全文HTML
--> --> --> 磷是导致封闭或半封闭水体富营养化的关键营养盐和限制因子,故水中低浓度磷,尤其是人工湿地、反硝化滤池等尾水深度处理单元中磷的强化去除是目前的研究热点。在各种除磷方法中,吸附法已被证明是一种高选择性和易于操作的途径[1-2]。近年来,生物炭以其较大的比表面积、多孔结构、丰富的表面官能团和较低的成本等优势受到人们的关注[3-4]。由于多数生物炭表面呈电负性,阴离子交换量不高且缺少功能性基团,对磷酸根的吸附能力较弱甚至出现负吸附[5-6]。然而,通过金属改性方法可以提高生物炭对磷的吸附能力[7]。金属原子易与磷酸盐离子形成配位络合物,从而增强吸附剂对磷酸盐的吸附效果[8]。金属磷酸盐的络合强度取决于其自由结合能,并与金属性质有关[9]。一般来说,金属阳离子的价态越高,离子半径越小,改性生物炭越有利于与磷酸根离子结合。蒋旭涛等[10]用小麦秸秆制备生物炭,并用氯化铁溶液改性,铁改性后生物炭的理论最大吸附量为改性前的19.4倍。LIU等[11]利用蛋壳和稻草制备的氧化钙-生物炭复合材料,在pH为5.0~11.0内表现出优异的磷酸盐吸附能力。因此,对生物炭进行金属改性来提高生物炭吸附除磷能力是一种行之有效的方法[12]。丰富的水生植物生长对水质净化至关重要,但湿地植物必须通过及时、定期收割才能实现水中营养物去除的强化,湿地处理技术产生的大量植株残体的减量化、无害化处置和资源化利用已成为迫切需求[13]。有研究[14-15]表明,农业废弃物衍生的生物炭吸附剂可以有效地捕获磷酸盐。与传统吸附剂相比,这种新兴的生物基吸附剂具有成本低、可再生、化学稳定和环境友好等优点[16]。本研究利用收割的湿地植物菖蒲制备生物炭,进行改性炭基质材料的优化制备,并探讨了制备材料的理化特征与吸附特性。
