 ,*中国农业科学院果树研究所, 农业部园艺作物种质资源利用重点实验室, 兴城 125100
,*中国农业科学院果树研究所, 农业部园艺作物种质资源利用重点实验室, 兴城 125100Proteome Analysis of Different Resistant Apple Cultivars in Response to the Stress of Ring Rot Disease
Caixia Zhang, Gaopeng Yuan, Xiaolei Han, Wuxing Li, Peihua Cong ,*Key Laboratory of Horticulture Crops Germplasm Resources Utilization, Ministry of Agriculture, Research Institute of Pomology, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Xingcheng 125100, China
,*Key Laboratory of Horticulture Crops Germplasm Resources Utilization, Ministry of Agriculture, Research Institute of Pomology, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Xingcheng 125100, China通讯作者:
责任编辑: 朱亚娜
收稿日期:2019-10-18接受日期:2020-04-26网络出版日期:2020-07-01
| 基金资助: |
Corresponding authors:
Received:2019-10-18Accepted:2020-04-26Online:2020-07-01

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (1640KB)摘要页面多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
引用本文
张彩霞, 袁高鹏, 韩晓蕾, 李武兴, 丛佩华. 不同抗性苹果品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫的差异蛋白质组分析. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 430-441 doi:10.11983/CBB19204
Zhang Caixia, Yuan Gaopeng, Han Xiaolei, Li Wuxing, Cong Peihua.
苹果(Malus domestica)作为多年生木本果树研究的模式植物, 其安全生产对世界水果产业可持续发展具有重要意义(Eccher et al., 2014)。一直以来, 苹果真菌病害的发生严重制约苹果产业可持续发展(Jurick II et al., 2011; Fan et al., 2011)。研究介导真菌病害抗性调控的分子机理是加速苹果抗病种质创新的有效途径。
苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(Ogata et al., 2000; 张计育等, 2012; Xu et al., 2015; 肖龙等, 2016)。研究表明, 应答病原菌胁迫时, 抗、感病品种的发病症状和免疫应答模式差异明显(周增强等, 2010; Xu et al., 2015)。以往关于苹果轮纹病的研究多关注其病害的防治方法、致病菌分离及抗性资源筛选等方面(Ogata et al., 2000; 张玉经等, 2010; 周增强等, 2010; 杨丽丽等, 2012), 而抗病机理相关研究较少。我们前期研究发现, 苹果应答病原菌胁迫过程中, 不同胁迫时间(0、24、48和72小时)内, 抗、感病株系在激素调节和免疫应答等方面存在显著差异(Chen et al., 2012a)。苹果叶片经轮纹病菌侵染后, 叶片叶绿体细胞内多个代谢过程可参与轮纹病菌的胁迫应答反应(肖龙等, 2016)。近年来, 我们开展的病原菌与苹果寄主互作的蛋白质组学研究表明, 病原菌诱导后, 寄主可通过启动多个途径实现对病原菌的防御响应, 包括光合作用、能量代谢、胁迫及抗性反应等各类蛋白的差异表达, 筛选鉴定了β-1,3-葡聚糖酶、APX、GPX、Hsps及Mal d1等抗病相关蛋白(Zhang et al., 2015; 张彩霞等, 2018)。此外, 利用iTRAQ (isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantization)定量鉴定技术, 我们还解析了抗病苹果品种华月应答链格孢菌侵染的抗性相关蛋白的表达特点(张彩霞等, 2018)。进一步针对Mal d1开展功能分析, 我们发现病原菌胁迫48小时内, Mal d1基因的表达量呈现先升后降的趋势, 于24小时达到峰值, 且表达量在抗、感病品种间存在显著差异。由此推测, 抗、感病苹果品种应答病原菌胁迫过程中, 不同胁迫时间的蛋白质组表达模式可能存在差异。同位素标记定量(isobaric tag, IBT)技术作为iTRAQ蛋白定量分析技术的升级版, 已在许多研究中得到成功应用(Chen et al., 2012b; Ramsubramaniam et al., 2013; Xing et al., 2017)。与常规iTRAQ定量分析技术相比, IBT蛋白定量技术鉴定蛋白数量更多、蛋白定量准确性更高、标记样品数量也更多(Paulo et al., 2015; Erickson et al., 2015)。鉴于苹果轮纹病病害发生的严重性, 以及抗病机制研究对于苹果抗病新种质开发的重要意义, 我们在前期工作基础上, 采用IBT标记定量结合液相色谱-串联质谱(LC-MS/MS)分析技术, 对病原菌处理前后4个不同时间点的抗病品种(R)华月和感病品种(S)金冠叶片总蛋白表达情况进行鉴定, 对抗性相关蛋白在抗、感病品种间的差异表达特点进行分析, 旨在为进一步认识抗、感病苹果品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫过程中启动的抗性机制提供参考。
1 材料与方法
本实验于2017-2019年, 在中国农业科学院果树研究所/农业部园艺作物种质资源利用重点实验室/国家苹果育种中心完成。1.1 材料来源及病原菌接种
实验所用抗病苹果(Malus domestica Borkh.)品种华月(杨振英等, 2010)及感病品种金冠(张玉经等, 2010)均来自国家苹果育种中心(辽宁兴城)杂种圃, 树龄均为10年, 树长势健壮, 均采用常规管理。实验于2018年5月开展, 分别采摘华月和金冠新梢部分15-20天叶龄的叶片, 选取大小均一、无机械损伤、无病虫药害的叶片, 表面经初步消毒, 再用无菌水清洗后, 置于无菌保湿大培养皿(直径14 cm)中。供试苹果轮纹病致病菌(Botryosphaeria berengeriana f. sp piricola)菌株LW-xc102由中国农业科学院果树研究所植物保护中心提供。将LW-xc102接种于马铃薯蔗糖琼脂(potato sugar agar, PSA)培养基上, 28°C培养7天, 至菌丝长满培养皿后备用。选取生长均一的LW-xc102菌丝培养物, 以直径5 mm的打孔器打下菌饼, 采用叶片正面针刺法(林月莉等, 2011)接种轮纹病菌。分别在叶片正面主脉两侧用灭菌牙签各刺1个接种点, 将菌饼正面贴于接种点上, 培养时共设4个时间点(0、6、24和48小时)。取样部位为去除接种及发病部位的其余叶片。抗病品种(R)华月取样叶片分别编号R-0h、R-6h、R-24h和R-48h; 感病品种(S)金冠取样叶片分别编号S-0h、S-6h、S-24h和S-48h。抗(R)、感(S)病品种叶片接种轮纹病菌实验均设3次生物学重复。
1.2 叶片总蛋白样品制备
抗(R)、感(S)病苹果叶片总蛋白样品制备参照酚抽提方法(Zhang et al., 2015)完成。总蛋白样品经室温风干后, 干粉重悬于裂解缓冲液(lysis buffer) (Zhang et al., 2015)中。采用BCA蛋白浓度检测试剂盒(GE, Cat No.80648356)完成蛋白样品定量。每样品分别取30 μg蛋白溶液, 采用12% SDS-PAGE电泳方法检测蛋白纯度。总蛋白样品保存于-80°C冰箱中备用。1.3 同位素标记定量(IBT)及质谱(LC-MS/MS)分析
蛋白样品IBT标记定量及LC-MS/MS分析实验均委托深圳华大基因研究院完成。具体步骤为: 将8个样品编号, 每个样品取100 μg蛋白溶液, 按40:1的比例加入2.5 μg trypsin酶, 37°C酶解12小时, 酶解肽段经Strata XC18柱除盐后真空抽干。肽段经0.2 mol·L-1 TEAB (Applied Biosystems, 美国)复溶, 终浓度达4 μg·μL-1。采用8标IBT试剂标记各蛋白肽段样品(R-0h: 114; R-6h: 115h; R-24h: 116N; R-48h: 116C; S-0h: 117N; S-h: 117C; S-24h: 118N; S-48h: 119)。将标记后的8组肽段样品等量混合, 真空抽干后, 用岛津LC-20AB液相色谱系统结合Gemini C18柱(5 μm, 4.6×250 mm)进行液相分离, 分离后的肽段分别合并后冷冻抽干。IBT标记实验重复3次, 共完成24个样品的标记定量。抽干后的肽段样品经流动相A (2% ACN, 0.1% FA)复溶, 20 000 ×g离心10分钟, 取上清进样。样品经Trap柱富集除盐后, 用岛津LC-20AD纳升液相色谱仪进行分离。选用自装C18柱(内径75 μm; 流速300 nL·min-1)进行梯度洗脱: 5%流动相B (98% ACN, 0.1% FA) 0-8分钟; 8%-35%流动相B 8-43分钟; 35%-60%流动相B 43-48分钟; 60%-80%流动相B 48-50分钟; 80%流动相B 50-55分钟; 5%流动相B 55-65分钟。
液相分离后肽段经Nano ESI源离子化后进入Q-Exactive串联质谱仪(Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose, CA)进行DDA (data-dependent acquisition)检测。主要参数设置: 离子源电压1 600 V; 一级质谱质荷比(m/z)扫描范围为350-1 600 m/z, 分辨率70 000; 二级质谱起始质荷比固定为100 m/z, 分辨率17 500。二级碎裂母离子筛选条件: 电荷2+到7+。离子碎裂模式为高能碰撞解离(HCD)。动态排除参数设为15秒。
1.4 生物信息学分析
原始质谱数据经Proteome Discoverer 2.2软件转换为MGF格式文件。利用Mascot 2.3.02蛋白质鉴定软件搜索NCBI中包含337 685个序列的苹果(Malus domestica fasta)数据库, 最终选定的可信蛋白必须包含至少1个可信的特异性(unique)肽段。Mascot搜索参数Type of search: MS/MS Ion search; Enzyme: Trypsin; Fragment Mass Tolerance: 0.05 Da; Mass Values: Monoisotopic; Variable modifications: Oxidation (M), IBT 8plex (Y); Peptide Mass Tolerance: 20 ppm; Fixed modifications: Carbamidomethyl (C), IBT 8plex (N-term), IBT 8plex (K); Database: Malus (337 685 sequences)。IBT数据的定量采用IQuant软件(Wen et al., 2014)完成。为降低假阳性率, 蛋白过滤参数设置为protein FDR≤0.01 (Savitski et al., 2015)。比较10个比对组(R-0h/S-0h、R-6h/S-6h、R-24h/S-24h、R-48h/S-48h、S-6h/S-0h、S-24h/S-0h、S-48h/S-0h、R-6h/R-0h、R-24h/R-0h和R-48h/R-0h), 筛选至少在2次生物学重复中均存在的蛋白定量信息开展进一步分析。利用Blast2go软件对差异表达蛋白(DEPs)进行GO (http://www.geneontology.org)注释分析。利用KEGG pathway (http://www.genome.jp/kegg)数据库对所鉴定的DEPs进行富集分析。筛选参数: Unique peptide≥2, Fold change大于1.5或小于0.67, P-value<0.05。对3次重复数据进行t-test检验, P<0.05为差异显著。倍数变化大于1.5或小于0.67被认为是差异表达蛋白。
1.5 实时荧光定量PCR (qRT-PCR)分析
筛选5个苹果轮纹病抗病功能基因进行qRT-PCR验证。RNA提取使用北京华越洋生物科技有限公司试剂盒, cDNA第1链合成采用宝生物工程(大连)有限公司试剂盒(Cat No.RR047A)。各基因的荧光定量引物使用NCBI在线软件(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/ primer-blast/index.cgi?LINK_LOC= BlastHome)设计, 引物序列见表1, 选用MdActin作为内参基因。qRT-PCR在CFX96TM Real-Time System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, USA)仪器上进行。反应体系为: 12.5 μL TB Green, 上、下游引物(10 μmol·L-1)各0.75 μL, 9 μL ddH2O, 2 μL cDNA, 总体积25 μL。反应条件为: 95°C预变性3分钟; 95°C变性5秒, 58°C退火30秒, 72°C延伸30秒, 40个循环。实验均设3次重复。实验所得数据采用2-ΔΔCT法计算(Livak and Schmittgen, 2001)。利用SPSS18.0软件进行差异显著性分析。Table 1
表1
表1荧光定量PCR引物序列
Table 1
| Accession No. | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| gi|657977120 | TCACCTTAGCCATCTTCTTCGC | TGCTAACTCGAACCCTGTGG |
