INDEPENDENT CONTINUOUS MAPPING METHOD FOR STRESS CONSTRAINT 1)
Long Kai*,2), Wang Xuan??, Ji Liang*收稿日期:2018-05-28接受日期:2018-12-30网络出版日期:2019-03-18
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-05-28Accepted:2018-12-30Online:2019-03-18
作者简介 About authors
2)龙凯,副教授,主要研究方向:连续体结构拓扑优化、材料拓扑优化设计.E-mail:longkai1978@163.com

摘要
大多数已有的拓扑优化研究为系统刚度最大化设计,尤其以体积比约束下的静态柔顺度最小化问题为典型.从工程角度出发,结构强度设计至关重要.以往的应力研究表明,应力约束拓扑优化存在着奇异性、约束数目庞大、高度非线性特性等诸多数值困难.为了实现应力约束下的拓扑优化设计,采用归一化p范数应力指标以减少单元应力约束数目.遵循独立连续映射建模方式,引入密度变量的倒变量函数作为设计变量.推导了应力约束函数和体积目标函数对设计变量的敏度,并基于一阶和二阶泰勒近似得到各自的显式表达式.通过构造的系列二次规划子问题,原拓扑优化问题采用序列二次规划算法高效求解.二维数值算例考察了结构刚度和强度设计结果的异同,以及不同应力约束上限值对应力约束拓扑优化结果的影响.通过提出方法与传统变密度法结果的比较,说明提出的独立连续映射方法在应力约束下具有可行性和有效性.优化结果也表明了考虑应力约束的连续体拓扑优化具有必要性.
关键词:
Abstract
Most existing study on topology optimization have concentrated on maximizing the system stiffness. Especially, the minimization of static compliance subject to the volume fraction is widespread in the formulation. From the engineering point of view, structural strength design is of vital importance. Past study on stress constraint have shown that an amount of numerical difficulties with the stress-constrain topology optimization exist including the so-called singularity, vast of stress constraints, highly nonlinear behavior and so on. To achieve the topological design under stress constraint requirement, the normalized stress measure using p-norm function is adopted for the reduction of stress constraints. Following the modeling manner of independent continuous mapping method, the reciprocal function of relative density is regarded as the design variables. The sensitivities of stress constraint and volume objective with respect to the design variable are derived, and their explicit expressions are formulated based on the first-order and second-order Taylor approximation respectively. By setting up the sub-problem in the form of a quadratic program, the original topology optimization problem is efficiently solved using the sequential quadratic programming approach. The difference between stiffness and strength design, as well as the effect of various upper bounds of stress value on the optimized results for stress constraint are investigated in 2D numerical examples. Through the comparison of the proposed method and traditional variable density method, the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed optimization approach in stress constrained problems are verified. The results also demonstrate that the consideration of stress constraint in continuum structure is indispensable.
Keywords:
PDF (8945KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
龙凯, 王选, 吉亮. 面向应力约束的独立连续映射方法 1). 力学学报[J], 2019, 51(2): 620-629 DOI:10.6052/0459-1879-18-169
Long Kai, Wang Xuan, Ji Liang.
引 言
