 , 唐金稳
, 唐金稳华南理工大学经济与贸易学院,广州 510006
The coordinated development of regional tourism innovation in the Pearl River Delta: Based on interduality theory
JIANGJinbo , TANGJinwen
, TANGJinwen收稿日期:2018-03-23
修回日期:2018-07-19
网络出版日期:2018-10-22
版权声明:2018《地理研究》编辑部《地理研究》编辑部
基金资助:
作者简介:
-->
展开
摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
-->0
PDF (1749KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章收藏文章
本文引用格式导出EndNoteRisBibtex收藏本文-->
1 引言
旅游业是创新驱动产业。从托马斯·库克(Thomas Cook)创办包价旅游,到风靡全球的KFC、Disney等旅游品牌的发展,无不证明创新在旅游发展中的重要作用。旅游创新日益改变人们的生活方式。Airbnb满足游客新的住宿需求,Uber提高出行的便利程度,虚拟技术增强游客的体验感知等。旅游创新除了技术创新的表征以外,也具有明显的空间特征。旅游资源的共享性,地理空间的邻近性,旅游市场的关联性等使得区域旅游创新呈现出区域的差异性[1]。此外,2015年7月28日的国务院常务会议提出“通过改革创新促进旅游投资和消费,推动现代服务业发展”;《“十三五”旅游业发展规划》中明确指出“理念创新,构建旅游发展新模式”。在旅游产业创新发展的时代背景下,****纷纷展开了旅游创新理论研究。李文兵等提出旅游创新包括旅游企业创新和区域旅游创新两种不同机制[1]。旅游创新,狭义上是指旅游产业创新,广义上是服务于旅游产业发展的一切创新活动[2]。区域协调有区域内协调和区域间协调之分,本文所指的区域创新协调是指珠三角九市各市区域内的创新发展协调,并非各市区际之间的协调。旅游创新的研究,国内外开始出现了从企业旅游创新向区域旅游创新的研究转向。相对于微观的旅游企业创新系统以及宏观的国家旅游创新系统,区域旅游创新系统是十分重要的中观层次旅游创新系统。区域旅游创新系统研究亟需拓展深化[3],已有的研究主要集中在概念模型、动力机制、参与主体等方面。区域旅游创新系统与一般创新系统不同之处在于其包括作为创新发起者的旅游吸引物和系统情境设计者的企业家精神[4]。学习型网络和跨部门合作是区域旅游创新系统的重要组成[5]。Pechlane提出,区域旅游创新系统形成的前提是——学习意愿、共同目标、利益相关者的能力和能够发挥作用的组织机构[6]。研究丹麦钓鱼旅游业后,****发现区域旅游创新参与主体有地方政府、旅游组织、旅游企业等[3]。但是,较之于旅游创新企业的研究,学术界忽视了对区域旅游创新演进规律应有的重视[1],区域旅游创新评价与测量的研究相对不足[7],缺少创新发生的过程和空间特征研究[8]。Camison等提出,应将熊彼特的创新理论和动态能力理论相结合,研究旅游创新,将传统方法中难以界定的投入产出(即存量指标)通过动态能力中的流量指标加以补充,据此评价不同区域的旅游创新能力[9]。具体而言,已有的区域旅游创新研究存在以下不足:第一,需要从地理学角度分析区域旅游创新的空间特征;第二,国内外区域旅游创新研究尚处于初始阶段,亟需尝试借助经典的系统学方法对区域旅游创新进行测量分析;第三,区域旅游创新研究的实证研究与案例分析不足,与区域旅游快速发展的现状形成反差。
珠江三角洲是中国经济发展的排头兵和创新高地,富足的资源环境、独特的地缘优势、活力高效的创新机制使珠三角区域旅游发展强劲、创新特征明显。但是该地区旅游创新的系统结构是什么?区域旅游创新能力和效率如何?区域旅游创新又具备什么样的空间特征?旅游创新在空间上一定均衡吗?基于此,本文拟借鉴二象对偶理论的动态研究法,开展区域旅游创新能力的综合研究,以对上述问题进行回答,具有极其重要的理论和现实意义。一方面,旅游创新测量研究相对不足,本文积极尝试构建区域旅游创新测量的指标体系,充实已有的旅游创新定量研究。以珠江三角洲为例,聚焦区域旅游创新,既是对已有的旅游创新系统研究的补充,也为国际上的区域旅游创新研究提供中国经验。另一方面,区域旅游创新是区域旅游竞争力的根本保证[1]。对区域旅游创新协调性进行研究,可以更好地理解区域旅游的发展情况,以期指导区域旅游可持续创新发展的实践。
2 研究方法与数据来源
2.1 研究区概况
本文选择中国珠三角的广州、深圳、佛山、珠海、东莞、肇庆、中山、惠州、江门等九市作为研究对象(图1)。珠三角是中国改革开放的先驱,是中国经济发展的排头兵,更是粤港澳大湾区城市群建设的主体所在①(① 粤港澳大湾区是在珠三角区域基础上加上香港、澳门两个特别行政区形成的都市群。2017年3月5日的政府工作报告首次提出,“要推动内地与港澳深化合作,研究制定粤港澳大湾区城市群发展规划”。)。该地区经济发展辐射带动华南、华中和西南等地区,其人口密集、资源富足,是中国创新能力最强、综合实力最强的三大区域之一。珠三角九市面积仅占全国面积的0.57%,但在2014年却创造了7.8万亿元的GDP,占全国的12%,仅次于长三角都市经济圈,成为中国大陆第二大经济总量的都市经济圈。殷实的经济基础,积极的创新氛围,密集的人口资源为旅游业的发展奠定了基础,致使其旅游经济发展强劲。2014年该地区旅游收入占全国的1/5,2014年珠三角九市旅游收入排名依次是广州、深圳、佛山、东莞、江门、惠州、珠海、肇庆、中山。 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1研究区位置图
-->Fig. 1Location of the study area
-->
2.2 研究方法
2.2.1 区域旅游创新的二象对偶特征 二象对偶理论②(② 高隆昌等在系统学的框架下提出二象对偶理论。他认为,“二象对偶”是客观世界中普遍存在的一种结构规律。)认为,任意系统可以分为相互对应的两个子系统,分别记为X和X*。两个子系统一虚一实,一系统是另一系统的整体映射,构成对立统一体[10]。二象对偶理论已在企业管理、区域经济、产业经济等领域得到广泛应用。区域旅游创新系统是一个开放系统,既有静态化的实体状态性质,也有动态发展的过程性质。其中,状态子系统是实象系统,体现在创新投入和创新产出的总量方面;过程子系统是抽象系统,其测评以创新转化率——旅游创新投入与旅游创新产出之比为主要衡量依据。在区域旅游创新系统中,过程系统和状态系统相互依赖,没有创新的动态发展变化就没有静态的创新产出,前阶段的创新产出是后阶段的创新准备;过程系统和状态系统存在映射关系,创新过程中的创新效率直接影响最终的创新产出,创新产出也会影响创新资源的再投入。总之,两个系统相互依存,相互影响,共同推动创新发展。只有区域旅游创新过程中两大系统之间保持高度协调,才能实现区域旅游创新系统的持续发展。
2.2.2 区域旅游创新的量与质 创新投入和创新产出是创新系统的核心组成[11]。旅游创新能力投入在某种程度上体现了创新能力的发展趋势和作用空间,是实现旅游创新的前提和基础。旅游创新产出能力包含了一系列的创新成果,例如旅游学术论文、旅游产品专利、旅游新产品、旅游收入、新的旅游企业等。从时间序列来看,某一阶段的创新活动会产生一定的乘数效应,旅游创新产出既是本阶段的创新成果,也是下一阶段的创新 投入[12]。
创新状态子系统反映了区域创新能力,而过程子系统反映了一阶段时间内的创新效率。本文研究区域创新状态子系统(创新能力)和过程子系统(创新效率)的协调发展情况。借鉴已有研究[17],用创新投入和产出之和计算创新能力,反映创新水平的量;用创新产出与创新投入之比计算创新效率,反映创新水平的质。区域旅游创新是创新系统内部量与质统一体。
2.3 指标体系构建
已有的文献显示,旅游创新评价过于依赖熊彼特的技术创新研究路径,展开以专利为指标的旅游业创新测量[13],忽略了非技术创新的研究,使得这些评价指标缺乏评价旅游创新能力的普适性。因此,开展旅游创新的测量工作的前提是亟需借鉴国际上创新评价方法,根据旅游业自身情况,建立能反映旅游产业特征的旅游创新的指标体系[14]。参考既有创新研究,构建了区域旅游创新投入指标和区域旅游创新产出指标(表1)。Tab. 1
表1
表1旅游创新能力评价的指标体系