| gi|658027651 | CTCCACTGTGCCTATTGCGA | GAGCCGGGTTAGCGAACAA |
| gi|658061109 | TTGATGCCAGCCCTGCAAAT | GGGCTTGAAGCTCGTTGTTG |
| gi|661567324 | GATTGCACCCCAGGCAATCA | TTGTGCTTCACGTAGCCGTA |
| gi|658009573 | AGGCATTCCCTCAGGACTAC | TTCCGACTTCATCCACTGC |
| MdActin | TGACCGAATGAGCAAGGAAATTACT | TACTCAGCTTTGGCAATCCACATC |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2 结果与讨论
2.1 华月、金冠苹果应答轮纹病菌侵染的发病特征
为比较抗、感病苹果品种应答轮纹病胁迫的发病特征, 本研究采用叶面针刺结合菌饼接种, 对华月和金冠苹果叶片发病过程进行观察。结果(图1)表明, 病原菌接种3小时, 华月和金冠叶片发病特征均不明显。接种6小时, 抗、感病叶片未见明显病斑。接种24小时, 华月叶片发病不明显, 部分叶片的接种部位可见病斑; 而感病品种金冠发病特征明显, 所有叶片均呈现明显病斑。接种48小时, 华月叶片仅在接种部位有病斑扩展; 而金冠叶片发病病斑均有明显扩展, 部分叶片坏死, 病斑呈现连片分布状态。抗、感病特征与前人关于华月(杨振英等, 2010)和金冠(张玉经等, 2010)的抗、感病表型描述一致。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1抗、感病苹果品种华月和金冠应答轮纹病菌侵染的发病特征比较
R: 抗病品种华月; S: 感病品种金冠。Bars=1 cm
Figure 1Comparison of morphological characteristics of resistant and susceptible apple cultivars Huayue and Golden Delicious in response to ring rot disease
R: Resistant cultivar Huayue; S: Susceptible cultivar Golden Delicious. Bars=1 cm
2.2 差异蛋白质鉴定与IBT定量
分别对病原菌处理前后4个时间点的抗病品种(R)华月和感病品种(S)金冠叶片进行总蛋白提取及IBT定量分析。结果显示, 24个样品共产生835 617张二级图谱, 在FDR≤0.01过滤标准下, 鉴定到9 816条肽段, 9 425条Unique肽段, 最终成功鉴定蛋白5 319个。进一步对已鉴定的差异蛋白进行显著性分析, 在Unique peptide≥2、Fold change>1.5、P-value<0.05的筛选条件下, 4个时间点(0、6、24和48小时), 抗(R)、感病(S)品种内(R/R、S/S)、品种间(R/S)各比对组共鉴定出171个DEPs, 其中抗性相关蛋白共46个(含重复), 分属7类18个不同蛋白。其它蛋白中重复鉴定2次以上的83个, 分属30个不同蛋白。鉴定数量唯一的蛋白共计42个(附录1)。
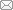
抗、感病品种间4个比对组(R-0h/S-0h、R-6h/S- 6h、R-24h/S-24h和R-48h/S-48h)共鉴定出71个DEPs, 其中39个为上调表达, 32个为下调表达; 感病品种内3个比对组(S-6h/S-0h和S-24h/S-0h、S-48h/S-0h)共鉴定出20个DEPs, 其中13个为上调表达, 7个为下调表达; 抗病品种内3个比对组(R-6h/R-0h、R-24h/ R-0h和R-48h/R-0h)共鉴定出80个DEPs, 其中上调表达39个, 下调表达41个(图2)。从表达特点来看, R-48h/S-48h及R-48h/R-0h两个比对组中, 下调DEPs数量均明显高于上调DEPs数量。而其余比对组均为上调数量多于下调数量或持平。总体来看, 感病品种3个比对组(S/S)仅有20个DEPs, 明显低于抗、感病品种间比对组(R/S)及抗病品种内比对组(R/R) (图2)。
图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2抗、感病苹果品种叶片应答轮纹病菌胁迫的差异表达蛋白(DEPs)分布
R: 抗病品种华月; S: 感病品种金冠
Figure 2Distribution of differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) of apple leaves susceptible and resistant to ring rot disease, respectively
R: Resistant cultivar Huayue; S: Susceptible cultivar Golden Delicious
2.3 差异表达蛋白(DEPs)的GO和KEGG代谢通路富集分析
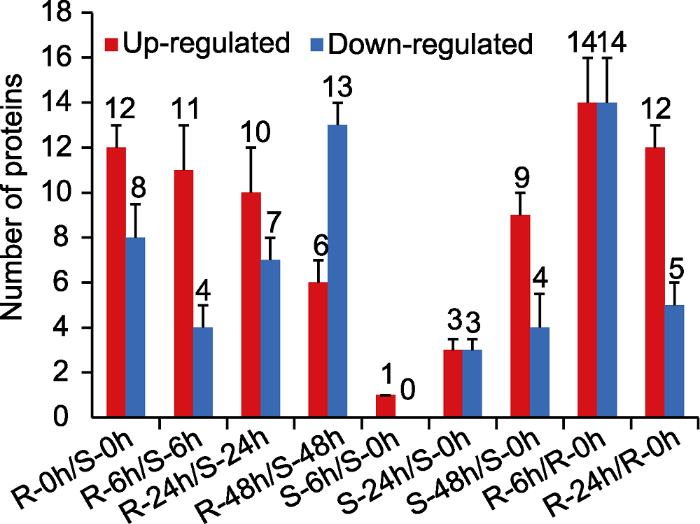
对鉴定到的DEPs进一步开展GO富集分析, 由于1个蛋白可以注释到多个GO条目(GO term)中, 171个DEPs共注释到686个GO条目, 其中细胞组分(cellular component)注释条目306个;分子功能(molecular function)注释条目166个;生物过程(biological process)注释条目214个(图3)。图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3抗、感病品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫的差异表达蛋白(DEPs)的Gene Ontology (GO)分析
Figure 3Enriched Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) in apple leaves resistant and susceptible to ring rot disease, respectively
将鉴定到的171个DEPs进行KEGG富集分析, 经P<0.05筛选后, 共有52个DEPs注释于18个显著差异代谢途径。其中9个DEPs注释于脂肪酸合成、延伸、代谢及不饱和脂肪酸合成相关途径, 13个DEPs注释于核糖体途径(表2)。
Table 2
表2
表2差异表达蛋白(DEPs)的KEGG Pathway富集分析
Table 2
| No. | Pathway | Pathway ID | DEPs with pathway annotation (326 in total) | All proteins with pathway annotation (14916 in total) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fatty acid biosynthesis | ko00061 | 2 (0.61%) | 19 (0.13%) | 0.011 |
| 2 | Fatty acid elongation | ko00062 | 3 (0.92%) | 9 (0.06%) | 0.040 |
| 3 | Arginine biosynthesis | ko00220 | 2 (0.61%) | 16 (0.11%) | 0.050 |
| 4 | Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | ko00250 | 2 (0.61%) | 23 (0.15%) | 0.037 |
| 5 | Cyanoamino acid metabolism | ko00460 | 2 (0.61%) | 20 (0.13%) | 0.022 |
| 6 | Other glycan degradation | ko00511 | 2 (0.61%) | 14 (0.09%) | 0.011 |
| 7 | Monoterpenoid biosynthesis | ko00902 | 5 (1.53%) | 12 (0.08%) | 0.035 |
| 8 | Sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis | ko00909 | 1 (0.31%) | 2 (0.01%) | 0.027 |
| 9 | Nitrogen metabolism | ko00910 | 4 (1.23%) | 28 (0.19%) | 0.014 |
| 10 | Sulfur metabolism | ko00920 | 1 (0.31%) | 12 (0.08%) | 0.036 |
| 11 | Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | ko00940 | 3 (0.92%) | 47 (0.32%) | 0.041 |
| 12 | Isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis | ko00950 | 2 (0.61%) | 16 (0.11%) | 0.028 |
| 13 | Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | ko01040 | 2 (0.61%) | 9 (0.06%) | 0.016 |
| 14 | Fatty acid metabolism | ko01212 | 2 (0.61%) | 32 (0.21%) | 0.030 |
| 15 | Ribosome | ko03010 | 13 (3.99%) | 200 (1.34%) | 0.005 |
| 16 | RNA transport | ko03013 | 2 (0.61%) | 33 (0.22%) | 0.031 |
| 17 | Homologous recombination | ko03440 | 1 (0.31%) | 5 (0.03%) | 0.039 |
| 18 | Circadian rhythm-plant | ko04712 | 3 (0.92%) | 9 (0.06%) | 0.026 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.4 差异表达蛋白(DEPs)的亚细胞定位
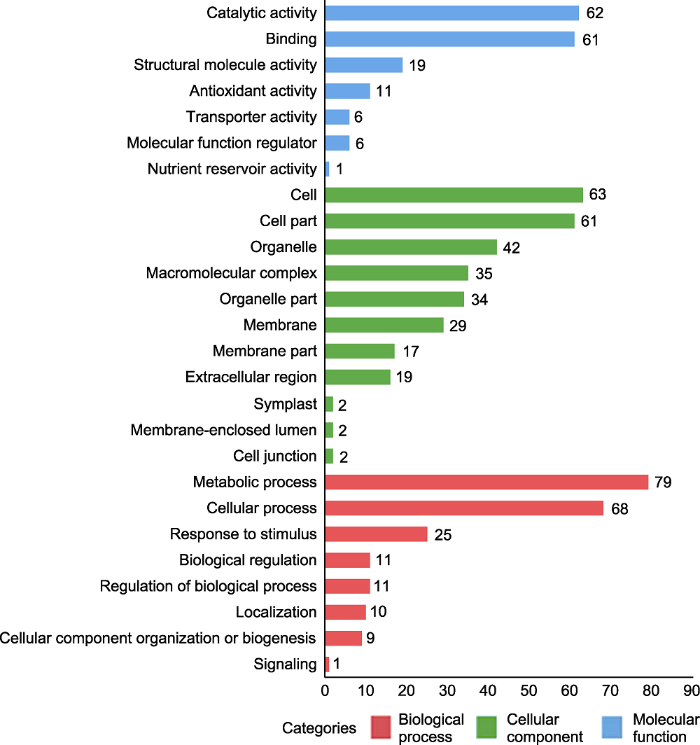
对171个DEPs进行亚细胞定位预测分析, 结果表明, 除S-6h/S-0h比对组鉴定的天冬氨酸蛋白酶结合蛋白(MDP0000301576)未得到预测结果, 其余9个比对组共170个DEPs预测定位于8个细胞器。其中, 57个(33.53%) DEPs定位于叶绿体(chlo), 54个(31.76%) DEPs定位于细胞质(cyto), 21个(12.35%) DEPs定位于胞外(extr), 15个(8.82%) DEPs定位于细胞核(nucl), 9个(5.29%) DEPs定位于线粒体(mito), 5个(2.94%) DEPs定位于细胞骨架(cysk), 5个(2.94%) DEPs定位于细胞质膜(plas), 4个(2.35%) DEPs定位于液泡膜(vacu) (图4)。图4
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4抗、感病苹果叶片应答轮纹病菌胁迫的差异表达蛋白(DEPs)的亚细胞定位
Chlo: 叶绿体; Cysk: 细胞骨架; Cyto: 胞液; Extr: 胞外; Mito: 线粒体; Nucl: 细胞核; Plas: 质膜; Vacu: 液泡膜
Figure 4Subcellular localization of differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) in apple leaves resistant and susceptible to ring rot disease, respectively
Chlo: Chloroplast; Cysk: Cytoskeleton; Cyto: Cytosol; Extr: Extracellular; Mito: Mitochondria; Nucl: Nucleus; Plas: Plasma membrane; Vacu: Vacuolar membrane
2.5 抗性相关蛋白差异表达分析
功能注释结果表明, 46个DEPs注释于7类抗性相关蛋白。其中, 14个DEPs鉴定为类甜蛋白(thaumatin-like protein), 8个DEPs鉴定为过氧化物酶(peroxidase), 7个DEPs鉴定为多酚氧化酶(polyphenol oxidase), 6个DEPs鉴定为过敏原蛋白(major allergen Mal d1), 6个DEPs鉴定为几丁质酶(chitinase), 4个DEPs鉴定为内切葡聚糖酶(endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase), 1个DEP鉴定为主乳胶蛋白(MLP-like protein 423)。其中, 鉴定为类甜蛋白、过氧化物酶、多酚氧化酶和几丁质酶的4类抗性相关的35个DEPs在不同比对组中表达趋势均不一致, 而鉴定为过敏原蛋白、主乳胶蛋白和内切葡聚糖酶的3类抗性相关的11个DEPs在不同比对组中差异表达趋势相同, 均呈现一致的上调/下调表达(图4; 附录1)。值得注意的是, 主乳胶蛋白仅在1个比对组(R-6h/S-6h)中呈现明显的上调表达。鉴定为内切葡聚糖酶的4个DEPs仅在3个比对组(R-0h/S-0h、R-48h/ S-48h和R-48h/R-0h)中呈现明显的下调表达。鉴定为多酚氧化酶的7个DEPs在4个比对组(R-0h/S-0h、R-6h/S-6h、S-48h/S-0h和R-6h/R-0h)中呈现明显的上调表达, 而在另3个比对组(R-48h/S-48h、R-6h/ R-0h和R-48h/R-0h)中呈现明显的下调表达。鉴定为几丁质酶的6个DEPs在品种间的4个比对组(R-0h/ S-0h、R-6h/S-6h、R-24h/S-24h和R-48h/S-48h)中均呈现明显的下调表达, 而在感病品种的1个比对组(S-48h/S-0h)中呈现明显的上调表达。