自1988年Bendsoe和Kikuchi[1]提出连续体结构拓扑优化概念以来,拓扑优化方法及应用得到了广泛的关注[2-5].早期的拓扑优化研究大多集中在结构刚度设计上,以体积比约束下的结构柔顺度最小化问题最为典型.强度要求是工程结构设计必须满足的条件之一. 基于强度要求的拓扑优化设计分为应力约束和最大应力最小化两类. 对于工程问题来说,一味降低最大应力会造成结构的冗余,应力约束下的结构重量最小化模型更符合工程习惯,但涉及到的理论问题也更困难. 应力约束问题的难点之一在于设计空间的退化,程耿东和郭旭[6]首先发现了应力约束中设计空间的奇异性问题,并提出了$\varepsilon$松弛列式解决方法. 基于单元各向同性惩罚微结构(solid isotropic microstructures with penalization, SIMP)方法求解应力约束问题,拓扑优化列式中包含大量的局部单元应力约束方程,导致了优化求解的困难. 一种解决思路是利用最大值包络函数以取代局部应力约束,常见包络函数有$p$范数[7]和KS范数[8]. 除上述数值问题外,应力约束具有高度非线性特征. 这种非线性特征体现在优化结果对优化模型参数、求解器参数高度敏感,优化迭代易出现反复震荡. 正因为如此,一些文献的处理方法是在拓扑优化模型中增加了柔顺度约束或目标,通过正则化处理达到稳定优化求解的目的[9-10]. 在现有的SIMP方法中,为了抑制棋盘格现象,通常采用密度过滤或节点密度变量,这也不可避免带来了最终设计存在着中间密度单元[11]. 此外,文献[12]指出即使应用了过滤措施,应力约束拓扑优化结果仍存在着网格依赖性现象.
应力相关的拓扑优化研究也延伸到水平集方法[13-14]和双向渐进式拓扑优化方法[15-17]中.最大应力通常发生在结构的内外边界,而水平集下的拓扑优化结果具有光滑且界面清晰的轮廓,在应力约束问题解决上具有一定的优势.
隋允康等[18]于1996年提出独立连续映射(independent continuous mapping, ICM)方法,方法引入单元密度倒数函数作为设计变量,将优化模型巧妙处理成线性约束下的二次规划,配合序列二次规划法求解,具有稳健、高效的优势. 迄今为止,ICM方法在应力、节点位移、固有频率、屈曲因子等约束下的研究成果集中体现在专著中[19-20]. 近年来,方法在多相材料拓扑优化、瞬态热传导问题、材料与结构一体化中也有所发展[21-23]. 在应力约束问题上,早期的ICM方法沿袭了满应力法的优化策略[24]. 在此之后,利用第四强度理论,将单元应力约束转化为单元应变能约束,采用总应变能约束这一必要条件来取代单元应变能约束[25-27]. ICM方法也尝试采用抛物线型凝聚函数实现单元应变能的约束[28].
尽管总应变能约束能从结构整体上把握结构传力路径,但在局部应力的处理上仍不完善. 本文以结构总体积最小化为目标,单元应力为约束建立拓扑优化模型. 通过$p$范数函数来包络单元应力函数. 遵循ICM方法建模原则,引入了单元倒变量函数为设计变量,分别以一阶泰勒和二阶泰勒近似表达应力约束和体积目标函数. 在形成的二次规划近似模型上,采用序列二次规划算法求解. 最后通过经典二维数值算例验证了方法的可行性和有效性.
1 应力约束下的拓扑优化建模与求解
1.1 拓扑优化建模
以体积最小化为目标、单元应力为约束建立拓扑优化模型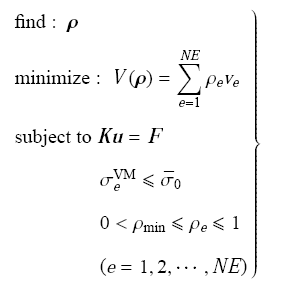
式中,$\rho_{e}$为单元$e$的密度变量;$\sigma _e^{\rm VM}$为单元的等效应力,其数学表达式见后面的推导.$\bar {\sigma }_0$为实体材料的强度. 单元最小密度值$\rho_{\min}$用于避免结构分析和优化中的数值奇异性,取值$\rho_{\min}=1.0\times 10^{-3}$.$NE$为设计域内单元总数.
单元弹性矩阵${\pmb D}_{e}$采用幂指数插值表达
式中,$\alpha$为弹性矩阵插值参数,取值$\alpha =3$. 由式(2)可知,当单元密度值为1,对应的弹性矩阵为${\pmb D}_{0}$,单元应力表达式为
式中,${\pmb B}_{\rm c}$为单元中心处的应变矩阵,${\pmb u}_{e}$为单元$e$的位移列阵.
单元应力分量表达式为
基于$ \bar{\pmb \sigma }_e$计算的等效应力表达为
根据第四强度理论,${\pmb M}$表达式为
为了消除应力约束的奇异性,材料强度设置为密度变量的函数,采用幂指数惩罚模型有
式中$\beta$为强度惩罚参数.
优化模型(1)中的应力约束方程可表达为
即
令$\gamma = \alpha-\beta$,定义单元惩罚应力和对应的等效应力为
约束方程简化为
1.2 应力约束的凝聚化处理
拓扑优化模型中的应力约束个数与单元数相关,约束方程数量庞大导致优化求解的困难. 这里采用包络函数以减少约束数目式中,$p$为包络参数.$p$趋于无穷大时,$\sigma^{\rm PN}$等同 于$\max(\sigma _e^{\rm VM} / \bar {\sigma }_0)$,应力约束方程表达为$\sigma^{\rm PN} \leqslant$1.$p$取值过大将使得包络函数的非线性程度增大,导致优化求解过程反复震荡. 当$p$取值较小,凝聚函数无法取代包络对象的最大值. 为了克服该缺陷,引入修正系数的约束方程表达为
式中$cp$为修正系数. 在每一轮轮优化求解前,修正系数通过下式计算得到
1.3 敏度分析与应力约束的显式表达
由式(12)可得以平面结构为例,设单元$e$应力分量为$ \{ \sigma _{ex}$,$\sigma _{ey}$,$ \tau _{exy} \}^{\rm T}$,$\sigma _e^{\rm VM}$对应力分量的偏导数为
由式(10a)两边对密度变量求导可得
当且仅当$i= e$时,$\frac{\partial \rho _e^\gamma }{\partial \rho _i } \ne 0$,则
静力学平衡方程${\pmb K}{ \pmb U} ={\pmb F}$两边对$\rho_i$求导得
即
由此可得
则有
当外界载荷具有设计无关性时,则$\frac{\partial {\pmb F}}{\partial \rho _e } ={\bf 0}$.
建立伴随方程
则
由式(24)得到敏度值后,采用数学规划求解类算法更新变量,如序列线性规划、凸线性化(convex linearization, CONLIN)[29]、移动渐进线法(method of moving asymptotes, MMA)[30-31]等,上述常见优化求解算法均基于一阶敏度信息求解.
1.4 ICM优化建模与求解
遵循ICM方法建模思路,引入密度的倒变量函数作为设计变量由式(25)可得
基于链式求导法则有
将体积函数采用设计变量表达为
由此可得体积函数的一阶、二阶敏度表达式为
基于上述敏度信息,应力约束函数采用一阶泰勒展开得到显式表达式
式中上标$l$代表第$l$轮优化迭代.
总体积目标函数采用二阶泰勒展开得到显式表达式,忽略其常数项可得优化模型(1)的近似子模型列式
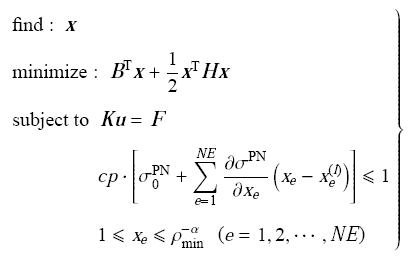
式中列阵${\pmb B}$由体积函数的一阶敏度组成,${\pmb H}$为仅对角线非零的海瑟 (Hessian) 矩阵.优化列式(32)是标准的二次规划模型,为了克服拓扑优化中设计变量庞大的困难,通常转化为对偶模型并采用二次规划算法(sequential quadratic programming, SQP)求解,具体过程可参考文献[19,20].
为了稳定优化求解,引入了运动极限M($m >0$). 在每一轮优化迭代中单元密度值变化范围为
优化数值算例经验表明,$ m$对优化求解的稳定性影响较大. 设计变量$x_{e}$在每轮优化迭代的限定范围为
为消除拓扑优化结果中的棋盘格现象,ICM方法采用了数字图像处理中的过滤方法[32 -33].
2 数值算例与讨论