Tab. 1Index system of evaluation of tourism innovation ability
| 指标类别 | 评价领域 | 评价指标 | 指标选取依据 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 旅游创新投入 | 创新经费 | 旅游业R&D经费支出占旅游总收入比例(X1) | 文献[15] 文献[16] 文献[12] OECD科学、技术和 产业计分表指标体系 |
| 创新人员 | 旅游业科研人员占旅游从业人员总数比例(X2) | ||
| 研发机构 | 设置旅游管理专业的院校数(X3) | ||
| 旅游规划资质单位数量(X4) | |||
| 设备投入 | 旅游固定资产投资额(X5) | ||
| 旅游创新产出 | 知识产出 | 旅游学术论文发表数(Y1) | 文献[15] 文献[16] 欧盟创新记分牌EIS 欧盟IS4S 奥斯陆手册(2005) 文献[17] |
| 旅游专利申请数(Y2) | |||
| 创新经济绩效 | 旅游总收入增长率(Y3) | ||
| 市场创新开拓 | 国际游客占全部游客的比例(Y4) | ||
| 旅游外汇收入(Y5) | |||
| 旅游展销会年举办数量(Y6) | |||
| 旅游规模变化 | 高等级旅游企业新增数量(Y7) |
新窗口打开
其中,旅游创新能力投入是实现旅游创新的前提和基础,可以从创新经费、创新人员、研发机构和设备投入四个方面来测量,其对应的指标是:旅游业R&D经费支出占旅游GDP比例、旅游业科研人员占从业人员总数比例、含旅游管理专业的高等学校数与旅游规划资质单位数量、旅游固定资产投资总额[15,16]。在确定区域旅游创新产出指标时,除了选择旅游学术论文发表数、旅游专利申请数等技术创新产出指标外,还选择了旅游总收入增长率、国际游客占全部游客的比例、旅游外汇收入、旅游展销会年举办数量、高等级旅游企业新增数量等非技术创新产出指标,其分别代表创新知识产出、创新经济绩效、市场创新开拓和旅游规模变化等方面[15,16,17]。
2.4 数据来源
创新活动具有一定的时间特征,是周期性的活动,投入产出之间存在一定的时间滞后性[18]。同样地,区域旅游创新也存在时间滞后性问题,不同时期不同区域的区域旅游创新的时滞问题存在差异。参照相关研究[19,20],本文假设区域旅游创新从创新投入到创新产出的递延周期为一年。因此,珠三角区域旅游创新投入指标选取2013年数据,区域旅游创新产出指标选取2014年数据。各指标原始数据来源于相应年份的《广东省科技统计年鉴》《广东省旅游培训情况报告》和《国民经济和社会发展统计公报》以及相关的官方网站。具体地,旅游业R&D经费支出占旅游总收入比例(X1)、旅游业科研人员占旅游从业人员总数比例(X2)等数据来自《广东省科技统计年鉴》,前者是按照旅游业总收入占地区GDP比例,同时假定R&D经费增长率等于GDP增长率进行粗略估算;后者是按照旅游业总收入占地区GDP比例,同时假定旅游业科研人员增长率等于GDP增长率进行估算。设置旅游管理专业的院校数(X3)来自《广东省旅游培训情况报告》。旅游规划资质单位(X4)是指乙级资质以上的旅游规划企业,其数据来自《广东省国家旅游规划设计单位资质等级情况的公告》。旅游固定资产投资额(X5)来自九市《国民经济和社会发展统计公报》,其按照旅游总收入占全市GDP比例再乘以全社会固定资产计算。旅游学术论文发表数(Y1)是使用CNKI数据库进行中文文献检索,使用Elsevier SDOL数据库进行外文文献检索,检索词为“地区+旅游、游憩、酒店、旅行社、景区”。旅游专利申请数(Y2)是利用国家知识产权局专利检索数据库,以城市名为地址,以“旅游”“导览”“酒店”“旅行社”“景区”“景点”“宾馆”为名称进行检索,剔除明显不相关的专利获得。旅游总收入增长率(Y3)、国际游客占全部游客的比例(Y4)、旅游外汇收入(Y5)等数据来自九市《国民经济和社会发展统计公报》。旅游展销会年举办数量(Y6)检索自各地展会安排表。高等级旅游企业新增数量(Y7)是新增加的四星级以上(含四星级)酒店、4A景区以上(含4A景区)和国际旅行社等旅游企业,其数据来源于各市统计年鉴、统计公报和旅游局官网相关统计信息。
2.5 数据计算处理
2.5.1 指标权重的确定 在确定旅游业创新能力指标的权重之前,首先向旅游业专家发放问卷,本轮共发放问卷15份,收回有效问卷11份。专家按照9分位的比率,对旅游业创新能力指标体系中的各个指标之间的相对重要程度进行两两对比打分。对所得分值运用均值法进行处理,从而得到各级指标的判断矩阵,然后利用层次分析法计算各个指标的权重,并进行一致性检验。各指标对应的指标权重具体赋值见表2。Tab. 2
表2
表2旅游业创新能力评价指标的权重
Tab. 2The weight of evaluation index of tourism innovation ability
| 指标类别 | 评价指标 | 权重 |
|---|---|---|
| 旅游创新投入 | X1以旅游业R&D经费支出占旅游总 收入比例 | 0.0817 |
| X2旅游业科研人员占旅游从业人员 总数比例 | 0.0942 | |
| X3设置旅游管理专业的院校数 | 0.0928 | |
| X4旅游规划资质单位数量 | 0.0688 | |
| X5旅游固定资产投资额 | 0.1224 | |
| 旅游创新产出 | Y1旅游学术论文发表数 | 0.0895 |
| Y2旅游专利申请数 | 0.1337 | |
| Y3旅游总收入增长率 | 0.0514 | |
| Y4国际游客占全部游客的比例 | 0.0434 | |
| Y5旅游外汇收入 | 0.0684 | |
| Y6旅游展销会年举办数量 | 0.0503 | |
| Y7高等级旅游企业新增数量 | 0.1034 |
新窗口打开
2.5.2 数据的无纲量化处理 由于表1中各指标的数量级并不相同,其数据无法直接比较与计算。一般采用
式中:
2.5.3 区域旅游创新子系统发展水平测量 (1)状态子系统发展水平(创新能力)的测量
根据表2中的权重,加权计算状态子系统发展水平,区域旅游状态子系统是创新投入和创新产出各指标的加权之和,其公式如下:
(2)过程子系统发展水平(创新效率)的测量
借助旅游创新产出与旅游创新投入的比值,测量区域旅游创新过程子系统的发展水平,其公式为:
2.5.4 区域旅游创新系统综合发展水平测量 基于二象子系统S1、S2的发展协调程度以测量和评价区域旅游创新系统的发展水平。在评价创新协调度时,首先借用公式(1)对L(S1)、L(S2)进行标准化处理,标准化后二象子系统的发展水平记为L'(S1)、L'(S2),更加简洁可比。再次,在L'(S1)、L'(S2)的基础上计算区域旅游创新综合发展水平。鉴于区域创新系统演化的评价包括过程子系统和状态子系统,本文采用公式(4)计算珠江九市区域旅游创新系统的综合发展能力。
2.5.5 区域旅游创新系统协调发展水平测量 协调水平是用来评价区域旅游创新系统中二象子系统之间是否协调的定量指标[18],该指标用L'(S1)和L'(S2)的相对离差系数VC来计算,离差越小,子系统协调度越高,反之,越低;计算公式如下:
式中:VC最小时,
式中:K为系数,K≥1。由于在式(6)中,0≤C≤1,因此,通常取K=1。运用式(6)计算区域旅游创新协调水平。综合式(4)、式(6)计算结果,珠三角九市的区域旅游创新系统的综合发展水平和协调发展水平见表3。
Tab. 3
表3
表3珠三角九市的区域旅游创新系统协调发展的实证测量
Tab. 3An empirical survey on the coordinated development of regional tourism innovation system in the nine cities of Pearl River Delta, China
| 地级市 | 状态子系统 发展水平L'(S1) | 过程子系统 发展水平L'(S2) | 区域旅游创新系统综合 发展水平CL(S) | 区域旅游创新系统协调 发展水平C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 广州 | 1.000 | 0.302 | 0.651 | 0.712 |
| 深圳 | 0.612 | 0.576 | 0.594 | 0.999 |
| 珠海 | 0.302 | 0.391 | 0.346 | 0.984 |
| 佛山 | 0.284 | 0.366 | 0.325 | 0.984 |
