米倩,
刘迪,
付森林,
王旭刚,
郭大勇,
周文利
河南科技大学农学院/洛阳市植物营养与环境生态重点实验室 洛阳 471023
基金项目:国家重点研发计划项目(2017YFD0201700)资助
详细信息
通讯作者:徐晓峰, 主要从事农田养分资源管理、农业废弃物资源化研究。E-mail: xuxf101@163.com
中图分类号:S158.5计量
文章访问数:79
HTML全文浏览量:38
PDF下载量:25
被引次数:0
出版历程
收稿日期:2021-03-26
录用日期:2021-08-29
网络出版日期:2021-08-27
刊出日期:2021-11-10
Effect of phosphorus fertilizer rate on phosphorus fractions contents in calcareous soil and phosphorus accumulation amount in crop
XU Xiaofeng,,MI Qian,
LIU Di,
FU Senlin,
WANG Xugang,
GUO Dayong,
ZHOU Wenli
College of Agriculture, Henan University of Science and Technology / Luoyang Key Laboratory of Plant Nutrition and Environmental Ecology, Luoyang 471023, China
Funds:This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFD0201700)
More Information
Corresponding author:XU Xiaofeng, E-mail: xuxf101@163.com
摘要
HTML全文
图
参考文献
相关文章
施引文献
资源附件
访问统计
摘要
摘要:为了明确磷肥减量施用对石灰性土壤磷组分及其与作物磷积累量关系的影响, 设置3个施磷量, 按纯磷计分别为150 kg·hm?2(P150)、37.5 kg·hm?2(P37)和0 kg·hm?2(P0), 经过连续2年4季冬小麦-夏玉米轮作, 采用Hedley土壤磷组分分组法, 研究土壤磷组分含量的变化及其存储贡献率、输出贡献率, 并采用回归分析、通径分析和结构方程模型探讨土壤关键磷组分及其与磷肥施用量、作物磷积累量间的关系。结果表明, 与P37处理相比, P150处理导致土壤全磷显著增加, 并显著提高阴离子交换树脂态无机磷组分(resin_Pi)、NaHCO3提取态无机磷(NaHCO3_Pi)、NH4OAc提取态无机磷(NH4OAc_Pi)、NaOH-Na2S2O6提取态无机磷(Fe_Pi)和NaHCO3提取态有机磷(NaHCO3_Po)等组分含量(P<0.05)。P0处理与P37处理相比, 土壤磷及其组分含量无显著变化。土壤无机磷组分和有机磷组分的存储贡献率分别为72.6%和23.8%。土壤盈余磷主要存储在HCl提取态无机磷(HCl_Pi)、Fe_Pi、NH4OAc_Pi、resin_Pi和HCl提取态有机磷(HCl_Po)等组分中。土壤无机磷组分的输出贡献率为41.0%, 有机磷组分的输出贡献率为56.4%。其中HCl_Po、Fe_Pi和NH4OAc_Pi的输出贡献率分别为39.44%、17.36%和13.06%。HCl_Pi和resin_Pi的输出贡献率仅为1.91%和0.40%。在结构方程模型中, 施磷量对Fe_Pi、HCl_Pi、NH4OAc_Pi、resin_Pi、NH4F_Po、NaHCO3_Pi和NaHCO3_Po等组分的载荷因子分别为0.078、0.077、0.061、0.036、0.018、0.015和0.012。Fe_Pi、NH4OAc_Pi和HCl_Po等组分对作物磷积累量的载荷因子分别为0.355、0.334和?0.039。上述结果表明, 石灰性土壤中, Fe_Pi、NH4OAc_Pi和HCl_Po是关键磷组分, 其中Fe_Pi和NH4OAc_Pi在不施磷时易消耗, 但也易通过施磷得到补充; HCl_Po有效性高, 不易更新。HCl_Pi有效性低, 是磷肥当季有效性低的重要原因。建议磷肥施用量的决策应以关键磷组分的存储贡献率为依据。
关键词:石灰性土壤/
土壤磷组分/
结构方程模型/
减量施磷/
输出贡献率
Abstract:Excessive application of phosphate fertilizer wastes phosphorus resources and induces eutrophication in lakes and rivers. To study the effect of reduction of phosphorus fertilizer on phosphorus fractions in calcareous soil and its relationship with crop phosphorus accumulation, three treatments were set up, i.e., phosphorus application rates of 150 kg?hm?2 (P150), 37.5 kg·hm?2 (P37), and 0 kg?hm?2 (P0). After two consecutive years of “winter wheat-summer maize” crops rotation, the changes in the contents of soil phosphorus fractions were studied using Hedley soil phosphorus fractionation method, and the storage contribution rate and output contribution rate of each fraction were also estimated. The relationship between soil phosphorus fractions contents, phosphorus fertilizer application rate, and crop phosphorus uptake amount were explored by using regression analysis, path analysis, and structural equation model. The results showed that compared with P37, P150 led to a significant increase in soil total phosphorus content. The contents of inorganic phosphorus extracted with anion exchangeresin (resin_Pi), with NaHCO3 (NaHCO3_Pi), with NH4OAc (NH4OAc_Pi) and with NaOH-Na2S2O6 (Fe_Pi), and organic phosphorus extracted with NaHCO3 (NaHCO3_Po) in P150 were significantly higher than those in P37, while the other fractions showed no significant change. P0 did not cause a significant decrease in the contents of soil phosphorus fractions. The storage contribution rates of soil inorganic phosphorus