本节采用二维结构数值算例来验证所提方法的可行性和有效性. 不失一般性,算例中的材料和尺寸数据为无量纲量,材料的弹性模量和泊松比值分别为1和0.3,平面厚度为1. 初始结构的单元密度值取1,即设计区域全部为实体材料,对应的参考体积为$V_{0}$. 各数值算例中的包络函数参数$p =8$,惩罚应力参数$\gamma =0.8$,运动极限$m =0.02$. 为了方便结构后处理,以优化结构体积与初始结构体积的比值$V/V_{0}$作为目标函数.算例1$L$型结构尺寸及边界条件如图1(a)所示,顶端全约束,右上角点受到垂直向下的载荷作用.为了避免应力集中,载荷均 匀分布在如图1所示的6个邻近节点上.初始结构应力分布如图1(b)所示,最大应力位置发生$L$型结构拐点处,最大值为0.777. 设许用应力值为0.55.基于本文方法的体积比和最大应力优化迭代历程如图2所示. 拓扑优化结构及对应的应力分布如图3所示.
图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1L型结构示意图及初始结构应力分布
Fig.1Illustration of L-shape structure and corresponding stress distribution of the initial design
图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2基于ICM方法的体积比和最大应力迭代历程
Fig.2Iteration histories of volume fraction and maximum stress based on ICM method
图3
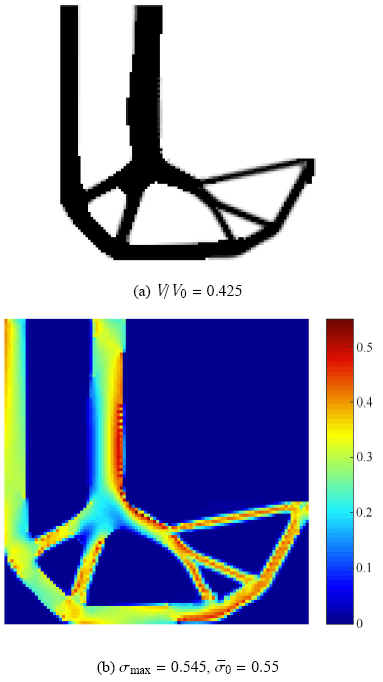 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3基于ICM方法的拓扑优化结果
Fig.3Optimized results based on ICM method
为了说明ICM方法的可行性,优化结果将与基于MMA算法求解的SIMP方法对比,由于无法严格满足设定的收敛条件,指定最大优化迭代步为200步,拓扑优化结构及其对应的应力分布如图4所示.
图4
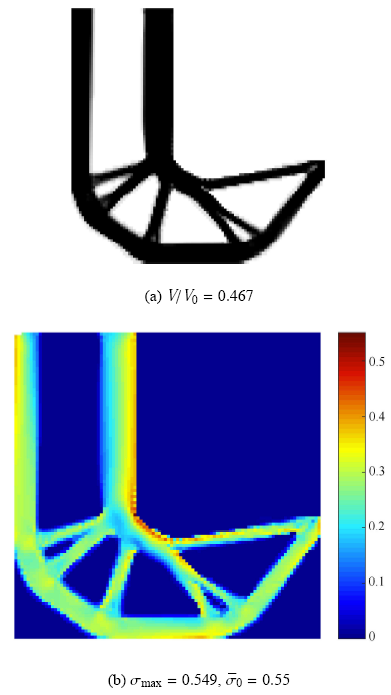 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4基于SIMP方法的拓扑优化结果
Fig.4Optimized results based on SIMP method
由图3和图4结果对比可知,原有应力集中的拐角处均演化为圆弧结构,从而大大缓解了应力集中,两种方法下的拓扑优化设计均满足应力约束要求.
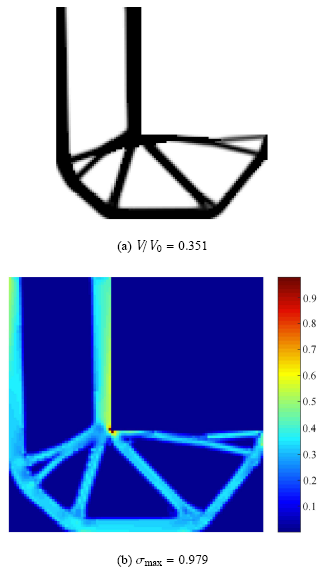
算例2 在算例1中,ICM方法得到的拓扑优化结构具有柔顺度值(compliance)248.64. 以往的ICM方法通常设置总应变能约束来实现全局应力约束,为了说明与以往方法的区别,指定该柔顺度值为约束上限值,采用ICM方法求解体积最小化问题,得到的拓扑构型及应力分布如图5所示.
图5
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5柔顺度约束下的拓扑优化结果
Fig.5Optimized results subject to compliance constraint
由图3和图5对比可知,刚强度要求下的优化设计结果有所不同. 在刚度设计要求下,$L$型梁保留了原有直角结构,无法消除应力集中现象. 以往的ICM方法在处理全局应力约束时,采用总应变能约束,能够在整体上把握传力路径特征,但是无法实现结构的细节设计,优化结果进一步说明了考虑局部应力约束的拓扑优化设计具有必要性.
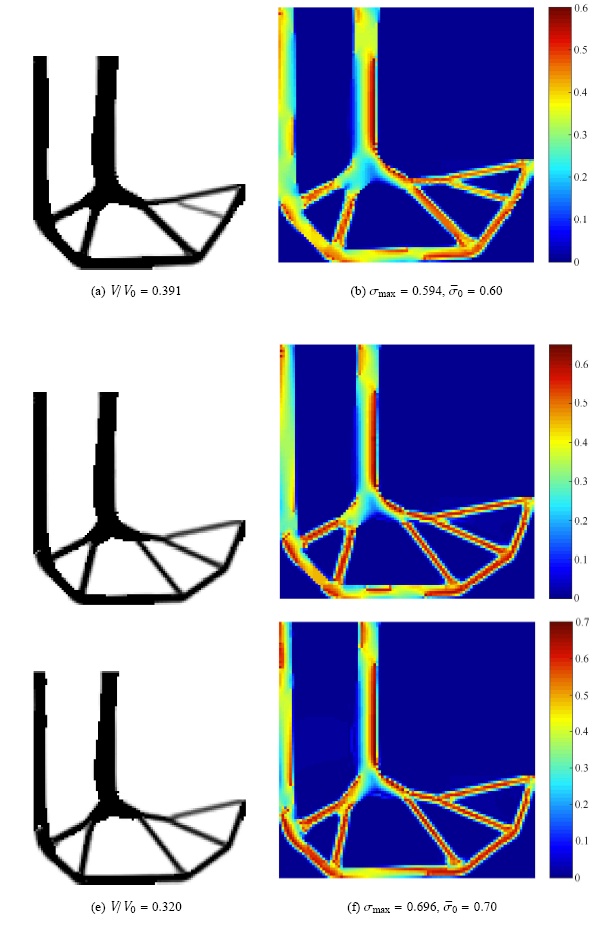
算例3 为了考察不同约束限制对拓扑优化结果的影响,取许用应力约束上限为0.6,0.65和0.7,不同应力约束下的拓扑优化结果如图6所示.
图6
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6不同强度约束下的拓扑优化结果
Fig.6Optimized results under various strength requirement
由图6可知,材料强度越高,则优化结构越轻,这一优化结果符合工程直觉.不同材料强度下的结构应力分布均匀,发挥了整个结构的潜力,达到了轻量化设计的目的.
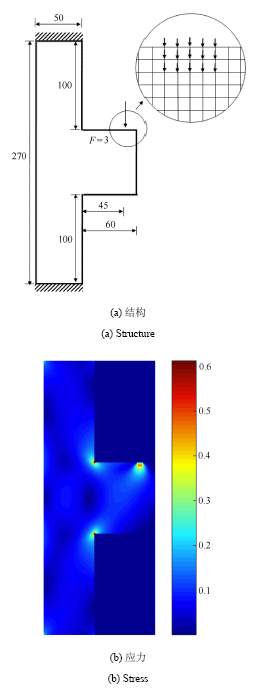
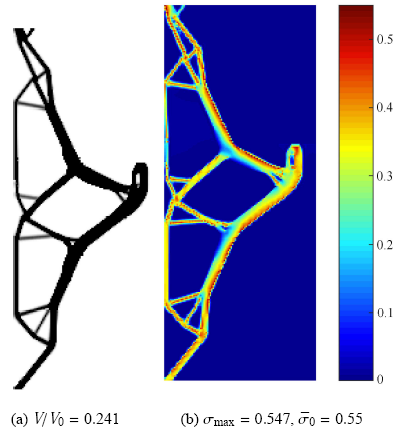
算例4 结构尺寸及边界条件如图7(a)所示,其中上下端全约束,结构右侧受到垂直向下的载荷作用,为了避免应力集中,载荷均匀分布在如图所示的15个节点上. 结构的两个直角拐角均为应力集中区域. 初始结构的应力分布如图7(b),其最大应力值为0.612,设许用应力值为0.55. 基于ICM方法得到的拓扑优化结构及应力分布如图8所示.
图7
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图7结构示意及初始结构应力分布
Fig.7Illustration of design domain and corresponding stress distribution of the initial design
图8
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图8基于ICM方法的拓扑优化结果
Fig.8Optimized results based on ICM method
由图8可知,原有结构的直角部分演化成略带圆角的形状,结构的应力分布均匀,最大应力值小于材料强度值,满足设定应力约束要求. 相比较原结构,在应力约束值比原有结构应力最大值还小的情况下,结构体积大幅下降. 上述结果分析证明了本文提出方法在指定应力约束下的拓扑优化中具有可行性和有效性.
3 结 论
应力约束下的结构拓扑优化具有重要的工程意义,本文提出面向应力约束的独立连续映射拓扑优化方法. 方法分别对单元应力和材料强度进行插值处理;为了减少单元应力约束方程个数,基于包络函数建立应力约束方程,推导了相应敏度表达式. 遵循ICM建模思路,建立了体积最小化和应力约束的拓扑优化模型. 显式化表达了目标体积与应力约束函数表达式,采用序列二次规划法优化求解,主要得到以下结论:(1)通过二维数值优化算例结果可知,提出的ICM方法在结构强度拓扑优化设计中具有可行性和有效性,优化迭代历程稳健.
(2)与刚度设计结果对比,柔顺度约束代表的刚度设计结果无法反映结构局部应力特性,考虑局部应力约束下的拓扑优化方法具有必要性.
(3)与以往的满应力设计有所不同,本文提出的方法采用了序列二次规划法求解,统一了ICM方法在节点位移、整体频率约束问题的优化求解方式,方法有望进一步推广到各类不同约束条件下的工程结构设计中.
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