| 惠州 | 0.218 | 0.294 | 0.256 | 0.978 |
| 东莞 | 0.256 | 0.349 | 0.302 | 0.976 |
| 中山 | 0.218 | 0.612 | 0.415 | 0.776 |
| 江门 | 0.264 | 0.344 | 0.304 | 0.983 |
| 肇庆 | 0.130 | 0.260 | 0.195 | 0.888 |
新窗口打开
3 结果分析
陈伟等****的研究提供了协调发展和综合发展两个方面的量化标准[17,21],以显示不同的发展程度(表4)。Tab. 4
表4
表4协调创新发展的评判标准(协调发展值)
Tab. 4The evaluation criteria of coordinated innovation development (coordinated development)
| 协调发展值 | 0.9~1.0 | 0.8~0.9 | 0.6~0.8 | 0~0.6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 等级 | 非常协调 | 基本协调 | 弱协调 | 不协调 |
| 综合发展值 | 0.8~1.0 | 0.6~0.8 | 0.4~0.6 | 0~0.4 |
| 等级 | 优秀 | 良好 | 中等 | 差 |
新窗口打开
根据表3中区域旅游创新系统的综合发展水平和协调发展水平的实证结果,结合表4中的评判标准,将珠三角九市的区域旅游创新系统的协调发展情况归为5类(图2),并呈现出“整体不均衡、局部聚集”的区域旅游创新的空间结构。具体分析如下:
(1)区间Ⅰ。该区间的综合发展值介于0.4~0.6,区域旅游创新系统综合发展水平等级为“中等”;协调发展值介于0.9~1.0,二象子系统非常协调。深圳处于该区间,说明深圳的旅游创新整体实力尚处中等水平,存在一定提升空间。深圳旅游创新的协调度较高,究其原因,深圳是中国经济特区,全国科技创新基地;其经济实力雄厚,拥有强有力的经济实力支撑旅游业创新,旅游投入产出效率较高;地方科技和人才的培养促进了旅游业创新能力的提升;良好的政策环境促进了旅游创新活动的产生。但以商务旅游为主,以“都市风情”“主题公园”“滨海休闲”和“高尔夫之都”等为其旅游特色,仍停留于开创之初形象阶段,多年来并没有实质性创新,深圳的旅游创新整体水平仍有待提升。因此,今后需要借助毗邻香港的地缘优势,加大旅游创新投入,丰富旅游业态和产品类型,强化相关产业对旅游业发展的支撑,发挥创新基地引领的示范作用,提高旅游创新成果的转化利用率。
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2珠三角九市区域旅游发展的城市分布图
-->Fig. 2The distribution of regional tourism development in the nine cities of Pearl River Delta
-->
(2)区间Ⅱ。该区间限的综合发展值介于0~0.4,表明区域旅游创新系统的综合发展水平等级较差;但其协调发展值介于0.9~1.0,说明二象子系统非常协调。在区域旅游创新系统处在培育初期,其资源相对不足,创新机制相对不完善,二象子系统往往呈现量小低水平下的协调状态,这是创新发展的极端类型[22]。九市中的珠海、佛山、惠州、东莞和江门处于该区间。其中,佛山、东莞、惠州作为重要的制造业城市,虽然其经济总值较高,2014年度三个城市在广东省中GDP排名分别是第三、第四、第五,但是工业产值占比大,所以相对于深圳来说,这5个城市的旅游总收入占比较少,旅游创新投入不足。加之,旅游业与其它产业融合发展不足,旅游业创新活动的空间面较窄。此外,江门和珠海的经济实力稍逊色于前面三个城市,2014年度GDP排名为第九、第十,城市创新动力不足,即旅游科研经费和科研人员等资源匮乏。总之,改变5个城市旅游创新投入和旅游创新产出均为低下的现状,需要从创新机制、创新政策、创新环境等角度入手。尤其是亟需完善创新政策,积极支持旅游创新投入,吸引更多的旅游资本,加强旅游人才建设;促进旅游专利申请、鼓励旅游学术科研活动,促成旅游创新成果的利用,全面提升旅游创新的综合能力。
(3)区间Ⅲ。该区间的综合发展值介于0~0.4,其区域旅游创新的综合发展水平较差;协调发展值介于0.8~0.9,二象子系统基本协调;位于该区间地区的旅游创新是低水平下的基本协调。肇庆处于该区间,其创新过程中,综合发展水平和协调发展水平之间出现了背离端倪。与处于区间Ⅱ的5个城市有极为相似之处。差异是,其创新协调发展稍弱。主要原因是肇庆市经济实力中等,旅游创新投入不足;创新环境中信息联通程度较弱;缺乏旅游高素质人才,产业知识积累和转化能力较低。为此,需发挥旅游资源丰富的先天优势,加大创新投入,凭借生态环境和地理区位优势,吸引优秀专业人才,提升旅游创新的综合实力。
(4)区间IV。该区间的综合发展值介于0.4~0.6,协调发展值介于0.6~0.8。表明该区域旅游创新系统的综合发展处于中等水平,而创新系统为弱协调态势。中山处于该区间,说明中山的区域旅游创新属于中等水平的弱协调创新类型。中山市旅游发展情况与位于V区间的广州市相似。两者的差异仅在于,前者创新状态子系统的发展水平(即创新能力)逊色于后者。主要是因为其经济水平通过投入机制影响着旅游创新能力发展。中山市的GDP排名第6,远较排名第一的广州市落后。虽然其工业创新强,但是中山故居等知名旅游产品创新严重不足。今后,中山市应提高旅游创新的投入总量,提高旅游创新产出效率,在促进旅游创新量的提高同时,促进其旅游创新更好协调发展。
(5)区间V。该区间的综合发展值介于0.6~0.8,协调发展值介于0.6~0.8。说明区域旅游创新系统的综合发展水平良好,而创新系统呈现弱协调态势。该类地区的区域旅游创新属于良好水平状态下的弱协调创新类型。广州落在该区间,说明广州的旅游经济发展势头较猛,区域旅游创新系统的创新能力领先珠三角九市,但其创新效率没有达到最优化,尚有改进空间。未来,广州市需要合理配置旅游资源,提高旅游资源利用率,提高旅游创新的投入产出比,使之朝向创新能力与协调水平发展“双优”方向发展。
4 结论与讨论
基于二象对偶理论,本文从区域旅游创新系统发展的时间演变视角,将区域旅游创新系统分为以创新能力为表征的状态子系统和以创新效率为测度的过程子系统。二象系统在旅游创新中的运用再次佐证了区域旅游创新系统具有完备的时空特性。通过对珠三角九市的区域旅游创新系统的综合发展水平、创新子系统的协调水平进行评价、计算、归类后,得出以下结论:(1)珠三角九市旅游创新特征突出表现为,创新综合能力处于良好至差的整体状态,并以“差”为主体,占六城市之多。没有一个城市进入优级旅游创新能力区间。这充分说明,尽管地处产业创新高地的大背景中,珠三角区域旅游业创新却相对滞后。再次印证了此前有关旅游产业结构相关研究的结论[22]。与此同时,珠三角区域旅游创新的协调发展却表现为较高层次,除了广州、中山两大城市为弱协调创新之外,其他城市均进入“基本协调”“非常协调”层次,尤其是“非常协调”城市达到六个之多。但与综合创新能力相比,则显示出珠三角多数城市的旅游创新处于错位的低水平下协调创新状态。这充分说明,珠三角现有的旅游总量多为发达商业、制造业的伴生物,并非旅游创新的直接产物。
(2)珠三角九市旅游创新发展呈现U型结构态势(图3)。其中U型的两段是广州、中山和深圳,广州、中山的旅游创新呈现出创新能力较强,但是协调度不高;而深圳的旅游创新能力较强,协调度较高。U型的底端是区域旅游创新综合水平较低,协调度较高,主要有:肇庆、珠海、佛山、惠州、东莞、江门等城市。
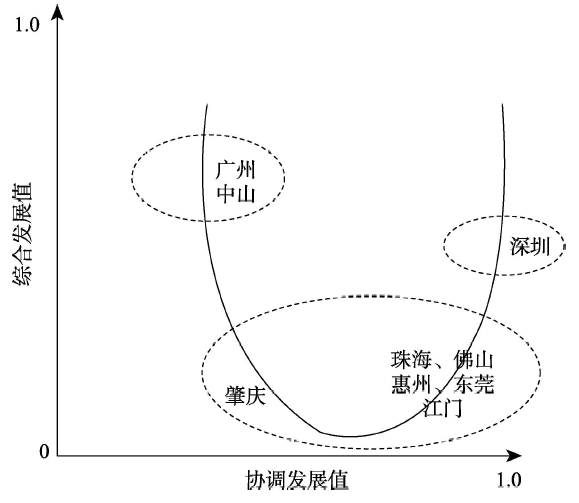 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3珠三角九市发展的U型结构
-->Fig. 3U structure of the development of 9 cities in Pearl River Delta
-->
(3)区域旅游创新不仅取决于创新的综合实力,而且取决于二象子系统的协调发展,也就是状态子系统和过程子系统的协同共进。广州、深圳应该继续发挥旅游产业的特色优势,进一步提升创新水平(深圳)和创新协调度(广州),成为广东省乃至于全国的旅游创新示范基地。