2.6 抗性相关蛋白编码基因的表达模式
为验证抗、感病品种4个时间点IBT定量蛋白质组比较分析结果的可信度, 我们对筛选后的5个抗性相关蛋白的编码基因进行qRT-PCR表达分析。结果(图5)发现, 抗、感病品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫过程中, 过敏原蛋白Mal d1及主乳胶蛋白MLP423编码基因的表达模式与IBT定量蛋白质组比较分析结果一致(图5B, E)。类甜蛋白和多酚氧化酶编码基因的表达模式与蛋白质组鉴定结果部分一致(图5A, D)。β-1,3-葡聚糖酶编码基因的表达模式与IBT定量蛋白质组比较分析结果相反(图5C)。图5
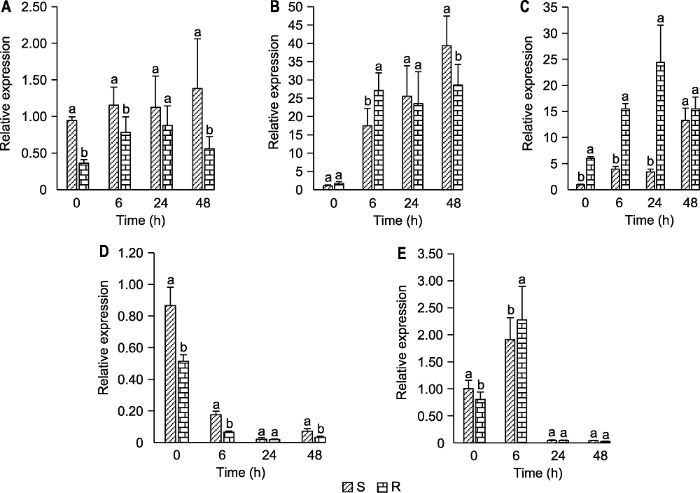 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5抗、感病苹果叶片轮纹病关键抗病相关蛋白编码基因的实时荧光定量PCR分析
(A) 类甜蛋白编码基因(MD04G1018400); (B) Mal d1编码基因(MD16G1160700); (C) β-1,3-葡聚糖酶编码基因(MD11G1189000); (D) 多酚氧化酶编码基因(MD10G1299100); (E) MLP423编码基因(MD16G1088600)。R: 抗病品种华月; S: 感病品种金冠; 不同小写字母表示抗病与感病品种间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 5Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of genes encoding key resistance-related proteins in apple leaves resistance and susceptible to ring rot disease
(A) A gene encoding a thaumatin (MD04G1018400); (B) The gene encoding Mal d1 (MD16G1160700); (C) A gene encoding a beta-1,3-glucosidase (MD11G1189000); (D) A gene encoding a polyphenol oxidase (MD10G1299100); (E) The gene encoding MLP423 (MD16G1088600). R: Resistant cultivars Huayue; S: Susceptible cultivars Golden Delicious; Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between resistant and susceptible cultivars (P<0.05).
2.7 讨论
苹果真菌病害的发生严重影响其树体发育、产量与品质, 制约苹果产业的可持续发展。研究真菌病害抗性调控的分子机理对于加速苹果抗病种质创新具有重要意义(Jurick II et al., 2011; Fan et al., 2011; Mazzeo et al., 2014)。本研究利用高通量的IBT标记定量蛋白质组分析技术, 筛选病原菌处理前后4个不同时间点, 抗(R)、感(S)病品种华月和金冠在不同比对组中差异表达的抗性相关蛋白, 进一步认识了关键抗性相关蛋白的表达特点。2.7.1 差异表达蛋白(DEPs)分离鉴定及表达特点分析
蛋白质分离鉴定技术是影响蛋白质组学研究的关键(Chen et al., 2012b)。已有的相关研究多基于2-DE结合质谱鉴定, 筛选的DEPs仅为有限的几十个(张彩霞等, 2015; 孙天骅等, 2018)。本研究利用升级后的IBT标记定量分析技术(Ramsubramaniam et al., 2013; Xing et al., 2017), 分别对病原菌处理前后4个时间点的抗、感病品种华月和金冠叶片进行总蛋白分析, 成功鉴定到5 319个蛋白, 显著多于以往研究鉴定的蛋白数量。
显著性分析表明, 抗、感病品种10个比对组中共鉴定到171个DEPs, 分属90个不同蛋白。抗、感病品种间4个比对组中共71个DEPs发生显著变化, 且上、下调蛋白数量差异不明显(分别为39和32个)。然而, 感病品种金冠应答病原菌胁迫的3个比对组中仅有20个DEPs发生显著差异表达, 且上调DEPs数量(13个)远多于下调DEPs数量(7个); 抗病品种华月应答病原菌胁迫的3个比对组中有80个DEPs发生显著差异表达, 且上、下调DEPs数量基本一致(39和41个) (图2)。由此表明, 从蛋白质表达水平看, 感病品种应答轮纹病菌侵染过程的DEPs数量明显少于抗病品种, 该表达特点可能与品种基因型有关。
本研究中, 抗病品种华月经轮纹病菌侵染24小时, 共17个DEPs发生显著变化, 其中上、下调DEPs分别为12和5个。结合我们前期基于iTRAQ技术开展的华月应答斑点落叶病菌胁迫相关研究结果, 即病原菌胁迫24小时后, 有53个DEPs呈现显著差异表达, 且下调DEPs (44个)远多于上调DEPs (9个) (张彩霞等, 2018)。通过比较发现, 同一品种应答不同病原菌侵染的DEPs表达特点相反, 推测该结果可能与寄主细胞针对不同病原菌胁迫所产生的不同应激反应相关。
以往关于抗、感病品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫的蛋白质组研究仅以0和24小时2个时间点、4组样品进行差异分析(孙天骅等, 2018), 受2-DE技术的局限性, 鉴定DEPs数量有限。本研究通过对抗、感病品种4个时间点的8组样品进行差异表达分析, 显示抗、感病品种在病原菌胁迫48小时后, 3个比对组(R-48h/S- 48h、S-48h/S-0h和R-48h/R-0h)的DEPs数量(67个)远多于胁迫24小时后3个比对组(R-24h/S-24h、S-24h/S-0h和R-24h/R-0h)的DEPs数量(40个) (图2)。进一步表明病原菌胁迫时间也是影响DEPs表达的重要因素。
针对171个差异表达蛋白开展的GO富集及KEGG pathway分析, 细胞组分、分子功能和生物过程共注释到686个GO条目。进一步筛选后发现52个DEPs注释于KEGG的18个显著差异途径, 表明同一蛋白可在多个生物学过程中发挥功能, 且多个蛋白可能参与同一通路。
叶绿体作为植物的重要细胞器, 是光合作用及其它重要生物学过程发挥作用的场所(Berger et al., 2004; Dinakar et al., 2012)。近年来研究表明, 植物与病原菌互作过程中, 多种病程相关蛋白的差异表达发生于叶绿体(Berger et al., 2007; Li et al., 2014; 肖龙等, 2016)。本研究中, 鉴定到的DEPs有1/3定位于叶绿体, 进一步表明轮纹病菌胁迫前后, 苹果叶片细胞中叶绿体蛋白广泛参与了胁迫应答。
2.7.2 关键抗性相关蛋白的差异表达是影响抗、感病苹果品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫的关键因素
本研究中, 10个比对组共46个DEPs (22.8%)注释于7类抗性相关蛋白。其中, 鉴定为类甜蛋白的有14个DEPs。在轮纹病菌胁迫前, 华月(R)叶片中类甜蛋白表达量显著高于金冠(S), 随着胁迫时间的延长, 华月(R)叶片中类甜蛋白的表达量不断降低, 而感病品种金冠(S)叶片中类甜蛋白的表达量显著上调。类甜蛋白是植物应答病原菌胁迫的重要病程相关蛋白(PR-5) (Kim et al., 2009), 已有研究证实类甜蛋白在苹果叶片应答褐斑病菌胁迫前后呈现显著上调表达(Li et al., 2014)。本研究中, 类甜蛋白在华月(R)和金冠(S) 2个品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫过程中呈现相反的表达模式, 推测该蛋白的差异表达与2个品种的不同抗性有关。
过氧化物酶(POD)是植物应答病原菌胁迫的重要防御酶系, 也是植物细胞内清除活性氧的关键酶(Christensen et al., 1998; Dietz et al., 2006; Kornas et al., 2010)。研究证实, 大豆(Glycine max)叶片经叶斑病菌侵染后, POD表达量显著上调(Borges et al., 2013), 在烟草(Nicotiana tabacum)中过表达POD编码基因, 可显著提高其抗病性(Dietz et al., 2006)。本研究中, 轮纹病菌胁迫前, POD表达量在华月(R)叶片中显著高于金冠(S), 推测POD是2个品种抗病性差异的关键蛋白之一。在应答轮纹病菌胁迫过程中, 抗病品种POD表达量不断下调, 而感病品种POD表达量不断上调, 进一步推测在抗、感病品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫过程中, 抗病品种通过不断分解POD, 调控叶片细胞内活性氧浓度, 以抵御病原菌侵染。
多酚氧化酶(polyphenol oxidases, PPOs)存在于多种植物中, 是重要的氧化还原酶类防御酶系, 可参与植物的多种防御反应。研究表明, 过表达PPO的转基因番茄(Lycopersicon esculentum)叶片, 其细菌抗病性显著增强(Li and Steffens, 2002; Thipyapong et al., 2004)。徐鹏飞等(2010)研究表明, 不同抗性大豆品种在应答病原菌侵染过程中PPO活性存在显著差异, 且抗病品种PPO活性高于感病品种。Golba等(2012)研究证实, 苹果的多酚类物质在苹果应答黑星病菌侵染过程中具有瞬时防御作用。虽然PPO是主要防御酶系, 但在抵御病原菌侵染过程中, PPO发挥作用需要同时满足存在酚类基质, 且PPO能够直接与酚类基质发生作用。由此表明, PPO防御作用的发挥与宿主及病原菌均有一定的相关性, 如果宿主本身酚类浓度过低, 则对病原菌无防御作用。本研究中, PPO在抗、感病品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫的多个比对组中呈现不同的上、下调表达模式, 而在转录水平分析中, PPO表达模式均为下调, 尤其是随着胁迫时间的延长PPO表达量不断降低, 推测该结果可能与抗、感病品种叶片细胞自身PPO活性差异以及侵染过程中病原菌酚类基质变化有关, 具体影响因素尚待进一步研究证实。
过敏原蛋白(major allergen Mal d1)是苹果属植物重要的抗性相关蛋白(Breiteneder and Ebner, 2000)。我们前期基于2-DE技术开展的苹果叶片应答轮纹病菌胁迫研究表明, Mal d1蛋白在病原菌胁迫前后呈明显的上调表达(Zhang et al., 2015); 进一步从转录水平证实, Mal d1基因在苹果叶片中的表达量明显高于花和果实, 且抗病苹果品种中Mal d1基因的表达量明显高于感病品种(宗泽冉等, 2017)。本研究中, Mal d1在R-0h/S-0h和R-6h/S-6h两个品种间的比对组中均显著上调表达, 且与Mal d1的qRT-PCR表达模式一致; 在感病、抗病品种内的3个比对组中也显著上调表达, 与我们前期开展的苹果应答斑点落叶病菌胁迫蛋白质组分析及转录水平分析结果一致, 表明Mal d1在苹果抗、感病品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫的防御反应过程中发挥重要作用。
几丁质酶是植物细胞抵御病原真菌侵染的重要抗病蛋白, 在寄主植物细胞受病原菌胁迫过程中可被强烈诱导(Grover, 2012)。研究发现, 几丁质酶仅在抗病品种响应病原菌侵染过程中显著上调表达, 推测几丁质酶是苹果应答斑点落叶病菌侵染的重要防御酶系(Ni et al., 2017)。本研究中, 几丁质酶在抗病品种中的表达量显著低于感病品种, 推测不同抗性品种应答不同病原真菌的侵染时, 几丁质酶会呈现不同的表达模式, 具体原因有待深入分析。
β-1,3-葡聚糖酶也是植物细胞内重要的抗性相关蛋白(Li et al., 2011), 在植物应答病原真菌侵染过程中, 可通过直接分解真菌细胞壁或通过释放消化壁诱导植物自身防御反应, 最终保护植物免受真菌侵染(Li et al., 2014)。已有研究证实, 葡聚糖酶在感病品种中表达量显著高于抗病品种(Ni et al., 2017)。本研究中, 轮纹病菌侵染48小时内, 感病品种中β-1,3-葡聚糖酶表达量高于抗病品种, 与以往研究结果一致。然而, 转录水平分析结果表明, β-1,3-葡聚糖酶在抗病品种中表达量高于感病品种。具体机制有待进一步阐明。
主乳胶蛋白(MLP-like protein 423)是一种低分子量的抗性相关蛋白, 在植物抗病或逆境应答中起关键作用(Sun et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2016)。我们前期研究表明, 华月苹果叶片应答轮纹病菌胁迫前后, MLP蛋白呈现明显的下调表达。本研究中, MLP在华月苹果叶片应答轮纹病菌胁迫前后表达无显著差异, 然而在R-6h/S-6h比对组中呈现显著上调表达, 推测MLP蛋白也是华月、金冠2个品种抗病性差异相关的关键功能蛋白。
3 结论
在抗、感病苹果品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫过程中, 共筛选到7类抗性相关蛋白的表达模式存在显著差异。其中类甜蛋白、过氧化物酶和几丁质酶3类DEPs可能是不同品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫抗性差异的关键因子。多酚氧化酶、主乳胶蛋白、内切葡聚糖酶和过敏原蛋白4类蛋白可能通过表达量的调节应答轮纹病菌胁迫反应。研究结果为进一步解析抗、感病苹果品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫的抗性机制提供参考。附录1
抗、感苹果品种叶片应答轮纹病菌胁迫的差异表达蛋白Appendix 1
Differentially expressed proteins detected in apple leaves resistant and susceptible to ring rot diseasehttp://www.chinbullbotany.com/fileup/1674-3466/PDF/t19-204.pdf
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
URL [本文引用: 1]

