 ,1,2, 赵鹏军3,4, 周尚意5, 邓祥征2,6, 王琛7
,1,2, 赵鹏军3,4, 周尚意5, 邓祥征2,6, 王琛7Disciplinary structure and development strategy ofhuman geography in China
FAN Jie ,1,2, ZHAO Pengjun3,4, ZHOU Shangyi5, DENG Xiangzheng2,6, WANG Chen7
,1,2, ZHAO Pengjun3,4, ZHOU Shangyi5, DENG Xiangzheng2,6, WANG Chen7收稿日期:2021-04-28修回日期:2021-09-6
| 基金资助: |
Received:2021-04-28Revised:2021-09-6
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
樊杰(1961-), 男, 陕西西安人, 研究员, 博士生导师, 中国地理学会会员(S110005375M), 主要从事经济地理学和区域可持续发展研究。E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (1046KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
樊杰, 赵鹏军, 周尚意, 邓祥征, 王琛. 人文地理学学科体系与发展战略要点. 地理学报, 2021, 76(9): 2083-2093 doi:10.11821/dlxb202109003
FAN Jie, ZHAO Pengjun, ZHOU Shangyi, DENG Xiangzheng, WANG Chen.
1 人文地理学现状与目标
1.1 人文地理学沿革简况
中国现代人文地理学始于20世纪的20—30年代,一批欧美留学归国的地理****全面开启了中国现代人文地理学科研和教育事业,人地关系、人口分布和聚落地理、工农业和交通布局、政治和文化地理、流域与边疆区域考察研究等选题几乎覆盖了人文地理学的所有分支学科,填补了中国现代人文地理学研究的众多空白领域。中华人民共和国成立后,中国人文地理学仿效苏联学科设置,摒弃了社会文化地理和聚落地理[1],经济地理学一枝独秀,在工农业和交通地理学领域形成了强大的研究团队和丰富的成果积累,并提升了中国经济地理学研究的定量化水平[2]。1978年改革开放后,中国人文地理学与世界发达国家人文地理学接轨,包括城市地理学、旅游地理学、社会文化地理学、交通运输地理学等得到全面复兴[3,4],逐步形成了新兴的人文地理学分支学科与经典的经济地理学并重的学科新格局。其中,人地关系地域系统理论始终是中国人文地理学学科发展的基石[5,6]。中国人文地理学在满足国家战略需求方面也取得了标志性科研成就,例如,点轴理论与国土空间开发“T”字型结构、PRED(人口、资源、环境、发展)理论、主体功能区划和国土空间规划理论方法、“一带一路”共享发展模式和地缘政治关系、城市群可持续发展与乡村振兴研究等为科学制定重大地域开发战略做出了重要贡献[7]。近年来,随着后工业化社会的发展,人文地理学发展出来了视角更加微观、研究思维更加融合社会科学等趋势,主要表现在对知识创造、大众消费、女性权利、种族与经济隔离、社会公平与大众福祉等的关注,研究方法综合集成自然科学和社会科学的特色。1.2 人文地理学现状特征
中国人文地理学研究基本遵循了在现实需求中凝练关键科学命题,在解决问题中实现创新和推进学科发展,在学科建设的支撑下提升服务国家需求的质量水平的范式[8,9]。中国人文地理学发展现状可以概括为:① 聚焦区域研究,开展全球、国家和地方不同空间尺度的区域可持续发展综合研究。这类研究在中国特色人文地理学形成中具有标志性和统领性作用,也是中国人文地理学对全球同学科发展创新性贡献最集中和最显著的领域[8]。② 形成了现代中国人文地理学的三大支柱,即以人类生存地域特征为主要研究对象的城市和乡村地理研究、以人类生产活动地理过程为主要研究对象的经济地理研究、以游憩休闲活动空间为主要研究对象的旅游地理学。③ 社会文化地理和政治地理蓬勃兴起,随着政治、社会、文化因素在人文地理格局形成与演化中的作用越来越提高,其学科建设将越来越有助于准确地揭示人类活动空间过程的基本规律[10],社会发展需求强劲,而且在丰富和完善中国人文地理学方面具有关键作用和良好前景。④ 中国人文地理学的研究方法也发生了转变,从依靠实地调研对局地的研究、运用统计数据简单分析对整体和历史过程的研究、以及运用基本原理与经验积累开展的定性研究,开始转向在地理学以及经济学、社会学、管理学等基本理论和机理模型指引下,大量运用遥感数据、多源大数据、以及现代计算机技术支撑的分析模拟方法[11]。1.3 人文地理学学科发展问题
中国当前人文地理学发展存在的主要问题可以归纳总结如下:① 与在国家决策应用领域取得的突出成果相比,系统性、基础性的理论产出不够,特别是能够引领国际学术发展的理论成果不多;② 与研究议题的时代感强、新题目新领域新学科分支发展迅猛相比,农业地理学、工业地理学、人口地理学等传统部门人文地理学发展缓慢,世界地理、国别地理、中国地理和乡土地理等区域地理学发展动力不足;③ 与同人文社会学科融合显著强化相比,同自然科学的交叉不足,特别是在发展复杂性科学的学科理论和研究范式方面尤为欠缺。1.4 人文地理学学科发展目标
未来15年中国人文地理学的发展目标主要有:① 以探索现代人类活动空间分布及其变化规律为主题,促进人文地理学与自然地理和环境要素的交叉融合研究;② 推动人文地理学的全球视野和国际合作,适应全球地缘政治经济关系与区域响应的演变趋势,面向中国调整全球战略,提升中国人文地理学的全球影响力和国际话语权;③ 坚持人文地理学服务国家战略决策的优秀传统,支撑优化国土空间开发保护格局和空间治理体系现代化。④ 通过不断增强中国人文地理学业已形成的研究特色和发展优势,弥补制约中国人文地理学发展的短板。持续创新和丰富人文地理学的分支学科和交叉领域,努力构筑具有全球影响并引领发展中国家人文地理学科发展的新格局。⑤ 鼓励大数据、人工智能等新技术方法在人文地理研究中的使用;⑥ 完善与中国大国地位和国家发展需求相匹配的人文地理学学科体系。2 人文地理学学科主要领域
归纳学科发展现状,中国人文地理学业已形成四大领域,即综合人文地理学领域、经济地理学领域、城市和乡村地理学领域、社会文化和政治地理学领域。2.1 综合人文地理学
综合人文地理学发展关键是建立了人地关系地域系统理论,揭示人地系统中人与自然相互作用规律,从空间结构、时间过程、组织序变、整体效应、协同互补等方面,为全球、国家和地方可持续发展提供理论基础[6],并有效地规避了发达国家一度因人文化和社会化导致人文地理学空心化[5, 12]。人地关系地域系统理论区域可持续发展研究在认识全球、全国或区域的人地关系系统的整体优化、综合平衡及有效调控机理与途径方面形成了重大的科学成果产出,如PRED(人口、资源、环境和发展)研究主题的凝练与应用、地域功能理论与主体功能区划应用、城市群资源环境基础与效应等,坚持区域综合研究,为全球人文地理学的区域研究回归树立了榜样[13]。从自然承载力延伸到综合承载力、从地理环境与经济社会发展的综合、从地域分异到区域发展模式、从区域发展机理到空间治理体系等,区域可持续发展研究取得系统性成果,在主体功能区战略、重大区域发展战略和“一带一路”愿景的形成和实施中,发挥了科技支撑的主体作用,受到国际同行和国家决策层的认可[14,15,16]。自2000年以来,中国人口地理学在人口迁移流动和人口城镇化等问题的研究中做出了重要贡献[17,18],先后经历了从以人口宏观空间格局分析为主导,到注重微观个体人口学过程的转变,这一转变很大程度上得益于与人口学的交叉融合,但同时也使其越来越脱离地理学的范畴[19]。2.2 经济地理学
经济地理学是在中国发展历史悠久且特色鲜明的地理学分支,其特色是综合运用经济学价值规律、自然科学生态平衡法则及物质能量流动原理、社会科学的社会公平理念、历史演变逻辑与数量分析等理论方法,结合地理学的综合观和时空分异,阐释区域发展规律[20,21]。针对新经济地理现象和机制开展创新研究,形成了产业创新空间、金融地理、信息化体系布局[22]。针对典型区域如大江大河流域、海岸带、山地、资源枯竭型城市、老工业基地等开展经济地理学研究[23,24]。由于中国经济地理学强调人地关系及可持续性、基于地区比较优势注重差异化发展、强调国际前沿与中国特色相结合,所以在新世纪以来中国空间治理和区域规划中发挥了重要的作用[13]。经济地理学当前发展现状具有以下特点:研究对象实现了企业活动为主的全链条纵向拓展和以企业与地理关系为焦点的横向拓展[25,26];理论经济地理学、部门经济地理学、公司(企业)地理学、区域经济地理学、演化经济地理学等各个分支学科发展迅速[27];区域与地方发展、全球化和国际劳动地域分工、产业集群、国家和地方创新体系、金融地理、交通地理等研究成果产生国际影响[28,29],并支撑国家综合交通规划等决策制定[30]。旅游地理研究则建立基于“过程—结构—机制”中国本土化的旅游地理学理论体系[8, 31]。2.3 城市地理学和乡村地理学
