 ,1,2, 延军平1,2, 汪成博1,21.
,1,2, 延军平1,2, 汪成博1,21. 2.
Universities and geographical research development in China based on the bibliometrics analysis
WU Yaqun1,2, LI Shuangshuang ,1,2, YAN Junping1,2, WANG Chengbo1,21.
,1,2, YAN Junping1,2, WANG Chengbo1,21. 2.
通讯作者:
收稿日期:2018-04-20修回日期:2019-10-18网络出版日期:2020-02-25
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-04-20Revised:2019-10-18Online:2020-02-25
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
武亚群(1993-),女,山西武乡人,硕士,研究方向为人文地理与区域灾害防治E-mail:1511107932@qq.com。

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (4244KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
武亚群, 李双双, 延军平, 汪成博. 中国高校地理研究发展与态势. 地理学报[J], 2020, 75(2): 302-317 doi:10.11821/dlxb202002007
WU Yaqun.
1 引言
目前,无论从学科发展,还是从国家经济社会发展需求看,地理学正面临着新任务,也迎来发展的新机遇[1]。因此,回顾中国地理学发展历程,厘清地理学发展态势,对推动地理学发展具有积极作用。在国内研究中,不少****结合论文统计或文献计量方法,对国际地理学期刊[2]、国内地理学期刊[3,4,5,6,7]、地理学及其分支领域发展特征与趋势[8,9,10,11]、中国地理学国际影响力变化进行研究[12],旨在阐明中国在国际地理科学研究机构竞争力现状[13];还有****对中美地理学发展脉络[14]、中日地理****写作年龄进行分析[15]。梳理已有研究发现,前期研究主体多集中于地学分支学科或某种地理刊物,以高等院校为研究对象,探讨中国高校地理发展时空规律的研究相对较少。研究机构层面,中国地理研究发展是高等院校和科研院所共同推动,但是两者研究各有侧重。其中,科研院所侧重理论创新及实践应用,高等院校侧重学科基础性理论和区域可持续发展,并承担着中小学地理教师培养和教学理论创新[16]。值得关注的是,20世纪80年代末,许多高校将地理系改名为“资源环境学院(系)”“城市与资源学院(系)”“资源环境与旅游学院”,反映出地理学科发展在新的市场经济条件下面临诸如高校招生困难、学生就业困难等现实问题[17];进入21世纪,中国地理学发展环境得到很大改善,陆续有高校转型发展,在院系名称中加入“地理”。回归地理学,加强地理****的学术认同,反思地理研究的知识结构,成为当前中国地理学关注的热点问题[18]。因此,在地理学发展新时期,审视地理学在中国高校的发展格局,阐明地理学在不同类型、不同区域高校的发展历程,分析高校地理知识产出的影响因素,对未来中国地理宏观政策制定具有现实意义。
在研究方法上,综合科研产出数量、科研产出质量和科研产出影响力三方面可以反映高校的科研水平,而论文是科研产出的重要载体[19]。近年来中国高校发表科学引文索引(Science Citation Index, SCI)论文总数增幅明显,但是反映中国高校地理研究的学术形象和影响力,在一定程度上还是国内综合性地理学术期刊[20]。这是由地理学区域性和综合性的学科特征决定,也与中国地理研究紧紧围绕国家重大需求,解决区域可持续发展面临关键问题的学科定位有关。《地理学报》《地理研究》《地理科学》和《地理科学进展》(简称“4地”期刊)是中国最主要的综合性地理学学术期刊,无论论文的数量和质量,还是期刊的国际影响力均在不断提高,可在一定程度上反映中国高校地理研究的发展历程[21,22,23,24]。基于此,本文以1986—2018年“4地”期刊发表论文为基础数据,对“不同类别高校”“不同区域高校”地理研究的发展变化特征进行分析,进而从发展基础、内外驱动、环境条件和科研支持等4个方面,探讨影响中国高校地理研究发展因素,以期为中国高校地理学发展提供理论基础。