1.1. 实验原料
菖蒲采自太湖流域某污水厂人工湿地,自来水洗净后再用去离子水冲洗,晾干表面水分后剪成1~2 cm小段,置于烘箱353~373 K烘干,经破碎机粉碎后过80目标准筛,制得菖蒲粉,密封保存备用。硫酸亚铁(FeSO4·7H2O)和氢氧化钠(NaOH)分别购自天津市大茂化学试剂厂和江苏强盛功能化学股份有限公司,均为分析纯。1.2. 生物炭制备
按固液比1∶20(g∶mL)将菖蒲粉浸渍到的NaOH(0.5 mol·L?1)溶液中,搅拌均匀后置于150 r·min?1的恒温摇床中振荡3 h,静置后滤掉上清液后用去离子水洗涤,在373 K的烘箱中烘干。取适量烘干样加入到一定浓度的FeSO4·7H2O溶液中(固液比为1∶10),操作条件同前,进行振荡、浸渍、洗涤烘干,得到铁改性菖蒲生物炭前驱体。坩埚加盖密封,置于管式炉中,升温至相应温度(573、623、673、723和773 K,相应记为MBC573、MBC623、MBC673、MBC723、MBC773)热解2 h,冷却至室温后过100目标准筛备用,制得NaOH浸渍预处理铁改性菖蒲生物炭(MBC)。未改性制备菖蒲生物炭(BC)样品(无NaOH浸渍以及FeSO4·7H2O溶液处理)相应记为BC573、BC623、BC673、BC723、BC773。1.3. 动力学吸附实验
分别取0.01 g MBC于150 mL锥形瓶中,依次加入50 mL初始质量浓度为5 mg·L?1的磷溶液(pH=7)。在288、298和308 K,转速为150 r·min?1的水浴摇床中恒温振荡。间隔一定时间分别取上清液过0.45 μm微孔滤膜,测定滤液中的磷浓度。