HTML
--> --> -->| Dataset profile | ||||||
| Dataset Title | Wildfire | Lightning detection | Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | Aerosol monitoring | Soil moisture | Precipitation estimation |
| Time range | 2009–present | 2018–present | 2006–present | 2009–present | 2011–present | 2005 – present |
| Geographical scope | China area and full-disk area for those products derived from FY-2 Global coverage for those products derived from FY-3 Asia area and full-disk area for those products derived from FY-4A | |||||
| Data format | HDF5.0 and AWX2.1 for those products derived from FY-2 HDF5.0 for those products derived from FY-3 NetCDF for those products derived from FY-4A | |||||
| Data volume | 150 KB d?1 for FY-3, 1 MB h?1 for FY-4A | 100 KB min?1 | 250 m: 7 GB 10-d?1, 1 km: 500 m 10-d?1, 5 km: 280 m 10-d?1 | 642 MB file?1 for FY-3, 5 MB file?1 for FY-4A | 6 MB file?1 for FY-3 | 250 KB to 20 MB file?1 |
| (to be continued) | ||||||
| (Continued) | ||||||
| Dataset profile | ||||||
| Data service system | Fengyun satellite data sharing service system (http://data.nsmc.org.cn). | |||||
| Sources of founding | National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFB0504900, 2018YFB0504905). | |||||
| Database composition | 1. The wildfire database contains two types of data: 1) The global wildfire product comprises 1 file per day. 2) The geostationary wildfire product has two types: full-disk product containing 40 files per day, and rapid scan product containing 165 files per day. 2. The lightning detection database contains two types of data: 1) The lightning event product comprises 1 file per minute. 2) The lightning group product also contains 1 file per minute. 3. The NDVI product database contains three types of data of different spatial resolutions. 1) The 10-daily global NDVI product has three datasets of different spatial resolutions. 2) The monthly global NDVI product contains 1 dataset of 5 km resolution. 4. The aerosol monitoring product contains two types of data. 1) The global aerosol monitoring product consists of aerosol on land surface and aerosol on ocean surface. Each kind contains 648 files per day. 2) The geostationary composited aerosol product consists of a full-disk product containing 40 files per day, and a rapid scan product containing 165 files per day. 5. The soil moisture database contains daily, 10-daily, and monthly products. Each product contains 1 file. 6. The precipitation estimation product contains two types of data: 1) The global precipitation estimation product generated by MWHS and MWRI instruments onboard FY-3. There are 14–15 files for one day. 2) The geostationary precipitation estimation product consists of five different frequency products. There are two types of area (full disk and China area) in both FY-2 and FY-4 satellite product. | |||||
The Chinese meteorological satellite series Fengyun (FY), together with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) series in the U.S.A. and the polar orbiting meteorological satellite (METOP) series in Europe, has become a main pillar used to construct Earth’s operational observation system. Since the first satellite (FY-1A) was successfully launched in 1988, four series have been developed, and seventeen additional satellites have been launched. The second-generation polar orbital mission [also called Low Earth Orbit (LEO)] FY-3 and second-generation geostationary orbital mission [also called Geosynchronous Equatorial Orbit (GEO)] FY-4A series have output stable data with remarkable quality (Yang et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2019a, 2020a).
At present, seven satellites operate in orbit, including three FY-2 satellites, three FY-3 satellites, and one FY-4 satellite. FY-2 is the first-generation geostationary orbital satellite from China. Eight FY-2 satellites have been successfully launched. FY-2H, FY-2G, and FY-2F are still operating at 79°E, 99.5°E, and 112°E above the equator, respectively. FY-4 is the second-generation geostationary orbital satellite from China, which has successfully launched the first satellite of this series in the year of 2017. FY-4A has advanced earth observation capabilities and provides a better temporal resolution than the FY-2 series satellites (Yang et al., 2017; Min et al., 2017). Compared with the first-generation polar orbital satellites in the FY-1 series, the new generation polar orbital satellite FY-3 series expands the single onboard instrument to include more than 10 instruments. FY-3A and FY-3B have 11 instruments onboard, FY-3C has 12 instruments onboard, and FY-3D has 10 instruments onboard. The FY-3 series provides higher resolution images with more spectral coverage from the ultraviolet, visible, infrared, to microwave bands (Xu et al., 2010; Yang et al., 2012). Based on space-ground architecture, the National Satellite Meteorological Center (NSMC) has developed a comprehensive data service system that has been available to the public since 2005 (Chen et al., 2008). After more than 30 years of development since the first FY satellite was launched, the usage of FY satellite data has dramatically increased, not only in the meteorological community but also in remote sensing applications and other benefitting fields. With the promotion of open access to the FY satellite data, many new potential applications have been emphasized. After over three decades of development, FY satellites have recorded and complied extremely valuable information over a long period. These long-term datasets are especially useful in meteorological analysis, climate change monitoring, environment change detection, earth surface observation, and other related fields.
2
2.1. Visible and infrared optical instruments
Optical instruments are the classical payloads mounted on both FY LEO satellites and FY GEO satellites, which have been operational for over 30 years. The performance of these instruments has gradually improved. A visible and infrared radiometer (VIRR) was installed on the FY satellite for series FY-1A to FY-3C but was later replaced by a higher-performance optical instrument, referred to as the medium resolution spectral imager (MERSI). The VIRR of the FY-1 series, also referred to as the multichannel visible infrared scanning radiometer (MVISR), had 5–10 channels ranging from 0.43 to 12.5 μm (FY-1A and FY-1B had 5 channels, FY-1C and FY-1D had 10 channels) with maximum 1.1 km spatial resolution. The VIRR on the FY-3 series continued to use nearly the same configuration as the VIRR on the FY-1D series. Meanwhile, a new optical instrument, MERSI, was tested on the FY-3 series. MERSI enhanced the spectral and spatial resolution to a maximum resolution of 250 m with more than 20 channels [MERSI on FY-3A, FY-3B, and FY-3C had 20 channels and MERSI-2 on FY-3D had 25 channels (0.413-12 μm)]. Level 1 data from the FY-1C and FY-1D series was archived in two formats: High Resolution Picture Transmission (HRPT) and Delayed Picture Transmission (DPT). HRPT data was received and processed in real time by ground segmentation when the satellite flew over the ground station. DPT data was temporarily stored on the satellite’s local storage and transmitted when the satellite passed the ground station. Therefore, DPT data were stored for a whole orbit, and HRPT data were stored for part of an orbit. At present, the VIRR and MERSI instruments on the FY-3B satellite are on a morning orbit taking operational global optical observations. The VIRR on FY-3C and the MERSI-2 on FY-3D operate on an afternoon orbit.For geostationary orbitals, the FY-2 and FY-4 satellites played an important role in monitoring the Asia-Pacific and Indian Ocean areas. The visible and infrared spin scan radiometer (VISSR) is a stable instrument that has generated continuous full-disk earth observation data from the FY-2C satellite successfully since operation began in 2005. At present, the VISSR instrument on the FY-2F/G/H series and the Advanced Geosynchronous Radiation Imager (AGRI) on the FY-4A satellite are still operational for geostationary orbitals.
Available visible and infrared optical instrument data from FY satellites is listed in Table 1.
| 130 | Satellite | Number of Channels | Resolution | Swath |
| VIRR | FY-1A(S) FY-1B(S) | 5 (0.45–12 μm) | 1.1 km | 2800 km |
| VIRR | FY-1C(S) FY-1D(S) FY-3A(S) FY-3B(O) FY-3C(O) | 10 (0.455–12 μm) | 1.1 km | 2800 km |
| MERSI | FY-3A(S) FY-3B(O) FY-3C(S) | 20 (0.412–11.5 μm) | 250 m at 5 channels 1 km at 15 channels | 2900 km |
| MERSI-2 | FY-3D(O) | 25 (0.412–12.5 μm) | 250 m at 6 channels 1 km at 19 channels | 2900 km |
| VISSR | FY-2A(S) FY-2B(S) FY-2C(S) FY-2D(S) FY-2E(S) FY-2F(O) FY-2G(O) FY-2H(O) | 5 (0.55–12.5 μm) | 1.25 km at 1 channel 4 km at 4 channels | Full disk or rapid scan |
| AGRI | FY-4A(O) | 14 (0.47–13.5 μm) | 500 m at 1 channel 1 km at 2 channels 2 km at 4 channels 4 km at 7 channels | Full disk or Asia area |
| Note: (O) means the instruments are operational, (S) means the instruments have been shut down. | ||||
Table1. Visible and infrared optical imaging instrument data.