Optimal shape design of structural elements based on boundary variations results in final designs that are topologically equivalent to the initial choice of design, and general, stable computational schemes for this approach often require some kind of remeshing of the finite element approximation of the analysis problem. This paper presents a methodology for optimal shape design where both these drawbacks can be avoided. The method is related to modern production techniques and consists of computing the optimal distribution in space of an anisotropic material that is constructed by introducing an infimum of periodically distributed small holes in a given homogeneous, isotropic material, with the requirement that the resulting structure can carry the given loads as well as satisfy other design requirements. The computation of effective material properties for the anisotropic material is carried out using the method of homogenization. Computational results are presented and compared with results obtained by boundary variations.
DOIURL

ABSTRACT It is of great importance for the development of new products to find the best possible topology or layout for given design objectives and constraints at a very early stage of the design process (the conceptual and project definition phase). Thus, over the last decade, substantial efforts of fundamental research have been devoted to the development of efficient and reliable procedures for solution of such problems. During this period, the researchers have been mainly occupied with two different kinds of topology design processes; the Material or Microstructure Technique and the Geometrical or Macrostructure Technique. It is the objective of this review paper to present an overview of the developments within these two types of techniques with special emphasis on optimum topology and layout design of linearly elastic 2D and 3D continuum structures. Starting from the mathematical-physical concepts of topology and layout optimization, several methods are presented and the applicability is illustrated by a number of examples. New areas of application of topology optimization are discussed at the end of the article. This review article includes 425 references.
DOIURL