采用准一级动力学模型(式(1))、准二级动力学模型(式(2))和颗粒内扩散模型(式(3))对MBC的动力学数据进行拟合。式中:t为吸附时间,min;qe和qt为平衡时和t时刻的吸附量,mg·g?1;k1为准一级反应速率常数,min?1;k2为准二级反应速率常数,g·(mg·min)?1;k3为颗粒内扩散反应速率常数,mg·(g·min1/2)?1;C为常数。
1.4. 等温吸附实验
分别取0.01 g MBC于150 mL锥形瓶中,依次加入50 mL不同浓度梯度(0.5~20 mg·L?1)的磷溶液(pH=7),分别于288、298和308 K,在转速为150 r·min?1的水浴摇床中恒温振荡24 h。反应结束后取上清液过0.45 μm微孔滤膜,测定滤液中的磷浓度。采用Langmuir模型(式(4))和Freundlich模型(式(5))对MBC吸附磷的数据进行拟合。式中:ce为平衡时吸附质的浓度,mg·L?1;qe为平衡吸附容量,mg·g?1;qmax为最大吸附容量,mg·g?1;KL为Langmuir常数;KF为Freundlich常数。
1.5. 影响因素实验
热解温度。分别取不同温度下制备的0.01 g BC和0.01 g MBC于150 mL锥形瓶中,依次加入50 mL质量浓度为5 mg·L?1的磷溶液(pH=7),其他反应条件同1.4节。改性剂浓度。分别取0.01 g 改性剂浓度为0.25、0.5、0.75、1.0、1.25、1.5、2.0 mol·L?1制备的MBC于150 mL的锥形瓶中,依次加入50mL质量浓度为5 mg·L?1的磷溶液(pH=7),其余反应条件同1.4节。
