上限约束值.
3 结构柔顺度上限的物理意义
不难看出,给出的 MVCC 模型比 MCVC 模型合理,原因在于:(1)追求体积最小化符合工程设计的常规做法;
(2)MVCC 模型避免了 MCVC 模型选取给定体积的先验性做法;
(3)在多载荷工况下,该模型依然是单目标问题.
不过,若想用 MVCC 模型代替 MCVC 模型,还是有前提条件的:必须给出结构柔顺度约束的物理解释,并且提供结构柔顺度上限的计算途径.
为此,做一点深入的探讨,先看式 (5),其中第 $j$ 号载荷工况结构柔顺度(即 2 倍的结构应变能)为
显然,总位移向量 ${\pmb U}_j$ 越大,则结构刚度越小,即结构柔顺度越大,换句话讲,式 (9) 表明结构柔顺度是与结构刚度性质相反的量.
如何给出第 $j$ 号载荷工况结构柔顺度的上限 $\overline {C_j }$,使结构柔顺度达到某个限度,以保证结构的刚度呢?其实这是一件十分困难的事情.在各种结构设计规范中,往往控制结构最大变形点的位移,不仅给不出整体位移即结构柔顺度的控制值,而且即使单点的位移控制值,也只是凭经验的规定.
似乎陷入了困境,其实换写结构柔顺度为单元柔顺度之和的形式,就能够走出``柳暗花明''的境地
每个单元的柔顺度平等地依赖于单元的应力和应变,而应力与强度相关联,应变与刚度相关联. 强度在材料力学中, 已经由经验上升为科学了.
为此,应当从对于强度贡献的角度,重新认识结构柔顺度.必要的做法是:借助于广义郑玄-虎克定律的弹性矩阵 ${\pmb D}$ (由弹性模量、剪切模量和泊松比组成),用应力表示应变 ${\pmb\varepsilon}_{ij} = {\pmb D}^{ - 1} {\pmb\sigma} _{ij}$,于是,式 (10) 转化为式 (11)
从式 (11) 看,结构柔顺度也是结构整体的强度指标了.式 (9) 与式 (11) 分别给出了结构刚度和结构强度指标的诠释,二者是否因此而矛盾呢?其实相反,它恰恰说明刚度和强度是同一个力学性能的两个方面,广义郑玄-Hooke 定律的弹性矩阵早就联通了这两个方面.
如何借助式(11)推得出结构柔顺度上限 $\bar {C}$? ICM (independent, continuous and mapping) 方法,提出了全局化应力约束的概念$^{[1\hbox{-}3,27\hbox{-}28]}$,而且是用之表述结构柔顺度上限约束的一种形式.对某点的 Mises 应力,其表达式为
其中,$\sigma _{\rm m} $ 为 Mises 应力,$\sigma _1 $, $\sigma_2 $ 及 $\sigma _3 $ 为 3 个主应力.
而单元的畸变比能为
式中, $E$ 和 $\mu $ 分别为材料的弹性氏模量和泊松比.
按第四强度理论,应力约束可写为
其中,$[\sigma ]$ 为材料许用应力.
将式 (14) 代入式 (13) 得
很可惜,式 (15) 的左边不是单元应变比能,而是单元畸变比能,因而目前尚不能建立单元应变能与材料许用应力之间的强度条件. 不过,由于单元应变比能大于或等于单元畸变比能
其中,$e_i $ 及 $v_i$ 分别为单元 $i$ 的应变能及体积;所以,在式 (15) 的不等式中间插入单元应变能,即
强度条件式 (15) 是偏于安全的,这是对于单元应力约束式 (14) 用单元应变能的近似替换.
对所有单元求和得到结构应变能 $\varXi $
上式在 ICM 方法中被称为全局性应力约束不等式.而在本文中,式 (18) 给出了结构应变能(即柔顺度/2) 上限 $\bar{C}$,或 者称为结构许用应变能 $[\varXi ] = \bar {C} / 2$