为探索高效、稳定且操作简便的苹果轮纹病室内评价方法,选用分离菌株Slq0803-1-1-1菌饼分别对离体富士苹果两年生枝条以及当年生嫩梢、叶片和成熟果实4种材料进行接种,并对试验结果和接种方法进行比较分析。结果显示,在有伤和无伤条件下各接种材料接种无菌PDA块均不发病,接种病菌仅在有伤情况下致病;枝条烫伤接种发病最慢且病斑最小,嫩梢针刺1针接种较叶痕接种发病明显; 1针及10针刺伤接种叶片正、反面,正面1针刺伤接种发病较快且一致;果实去除果皮接种较1针、10针刺伤后接种发病显著。用4个致病力不同的菌株验证,发现4种离体材料均能验证不同菌株间的致病力差异,且结果与田间无伤接种当年生新梢一致。说明4种离体材料均可准确、快速评价苹果轮纹病,其中正面针刺1针接种叶片的方法最优。
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 3]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1093/jxb/erm298URLPMID:18182420 [本文引用: 1]

Phytopathogen infection leads to changes in secondary metabolism based on the induction of defence programmes as well as to changes in primary metabolism which affect growth and development of the plant. Therefore, pathogen attack causes crop yield losses even in interactions which do not end up with disease or death of the plant. While the regulation of defence responses has been intensively studied for decades, less is known about the effects of pathogen infection on primary metabolism. Recently, interest in this research area has been growing, and aspects of photosynthesis, assimilate partitioning, and source-sink regulation in different types of plant-pathogen interactions have been investigated. Similarly, phytopathological studies take into consideration the physiological status of the infected tissues to elucidate the fine-tuned infection mechanisms. The aim of this review is to give a summary of recent advances in the mutual interrelation between primary metabolism and pathogen infection, as well as to indicate current developments in non-invasive techniques and important strategies of combining modern molecular and physiological techniques with phytopathology for future investigations.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1067/mai.2000.106929URLPMID:10887301 [本文引用: 1]