(4)依据上述研究,应采取相关措施大力推动珠三角九市旅游创新的协调发展,以提升区域旅游创新的整体水平。第一,加大旅游业创新投入,制定鼓励旅游产业创新活动的政策,完善旅游业创新环境,营造旅游创新良好的氛围,尤其是旅游创新能力水平低的地区,应不断完善创新机制,确保创新人才和经费的投入,形成旅游创新学习型区域[23]。第二,强化旅游产业创新支撑,提升旅游业创新产出能力。全面提高从业人员的整体素质,培养创新性旅游人才,大力推动旅游人才智库建设,从源头强化旅游知识生产与转化。尤其是在旅游与商业、制造业、文化产业的融合中,确立其创新方向与领域。第三,区域协同创新的过程,是区域间增长传递的实现过程。为加速旅游创新扩散和溢出,应充分发挥空间邻近性对旅游创新的促进作用[24],发挥粤港澳大湾区城市群中香港、澳门对珠三角地区旅游创新辐射作用,加强广州、深圳与其他城市之间的合作创新,推动区域旅游创新协调发展。同时,积极引导旅游创新资源在区域间的合理配置,促进区域间相关产业创新对旅游创新的支撑拉动作用。
致谢:本文数据搜集得到广州智识管理咨询有限公司蒋婷婷女士的大力协助,特此致谢!本文得到了华南理工大学博士生国外短期访学项目资助,一并深表感谢!
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
| [1] | . 旅游创新认知误区极大限制了研究者对旅游创新规律的探索.在反思 旅游创新研究的前提下,分析了旅游创新认知误区的形成原因与修正路径,研究了由库克旅行社创建所引发的旅游企业创新崛起之路,并对区域旅游创新演进的基础 与创新演进的动力进行了探索,旨在还原旅游创新实践的真实面目,以推动旅游创新研究的深入. 旅游创新认知误区极大限制了研究者对旅游创新规律的探索.在反思 旅游创新研究的前提下,分析了旅游创新认知误区的形成原因与修正路径,研究了由库克旅行社创建所引发的旅游企业创新崛起之路,并对区域旅游创新演进的基础 与创新演进的动力进行了探索,旨在还原旅游创新实践的真实面目,以推动旅游创新研究的深入. |
| [2] | . 旅游创新是旅游产业可持续发展的重要推动力,本文在文献研究和实地调研基础上,采用服务导向 方法,结合技术创新的分析视角,对旅游创新的概念、特征和类型进行了深入探讨。创新通常具有"新颖性"和"应用性"两方面内涵,其中对"新颖性"的判定需 要从时间、空间、范围三个维度来考虑。"旅游创新"是创新中的一类,狭义的旅游创新是旅游产业内发生的所有创新。除此之外,广义的旅游创新还包括旅游产业 外部一切服务于旅游(活动)的创新。与技术创新、以及其他服务部门的创新相比较,旅游创新有自己的独特特点,旅游创新可以按照不同的标准划分类型。 . 旅游创新是旅游产业可持续发展的重要推动力,本文在文献研究和实地调研基础上,采用服务导向 方法,结合技术创新的分析视角,对旅游创新的概念、特征和类型进行了深入探讨。创新通常具有"新颖性"和"应用性"两方面内涵,其中对"新颖性"的判定需 要从时间、空间、范围三个维度来考虑。"旅游创新"是创新中的一类,狭义的旅游创新是旅游产业内发生的所有创新。除此之外,广义的旅游创新还包括旅游产业 外部一切服务于旅游(活动)的创新。与技术创新、以及其他服务部门的创新相比较,旅游创新有自己的独特特点,旅游创新可以按照不同的标准划分类型。 |
| [3] | . For more than two decades, the ‘innovation systems approach’ has been a favoured framework for micro-economic research in new institutional economics in many Western countries. The concept allows for a better understanding of the complex driving forces and mechanisms that mediate the conditions, the extent and the outcomes of innovative behaviour. However, the ideas behind ‘national’, ‘regional’ and ‘sectoral’ innovation systems remain to be tested in tourism. With environmental protection and tourism development as objectives, the Sea Trout Funen initiative started in 1989 as a collaboration between the county council, the Anglers' Association, tourism businesses and a hatching plant. The activities merit the label ‘tourism innovation system’, first, because there are stable relations between a large number of actors from the public, voluntary and business sectors with intermittent links to educational institutions. Secondly, the relationship has proven to be mutually beneficial and synergetic. Thirdly, examples are found of consequential innovations in terms of products and services for tourists, in terms of environmental protection and development methods and in terms of the development of human resources. Fourthly, the innovation system has been able to benefit distinctly and positively from external opportunities, such as new regulations. |
| [4] | . This paper proposes a model of an attractor‐based innovation system for understanding tourism. Key components of the model are the attractor (that which attracts visitors), scene‐maker, scene, collaborative networks between tourism and other firms and, finally, the crucial function of the scene‐taker. Findings from eight in‐depth case studies taken from around the world are summarized in the form of seven hypotheses concerning the operations of such innovation systems. It is argued that scene‐takers, in the form of individual entrepreneurs and organizations, perform a crucial function in the innovation system in developing and maintaining the scene. Finally, some policy implications for building such a system are suggested. |
| [5] | . (2017). Networking and learning for tourism innovation: evidence from the Western Cape. Tourism Geographies: Vol. 19, Tourism Planning and Development, pp. 340-361. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2016.1183142 |