fractions and organic phosphorus fractions were 72.6% and 23.8%, respectively. Among them, the storage contribution rates of inorganic phosphorus extracted with HCl (HCl_Pi), Fe_Pi, NH4OAc_Pi, resin_Pi, and organic phosphorus extracted with HCl (HCl_Po) were 24.45%, 18.1%, 13.62%, 11.15%, and 9.30%, respectively. The output contribution rate of soil inorganic phosphorus fractions was 41.0%, and that of organic phosphorus fractions was 56.4%. Among them, the output contribution rates of HCl_Po, Fe_Pi, and NH4OAc_Pi were 39.44%, 17.36%, and 13.06%, respectively. The output contribution rates of HCl_Pi and resin_Pi were only 1.91% and 0.40%, respectively. In the structural equation model, the load factors of phosphorus fertilizer application rate on Fe_Pi, HCl_Pi, NH4OAc_Pi, resin_Pi, organic phosphorus extracted with NH4F (NH4F_Po), NaHCO3_Pi, and NaHCO3_Po were 0.078, 0.077, 0.061, 0.036, 0.018, 0.015, and 0.012, respectively. The load factors of Fe_Pi, NH4OAc_Pi, and HCl_Po on crop phosphorus uptake were 0.355, 0.334, and ?0.039, respectively. The above results show that in calcareous soil, Fe_Pi, NH4OAc_Pi, and HCl_Po were the key phosphorus fractions. Among them, Fe_Pi and NH4OAc_Pi were easily consumed when no phosphorus fertilizer was applied, but they can be easily supplemented by phosphorus fertilizer application. However, HCl_Po was available to the crop but was not easily replenished by phosphorus fertilizer application. The high storage contribution rate and low output contribution rate of HCl_Pi fraction were the important reasons for the low efficiency of phosphate fertilizer in the current season. It is suggested that the choice of phosphorus application rate should be based on the storage contribution rate of the key phosphorus fractions.
Key words:Calcareous soil/
Phosphorus fractions in soil/
Structural equation model/
Reducing phosphorus rate/
Output contribution rate
HTML全文
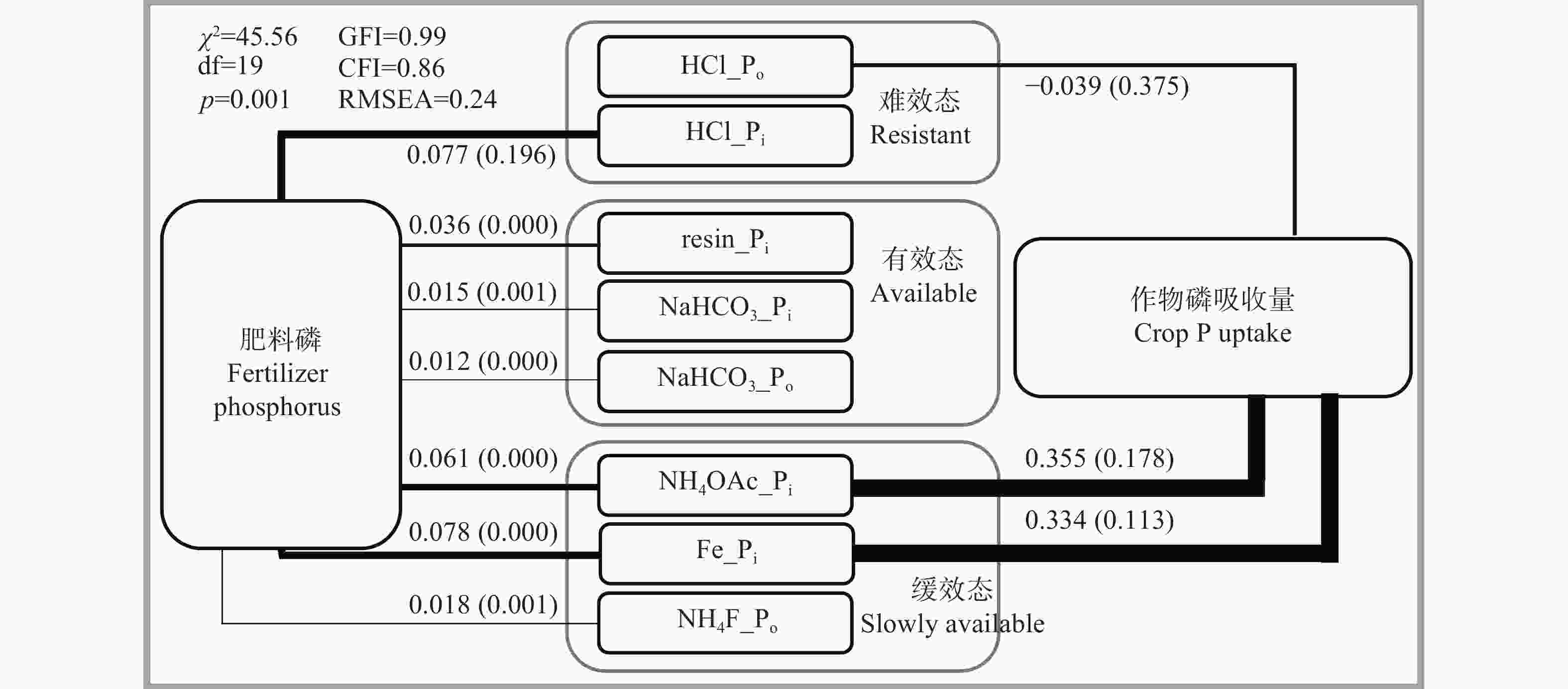
图1肥料磷在土壤磷组分中的分配及磷组分对作物磷吸收量的贡献
各磷组分说明见表1的表注。线段宽度代表载荷因子大小, 线段上数值为“载荷因子(P值)”。The description of each phosphorus fraction is shown in the note of Table 1. The width of line segment represents the load factor size, and the value on the line segment is “load factor (P value)”.
Figure1.Distribution of fertilizer phosphorus in soil phosphorus fractions and contributions of phosphorus fractions to crop phosphorus uptake
 下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片
下载: 全尺寸图片幻灯片表1不同施磷处理下土壤各磷组分及总磷含量
Table1.Contents of phosphorus fractions and total phosphorus in soil under different phosphorus rates
| 施磷量 Phosphorus rate (kg·hm?2) | resin_Pi | NaHCO3_Pi | NH4OAC_Pi | NH4F_Pi | Fe_Pi | HCl_Pi | res_P |
| 0 (P0) | 6.61±0.96b | 6.01±0.48c | 77.11±5.54b | 30.67±2.25a | 31.42±5.12b | 274.08±25.01a | 326.50±22.03a |
| 37 (P37) | 6.72±0.67b | 7.29±0.31bc | 80.73±3.15b | 31.68±1.73a | 36.23±10.52b | 274.61±43.99a | 327.23±76.24a |
| 150 (P150) | 17.64±4.71a | 9.43±2.62a | 94.07±4.95a | 34.69±11.81a | 53.96±3.58a | 298.57±64.08a | 330.81±42.40a |
| 施磷量 Phosphorus rate (kg·hm?2) | resin_Po | NaHCO3_Po | NH4OAC_Po | NH4F_Po | Fe_Po | HCl_Po | TP |
| 0 (P0) | 11.81±0.99b | 0.37±0.15b | 11.26±0.98a | 6.44±1.63ab | 33.86±6.19a | 236.25±27.04a | 1052.38±20.38b |
| 37 (P37) | 13.36±0.87b | 0.67±0.58b | 12.25±2.49a | 7.42±2.20ab | 34.73±11.62a | 247.18±36.04a | 1080.09±64.76b |
| 150 (P150) | 17.08±5.96ab | 4.51±4.75a | 13.53±11.72a | 11.52±5.21a | 35.98±6.88a | 256.29±49.04a | 1178.07±11.25a |