生物炭添加量。分别取2.5、5、10、20、30、40、50 mg MBC于150 mL的锥形瓶中,依次加入50 mL质量浓度分别为0.5、1、5 mg·L?1的磷溶液(pH=7),其余反应条件同1.4节。
溶液初始pH。调节磷溶液pH为3~11并添加0.01 g MBC于150 mL的锥形瓶中,其余反应条件同1.4节。
共存离子。共存离子分别为Cl?、




1.6. 生物炭材料性能表征
采用元素分析仪(vario PYRO cube型,德国Elementar公司)测定生物炭改性前后化学元素的百分含量;采用全自动比表面积测定仪(Micromeritics型,美国麦克仪器)测定生物炭的比表面积、孔径等参数;采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM-EDS,Quanta FEG 250,美国FEI公司)观察生物炭改性前、后的相貌特征与材料表面元素分布并测其含量;采用X-射线衍射仪(XRD,Rigaku TTRAX III,日本理学株式会社)分析吸附磷前、后改性生物炭材料的晶型结构;采用傅里叶红外光谱仪(FT-IR,Nicolet iS50型,美国TthermoFisher公司)测定改性生物炭材料改性前、后表面特征官能团;采用Zeta电位仪(Zetasizer Nano ZS 90型,英国Malvern公司)对改性生物炭的表面电性进行测定。1.7. 数据处理
数据处理使用Excel 2019,XRD数据通过jade 6.0进行物相检索,图形绘制与动力学模型、等温吸附模型拟合使用Origin 2021。2.1. 生物炭材料的优化制备
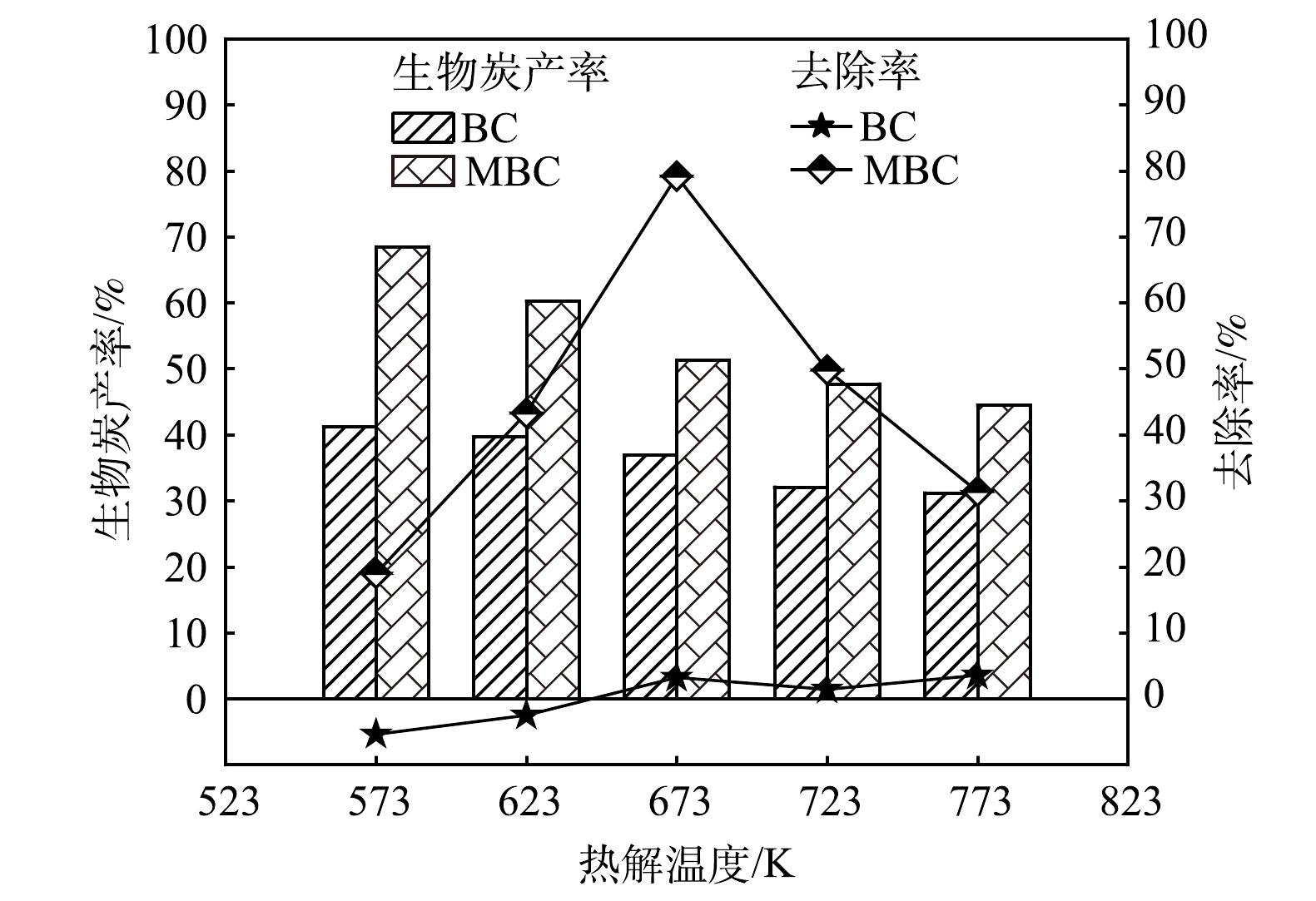