Topology optimization is the process of determining the optimal layout of material and connectivity inside a design domain. This paper surveys topology optimization of continuum structures from the...
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

This paper presents a so-called -relaxed approach for structural topology optimization problems of discrete structures. The distinctive feature of this new approach is that unlike the typical treatment of topology optimization problems based on the ground structure approach, we eliminate the singular optima from the problem formulation and thus unify the sizing and topology optimization within the same framework. As a result, numerical methods developed for sizing optimization problems can be applied directly to the solution of topology optimization problems without any further treatment. The application of the proposed approach and its effectiveness are illustrated with several numerical examples.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL

Considering stress-related objective or constraint functions in structural topology optimization problems is very important from both theoretical and application perspectives. It has been known, however, that stress-related topology optimization problem is challenging since several difficulties must be overcome in order to solve it effectively. Traditionally, SIMP (Solid Isotropic Material with Penalization) method was often employed to tackle it. Although some remarkable achievements have been made with this computational framework, there are still some issues requiring further explorations. In the present work, stress-related topology optimization problems are investigated via a level set-based approach, which is a different topology optimization framework from SIMP. Numerical examples show that under appropriate problem formulations, level set approach is a promising tool for stress-related topology optimization problems.
DOIURL

SUMMARYAlthough the phenomenon of stress concentration is of paramount importance to engineers when they are designing load-carrying structures, stiffness is often used as the solely concerned objective or constraint functional in the studies of optimal topology design of continuum structures. Sometimes this will lead to optimal designs with severe stress concentrations that may be highly responsible for the fracture, creep, and fatigue of structures. The aim of the present work is to develop some effective numerical techniques for designing stiff structures with less stress concentrations. This is achieved by introducing some specific stress measures, which are sensitive to the existence of high local stresses, in the problem formulation and resolving the corresponding optimization problem numerically in a level set framework. Our study indicates that with use of the proposed numerical schemes, some intrinsic difficulties in stress-related topology optimization of continuum structures can be overcome in a natural way. Copyright 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

This paper proposes two effective constraint schemes to address the stress-constrained topology optimization of continuum structures. By considering the maximum stress measure in the global and local forms, respectively, the STM (stability transformation method)-based stress correction scheme and the violated set enhanced stress measure are developed to tackle the challenging issues from numerous local stress constraints and highly nonlinear stress behavior. Particularly, a stress aggregation function is involved in the design sensitivity analysis. Moreover, the nodal variable based SIMP method and adjoint sensitivity analysis are employed to solve the optimum topological design problems with two different optimization formulations. Finally, several representative examples demonstrate the validity of the present approach. It is also indicated that the numerical performance of the stress aggregation function is closely related to the problem formulation of topology optimization. The STM-based stress correction scheme is appropriate to the material volume minimization design, while the violated set enhanced stress measure is suitable for the mean compliance minimization design. Meanwhile, the proposed optimization approach can handle the stress-constrained topology optimization with easy implementation, low computational cost and stable convergence.
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

This article presents an application of stress-constrained topology optimization to compliant mechanism design. An output displacement maximization formulation is used, together with the SIMP approach and a projection method to ensure convergence to nearly discrete designs. The maximum stress is approximated using a normalized version of the commonly-used p-norm of the effective von Mises stresses. The usual problems associated with topology optimization for compliant mechanism design: one-node and/or intermediate density hinges are alleviated by the stress constraint. However, it is also shown that the stress constraint alone does not ensure mesh-independency.
DOIURL