| 不同小写字母表示P<0.05水平不同施磷量间差异显著。resin_Pi: 阴离子交换树脂态无机磷; resin_Po: 阴离子交换树脂态有机磷; NaHCO3_Pi: NaHCO3提取态无机磷; NaHCO3_Po: NaHCO3提取态有机磷; NH4OAC_Pi: NH4OAc提取态无机磷; NH4OAC_Po: NH4OAc提取态有机磷; NH4F_Pi: NH4F提取态无机磷; NH4F_Po: NH4F提取态有机磷; Fe_Pi: NaOH-Na2S2O6提取态无机磷; Fe_Po: NaOH-Na2S2O6提取态有机磷; HCl_Pi: HCl提取态无机磷; HCl_Po: HCl提取态有机磷; res_P: 残渣态磷; TP: 全磷。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different phosphorus rates at P<0.05. resin_Pi: inorganic phosphorus extracted with anion exchangeresin; resin_Po: organic phosphorus extracted with anion exchangeresin; NaHCO3_Pi: inorganic phosphorus extracted with NaHCO3 solution; NaHCO3_Po: organic phosphorus extracted with NaHCO3 solution; NH4OAC_Pi: inorganic phosphorus extracted with NH4OAc solution; NH4OAC_Po: organic phosphorus extracted with NH4OAc solution; NH4F_Pi: inorganic phosphorus extracted with NH4F solution; NH4F_Po: organic phosphorus extracted with NH4F solution; Fe_Pi: inorganic phosphorus extracted with NaOH-Na2S2O6 solution; Fe_Po: organic phosphorus extracted with NaOH-Na2S2O6 solution; HCl_Pi: inorganic phosphorus extracted with HCl solution; HCl_Po: organic phosphorus extracted with HCl solution; res_P: residual phosphorus; TP: total phosphorus. | |||||||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表2不同土壤磷组分对磷在土壤中存储和输出的贡献
Table2.Contribution rates of soil phosphorus fractions to storage and output of phosphorus in soil
| 项目 Item | resin_Pi | NaHCO3_Pi | NH4OAc_Pi | NH4F_Pi | Fe_Pi | HCl_Pi | 合计 Total |
| 输出贡献率 Output contribution rate | 0.40 | 4.62 | 13.06 | 3.64 | 17.36 | 1.91 | 41.00 |
| 存储贡献率 Storage contribution rate | 11.15 | 2.18 | 13.62 | 3.07 | 18.10 | 24.45 | 72.57 |
| 项目 Item | resin_Po | NaHCO3_Po | NH4OAc_Po | NH4F_Po | Fe_Po | HCl_Po | 合计 Total |
| 输出贡献率 Output contribution rate | 5.59 | 1.08 | 3.57 | 3.54 | 3.14 | 39.44 | 56.37 |
| 存储贡献率 Storage contribution rate | 3.80 | 3.92 | 1.31 | 4.18 | 1.28 | 9.30 | 23.78 |
| 各磷组分说明见表1的表注。 The description of each phosphorus fraction is shown in the note of Table 1. | |||||||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表3作物磷吸收量与土壤磷组分含量多元回归及通径分析结果
Table3.Multiple regression and path analysis between soil phosphorus fractions contents and phosphorus uptake amount of crop
| 项目 Item | 系数 Coefficient | P值 P value | 直接效应 Direct effect | 间接效应 Indirect effect | 总效应 Total effect |
| 截距 Intercept | ?19.07 | 0.67 | — | — | — |
| resin_Pi | ?1.99 | 0.16 | ?0.74 | 1.34 | 0.60 |
| NaHCO3_Pi | 3.47 | 0.06 | 0.72 | ?0.16 | 0.56 |
| NH4OAc_Pi | 0.44 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 0.53 |
| NaHCO3_Po | 2.80 | 0.11 | 0.56 | ?0.05 | 0.51 |
| NH4F_Pi | 1.70 | 0.05 | 0.68 | ?0.20 | 0.48 |
| resin_Po | ?1.85 | 0.10 | ?0.64 | 0.82 | 0.19 |
| res_P | 0.07 | 0.22 | 0.26 | ?0.09 | 0.17 |
| NH4OAc_Po | ?0.81 | 0.29 | ?0.30 | 0.45 | 0.15 |
| NH4F_Po | 2.07 | 0.13 | 0.60 | ?0.57 | 0.03 |
| HCl_Po | ?0.07 | 0.23 | ?0.25 | 0.04 | ?0.21 |
| 各磷组分说明见表1的表注。 The description of each phosphorus fraction is shown in the note of Table 1. | |||||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表4磷肥施用量与土壤磷组分含量的线性回归方程
Table4.Regression relationship between soil phosphorus fractions contents and phosphorus fertilizer rate
| 磷组分 Phosphorus fraction | 截距 Intercept | 斜率 Slope | R2 | P值 P value |
| Fe_Pi | 3.28 | 7.40 | 0.66 | 1.02×10?6 |
| NH4OAc_Pi | 7.63 | 6.09 | 0.69 | 4.21×10?7 |