1)热解温度对吸附除磷效果的影响。图1为不同热解温度下制备的生物炭材料吸附除磷性能。在573 K和623 K热解终温下制备的BC对磷均没有吸附去除能力,甚至生物质体内的磷会释放到溶液中,成为新的污染源;随着热解温度的升高,生物炭内部孔隙发育,生物炭比表面积、碱性官能团不断增加,从而暴露更多与磷的吸附结合点位。但由于炭表面金属含量[17]、分布[18]和晶相比例[19]等状况限制,磷吸附能力的提升有限,本实验中,在热解终温为773 K时磷去除率仅为3.55%。MBC随热解温度的升高,吸附除磷效率先升高后降低,673 K时MBC对磷的吸附去除效率达到79.18%。在已有金属改性生物炭的吸附研究中也发现类似规律,热解温度过高和过低均不利于磷的吸附[20]。热解温度过低会影响生物炭孔隙结构的形成与丰度,导致生物炭比表面积较小[21];热解温度过高会破坏生物炭孔隙结构,同时会增加生物炭的黏性,使生物炭吸附剂在溶液体系中分布不均,影响其吸附除磷能力。在相同热解温度下,MBC吸附除磷能力强于BC。其原因是:一方面可能是生物质经NaOH处理后内部孔道杂质被清除,增加了生物质的可负载面积;另一方面,经NaOH处理后,生物质表面及内部残留OH?与Fe2+改性剂生成Fe(OH)2均匀地负载在生物质表面及内部。生物质炭的产率是衡量生物炭吸附剂制备成本的一个重要指标,由图1可知,BC和MBC的产率与热解温度成反比,两者产率分别为31.3%~41.2%和44.5%~68.5%。综合考虑生物炭的产率和吸附效果,选择673 K热解温度下制备的MBC进行后续研究。