| [6] | . |
| [7] | . |
| [8] | . 创新是区域经济发展的重要驱动力,创新地理研究得到了西方地理学界的重视。追溯西方创新地理研究的发展历程:从创新的空间特征描述,经区域创新集聚机制探索,到跨区域知识传播和创新网络演化机理的研究;系统梳理了20世纪90年代以来西方创新地理研究的代表人物、空间尺度、研究内容、主要观点和研究方法。研究发现:西方创新地理研究存在以下缺憾:重视创新组织,忽略了创新个体和组织之间的互动关系研究;重视理论反思,缺乏对实证研究的重视和方法的突破;欧美研究占绝对主流,缺乏基于发展中国家实证的反思。因此,未来应围绕着创新主体,运用定量和定性相结合的研究方法,建立基于中国等发展中国家实践的新型创新地理研究框架。 . 创新是区域经济发展的重要驱动力,创新地理研究得到了西方地理学界的重视。追溯西方创新地理研究的发展历程:从创新的空间特征描述,经区域创新集聚机制探索,到跨区域知识传播和创新网络演化机理的研究;系统梳理了20世纪90年代以来西方创新地理研究的代表人物、空间尺度、研究内容、主要观点和研究方法。研究发现:西方创新地理研究存在以下缺憾:重视创新组织,忽略了创新个体和组织之间的互动关系研究;重视理论反思,缺乏对实证研究的重视和方法的突破;欧美研究占绝对主流,缺乏基于发展中国家实证的反思。因此,未来应围绕着创新主体,运用定量和定性相结合的研究方法,建立基于中国等发展中国家实践的新型创新地理研究框架。 |
| [9] | . This paper offers a diagnosis of the "state of the issue" regarding the measurement of innovation in the tourism industry at the company level, and some recommendations for overcoming identified problems. The study addresses two central issues: how existing secondary databases of innovative activity define the boundaries of the tourism industry, and the degree to which these databases reflect the particular characteristics of this economic activity. It is concluded that these analyses present serious biases and anomalies hindering the understanding of the situation at the micro level and complicating the issue of international comparability, and the analyses do not capture the internal heterogeneity of innovative behavior of tourism companies from specific, intra-sectoral activities. The problems concern inappropriate indicators and the need for survey methods to complement the development of innovation scoreboards in secondary sources. The study concludes by detailing a set of proposals that should be considered in the context of a scoreboard to provide a comprehensive view of a tourism firm's technological and organizational innovations, as well as its innovative capabilities, combining Schumpeterian theory and the dynamic-capabilities-based approach, and also making cross-national comparisons feasible. Published by Elsevier Ltd. |
| [10] | . 基于产业创新系统的时空演化特征,运用二象对偶理论将产业创新系 统视为由状态子系统和过程子系统二象子系统构成的具备完全时空意义的动态系统.其中,前者是客观实在的物质子系统,后者则是由该物质子系统所映射的属性构 成的虚像子系统.从这一新视角,研究产业创新系统演化的本质,重新界定产业创新系统协调发展的内涵,并构建产业创新系统二象子系统之间协调发展的评价模 型. . 基于产业创新系统的时空演化特征,运用二象对偶理论将产业创新系 统视为由状态子系统和过程子系统二象子系统构成的具备完全时空意义的动态系统.其中,前者是客观实在的物质子系统,后者则是由该物质子系统所映射的属性构 成的虚像子系统.从这一新视角,研究产业创新系统演化的本质,重新界定产业创新系统协调发展的内涵,并构建产业创新系统二象子系统之间协调发展的评价模 型. |
| [11] | . . |
| [12] | . . |
| [13] | . 在社会的发展下,我国旅游产业也得到了长足的发展,但是,在各种因素的影响下,人们往往将历史文化、自然风光开发放置在主要地位,未意识到旅游创新的作用。实际上,对于任何产业而言,创新都是促进其发展的重点途径,因此,我国旅游创新与旅游经济增长两者之间关系的研究也成为一个重点课题。 . 在社会的发展下,我国旅游产业也得到了长足的发展,但是,在各种因素的影响下,人们往往将历史文化、自然风光开发放置在主要地位,未意识到旅游创新的作用。实际上,对于任何产业而言,创新都是促进其发展的重点途径,因此,我国旅游创新与旅游经济增长两者之间关系的研究也成为一个重点课题。 |
| [14] | . 旅游创新研究是新兴的研究热点,国外学术界对旅游创新的研究主要有以下三个视角:在分类的基 础上探讨不同类型的旅游创新及其特征,在知识管理理论框架下研究旅游创新过程以及从系统论视角研究旅游创新系统和旅游产业集群。但目前旅游创新研究还处在 起步阶段,缺乏系统的理论体系,对旅游创新的公共政策支撑、绩效评价等方面的研究也相对滞后,今后的研究应致力于弥补这方面的缺憾. . 旅游创新研究是新兴的研究热点,国外学术界对旅游创新的研究主要有以下三个视角:在分类的基 础上探讨不同类型的旅游创新及其特征,在知识管理理论框架下研究旅游创新过程以及从系统论视角研究旅游创新系统和旅游产业集群。但目前旅游创新研究还处在 起步阶段,缺乏系统的理论体系,对旅游创新的公共政策支撑、绩效评价等方面的研究也相对滞后,今后的研究应致力于弥补这方面的缺憾. |
| [15] | . |
| [16] | . This survey reviews the growing use of patent data in economic analysis. After describing some of the main characteristics of patents and patent data, it focuses on the use of patents as an indicator of technological change. Cross-sectional and time-series studies of the relationship of patents to R&D expenditures are reviewed, as well as scattered estimates of the distribution of patent values and the value of patent rights, the latter being based on recent analyses of European patent renewal data. Time-series trends of patents granted in the U.S. are examined and their decline in the 1970s is found to be an artifact of the budget stringencies at the Patent Office. The longer run downward trend in patents per R&D dollar is interpreted not as an indication of diminishing returns but rather as a reflection of the changing meaning of such data over time. The conclusion is reached that, in spite of many difficulties and reservations, patent data remain a unique resource for the study of technical change. |