| resin_Pi | 5.41 | 3.65 | 0.76 | 2.11×10?8 |
| resin_Po | 1.21 | 2.48 | 0.41 | 4.32×10?4 |
| NaHCO3_Pi | 6.32 | 1.76 | 0.61 | 4.63×10?6 |
| NH4F_Po | 5.68 | 1.66 | 0.25 | 7.56×10?3 |
| NaHCO3_Po | 0.47 | 1.27 | 0.37 | 9.83×10?4 |
| 各磷组分说明见表1的表注。 The description of each phosphorus fraction is shown in the note of Table 1. | ||||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV表5土壤磷组分含量及施肥量和作物磷吸收量的相关关系
Table5.Correlations between soil phosphorus fractions contents, phosphorus fertilizer rate and crop phosphorus absorption
| NaHCO3_Pi | NH4OAc_Pi | NH4F_Pi | Fe_Pi | HCl_Pi | resin_Po | NaHCO3_Po | NH4OAc_Po | NH4F_Po | Fe_Po | HCl_Po | res_P | P_uptake | Papplying | |
| Resin_Pi | 0.57** | 0.72** | 0.39 | 0.77** | 0.07 | 0.32 | 0.80** | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.22 | 0.60** | 0.88** |
| NaHCO3_Pi | 0.70** | 0.36 | 0.64** | 0.45* | 0.72** | 0.28 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.20 | ?0.01 | ?0.10 | 0.56** | 0.79** | |
| NH4OAc_Pi | 0.29 | 0.81** | 0.20 | 0.65** | 0.50* | 0.09 | 0.42* | 0.10 | 0.11 | ?0.05 | 0.53** | 0.83** | ||
| NH4F_Pi | 0.38 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.54** | ?0.19 | 0.05 | 0.09 | ?0.21 | 0.48* | 0.38 | |||
| Fe_Pi | 0.15 | 0.51* | 0.68** | 0.15 | 0.33 | ?0.32 | 0.14 | ?0.03 | 0.57** | 0.82** | ||||
| HCl_Pi | 0.20 | ?0.06 | 0.45* | 0.14 | 0.37 | ?0.68** | ?0.36 | 0.30 | 0.27 | |||||
| resin_Po | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.62** | 0.27 | 0.26 | ?0.16 | 0.19 | 0.66** | ||||||
| NaHCO3_Po | ?0.26 | 0.00** | ?0.15 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.51* | 0.63** | |||||||
| NH4OAc_Po | 0.29 | 0.00** | 0.06 | ?0.50* | 0.15 | 0.22 | ||||||||
| NH4F_Po | 0.13 | 0.38 | ?0.17 | 0.03 | 0.53** | |||||||||
| Fe_Po | ?0.30 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.17 | ||||||||||
| HCl_Po | ?0.07 | ?0.21 | 0.18 | |||||||||||
| res_P | 0.17 | 0.05 | ||||||||||||
| P_uptake | 0.59** | |||||||||||||
| 各磷组分说明见表1的表注。Papplying: 施磷量; P_uptake: 吸磷量。*和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著相关。 The description of each phosphorus fraction is shown in the note of Table 1. Papplying: phosphorus rate; P_uptake: phosphorus uptake. * and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. | ||||||||||||||
 下载: 导出CSV
下载: 导出CSV参考文献
| [1] | 王莹, 方俊文, 李博. 2019年我国磷复肥行业运行情况及发展趋势[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2020, 35(8): 1?8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6220.2020.08.002 WANG Y, FANG J W, LI B. Production and developing trends of phosphate and compound fertilizer industry in China in 2019[J]. Phosphate & Compound Fertilizer, 2020, 35(8): 1?8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6220.2020.08.002 |
| [2] | 杜振宇, 王清华, 周健民, 等. 磷在潮土肥际微域中的迁移和转化[J]. 土壤学报, 2012, 49(4): 725?730 doi: 10.11766/trxb201104190141 DU Z Y, WANG Q H, ZHOU J M, et al. Movement and transformation of phosphorus in fertilizer microsites in a fluvo-aquic soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2012, 49(4): 725?730 doi: 10.11766/trxb201104190141 |
| [3] | 吉庆凯, 王栋, 杨文宝, 等. 长期施磷对玉米-小麦轮作系统作物产量和磷素吸收及土壤磷积累的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(7): 2469?2476 JI Q K, WANG D, YANG W B, et al. Effects of long-term phosphorus application on crop yield, phosphorus absorption and soil phosphorus accumulation in maize-wheat rotation system[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(7): 2469?2476 |
