 ,1,2, 袁林旺3, 裴韬2,4, 黄昕5, 刘广6, 郑东海1,2
,1,2, 袁林旺3, 裴韬2,4, 黄昕5, 刘广6, 郑东海1,2Disciplinary structure and development strategy ofinformation geography in China
LI Xin ,1,2, YUAN Linwang3, PEI Tao2,4, HUANG Xin5, LIU Guang6, ZHENG Donghai1,2
,1,2, YUAN Linwang3, PEI Tao2,4, HUANG Xin5, LIU Guang6, ZHENG Donghai1,2通讯作者:
收稿日期:2021-04-13修回日期:2021-08-27
| 基金资助: |
Received:2021-04-13Revised:2021-08-27
| Fund supported: |

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (1925KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
李新, 袁林旺, 裴韬, 黄昕, 刘广, 郑东海. 信息地理学学科体系与发展战略要点. 地理学报, 2021, 76(9): 2094-2103 doi:10.11821/dlxb202109004
LI Xin, YUAN Linwang, PEI Tao, HUANG Xin, LIU Guang, ZHENG Donghai.
1 信息地理学学科形成
随着对地观测、智能感知、物联网、大数据、云计算、人工智能等信息科学与技术的迅速发展和广泛应用,地理科学发展的背景和条件发生了巨大的改变,地理科学与信息科学与技术的深度融合催生了信息地理学的概念,使地理科学具备了技术科学的属性。“天—空—地”一体化遥感立体观测、物联网和社会感知体系的建立和发展,实现了对自然、人文各类要素信息的实时动态采集与接入,遥感和地理信息技术强烈驱动了地理科学的革新。地理数据融合集成技术、地理系统集成模型与决策支持系统的发展,使得对地球表层系统的深入理解以及现实世界中的决策优化,都愈发依赖于信息空间中的综合分析模型和情景预估。虚拟现实、增强现实和数字孪生等技术的发展则日渐模糊了物理世界和现实世界的界限,实现了自然地理空间、人文社会空间和信息空间的多重交互。然而,当前地理信息领域的研究也出现了过度技术导向,越来越与信息科学亲缘,而疏离地理科学。因此,亟需重塑信息地理学,强化服务以人类生存环境为研究对象的地理科学,促进地理科学更加系统化、科学化和现代化,大力推动地理科学的整体发展。信息地理学是以信息技术为主要手段,研究地球表层系统中自然、人文、地理信息要素的分布特征、时空分异、空间联系,以及地理空间数据、信息的采集、传输、存储、表达、分析和应用的地理科学分支学科。信息地理学是一门自然地理、人文地理与信息科学技术深度融合的新兴交叉的地理科学二级学科,具有很强的技术科学属性,是地理科学中独特且不可或缺的组成部分[1]。这主要体现在:① 完善地理科学的学科体系,通过信息手段有机联系地理科学众多分支研究领域,深化地理科学各分支领域的定量化和科学化研究,实现地理科学从过去和现状的定量描述到对未来的定量预测;② 吸收和引进信息科学等相关学科和领域的最新进展,如大数据、人工智能、物联网等,提高数据和知识的综合与集成水平,为解决复杂地理科学问题,更加深入地理解和模拟地球表层系统提供关键手段;③ 作为自然地理、人文地理与社会服务的媒介,将地理科学研究成果输出到其它领域,促进区域协调与人类可持续发展。与传统的地理信息科学和遥感相比,信息地理学的概念更聚焦于“地理学”,有助于促进遥感、地理信息科学的发展和应用回归地理科学(表1)。信息地理学绝不是一个封闭的边界,它在生长中,因此亟需热烈的讨论。在《中国学科及前沿领域发展战略研究(2021—2035)》地理科学的学科规划背景下,本文尝试给出信息地理学的学科体系和发展战略,以期启动对信息地理学的讨论,促进信息地理学的完善和发展。
Tab. 1
表1
表1信息地理学、地理信息科学、遥感与地理信息科学等学科名称对比
Tab. 1
| 学科名称 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 信息地理学 | 和自然地理、人文地理对应,把地理学的技术——遥感、GIS、地理大数据、表层地球系统科学模拟进行统一 | 有把信息的空间关系作为唯一研究对象的歧义 |
| 地理信息科学 | 学界广泛接受 | 对遥感涵盖不多,也基本不涉及地球表层系统科学的模拟,偏重于地理信息系统和地图学 |
| 遥感与地理信息科学 | 同时涵盖遥感和地理信息科学 | 学科名称太长,遥感不全是地理科学研究范畴,如传感器、大气、海洋遥感等 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2 信息地理学分支学科特征
遥感、地理信息、物联网、大数据与人工智能等技术的快速发展极大推动了地理科学的革新,促进了信息地理学的形成和发展,并逐渐形成地理遥感科学、地理信息科学和地理数据科学3个分支学科(图1)。图1
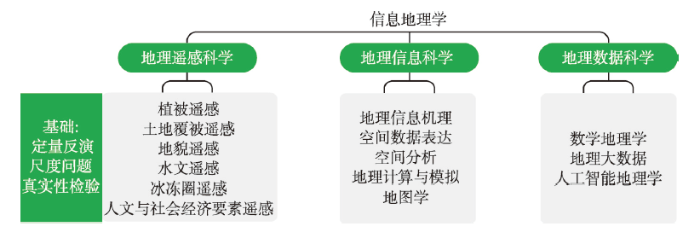 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1信息地理学的学科体系
Fig. 1The disciplinary structure of information geography