Molecular biology and biochemical techniques have significantly advanced the knowledge of allergens derived from plant foods. Surprisingly, many of the known plant food allergens are homologous to pathogenesis-related proteins (PRs), proteins that are induced by pathogens, wounding, or certain environmental stresses. PRs have been classified into 14 families. Examples of allergens homologous to PRs include chitinases (PR-3 family) from avocado, banana, and chestnut; antifungal proteins such as the thaumatin-like proteins (PR-5) from cherry and apple; proteins homologous to the major birch pollen allergen Bet v 1 (PR-10) from vegetables and fruits; and lipid transfer proteins (PR-14) from fruits and cereals. Allergens other than PR homologs can be allotted to other well-known protein families such as inhibitors of alpha-amylases and trypsin from cereal seeds, profilins from fruits and vegetables, seed storage proteins from nuts and mustard seeds, and proteases from fruits. As more clinical data and structural information on allergenic molecules becomes available, we may finally be able to answer what characteristics of a molecule are responsible for its allergenicity.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1021/ac203467qURLPMID:22404494 [本文引用: 2]

Isobaric tags have broad applications in both basic and translational research, as demonstrated by the widely used isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ). Recent results from large-scale quantitative proteomics projects, however, indicate that protein quantification by iTRAQ is often biased in complex biological samples. Here, we report the application of another isobaric tag, deuterium isobaric amine reactive tag (DiART), for quantifying the proteome of Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis (T. tengcongensis), a thermophilic bacterium first discovered in China. We compared the performance of DiART with iTRAQ from several different aspects, including their fragmentation mechanisms, the number of identified proteins, and the accuracy of quantification. Our results revealed that, as compared with iTRAQ, DiART yielded significantly stronger reporter ions, which did not reduce the number of identifiable peptides, but improved the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) for quantification. Remarkably, we found that, under identical chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) conditions, DiART exhibited less reporter ions ratio compression than iTRAQ, probably due to more reporter ions with higher intensities produced by DiART labeling. Taken together, we demonstrate that DiART is a valuable alternative of iTRAQ with enhanced performance for quantitative proteomics.
DOI:10.1104/pp.118.1.125URLPMID:9733532 [本文引用: 1]

Lignin is an integral cell wall component of all vascular plants. Peroxidases are widely believed to catalyze the last enzymatic step in the biosynthesis of lignin, the dehydrogenation of the p-coumaryl alcohols. As the first stage in identifying lignin-specific peroxidase isoenzymes, the classical anionic peroxidases found in the xylem of poplar (Populus trichocarpa Trichobel) were purified and characterized. Five different poplar xylem peroxidases (PXP 1, PXP 2, PXP 3-4, PXP 5, and PXP 6) were isolated. All five peroxidases were strongly glycosylated (3.6% to 4.9% N-glucosamine), with apparent molecular masses between 46 and 54 kD and pI values between pH 3.1 and 3.8. Two of the five isolated peroxidases (PXP 3-4 and PXP 5) could oxidize the lignin monomer analog syringaldazine, an activity previously correlated with lignification in poplar. Because these isoenzymes were specifically or preferentially expressed in xylem, PXP 3-4 and PXP 5 are suggested to be involved in lignin polymerization.
DOI:10.1093/jxb/erj160URLPMID:16606633 [本文引用: 2]

In 1996, cDNA sequences referred to as plant peroxiredoxins (Prx), i.e. a 1-Cys Prx and a 2-Cys Prx, were reported from barley. Ten years of research have advanced our understanding of plant Prx as thiol-based peroxide reductases with a broad substrate specificity, ranging from hydrogen peroxide to alkyl hydroperoxides and peroxinitrite. Prx have several features in common. (i) They are abundant proteins that are routinely detected in proteomics approaches. (ii) They interact with proteins such as glutaredoxins, thioredoxins, and cyclophilins as reductants, but also non-dithiol-disulphide exchange proteins. By work with transgenic plants, their activity was shown to (iii) affect metabolic integrity, (iv) protect DNA from damage in vitro and as shown here in vivo, and (v) modulate intracellular signalling related to reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species. (vi) In all organisms Prx are encoded by small gene families that are of particular complexity in higher plants. A comparison of the Prx gene families in rice and Arabidopsis thaliana supports previous suggestions on Prx function in specific subcellular and metabolic context. (vii) Prx gene expression and activity are subjected to complex regulation realized by an integration of various signalling pathways. 2-Cys Prx expression depends on redox signals, abscisic acid, and protein kinase cascades. Besides these general properties, the chloroplast Prx have acquired specific roles in the context of photosynthesis. The thioredoxin-dependent peroxidase activity can be measured in crude plant extracts and contributes significantly to the overall H(2)O(2) detoxification capacity. Thus organellar Prx proteins enable an alternative water-water cycle for detoxification of photochemically produced H(2)O(2), which acts independently from the ascorbate-dependent Asada-Halliwell-Foyer cycle. 2-Cys Prx and Prx Q associate with thylakoid membrane components. The mitochondrial PrxII F is essential for root growth under stress. Following a more general introduction, the paper summarizes present knowledge on plant organellar Prx, addressing Prx in signalling, and also suggests some lines for future research.
URLPMID:22118613 [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1021/ac503934fURLPMID:25521595 [本文引用: 1]

As a driver for many biological processes, phosphorylation remains an area of intense research interest. Advances in multiplexed quantitation utilizing isobaric tags (e.g., TMT and iTRAQ) have the potential to create a new paradigm in quantitative proteomics. New instrumentation and software are propelling these multiplexed workflows forward, which results in more accurate, sensitive, and reproducible quantitation across tens of thousands of phosphopeptides. This study assesses the performance of multiplexed quantitative phosphoproteomics on the Orbitrap Fusion mass spectrometer. Utilizing a two-phosphoproteome model of precursor ion interference, we assessed the accuracy of phosphopeptide quantitation across a variety of experimental approaches. These methods included the use of synchronous precursor selection (SPS) to enhance TMT reporter ion intensity and accuracy. We found that (i) ratio distortion remained a problem for phosphopeptide analysis in multiplexed quantitative workflows, (ii) ratio distortion can be overcome by the use of an SPS-MS3 scan, (iii) interfering ions generally possessed a different charge state than the target precursor, and (iv) selecting only the phosphate neutral loss peak (single notch) for the MS3 scan still provided accurate ratio measurements. Remarkably, these data suggest that the underlying cause of interference may not be due to coeluting and cofragmented peptides but instead from consistent, low level background fragmentation. Finally, as a proof-of-concept 10-plex experiment, we compared phosphopeptide levels from five murine brains to five livers. In total, the SPS-MS3 method quantified 38247 phosphopeptides, corresponding to 11000 phosphorylation sites. With 10 measurements recorded for each phosphopeptide, this equates to more than 628000 binary comparisons collected in less than 48 h.
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:20559571 [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s00425-002-0750-4URLPMID:12029473 [本文引用: 1]

Polyphenol oxidases (PPOs; EC 1.10.3.2 or EC 1.14.18.1) catalyzing the oxygen-dependent oxidation of phenols to quinones are ubiquitous among angiosperms and assumed to be involved in plant defense against pests and pathogens. In order to investigate the role of PPO in plant disease resistance, we made transgenic tomato ( Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. cv. Money Maker) plants that overexpressed a potato ( Solanum tuberosum L.) PPO cDNA under control of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. The transgenic plants expressed up to 30-fold increases in PPO transcripts and 5- to 10-fold increases in PPO activity and immunodetectable PPO. As expected, these PPO-overexpressing transgenic plants oxidized the endogenous phenolic substrate pool at a higher rate than control plants. Three independent transgenic lines were selected to assess their interaction with the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. The PPO-overexpressing tomato plants exhibited a great increase in resistance to P. syringae. Compared with control plants, these transgenic lines showed less severity of disease symptoms, with over 15-fold fewer lesions, and strong inhibition of bacterial growth, with over 100-fold reduction of bacterial population in the infected leaves. These results demonstrate the importance of PPO-mediated phenolic oxidation in restricting plant disease development.
DOI:10.1186/1477-5956-12-7URLPMID:24507458 [本文引用: 3]