2
2.2. Microwave instruments
Three kinds of microwave instruments have been installed on the FY-3 satellites since 2008: microwave radiation imagers (MWRIs), microwave thermometers (MWTSs), and microwave hygrometers (MWHSs). Level 1 data was named and archived in two parts: the ascending part and the descending part. Five microwave instruments remain, including MWRI on FY-3D, MWTS-2 on FY-3D, MWHS on FY-3B, and MWHS-2 on FY-3C/D. FY-3B started its secondary operation in July 2020.Available microwave instrument data from FY satellites is listed in Table 2.
| Name | Satellite | Number of Channels | Resolution | Swath |
| MWRI | FY-3A(S) FY-3B(S) FY-3C(S) FY-3D(O) | 10 (10.65–89 GHz) | Changing with frequency, consistent with an antenna diameter of 90 cm | 1400 km |
| MWTS | FY-3A(S) FY-3B(S) | 4 (50.3–57.29 GHz) | 70 km | 2200 km |
| MWTS-2 | FY-3C(S) FY-3D(O) | 15 (50.3–57.29 GHz) | 32 km | 2250 km |
| MWHS | FY-3A(S) FY-3B(O) | 5 (150–183.31 GHz) | 16 km | 2700 km |
| MWHS-2 | FY-3C(O) FY-3D(O) | 15(89.0–183.31 GHz) | 32 km at window channels and band 118 GHz 16 km at band 183 GHz | 2700 km |
| Note: (O) means the instruments are operational, (S) means the instruments have been shut down. | ||||
Table2. Microwave instrument data.
2
2.3. Infrared (IR) sounding instruments
Infrared (IR) sounding technology was used on the FY-3 and FY-4 satellites targeted at detecting earth-atmosphere systems at a hyperspectral resolution. An infrared atmospheric sounder (IRAS) was installed on FY-3A, FY-3B, and FY-3D. Its successor instrument, the infrared hyperspectral atmospheric sounder (HIRAS), was installed on the FY-3D satellite, which used the world’s most advanced Fourier interference monitoring technology. The world’s first infrared sounding instrument in geostationary orbit was the geostationary interferometric infrared sounder (GIIRS), which was installed on the FY-4A satellite. Three sounding instruments are still operational, two in polar orbit (IRAS on FY-3B and HIRAS on FY-3D) and one in geostationary orbit (GIIRS on FY-4A).Available IR sounding instrument data from FY satellites is listed in Table 3.
| Name | Satellite | Number of Channels | Resolution | Swath |
| IRAS | FY-3A(S) FY-3B(O) FY-3C(S) | 26 (0.69–14.95 μm) | 17.4 km | 2250 km |
| HIRAS | FY-3D(O) | 1370 (3.92–15.38 μm) | 16 km | 2200 km |
| GIIRS | FY-4A(O) | 1650 (0.55–14.3 μm) | 16 km | China area (5000 km × 5000 km) mesoscale area (1000 km × 1000 km) |
| Note: (O) means the instruments are operational, (S) means the instruments have been shut down. | ||||
Table3. IR sounding instruments.
| Type | Product name | Product specifications | Format | ||||
| Temporal type | Spatial resolution | ||||||
| Hourly | Daily | Ten-Daily | Monthly | ||||
| Cloud and radiation | Cloud total amount | ? | √ | ? | ? | 4 km | Raw |
| Outgoing longwave radiation | ? | √ | √ | √ | 50 km | Raw | |
| Ocean | Sea surface Temperature | ? | √ | √ | √ | 5 km | Raw |
| Cryosphere | Snow cover | ? | √ | √ | ? | 5 km | Raw |
| Land and ecology | Vegetation index | ? | ? | √ | ? | 1 km, 4 km | Raw |
| Note: The symbol √ means this product is available. | |||||||
Table4-1. FY-1 product list.
| Type | Product name | Product specifications | Format | ||||
| Temporal type | Spatial resolution | ||||||
| Hourly | Daily | Ten-Daily | Monthly | ||||
| Atmosphere | Atmospheric motion vector | √ | ? | ? | ? | ? | HDF5.0 |
| Dust detection | √ | ? | ? | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Humidity | √ | ? | ? | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Precipitation estimation | √ | ? | ? | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Precipitation index | √ | ? | ? | √ | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Total precipitable water | √ | ? | ? | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Upper-tropospheric humidity | √ | ? | ? | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Ocean | Sea surface temperature | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 km | HDF5.0 |
| Cryosphere | Snow cover | √ | ? | √ | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 |
| Cloud and radiation | All sky radiation | √ | ? | ? | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 |
| Blackbody brightness temperature | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Clear sky radiation | √ | ? | ? | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Cloud classification | √ | ? | ? | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Cloud detection | √ | ? | ? | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Cloud top temperature | √ | ? | ? | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Cloud total amount | √ | ? | ? | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Outgoing Long wave Radiation | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Surface solar irradiance | √ | ? | ? | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Cloud total amount | √ | ? | ? | ? | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Land and ecology | Land surface temperature | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 km | HDF5.0 |
| Note: The symbol √ means this product is available. | |||||||
Table4-2. FY-2 product list.
2
4.1. Wildfire monitoring product
Forests and grasslands are very important resources in the environment. Based on the Chinese environmental resource survey, the forest coverage rate is only 16.55%, which is lower than the global average level by more than 10.48%. The grassland coverage rate is 41.7%, and the per capita occupation rate is only half of the world’s average. Wildfire detection represents an important challenge to environmental protection. Since the 1980s, researchers have used metrological satellites to monitor wildfires (Matson et al., 1984). Wildfire images from satellites were first used to combat forest fires that occurred in the Greater Khingan Range, Heilongjiang Province, in 1987 (Liu et al., 2004; Li et al., 2017. Since then, wildfire detection has become an important product of meteorological satellites. Both polar and geostationary orbital FY meteorological satellites have been used in wildfire monitoring. The VIRR and MERSI instruments onboard the FY-1 and FY-3 satellites had special bands for wildfire detection. A newer wildfire identification algorithm that utilized the infrared, mid-infrared and far-infrared bands was used in the MERSI-2/FY-3D satellites (Fig. 1). Moreover, the AGRI instrument on the FY-4A satellite can be used for wildfire detection and its fire product has a higher temporal resolution.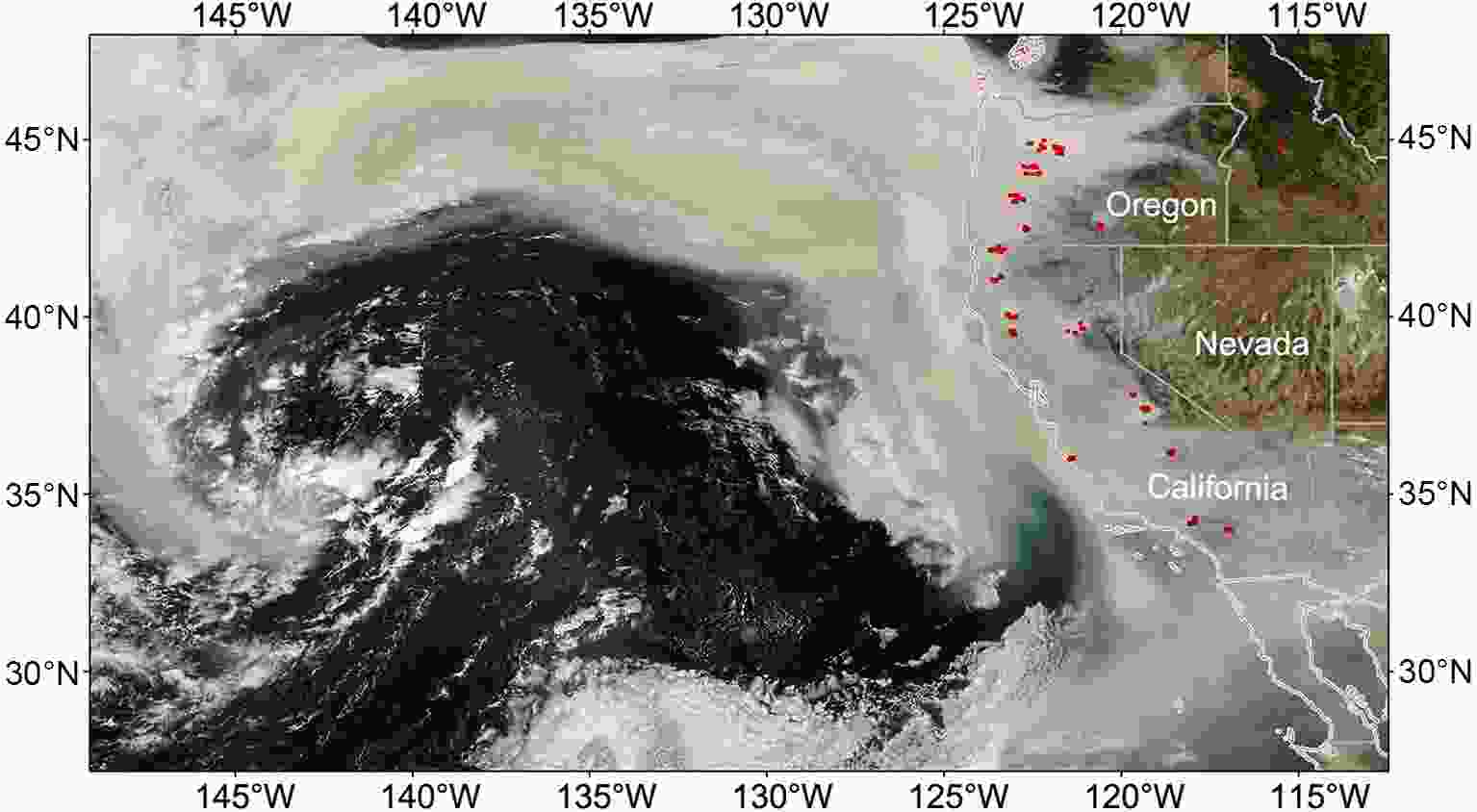 Figure1. Wildfire detection in the western part of the U.S.A. with the FY-3D MERSI-2 satellite on 12 September 2020.