推导的结果对于结构柔顺度上限有了明确的物理解释,也得到了简洁的计算方法.从而印证了 MVCC 模型的合理性.
必须指出,MVCC 模型尚不能完全代替所有的应力约束,因为全局性满足的应力约束条件不能保证应力在每一点都满足约束,它的求和方式只是满足了必要条件而不是充分条件.
这种全局性特点极大减少了约束数目,而且能够在连续体结构拓扑优化中得到最佳传力路径,若想应力约束的逐一满足,可以很容易地补充其他措施予以实现.
虽然本文主旨在于讨论互逆规划及其用于合理建立结构拓扑优化模型,但是顺便叙述一下如何在MVCC模型上作少许修补,使之能够容易 适用应力约束问题,以飨感兴趣的读者朋友.限于篇幅,下面予以简单介绍.
通常在载荷作用点及边界等个别部位,可能存在应力超过许用应力.为尽量减少应力超限单元的数量,可以采用对结构许用应变能约束值进行修正的办法,即
其中[2-3]
为使应力约束达到应力饱满状态,仿造满应力公式,对式 (20) 修正的应力等效的全局应变能约束值在迭代过程中进行动态调整
其中,$\overline \varXi ^{(k)}$ 及 $\overline \varXi ^{(k +1)}$为第 $k$ 及第 $k+1$ 步的全局应变能约束值,$[\sigma ]$ 为许用应力值,$\sigma _{\max }^{(k)} $ 为第 $k$ 步的结构最大 Mises 应力.
5 数值算例
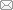
为了便于进行数值比较,本文针对结构拓扑优化问题:分别编制了 MCVC 模型和 MVCC 模型的程序.优化求解器 采用针对一类可分离凸规划的对偶显式求解 DP-EM (explicit model of dual programming) 方法[29-30],也可用 ICM 法中常用的序列二次规划法$^{[1 \hbox{-}3]}$. 收敛准则采用与文献[31] 相同的准则.计算了一批算例,篇幅所限,仅列举1个例题.单工况MBB梁拓扑优化,基结构宽为 300 mm、高 50 mm,集中载荷 $F=200$ N 作用于跨中顶点,左、右下角分别为铰支及滑动铰支约束,材料弹性模量 $E =210$ GPa,泊松比为 0.3.取一半结构进行分析,计算简图如图 1 所示,采用150$\times $50网格.为避免应力集中,$F$ 分散作用在相邻的 4 个结点上,右下角竖向约束也分散在 2 个结点上.过滤半径为 1.5 mm, MCVC 模型的惩罚因子取 $p=3$,收敛精度分别取 0.01.
图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1MBB梁问题取一半结构进行分析及优化的模型
Fig.1Half of structure for analysis and optimization of the MBB beam
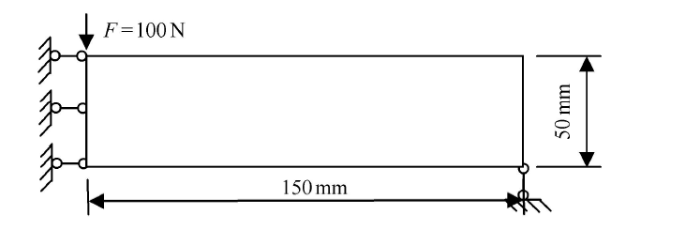
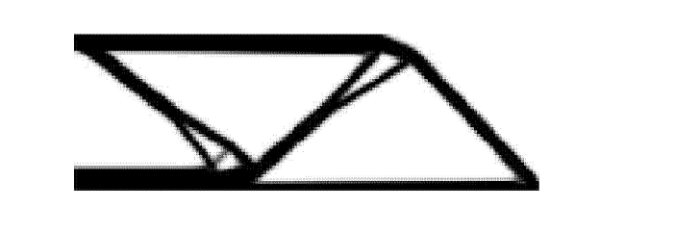
许用应力 $[\sigma ] = 100$ MPa,按式 (19) 计算得到 $[\varXi ]= 150.76$ N$\cdot$mm,对应基结构时的结构应变能为 $\varXi ^0 =2.72$ N$\cdot$mm,从而按式(20)计算得到 $\xi =0.040 3$,$\overline \varXi = 6.07$ N$\cdot$mm.计算得到体积极小为目标,全局应变能约束下 (MVCC 模型)的最优拓扑如图 2 所示.对应的 Mises 应力分布如图 3 所示. 最优体积比为 29.96%. 最大应力为 100.00 MPa.