BACKGROUND: Apple, an invaluable fruit crop worldwide, is often prone to infection by pathogenic fungi. Identification of potentially resistance-conferring apple proteins is one of the most important aims for studying apple resistance mechanisms and promoting the development of disease-resistant apple strains. In order to find proteins which promote resistance to Marssonina coronaria, a deadly pathogen which has been related to premature apple maturation, proteomes from apple leaves inoculated with M. coronaria were characterized at 3 and 6 days post-inoculation by two dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE). RESULTS: Overall, 59 differentially accumulated protein spots between inoculation and non-inoculation were successfully identified and aligned as 35 different proteins or protein families which involved in photosynthesis, amino acid metabolism, transport, energy metabolism, carbohydrate metabolism, binding, antioxidant, defense and stress. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was also used to examine the change of some defense and stress related genes abundance under inoculated conditions. CONCLUSIONS: In a conclusion, different proteins in response to Marssonina coronaria were identified by proteomic analysis. Among of these proteins, there are some PR proteins, for example class III endo-chitinase, beta-1,3-glucanase and thaumatine-like protein, and some antioxidant related proteins including aldo/keto reductase AKR, ascorbate peroxidase and phi class glutathione S-transferase protein that were associated with disease resistance. The transcription levels of class III endo-chitinase (L13) and beta-1, 3-glucanase (L17) have a good relation with the abundance of the encoded protein's accumulation, however, the mRNA abundance of thaumatine-like protein (L22) and ascorbate peroxidase (L28) are not correlated with their protein abundance of encoded protein. To elucidate the resistant mechanism, the data in the present study will promote us to investigate further the expression regulation of these target proteins.
DOI:10.1007/s00299-010-0934-5URL [本文引用: 1]

A functional contribution of pathogenesis-related 1 (PR-1) proteins to host defense has been established. However, systematic investigation of the PR-1 gene family in grapevine (Vitis spp.) has not been conducted previously. Through mining genomic databases, we identified 21 PR-1 genes from the Vitis vinifera genome. Polypeptides encoded by putative PR-1 genes had a signal sequence of about 25 residues and a mature protein of 10.9-29 kDa in size. PR-1 mature proteins contained a highly conserved six-cysteine motif and pI values ranging from 4.6 to 9. A major cluster with 14 PR-1 genes was mapped to a 280-kb region on chromosome 3. One particular PR-1 gene within the cluster encoding a basic-type isoform (pI 7.77), herein named VvPR1b1, was isolated from various genotypes of grapevine (Vitis spp.) for functional studies. Sequence analysis of PCR-amplified DNA revealed that all genotypes contained a single VvPR1b1 gene except for a broad-spectrum bacterial and fungal disease resistant Florida bunch grape hybrid, 'BN5-4', from which seven different homologues were identified. Duplication of VvPR1b1-related genes encoding acidic-type PR-1 isoforms was also observed among several genotypes. However, transgenic expression analysis of grapevine PR-1 genes under strong constitutive promoters in transgenic tobacco revealed that only the basic-type VvPR1b1 gene duplicated in 'BN5-4' was capable of conferring high level resistance to bacterial disease caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci.
DOI:10.1006/meth.2001.1262URLPMID:11846609 [本文引用: 1]

The two most commonly used methods to analyze data from real-time, quantitative PCR experiments are absolute quantification and relative quantification. Absolute quantification determines the input copy number, usually by relating the PCR signal to a standard curve. Relative quantification relates the PCR signal of the target transcript in a treatment group to that of another sample such as an untreated control. The 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method is a convenient way to analyze the relative changes in gene expression from real-time quantitative PCR experiments. The purpose of this report is to present the derivation, assumptions, and applications of the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. In addition, we present the derivation and applications of two variations of the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method that may be useful in the analysis of real-time, quantitative PCR data.
DOI:10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.10.031URLPMID:24262994 [本文引用: 1]

Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. radicis-lycopersici (FORL) leading to fusarium crown and root rot is considered one of the most destructive tomato soilborne diseases occurring in greenhouse and field crops. In this study, response to FORL infection in tomato roots was investigated by differential proteomics in susceptible (Monalbo) and resistant (Momor) isogenic tomato lines, thus leading to identify 33 proteins whose amount changed depending on the pathogen infection, and/or on the two genotypes. FORL infection induced accumulation of pathogen-related proteins (PR proteins) displaying glucanase and endochitinases activity or involved in redox processes in the Monalbo genotype. Interestingly, the level of the above mentioned PR proteins was not influenced by FORL infection in the resistant tomato line, while other proteins involved in general response mechanisms to biotic and/or abiotic stresses showed significant quantitative differences. In particular, the increased level of proteins participating to arginine metabolism and glutathione S-transferase (GST; EC 2.5.1.18) as well as that of protein LOC544002 and phosphoprotein ECPP44-like, suggested their key role in pathogen defence.
DOI:10.1007/s11295-017-1104-5URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1007/BF02463946URL [本文引用: 2]

We examined the phytopathological and biological characters ofBotryosphaeria spp. isolated from apples and other deciduous fruit trees, and determined the nucleotide sequences of their rDNA ITS regions. TheBotryosphaeria isolates from deciduous fruit trees can be divided into three groups based on their production of warts on twigs, size of the conidia, and nucleotide sequences of rDNA ITS 1, ITS 2 and 5.8S rDNA. Isolates ofBotryosphaeria in ITS group A produced conidia of intermediate size and showed warts on infected twigs prior to the development of ring rot on fruit. This group was common on deciduous fruit trees in Japan as a causal agent of ring rot and wart bark diseases of apples and pears; and it appears similar to theB. dothidea from the US that was isolated from apple exhibiting white rot. The ITS group BBotryosphaeria produced small conidia and induced shoot blight without wart development prior to the development of ring rot on fruit. This group was localized on pear, persimmon, and kiwi fruit in restricted areas of Japan. The ITS group CBotryosphaeria consisted ofB. obtusa, the causal agent of apple black rot in the US, which produced large dark brown conidia.
DOI:10.1002/pmic.201400154URLPMID:25195567 [本文引用: 1]

Multiplexed isobaric tag based quantitative proteomics and phosphoproteomics strategies can comprehensively analyze drug treatments effects on biological systems. Given the role of mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK) signaling in cancer and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-dependent diseases, we sought to determine if this pathway could be inhibited safely by examining the downstream molecular consequences. We used a series of tandem mass tag 10-plex experiments to analyze the effect of two MEK inhibitors (GSK1120212 and PD0325901) on three tissues (kidney, liver, and pancreas) from nine mice. We quantified approximately 6000 proteins in each tissue, but significant protein-level alterations were minimal with inhibitor treatment. Of particular interest was kidney tissue, as edema is an adverse effect of these inhibitors. From kidney tissue, we enriched phosphopeptides using titanium dioxide (TiO2 ) and quantified 10 562 phosphorylation events. Further analysis by phosphotyrosine peptide immunoprecipitation quantified an additional 592 phosphorylation events. Phosphorylation motif analysis revealed that the inhibitors decreased phosphorylation levels of proline-x-serine-proline (PxSP) and serine-proline (SP) sites, consistent with extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) inhibition. The MEK inhibitors had the greatest decrease on the phosphorylation of two proteins, Barttin and Slc12a3, which have roles in ion transport and fluid balance. Further studies will provide insight into the effect of these MEK inhibitors with respect to edema and other adverse events in mouse models and human patients.
DOI:10.1039/c3mb70358dURL [本文引用: 2]

We describe the use of an isobaric tagging reagent, Deuterium isobaric Amine Reactive Tag (DiART), for quantitative phosphoproteomic experiments. Using DiART tagged custom mixtures of two phosphorylated peptides from alpha casein and their non-phosphorylated counterparts, we demonstrate the compatibility of DiART with TiO2 affinity purification of phosphorylated peptides. Comparison of theoretical vs. experimental reporter ion ratios reveals accurate quantification of phosphorylated peptides over a dynamic range of more than 15-fold. Using DiART labelling and TiO2 enrichment (DiART-TiO2) with large quantities of proteins (8 mg) from the cell lysate of model fungus Aspergillus nidulans, we quantified 744 unique phosphopeptides. Overlap of median values of TiO2 enriched phosphopeptides with theoretical values indicates accurate trends. Altogether these findings confirm the feasibility of performing quantitative phosphoproteomic experiments in a cost-effective manner using isobaric tagging reagents, DiART.
DOI:10.1074/mcp.M114.046995URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s11033-009-9707-zURLPMID:19680785 [本文引用: 1]

This is the first reports on isolation and expression analysis of a major latex-like protein (MLP151) gene in Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. A full-length cDNA of MLP151 was 850 bp and contained a 456 bp open reading frame encoding a polypeptide of 151 amino acids. A theoretical pI value of MLP151 was 4.86 and calculated molecular weight was about 16.87 kDa. The MLP homolog proteins are found in various plants and the neighbor-joining analysis revealed that MLP151 has the closest distance with Sn-1 (bell pepper, MLP homolog gene). We analyzed the expression of MLP151 in different levels in various organs of ginseng and plantlet. In the result, the gene was low expressed in plantlet. We treated the ginseng plantlets with nine kinds of different stresses and analyzed the expression profile of MLP151. Transcript levels were significantly induced by stress treatment of light and mannitol, whereas transcript levels were drastically decreased in dark, H(2)O(2), salicylic acid and wounding samples.
DOI:10.1007/s00425-004-1330-6URL [本文引用: 1]