Figure1. Wildfire detection in the western part of the U.S.A. with the FY-3D MERSI-2 satellite on 12 September 2020.The forest fire product from MERSI-2 was validated by artificial identification. For example, a forest fire was detected by MERSI-2 in Hebi city in the Henan Province of China from 1300–1500 local time on 26 March 2019. With cooperation between the NSMC and local forest fire investigators, the location of the fire detected by MERSI-2 was validated. The validation results showed that the distance between the real fire location and the estimated point was approximately 0.0024° to 0.0049° longitude and 0.0008° to 0.0058° latitude (Zheng et al., 2020). The positioning accuracy of the MERSI-2 wildfire product reached 250 meters, which is better than the 1 km resolution of the previously used instrument. In addition, the differences between the neighboring fire pixels were separated in the MERSI-2/FY-3D wildfire product retrieved from the far-infrared band because there was no solar radiation interference. This feature can be used in the determination of the ignition point of the fire.
The specifications of the FY wildfire products are shown in Table 5.
| Type | Product name | Product specifications | Format | ||||
| Temporal type | Spatial resolution | ||||||
| Hourly | Daily | Ten-Daily | Monthly | ||||
| Atmosphere | Aerosol optical depth | ? | √ | √ | √ | 1 km, 5 km | HDF5.0 |
| Humidity profile | ? | √ | ? | ? | 33 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Temperature profile | ? | √ | ? | ? | 33 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Atmospheric Total Cloud liquid water | ? | √ | √ | √ | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Dust storm index | ? | √ | ? | ? | 1 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Microwave rain rate | ? | √ | ? | √ | 25 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Fog detection | ? | √ | ? | ? | 1 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Precipitation | ? | √ | ? | ? | 1 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Perceptible water | ? | √ | √ | √ | 1 km, 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Rain detection | ? | √ | ? | ? | 15 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Total ozone | ? | √ | ? | ? | 50 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Vertical humidity profile | ? | √ | ? | ? | 33 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Vertical temperature profile | ? | √ | ? | ? | 33 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Ocean | Sea surface Temperature | ? | √ | √ | ? | 25 km | HDF5.0 |
| Sea surface wind speed | ? | √ | √ | ? | 25 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Cryosphere | Sea ice | ? | √ | √ | √ | 12 km | HDF5.0 |
| Snow cover | ? | √ | √ | √ | 1 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Snow depth | ? | √ | √ | √ | 25 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Snow water equivalent | ? | √ | √ | √ | 25 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Cloud and radiation | Albedo | ? | √ | ? | ? | 1 km | HDF5.0 |
| Cloud amount | ? | √ | √ | √ | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Cloud mask | ? | √ | 1 km | HDF5.0 | |||
| Cloud optical depth | ? | √ | √ | √ | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Cloud phase | ? | √ | ? | ? | 1 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Cloud type | ? | √ | ? | ? | 1 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Cloud top temperature | ? | √ | √ | √ | 1 km, 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Cloud top height | ? | √ | √ | √ | 1 km, 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Cloud water content | ? | √ | ? | √ | 25 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Outgoing longwave radiation | ? | √ | √ | √ | 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Land and ecology | Albedo | ? | √ | ? | ? | 1 km | HDF5.0 |
| Fire detection | ? | √ | ? | 1 km | HDF5.0 | ||
| Land cover | ? | √ | ? | ? | 1 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Land surface reflectance | ? | √ | ? | ? | 250 m, 1 km, 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Land surface Temperature | ? | √ | √ | √ | 25 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Fire detection | ? | √ | ? | 1 km | HDF5.0 | ||
| Soil moisture | ? | √ | √ | √ | 25 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Normalized difference vegetation index | ? | ? | √ | √ | 250 m, 1 km, 5 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Leaf area index | ? | ? | √ | √ | 25 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Fraction of photosynthetically active radiation | ? | ? | √ | √ | 25 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Net primary productivity | ? | ? | √ | √ | 25 km | HDF5.0 | |
| Note: The symbol √ means this product is available. | |||||||
Table4-3. FY-3 product list.
2
4.2. Lightning detection product
Lightning data are new and originate from convective detection products because lightning is closely related to convective properties, such as the content of graupel and hail, the volume of updrafts, and the maximum vertical velocity. (Carey and Rutledge, 1996). Lightning imagery sensors on tropical rainfall measuring missions (TRMMs) can be used for tropical rainfall estimation (DeMaria et al., 2012; Xu et al., 2017). Space-based lightning data can provide valuable information for meteorological and climate research (Boccippio et al., 2000; Christian et al., 2003; Cecil et al., 2005, 2014). The lightning mapping imager (LMI, Yang et al., 2017; Cao et al., 2012, 2018) on the FY-4A satellite, which is one of the first lightning detection sensors employed in geostationary orbit, provides event (level 1B product) and group and flash products (level 2 product). The detector size of LMI is 400 × 600 pixels. The observation area covers China from March to September and western Australia and the South Indian Ocean from September to March (Fig. 2).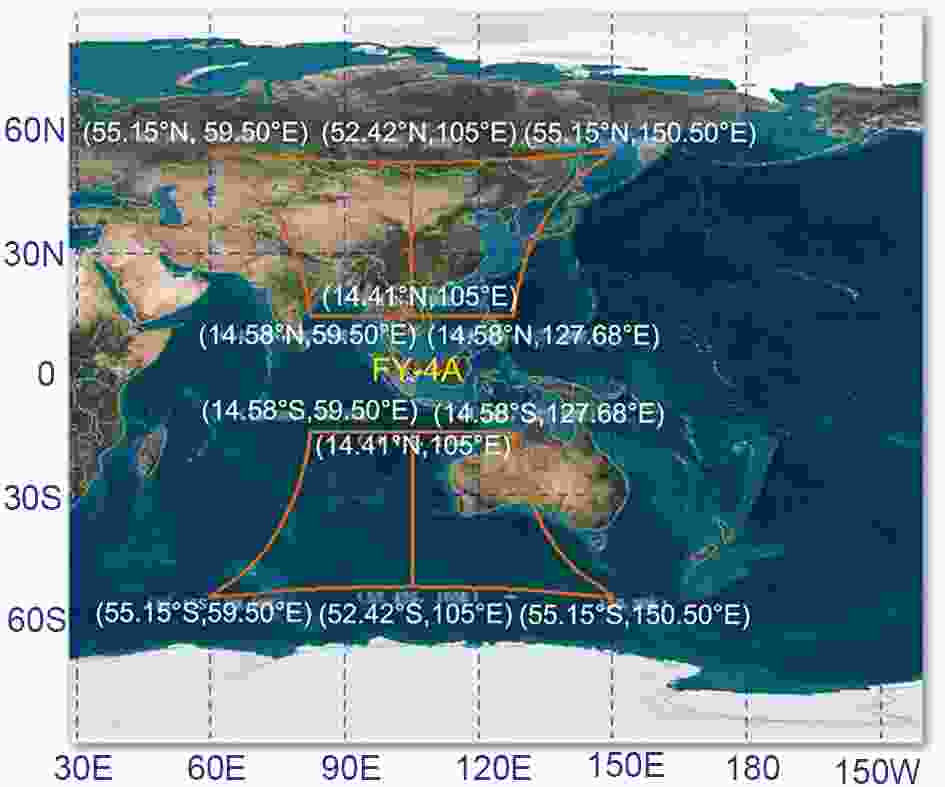 Figure2. FY-4A LMI coverage area.