| [4] | 李发, 王农, 徐应明, 等. 水稻土对磷的吸持能力及环境风险研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(12): 4734?4739 LI F, WANG N, XU Y M, et al. Characteristics of phosphorus sorption capacity and its environmental risk in paddy soils[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(12): 4734?4739 |
| [5] | GUPPY C N, MCLAUGHLIN M J. Options for increasing the biological cycling of phosphorus in low-input and organic agricultural systems[J]. Crop and Pasture Science, 2009, 60(2): 116 doi: 10.1071/CP07157 |
| [6] | TIAN L Y, GUO Q J, YU G R, et al. Phosphorus fractions and oxygen isotope composition of inorganic phosphate in typical agricultural soils[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 239: 124622 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124622 |
| [7] | 汪洪, 宋书会, 张金尧, 等. 土壤磷形态组分分级及31P-NMR技术应用研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(2): 512?523 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.16066 WANG H, SONG S H, ZHANG J Y, et al. Research advance in soil phosphorus fractionations and their characterization by chemical sequential methods and 31P-NMR techniques[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(2): 512?523 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.16066 |
| [8] | TIESSEN H, STEWART J W B, COLE C V. Pathways of phosphorus transformations in soils of differing pedogenesis[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1984, 48(4): 853?858 doi: 10.2136/sssaj1984.03615995004800040031x |
| [9] | COSTA M, GAMA-RODRIGUES A, GON?ALVES J, et al. Labile and non-labile fractions of phosphorus and its transformations in soil under Eucalyptus plantations, Brazil[J]. Forests, 2016, 7(12): 15 doi: 10.3390/f7010015 |
| [10] | 赵伟, 杨圆圆, 蒋丽媛, 等. 减施磷肥提高设施番茄氮磷钾生理效率并减少土壤速效磷累积[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(10): 1710?1718 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.18427 ZHAO W, YANG Y Y, JIANG L Y, et al. Reducing conventional phosphorus input increase physiological efficiencies of absorbed nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in greenhouse tomato and decrease soil available phosphorus accumulation[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(10): 1710?1718 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.18427 |
| [11] | 陈浩, 汪玉, 袁佳慧, 等. 太湖稻麦轮作区减施磷肥对土壤供磷和小麦吸收磷的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(4): 741?746 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1551 CHEN H, WANG Y, YUAN J H, et al. The effect of phosphorus-reduction on soil phosphorus supply and wheat phosphorus uptake in a rice-wheat rotation system in the Taihu Lake Region[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(4): 741?746 doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1551 |
| [12] | 蒋柏藩, 顾益初. 石灰性土壤无机磷分级体系的研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 1989, 22(3): 58?66 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.1989.03.012 JIANG B F, GU Y C. A suggested fractionation scheme of inorganic phosphorus in calcareous soils[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1989, 22(3): 58?66 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.1989.03.012 |
| [13] | 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000: 172–178 LU R K. Analysis Methods of Soil Agrochemistry[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000: 172–178 |