图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2MVCC 得到的最优拓扑
Fig.2Optimized topology obtained by the MVCC model
图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3MVCC 模型得到最优拓扑的Mises应力分布
Fig.3Mises stress distribution of the optimized topology obtained by the MVCC model
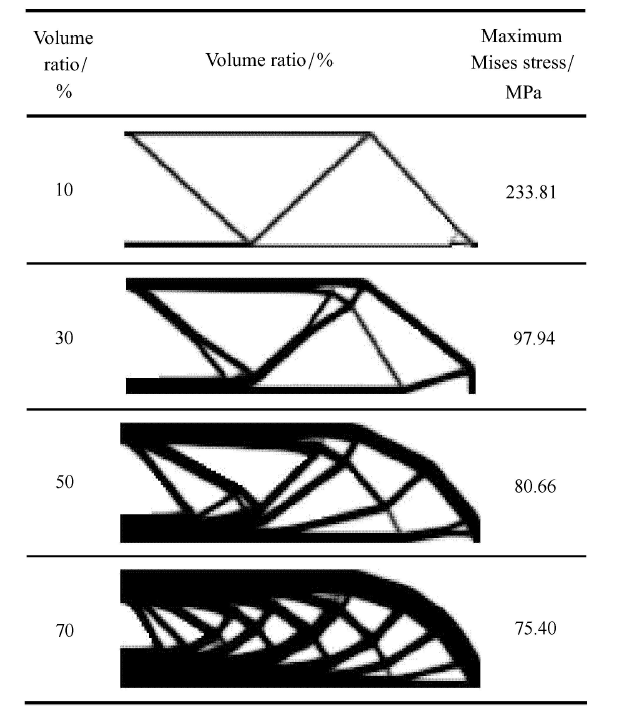
采用不同的体积比约束值,计算得到体积约束下结构柔顺度极小化 (MCVC 模型)的最优拓扑图形及对应结构最大 Mises 应力如表 1 所示.
Table 1
表1
表1MCVC 模型不同体积比约束时得到的不同拓扑及对应的最大 Mises 应力
Table 1
 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
对比可以看到,MVCC 模型可以关联上全局化应力约束条件,对应于应力约束值 100 MPa,得到唯一的最优拓扑.但 MCVC 模型对不同的体积比约束值,会得到不同的最优拓扑,对应的最大 Mises 应力也不同.无法预先通过指定体积比约束值使得最优拓扑结构的应力满足约束强度条件.
多工况的算例计算结果同样验证了上述结论,篇幅所限,不再列举.
6 结语
本文的贡献体现在数学规划和结构拓扑优化模型的合理性两个方面:(1)对比对偶规划概念,提出了互逆规划的概念,详细阐述了两种规划之间的区别.
(2)在结构拓扑优化中应用互逆规划理论,明确了 MCVC 模型与 MVCC 模型并不是一对对偶规划问题,而是一对互逆规划问题.
(3)作为互逆规划的 m 方的 MCVC 模型在不同的体积比下,会得到不同的最优拓扑,实际工程中难以确定选用哪一个是合理的.不同方案的强度指标是不同的,但预先又无法确定一个体积比约束能够使强度条件正好满足.
(4)MCVC 模型在多工况情况下,还面临不同工况的柔顺度在进行多目标组合时的加权困扰,因为指定不同的加权系数会得到不同的最优拓扑,导致此模型的合理性受到质疑.
(5)借助于互逆规划,推导得到了作为互逆规划s方的 MVCC 模型,其合理性体现在多载荷工况下,它也是一个单目标问题,同时免除了 MCVC 模型先验决定体积上限的不合理性.
(6)阐释了 MVCC 模型中结构柔顺度约束的物理意义,并且推导出来了结构柔顺度约束上限或称为许用结构应变能的计算公式,进一步说明了 ICM 方法关联于全局化应力约束的工作.
(7)介绍了在 MVCC 模型上稍加处理就可以较满意地解决结构拓扑优化的应力约束问题,该算法极大地节省了应力约束处理的昂贵计算量.
(8) 数值算例验证了 MCVC 模型存在的不足以及 MVCC 模型的合理性.
从互逆规划的观念出发,呼吁从事结构优化的国内外同仁们,能够关注本文所意识到的问题及其对策,以便使包括连续体拓扑在内的结构优化研究,能够与时俱进、稳健地得到发展.
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 4]
[本文引用: 4]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 6]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID

Although the twin support vector regression (TSVR) method has been widely studied and various variants are successfully developed, the structural risk minimization (SRM) principle and model's sparseness are not given sufficient consideration. In this paper, a novel nonparallel support vector regression (NPSVR) is proposed in spirit of nonparallel support vector machine (NPSVM), which outperforms existing twin support vector regression (TSVR) methods in the following terms: (1) For each primal problem, a regularized term is added by rigidly following the SRM principle so that the kernel trick can be applied directly to the dual problems for the nonlinear case without considering an extra kernel-generated surface; (2) An ε-insensitive loss function is adopted to remain inherent sparseness as the standard support vector regression (SVR); (3) The dual problems have the same formulation with that of the standard SVR, so computing inverse matrix is well avoided and a sequential minimization optimization (SMO)-type solver is exclusively designed to accelerate the training for large-scale datasets; (4) The primal problems can approximately degenerate to those of the existing TSVRs if corresponding parameters are appropriately chosen. Numerical experiments on diverse datasets have verified the effectiveness of our proposed NPSVR in sparseness, generalization ability and scalability.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

A generalization of the Moving-Domain Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics (MoD-QM/MM) hybrid method [Gascon, J. A.; Leung, S. S. F.; Batista, E. R.; Batista, V. S. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2006, 2, 175-186] is introduced to provide a self-consistent computational protocol for structural refinement of extended systems. The method partitions the system into molecular domains that are iteratively optimized as quantum mechanical (QM) layers embedded in their surrounding molecular environment to obtain an ab initio quality description of the geometry and the molecular electrostatic potential of the extended system composed of those constituent fragments. The resulting methodology is benchmarked as applied to model systems that allow for full QM optimization as well as through refinement of the hydrogen bonding geometry in Oxytricha nova guanine quadruplex for which several studies have been reported, including the X-ray structure and NMR data. Calculations of (1)H NMR chemical shifts based on the gauge independent atomic orbital (GIAO) method and direct comparisons with experiments show that solvated MoD-QM/MM structures, sampled from explicit solvent molecular dynamics simulations, allow for NMR simulations in much improved agreement with experimental data than models based on the X-ray structure or those optimized using classical molecular mechanics force fields.
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Active development of quantum informational components such as quantum computers and quantum key distribution systems requires parameter characterization of single photon detectors. A key property of the single photon detectors is detection efficiency. One of the methods of the detection efficiency measurement, as listed in the international standard ETSI, is the reference-free twin-photon-based Klyshko method. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of this method depends on the combination of the pump wavelength, the nonlinear crystal's axis angle, and the type of detector's sensitive element. When the combination is difficult, one has to deal with the low SNR of the detector counts measurement. To gain the high SNR, one has to average the long record complicated with the "random telegraph signal" noise. This type of noise exhibits high spectral density at a zero frequency, where simple averaging works. The heterodyne based method we have proposed is to perform averaging at the higher frequency of the modulation introduced to the standard Klyshko measurement scheme. The method was numerically simulated and experimentally tested. The 14 times improvement in SNR for the proposed method relative to the simple averaging was demonstrated by the numerical simulation and confirmed experimentally.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