Figure2. FY-4A LMI coverage area.Event signals are the fundamental lightning cell detected by the FY-4 LMI. Event signals are detected by the real-time event processor of the FY-4 LMI by background subtraction, threshold comparison, and pixels extraction of radiation values exceeding thresholds. With an event-group-flash tree structure, based on a clustering algorithm, cluster events are grouped into the products of group and flash. One-minute LMI event and group products are generated in NetCDF format (Fig. 3). A historical and near-real-time product can be downloaded from the FY satellite data center (
 Figure3. Lightning event (a) and group (b) distributions [Reprinted from (Cao et al., 2018)]. This figure shows a strong convection over south of Gansu province and Jiangxi province in China. Red pixels mean more lighting events and blue pixels mean less lightning events.
Figure3. Lightning event (a) and group (b) distributions [Reprinted from (Cao et al., 2018)]. This figure shows a strong convection over south of Gansu province and Jiangxi province in China. Red pixels mean more lighting events and blue pixels mean less lightning events.The FY-4A lightning product was validated based on ground observations. Compared with the ground lightning imager, the total frequency of FY-4A satellite-captured lightning events was approximately ten times that of the ground observations due to the different observation methods. Figure 4 shows that the trends of lightning statistics were similar to those captured by two other types of detectors (Ren et al., 2020). However, in some situations, such as T1 and T3, the figure shows relatively high values for the ground-based observations. The T2 event shows a trend opposite to those of T1 and T3.
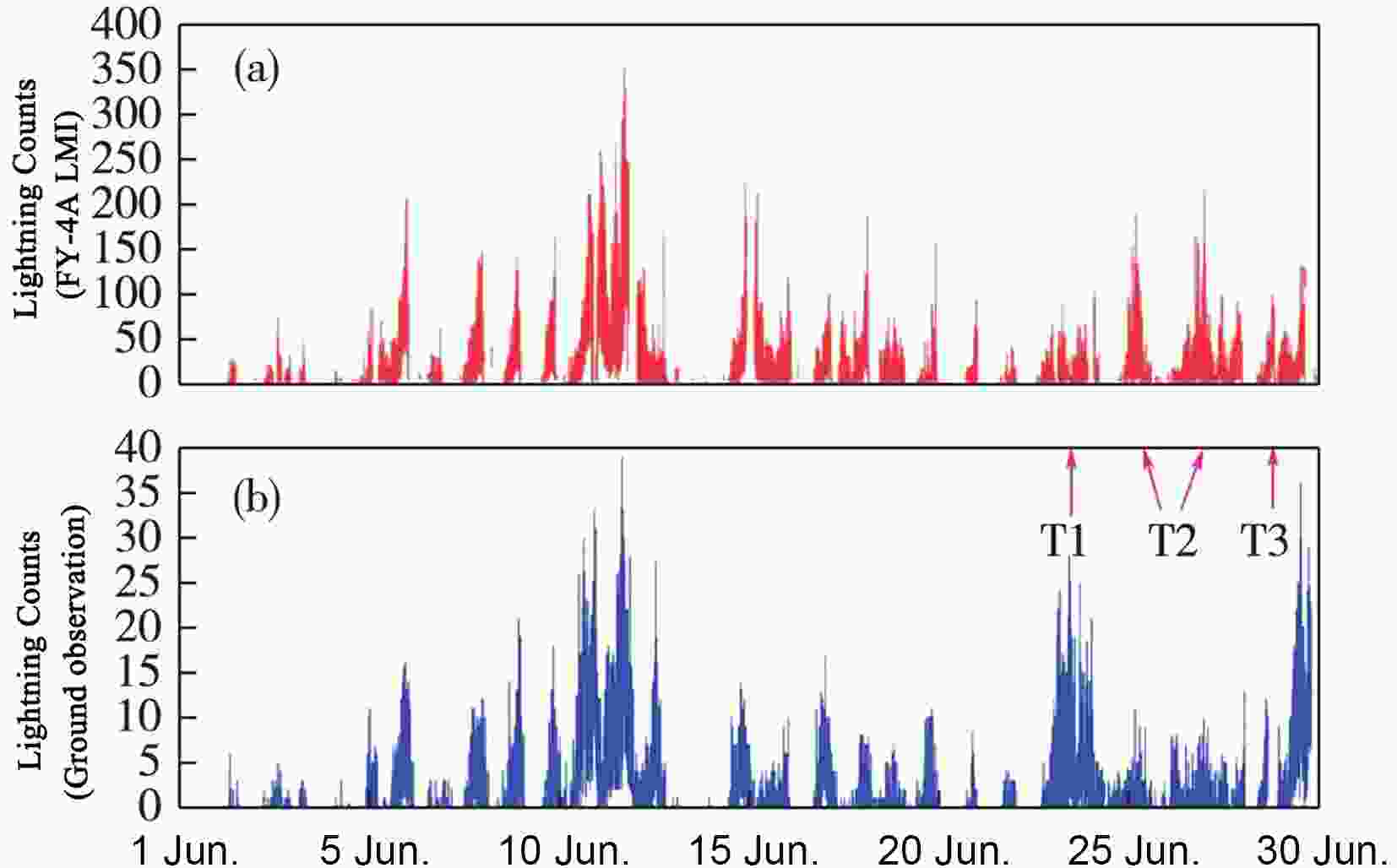 Figure4. Comparison between LMI events and ground observations [Reprinted from (Ren et al., 2020)]. This figure shows that the distribution of FY-4A LMI and ground observation were similar for June and it also shows different trends in T1, T2 and T3.
Figure4. Comparison between LMI events and ground observations [Reprinted from (Ren et al., 2020)]. This figure shows that the distribution of FY-4A LMI and ground observation were similar for June and it also shows different trends in T1, T2 and T3.The specifications of the FY lightning products are shown in Table 6.
| Type | Product name | Product specifications | Format | |||||
| Temporal type | Spatial resolution | |||||||
| Minutely | Hourly | Daily | Ten-Daily | Monthly | ||||
| Atmosphere | Aerosol optical depth | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 1 km | NetCDF |
| Atmospheric correction image | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 1 km | NetCDF | |
| Atmospheric motion vector | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 64 km | NetCDF | |
| Convective initiation | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Fog detection | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Dust detection | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Total column precipitable water | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Vertical moisture profile | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 16 km | NetCDF | |
| Vertical temperature profile | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 16 km | NetCDF | |
| Lightning detection | √ | ? | ? | ? | ? | 78 km | NetCDF | |
| Liquid profile water | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Rainfall rate | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Tropopause folding | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Ocean | Sea surface temperature | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF |
| Cloud and radiation | All sky radiation | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF |
| Clear sky masks | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Clear sky radiation | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Cloud optical depth | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Cloud phase | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Cloud top height | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Cloud top pressure | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Cloud top temperature | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Cloud type | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Downward long wave radiation: surface | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Outgoing long wave radiation | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Upward long wave radiation: surface | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Reflected shortwave radiation: TOA | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Surface solar irradiance | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Land surface | Fire/hot spot | √ | √ | ? | ? | ? | 2 km | NetCDF |
| Land surface temperature | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 4 km | NetCDF | |
| Land surface emissivity | ? | √ | ? | ? | ? | 12 km | NetCDF | |
| Note: The symbol √ means this product is available. | ||||||||
Table4-4. FY-4 product list.