In this paper, we develop an efficient and flexible design method that integrates the B-spline finite cell method (B-spline FCM) and the level set function (LSF) for stress constrained shape and topology optimization. Any structure of complex geometry is embedded within an extended, regular and fixed Eulerian mesh no matter how the structure is optimized. High-order B-spline shape functions are further implemented to ensure precisions of stress analysis and sensitivity analysis. Meanwhile, level set functions, i.e., implicit functions are used to enable topological changes of the considered structure through smooth boundary variations. Involved parameters rather than the conventional discrete form of LSF are directly taken as design variables to facilitate the numerical computing process. To be specific, the LSF is constructed by means of R-functions that incorporate cubic splines as implicit functions to offer flexibilities for shape optimization within the framework of fixed mesh, while the compactly supported radial basis functions (CS-RBFs) are employed as implicit functions for stress constrained topology optimization. It is shown the proposed FCM/LSF method is a convenient approach that makes it possible to calculate stress and stress sensitivities with high precision. Representative examples of shape and topology optimization with and without stress constraints are solved with success demonstrating the advantages of the FCM/LSF method.
DOIURL

This paper aims at dealing with realistic and challenging design problems of stress constrained topology optimization with free-form design domains. First, the concept of level set function (LSF) based modelers is introduced to transform this kind of problems into the Boolean conjunction operation of a topology variation modeler (TVM) onto a free-form design domain modeler (FDDM). Such an operation is mathematically realized by means of the so-called R-functions in the form of implicit LSFs. Within this framework, topology optimization problems are classified into two general cases depending upon the existence of non-designable solid feature. Analytical sensitivity analysis formulas are further derived. Compared with the existing level set based method, the important sensitivity property of design domain preserving makes it possible to avoid automatically the boundary violation of the design domain caused by the zero level set movement and both the topology and boundary shape of the free-form design domain can be simultaneously optimized. Second, the implementation of the finite cell method (FCM) ensures the stress computing accuracy in the fixed mesh due to the use of high-order shape functions and adaptive integration scheme. The combination of the active-set strategy and the dynamic aggregation technique also reduces the number of local stress constraints greatly. Finally, representative examples are presented to illustrate the conveniences and effectiveness of the proposed method.
DOIURL

This paper presents a topology optimization framework for optimizing the fracture resistance of two﹑hase composites considering interfacial damage interacting with crack propagation through a redistribution of the inclusions phase. A phase field method for fracture capable of describing interactions between bulk brittle fracture and interfacial damage is adopted within a diffuse approximation... [Show full abstract]
DOIURL

工程结构设计时经常需要限制最大名义应力,以避免发生断裂或疲劳破坏,一个有效的策略是采用拓扑优化方法.常规的双向渐进结构优化法(bi-evolutionary structural optimization,BESO)不能有效求解应力约束拓扑优化问题,为此本文提出一种改进的双向渐进结构优化方法,处理体积和应力约束下的最小柔顺性问题.引入基于K-S函数的全局应力度量,以减小大量局部应力约束引起的计算代价.采用拉格朗日乘子法将应力约束函数引入到目标函数,然后由二分法确定合适的拉格朗日乘子的值使得应力约束得到满足.而且,详细推导了基于BESO方法的应力约束拓扑优化模型及其灵敏度列式,最后通过三个典型拓扑优化算例验证改进方法的有效性.为展示考虑应力约束的优点,将应力约束设计与传统的基于刚度的设计进行了比较.结果表明,改进的BESO方法优化迭代过程稳健,获得了边界灰度单元很少的清晰的拓扑构型,并实现了有效降低应力集中效应的设计.
DOIURL

工程结构设计时经常需要限制最大名义应力,以避免发生断裂或疲劳破坏,一个有效的策略是采用拓扑优化方法.常规的双向渐进结构优化法(bi-evolutionary structural optimization,BESO)不能有效求解应力约束拓扑优化问题,为此本文提出一种改进的双向渐进结构优化方法,处理体积和应力约束下的最小柔顺性问题.引入基于K-S函数的全局应力度量,以减小大量局部应力约束引起的计算代价.采用拉格朗日乘子法将应力约束函数引入到目标函数,然后由二分法确定合适的拉格朗日乘子的值使得应力约束得到满足.而且,详细推导了基于BESO方法的应力约束拓扑优化模型及其灵敏度列式,最后通过三个典型拓扑优化算例验证改进方法的有效性.为展示考虑应力约束的优点,将应力约束设计与传统的基于刚度的设计进行了比较.结果表明,改进的BESO方法优化迭代过程稳健,获得了边界灰度单元很少的清晰的拓扑构型,并实现了有效降低应力集中效应的设计.
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOIURL

在多相材料的结构拓扑优化问题中,通常给定各相材料体积约束或材料总重量约束作为材料的控制用量.在结构轻量化设计的实际工程背景下,以结构总重量最小化为目标的优化模型具有明确的工程意义.针对含多相材料的稳态传热结构拓扑优化问题,提出了以结构总重量最小化为目标和给定热柔顺度为约束的多工况连续体结构拓扑优化建模方法.遵循独立连续映射建模方式,采用两类独立拓扑变量分别表征单元热传导矩阵和单元重量状态.推导了热柔顺度和总重量对设计变量的敏度,基于一阶和二阶泰勒展开得到各自的近似表达式.通过求解偏微分方程,实现了约束函数一次项过滤,消除了棋盘格现象和网格依赖性问题,并保证了约束方程在过滤后严格成立.建立的近似优化模型具有二次函数形式的目标函数和一次函数形式的约束函数.基于对偶序列二次规划方法对优化模型进行求解直至收敛.通过四个三维结构数值算例分析对比了热柔顺度约束限值、不同材料混合及多工况、多约束条件对优化结果的影响.数值算例结果表明,本文提出的优化方法在基于多相材料的多工况稳态热传导结构轻量化设计中具有可行性和有效性.
DOIURL