2.1 地理遥感科学
遥感科学与技术被广泛应用于地球系统科学的各个分支学科以及生态、环境、农业、林业、交通、城市等众多领域。本文所述及的地理遥感科学,是指遥感科学与技术和地理科学交叉所产生的基础科学问题以及遥感在地理科学各分支学科中的应用(图1)。遥感的迅猛发展为自然地理、人文地理、可持续发展与人地系统研究提供了重要信息源和科技支撑,并促进了定量反演、真实性检验和尺度转换等遥感基础性研究的发展。随着遥感辐射传输建模和基于先验知识的定量遥感反演理论逐步完善,多源遥感协同反演理论和方法不断深入[2,3,4],以全球陆表定量遥感产品和多源协同定量遥感生产系统为标志,中国具备了全球长时间序列定量遥感产品的生产能力[5];定量遥感产品的真实性检验在理论方法体系构建方面取得了长足进展,发展了遥感像元尺度地面真值获取方法,构建了遥感产品真实性检验网;同时提出了“自下而上的归纳方法和自上而下的演绎方法”的遥感尺度问题研究思路[6],并通过开展黑河生态水文遥感试验[2],推动了遥感尺度转换理论和实验方法走向成熟。
在遥感科学和地理科学的结合方面,地理遥感科学逐渐形成了植被遥感[7]、土地覆被遥感[8]、地貌遥感、水文遥感、冰冻圈遥感[9]、人文与社会经济要素遥感等主要应用分支[10](图2),并以前所未有的深度和广度推动地理科学的发展。在1:100万中国植被图、全国森林资源图等制图方面,遥感发挥了重要作用,中国先后发布了全球首套30 m和10 m分辨率的土地覆被数据集[8, 11],并研发了1985—2018年全球30 m逐年不透水面数据产品及其他高分辨率土地覆被产品[12];基于定位、定量和定性相统一的遥感和GIS技术形成的《中华人民共和国地貌图集》[13],为地貌学研究提供了准确的基础数据支撑;历时10年完成的2期黑河遥感试验,实现了遥感和生态—水文集成的深度结合[2]。此外,在以遥感观测的长周期、多尺度、宏观和微观的多源信息为支持,以地球大数据为技术促进机制的条件下,进一步促进了联合国可持续发展目标的遥感定量评估[14]。
图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2遥感和地理科学的结合
Fig. 2The integration of remote sensing and geographic science
2.2 地理信息科学
国际地理信息系统(GIS)的发展萌发于20世纪60年代,Goodchild[15]在此基础上于1992年提出了地理信息科学(GIScience)的概念。GIS于20世纪70年代末引入中国,陈述彭院士等老一辈科学家倡导并组织了中国地理信息科学研究,提出了“地学信息图谱”等一系列概念和方法,促进了地理信息科学方法论的发展。从1990年到2000年,中国****主要在GIS构建模式、数字高程分析、矢栅一体化时空数据模型[16]、面向对象GIS[17]、GIS时空数据模型、空间统计与分析等领域进行理论与方法的探索,在软件平台上开始打造具有自主知识产权的Super Map、MapGIS、GeoStar等国产GIS软件。2000年以来,随着地理信息科学理论的深入研究以及数字地球、数字中国建设的需求牵引,GIS的应用不断深入,中国****在虚拟地理环境[18]、空间拓扑关系[19]、地理空间统计[20]、地理数据挖掘、地理空间不确定性、元胞自动机与地理模拟系统[21]、地理时空预测等方面进行了方法与技术创新。2010年以来,随着智慧城市建设的快速开展[22,23],GIS已经成为城市管理、土地利用、公共健康、灾害监测等领域的基础支撑平台,中国自主发展的各GIS平台和相关软件发展迅猛,2015年国产GIS软件国内市场占有率首次突破50%。2018年以来,中国地理信息科学在新ICT(Information and Communications Technology)技术、地理大数据[24]、人工智能、泛在地理信息服务等领域进展明显,提出并形成了一系列国际领先的基础理论和关键技术,如提出了全空间信息系统[25]、全息地图[26]、地理场景学[27]、社会感知[28]等一系列原创的理论方法,并在地球大数据集成[29]、行为轨迹与行为空间等领域取得了突出进展。地理信息科学与技术的发展和应用已经远远超越了地理科学研究的范畴,并从科学研究和行业应用逐步走向大众化、社会化服务。2.3 地理数据科学
地理数据科学的研究主要包括数学地理学、地理大数据和机器学习,以及人工智能地理学(图1)[30]。大数据与人工智能的冲击推动了地理数据科学的形成和发展。中国****在数学地理方法的进展不仅超越了统计学方法的范畴,还涉及机器学习方法、演化方法、复杂网络理论等[31]。以对地观测、传感网、VGI、人类行为等为代表的多种地理数据快速汇聚形成了一系列庞大的地理数据资源池,并以此为基础发展了面向地理大数据的系列标准规范、数据模型、聚合方法、传输模型、共享模式以及基础设施等,实现了对GIS、RS、GPS、SDSS(空间决策支持系统)等的有机集成,完善了地球表层系统科学数据集成与共享网络[32,33]。基于海量对地观测数据和多源融合数据,中国****构建了地球大数据平台[29],为地球科学研究提供了新视角和新方法,并在支持联合国可持续发展目标[14]和“数字一带一路”[29]方面发挥了巨大的作用。基于人类行为大数据,建立了人类时空行为特征的分析方法,发展了社会感知的研究框架[28],促进了社会大数据的发展和突破。随着地理大数据的快速发展,数据中蕴藏的复杂(非线性)关系、多元协同及时空耦合特征、超大规模的计算量等,使得传统的统计学方法已经难以适应,而以深度学习为代表的人工智能方法的突破,给大数据的处理注入活力,同时也快速深入到地理大数据的计算中。中国****已将深度学习神经网络应用于遥感影像、街景图片、文本数据、社交媒体等大数据中的处理并取得重要突破。其中,深度学习在时序、空间、光谱、视角、语义等多源信息融合方面,取得了显著优于传统方法的效果[34](图3)。图3