2 资料与方法
2.1 资源来源
以高校在“4地”期刊的发文量为基础,文献资料获取分为2个层面:中国地理高校名录的筛选与确定;“4地”期刊发文量信息的标准与获取。① 地理高校名录筛选:为了保证选取的高校具有代表性,参考《地理科学三十年:从经典到前沿》中地理类高校信息[25],补充含有地理学一级学科硕士授权点的6所高校,以39所高校为代表,对中国高校地理发展格局进行研究。
② 期刊发文量获取:以中国知网为检索来源,时间节点截至2019年1月25日,对中国39所高校在1986—2018年于“4地”期刊的发文量进行检索。具体流程如下:进入高级检索栏,在文献来源输入“4地”刊名,输入高校名称,整理高校在1986—2018年的发文量信息,以此为基础数据进行统计分析。
2.2 中国地理研究——高等院校与科研院所的差异
无论是在世界,还是在中国,高等院校和科研院所承担的职能均是有所差异。其中,高等院校职能为:教育、科研和社会服务,其侧重于教育,特别是基础知识的传承与创新;科研院所则在兼顾传承基础上,更加重视科学研究与实践应用,并且以解决国家重大需求为驱动。例如;为解决关系国家全局与制约长远发展的资源环境问题,建立中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所;面向干旱区生态、环境、资源问题,以干旱区水土资源利用与生态安全为重点,建立中国科学院新疆生态与地理研究所。在研究主体中,高等地理院校多侧重于教学,研究主体为教授和副教授等,研究所则以研究员和副研究员为主体。在科研经费和产出体量方面,研究所高于高等院校,且科研产出体量也高于高等院校。在历史沿革方面,1952年中国进行高等院校调整,设置地理学高等院校有5所综合性大学、3所师范大学,19所高等师范院校,这些学校成为后期高校地理研究的主体;地理科研院所则依托于中国科学院,发展始终面向国家重大战略需求,这一点在竺可桢1965年发布报告《中国科学院地理研究工作方向和任务的初步设想》体现的尤为明显[26]。可以看出,中国地理高等院校和科研院所在历史沿革、发展定位、隶属系统,还是研究主体、研究产出,两者均存在差异(表1)。
Tab. 1
表1
表1中国高校和科研院所研究特征
Tab. 1
| 指标 | 高校 | 科研院所 |
|---|---|---|
| 发展定位 | 教学+科研 | 以科研为主 |
| 隶属系统 | 教育系统 | 科研系统 |
| 服务对象 | 地方发展 | 国家战略 |
| 研究人员 | 教授、副教授等 | 研究员、副研究员等 |
| 研究侧重 | 基础理论研究 | 理论创新与实践应用 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.3 演化趋势分类
1986—2018年中国39所高校发文量形成不同发展曲线,为了方便描述高校地理学发展变化特点,按发展形态归为3种类型(图1):①“S”型增长曲线。表示高校地理研究发文量先稳定或缓慢增加,中期快速增长,后期维持稳定或呈下降趋势,该类型主要反映中国高校地理学“缓慢发展—快速发展—发展停滞”的阶段性变化特征,以北京大学为典型;②“J”型增长曲线:发文量前期低位波动或缓慢增加,后期呈现快速上升,该类型表征后期快速发展的中国地理高校,以河南大学为典型;③ 线型增长曲线:高校发文量呈直线上升,说明高校地理学呈现快速发展,以东北师大为典型。图1
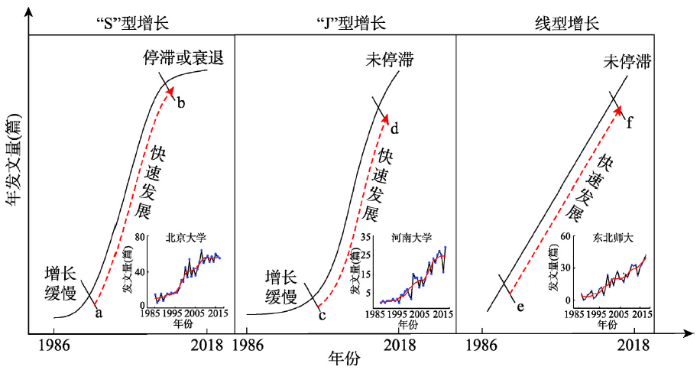 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1中国地理高校“4地”期刊发文量的演化过程
Fig. 1The evolution pattern of articles published by Chinese universities in four major geographic journals
2.4 发文等级划分