We propose a novel dynamic image reconstruction method from PET listmode data that could be particularly suited to tracking single or small numbers of cells. In contrast to conventional PET reconstruction our method combines the information from all detected events not only to reconstruct the dynamic evolution of the radionuclide distribution, but also to improve the reconstruction at each single time point by enforcing temporal consistency. This is achieved via optimal transport regularization where in principle, among all possible temporally evolving radionuclide distributions consistent with the PET measurement, the one is chosen with least kinetic motion energy. The reconstruction is found by convex optimization so that there is no dependence on the initialization of the method. We study its behaviour on simulated data of a human PET system and demonstrate its robustness even in settings with very low radioactivity. In contrast to previously reported cell tracking algorithms, our technique is oblivious to the number of tracked cells. Without any additional complexity one or multiple cells can be reconstructed, and the model automatically determines the number of particles. For instance, four radiolabelled cells moving at a velocity of 3.1 mm/s and a PET recorded count rate of 1.1 cps (for each cell) could be simultaneously tracked with a tracking accuracy of 5.3 mm inside a simulated human body.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]

提出和论证了改善保守近似的展开“准则”及其定理;提出了基于两点累积信息的原/倒变量近似、论证了其凸凹性不变的优点;提出了应用它的对偶优化方法及其在桁架优化的实现;提出和证明了有关收敛性定理。
URL [本文引用: 1]

提出和论证了改善保守近似的展开“准则”及其定理;提出了基于两点累积信息的原/倒变量近似、论证了其凸凹性不变的优点;提出了应用它的对偶优化方法及其在桁架优化的实现;提出和证明了有关收敛性定理。
DOIURL [本文引用: 2]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

The aim of this article is to evaluate and compare established numerical methods of structural topology optimization that have reached the stage of application in industrial software. It is hoped that our text will spark off a fruitful and constructive debate on this important topic.
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

In this study, the PMUs are placed to operate in normal and islanded cases taking into account power system observability, reliability, Communication Infrastructure (CI), and latency time associated with this CI. Moreover, the economic study for additional new data transmission paths is considered as well as the preexisting Communication Devices (CDs) and the availability of predefined locations of some PMUs in some buses. The PMUs placement and their communication network topology and link channel capacity are co-optimized simultaneously. Two different approaches are applied to optimize the objective function; the first approach is combined from Binary Teaching Learning Based Optimization Algorithm (BTLBOA) and the Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) algorithm, while the second approach is based on BTLBOA. The proposed approaches are examined using IEEE 118-bus systems.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

Along with supernumerary bones, sesamoids, defined as any organized intratendinous/intraligamentous structure, including those composed of fibrocartilage, adjacent to an articulation or joint, have been frequently considered as enigmatic structures associated with the joints of the skeletal system of vertebrates. This review allows us to propose a dynamic model to account for part of skeletal phenotypic diversity: during evolution, sesamoids can become displaced, attaching to and detaching from the long bone epiphyses and diaphysis. Epiphyses, apophyses and detached sesamoids are able to transform into each other, contributing to the phenotypic variability of the tetrapod skeleton. This dynamic model is a new paradigm to delineate the contribution of sesamoids to skeletal diversity. Herein, we first present a historical approach to the study of sesamoids, discussing the genetic versus epigenetic theories of their genesis and growth. Second, we construct a dynamic model. Third, we present a summary of literature on sesamoids of the main groups of tetrapods, including veterinary and human clinical contributions, which are the best-studied aspects of sesamoids in recent decades. Finally, we discuss the identity of certain structures that have been labelled as sesamoids despite insufficient formal testing of homology. We also propose a new definition to help the identification of sesamoids in general. This review is particularly timely, given the recent increasing interest and research activity into the developmental biology and mechanics of sesamoids. With this updated and integrative discussion, we hope to pave the way to improve the understanding of sesamoid biology and evolution.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