2)改性剂浓度对吸附除磷效果的影响。不同浓度FeSO4·7H2O溶液浸渍制备的MBC对磷的吸附去除效果如图2所示。在Fe2+改性剂浓度由0.5 mol·L?1增加至0.75 mol·L?1的过程中,磷去除率的增幅较为明显,吸附容量最高达到21.35 mg·g?1;当Fe2+改性剂浓度增加至1.0 mol·L?1时,对磷的去除效果最优,去除率达到98.48%,此时对磷的吸附容量为24.62 mg·g?1。其原因可能是:生物质表面可供负载面积一定,Fe2+改性剂浓度增加,生物质表面金属离子负载量趋于饱和,并在Fe2+改性剂浓度为1.0 mol·L?1时达到最大;随后,生物质表面负载的金属离子开始堆积,堵塞生物炭的孔隙,使其比表面积减小。因此,后续实验选择1.0 mol·L?1改性剂制备MBC。
2.2. 改性前后生物炭材料的表征结果
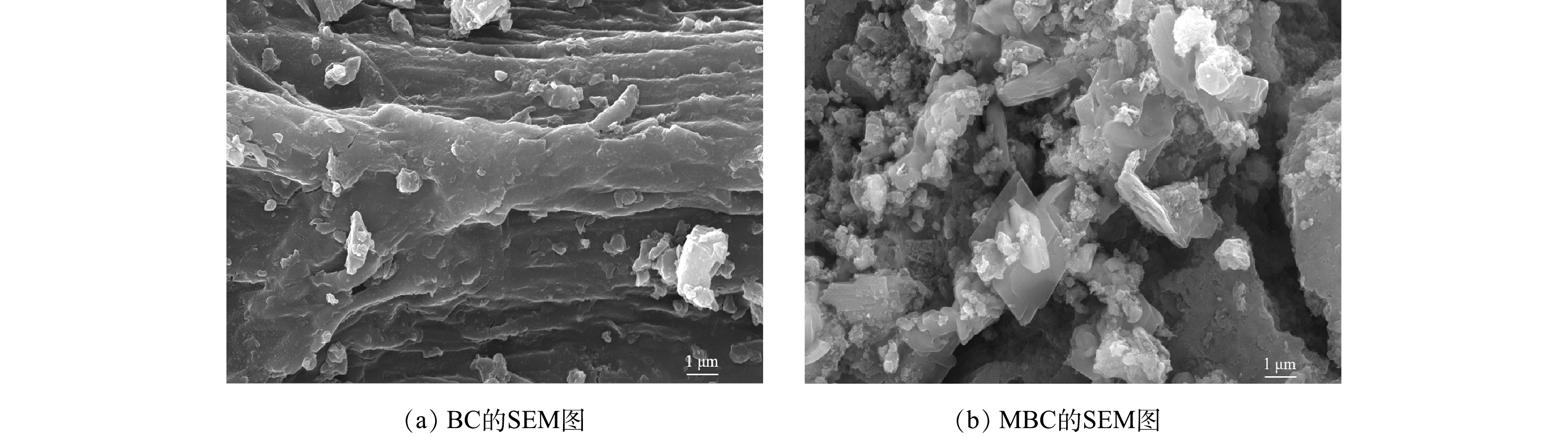
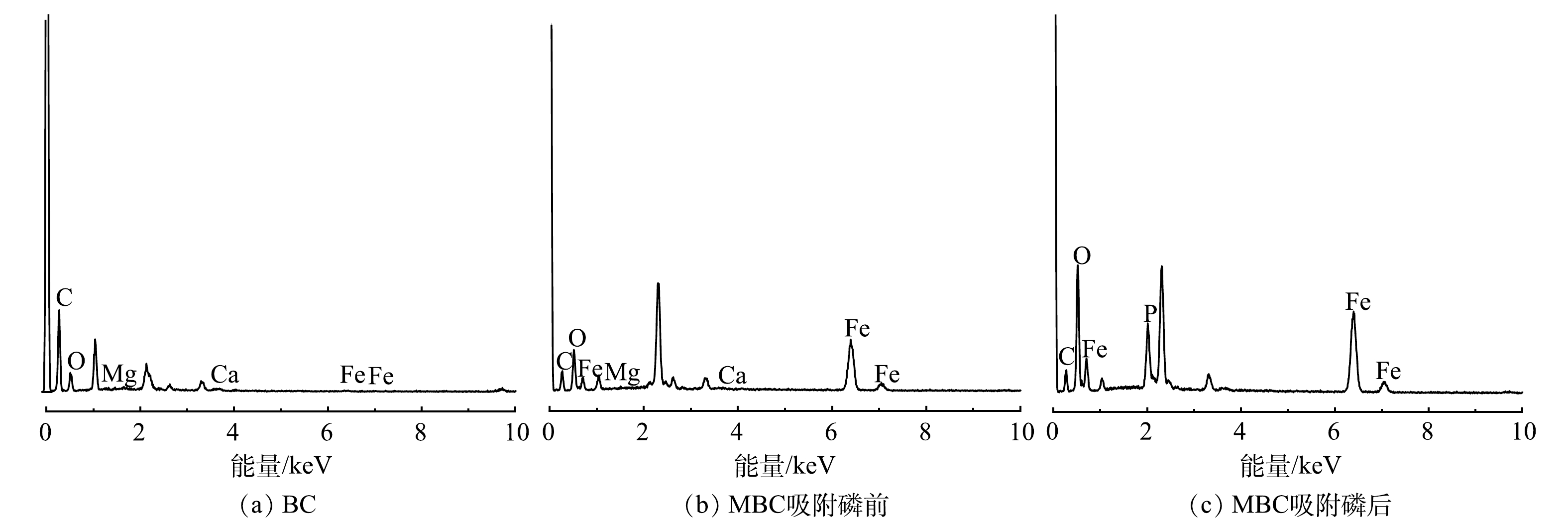
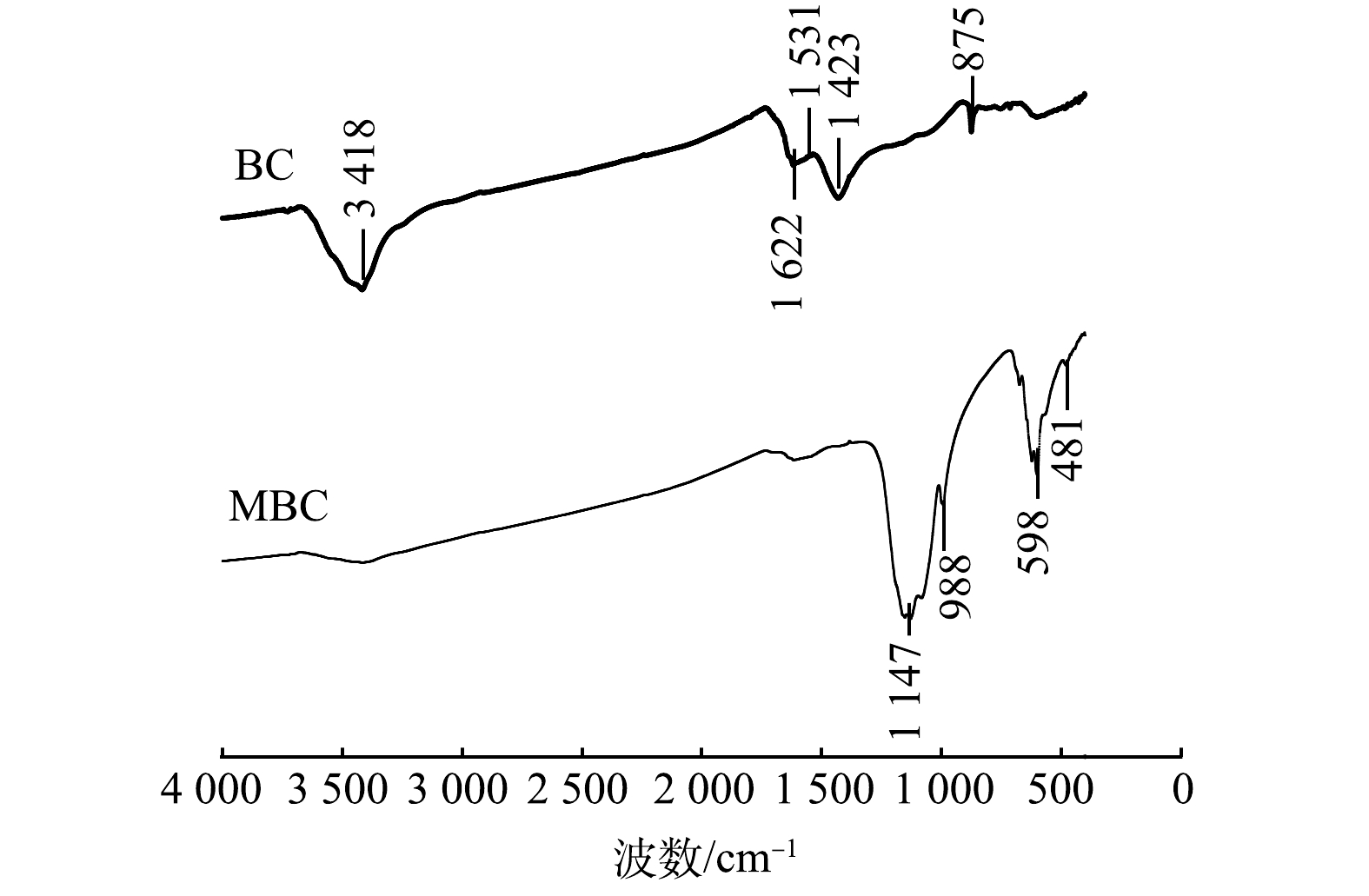
1) SEM-EDS分析。图3(a)、图3(b)分别为BC和MBC的SEM表征结果。可以看出,BC表面存在条状褶皱纹路,附着有一些颗粒;而MBC表面更为粗糙,覆盖着一层片状和颗粒状晶体,且存在众多微孔结构(<2 nm)。图4为生物炭材料的EDS图。对改性前后生物炭表面的元素分析可以发现,BC中C、O、Fe的质量分数为62.8%、22.4%和0.5%,MBC中C、O、Fe的质量分数为31.0%、21.9%和26.9%,表明铁元素被成功负载到BC表面上。吸附反应后,MBC中上述元素的质量分数分别为20.0%、34.4%和27.5%。对比吸附前、后MBC质量分数可知,铁元素含量几乎不变,说明负载的铁氧化合物不易脱落、稳定性较好。2) FT-IR图谱分析。BC和MBC的FT-IR的表征结果如图5所示。