| [14] | 杜艳玲, 周怀平, 杨振兴, 等. 长期施肥下褐土中不同磷组分对磷素盈余的响应[J]. 华北农学报, 2018, 33(3): 224?231 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2018.03.033 DU Y L, ZHOU H P, YANG Z X, et al. Response of different P component to P balance in cinnamon soil under long-term fertilization[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2018, 33(3): 224?231 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2018.03.033 |
| [15] | 谢英荷, 洪坚平, 韩旭, 等. 不同磷水平石灰性土壤Hedley磷形态生物有效性的研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2010, 24(6): 141?144 XIE Y H, HONG J P, HAN X, et al. Study on soil bioavailability of the Hedley P forms in calcareous soil with different phosphorus level[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 24(6): 141?144 |
| [16] | YANG X, POST W M. Phosphorus transformations as a function of pedogenesis: a synthesis of soil phosphorus data using Hedley fractionation method[J]. Biogeosciences, 2011, 8(10): 2907?2916 doi: 10.5194/bg-8-2907-2011 |
| [17] | 王海龙, 张民, 刘之广, 等. 多年定位试验条件下不同施磷水平对土壤无机磷分级的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(5): 318?324 WANG H L, ZHANG M, LIU Z G, et al. Effects of different phosphorus application levels on the inorganic phosphorus fraction under multi-year location experiment[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(5): 318?324 |
| [18] | 廖文华, 刘建玲, 黄欣欣, 等. 潮褐土上蔬菜产量和土壤各形态磷变化对长期过量施磷的响应[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(4): 894?903 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.16333 LIAO W H, LIU J L, HUANG X X, et al. Responses of vegetable yield and changes of phosphorus fractions in cinnamon soil to long-term excess phosphorus application[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(4): 894?903 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.16333 |
| [19] | 张为政. 土壤磷组分的通径分析及其相对有效性[J]. 土壤学报, 1991, 28(4): 417?425 ZHANG W Z. Path analysis and relative availability of inorganic and organic phosphorus fractions in soils[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1991, 28(4): 417?425 |
| [20] | ACKSEL A, BAUMANN K, HU Y F, et al. A critical review and evaluation of some P-research methods[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2019, 50(22): 2804?2824 doi: 10.1080/00103624.2019.1679165 |
| [21] | GAMA-RODRIGUES A C, SALES M V S, SILVA P S D, et al. An exploratory analysis of phosphorus transformations in tropical soils using structural equation modeling[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2014, 118(1/2/3): 453?469 |
| [22] | HOU E Q, CHEN C R, KUANG Y W, et al. A structural equation model analysis of phosphorus transformations in global unfertilized and uncultivated soils[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2016, 30(9): 1300?1309 doi: 10.1002/2016GB005371 |
| [23] | LIANG Y T, XIAO X, NUCCIO E E, et al. Differentiation strategies of soil rare and abundant microbial taxa in response to changing climatic regimes[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2020, 22(4): 1327?1340 doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14945 |
| [24] | XU P D, LIU Y R, ZHU J, et al. Influence mechanisms of long-term fertilizations on the mineralization of organic matter in Ultisol[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2020, 201: 104594 doi: 10.1016/j.still.2020.104594 |