中国城市地理学注重面向国家战略需求,更具规范性和战略性[32]。近年来,已在中国城市化、郊区化动力机制以及中国城市群、都市连绵区研究、区域一体化等方面形成了具有中国特色的理论[33,34],对城市居民行为、城市历史与文化、生态与环境以及城市全球化和国际化的研究日益关注[35],注重分析复杂多元的城市社会,城市犯罪、城市公平、流动人口对城市的影响等多维度研究越来越受到关注[36,37],并极具实践指导性,为中国城镇体系规划编制和发展做出了重要贡献[38]。乡村地理的研究经历了1978年前成为中国人文地理学的重点优势学科、1978年后学科研究力量显著削弱、进入21世纪后得以逐步复兴的一个发展历程。在复兴过程中开拓新的研究领域、聚焦具有现实应用和学科前沿时代感的研究命题[8],包括:农业与乡村地理学的综合研究、农村空心化与空心村整治并向地理工程拓展的乡村发展问题研究、乡村聚落空间特征及其演化研究、乡村生态和乡村景观研究,并服务乡村振兴、乡村脱贫、城乡协调发展等决策制定[39,40]。2.4 社会文化地理学和政治地理学
在中国,社会地理学、文化地理学和政治地理学是人文地理学科体系中的后发分支。该学科群基本既延续了1978—2000年的发展态势、特点和范畴,也开拓、借鉴了新的研究范式和应用领域。这改变了中国人文地理学的整体面貌。社会地理学研究相对薄弱,主要探讨不同社会群体的空间活动、社会生态,以及与犯罪、贫困等社会问题相关的地理问题[41]。文化地理学成果相对较多,既集中在文化源地、文化扩散、文化生态、文化整合、文化景观、传统文化区等主题上[42,43],也探索了新文化地理学的研究范式。文化地理****参与了文化产业、城市更新、文物和非遗保护、地名管理等应用领域的研究项目。政治地理学以往一直侧重行政区划地理学的研究,近年来扩展到地缘政治、地缘政治经济,借鉴了国外以多尺度/跨尺度为特色的新政治地理学研究,重点探讨热点地区和全球政治格局、中国和平崛起的地缘战略、全球资源地缘格局与中国资源安全战略,以及组织开展中国周边地缘环境与地缘经济合作研究[44,45]。3 人文地理学学科战略布局
人文地理学按照5个分支学科群进行学科战略布局(图1)。图1
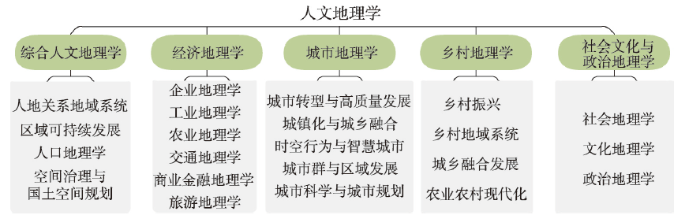 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1人文地理学五大分支学科战略布局图
Fig. 1The discipline system of human geography in China
3.1 综合人文地理学
综合人文地理包括“人地系统耦合过程”“可持续地理格局”和人口地理学。主要开展人地关系地域系统理论方法体系研究;聚焦经济社会空间结构有序化过程以及区域发展格局稳定态等关键科学问题,开展空间结构和区域发展综合研究;面向全球治理新动向和中国空间治理现代化需求,开展空间治理体系和国土空间规划体系基础理论方法的人文地理学研究;提升可持续发展的国际话语权,大力推进面向联合国可持续发展目标的人地关系量化评价和情景预测研究;提升技术方法水平,鼓励基于大数据分析和人工智能技术的人地关系识别,研发高精度的区域可持续地理探测器。中国人口地理学应主要关注人口空间分布、人口迁移和流动、人口城镇化、人口与资源环境的关系、流动人口犯罪等方面,尤其是要提高人口、资源、环境与可持续发展关系等复杂系统的定量研究水平。并积极开拓老龄化、人口脆弱性、人类福祉等新研究方向,为世界人口的共性问题提供中国范式。此外,还要重视全球、区域、重点国别和乡土人文地理研究,关注典型历史时期的历史人文地理的研究。通过理论提升促进中国综合人文地理学研究范式的不断成熟,扩大在全球人文地理学和地球系统科学发展中的影响力,在实施“未来地球(Future Earth)”科学计划、“宜居地球”和全球可持续发展目标中发挥引领作用。3.2 经济地理学
完善企业地理学,大力推进企业活动空间特征研究,形成引领国际的理论成果。积极复兴工业地理学、农业地理学、商业地理学、交通地理学等传统分支学科。促进旅游地理学、金融地理学等新兴分支学科。引导经济地理学从聚焦经济活动在不同地理尺度上的空间区位和分布、空间组织和空间关系的研究,拓展到对全球和区域地理过程和格局形成的经济成本和效益分析、制度机理分析、行为决策分析等领域;在注重企业和公司作为经济活动微观主体的同时,关注自然圈层和社会文化圈层等对经济活动空间过程的宏观影响;注重不同类型的经济行动以及包括研发、生产、流通、消费、回收利用等全链条空间响应研究的同时,创新并不断加强对非实体经济活动、以及新产业、新业态、新模式的经济地理研究;从聚焦国家和地方产业竞争能力和经济发展水平,拓展到对人类福祉和社会公平的影响。从经济活动的地理记录、现象描述、过程—格局分析为主的方法,向经济活动与地理环境关系的多学科解释、综合模拟预测等方法拓展。支撑国家创建人类命运共同体战略,为促进欠发达地区经济发展、改善人类福祉、减少贫困、缩小区域不平衡、节约高效利用经济资源、大力发展绿色经济等贡献中国经济地理学智慧。面向经济高质量发展、乡村振兴等国家新战略要求,研究经济要素在城乡不同区域、不同发展水平上的布局与流动演化规律及其调控机理;丰富全球经济地理学理论方法,引领发展中国家的经济地理学发展。3.3 城市地理学
城市地理学要继续加强城镇化、城市转型、城市群与区域发展、城市规划与管理等传统方向研究。聚焦具有重大国家战略需求且具有中国特色的城市地理问题开展研究,包括新型城镇化、城市高质量发展、都市圈、城乡生活圈、城市—区域可持续发展与融合、城市治理等。适应科学技术发展趋势,拓展智慧城市、韧性城市、城市计算、城市科学等新兴方向研究。面向建立人类命运共同体,开展低碳城市与气候变化、城市灾害、城市社会公平、全球化时代的城市发展应对等研究。3.4 乡村地理学
乡村地理学要加强乡村振兴、乡村地域系统、城乡融合发展、农业农村现代化等领域研究。乡村地理学应立足未来中国乡村发展的特殊性,以乡村发展转型为切入点,开展乡村地理学研究,重视乡村聚落重构的特征、动力机制、典型模式方面的研究,构建系统的乡村聚落空间转型的理论体系,加强乡村振兴、乡村地域系统、城乡融合发展、农业农村现代化等领域研究,探讨中国乡村发展与规划管理间的作用关系、以及城乡聚落体系演变中的驱动因素和协调途径。3.5 社会文化地理学和政治地理学
社会应加快社会文化地理学理论方法的本土化进程,在学习和理解国外社会文化地理学的基础上,建构和壮大具有中国地域特色的社会文化地理学。突出人的世界观、价值观和人生观等社会文化地理学研究独特的基本思考出发点,揭示人类空间行为背后的文化驱动力,探讨文化驱动力指引的社会空间制度和组织的空间差异,社会空间关系等社会地理主题,以及身份(权利、权力)、领土、地缘关系等政治地理主题,探索、培育和发展与相关学科结合的研究领域,为其他学科提供地理学的认识视角和分析工具。建构中国特色的社会文化地理学理论方法体系,在中国参与全球治理和提升国家空间治理现代化过程中凸显学科价值。4 人文地理学优先发展领域与重点方向
4.1 优先发展领域目标
高度关注全球性变局影响与反馈作用,实现可持续发展和高质量发展区域模式的研究突破,发展新时期人地关系地域系统基础理论,促使人口地理学回归与创新发展,在全球人文地理学融入统一地理学、“Future Earth”研究计划和“宜居地球”研究计划中发挥引领和示范作用。适应国家产业体系重构趋势,围绕新产业、新业态、新经济空间、新生产模式,创建重大生产力布局原理,完善经济地理学分支学科体系。深化新型城镇化过程与空间格局、城市群、新农村地域研究,形成一批揭示第四次城镇化高潮以来、特别是发展中国家城镇化规律的理论与应用成果。关注全球和国家尺度自然资源和人口系统可持续性食物安全格局的影响,探索交通等基础设施同经济活动组织和空间格局的动态交互过程、高速交通运输技术下(高铁、互联网、物联网等)的空间相互作用规律特征、流空间发育规律及其对基础设施、特别是新型基础设施体系布局的影响,培育国土安全和国土品质研究领域的新增长点。加强与发达国家在社会文化转型领域研究前沿的接轨,健全中国社会文化地理研究体系,探索全球战略格局重构的地缘政治基础。面向空间治理现代化需求,形成阐释空间治理模式、区域政策和协调发展机制的系统理论,形成大数据环境下的人类活动认知、区域分析与辅助决策系统,显著提升人文地理学服务决策管理的理论水平和分析模拟能力。4.2 人地系统与区域可持续发展重点研究方向