2
4.3. Vegetation monitoring product
Changes in vegetation on the land surface influence energy flows, climatic conditions, hydrologic settings, and geochemical cycles experienced on Earth. It is also a sensitive indicator of climate change and environmental change (Yang et al., 2017). Compared with traditional methods, remote sensing can quickly obtain surface information over a large area. With this information, the surface vegetation status can be calculated by direct or indirect inversion. Effective monitoring of vegetation changes in recent decades has been greatly supported by the multiple continuous developments made in remote sensing instruments and technologies, including the development of the FY satellite system. After the first FY satellite was launched in 1988, the vegetation product was generated from the FY-1 satellite observations with a 1 km × 4 km resolution for the area covering China. The normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) product measured by the VIRR, MERSI, and MERSI-2 instruments of the FY-3D satellite uses the same algorithm as that of the advanced very high resolution radiometer (AVHRR) and moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS). Compared with AVHRR and MODIS, MERSI and MERSI-2 monitor more channels in total and have more solar bands, which can be used in more environmental applications. With the new MERSI-2 VI algorithm and high-quality cloud detection algorithm developed and operated by the NSMC (Fig. 5), the MERSI-2 NDVI product shows a good correlation with the MODIS NDVI product (Fig. 6). Figure5. FY-3D MERSI-2 global NDVI product for July 2020.
Figure5. FY-3D MERSI-2 global NDVI product for July 2020.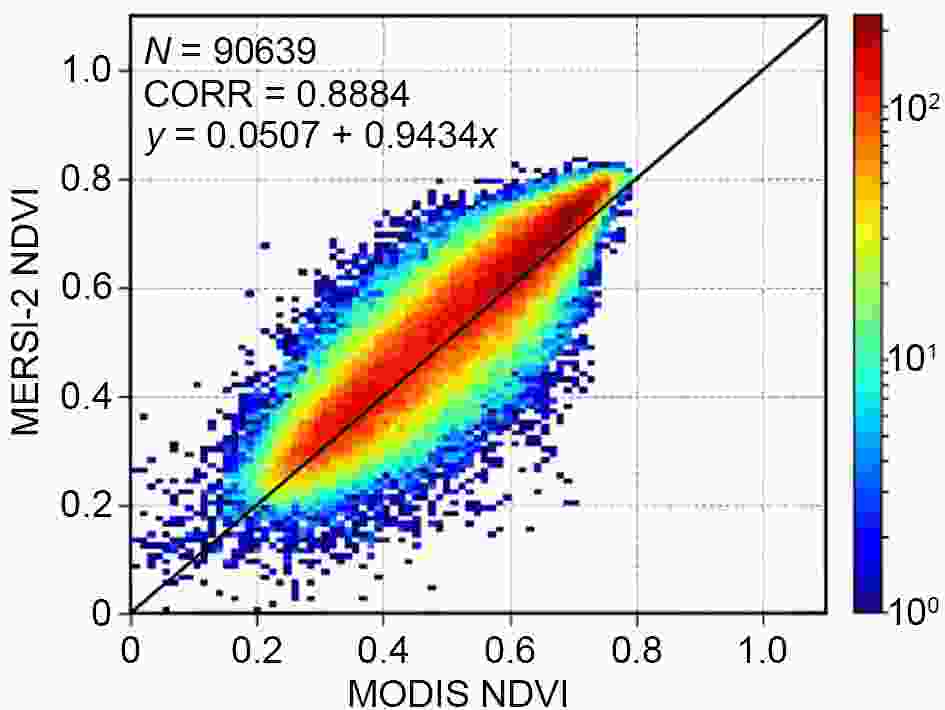 Figure6. Comparison between the FY-3D satellite MERSI-2 product and the MODIS NDVI product [Reprinted from (Han et al., 2020)].
Figure6. Comparison between the FY-3D satellite MERSI-2 product and the MODIS NDVI product [Reprinted from (Han et al., 2020)].The specifications of the FY NDVI products are shown in Table 7.
| Satellite | Instrument | Temporal Parameter | Spatial range | Format |
| FY-3A | VIRR | Daily (2009.11.08–2016.04.12) | Global | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3B | VIRR | Daily (2010.12.14–2020.05.31) | Global | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3C | VIRR | Daily (2014.05.30–2020.02.03) | Global | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3D | MERSI-2 | Daily (2019.04.30 until present) | Global | HDF5.0 |
| FY-4A | AGRI | Minutely (2019.01.18 until present) | Asia | NetCDF |
Table5. Wildfire products from FY meteorological satellites.
2
4.4. Aerosol monitoring product
Aerosols are one of the most important key parameters used to evaluate air pollution. A number of satellites have the capability to detect aerosols because the detection of air pollution is considered to be one of the most important targets for developing remote sensing satellites. For optical instruments, aerosol products can be generated with visible band data and aerosol optical depth (AOD) retrieval algorithms. Aerosol products derived from MODIS have been widely used and validated since 2000. The MERSI, and VIRR instruments on the FY-3A satellite were the first Chinese-developed instruments to apply AOD retrieval (Zhang, et al., 2009; Zhang, et al., 2020b). The first AOD product started in March 2009. The dark dense vegetation (DDV) and ocean algorithm products were used to generate daily global aerosol products to evaluate air pollution. The spatial resolution of AOD is 1 km × 5 km. For the first three FY-3 satellites, the aerosol product was divided into two parts (land surface and sea surface) because different algorithms were used in the process flow of the AOD product. To help users better apply aerosol products in their work, these two products were combined into one dataset (Fig. 7). The quality of FY-3 AOD products was validated using Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) observations and the datasets were compared with MODIS (Yang et al.,2020, Fig. 8). The result shows that the FY-3 AOD performs well. Since the FY-4A satellite was launched, the AGRI instrument measured the corresponding channels for the dark target algorithm, which was applied in the generation of the AOD product (Zhang et al., 2019, Fig.9). These aerosol optical property products include the AOD product, Angstrom exponent, and fine mode fraction for each pixel. The spatial resolution of AOD is 4 km for full-disk coverage.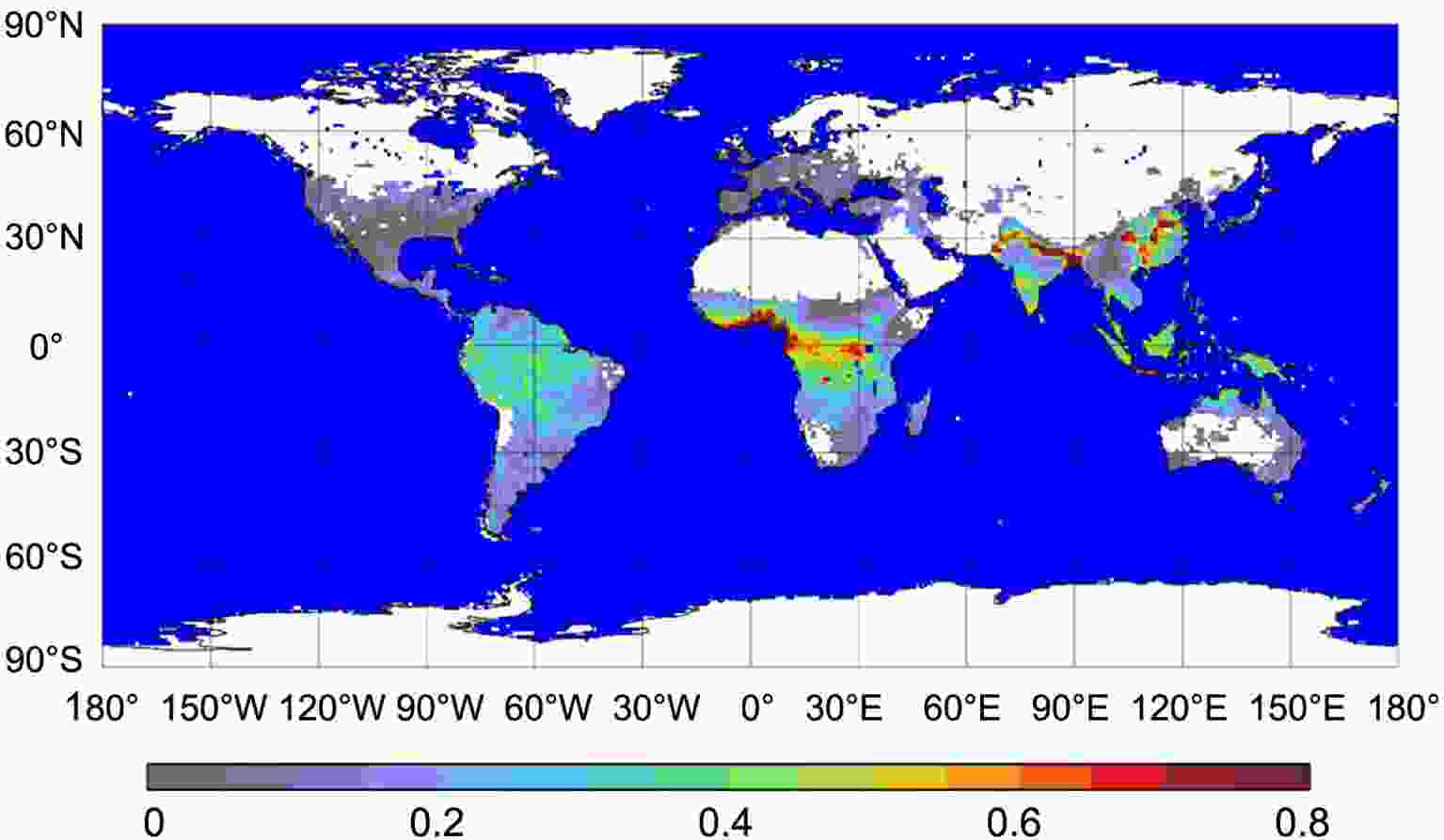 Figure7. Global AOD distribution with the FY-3D MERSI-2 instrument [Reprinted from (Yang et al., 2019)].