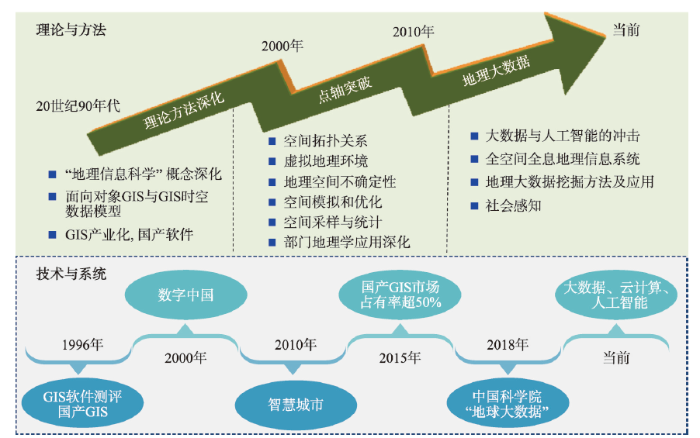 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图320世纪90年代以来地理信息科学发展历程及关键成果
Fig. 3Developments history and key achievements of geographic information science in the past 20 years
3 信息地理学学科发展战略布局
信息地理学的发展关系到整个地理科学发展的全局,应从学科体系设计、基础理论研究、关键方法攻关、集成平台构建、支撑可持续发展和国家重大决策等方面做好前瞻性的战略布局:① 紧密围绕地理科学的核心问题,加强信息地理学的基础研究,构建完整的信息地理学学科体系;② 引进和发展信息领域的前沿研究成果,推进智能地理分析、地球大数据、地球表层系统综合模拟与数据同化等方面的关键基础理论与方法,建立地理大数据平台、地球表层系统科学模拟平台、可持续发展决策支持系统,为地理科学夯实信息基础设施;③ 发展和推进信息地理学的综合应用,促进地理数据—信息—知识—决策的贯通,在更高水平上支持国家与区域可持续发展。3.1 地理遥感科学
大力发展地理遥感科学的基础理论与方法,深入开展遥感在地理科学各分支领域的应用,发展地理遥感基础产品,提升对地理科学与联合国可持续发展目标的服务能力;加强遥感机理、地球表层系统模型、地球大数据方法以及遥感信息与地球表层系统模型的同化研究,着重解决地理科学中存在的定量反演、尺度转换和真实性检验三大科学难题,推动地理科学的重大突破和发现。3.2 地理信息科学
利用信息技术,构建地理空间认知、表达、分析、模拟、预测、优化方法,探索自然地理空间、人文社会空间在地理信息空间中的表达与耦合方式,开展地理场景建模,致力研究地理信息系统实现和应用中的基础科学问题,发展解决中国地理信息产业卡脖子问题的基础理论与关键技术。3.3 地理数据科学
借助快速发展的数字地球、大数据、云计算、人工智能等新兴技术,结合遥感信息分析与应用、地理信息及地理分析手段,实现观测、数据与模型资源的整合,自动提取和发现隐含的地理知识与规律,刻画多尺度地理事件与地理要素的时空联系,揭示其发生本质,从而解决“地理数据爆炸,但地理知识贫乏”这一主要矛盾。4 信息地理学优先领域发展目标
信息地理学的优先发展目标有:① 持续发展地理遥感科学的基础理论研究,发展地理要素遥感辐射传输模型,优先突破遥感尺度转换、真实性检验等理论方法;② 发展地球表层系统观测、数据、模型基础设施和模拟平台,形成一批针对自然和人文要素的先进遥感新算法,提高国产卫星遥感数据产品的生产与应用能力,持续提供遥感产品服务,彻底改变“数据多产品少”和地理科学研究严重依赖国外遥感数据产品的局面,为支撑中国地理科学跨越式发展和地球表层系统科学前沿探索夯实地理信息基础;③ 发展三元空间支撑下的地理信息综合模型和地球大数据分析方法,发展具有自主知识产权的地理场景建模与集成分析、地理大数据位置聚合分析与服务、多模态地理信息表达与交互的技术与方法体系,研发包括过程机理模型和机器学习相结合的地理智能和地理模拟系统,加大力度发展具有自主知识产权和国际竞争力的地理信息平台和行业软件; ④ 构建支撑多角色、多数据、多圈层、多情景协同模拟的综合地理建模平台,实现地理数据—信息—知识—决策的贯通,为国家空间规划与区域可持续发展贡献信息地理学的智慧。5 信息地理学优先领域重点方向
5.1 信息地理学基础理论和原理方法
信息地理学基础理论和原理方法主要包括:① 在信息地理学基础理论框架方面,对信息空间中信息的时空分布、演化过程和要素相互作用规律进行系统解析,形成信息时空分布和格局特征分析的理论与方法;② 在多元信息智能分析与模拟的基础理论与方法方面,研究“形数理机”融合的多元信息集成表达理论,探索多源数据的统一组织与集成方法,研究结构化和非结构化的地理数据空间分析、推理、决策和服务模型,构建包括过程机理模型和机器学习相结合的地理智能和地理模拟系统;③ 在多元信息自适应计算理论与方法方面,发展地理规律驱动的空间数据结构与索引方法,研发地理大数据高维空间描述和分析的数据模型、数据结构、协同计算与系统建模方法,突破移动GIS、三维GIS、大数据与智慧城市等领域空间计算方法的性能瓶颈;④ 在信息地理空间表达与全息制图方面,突破地理大数据高维空间描述、实时动态表达、虚实融合展示的关键理论方法,发展数据驱动的虚拟地理环境构建方法,实现全视角、全要素、全信息、全内容的地理信息全息表达。5.2 地理遥感科学研究
