摘要/Abstract
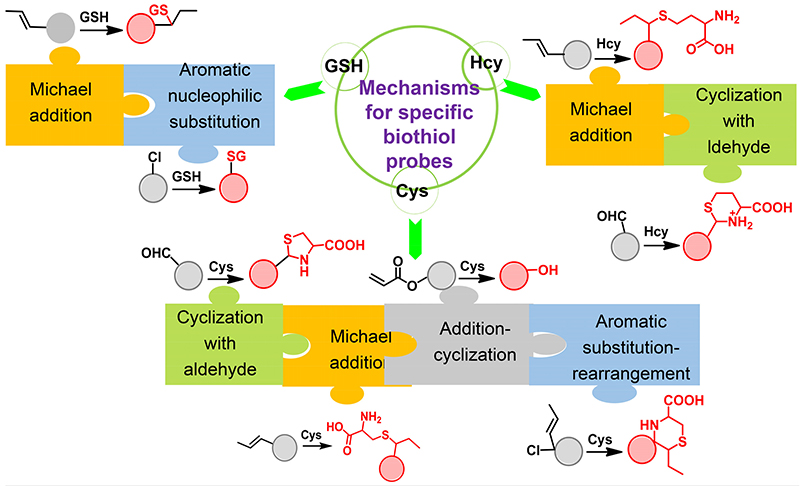
生物硫醇(包含半胱氨酸、高半胱氨酸和谷胱甘肽)在生命活动中扮演了重要的角色, 其浓度的异常变化与某些疾病息息相关, 因此对硫醇的检测具有重要意义. 荧光探针因具有灵敏度高、时空分辨率好、无损伤、可视化等优势, 在生物硫醇的检测方面得到了高度重视. 利用硫醇在分子结构上的共同点(含巯基的氨基酸)和差异(分子大小、亲核性、空间位阻、细胞内含量), 可通过迈克尔加成、亲核芳基取代、加成环化等反应实现对硫醇的选择性检测. 综述了近3年来硫醇荧光探针领域的研究进展. 首先介绍了对硫醇有选择性识别的荧光探针, 随后分类讨论了对半胱氨酸、高半胱氨酸和谷胱甘肽各具有特异性检测的荧光探针, 并重点介绍了分子设计、识别机理、荧光性质和成像应用, 初步探讨了部分探针在监测细胞生命活动中的作用, 同时还对本领域的发展提出了展望.
关键词: 硫醇, 荧光探针, 半胱氨酸, 高半胱氨酸, 谷胱甘肽, 进展
Biothiols, including cysteine (Cys), homocysteine (Hcy) and glutathione (GSH), play an important role in life activities, and the fluctuation of their concentrations is closely related to many diseases. Therefore, it is of great importance to detect the content of biothiols. Among all varieties of techniques, the fluorescent probe demonstrates tremendous advantages ascribed to its good sensitivity, high temporal-spatial resolution, noninvasiveness and visualization. Taking advantage of the commonality and differences among the three thiols, namely, the similar reactive groups of sulfhydryl group and amino group, and the different molecular size, nucleophilicity, steric hindrance and intracellular contents, various recognition mechanisms, such as Michael addition, aromatic nucleophilic reaction and concerted addition and cyclization reaction, are all implemented to realize the specific detection of biothiols. The research progress of thiol fluorescent probes in recent three years is reviewed. The fluorescent probes that can selectively respond to biothiols as well as to Cys, Hcy and GSH are systemically analyzed and summarized. The molecular design, recognition mechanism, fluorescence properties and imaging applications are emphasized,, and the application of biothiol fluorescent probe on monitoring life activities is preliminary introduced. In addition, a perspective of future development in this area is also presented.
Key words: biothiol, fluorescent probe, cysteine, homocysteine, glutathione, advance
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