4.2.1 人地关系地域系统研究 围绕“人地系统耦合过程”和“可持续地理格局”两大主题,研究多要素、多界面、多尺度过程和格局的成因机理与模拟技术,完善人地关系地域系统理论和方法体系。重点研究方向包括:全球气候变化和自然地理环境变化对人类活动的影响及其空间分布响应,人类活动圈层与地球不同自然圈层物质、能量、信息交换的界面过程与区域效应;自然资源约束、生态文明建设与产业转型、文化转型和地域功能转型的互馈作用;人类活动空间分布地带性的影响,人类活动空间分布格局变化的稳定态及其驱动力;人类生产生活活动空间格局与自然地理环境格局耦合特征、可持续性和尺度效应,地域复合功能形成机理及其冲突协调机制;人地关系耦合进程中的经济效率与社会公平、民生福祉之间的关系;流空间和传统空间的耦合效应,近、远程空间相互作用与区域依赖性,尺度转换中空间相互作用的特征及效应,流功能、流规模经济与集聚经济以及流空间结构与演变规律,地域系统开放性及流空间变动导致人地关系变化的基本规律;经济—社会—生态耦合调控的空间治理模式及其体制机制保障;人口低生育率、老龄化的空间分布差异性及其对陆表自然和人文格局的影响,人口、劳动力、创新人才流动对区域生态、经济和社会系统脆弱性的影响,后疫情时代人口脆弱性以及“一带一路”倡议背景下人口迁移规律,以人为本建立兼顾弱势群体生活空间和实现人口在不同聚落与生产空间均衡配置的途径;运用遥感、GIS和大数据技术开展人地关系量化与评价、人地系统耦合过程和可持续地理格局的模拟分析、预测预判和调控优化。4.2.2 空间治理与国土空间规划研究 以全球治理新动向和中国空间治理现代化为引导,建构空间治理理论创新、空间规划基础能力建设和地理知识决策管理应用等三位一体的研究体系,增强人文地理学的综合和基础功能。重点研究方向包括:探索与自然科学、社会科学、工程技术融合途径、以及统领大科学建构服务空间治理现代化的理论体系,增强基础数据采集、共享和分析能力并完善模拟、预测和优化模型方法,构建面向空间治理现代化需求的科技知识的创造传承、学习传播、实践应用体系;实现空间综合效益最优的基本约束条件、目标体系和国土空间规划途径,自然环境系统与人类社会系统耦合中的自然承载能力、空间承载能力以及地域功能适宜性,地域功能、空间结构和区域政策的互馈作用与响应机制;中国特色社会主义制度下的政府与市场在空间治理中的作用及合理匹配,全球治理演变的轨迹、拐点、时空效应和区域响应。服务国家长三角一体化、粤港澳大湾区、长江经济带大保护和黄河流域高质量发展等区域重大战略,研究人地关系地域系统协调与区域可持续发展的转型及其调控。
4.2.3 大数据环境下的区域分析与辅助决策系统 注重大数据带来的人文地理学研究范式和方法创新,进而推动理论建设和学科发展。重点包括:人类活动时空大数据采集与处理技术,应用大数据感知分析人类生产和生活活动全领域、全过程及空间组织变化,提升对人类活动的跨时空间尺度特征的认知能力,反演人流、物流、技术流、金融流和信息流的空间格局与动态过程,实现大数据方法技术同传统人文地理学研究范式和方法互补与互动,检验、修订和创新发展经典人文地理学理论,建立基于大数据的人文地理过程与格局模拟器,建立基于大数据的城市与区域系统模拟、调控优化人机互动可视化平台和辅助决策系统。
4.3 经济地理学重点研究方向
适应新产业和新业态空间组织变化,以全球化和地方化、创新空间和企业生长、实体经济与虚拟经济空间结构演变为重点,推动产业布局理论创新和经济地理学复兴。重点研究方向包括:全球化与地方化新趋势及其驱动机制,全球产业链、供应链、价值链和创新链的空间分布特征、演变与区域响应,跨国投资和国际贸易格局对地缘经济系统的影响,全球生产网络、分布式生产系统和跨国公司空间组织的机理,经济全球化、产业转移和国家经济安全性的关系与相互适应;企业成长消亡的生命周期微观机理与产业分布格局演变的宏观机理之间的内在关联,新产业区位论、新业态公司地理论和新管理模式的产业空间结构理论,企业创新空间环境和地方产业竞争力的生长因素及途径,企业为主体的国家和地方技术创新体系与产业布局的耦合,产业智慧化的空间响应与效应;区域经济要素流动规律及空间相互作用、经济活动的空间集聚与分散的趋势,产业集群、地域经济综合体演化和空间组织效率,中国制造复兴的空间组织响应与现代服务业空间布局原理,产业生态化和生态产业化下的区域治理模式创新,行为经济空间、关系经济地理及其对经济地理学学科发展的影响;基础设施与经济活动的时空间关系,交通设施网络变化对经济活动组织,互联网、物联网、高速交通方式等新兴基础设施对于经济活动区位选择、经济空间格局及其变化的影响;全球气候变化和极端天气等自然灾害等对于基础设施的致灾机理及其预警防控,基础设施对于灾害响应、适应及其韧性能力构建,基础设施绿色低碳模式及其实现路径。4.4 城市地理学和乡村地理学重点研究方向
4.4.1 新型城镇化背景下的城市地理学 面向以人为核心的新型城镇化和城乡融合发展的战略目标,探索适用于发展中国家城市发展的理论体系和方法创新。重点研究方向包括:高质量发展的新型城镇化内涵与机制,都市圈、城市群和城市区域的形成机理与城乡融合的引导机制,不同聚落形态规模职能等值发展原理,城市经济、社会、文化和制度空间及其转型的多尺度、多维度和多视角的理解与阐释,韧性城市、可持续城市化和城市智慧化、生态化的位序特征及空间效应,人工智能和大数据等新技术模拟分析与预测城市化过程的方法。4.4.2 乡村振兴背景下的乡村地理学 基于城乡发展转型、体制机制转换的背景,以可持续城乡发展、一体化城乡体系和乡村聚落空间重构为主线,发展现代乡村地理学理论方法、服务乡村振兴国家战略。重点研究方向包括:中国特色乡村地域体系的职能演变和空间结构理论;城镇化和工业化进程对乡村聚落功能的重组和转型的影响;乡村内部要素和外部调控共同作用下乡村聚落重构方法及理论;新时代城乡融合发展下乡村聚落演变过程中的动力机制和空间分异特征;乡村振兴中农户生产生活方式转变及空间组织模式;乡村振兴规划与决策的协同效应及对乡村聚落演变、城乡一体化和城乡聚落体系生成的作用;城乡融合过程中,乡村产业发展与乡村文化的传承与保护协同模式研究;乡村振兴战略下乡村地域特色的传承与现代化农村建设的相互关系以及调控策略。
4.5 社会文化地理学和政治地理学重点研究方向
4.5.1 人类命运共同体概念下的社会文化地理学 重点研究方向包括:① 为克服只分析社会文化,无法突出地理学分析特色的缺陷,为克服简单因果分析的缺陷,鼓励在自然、生计、社会、意识形态的“四层一体”系统中,探究社会文化在复杂因果网络中的作用机制。② 为建立人类命运共同体,促进人与自然和谐共生的目标,鼓励探索中外不同人群的价值观,其中既包括人对自己、人对他人的价值观,也包括人对自然的价值观。了解这些价值观的差异,有助于理解人们划界、投资、消费、迁移、转移支付等空间行为的深层原因,从而寻找共同的目标。③ 为传承和弘扬中华优秀传统文化,鼓励探究和发掘优秀传统文化的地理特性,这些优秀传统文化既适应地方系统,也具备空间传播能力、代际传承能力。其中的学术探索重点是文化空间扩散和文化空间升尺度。④ 为激发人们在技术、制度和观念上的文化创新,鼓励探索创新的各类环境特征,尤其是多空间尺度要素叠加后的环境特征。4.5.2 新地缘关系背景下的世界地理研究 重点研究方向包括:① 为应对新的世界格局到来所产生的挑战,面向新时代的全球治理和世界和平,凸显地理学的分析视角,鼓励探索世界格局调整期的地缘体、地缘关系演变的地理表达。在尺度政治、领域政治、批判地缘政治等政治学的概念上,探索地理学的核心概念。② 为克服地缘政治研究与地缘经济研究的脱节,鼓励探索地缘政治与地缘经济的结合机制,以地理学的区域性和综合性特色,与国际政治、国际金融、国际贸易等学科有所区别。③ 为应对太空竞争与合作、国际海域资源的和平利用中的新问题,鼓励研究国际权益的地理格局形成机制,探究各类资源权力、边界制定与管治、跨界流动的方向与强度。鼓励在全球、亚太、中国周边、中国内部的不同尺度单元上开展研究,并分析不同空间尺度的研究结论的转换。
5 结语
中国人文地理学科发展源远流长,门类众多,是一门既古老又年轻、既传统又现代的地理学核心学科[46]。传统学科分支在稳定发展中不断创新,新兴学科也不断涌现,形成了综合人文地理学、经济地理学、城市地理学、乡村地理学、社会文化地理学、地缘政治地理学等多学科体系。中国人文地理学学科发展的动力主要来自人类活动发展和演变、政策决策需求、对人类活动的新理论认知、数据分析与处理技术的革新以及地理学其他分支的发展等[47]。尤其是中国构建人类命运共同体的战略布局、丰富悠久的社会文化底蕴和蓬勃发展的中国特色社会主义伟大事业,正在促进中国人文地理学科朝着赶超世界和独具特色的方向快速发展。致谢
成文过程中陈发虎、林初升、熊巨华等提出了宝贵的意见,方创琳、龙花楼、朱竑、刘卫东、刘云刚、刘彦随、杜德斌、李平、宋长青、张平宇、张虹鸥、苗长虹、金凤君、段学军、贺灿飞、柴彦威、韩增林、薛德升等参与讨论,在此一并表示感谢。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2307/140646URL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.11821/xb199802001 [本文引用: 2]