We propose a fictitious domain method for topology optimization in which a level set of the topological derivative field for the cost function identifies the boundary of the optimal design. We describe a fixed-point iteration scheme that implements this optimality criterion subject to a volumetric resource constraint. A smooth and consistent projection of the region bounded by the level set onto the fictitious analysis domain simplifies the response analysis and enhances the convergence of the optimization algorithm. Moreover, the projection supports the reintroduction of solid material in void regions, a critical requirement for robust topology optimization. We present several numerical examples that demonstrate compliance minimization of fixed-volume, linearly elastic structures.
DOIURLPMID [本文引用: 1]

The dynamic structural development of plants can be seen as a strategy for exploiting the limited resources available within their environment, and we would expect that evolution would lead to efficient strategies that reduce costs while maximizing resource acquisition. In particular, perennial species endemic to habitats with shallow soils in seasonally dry environments have been shown to have a specialized root system morphology that may enhance access to water resources in the underlying rock. This study aimed to explore these hypotheses by applying evolutionary algorithms to a functional-structural root growth model.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
URL [本文引用: 1]

利用Mises强度理论,提出了应力约束全局化策略,将局部的应力约束问题转化为结构整体的应变能约束问题. 基于ICM(独立、连续、映射)方法,引入了独立、连续的拓扑变量,对单元重量、单元刚度和单元许用应力的过滤函数进行了选择,建立了以重量为目标,以结构应变能代替应力约束的多工况下连续体结构拓扑优化模型,寻找到了多工况下的最佳传力路径. 运用对偶二次规划方法对上述优化模型进行了求解. 另外,利用PCL语言,在MSC/PATRAN的开发平台上,实现了应用应力约束全局化策略进行连续体结构拓扑优化的模块化处理. 数值算例表明了该方法的可行性和有效性.
URL [本文引用: 1]

利用Mises强度理论,提出了应力约束全局化策略,将局部的应力约束问题转化为结构整体的应变能约束问题. 基于ICM(独立、连续、映射)方法,引入了独立、连续的拓扑变量,对单元重量、单元刚度和单元许用应力的过滤函数进行了选择,建立了以重量为目标,以结构应变能代替应力约束的多工况下连续体结构拓扑优化模型,寻找到了多工况下的最佳传力路径. 运用对偶二次规划方法对上述优化模型进行了求解. 另外,利用PCL语言,在MSC/PATRAN的开发平台上,实现了应用应力约束全局化策略进行连续体结构拓扑优化的模块化处理. 数值算例表明了该方法的可行性和有效性.
URL [本文引用: 1]

由于应力约束按单元计,加之多工况,使得连续体结构拓扑优化由于约束数目太多,导致应力敏度分析计算量太大而无法接受。基于第四强度理论提出了应力约束条件全局化处理的方法,化为全局替代约束——总应变能约束,用ICM方法对总应变能约束条件下的连续体结构拓扑优化进行建模及求解,其过程分为三步:第一步选择最大应变能对应的工况,在给定重量下求出最小结构总应变能;第二步提出一个数值经验公式,借助第一步的结果,计算出各工况下的许用总应变能;第三步以第二步计算出来的各工况的许用总应变能作为约束,以重量为目标建立模型并求解。顺便指出,第二步的处理方法可以处理载荷相差特别大的情况,即病态载荷情况。数值算例表明:全局性应力约束可以更好地得到传力路径,对于处理多工况问题具有优势。
URL [本文引用: 1]

由于应力约束按单元计,加之多工况,使得连续体结构拓扑优化由于约束数目太多,导致应力敏度分析计算量太大而无法接受。基于第四强度理论提出了应力约束条件全局化处理的方法,化为全局替代约束——总应变能约束,用ICM方法对总应变能约束条件下的连续体结构拓扑优化进行建模及求解,其过程分为三步:第一步选择最大应变能对应的工况,在给定重量下求出最小结构总应变能;第二步提出一个数值经验公式,借助第一步的结果,计算出各工况下的许用总应变能;第三步以第二步计算出来的各工况的许用总应变能作为约束,以重量为目标建立模型并求解。顺便指出,第二步的处理方法可以处理载荷相差特别大的情况,即病态载荷情况。数值算例表明:全局性应力约束可以更好地得到传力路径,对于处理多工况问题具有优势。
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]
