摘要/Abstract
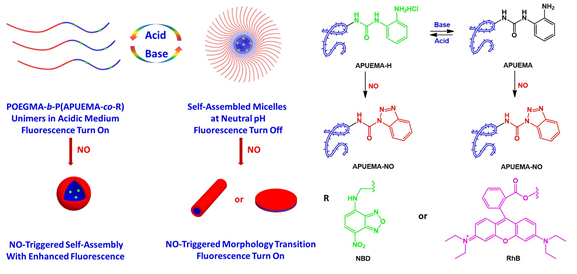
一氧化氮(NO)是一种普遍存在的生理信号分子,但利用NO作为触发方法来精细调节仿生聚合物的自组装行为的研究却很少.本工作报道一种独特的具有一氧化氮(NO)反应特性的新型pH响应双亲水性嵌段共聚物(double hydrophilic block copolymer,DHBC),其中NO可以自发地触发聚(寡聚乙二醇甲醚甲基丙烯酸酯)-嵌段-聚(NO响应性基元-共-7-硝基苯并呋咱衍生物)(POEGMA-b-P(APUEMA-co-NBD))双亲水嵌段共聚物,分别在酸性和中性环境中发生自组装和形态转变.在引入荧光团之后,这些转变还可以和NO存在下光致诱导电子转移过程被阻断导致荧光增强相关联,从而提供了观察细胞内NO的机会.
关键词: 一氧化氮, 响应性, 荧光探针, 成像
Nitric oxide (NO) is a ubiquitous physiological signal messenger, but the use of NO as a trigger event to delicately tune the self-assembly behaviors of biomimetic polymers has been far less exploited. In this work, a single primary amine-containing 2-(3-(2-aminophenyl)ureido)ethyl methacrylate (APUEMA) monomer was first synthesized by the reaction between o-phenylenediamine and 2-isocyanatoethyl methacrylate. Then, the well-defined double hydrophilic block copolymer (DHBC), poly[oligo(ethylene glycol)methyl ether methacrylate]-b-poly[2-(3-(2-aminophenyl)ureido)ethyl methacrylate-co-4-(2-methylacryloyloxyethylamino)-7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole)] (POEGMA-b-P(APUEMA-co-NBD)), was synthesized via sequential reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. Since there is a free amine group in the APUEMA monomer, it can be competent to quench the fluorescence of dyes and react with NO showing NO-responsiveness property. The reaction product of APUEMA and NO was purified by column chromatography, and 1H and 13C NMR results displayed the formation of urea-functionalized benzotriazole residual. The pKa values of APUEMA monomer and POEGMA-b-P(APUEMA-co-NBD) block polymer were measured to be 3.36 and 2.15, respectively, indicating that APUEMA monomer and PAPUEMA moieties of POEGMA-b-P(APUEMA-co-NBD) showed hydrophilic ability at acidic medium and hydrophobic ability at neutral medium. The aqueous solution of POEGMA-b-P(APUEMA-co-NBD) block copolymer exhibited a small diameter with about 5.0 nm at pH 2.0, which illustrates that block copolymer can dissolve into water with a unimer state. After changing the solution pH value to 7, the solution diameter increased to about 10 nm recorded by dynamic light scattering (DLS). Transmission electron microscope (TEM) results displayed micelles of POEGMA-b-P(APUEMA-co-NBD) block copolymer aqueous solution with spherical structures at pH 7.4. Furthermore, the fluorescence intensity of the block copolymer solution was decreased quickly after the pH value increased from 2 to 7. The NO-responsive property of block copolymer POEGMA-b-P(APUEMA-co-NBD) was also detected by DLS and fluorescent spectrometry methods. At pH 2.0, the diameter of the block copolymer aqueous solution increased from 5 nm to about 150 nm upon sparging with NO for 24 h. At pH 7.0, the diameter of block copolymer micelles increased from 10 nm to about 100 nm after exposure to NO for 24 h. The transmittance of POEGMA-b-P(APUEMA-co-NBD) block copolymer aqueous solution at pH 2.0 or pH 7.0 decreased upon NO addition, which were in accorded with DLS results. Moreover, the fluorescence intensity of the block copolymer solution at pH 2.0 improved rapidly upon sparging with NO for 0.5 h, implying that the NO-triggered self-assembly of micelles decreased environmental polarity. The fluorescence intensity decreased with further addition. The fluorescence intensity of block copolymer micelles at pH 7.0 exhibited 15-fold increased after addition with NO for 24 h. The in vitro study of block copolymer POEGMA-b-P(APUEMA-co-NBD) was conducted in normal MRC-5 cells. The block copolymer showed negligible cytotoxicity even at the block copolymer concentration of 100 g/mL. We herein report on a novel pH-responsive DHBC with unique NO-reactive feature, where NO can spontaneously trigger the self-assembly and morphological transformation in acidic and neutral milieus, respectively. After the introduction of fluorophores, these transitions are also associated with significant fluorescence turn-on due to eliminations of photoinduced electron transfer (PET) process in the presence of NO, imparting the opportunities to visualize intracellular NO.
Key words: nitric oxide, responsive, fluorescent probe, imaging
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