为了反映中国高校地理研究发展的空间差异性,对高校2014—2018年发文量进行标准化转换、欧氏距离计算,采取可变类平均法进行系统聚类分析。依据聚类结果,将中国39所地理研究高校,按“4地”期刊发文量分为3个量级,其中高发文量高校有6所、中发文量高校有15所,低发文量高校有18所(图2)。图2
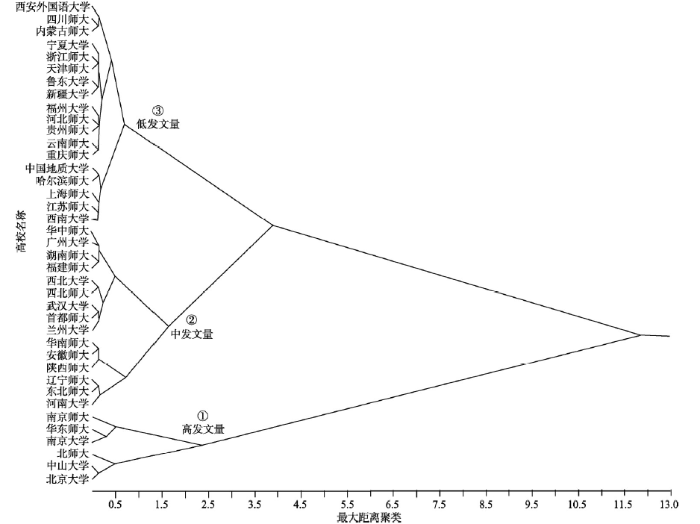 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图21986-2018年中国高校“4地”期刊发文量聚类分析
Fig. 2The clustering analysis of articles published by Chinese universities in four major geographic journals
2.5 高校发文指数
高校发文指数,是借助某类高校的平均发文量与中国高校平均发文量的比值,反映地理发文量在中国高校的相对位置。当发文指数大于1,说明该类高校地理发文量高于中国高校的平均值。高校发文指数(SPij)计算公式如下:式中:SPij为i类高校j年在“4地”期刊的发文指数;Pij为i类高校j年在“4地”期刊发文总数;i为高校类别,主要包括两种类型:以高校类别分类,即“985”“211”和其他类高校;以地区为分类标准分为东部高校、中部高校和西部高校;ni为i类高校数量;N为总高校数。
3 结果分析
3.1 不同类别中国高校地理研究的发展态势
对1986—2018年“985”高校、“211”高校、其他类高校(即非“985”“211”高校)年均发文量的统计分析,可以反映出不同类别高校地理学研究的总体水平,以及不同类别高校地理学发展的水平差异与时间变化特征。1986—2018年,“985”高校、“211”高校、其他类高校发文量均呈上升趋势,其增长速率分别为13篇/10a、4篇/10a、3篇/10a,说明“211”高校、其他类高校与“985”高校相比,发文量增加速率差距相对较大。同时,“985”高校发文量明显高于其他两类,且1998年之后发文量绝对差距逐年增加,“211”高校略高于其他类高校(图3a)。图3
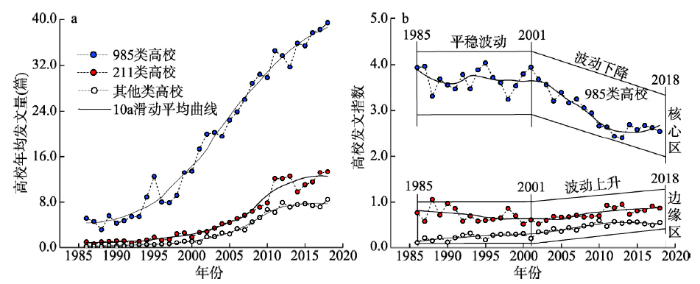 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图31986-2018年不同类别中国高校“4地”期刊发文量的趋势特征
Fig. 3Variation of articles published in four major geographic journals by universities sponsored by Projects 985 & 211 and other universities in China during 1986-2018
为阐明不同类别高校地理研究发展差异,分别对“985”高校、“211”高校、其他类高校发文指数的逐年变化进行统计(图3b)。结果表明,1986—2018年,“985”高校发文指数始终大于1,处于发展格局的核心区,而“211”高校、其他类高校的发文指数均小于1,处于发展格局的边缘区。在具体相对变化上,“985”高校发文指数整体呈下降趋势,其变化过程可以分为2个阶段,即1986—2001年为平稳波动期,2002—2018年为波动下降期;“211”高校和其他高校发文指数整体保持平稳。对比三类高校1986—2018年发文指数变化发现,三类高校地理学发展水平的相对差距整体呈现降低趋势。
在关注宏观趋势变化同时,对三类高校的年发文量进行了量化处理,以分析不同类别高校地理学发展的内部差异(图4)。具体而言,① 在“985”高校中,北京大学和南京大学在1992年发文量逐渐稳定,且具有较高的发文量,为高发文量的核心群体,其他高校则在1999年前后发文量趋于稳定,形成地理研究的核心;②“211”高校在2005年之后普遍发展,形成以中、高发文量为主的集聚区。其中,南京师范大学、东北师范大学、陕西师范大学、西北大学和华南师范大学等5所高校形成相对高发文量群体,湖南师范大学、华中师范大学、西南大学、中国地质大学、新疆大学、福州大学等6所高校形成中等发文量群体;③ 对于其他类高校而言,多数高校在2006年之后陆续发展,形成高、中、低发文量高校均衡分布的格局。其中,安徽师范大学、河南大学、西北师范大学、首都师范大学、辽宁师范大学等5所高校形成相对高发文量集聚区,云南师范大学、福建师范大学、河北师范大学等10所高校形成中等发文量群体,四川师范大学、天津师范大学、西安外国语大学等5所高校形成低发文量群体。