| [25] | LI Y H, JONES D L, CHEN Q, et al. Acidification and anaerobic digestion change the phosphorus forms and distribution in particle fractions of cattle slurry and phosphorus dynamics in soil after application[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2020, 200: 101?111 doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2020.09.005 |
| [26] | KAMEL G, GUILLAUME B. Structural Equatin Modeling with Lavaan[M]. London: Wiley, 2019: 73–85 |
| [27] | 曹莹菲, 张红, 刘克, 等. 不同施肥方式对土土壤磷素各组分含量的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2015, 33(5): 115?120 doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2015.05.21 CAO Y F, ZHANG H, LIU K, et al. Effects of different fertilization implementations on phosphorus fraction of manural loessial soil[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2015, 33(5): 115?120 doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2015.05.21 |
| [28] | 吴璐璐, 张水清, 黄绍敏, 等. 长期定位施肥对潮土磷素形态和有效性的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2021, 52(2): 379?386 WU L L, ZHANG S Q, HUANG S M, et al. Effect of long-term fertilization on phosphorus fraction and availability in fluvo-aquic soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2021, 52(2): 379?386 |
| [29] | 杨振兴, 周怀平, 解文艳, 等. 长期施肥褐土不同磷组分对磷素盈余的响应[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(5): 924?933 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.19291 YANG Z X, ZHOU H P, XIE W Y, et al. Response of phosphorus components to phosphate surplus in cinnamon soil under long-term fertilization[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(5): 924?933 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.19291 |
| [30] | 金欣, 姚珊, Batbayar Javkhlan, 等. 冬小麦–夏休闲体系作物产量和土壤磷形态对长期施肥的响应[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(6): 1660?1671 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.18260 JIN X, YAO S, JAVKHLAN B, et al. Response of wheat yield and soil phosphorus fractions to long-term fertilization under rainfed winter wheat-summer fallow cropping system[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2018, 24(6): 1660?1671 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.18260 |
| [31] | 宋书会. 磷肥减施及覆膜条件下黑土磷素供应特征与转化机制[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2019 SONG S H. Phosphorus supply and transformation in mollisol under reduced phosphate rate and plastic film mulching[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2019 |
| [32] | 陈磊, 云鹏, 高翔, 等. 磷肥减施对玉米根系生长及根际土壤磷组分的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(6): 1548?1557 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.16061 CHEN L, YUN P, GAO X, et al. Effects of reducing phosphorus fertilizer rate on root growth and phosphorus fractions in rhizosphere soils of summer maize[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2016, 22(6): 1548?1557 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.16061 |
| [33] | 侯云鹏, 王立春, 李前, 等. 覆膜滴灌条件下基于玉米产量和土壤磷素平衡的磷肥适用量研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(20): 3573?3584 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.20.008 HOU Y P, WANG L C, LI Q, et al. Research on optimum phosphorus fertilizer rate based on maize yield and phosphorus balance in soil under film mulched drip irrigation conditions[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(20): 3573?3584 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.20.008 |
| [34] | 王斌, 刘骅, 马义兵, 等. 长期施肥对灰漠土无机磷组分的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2017, 48(4): 917?921 WANG B, LIU H, MA Y B, et al. Effect of long-term fertilization on fractions of inorganic phosphorus in grey desert soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2017, 48(4): 917?921 |