地理遥感科学研究包括:① 在遥感定量反演方面,重点突破茂密植被和冰川透视观测、城市结构等遥感探测机理,研究陆表过程参量的多源遥感协同反演理论、模型同化方法,发展基于大数据、机器学习、人工智能等前沿技术的定量遥感反演新理论和新方法;② 在真实性检验方面,突破遥感像元尺度的观测新技术和融合地理要素时空变化规律的像元尺度真值估计新理论;③ 在尺度问题方面,加强多尺度数据的遥感观测试验,发展地理时空数据尺度转换理论和融合多种时空尺度的转换方法;④ 在植被遥感方面,研究植被高分辨率动态监测、植被三维结构和功能要素监测的方法,拓展新型荧光遥感应用,研发全球和区域尺度的植被参数长时序产品;⑤ 在土地覆被遥感方面,构建地理大数据新阶段的土地覆被分类体系,发展面向深度学习的土地覆被智能化制图方法,研发全球和中国尺度的全球中高分辨率土地覆被时序产品;⑥ 在地貌遥感方面,深化面向地貌学的多源遥感数据分析和综合利用能力,加强基于人工智能算法自动提取及识别地貌信息的方法研究,发展地貌变化高分辨率遥感监测系统;⑦ 在水文遥感方面,研发天—空—地一体化的流域关键水文要素观测体系,融合天—空—地多源遥感观测,结合模型、同化、人工智能等多种方法,构建水文大数据平台,发展长时间序列/实时、高精度、高时空分辨率、水量闭合的水循环遥感产品,提高水文预测和水资源管理能力;⑧ 在冰冻圈遥感方面,优化冰冻圈遥感监测体系,发展专门针对冰冻圈快速变化的卫星观测计划并开展卫星组网观测和长时序高质量的冰冻圈数据产品;⑨ 在人文地理与可持续发展遥感方面,在大数据平台、数字地球、智能信息处理算法和主动服务模式等方面开展创新性研究,融合遥感产品服务于地学建模和地理分析,服务于联合国可持续发展目标、“一带一路”“美丽中国”“新型城镇化”等国家战略与需求。5.3 地理信息科学研究
地理信息科学研究包括:① 在地球信息模型及场景地理信息系统方面,重点发展方向包括地球系统抽象描述的概念模型与信息模型、场景地理信息系统基础理论与方法、地理信息位置聚合的基础理论与方法、基于物质/事件的地理信息建模与分析的新理论新方法、三元空间演化信息地理学和地理场景的虚实融合表达方法;② 在地理系统的信息建模与模拟方面,研究全方位、全视角、全内容的地理信息获取方式,发展多源地理数据的时空集成框架与数据融合方法,研究地理系统的综合建模、模拟与分析方法,实现地理场景协同建模,提升对地理系统的过程模拟和空间优化的分析能力;③ 在地理信息系统关键技术方面,发展自动化、高效的地理场景模型构建方法,研究面向地球圈层结构、多地理要素综合的GIS建模与分析方法和智能地理分析方法,发展移动GIS、三维GIS、大数据与智慧城市等应用GIS平台,创新GIS全媒体表达与交互方法,支撑国家战略与区域发展等领域的应用。5.4 地理数据科学研究
地理数据科学研究包括:① 在地理大数据的理论和应用方面,研究地理大数据和泛在地理数据的理解、聚合与共享的理论与方法,突破地理大数据加工和分析的关键技术,研究面向时空大数据综合分析的数据模型、数据结构、协同计算与系统建模方法,突破地理大数据高维空间描述、实时动态表达、虚实融合展示、空间信息深度学习等关键方法与技术,完善地理大数据标准,形成国家地理大数据战略高地;② 在社会计算与感知方面,结合泛在传感器的普及应用,将社交媒体、人类轨迹、众源标记等空间大数据与遥感数据进行融合,实现“以人知地”和“以地知人”;③ 在人工智能地理学方面,研发以地理规律和相互作用为基础的表达—分析—计算一体化的新型地理深度神经网络,建立地学场景的专属深度智能网络模型,研究基于人工智能的复杂多源地理大数据融合建模、动态感知和因果网络分析方法,突破人工智能技术在地理信息组织管理、时空分析、建模模拟、交互表达的应用瓶颈,提升对地理现实世界过去、现在和未来数字化重构、分析与预估的智能化水平;④ 在数学地理学方面,研究基于非欧几何的时空融合的地理时空框架,构建多测度、多尺度、形式化、可计算的地理时空统一表达的数学模式,建立多尺度、多层次的地理现象数学表达与特征测度模型,构造数学地理学建模与模拟的方法体系。6 结语
信息地理学是基于信息科学理论及方法认识和利用地理信息的地理科学分支学科,是地理科学研究的重要工具和手段。特别是在现代信息技术条件下,随着地理信息数据的快速增加,信息地理学的作用和地位进一步凸显。以《中国学科及前沿领域发展战略研究(2021—2035)》地理科学的学科规划为契机,本文重新梳理了信息地理学的形成、定义和学科体系,重点阐述了信息地理学的学科发展战略布局、优先领域发展目标和重点方向。本文关于信息地理学定义、学科体系和发展方向的重塑将促进遥感、地理信息科学与技术的发展和应用回归地理科学,进一步强化地理科学研究,使其更加系统化、科学化和现代化,促进地理科学的整体发展。本文并不是给出信息地理学的定论,而是启动这一讨论[35,36,37]。本文关于信息地理学学科体系和发展战略要点的概述仍需进一步完善,以期加快推动信息地理学的发展。致谢
成文过程中得到陈发虎、郭华东、龚健雅、闾国年、黎夏、刘瑜、张兵、葛咏、刘良云等****的帮助和建议,在此表示感谢。参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1175/BAMS-D-12-00154.1URL [本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201309001 [本文引用: 1]

With regard to the national needs and basic research, several critical issues should be addressed in quantitative remote sensing: inefficient use of mass remote sensing data, inadequate universality and systematicness of quantitative remote sensing research, and limits in remote sensing applications. Therefore, Remote Sensing Science (RSS) research subjects need to be integrated