图4
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图41986-2018年不同类别的中国高校“4地”期刊发文量的空间特征
Fig. 4Spatial pattern of articles published in four major geographic journals by universities sponsored by Projects 985 & 211 and other universities in China during 1986-2018
3.2 不同区域中国高校地理研究的发展态势
从不同区域高校地理发展趋势角度分析,1986—2018年东部高校、中部高校、西部高校发文量均呈上升趋势,增长速率分别为7篇/10a、5篇/10a和3篇/10a,体现了不同区域高校地理学发展速度存在差异。东部高校发文量高于中、西部高校,且在1994年出现东西部高校发文量绝对差距增加;中部高校发文量要高于西部高校,且发文量绝对差距年际变化呈“增大—减小—增大”的阶段性变化,即1998—2006年差距增大,2007—2013年差距逐渐减小,2014—2018年差距再次增大(图5a)。在高校发文指数变化上,1986—2018年东部高校发文指数始终大于1,中部高校发文指数在1上下波动,西部高校发文指数始终小于1。可以看出,与中国高校地理发展平均水平相比,东部高校依然具有优势,且高于中西部高校的发展(图5b)。图5
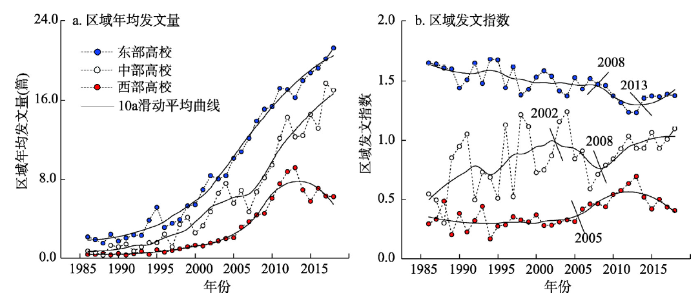 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图51986-2018年区域视角下中国高校“4地”期刊发文量的趋势特征
Fig. 5Variation of articles published by Chinese universities in four major geographic journals based on regional perspective during 1986-2018
在不同高校具体发展过程中,① 东部高校发文指数整体呈下降趋势,变化过程可分为3个阶段,即1986—2008年为缓慢下降期,2009—2012年为快速下降期,2013—2018年为缓慢上升期;② 中部高校发文指数整体呈上升趋势,但是波动幅度较大,发展阶段可以分为3个时期,即1986—2002年为波动上升期,2003—2007年为波动下降期,2008—2018年为波动上升期;③ 对于西部高校发文指数而言,增长速率略低于中部高校,其中1986—2005年为平稳波动期,2006—2013为缓慢上升期,2014—2018年发文指数呈现下降趋势。从时间演化角度看,东部和中部高校的地理发展水平相对差距呈减小,而两者与西部高校发展水平相对差距逐渐增加。
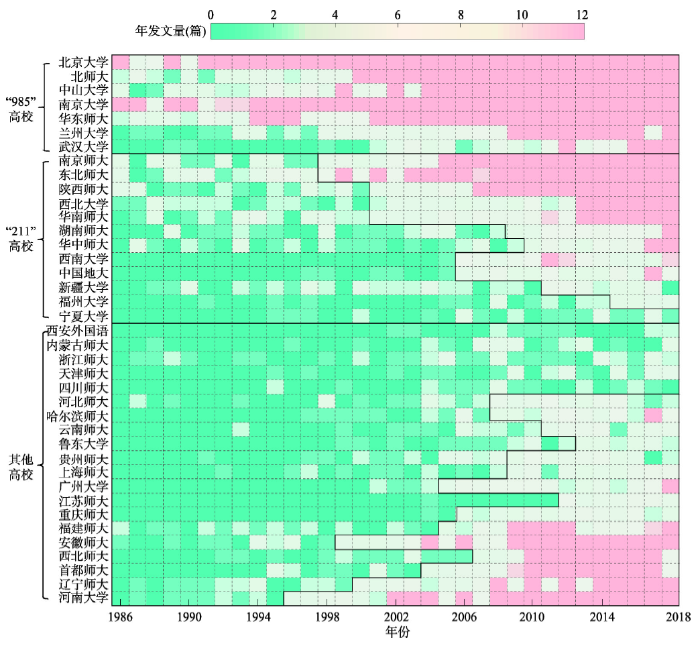
利用1986—2016年中国39所高校在“4地”期刊的发文量数据,绘制中国高校地理发展热图,以分析不同区域高校地理学发展的空间差异(图6)。结果表明:① 东部高校发文量以北京、上海、广州和南京为中心,形成高发文量集聚区,其与中国高等教育资源集聚的空间格局一致;② 对于中部高校而言,2004年后发文量呈现快速上升,逐渐由低发文量向中高发文量等级发展,并形成以中、高发文量为主的空间集聚。其中,东北师范大学、河南大学和安徽师范大学最为突出,形成高发文量集聚中心;③ 西部高校发文量于2006年后也陆续发展,形成高、中、低发文量均衡分布的格局。其中,陕西师范大学、兰州大学、西北师范大学、西北大学等4所西北高校形成高发文量群体,西南大学、贵州师范大学、重庆师范大学、新疆大学、云南大学等5所高校形成中发文量群体,四川师范大学、宁夏大学、内蒙古师范大学和西安外国语大学等4所高校形成低发文量群体。综合高校空间区位和发文量格局,西部高校地理发展总体呈“西北强—西南弱”的格局。
图6