Figure7. Global AOD distribution with the FY-3D MERSI-2 instrument [Reprinted from (Yang et al., 2019)].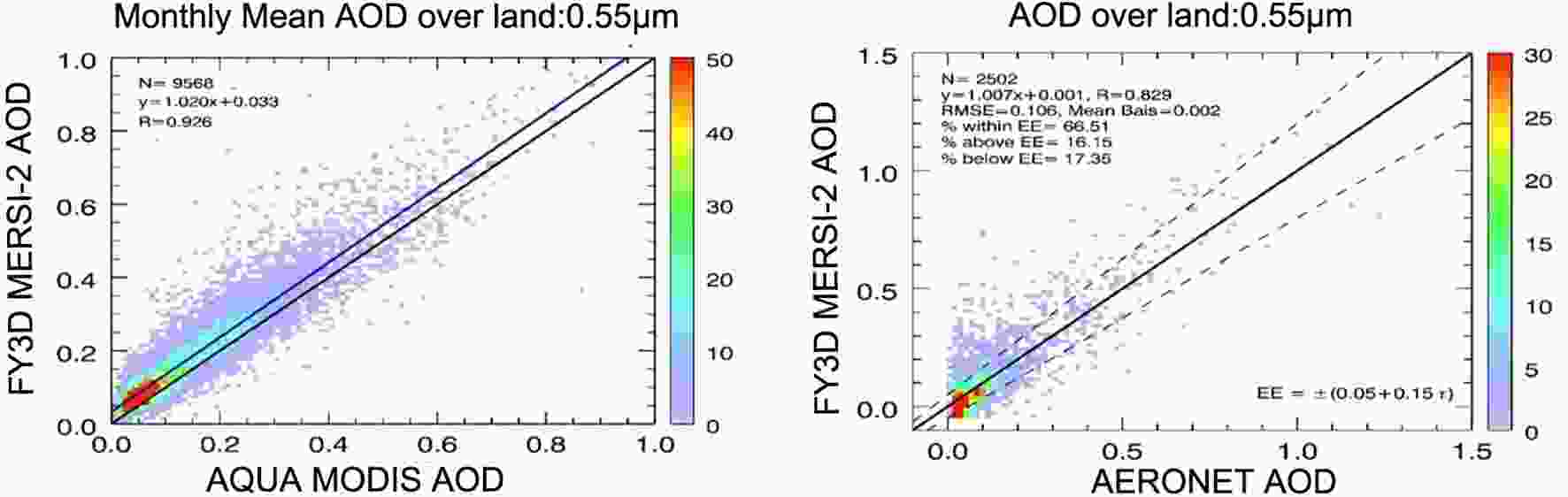 Figure8. Verification of AOD product derived from the MERSI-2/FY-3D satellite. [Reprinted from(Yang et al., 2019)].
Figure8. Verification of AOD product derived from the MERSI-2/FY-3D satellite. [Reprinted from(Yang et al., 2019)].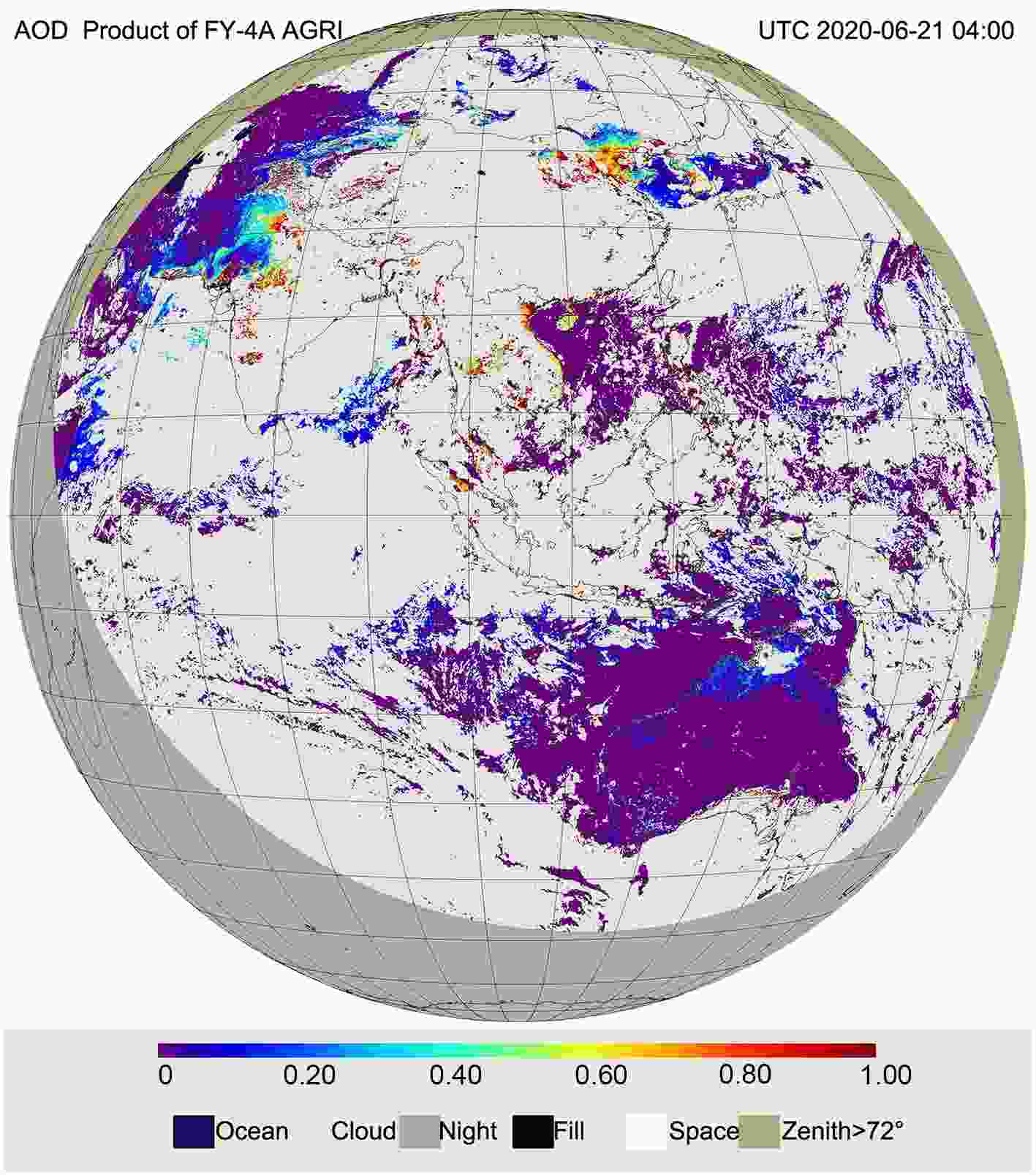 Figure9. AOD product from the AGRI/FY-4A satellite at 0400 UTC 21 June 2020.