with other disciplines in order to advance our understanding of RSS. In the authors' opinion, due to the heterogeneity of the geo-surface, generalization and modeling on the basis of experimental data, as opposed to individual interpretation of a specific location, could be the key for the future research. Combining "a top-down deduction method" with "a bottom-up induction method" in integrative physical geography in China, we want to build a methodological framework to resolve the central issues of RSS, for instance, the "scale effect", and to create several open platforms (such as data, inversion and computer simulation), and to bring together experts from different disciplines.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1360/N072018-00117URL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.scib.2019.03.002URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/20964471.2020.1730568URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1080/02693799208901893URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1360/zd-2011-41-4-549URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201701010 [本文引用: 1]

Spatial stratified heterogeneity is the spatial expression of natural and socio-economic process, which is an important approach for human to recognize nature since Aristotle. Geodetector is a new statistical method to detect spatial stratified heterogeneity and reveal the driving factors behind it. This method with no linear hypothesis has elegant form and definite physical meaning. Here is the basic idea behind Geodetector: assuming that the study area is divided into several subareas. The study area is characterized by spatial stratified heterogeneity if the sum of the variance of subareas is less than the regional total variance; and if the spatial distribution of the two variables tends to be consistent, there is statistical correlation between them. Q-statistic in Geodetector has already been applied in many fields of natural and social sciences which can be used to measure spatial stratified heterogeneity, detect explanatory factors and analyze the interactive relationship between variables. In this paper, the authors will illustrate the principle of Geodetector and summarize the characteristics and applications in order to facilitate the using of Geodetector and help readers to recognize, mine and utilize spatial stratified heterogeneity.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201903014 [本文引用: 1]