Academician Wu Chuanjun is an outstanding geographer of China, well known home and abroad. In his academic career of 60 odd years, Professor Wu has made significant contributions to the development of geographical study and national construction in China, and has been taking a leading role in the process of increasing international recognition of Chinese geography and enhancing international communication of China’s geographical circle with foreign colleagues through his continuous hard efforts and serious commitment. This paper elaborates briefly the profound geographical thoughts of Professor Wu, and gives a concise introduction to his remarkable contributions to the overall development of geography in China, with focus on his significant achievements in the aspects of strengthening agriculture geography and land use study, defining the development orientations of China’s economic geography, opening up new research fields such as territorial planning and sustainable development, initiating and organizing the renewal of China’s human geography, organizing the internal cooperation in China’s geographical society, promoting international academic communication, etc.. This paper also gives insight discussions on the theory of man-earth areal system, the essence of geographical thoughts of Professor Wu, mainly referring to the background, conceptions and its relationship with sustainable development of the theory. Professor Wu creatively put forward the theoretical term of “man earth areal system”, and stresses that man earth relationship remains as the core of geographical study in all developmental stages of the discipline. He proposed that the major contents of geographical study should include following issues: general theories about the formation, functional structure and development of man earth areal system; study on the relationship among sub systems of man earth areal system, such as interaction intensity analysis, potential assessment, effect evaluation and risk analysis; study on the basic rules concerning the material and energy flow and convey in man earth areal system and approaches of overall systematic control; analysis of areal capacity of population; study on the dynamic models; analysis of areal differences and areal categorizing; study on the improved monitoring and modeling of coordinated man earth relationship of various types of regions of different spatial levels and scopes, and so on. Professor Wu has long been paying great efforts in training qualified personnel for the long term prosperity of China’s geographical career, with remarkable results concerning various fields and levels. With his most respected age of eighty approaching, Professor Wu is still on his important career mission with full energy and wisdom, providing strategic support to the development of China’s geographical study towards the 21st century.
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 4]
[本文引用: 4]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2017.05.001 [本文引用: 1]