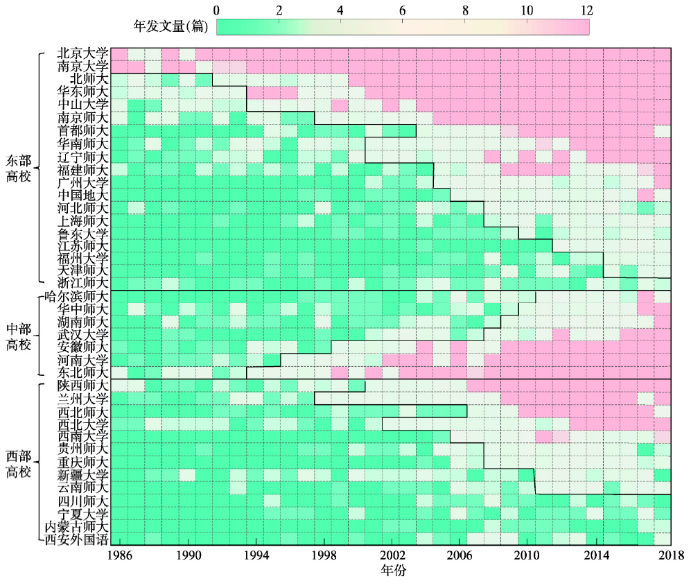 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图61986-2018年区域视角下中国高校“4地”期刊发文量的空间特征
Fig. 6Spatial pattern of articles published by Chinese universities in four major geographic journals based on regional perspective
3.3 中国高校地理研究发展形态与演化趋势
结合高校地理发展演化特点和高校发文量聚类结果,对不同类别高校、不同区域高校地理发展演化特征进行分析(图7)。其中,区域类型、高校类型、发文等级、发展形态各包括3种类型,构成复杂的四维数据结构,可细分为81个小类。为避免多层数据组合关系带来数据可视化的复杂性。在此,以地域分区(东部、中部和西部地区)为基础,构建多维分形结构树,以类型节点逐级分形,如东部地区1级节点分类为:“985”高校、“211”高校和其他高校,2级节点分类为:发文量等级,即高、中、低三类,3级节点分类为:发展形态,即“J”型、“S”型和线性增长类型。同时,定量统计不同类型组合高校数目,可更清晰地表达中国高校地理研究发展的变化特征。结果表明:图7
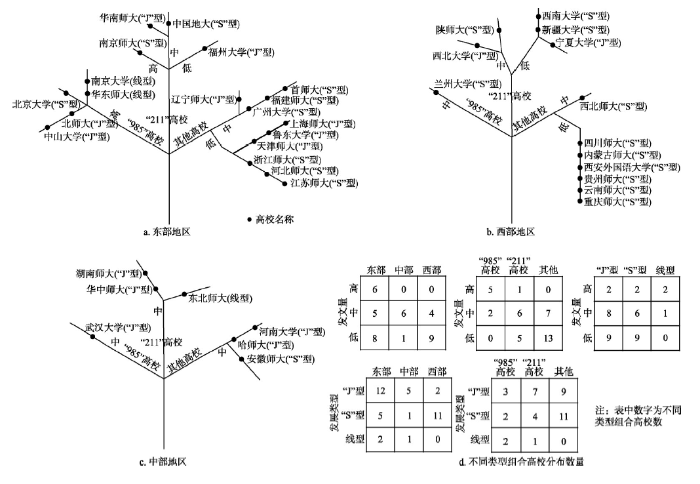 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图7中国高校地理研究发展态势
Fig. 7The pattern of geographical research development in Chinese universities
(1)从不同类别高校分析,“985”高校发文量曲线呈“J”型和线型总数(5所)多于呈“S”型的高校(2所),高、中、低发文量高校分别为5所、2所、0所,且高发文量6所高校中,除南京师范大学外,北京大学、中山大学、南京大学、北京师范大学和华东师范大学均为“985”高校,反映出“985”高校地理发展水平相对较高;在“211”高校中,发文量曲线呈“J”型和线型变化的高校总数(8所)是“S”型高校(4所)的2倍,且均属于中、低发文量,说明“211”高校发文量曲线多以后期发展型、持续发展型为主,近年来地理学展现良好的发展趋势;对于其他类高校而言,发文量曲线呈“J”型和线型的高校总数(9所)少于呈“S”型的高校(11所),且发文量为中、低类型,说明其他类高校地理研究发展呈现增长与停滞并存,且短时间内与“985”“211”高校依然存在差距。
(2)从不同区域高校分析,东部地区是高发文量高校的唯一分布区域,发文量曲线呈“J”型和线型的总数(14所)高于呈“S”型的高校(5所),低发文量高校数量(8所)低于中高发文量高校总数(11所),说明东部高校地理研究发展水平较高,但高校内部地理研究发展水平存在差异;对于中部地区而言,发文量曲线呈“J”型、线型和“S”型的高校数量分别为5所、1所、1所,且全部为中、低发文量。反映中部高校发文量偏低,发文量曲线以后期发展型为主;西部地区发文量曲线呈现“J”型和线型变化的高校总数为2所,少于呈“S”型的11所,均为中、低发文量。说明西部高校地理发展水平与中部地区类似,但是呈现后期停滞型高校要多于中部地区。
(3)从发展历程与发文数量分析,发文量曲线呈“J”型和线型的高校总数为21所,高于呈现“S”型变化的高校(17所);中、低发文量的高校总数(33所)也多于高发文量的高校(6所)。由此可见,中国高校地理研究发展多以后期发展型和持续发展型居多,同时发展突出高校数量偏少,未来中国高校地理研究仍有较大的提升空间。
3.4 中国高校地理研究发展的影响因素
中国高校地理研究态势分析,实质是地理知识产出的空间分异,更深层是地理科研活动空间不均衡的阐释。具体而言,中国高校地理学科发展受诸多因素影响,包括环境条件、内外动力、支撑条件、发展基础。其中,地理环境和区域问题是地理学发展的环境条件;社会与国家需求、科研人员自身动力是促进高校地理学发展的内外动力;科研项目和学校实力是支撑地理学发展的重要力量;学科传统和时代创新是地理学的发展基础(图8)。图8
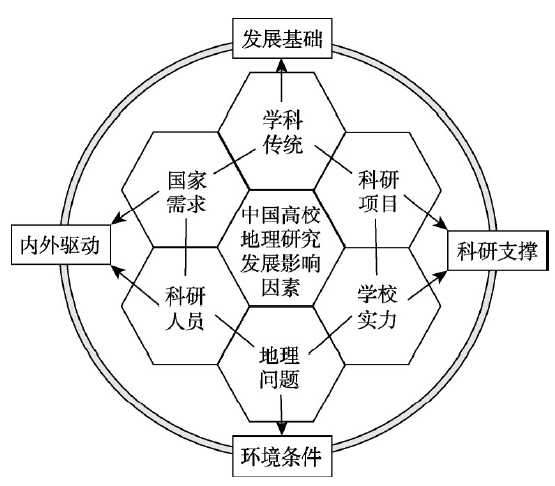 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图8中国高校地理研究发展的影响因素