| [35] | 李若楠, 王政培, BATBAYAR Javkhlan, 等. 等有机质土有效磷和无机磷形态的关系[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(21): 3852?3865 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.21.014 LI R N, WANG Z P, JAVKHLAN B, et al. Relationship between soil available phosphorus and inorganic phosphorus forms under equivalent organic matter condition in a tier soil[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(21): 3852?3865 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.21.014 |
| [36] | 许艳, 张仁陟. 陇中黄土高原不同耕作措施下土壤磷动态研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2017, 54(3): 670?681 XU Y, ZHANG R Z. Dynamics of soil phosphorus as affected by tillage on the Loess Plateau in central Gansu, China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2017, 54(3): 670?681 |
| [37] | 朱芸芸, 李敏, 曲博, 等. 芦苇根际土壤有机磷组分的季节变化及与磷酸酶活性的关系[J]. 土壤, 2016, 48(6): 1108?1113 ZHU Y Y, LI M, QU B, et al. Seasonal variations of organic phosphorus composition and their relationship with phosphatase activity in Phragmites communis rhizosphere soil[J]. Soils, 2016, 48(6): 1108?1113 |
| [38] | 刘津, 李春越, 邢亚薇, 等. 长期施肥对黄土旱塬农田土壤有机磷组分及小麦产量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(1): 157?164 LIU J, LI C Y, XING Y W, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil organic phosphorus fractions and wheat yield in farmland of Loess Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(1): 157?164 |
| [39] | 孙锋, 曾令达, 彭长连, 等. 南美蟛蜞菊、蟛蜞菊和杂交蟛蜞菊土壤磷组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2021, 58(3): 798?804 SUN F, ZENG L D, PENG C L, et al. Effect of growing of Wedelia trilobata,W. chinensis or their hybrid on soil phosphorus fractionation in south China and their affecting factors[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2021, 58(3): 798?804 |
| [40] | 曾晓敏, 范跃新, 林开淼, 等. 亚热带不同植被类型土壤磷组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(7): 2156?2162 ZENG X M, FAN Y X, LIN K M, et al. Characteristics of soil phosphorus fractions of different vegetation types in subtropical forests and their driving factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(7): 2156?2162 |
| [41] | QU Y, WANG C, GUO J S, et al. Characteristics of organic phosphorus fractions in soil from water-level fluctuation zone by solution 31P-nuclear magnetic resonance and enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 255: 113209 doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113209 |
| [42] | 袁佳慧, 汪玉, 王慎强, 等. 稻麦轮作磷肥减施下水稻土磷素生物有效性特征[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2018, 34(7): 599?605 doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2018.07.004 YUAN J H, WANG Y, WANG S Q, et al. Characteristic of soil P availability in reduced P-input rice-wheat cropping rotation paddy soils[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2018, 34(7): 599?605 doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2018.07.004 |
| [43] | 王静, 王磊, 张爱君, 等. 长期增施有机肥对土壤不同组分有机磷含量及微生物丰度的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2020, 36(9): 1161?1168 WANG J, WANG L, ZHANG A J, et al. Effects of long-term organic fertilization on the content of soil organic phosphorus fractions and abundance of soil microorganism[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2020, 36(9): 1161?1168 |
