摘要/Abstract
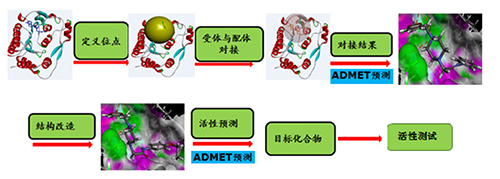
由甲基转移酶和RNA聚合酶组成的多功能蛋白(NS5)是寨卡病毒复制过程中起主要作用的蛋白组分,其甲基转移酶(5M5B)部分是病毒复制和宿主固有免疫应答的中心参与者,因此被作为潜在抗寨卡病毒药物开发的首选靶标蛋白.将5M5B作为受体,利用其已知的结合位点与200多万个化合物小分子进行虚拟筛选,得到抗寨卡病毒的先导化合物2a,并对该先导化合物进行结构优化、改造、活性预测、化学合成、药理活性研究.使用1H NMR和13C NMR对所有合成的化合物进行了表征,并进行了体外活性测试.结果表明化合物3a[IC50=(7.69±0.36)μmol·L-1]的体外活性优于广谱抗病毒药利巴韦林活性[IC50=(8.15±0.42)μmol·L-1],本研究的方法与结果对寨卡病毒抑制剂的结构设计研究具有重要的指导作用.
关键词: 寨卡病毒抑制剂, 虚拟筛选, 构效关系, 结构改造
NS5 is a protein component which plays a main role in replication of Zika virus, and its component part-methyl-transferase (5M5B) is the central participants of virus replication and host innate immune response. So it is used as the preferred protein of potential antiviral drugs development. Using 5M5B as receptors and using its binding sites to screen with over 2 million small molecule compounds, the leading compounds of anti-Zika virus were obtained. The structural optimization, activity prediction, chemical synthesis and pharmacological activity of the leading compound were studied. All the synthesized compounds were characterized by 1H NMR and 13C NMR. The antiviral activity of compound 3a is better than that of ribavirin (IC50=(7.69±0.36) μmol·L-1 for 3a vs IC50=(8.15±0.42) μmol·L-1 for ribavirin).
Key words: ZIKV inhibitor, virtual screening, structure-activity relationship (SAR), structural transformation
PDF全文下载地址:
点我下载PDF