Polyphenol oxidases (PPOs; EC 1.14.18.1 or EC 1.10.3.2) catalyze the oxidation of phenolics to quinones, highly reactive intermediates whose secondary reactions are responsible for much of the oxidative browning that accompanies plant senescence, wounding, and responses to pathogens. To assess the impact of PPO expression on resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato we introduced a chimeric antisense potato PPO cDNA into tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.). Oxidation of caffeic acid, the dominant o-diphenolic aglycone of tomato foliage, was decreased ca. 40-fold by antisense expression of PPO. All members of the PPO gene family were downregulated: neither immunoreactive PPO nor PPO-specific mRNA were detectable in the transgenic plants. In addition, the antisense PPO construct suppressed inducible increases in PPO activity. Downregulation of PPO in antisense plants did not affect growth, development, or reproduction of greenhouse-grown plants. However, antisense PPO expression dramatically increased susceptibility to P. syringae expressing the avirulence gene avrPto in both Pto and pto backgrounds. In a compatible (pto) interaction, plants constitutively expressing an antisense PPO construct exhibited a 55-fold increase in bacterial growth, three times larger lesion area, and ten times more lesions cm–2 than nontransformed plants. In an incompatible (Pto) interaction, antisense PPO plants exhibited 100-fold increases in bacterial growth and ten times more lesions cm–2 than nontransformed plants. Although it is not clear whether hypersusceptibility of antisense plants is due to low constitutive PPO levels or failure to induce PPO upon infection, these findings suggest a critical role for PPO-catalyzed phenolic oxidation in limiting disease development. As a preliminary effort to understand the role of induced PPO in limiting disease development, we also examined the response of PPO promoter::
 -glucuronidase constructs when plants are challenged with P. syringae in both Pto and pto backgrounds. While PPO B inducibility was the same in both compatible and incompatible interactions, PPO D, E and F were induced to higher levels and with different expression patterns in incompatible interactions.
-glucuronidase constructs when plants are challenged with P. syringae in both Pto and pto backgrounds. While PPO B inducibility was the same in both compatible and incompatible interactions, PPO D, E and F were induced to higher levels and with different expression patterns in incompatible interactions.DOI:10.1093/jxb/erv477URLPMID:26512059 [本文引用: 1]

Drought stress is one of the disadvantageous environmental conditions for plant growth and reproduction. Given the importance of abscisic acid (ABA) to plant growth and abiotic stress responses, identification of novel components involved in ABA signalling transduction is critical. In this study, we screened numerous Arabidopsis thaliana mutants by seed germination assay and identified a mutant mlp43 (major latex protein-like 43) with decreased ABA sensitivity in seed germination. The mlp43 mutant was sensitive to drought stress while the MLP43-overexpressed transgenic plants were drought tolerant. The tissue-specific expression pattern analysis showed that MLP43 was predominantly expressed in cotyledons, primary roots and apical meristems, and a subcellular localization study indicated that MLP43 was localized in the nucleus and cytoplasm. Physiological and biochemical analyses indicated that MLP43 functioned as a positive regulator in ABA- and drought-stress responses in Arabidopsis through regulating water loss efficiency, electrolyte leakage, ROS levels, and as well as ABA-responsive gene expression. Moreover, metabolite profiling analysis indicated that MLP43 could modulate the production of primary metabolites under drought stress conditions. Reconstitution of ABA signalling components in Arabidopsis protoplasts indicated that MLP43 was involved in ABA signalling transduction and acted upstream of SnRK2s by directly interacting with SnRK2.6 and ABF1 in a yeast two-hybrid assay. Moreover, ABA and drought stress down-regulated MLP43 expression as a negative feedback loop regulation to the performance of MLP43 in ABA and drought stress responses. Therefore, this study provided new insights for interpretation of physiological and molecular mechanisms of Arabidopsis MLP43 mediating ABA signalling transduction and drought stress responses.
URLPMID:25069810 [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.cbd.2017.05.004URLPMID:28601631 [本文引用: 2]

Sea cucumbers are an important economic species and exhibit high yield value among aquaculture animals. Purple sea cucumbers are very rare and beautiful and have stable hereditary patterns. In this study, isobaric tags (IBT) were first used to reveal the molecular mechanism of pigmentation in the body wall of the purple sea cucumber. We analyzed the proteomes of purple sea cucumber in early pigmentation stage (Pa), mid pigmentation stage (Pb) and late pigmentation stage (Pc), resulting in the identification of 5580 proteins, including 1099 differentially expressed proteins in Pb: Pa and 339 differentially expressed proteins in Pc: Pb. GO and KEGG analyses revealed possible differentially expressed proteins, including
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0122233URLPMID:26086845 [本文引用: 4]