Figure9. AOD product from the AGRI/FY-4A satellite at 0400 UTC 21 June 2020.The specifications of the FY aerosol products are shown in Table 8.
| Satellite | Instrument | Type | Temporal Parameter | Resolution | Format |
| FY-4A | LMI | Event | Every minute (2018.03.12 until present) | 78 km | NetCDF |
| FY-4A | LMI | Group | Every minute (2019.01.18 until present) | 78 km | NetCDF |
Table6. Lightning products from FY meteorological satellites.
2
4.5. Soil moisture product
Surface soil moisture is a key terrestrial water storage indicator that governs hydrological processes and influences weather and climate systems (Entekhabi et al., 2010; Du et al., 2012). Space-borne microwave radiometers characterized by a relatively low spatial resolution and a high temporal sampling enable the rapid assessment of soil moisture every 1–3 days (Bindlish et al., 2009). Among these satellite sensors, the MWRIs on the FY-3 series satellites have provided global measurements of surface wetness since 2008. The FY-3/MWRI instrument operates at five different frequencies, 10.65, 18.7, 23.8, 36.5, and 89 GHz, with dual polarization. The spatial resolution of the FY-3B/MWRI soil moisture product is 25 km (Table 9). The long-term and continuous operation of the MWRI instruments benefit a variety of applications, including effective crop yield assessment and drought risk mitigation (Sun et al., 2014).The MWRI soil moisture product algorithm was built based on the zero-order radiative transfer mode (Mo et al., 1982), where satellite-observed emissivity consists of contributions from vegetation, interactions between vegetation and the underlying soil surface, and the soil surface. For deriving soil moisture, the following steps are taken sequentially (Liu et al., 2013) to correct for vegetation and surface roughness: (a) estimate the physical temperature using the brightness temperature (Tb) at 37 GHz (Holmes et al., 2009); (b) calculate the vegetation transmissivity using vegetation water content estimated from an ancillary NDVI dataset (Jackson et al., 1999, 2010); and (c) obtain the soil moisture using a Qp-based inversion model (Shi et al., 2006). The Qp model is a parameterized soil surface emission model that has a similar accuracy as rigorous theoretical models (e.g., the advanced integral equation model) while maintaining a simple form (Shi et al., 2006). For MWRI, the Qp-based inversion model minimizes the effects of surface roughness and derives the volumetric soil moisture (VSM) using both V- and H-polarized Tb observations in the X-band (Shi et al., 2006).
The MWRI soil moisture product was validated using similar instrument observations. A comparison between the FY-3D/MWRI soil moisture product and the GCOM-W1/AMSR2 soil moisture product was performed. The results demonstrated that the root mean square error was within 0.06 cm3 cm?3 in the medium to low vegetation cover areas.
The comparison result between the MWRI and AMSR2 soil moisture products is shown in Table 10.
| Satellite | Instrument | Temporal Parameter | Spatial range | Resolution | Format |
| FY-1D | VIRR | Ten-Daily (2006.01.01–2008.07.11) | China | 1 km, 4 km | HDF4.5 |
| FY-3A | VIRR | Ten-Daily (2010.01.10–2018.03.10) Monthly (2010.04–2018.02) | Global | 1 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3A | MERSI | Ten-Daily (2010.01.31–2018.03.10) Monthly (2010.03-2018.02) | Global | 250 m | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3B | VIRR | Ten-Daily (2011.06.10–2020.05.31) Monthly (2011.06-2020.05) | Global | 1 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3B | MERSI | Ten-Daily (2011.06.10–2020.05.31) Monthly (2011.11-2020.05) | Global | 250 m | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3C | VIRR | Ten-Daily (2014.05.10–2020.02.03) Monthly (2014.09-2020.01) | Global | 1 km, 5 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3C | MERSI | Ten-Daily (2014.05.10–2015.05.31) Monthly (2014.09–2015.04) | Global | 250 m, 5 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3D | MERSI-2 | Ten-Daily (2019.04.30 until present) Monthly (2019.04 until present) | Global | 250 m, 1 km, 5 km | HDF5.0 |
Table7. NDVI products from FY meteorological satellites.
2
4.6. Precipitation estimation product
Satellite precipitation estimations have significant value for severe weather forecasting and agricultural production. Compared with ground observations, satellite observations can monitor convection from space at higher resolution and greater spatial coverage, especially for mesoscale convective system (MCS). MCS events are a main source of heavy rainfall. Satellite images show important features of MCS events while they move, arrange, and evolve. Since the 1990s, the relationship between cloud top Tb of infrared channel images and rainfall has been revealed (Lu and Wu, 1997; Fang and Qin, 2006; Min et al., 2020). From water vapor channel images, the ascending movement and water vapor environment in the middle and upper troposphere, which are favorable to the occurrence and development of rainstorm clouds, can be observed (Qin et al., 2005). With the development of satellite observation technology, Tb observation from visible, infrared, and microwave detection instruments on the FY-3 satellite can be used in cloud liquid water and multilayer cloud analysis (Wang et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2019). The precipitation estimation product was one of the most important products to both polar orbit and geostationary orbit FY satellites. Table 11 shows the precipitation estimation product list for FY satellites.| Satellite | Instrument | Temporal Parameter | Spatial range | Resolution | Format |
| FY-3A | MERSI | Daily (2009.03.13–2018.02.11) Ten-Daily (2010.01.10–2018.02.20) Monthly (2010.01–2018.02) | Global land surface | 1 km 5 km 5 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3A | MERSI | Daily (2009.03.13–2014.09.21) Ten-Daily (2010.01.10–2014.09.30) Monthly (2010.01–2014.09) | Global sea surface | 1 km 5 km 5 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3B | VIRR | Daily (2010.12.14–2020.05.31) | Global sea surface | 1 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3B | MERSI | Daily (2010.12.14–2020.05.31) Ten-Daily (2011.06.20–2020.05.31) Monthly (2011.06–2020.05) | Global | 1 km 5 km 5 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3C | VIRR | Every Arch (2014.05.23–2020.02.03) Daily (2014.05.30–2020.02.03) Ten-Daily (2014.07.31–2020.01.31) Monthly (2014.07–2020.01) | Global sea surface | 1 km 5 km 5 km 5 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3C | MERSI | Every arch(2014.05.23–2015.05.30) Daily(2014.05.15–2015.05.30) Ten-Daily (2014.05.10–2015.05.20) Monthly (2014.06–2015.04) | Global | 1 km 5 km 5 km 5 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3D | MERSI-2 | Every arch (2018.05.26 until present) Daily(2018.08.17 until present) Ten-Daily (2019.05.10 until present) Monthly (2019.05 until present) | Global | 1 km 5 km 5 km 5 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-4A | AGRI | Every hour (2020.03.01 until present) | Full disk | 4 km | NetCDF |
Table8. Aerosol products from FY meteorological satellites.
Since 2005, FY-2 satellites can generate four kinds of products on precipitation estimation, which are in one-, three-, six-, and twenty-four-hour intervals, respectively. The FY-4A satellite has operational and higher frequency precipitation estimation products (Fig. 10) within five minutes interval. Verification of the quantitative precipitation estimation product between FY-4A and Himawari-8 shows that the mean error is 0.11 mm and the hit rate is 99%. The global precipitation estimation product is generated from MWHS and MWRI on FY-3 satellites since 2009.