Fig. 8Influencing factors of universities and geographical research development in China
3.4.1 环境条件:地理环境与区域问题 地球表层系统是地理研究的对象,地理环境是推动地理研究发展的科学资源[27]。长期以来,高校所在区域是高校地理学科发展的重要依托。一方面,从自然环境角度分析,西北地区丰富的自然条件、脆弱的生态环境,为研究人员提供了丰富的地学研究价值,促进了西北地区高等院校自然地理学科的快速发展;再如,华东师范大学、福建师范大学分别依托长江、闽江河口湿地生态系统,关注河口海岸区域特色,分析河口海岸生物地球化学过程,探讨河口三角洲沉积环境演变,为中国沿海地区资源开发、重大工程建设提供了坚实的研究基础。另一方面,从人文地理角度分析,北京大学对城乡结合部外来人口空间分布与分异、城中村流动人口的日常生活空间及其时空利用,以及北京城市犯罪的时空格局等问题进行探讨,丰富了人口和社会地理研究,反映出北京高校地理研究发展与北京的社会文化、经济发展联系密切[28]。
区域地理特色,往往是高校地理研究的出发点,也是高校地理研究创新、保持学科特色的源泉,更是高校地理学科内部结构形成的决定性因素。大数据时代的到来,交通条件的改善,地理****跨区域研究成为可能,空间距离不再是地理研究的阻碍[29]。在未来地理学发展中,东部高校不仅会保持较高的地理研究水平,也可能与中西部高校开展更多的跨区域合作研究。
3.4.2 内外驱动:国家需求与科研人员 “任务带学科”一直是1949年以来中国地理学发展的重要战略方针,这种发展范式在一定程度上促进了地理学科的发展,提高了地理学的科学水平和应用价值,体现了国家需求对地理学发展的积极推动作用[30]。2015年傅伯杰院士在中国地理学会第十一次全国会员代表大会的讲话表明:“当前地理学发展既是全球环境变化、全球经济一体化,以及全球地缘政治结构变化的决策需求,也是推进城镇化进程、产业优化升级、缓解资源环境压力、优化国土资源利用,实现可持续发展的现实需求”[31]。国家需求为地理发展提供了新机遇、指明了新方向。从人文地理学土地利用项目获得资助的情况分析,截至2017年底,国家自然科学基金项目(NSFC)主要针对快速城市化地区(沿海城市、核心城市群)、生态脆弱区(如农牧交错地带、西北干旱区)等地域类型的土地利用问题进行183项资助,这不仅推动了沿海高校的地理学发展,也为西部高校地理学发展提供了机遇[9]。但是,地理学对国家需求不断满足同时,也形成了各分支学科发展不平衡的局面,如何综合集成分支学科的研究成果,成为当前中国地理学面临的重要挑战之一。
作为中国地理学研究的主体,科研人员也会在自身动力、科研兴趣、以学术为职业发展取向愿望、职称晋升、成果申报、社会责任感等因素激励下发表学术论文,提升高校科研水平,推动高校地理研究发展,进而形成中国地理研究的空间分异[32]。值得一提的是,无论科研人员发表论文出发点是否存在差异,其对学科发展的推动作用都不可忽视。特色地理团队建设和发展,在一定程度上会促进高校地理学的跨越式的发展。如河南大学李小建、苗长虹、乔家君等在经济地理、乡村地理等领域的研究,以及安徽师范大学陆林、苏勤、焦华富等在旅游地理、城市地理领域的研究充分体现了科研团队对中国高校地理学的积极推动。
3.4.3 科研支撑:科研项目与学校实力 从影响高校地理研究的外部条件看,主要包括3个层面,即人力资源、物力资源、财力资源。一定程度上,基金项目也是人力、物力、财力资源的综合表现。国家自然科学基金作为科研工作开展的重要经费来源,保障了高校开展、实施、完成科研工作,也能通过引进人才、购买设备等形式增强学校实力[33]。高校实力越强,实验条件越好、科研人员科研能力越强,越有可能申请更多的科研项目[34]。在科研项目和学校实力的共同支撑下,中国高校地理科研人员开展学术活动,对地理知识产出起到促进作用。
39所高校中,地理研究发展水平较高的高校(中、高发文量高校)主要位于北京、上海、江苏、广东、陕西、兰州,与获得NSFC资助较多的省份分布基本吻合,体现了科研项目和学校实力在促进地理学发展中的重要作用[35]。但是,近年来受国家人才引进政策的限制,中国科学院和高水平院校培养的大量地理学青年人才不断向全国各地流动,使得地理学科青年基金的资助区域分布更加广泛,这种局面对推动东中西部高校的快速协调发展发挥了积极作用[36]。