在多相材料的结构拓扑优化问题中,通常给定各相材料体积约束或材料总重量约束作为材料的控制用量.在结构轻量化设计的实际工程背景下,以结构总重量最小化为目标的优化模型具有明确的工程意义.针对含多相材料的稳态传热结构拓扑优化问题,提出了以结构总重量最小化为目标和给定热柔顺度为约束的多工况连续体结构拓扑优化建模方法.遵循独立连续映射建模方式,采用两类独立拓扑变量分别表征单元热传导矩阵和单元重量状态.推导了热柔顺度和总重量对设计变量的敏度,基于一阶和二阶泰勒展开得到各自的近似表达式.通过求解偏微分方程,实现了约束函数一次项过滤,消除了棋盘格现象和网格依赖性问题,并保证了约束方程在过滤后严格成立.建立的近似优化模型具有二次函数形式的目标函数和一次函数形式的约束函数.基于对偶序列二次规划方法对优化模型进行求解直至收敛.通过四个三维结构数值算例分析对比了热柔顺度约束限值、不同材料混合及多工况、多约束条件对优化结果的影响.数值算例结果表明,本文提出的优化方法在基于多相材料的多工况稳态热传导结构轻量化设计中具有可行性和有效性.
DOIURL

The present work introduces a novel concurrent optimization formulation to meet the requirements of lightweight design and various constraints simultaneously. Nodal displacement of macrostructure and effective thermal conductivity of microstructure are referred as the constraint functions, which means taking into account both the load-carrying capabilities and the thermal insulation properties. The effective properties of porous material derived from numerical homogenization are used for macro-structural analysis. Meanwhile, displacement vectors of macrostructures from original and adjoint load cases are utilized for the sensitivity analysis of the microstructure. Design variables in form of reciprocal functions of relative densities are introduced and used for linearization of the constraint function. The objective function of total mass is approximately expressed by the second order Taylor series expansion. Then, the proposed concurrent optimization problem is solved using a sequential quadratic programming algorithm, by splitting into a series of sub-problems in the form of the quadratic program. Finally, several numerical examples are presented to validate the effectiveness of the proposed optimization method. The various effects including initial designs, prescribed limits of nodal displacement and effective thermal conductivity on optimized designs are also investigated. An amount of optimized macrostructures and their corresponding microstructures are achieved.
DOIURLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

将文[1]所提出的对拓扑变量的独立连续映射(ICM)的拓扑优化方法应用于连续体结构,从而建立了统一的以重量为目标,考虑应力和位移约束的连续体结构拓扑优化模型。通过对位移一应力拓扑解和各工况下应力拓扑解的综合协调,进而对于协调拓扑解按照阈值完成从离散到连续的反演,并且采用分层与加权策略克服了“荷载病态”困难.给出的经典的二维平面问题和三维连续体结构拓扑优化算例表明,这种统一的模型由骨架结构发展到连续体结构的优化也是成功的.
DOIURLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

将文[1]所提出的对拓扑变量的独立连续映射(ICM)的拓扑优化方法应用于连续体结构,从而建立了统一的以重量为目标,考虑应力和位移约束的连续体结构拓扑优化模型。通过对位移一应力拓扑解和各工况下应力拓扑解的综合协调,进而对于协调拓扑解按照阈值完成从离散到连续的反演,并且采用分层与加权策略克服了“荷载病态”困难.给出的经典的二维平面问题和三维连续体结构拓扑优化算例表明,这种统一的模型由骨架结构发展到连续体结构的优化也是成功的.
DOIURLMagsci

利用Mises强度理论,提出了应力约束全局化策略,将局部的应力约束问题转化为结构整体的应变能约束问题. 基于ICM(独立、连续、映射)方法,引入了独立、连续的拓扑变量,对单元重量、单元刚度和单元许用应力的过滤函数进行了选择,建立了以重量为目标,以结构应变能代替应力约束的多工况下连续体结构拓扑优化模型,寻找到了多工况下的最佳传力路径. 运用对偶二次规划方法对上述优化模型进行了求解. 另外,利用PCL语言,在MSC/PATRAN的开发平台上,实现了应用应力约束全局化策略进行连续体结构拓扑优化的模块化处理. 数值算例表明了该方法的可行性和有效性.
DOIURLMagsci

利用Mises强度理论,提出了应力约束全局化策略,将局部的应力约束问题转化为结构整体的应变能约束问题. 基于ICM(独立、连续、映射)方法,引入了独立、连续的拓扑变量,对单元重量、单元刚度和单元许用应力的过滤函数进行了选择,建立了以重量为目标,以结构应变能代替应力约束的多工况下连续体结构拓扑优化模型,寻找到了多工况下的最佳传力路径. 运用对偶二次规划方法对上述优化模型进行了求解. 另外,利用PCL语言,在MSC/PATRAN的开发平台上,实现了应用应力约束全局化策略进行连续体结构拓扑优化的模块化处理. 数值算例表明了该方法的可行性和有效性.
DOIURL