Understanding the defence mechanisms used by apple leaves against Alternaria alternate pathogen infection is important for breeding purposes. To investigate the ultrastructural differences between leaf tissues of susceptible and resistant seedlings, in vitro inoculation assays and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis were conducted with two different inoculation assays. The results indicated that the resistant leaves may have certain antifungal activity against A. alternate that is lacking in susceptible leaves. To elucidate the two different host responses to A. alternate infection in apples, the proteomes of susceptible and resistant apple leaves that had or had not been infected with pathogen were characterised using two-dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-TOF MS). MS identified 43 differentially expressed proteins in two different inoculation assays. The known proteins were categorised into 5 classes, among these proteins, some pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins, such as beta-1,3-glucanase, ascorbate peroxidase (APX), glutathione peroxidase (GPX) and mal d1, were identified in susceptible and resistant hosts and were associated with disease resistance of the apple host. In addition, the different levels of mal d1 in susceptible and resistant hosts may contribute to the outstanding anti-disease properties of resistant leaves against A. alternate. Taken together, the resistance mechanisms of the apple host against A. alternate may be a result of the PR proteins and other defence-related proteins. Given the complexity of the biology involved in the interaction between apple leaves and the A. alternate pathogen, further investigation will yield more valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms of suppression of the A. alternate pathogen. Overall, we outline several novel insights into the response of apple leaves to pathogen attacks. These findings increase our knowledge of pathogen resistance mechanisms, and the data will also promote further investigation into the regulation of the expression of these target proteins.
苹果轮纹病室内快速评价体系的建立
1
2011
... 供试苹果轮纹病致病菌(Botryosphaeria berengeriana f. sp piricola)菌株LW-xc102由中国农业科学院果树研究所植物保护中心提供.将LW-xc102接种于马铃薯蔗糖琼脂(potato sugar agar, PSA)培养基上, 28°C培养7天, 至菌丝长满培养皿后备用.选取生长均一的LW-xc102菌丝培养物, 以直径5 mm的打孔器打下菌饼, 采用叶片正面针刺法(
抗病与感病苹果叶片应答轮纹病菌侵染的蛋白质表达差异分析
2
2018
... 蛋白质分离鉴定技术是影响蛋白质组学研究的关键(
... 以往关于抗、感病品种应答轮纹病菌胁迫的蛋白质组研究仅以0和24小时2个时间点、4组样品进行差异分析(
苹果叶片应答轮纹病菌胁迫的叶绿体蛋白质组学分析
3
2016
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
... ).苹果叶片经轮纹病菌侵染后, 叶片叶绿体细胞内多个代谢过程可参与轮纹病菌的胁迫应答反应(
... 叶绿体作为植物的重要细胞器, 是光合作用及其它重要生物学过程发挥作用的场所(
疫霉根腐病菌毒素对大豆不同组织中多酚氧化酶的影响
1
2010
... 多酚氧化酶(polyphenol oxidases, PPOs)存在于多种植物中, 是重要的氧化还原酶类防御酶系, 可参与植物的多种防御反应.研究表明, 过表达PPO的转基因番茄(Lycopersicon esculentum)叶片, 其细菌抗病性显著增强(
不同抗性苹果果实受轮纹病菌侵染后亚显微结构的变化
1
2012
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
黄色苹果新品种‘华月’
2
2010
... 实验所用抗病苹果(Malus domestica Borkh.)品种华月(
... 为比较抗、感病苹果品种应答轮纹病胁迫的发病特征, 本研究采用叶面针刺结合菌饼接种, 对华月和金冠苹果叶片发病过程进行观察.结果(
苹果枝条表皮应答轮纹病菌侵染的蛋白质组学分析
1
2015
... 蛋白质分离鉴定技术是影响蛋白质组学研究的关键(
基于iTRAQ定量蛋白质组技术筛选‘华月’苹果斑点落叶病抗性相关蛋白
3
2018
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
... ).此外, 利用iTRAQ (isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantization)定量鉴定技术, 我们还解析了抗病苹果品种华月应答链格孢菌侵染的抗性相关蛋白的表达特点(
... 本研究中, 抗病品种华月经轮纹病菌侵染24小时, 共17个DEPs发生显著变化, 其中上、下调DEPs分别为12和5个.结合我们前期基于iTRAQ技术开展的华月应答斑点落叶病菌胁迫相关研究结果, 即病原菌胁迫24小时后, 有53个DEPs呈现显著差异表达, 且下调DEPs (44个)远多于上调DEPs (9个) (
北海棠病程相关蛋白MhPR8基因的克隆与表达
1
2012
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
苹果种质资源果实轮纹病抗性的评价
3
2010
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
... 实验所用抗病苹果(Malus domestica Borkh.)品种华月(
... 为比较抗、感病苹果品种应答轮纹病胁迫的发病特征, 本研究采用叶面针刺结合菌饼接种, 对华月和金冠苹果叶片发病过程进行观察.结果(
枝干苹果轮纹病人工接种方法与品种抗性评价
2
2010
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
... ;
抗苹果斑点落叶病基因Mal d1的克隆及功能鉴定
1
2017
... 过敏原蛋白(major allergen Mal d1)是苹果属植物重要的抗性相关蛋白(
Complex regulation of gene expression, photosynthesis and sugar levels by pathogen infection in tomato
1
2004
... 叶绿体作为植物的重要细胞器, 是光合作用及其它重要生物学过程发挥作用的场所(
Plant physiology meets phytopathology: plant primary metabolism and plant pathogen interactions
1
2007
... 叶绿体作为植物的重要细胞器, 是光合作用及其它重要生物学过程发挥作用的场所(
Differentially expressed proteins during an incompatible interaction between common bean and the fungus Pseudocercospora griseola
1
2013
... 过氧化物酶(POD)是植物应答病原菌胁迫的重要防御酶系, 也是植物细胞内清除活性氧的关键酶(
Molecular and biochemical classification of plant-derived food allergens
1
2000
... 过敏原蛋白(major allergen Mal d1)是苹果属植物重要的抗性相关蛋白(
Dynamics of growth regulators during infection of apple leaves by Alternaria alternata apple pathotype
1
2012
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
Comparative evaluation of two isobaric labeling tags, DiART and iTRAQ
2
2012
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
... 蛋白质分离鉴定技术是影响蛋白质组学研究的关键(
Purification and characterization of peroxidases correlated with lignification in poplar xylem
1
1998
... 过氧化物酶(POD)是植物应答病原菌胁迫的重要防御酶系, 也是植物细胞内清除活性氧的关键酶(
The function of peroxiredoxins in plant organelle redox metabolism
2
2006
... 过氧化物酶(POD)是植物应答病原菌胁迫的重要防御酶系, 也是植物细胞内清除活性氧的关键酶(
... )中过表达POD编码基因, 可显著提高其抗病性(
Photosynthesis in desiccation tolerant plants: energy metabolism and antioxidative stress defense
1
2012
... 叶绿体作为植物的重要细胞器, 是光合作用及其它重要生物学过程发挥作用的场所(
Apple(Malus domestica L. Borkh) as an emerging model for fruit development
1
2014
... 苹果(Malus domestica)作为多年生木本果树研究的模式植物, 其安全生产对世界水果产业可持续发展具有重要意义(
Evaluating multiplexed quantitative phosphopeptide analysis on a hybrid quadrupole mass filter/linear ion trap/orbitrap mass spectrometer
1
2015
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
Pathogen-induced MdWRKY1 in ‘Qinguan’ apple enhances disease resistance
2
2011
... 苹果(Malus domestica)作为多年生木本果树研究的模式植物, 其安全生产对世界水果产业可持续发展具有重要意义(
... 苹果真菌病害的发生严重影响其树体发育、产量与品质, 制约苹果产业的可持续发展.研究真菌病害抗性调控的分子机理对于加速苹果抗病种质创新具有重要意义(
Effects of apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.) phenolic compounds on proteins and cell wall-degrading enzymes of Venturia inaequalis
1
2012
... 多酚氧化酶(polyphenol oxidases, PPOs)存在于多种植物中, 是重要的氧化还原酶类防御酶系, 可参与植物的多种防御反应.研究表明, 过表达PPO的转基因番茄(Lycopersicon esculentum)叶片, 其细菌抗病性显著增强(
Plant chitinases: genetic diversity and physiological roles
1
2012
... 几丁质酶是植物细胞抵御病原真菌侵染的重要抗病蛋白, 在寄主植物细胞受病原菌胁迫过程中可被强烈诱导(
Identification of wild apple germplasm(Malus spp.) accessions with resistance to the postharvest decay pathogens Penicillium expansum and Colletotrichum acutatum
2
2011
... 苹果(Malus domestica)作为多年生木本果树研究的模式植物, 其安全生产对世界水果产业可持续发展具有重要意义(
... 苹果真菌病害的发生严重影响其树体发育、产量与品质, 制约苹果产业的可持续发展.研究真菌病害抗性调控的分子机理对于加速苹果抗病种质创新具有重要意义(
Molecular cloning and characterization of a thaumatin-like protein-encoding cDNA from rough lemon
1
2009
... 本研究中, 10个比对组共46个DEPs (22.8%)注释于7类抗性相关蛋白.其中, 鉴定为类甜蛋白的有14个DEPs.在轮纹病菌胁迫前, 华月(R)叶片中类甜蛋白表达量显著高于金冠(S), 随着胁迫时间的延长, 华月(R)叶片中类甜蛋白的表达量不断降低, 而感病品种金冠(S)叶片中类甜蛋白的表达量显著上调.类甜蛋白是植物应答病原菌胁迫的重要病程相关蛋白(PR-5) (
The key role of the redox status in regulation of metabolism in photosynthesizing organisms
1
2010
... 过氧化物酶(POD)是植物应答病原菌胁迫的重要防御酶系, 也是植物细胞内清除活性氧的关键酶(
Overexpression of polyphenol oxidase in transgenic tomato plants results in enhanced bacterial disease resistance
1
2002
... 多酚氧化酶(polyphenol oxidases, PPOs)存在于多种植物中, 是重要的氧化还原酶类防御酶系, 可参与植物的多种防御反应.研究表明, 过表达PPO的转基因番茄(Lycopersicon esculentum)叶片, 其细菌抗病性显著增强(
Screening and identification of resistance related proteins from apple leaves inoculated with Marssonina coronaria(EII. & J. J. Davis)
3
2014
... 叶绿体作为植物的重要细胞器, 是光合作用及其它重要生物学过程发挥作用的场所(
... 本研究中, 10个比对组共46个DEPs (22.8%)注释于7类抗性相关蛋白.其中, 鉴定为类甜蛋白的有14个DEPs.在轮纹病菌胁迫前, 华月(R)叶片中类甜蛋白表达量显著高于金冠(S), 随着胁迫时间的延长, 华月(R)叶片中类甜蛋白的表达量不断降低, 而感病品种金冠(S)叶片中类甜蛋白的表达量显著上调.类甜蛋白是植物应答病原菌胁迫的重要病程相关蛋白(PR-5) (
... β-1,3-葡聚糖酶也是植物细胞内重要的抗性相关蛋白(
PR-1 gene family of grapevine: a uniquely duplicated PR-1 gene from a Vitis interspecific hybrid confers high level resistance to bacterial disease in transgenic tobacco
1
2011
... β-1,3-葡聚糖酶也是植物细胞内重要的抗性相关蛋白(
Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method
1
2001
... 筛选5个苹果轮纹病抗病功能基因进行qRT-PCR验证.RNA提取使用北京华越洋生物科技有限公司试剂盒, cDNA第1链合成采用宝生物工程(大连)有限公司试剂盒(Cat No.RR047A).各基因的荧光定量引物使用NCBI在线软件(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/ primer-blast/index.cgi?LINK_LOC= BlastHome)设计, 引物序列见
Proteomic investigation of response to forl infection in tomato roots
1
2014
... 苹果真菌病害的发生严重影响其树体发育、产量与品质, 制约苹果产业的可持续发展.研究真菌病害抗性调控的分子机理对于加速苹果抗病种质创新具有重要意义(
Comparative iTRAQ proteomic profiling of susceptible and resistant apple cultivars infected by Alternaria alternata apple pathotype
2
2017
... 几丁质酶是植物细胞抵御病原真菌侵染的重要抗病蛋白, 在寄主植物细胞受病原菌胁迫过程中可被强烈诱导(
... β-1,3-葡聚糖酶也是植物细胞内重要的抗性相关蛋白(
Botryosphaeria spp. isolated from apple and several deciduous fruit trees are divided into three groups based on the production of warts on twigs, size of conidia, and nucleotide sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA ITS regions
2
2000
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
... ).以往关于苹果轮纹病的研究多关注其病害的防治方法、致病菌分离及抗性资源筛选等方面(
Effects of MEK inhibitors GSK1120212 and PD0325901 in vivo using 10-plex quantitative proteomics and phosphoproteomics
1
2015
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
Cost-effective isobaric tagging for quantitative phosphoproteomics using DiART reagents
2
2013
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
... 蛋白质分离鉴定技术是影响蛋白质组学研究的关键(
A scalable approach for protein false discovery rate estimation in large proteomic data sets
1
2015
... IBT数据的定量采用IQuant软件(
Isolation and expression analysis of a novel major latex-like protein (MLP151) gene from Panax ginseng
1
2010
... 主乳胶蛋白(MLP-like protein 423)是一种低分子量的抗性相关蛋白, 在植物抗病或逆境应答中起关键作用(
Antisense downregulation of polyphenol oxidase results in enhanced disease susceptibility
1
2004
... 多酚氧化酶(polyphenol oxidases, PPOs)存在于多种植物中, 是重要的氧化还原酶类防御酶系, 可参与植物的多种防御反应.研究表明, 过表达PPO的转基因番茄(Lycopersicon esculentum)叶片, 其细菌抗病性显著增强(
Major latex protein-like protein 43 (MLP43) functions as a positive regulator during abscisic acid responses and confers drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana
1
2016
... 主乳胶蛋白(MLP-like protein 423)是一种低分子量的抗性相关蛋白, 在植物抗病或逆境应答中起关键作用(
IQuant: an automated pipeline for quantitative proteomics based upon isobaric tags
1
2014
... IBT数据的定量采用IQuant软件(
IBT-based quantitative proteomics identifies potential regulatory proteins involved in pigmentation of purple sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus
2
2017
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
... 蛋白质分离鉴定技术是影响蛋白质组学研究的关键(
Multiple locus genealogies and phenotypic characters reappraise the causal agents of apple ring rot in China
2
2015
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
... ;
Proteome analysis of pathogen-responsive proteins from apple leaves induced by the Alternaria blotch Alternaria alternata
4
2015
... 苹果轮纹病是影响我国苹果生产的重要病害, 其致病菌常通过侵染苹果枝干、叶片和果实使寄主发病, 严重影响苹果树势、产量与品质(
... 抗(R)、感(S)病苹果叶片总蛋白样品制备参照酚抽提方法(
... )完成.总蛋白样品经室温风干后, 干粉重悬于裂解缓冲液(lysis buffer) (
... 过敏原蛋白(major allergen Mal d1)是苹果属植物重要的抗性相关蛋白(
备案号: 京ICP备16067583号-21
版权所有 © 2021 《植物学报》编辑部
地址:北京香山南辛村20号 邮编:100093
电话:010-62836135 010-62836131 E-mail:cbb@ibcas.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