This paper reveals the principle of geographic big data mining and its significance to geographic research. In this paper, big geodata are first categorized into two domains: earth observation big data and human behavior big data. Then, another five attributes except for "5V", including granularity, scope, density, skewness and precision, are summarized regarding big geodata. Based on this, the essence and effect of big geodata mining are uncovered by the following four aspects. First, as the burst of human behavior big data, flow space, where the OD flow is the basic unit instead of the point in traditional space, will become a new presentation form for big geodata. Second, the target of big geodata mining is defined as revealing the spatial pattern and the spatial relationship. Third, spatio-temporal distributions of big geodata can be seen as the overlay of multiple geographic patterns and the patterns may be changed with scale. Fourth, big geodata mining can be viewed as a tool for discovering geographic patterns while the revealed patterns are finally attributed to the outcome of human-land relationship. Big geodata mining methods are categorized into two types in light of mining target, i.e. classification mining and relationship mining. The future research will be facing the following challenges, namely, the aggregation and connection of big geodata, the effective evaluation of mining result and mining "true and useful" knowledge.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2015.02.001 [本文引用: 1]

As a spatial science, Geographical Information System (GIS) is characterized by its distinctive spatial thinking and perspectives. With a focus on spatial interrelations and interactions, GIS can be used to reveal the spatial distribution patterns and dynamic changes of objects, events, and phenomena. This article outlines the future prospects of the development of GIS based on the understanding of the spatial objects that it studies. Universal GIS with universal coordinate system will be developed when the study objects is the universe. Indoor GIS is to be studied and developed in case that GIS is applied to the indoor space where we spend about 80% of our time. GISs for underground and aqua-spaces also need to be developed since our activities have extended into solid