| [17] | . 区域创新不仅包括技术创新 ,而且包括组织创新、制度创新与管理创新。区域创新系统是国家创新系统的基础 ,它是一定区域内与创新全过程相关的组织、机构和实现条件所组成的网络体系 ,是由相关社会主体组成的一个社会系统。基于以上认识 ,遵循综合性、系统性与层次性、可操作性及引导性原则 ,本文构建了一套评估区域创新能力的指标体系 ,并尝试运用该指标体系对江苏省 13个地市创新能力进行了定量评价和分析 . 区域创新不仅包括技术创新 ,而且包括组织创新、制度创新与管理创新。区域创新系统是国家创新系统的基础 ,它是一定区域内与创新全过程相关的组织、机构和实现条件所组成的网络体系 ,是由相关社会主体组成的一个社会系统。基于以上认识 ,遵循综合性、系统性与层次性、可操作性及引导性原则 ,本文构建了一套评估区域创新能力的指标体系 ,并尝试运用该指标体系对江苏省 13个地市创新能力进行了定量评价和分析 |
| [18] | . . |
| [19] | . Based on the method of DEA,this paper analyses the performance of the regional innovation systems of our country. According to the characteristics of the concerned innovation system,the regional innovation systems are classified. We give the different suggestions about how to improve the innovating performance for the different categories of regional innovation systems. . Based on the method of DEA,this paper analyses the performance of the regional innovation systems of our country. According to the characteristics of the concerned innovation system,the regional innovation systems are classified. We give the different suggestions about how to improve the innovating performance for the different categories of regional innovation systems. |
| [20] | . . |
| [21] | . 以区域创新系统协调发展为研究对象,根据2000—2008年我国省级区域面板数据,应用协同学理论测算区域创新系统的协调发展度.研究结果表明:(1)考察期内,我国区域创新系统的协调发展度显著提高,其中,东部地区提高最快,中部次之,西部最慢;(2)创新系统协调发展度的地区间差异不断扩大,反映创新的地理集中态势日益明显;(3)区域创新系统的协调发展度大致可以分为五种类型,北京作为Ⅰ类地区属于良好协调发展类,上海作为Ⅱ类地区属于中度协调发展类,广东作为Ⅲ类地区属于勉强协调发展类,由部分东部地区和中部地区构成的Ⅳ类地区属于勉强协调发展类,由部分中部和西部地区构成的Ⅴ类地区属于中度失调衰退类.最后,分析了各类型区域创新系统协调发展的特点并提出了改进建议. . 以区域创新系统协调发展为研究对象,根据2000—2008年我国省级区域面板数据,应用协同学理论测算区域创新系统的协调发展度.研究结果表明:(1)考察期内,我国区域创新系统的协调发展度显著提高,其中,东部地区提高最快,中部次之,西部最慢;(2)创新系统协调发展度的地区间差异不断扩大,反映创新的地理集中态势日益明显;(3)区域创新系统的协调发展度大致可以分为五种类型,北京作为Ⅰ类地区属于良好协调发展类,上海作为Ⅱ类地区属于中度协调发展类,广东作为Ⅲ类地区属于勉强协调发展类,由部分东部地区和中部地区构成的Ⅳ类地区属于勉强协调发展类,由部分中部和西部地区构成的Ⅴ类地区属于中度失调衰退类.最后,分析了各类型区域创新系统协调发展的特点并提出了改进建议. |
| [22] | . Structural benefit analysis and structural relevance analysis are popular in the research of tourism. When referring to the relationship between the support of science and technology and tourism structural transformation and upgrading, the function and single impact of science and technology are the hotspots in research. Focusing on the regional structure, consumption structure and industrial structure, the authors lead the structural research of Guangdong province to a deep and systematic way and conclude the science and technology innovation path of tourism structural transformation and upgrading. The research shows that the geographic concentration of the six major tourism indexes such as tourism revenue and overnight tourist in the four major economic regions of Guangdong province is mainly between 70 and 90, which indicates the regional imbalance in tourism economics. Even though the tourism per capita consumption in Guangdong is above the national average level, its structure is not reasonable, which leads to a low number in basic tourism consumption when compared with developed countries and especially in the departments with high flexibility such as touring, catering and entertaining. The shift-share method is adopted to analyze the tourism structure of Guangdong