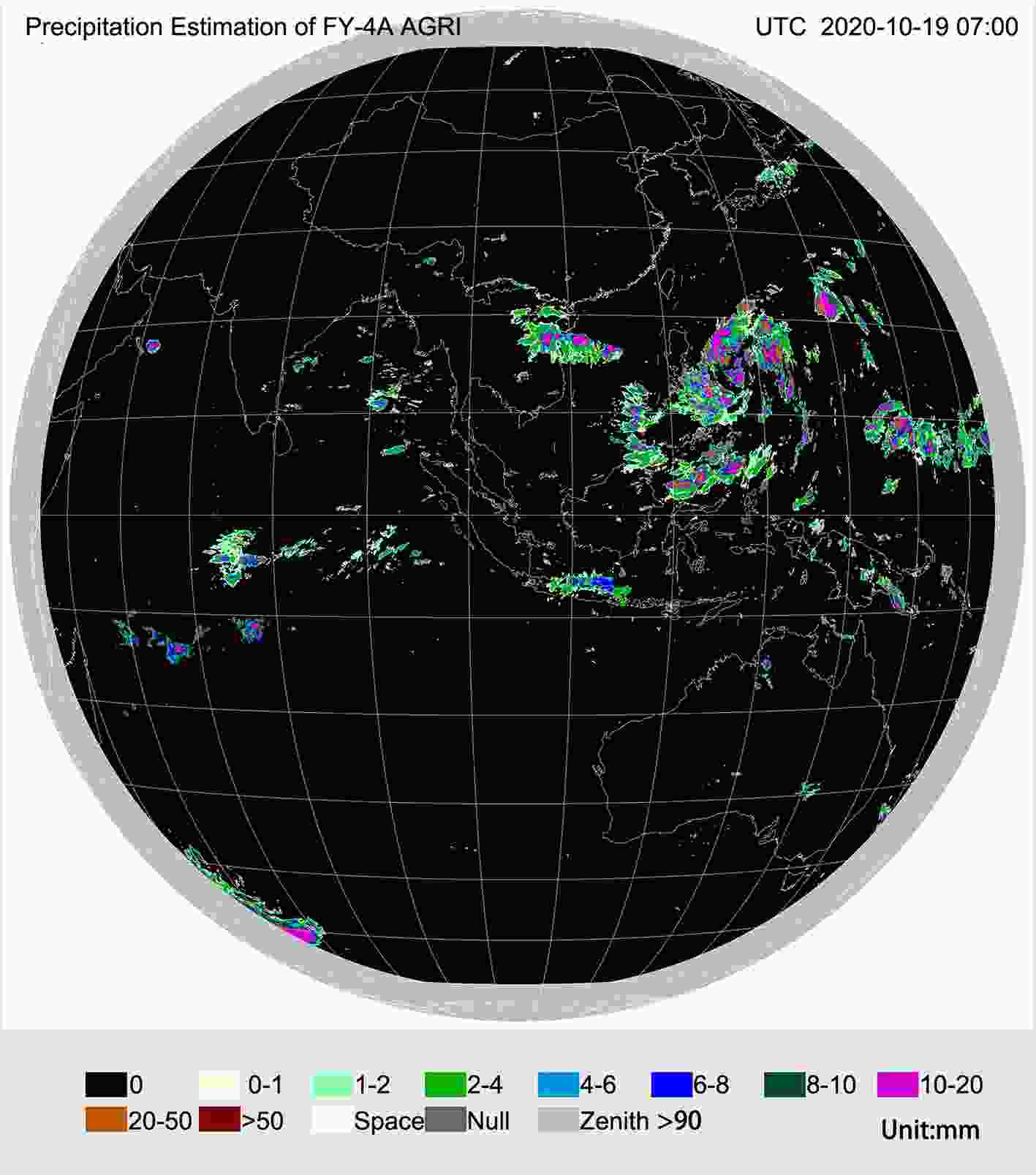 Figure10. Precipitation estimation product from the AGRI/FY-4A satellite at 0700 UTC 19 October 2020.
Figure10. Precipitation estimation product from the AGRI/FY-4A satellite at 0700 UTC 19 October 2020. Figure11. Global user distribution of the FY satellite data service.
Figure11. Global user distribution of the FY satellite data service.2
5.1. Web site
All level 1 data and products mentioned in this article can be found on the FY satellite data center Web site (2
5.2. Data Download Toolkit
The NSMC released a Fengyun Satellite Data Download Toolkit in 2018. This toolkit provided a new way to help users find and obtain FY satellite data. By setting a download default folder, this software will start downloading the data automatically when the order is prepared. Furthermore, this toolkit provides a kind of data reservation mechanism. This introduced a whole new experience in obtaining satellite products by allowing the user to order the selected data or products in a customized area with temporal parameters at a maximum of three months.2
5.3. Satellite Weather Application Platform 2.0 (SWAP 2.0)
SWAP 2.0 is an application platform that focuses on geostationary meteorological satellite data utilization, realizes a comprehensive display of the FY-4A and FY-2 series satellite data, provides interactive typhoon positioning/intensity estimations, and establishes a strong convective analysis system. SWAP 2.0 has the ability to display level 1 data, compose multiple channel data, play animation, render level 2 data, etc. SWAP 2.0 is available in two versions. The Web-based versions were released in three languages: Chinese, English, and Russian (2
5.4. Satellite Monitoring and Remote sensing Toolkit 2.0 (SMART 2.0)
SMART 2.0 is a comprehensive application platform for ecological remote sensing, monitoring, and application using FY-3 satellite data. It offers special application tools for professionals engaged in the remote sensing of natural hazards and ecological environments. SMART 2.0 fills many great functions, such as uniform operation management, multisource data displaying, universal tools of image processing and remote sensing, thematic information deriving, geographical information system (GIS) overlaying, and thematic product generation and dissemination.2
5.5. Mobile applications
The invention of smart mobile phones was a technology revolution that has changed people’s daily lives. To support applications on smart phones, several small applets and applications were developed using data from the FY satellites. Two of these applets were developed based on the WeChat platform. The first applet is called the FY Global Browser. This applet shows daily real color composite images with 250 m resolution, which are generated from FY-3D MERSI-2 satellite data. The second applet is called the FY Now. Real-time RGB-composited images can be displayed in the WeChat application based on the user’s location.Many of these products have been generated to monitor environment-related parameters using the capabilities of the FY meteorological satellites. Many efforts have been made to improve the data quality, timeliness, spatial resolution, and acquisition during the processing of the FY meteorological satellite ground segment. Compared with the same types of products generated by other satellites, vegetation and aerosol products have shown good accuracy and reliability. The advantages of the FY satellites include a high temporal resolution and more band choices. The lightning products are unique and provide a new parameter for analyzing convention. Wildfire products have been tested and used to develop forest and environmental protection plans. In the future, more products, including greenhouse gas monitoring, water body environment detection, and land surface analysis products, such as soil moisture and land surface temperature, will be developed and shared with the public.
With the rapid development of the Internet and cloud technology, new technologies will be implemented to improve FY data access and utilization. A cloud-based data sharing platform has been designed and will be built over the next two years. Massive amounts of FY data and products will be archived in this system. Users can transplant and run their own algorithms in this system with a universal plug-in standard. A scientific computing platform based on cloud computing and AI technologies will be brought to users to improve the potential FY data applications. In conclusion, FY data will be obtained and utilized in a more simple and convenient manner in the future.
Acknowledgements. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFB0504900, 2018YFB0504905). We thank the editor and reviewers for their constructive suggestions and comments.
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (
| Satellite | Instrument | Temporal Parameter | Spatial range | Resolution | Format |
| FY-3B | MWRI | Daily (2011.07.12–2019.08.19) | Global land surface | 25 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3C | MWRI | Daily (2014.05.13–2020.02.03) Ten-Daily (2014.05.13–2020.02.03) Monthly (2014.05.13–2020.02.03) | Global land surface | 25 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3D | MWRI | Daily (2018.07.12 until present) Ten-Daily (2018.07.12 until present) Monthly (2018.07.12 until present) | Global land surface | 25 km | HDF5.0 |
Table9. MWRI soil moisture product from FY meteorological satellites.
| Land cover type | Sparse shrub | Grass land | Crop land | Bare soil |
| correlation coefficient | 0.586 | 0.667 | 0.526 | 0.467 |
| RMSE | 0.049 | 0.055 | 0.059 | 0.042 |
Table10. Comparison result between the MWRI and AMSR2 soil moisture products.
| Satellite | Instrument | Temporal Parameter | Spatial range | Resolution | Format |
| FY-2C/D/E/F/G/H | VISSR | One-hourly, Three-hourly, Six-hourly, and Daily (2005.06.02 until present) | China | 5 km | AWX2.1 |
| One-hourly, Three-hourly, Six-hourly, and Daily (2005.06.02 until present) | Full-disk | 5 km | HDF5.0 | ||
| FY-3A/C/D | MWHS | Daily (2009.12.09 until present) | Global | 25 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-3B/C/D | MWRI | Daily (2011.11.07 until present) | Global | 25 km | HDF5.0 |
| FY-4A | AGRI | Five-minutely (2018.03.12 until present) | China | 4 km | NetCDF |
| Hourly (2018.03.12 until present) | Full-disk | 4 km | NetCDF |
Table11. Precipitation estimation product from FY meteorological satellites.