BC和MBC在1 622 cm?1附近均存在吸收峰,可能为C=C或酮、羧酸C=O的伸缩振动峰。BC在3 418、1 531、1 423和875 cm?1附近出现吸收峰,可能是酚或羟基(—OH)、C=C、芳香环的C—C伸缩及芳环的C—H振动引起的[22-23]。MBC在1 147 cm?1附近出现吸收峰,可能是由于C—OH和C—O的伸缩振动引起的。这说明MBC中脂肪族组分较多[24-25]。此外,MBC在400~900 cm?1内出现强度不同的吸收峰,说明在此范围有羧基、羰基、酚羟基等官能团存在。对改性前后生物炭的FT-IR图进行对比分析后发现,改性后芳香氢、芳烃等官能团消失,甲醇类、酸、脂肪族化合物等出现,说明较稳定的芳香骨架和羟基依然存在。
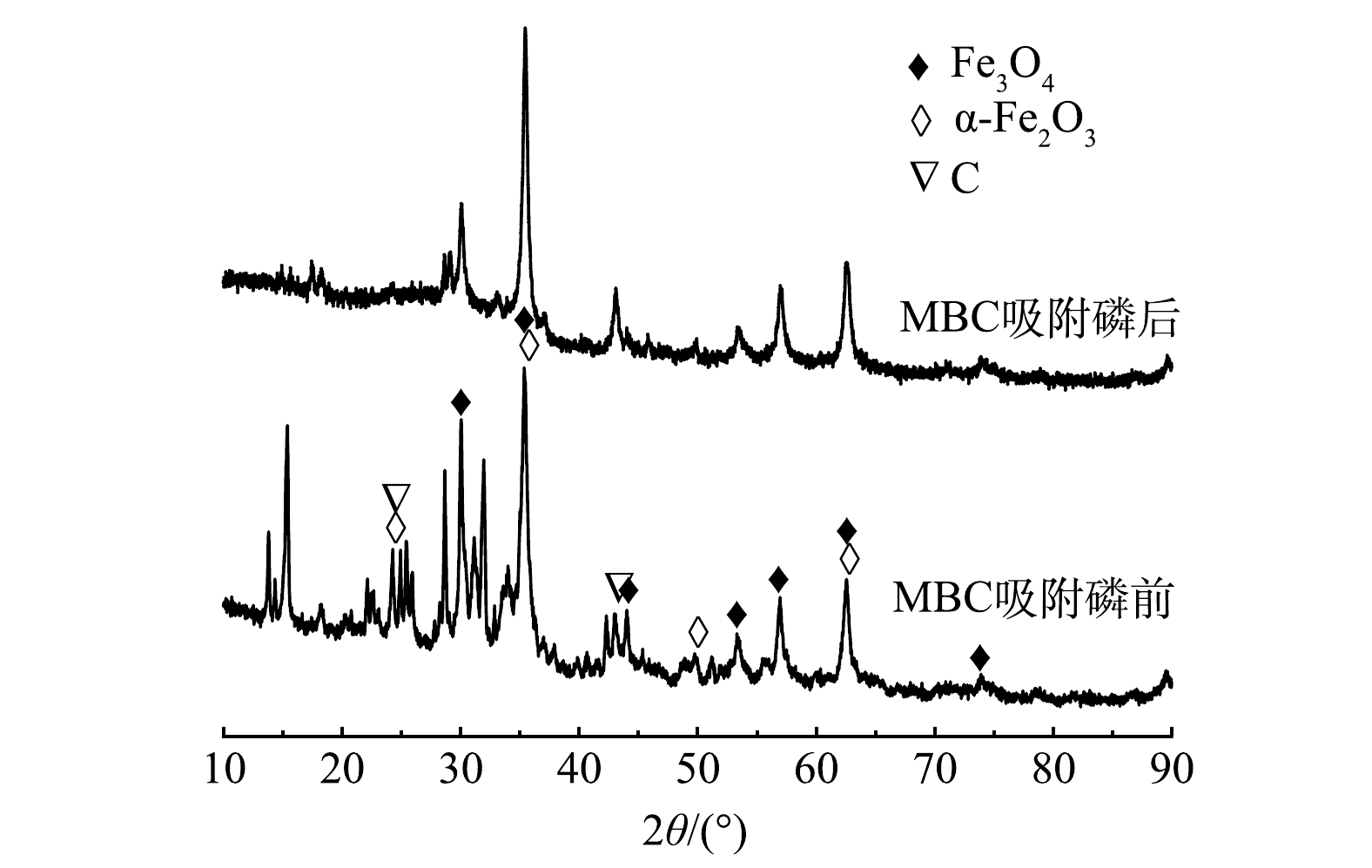
3) X-射线衍射分析。图6为MBC吸附磷前、后的XRD表征图谱。可以看出,在2θ为24.28°、43.18°处出现的衍射峰[26],表明Fe元素已被成功负载在生物炭表面,主要以Fe3O4(标准卡号01-072-2303)和α-Fe2O3(标准卡号00-024-0073)的矿物晶体组成,生物炭材料并未对Fe3O4和α-Fe2O3晶型产生较大影响。MBC在吸附磷后,Fe3O4和α-Fe2O3的峰强度均出现降低,但衍射峰位置并未发生明显偏移。结合改性生物炭前后FT-IR分析结果,可能是Fe3O4、α-Fe2O3和水配位形成羟基化表面,磷酸根离子与羟基发生配位交换作用,另外生物炭表面的铁和磷酸盐复合形成沉淀,促使磷酸盐的去除。