To determine the direction and the field of research is the soul of discipline development. Humanistic and Economic Geography is a subject changing in both research field and even research direction. Recognition of research fields and disciplines for Humanistic and Economic Geography is essential. On the basis of combing the main branch development stage of Humanistic and Economic Geography in China for decades, the paper summarized the response of Humanistic and Economic Geography to the transformation development background of the social. On the one hand, the intersectionality of the discipline should be insisted, with the theory of ‘man-land’system as the direction and the combination of theory with practice being adhered. Humanistic and Economic Geography scholars should be with a new attitude and new vision, to think about the future development of discipline key fields, the development idea and the innovation of the theory and method. For the major problems which disciplines involved in a long time, strategic and consultative, predictive and summative work will gradually increase. In the paper, the development trend of some important fields such as information and social space economic organization, the new pattern of regional economy and‘New Urbanization’were expounded; some new ideas about ‘international hot spots’and ‘international frontier’, the theory research and the relationship between the theory and practice were proposed; and then the author put forward the suggestion that‘Humanistic Geography’to be renamed as‘Humanistic and Economic Geography’.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201710014 [本文引用: 1]

Social and Cultural Geography (or SCG, for short), an academic journal with an international reputation in the areas of social and cultural geography, has created an interdisciplinary platform for scholarly discussions related to the spatiality of society and culture. Based on the statistical analysis of 949 articles that have been published since 2000 when the journal was launched, this paper attempts to take a close look at the authors, research areas, topics, the methods of data collection and analysis, in SCG with the aid of Citespace and Histcite software. We found that: (1) The number of published papers substantially grew and the research areas and source of authors are continually internationalized, which implies that social and cultural geography is increasingly internationally-recognized; (2) The research interests have witnessed the "cultural turn" and "policy turn" within geography, mainly focusing upon the emerging topics like power, identity, memory, home, mobility, race, religion, music and food, all of which are human-centered and highly relevant to social issues; (3) The research articles in SCG are mainly engaged in qualitative approaches, like interview, ethnography, participant observation, and focused group. (4) The Western scholars prefer multiple ways of data collection and evidence displaying including text analysis, analytical comparison, visual aid, which are less commonly used in China's geo-journals. In conclusion, by classifying and analyzing the journal articles published in SCG, this article tries to capture the up-to-date research tendency and methodological approaches in current Western social and cultural geographical academia in order to provide some insights for domestic geographical research.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2307/142563URL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1007/s11442-009-0515-0URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s11442-017-1413-5URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/xb199206010 [本文引用: 1]