3.4.4 发展基础:学科传统与时代创新 纵观中国高等院校地理学的发展历程,学科传统是影响学科发展的重要因素。新中国成立前,浙江大学、北京师范大学、中山大学、西北大学等已成立地理系,陕西师范大学、东北师范大学(前身)均开设了史地科,为自身地理学的发展奠定了基础。与此同时,中华人民共和国成立初期,由于地理教育事业发展,迫切需求中学地理教师,丁锡祉、黄国璋等地理****绝大多数选择在高等学校进行任职,也为高等院校地理研究发展,以及后期地理研究空间格局形成提供了人才基础[26]。1995年,“211工程”正式启动,为传统地理高校学科资源、影响力资源的集聚带来持续效应[37]。得益于优良的学科传统,以及高校自身对国家、社会需求的响应,西北大学、陕西师范大学、东北师范大学等传统地理高校都到较好的发展。其中,东北师范大学成为中部地区最早出现高发文量的院校,陕西师范大学、西北大学等则成为西部高校为数不多的高发文量的院校。
值得一提的是,学术传承对高等院校地理研究格局形成具有重要的影响,特别是在后期地理研究特色凝练和研究团队发展中起到至关重要的作用,其引领着重要成果的产出,也在一定程度上决定着中国高校地理研究的格局。比如华东师范大学地理科学学院前身为1951年成立的地理系,由浙江大学地理系迁并组建,时任浙江大学地理系主任的李春芬教授为其首任系主任。李春芬先生以整体性和差异性为切入,旁征博引阐释南美洲自然地理特征,为华东师范大学成为国内世界地理研究的高地,打下坚实基础[36]。中国历史地理学研究,主要集中于北京大学、陕西师范大学、南京大学等高校,其与学科传统有关,又受高校地理研究的特殊性影响。再如,北京大学王乃樑、崔之久教授、兰州大学李吉均教授、华东师范大学严钦尚教授、华南师范大学曾昭璇教授,在实践中解析地貌形态分异,在冰川地貌、海岸地貌、河口地貌取得丰富成果,并关注中国地貌科学人才培养,为高校地貌学长期发展提供了方向和不竭动力。
在时代创新方面,新研究范式的出现、新地理命题的产生以及新技术方法的应用,均对中国高校地理学科发展产生重要影响。一方面,当前大数据研究范式处于探索阶段,虽本体特征尚未达成共识,但新研究范式出现为中国高校地理学,尤其是人文地理学的定量研究提供全新的路径[38]。在高校机构建设中,北京师范大学和北京大学分别于2016年、2017年建立地理大数据平台,为地理专业的科研人员提供了全面的、丰富、专业的数据信息;另一方面,从地理研究应用角度分析,随着中国社会经济的快速发展,全球变化、环境发展等影响国民经济发展的关键领域,成为中国高校地理学的研究的新增长点[39]。在实践中,北京师范大学分别于2008年、2016年成立了全球变化与地球系统科学研究院、陆地表层系统科学与可持续发展研究院,为高校科研人员开展全球变化与地球系统科学的集成研究、陆地表层系统的综合研究提供了重要平台,促进了科研人员在相关领域的科研产出。
在新技术方法应用上,以地理信息系统为代表,引发地理学“计量革命”,也使得中国高校地理学科体系由早期自然地理学、经济地理学占主导的苏联模式,转变为自然地理学、人文地理学和地图与地理信息系统并存的新体系,为高校地理学科体系的完善提供了新思路,在某种意义上讲,GIS的出现拯救了地理学。在时代背景下,南京大学地理科学与海洋学院(原大地海洋科学系)1987年增设了地图学专业,并在2006年设立地理信息科学系。同时,随着3S以及网络、通讯、大数据等技术的发展,地理学对时空演化过程的描述,实现了由定性描述到定量化表达的转变,并将研究内容拓展至对地球表层系统的预测研究[18]。抓住时代创新机遇,迎接技术手段的提升,将对中国高校地理学转变研究方式、扩展研究内容产生重要影响。
4 结论与讨论
基于文献统计方法,以1986—2018年“4地”期刊发表的学术论文为基础,从不同类别高校、不同区域高校等视角,对中国高校地理研究的发展特征、演化趋势以及影响因素进行分析,主要结论如下:(1)中国不同类型高校地理研究快速发展,“985”高校主导的绝对差距依然存在,但是相对差距逐渐减小。从绝对指标分析,不同类别高校发文量与增长速率呈现出:“985”高校>“211”高校>其他高校,高校之间绝对差距在增大;从相对指标分析,“985”高校发文指数高于“211”高校、其他高校,但是“985”高校发文指数在2001年后呈下降,而其他类高校呈上升趋势,高校之间相对差距在减小。