province which shows a structural irrationality both in the fixed assets and the business income and a lack of competitiveness. In spite of the high ranking in the total amount of tourism, improvements in tourism competitiveness of Guangdong should be made immediately. Based on the innovation of science and technology, it is necessary to explore the potential of the tourism development in Guangdong. Thus, approaches such as updating the tourism facilities, introducing high-tech elements into tourism products, optimizing the product structure, industrial convergence and technology diffusion should be adopted to extend the industry chain and promote new types of tourism. Meanwhile, approaches like industrial competition and cooperation in regional tourism, the cluster of knowledge spillover and the science and technology guidance to regions with different tourism resources should be adopted to optimize the spatial structure of tourism. The innovation of science and technology should be put into practice to support the tourism structural transformation and upgrading in Guangdong province. . Structural benefit analysis and structural relevance analysis are popular in the research of tourism. When referring to the relationship between the support of science and technology and tourism structural transformation and upgrading, the function and single impact of science and technology are the hotspots in research. Focusing on the regional structure, consumption structure and industrial structure, the authors lead the structural research of Guangdong province to a deep and systematic way and conclude the science and technology innovation path of tourism structural transformation and upgrading. The research shows that the geographic concentration of the six major tourism indexes such as tourism revenue and overnight tourist in the four major economic regions of Guangdong province is mainly between 70 and 90, which indicates the regional imbalance in tourism economics. Even though the tourism per capita consumption in Guangdong is above the national average level, its structure is not reasonable, which leads to a low number in basic tourism consumption when compared with developed countries and especially in the departments with high flexibility such as touring, catering and entertaining. The shift-share method is adopted to analyze the tourism structure of Guangdong province which shows a structural irrationality both in the fixed assets and the business income and a lack of competitiveness. In spite of the high ranking in the total amount of tourism, improvements in tourism competitiveness of Guangdong should be made immediately. Based on the innovation of science and technology, it is necessary to explore the potential of the tourism development in Guangdong. Thus, approaches such as updating the tourism facilities, introducing high-tech elements into tourism products, optimizing the product structure, industrial convergence and technology diffusion should be adopted to extend the industry chain and promote new types of tourism. Meanwhile, approaches like industrial competition and cooperation in regional tourism, the cluster of knowledge spillover and the science and technology guidance to regions with different tourism resources should be adopted to optimize the spatial structure of tourism. The innovation of science and technology should be put into practice to support the tourism structural transformation and upgrading in Guangdong province. |