The characteristics and interrelations of three disciplines above-mentioned are expounded and compared.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2016.09.001 [本文引用: 1]

During the Fifth Plenum of the 18th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, the five development ideas of “innovation, coordination, green, open, and sharing” are proposed and will be implemented in the thirteenth Five-Year Plan. In the five ideas, innovation is regarded as the first driver to promote the development of economy, especially the theoretical innovation, institutional innovation, technological innovation and culture innovation. In the traditional industry base in Northeast China, innovation is undoubtedly the key point to solve the structural and institutional obstacles, enhance the development of energy and abilities, and explore new development mode. On the basis of exploring the relationship between innovation development and overall revitalization, this article analyzes the significance, implementation way, and countermeasures of innovation development for comprehensively revitalizing Northeast China. In the third part, the article proposes new ideas, new patterns and new mechanisms for comprehensively revitalizing northeast China. First, the article suggests that it is the most important policy to reconstruct the think-tank systems and build the first driver for industry development. Second, it proposes to implement the precision talent action plan and supply safeguard for comprehensively revitalizing northeast China. Third, it promotes action for stabling the agriculture yields and promoting the product quality, and further pushes the innovation of modern agricultural development. Fourth, it recommends implementing the innovation action for the whole industry chain, improving the productivity and increasing the production efficiency. Fifth, it puts forward to the perspective of taking the function zone to be the flat of innovation development environment and regional innovation carrier. On one hand, to realize the comprehensively revitalization northeast China, the central government should: 1) make breakthroughs in reform and innovation in important areas, including deepen reform of the administrative system, further streamline administration and delegate more power to lower-level governments; 2) usher in a new phase of Northeast China’s opening to the outside world and ensure its high standard performance; 3) advance agricultural modernization and rural reform and development; 4) use the innovation to support and lead economic structural improvement and upgrading. On the other hand, the Northeast China should make the most of the government's innovation and entrepreneurship drive to turn innovation into a major source of development, according to the document.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012003 [本文引用: 1]

Human geography is one of the three major branches of geography. Since the establishment of Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGSNRR, CAS) in 1940, human-economic geography has gone through several important periods, such as budding, rise, maturity, fluctuation and prosperity. Outstanding progress and remarkable results have been achieved in scientific research, cultivation of talents and service of national strategic decision-making. Pioneering achievements have been made in the study of economic geography, agricultural geography, industrial geography, transportation geography, urban geography, rural geography, tourism geography and regional sustainable development, which has driven the overall innovation and development of China's human-economic geography. The IGSNRR has undertaken a series of national tasks and attained major achievements in the fields of agricultural regional planning and land use research, industrial base construction and transportation layout, urban system construction and urbanization, regional development and planning. And it has made important contributions to supporting the national strategy and leading the development of human-economic geography. This research made a systematic review of the establishment and growth history, research fields, research teams and academic achievements of the human-economic geography of IGSNRR in the past 80 years, as well as its role in serving national and regional economic and social development. Through selecting 6216 papers (4576 in Chinese and 1640 in English) published by the human-economic geographers of the IGSNRR, research progress and academic achievements in stages are reviewed. Finally, new consideration and prospect were proposed to face the ecological civilization construction, new urbanization, rural revitalization strategy and beautiful China construction. Our purposes are to innovate the frontier theory of human-economic geography and establish a new interdisciplinary system, and strive to strengthen research on territorial space governance, regional sustainable development, human-earth system science, urbanization and rural revitalization, and innovation of national modern geography.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2307/141854URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/00343400802662625URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012011 [本文引用: 1]