earth such as shopping malls in subway stations and open water such as marine fishery. GIS is also useful when we deal with spatial issues involving micro-scale spaces such as sport fields or human body, therefore human GIS and sports GIS that describes and models sports activities will come into being. The coming of age of big data has created a new opportunity for the development of GIS. Spatial thinking and analysis will contribute greatly to the resolution of big data mining, even big data science.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2011.11.001 [本文引用: 1]

Location-based service is one of the key developing areas in modern information society. Linking all kinds of information with their explicit or implicit location(s) greatly promotes the geographical concepts to be more and more accepted and popularized. This paper mainly focused on the discussion on the contents of location based service with location-based map. At first, the authors explained the concept and its contents of location awareness and location computation from the point of view of geographical location and place. Moving location, or the position of a moving object, will be widely adopted and used while positioning system based on GPS and wireless communication are developed. Then, the authors discussed the difference and commonness between location map and general digital map. The semantic location will play key roles in the location-based services. On the basis of state-of-the-art navigation maps widely used in car navigation and internet map service, panoramic location-based map (PLM) is proposed as a new concept and new type of location map. It is a kind of digital map which store all the related data and information about the location and its surrounding events, matter and environment. The user will be served with the information of interest when he or she steps into a certain geographical fence. As location based service is developing and getting popular, PLM will become the most welcome map in the near future.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/00045608.2015.1018773URL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 3]
DOI:10.1111/gean.v53.1URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/19475683.2019.1612945URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/10095020.2020.1720529URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