| [23] | . Hassink R. and Klaerding C. The end of the learning region as we knew it; towards learning in space, Regional Studies. Since its launch in the mid-1990s, the learning region has been much debated by academics and applied in regional policies, which are as such positive signs. However, the concept has also been criticized for its fuzziness and its spatial (or regional) fetishism. By applying a cultural and relational perspective, the paper postulates a shift from the learning region concept that studies regions as places of learning to a new analytical framework, learning in space, which studies culture-influenced learning processes in relations or networks of people and organizations. Hassink R. and Klaerding C. 一如我们所知的学习型区域的终结:迈向在空间中学习,区域研究。学习型区域的概念自 1990 年代中期肇生后,便在学术界引发广泛的辩论,并将之应用于区域政策中,这些就其本身而言皆为正面的象征。但此一概念却也因为过度模糊与空间(或区域)崇拜而受到批评。本文采取文化与相对性之视角,提出由研究区域做为学习之地的学习型区域概念,转换为新的分析架构—在空间中学习,该架构研究在人际与组织关系和网络中,受到文化影响的学习进程。 学习型区域69在空间中学习69文化视角69相对性视角 Hassink R. et Klaerding C. La fin de la région d'apprentissage telle que nous la connaissons; vers l'espace d'apprentissage, Regional Studies. Depuis son lancement au milieu des années 1990, la région d'apprentissage est fortement remise en cause par les universitaires et mise en oeuvre quant à la politique régionale, ce qui constitue à ce titre un signe positif. Cependant, cette notion a fait l'objet de critiques pour son imprécision et pour son fétichisme spatial (ou régional). En abordant la question d'un point de vue culturel et relationnel, cet article cherche à postuler le passage de la notion d'une région d'apprentissage, qui considère les régions comme des lieux d'apprentissage, à un nouveau cadre analytique, à savoir l'espace d'apprentissage, qui étudie les processus d'apprentissage influencés par la culture dans le cadre des relations ou des réseaux de personnes et d'organisations. Région d'apprentissage69Espace d'apprentissage69Point de vue culturel69Point de vue relationnel Hassink R. und Klaerding C. Das Ende der gewohnten lernenden Region: auf dem Weg zum Lernen im Raum, Regional Studies. Seit ihrer Einführung Mitte der neunziger Jahre wurde die lernenden Region in der Wissenschaft ausführlich debattiert und in der Regionalpolitik umgesetzt, was an sich positive Zeichen sind. Allerdings wurde das Konzept auch für seine Verschwommenheit und seinen r01umlichen (oder regionalen) Fetischismus kritisiert. In diesem Beitrag postulieren wir durch Anwendung einer kulturellen und relationalen Perspektive eine Verlagerung von dem Konzept der lernenden Region, bei dem Regionen als Orte des Lernens untersucht werden, zu einem neuen analytischen Rahmen – dem Lernen im Raum –, bei dem kulturell beeinflusste Lernprozesse in Beziehungen oder Netzwerken von Menschen und Organisationen untersucht werden. Lernenden Region69Lernen im Raum69Kulturelle Perspektive69Relationale Perspektive Hassink R. y Klaerding C. El fin de la región de aprendizaje tal como la conocemos; hacia el aprendizaje en el espacio, Regional Studies. Desde su introducción a mediados de los noventa, la región de aprendizaje ha sido debatida en gran medida por académicos y aplicada en políticas regionales, lo que en sí son indicios positivos. Sin embargo, este concepto también se ha criticado por su ambigüedad y fetichismo espacial (o regional). Al aplicar una perspectiva cultural y relacional, en este artículo postulamos un cambio del concepto de región de aprendizaje que estudie las regiones como lugares de aprendizaje a una nueva estructura analítica, el aprendizaje en el espacio que estudie los procesos de aprendizaje influidos por la cultura en las relaciones o las redes de personas y organizaciones. Región de aprendizaje69Aprendizaje en el espacio69Perspectiva cultural69Perspectiva relacional |
| [24] | . . |