China's modernized transport strategies have been focused on building new infrastructures in areas with insufficient transport facilities, supplying the lack of new transport services, and investing in transport construction on a large scale since the 10th Five-Year Plan (2000-2005). However, these strategies are now facing new situations in population development, including population growth, migration, spatial relocation and agglomeration, and changes in lifestyle. It is imperative to investigate population-development oriented comprehensive modern transport system in order to implement people-oriented principles and the National Strategy of Strengthening Country in Transportation. This study presents some research results from the National Development and Reform Commission Key Research Project for the National 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025), "Population Development and Modern Transportation System Strategies in China". The study is based on theoretical mechanisms in the coupling and interaction between population and transport system. It conducts in-depth analyses on the new trends of population development and transport demand, and proposes a new "diamond" strategy for China's comprehensive transport system in order to cope with these new trends. According to this strategy, the new comprehensive modern transport system in China will have four "diamond pole" including Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, Yangtze River Delta, Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, and Chengdu-Chongqing region, four "diamond edges" including Beijing-Shanghai (Jing-Hu), Shanghai-Guangdong (Hu-Yue), Guangdong-Sichuan (Yue-Chuan), and Beijing-Sichuan (Jing-Chuan) transport corridors, two cross backbones including water transport along the Yangtze River and Beijing-Hong Kong-Macao transport corridors, and multiple transport hubs in cities with intensive intracity population movement flow. The study also proposes key missions to implement the new strategy in order to build population-development oriented comprehensive modern transport system in China, which includes supporting the national development and spatial plan, applying for the National Strategy of Strengthening Country in Transportation, and supplying high-quality transport services with a priority to the people.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201705001 [本文引用: 1]

Tourism geography is increasingly to be one of geography branch disciplines. However, with the background of "culture turn" and "social turn" in human geography research, tourism geography is criticized for losing "the flavor of geography", or "de-geographization tendency", "forgetting the hometown on the way rushing to alien land". With these concerns, The Tourism Geographies Commission of China Geography Association organizes a seminar to reflect the tourism geographies research in the past decades, to discuss the academic contribution of tourism geography, the characteristics and the generational transition of tourism geography. The conclusions include: (1) Tourism geographies is not far away from home, but the hometown: geography itself is changing. Tourism geography must adapt to the geography development in the new era; (2) The key characteristics of tourism geography are comprehensive and inclusive. We should persist in not only logical positivism, but also constructionism and humanism paradigm. The key research questions include mobility, spatial scale transfer and human-place relation; (3) Generation transition in tourism geographers is inevitable, not only in the way of teacher-student relation transition, but also research question, disciplinary identification and theoretical shift. Tourism geography should have their own series of research questions, and generations of geographers work together to facilitate the academic community.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/ijur.v44.1URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.03.001 [本文引用: 1]

Urbanization is the right way to build a well-off society and realize modernization for China. It determines not only the future of China, but also the development process of the world's urbanization. Chinese geographers have made important contributions to the urbanization development of China over the past 35 years. This is mainly manifested in the following aspects: 1) They put forward the concept of urbanization firstly and promoted the urbanization to be national strategy. 2) They took the lead in revising the three stage theory of urbanization proposed by Northam to the four stage theory. 3) They put forward a reasonable process about the development of China's urbanization which has been adopted by National New Urbanization Plan. 4) They developed a comprehensive zoning of China’s new urbanization and set up a reasonable pattern of China's new urbanization. 5) They took the lead in developing the quantitative measure methods and system of urbanization development quality, which provided technical support to improve the quality of urbanization development. 6) They earlier issued the development report of China’s new urbanization, and put forward the general patterns and the different patterns of the new urbanization development. 7) They put forward the theory and technical drawings of the coupling circle bewteen urbanization and eco-environment for the first time. Chinese geographers often act as the organizer of urbanization research which is multidisciplinary, and undertake the following responsibilities: 1) to comprehensively analyze the problems and foreign experiences of urbanization development; 2) to explore the driving mechanism and the basic laws of urbanization development; 3) to analyze the spatial pattern of urbanization and the difference model; 4) to reveal the coupling relationship between urbanization development and resource environment; 5) to simulate a variety of scenarios and make an early warning of urbanization development; 6) to choose the sustainable development road of improving urbanization quality. In the future, Chinese geographers will have the following missions on urbanization development: 1) to innovate the theory of new type urbanization quality improvement; 2) to optimize China's urbanization spatial pattern under the background of “Belt and Road”; 3) to reveal the interactive coupling mechanism and coupling law between urbanization and eco-environment; 4) to develop the intelligent decision support system for China’s urbanization development and give the guiding policies.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s11442-017-1445-x [本文引用: 1]

Mega-urban agglomerations are strategic core areas for national economic development and the main regions of new urbanization. They also have important roles in shifting the global economic center of gravity to China. However, the development of mega-urban agglomerations has triggered the interactive coercion between resources and the eco-environment. The interactive coupled effects between urbanization and the eco-environment in mega-urban agglomerations represent frontier and high-priority research topics in the field of Earth system science over the next decade. In this paper, we carried out systematic theoretical analysis of the interactive coupling mechanisms and coercing effects between urbanization and the eco-environment in mega-urban agglomerations. In detail, we analyzed the nonlinear-coupled relationships and the coupling characteristics between natural and human elements in mega-urban agglomerations. We also investigated the interactive coercion intensities between internal and external elements, and the mechanisms and patterns of local couplings and telecouplings in mega-urban agglomeration systems, which are affected by key internal and external control elements. In addition, we proposed the interactive coupling theory on urbanization and the eco-environment in mega-urban agglomerations. Furthermore, we established a spatiotemporal dynamic coupling model with multi-element, multi-scale, multi-scenario, multi-module and multi-agent integrations, which can be used to develop an intelligent decision support system for sustainable development of mega-urban agglomerations. In general, our research may provide theoretical guidance and method support to solve problems related to mega-urban agglomerations and maintain their sustainable development.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408008 [本文引用: 1]

Built on a database composed of major books and journals published in mainland China, this study examines and summarizes the development of urban geography in post-reform China for the last decades. It applies the methods of literature quantitative analysis to interrogate the modality of recent urban geography and its studies within China's mainland. The findings include: first, along with China's miracle economic growth the community of urban geography also sees a remarkable prosperity in the last years. In particular, the topics and contents of this field witness a sustained expansion and evolvement. Moreover, its research methods are becoming more and more scientific and standardized, while the scale of these studies is turning from macroscopic to microscopic level. Along with a remarkable increase of both topics and interdisciplinary approaches, the perspectives of urban geography studies turn to be even diversified. It is found that state policy and hot-spot topics have significant impacts upon the development or direction of urban geography research. In addition, the impacts of Western theory or schools upon the research in China's mainland are also prominent. We argue that the emphasis of both theoretical studies and their applications is a key feature of post-reform China's urban geography research, among which urbanization and urban system are two key directions. After a comparative analysis of our case with recent development of urban geography in the West and other contexts such as South Africa or Brazil, say the global south, we suggest that the future study of Chinese cities should further expand a global perspective, critically import western theories, explore new theories as well as interdisciplinary approaches, and further follow the academic standard of international communities.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190133 [本文引用: 1]

Urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development are not only the important strategic themes of China's modernization, but also the main frontier topics of rural regional system research in geography. Facing the problems of urban-rural segregation, human-land segregation and increasingly severe rural diseases in the process of rapid urbanization in China, urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are accelerated to be the national strategies. This research briefly analyses the economic and social background of rural revitalization and its significance in the new era. It is pointed out that the important responsibility of modern geography to face the national strategy and serve the rural revitalization is to deeply explore the major theories and scientific approaches of the coupling of man-land system, the integration of urban-rural development and the fit of the functions of villages-towns, while this paper focuses on the domestic research progress of rural revitalization strategy since it has been proposed for one year and the main contents and characteristics of this special issue. Finally, focusing on giving full play to the advantages and characteristics of geography, this paper expounds the theoretical frontiers and scientific and technological needs of the scientific research on rural revitalization in the new era. The ten frontier issues mainly include the differentiation and integration mechanism of urban and rural regional system; the transformation mechanism and scientific approach of rural regional system; the interaction principle and planning governance of agriculture, farmers and rural areas; the mutual feedback mechanism of rural natural-social-technical system; the coupling process and scenario simulation of rural man-land system; the suitability and carrying capacity of rural spatial reconstruction; and rural transformation developing endogenous power and synergy mechanism; new subjectivity and farmers' organization of rural revitalization; efficiency and transmission mechanism of scientific and technological innovation of rural revitalization; disaster and risk control mechanism of rural regional system. And we put forward some preliminary thoughts and suggestions for deepening the research of rural science and geography on rural revitalization in China.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408010 [本文引用: 1]

This paper firstly reviews the recent progress in the international research on agricultural geography and rural development, including the research fields, theory and methodology, and the developing trend. Then, the recent research progress, major achievements and their applications in economic development of agricultural geography and rural development in China are analyzed. Finally, the prospects for the new innovative research tasks and scientific propositions in the fields of agricultural geography and rural development in China to meet the needs of national strategies are put forward, based on comparison with related research progress abroad. Recent research progress includes the aspects of research achievements, the applications of new technologies and methodologies, and the influences and applications of major achievements. The summary of recent research achievements includes eight topics: (1) integrated research on agricultural and rural geography; (2) rural transformation development and rural restructuring; (3) integrated research on building a new countryside; (4) urbanization, rural hollowing and the renovation of hollowed villages; (5) the construction of key villages and specialized villages; (6) urban-rural integration development and urban-rural equalized development; (7) regional agriculture and rural development; and (8) the systematization and internationalization of research achievements.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201410011 [本文引用: 1]

A review of progress in cultural geography in mainland of China during the past ten years needs to be discussed. This paper constructs an analysis system which recent research projects and publications relate to. Some articles reviewed the research of cultural geography by Chinese scholars based on the view angle of five themes in traditional cultural geography. However, they did not tell the logical relation between key concepts and theories. The method of this paper is constructivism. It takes references to build up a "genealogy tree" of cultural geography. The main object in geography is "place and region". Cultural geography seeks to analyze the mechanism of place from the perspective of culture. This is the trunk of the "genealogy tree". "Relationships between layers" and "scaling of place" are two branches of this tree. They are two methods to explore place. This paper also puts main concepts and theories to the "tree". The three conclusions are as follows. The first is that many case studies done by Chinese cultural geographers are on mechanism of place making. Most are based on the methodology of structuralism. The second is that the major development by Chinese cultural geographers is increasing the volume of case studies which refer to interaction between different layers of cultural system, which do not only refer to nature-society nexus. The third is about scale conversion issues of cultural areas. Chinese cultural geographers have started to pay attention to this poorly developed theme.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408013 [本文引用: 1]

Since the new millennium, Chinese society has underwent constant "differentiation" and "change", and typical social and cultural phenomena are emerging unceasingly. Social and cultural geography research has attracted sustained attention from scholars. Based on summary of the evolution of the theory of social cultural geography in foreign context, this paper reviews the concerns and hotspots to which Chinese social cultural geography scholars have been given attention in the past ten years. In addition, combining the current situation of development of China, this research also puts forward some other important research areas that should be concerned, such as social and cultural traits of the indigenous geography, the influence of rights and capital on spatial form of social and cultural and place construction, the phenomenon of mobility and scale effect caused by migration between urban and rural areas. In addition, this paper places emphasis of the dialectical unity between the universality of knowledge and China's own socio-cultural characteristics.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201812001 [本文引用: 1]

This paper outlines the development trajectory and genealogical features of political geography in contemporary China. It first maps the development of political geography in Western academia and summarizes the genealogical characteristics of Western political geography. Taking the Western political geography as a baseline, it then discusses the establishment and development of political geography in contemporary China and divides this process into three stages since the founding of new China: the germination period, the stagnant period, and the revival period. Based on the work of extant (typical) scholars, related studies and relevant genealogical developments in each stage, this paper explores the main genealogical characteristics of political geography in China. Five major branches are extracted, which are respectively represented by Zhang Qiyun, Bao Juemin, Li Xudan, Zhang Wenkui and Wang Enyong. On this basis, this paper studies the similarity and difference between Chinese and Western political geography by focusing on their developing trajectories and features. This paper argues that: the development of political geography in China has been long influenced by the exogenous theories and notions and for this reason there is an apparent binary division between exogenous and endogenous political geography theories in China; the methodology, concepts and systems of this sub-discipline are still insufficient, and establishment of a unified academic community and the construction of subject knowledge system is therefore urgently needed. Finally, this paper proposes an agenda for future Chinese political geographical studies and calls for a more balanced and locally rooted Chinese political geography.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