(2)中国不同区域高校地理研究快速发展,东部高校主导的绝对差距依然存在,但是空间差异趋于减小。从绝对指标分析,不同区域高校发文量及发文量增长速率呈现:“东部高校>中部高校>西部高校”格局;从相对指标分析,东部高校发文量占比有所下降,中部、西部高校呈上升趋势,说明不同区域高校相对差距在减小。
(3)从不同类别高校内部发展特征分析,“985”高校地理发文量在1999年后基本稳定,形成中国高校地理研究的核心区;“211”高校在2005年后普遍发展,形成以中、高发文量为主的集聚区;其他类高校2006年后陆续发展,形成高、中、低发文量高校均衡分布格局。
(4)从不同区域高校内部发展特征分析,东部高校地理学在1986年之前便开始发展,并逐渐形成“北上广南”的地理研究集聚区;中部高校在2004年之后呈现较好的发展势头,其中东北师大、河南大学和安徽师大发展最为突出;西部高校在2006年之后陆续发展,总体呈现“西北强—西南弱”格局。
(5)综合发文量等级、曲线增长类型、学校类别和区位条件分析,发现中国地理高校发文量曲线呈“J”型和线型的高校总数(22所)高于“S”型的高校总数(17所),中、低发文量高校总数(33所)远高于高发文量高校(6所),说明中国高校地理研究演变过程,以后期发展型和持续发展型为主,高发文量高校数量依然较少。
地方与空间,是人本主义地理学的核心观念[40]。中国高校地理研究格局形成,也是人与地方、空间相互联系、相互作用的结果,更反映地理知识产出的空间不均衡特征。本文从环境条件、内外动力、支撑条件和发展基础等4个方面构建概念模型,对影响高校地理学发展的因素进行综合探讨,但对影响因素定量分析较少,尚未考虑不同高校受这些因素影响的差异性;也未考虑中国地理知识生产的空间溢出效应,即不同层次高校科研活动的相互交流和共同协作,对地理知识创新的影响。在未来研究中,需要分析不同要素对中国高校地理学的影响,在理论层面上凝练影响中国高校地理研究的因素范式,为促进高校地理学发展提供理论依据。具体研究方向如下:
(1)研究方法精细化。1961年美国****普赖斯发表《巴比伦以来的科学》,标志着科学计量学的诞生[41]。随着计算机技术的快速发展,科学计量学理论和方法不断完善。本文以经典地理学研究范式“格局—过程—机制”为思路,综合定性和定量方法,对中国高校地理格局特征以及影响因素进行分析。未来研究中,需借鉴科学计量学方法,利用Citespace和Histcite等文献统计软件,从研究产出和合作交流等角度,对当前数据库文献进行引用关系和知识图谱分析,探讨中国地理高校研究热点转变以及发展趋势。
(2)研究内容精细化。在研究内容上,本文分析中国高校地理发展格局时,以论文数量作为评价指标,在未来研究中需要创新方法体系,回答高等院校地理研究与研究所的贡献差异,即中国高校地理研究贡献具体是什么,学科贡献是否存在空间迁移轨迹,未来学科新的突破点在哪里等问题。与此同时,可从知识地理学角度出发,以“空间秩序”“时间序列”和“动因机制”为科学维度,结合“价值维度”和“伦理维度”,构建三维产出评价模型,明晰中国高校地理研究对中国地理的实质贡献[27, 42]。进而量化中国高校科研评价机制转变,中文权威核心期刊学术价值和认可度降低,对中国高校地理贡献性或创新性研究的影响[20]。
(3)研究视角精细化。在《地理科学三十年:从经典到前沿》序言中,郭正堂院士指出:“中国科技成就,不仅在成果产出,更在于学科建设和人才队伍建设。近30年,中国地理学经历了老一辈科学家不懈坚守、中年****承前启后、青年学子的快速成长”[25]。当前中国地理学理论也在不断发展,逐渐由理解“人—地关系”向设计“人—地协同”转变,为理解复杂的地球表层系统提供新的思考方向[43]。加之,中国地理学发展与国外地理学发展轨迹具有差异性,内生与外生的“二元结构”,使得中国高校地理研究既具有历史积淀和学术传承,又具有西方现代学科的理论体系和新兴学术思想[44,45,46]。在未来研究中,如何客观并准确地刻画中国地理学和国外地理发展历程,评价中国地理和国外地理的交流和发展,也是值得探索的方向。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