为克服应力约束下拓扑优化问题约束数目多、应力敏度计算量大的困 难,提出了应力约束化凝聚化的ICM方法.在利用Mises强度理论将应力约束转换成应变能约束后,提出了应力约束凝聚化的两条途径:其一为应力全局化的 方法,其二为应力约束集成化的方法.由此建立了多工况下以重量为目标、以凝聚化应变能为约束的连续体结构优化模型,并利用对偶理论对优化模型进行了求解. 4个数值算例表明:该方法具有较高的计算效率,得到的拓扑结构比较合理,不仅适用于二维连续体结构,也适用于三维连续体结构.
DOIURL

为克服应力约束下拓扑优化问题约束数目多、应力敏度计算量大的困 难,提出了应力约束化凝聚化的ICM方法.在利用Mises强度理论将应力约束转换成应变能约束后,提出了应力约束凝聚化的两条途径:其一为应力全局化的 方法,其二为应力约束集成化的方法.由此建立了多工况下以重量为目标、以凝聚化应变能为约束的连续体结构优化模型,并利用对偶理论对优化模型进行了求解. 4个数值算例表明:该方法具有较高的计算效率,得到的拓扑结构比较合理,不仅适用于二维连续体结构,也适用于三维连续体结构.
DOIURLMagsci

采用指数类函数为快滤函数的高精度逼近ICM(independent continuous and mapping)方法, 建立了以结构重量为目标, 应力和位移共同约束下的连续体结构拓扑优化模型. 利用结构畸变比能的方法全局化应力约束, 单位虚载荷法显式化位移约束, 归一化约束以解决约束限数量级不一致的问题. 针对不同性态的过滤函数, 给出了指数类快滤函数参数的取值方法. 单工况和多工况的算例表明了高精度逼近的ICM方法处理多种约束下连续体结构拓扑优化的可行性与有效性.
DOIURLMagsci

采用指数类函数为快滤函数的高精度逼近ICM(independent continuous and mapping)方法, 建立了以结构重量为目标, 应力和位移共同约束下的连续体结构拓扑优化模型. 利用结构畸变比能的方法全局化应力约束, 单位虚载荷法显式化位移约束, 归一化约束以解决约束限数量级不一致的问题. 针对不同性态的过滤函数, 给出了指数类快滤函数参数的取值方法. 单工况和多工况的算例表明了高精度逼近的ICM方法处理多种约束下连续体结构拓扑优化的可行性与有效性.
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

该文根据von Mises强度准则的畸变比能本质,计算单元畸变比能替代应力约束;依照应力全局化策略,定义结构畸变比能约束概念,求解应力约束下重量最小的连续体结构拓扑优化问题,急剧地减少了应力约束。构造许用应力和结构最大应力的比值含参数幂函数,对约束限进行动态修正。基于ICM(Independent Continuous and Mapping,独立、连续、映射)方法,采用指数型快滤函数建立了结构在畸变比能约束下的结构拓扑优化模型,并选取精确映射下的序列二次规划进行求解。数值算例表明:采用修正的结构畸变比能的应力全局化策略,对于结构拓扑优化问题的求解是有用和高效的。该文提出的方法对解决工况间存在病态载荷的问题也是有益的。
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

该文根据von Mises强度准则的畸变比能本质,计算单元畸变比能替代应力约束;依照应力全局化策略,定义结构畸变比能约束概念,求解应力约束下重量最小的连续体结构拓扑优化问题,急剧地减少了应力约束。构造许用应力和结构最大应力的比值含参数幂函数,对约束限进行动态修正。基于ICM(Independent Continuous and Mapping,独立、连续、映射)方法,采用指数型快滤函数建立了结构在畸变比能约束下的结构拓扑优化模型,并选取精确映射下的序列二次规划进行求解。数值算例表明:采用修正的结构畸变比能的应力全局化策略,对于结构拓扑优化问题的求解是有用和高效的。该文提出的方法对解决工况间存在病态载荷的问题也是有益的。
DOIURL [本文引用: 1]

A new and powerful mathematical programming method is described, which is capable of solving a broad class of structural optimization problems. The method employs mixed direct/reciprocal design variables in order to get conservative, first-order approximations to the objective function and to the constraints. By this approach the primary optimization problem is replaced with a sequence of explicit subproblems. Each subproblem being convex and separable, it can be efficiently solved by using a dual formulation. An attractive feature of the new method lies in its inherent tendency to generate a sequence of steadily improving feasible designs. Examples of application to real-life aerospace structures are offered to demonstrate the power and generality of the approach presented.
DOIURL

A new method for non-linear programming in general and structural optimization in particular is presented. In each step of the iterative process, a strictly convex approximating subproblem is generated and solved. The generation of these subproblems is controlled by so called moving asymptotes, which may both stabilize and speed up the convergence of the general process.
DOIURL

http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00158-002-0238-7
DOIURL

To ensure manufacturability and mesh independence in density-based topology optimization schemes, it is imperative to use restriction methods. This paper introduces a new class of morphology-based restriction schemes that work as density filters; that is, the physical stiffness of an element is based on a function of the design variables of the neighboring elements. The new filters have the advantage that they eliminate grey scale transitions between solid and void regions. Using different test examples, it is shown that the schemes, in general, provide black and white designs with minimum length-scale constraints on either or both minimum hole sizes and minimum structural feature sizes. The new schemes are compared with methods and modified methods found in the literature.
DOIURL

It is revealed that the local optimum is particularly prone to occur in multi-material topology optimization using the conventional SIMP method. To overcome these undesirable phenomena, reciprocal...