4)元素组成分析。改性前后生物炭材料元素组成分析见表1(ω为百分含量)。MBC与BC相比,ω(N)、ω(C)和ω(H)减少,ω(O)和ω(Fe)增加,可能是高温裂解条件下形成了铁的氧化物。MBC的ω(H)/ω(C)比值较低,说明其碳化程度较高,而高度碳化有助于芳香结构的形成[27];ω(O)/ω(C)比值较高,说明其亲水性较强。(ω(N)+ω(O))/ω(C)比值越大,表示材料极性官能团越多,生物炭的极性也越大。因此,经NaOH预处理后铁改性菖蒲生物炭显著提高了材料的亲水性和极性,有利于生物炭材料对磷的吸附。
5)比表面积与孔隙结构。改性前、后菖蒲生物炭的比表面积、孔径等参数的表征结果如表2所示。改性后生物炭比表面积增加了8.5倍,总孔容增加了5.8倍;改性前、后微孔比表面积所占总比表面积的比例由44.9%增至69.4%,微孔孔容占比由5.7%增加至12.2%;BC和MBC的平均孔径均小于20 nm,说明BC和MBC孔隙以微孔(<2 nm)和中孔(2~50 nm)为主。MBC比表面积增加的原因可能是NaOH浸渍疏通了生物质孔隙结构,同时兼具造孔功能[28],起到了良好扩展微孔作用;另外,生物炭表面和孔隙内部负载了金属氧化物,填充了微孔和介孔孔隙结构,使总比表面积、微孔比表面积和微孔孔容大幅增加,可在吸附磷的过程中提供更多吸附点位,增强磷的去除效果。
2.3. 改性生物炭吸附除磷特性
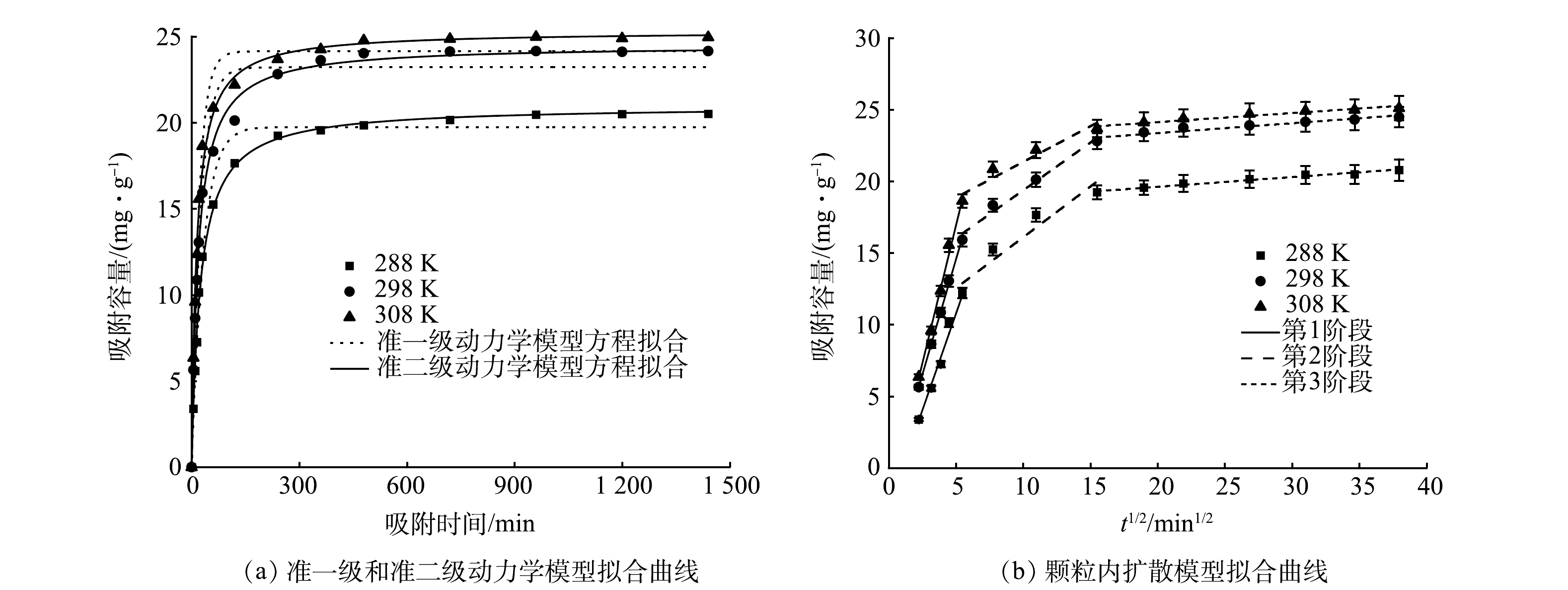
1)生物炭添加量对吸附除磷效果的影响。当MBC投加量为0.05 g·L?1时,磷的去除率分别为97.60%、82.70%和29.48%,吸附容量分别为9.76、16.54和29.48 mg·g?1;当MBC投加量为0.2 g·L?1时,磷的去除率增加至98.80%、97.1%和96.0%,而吸附容量降为2.46、4.86和24.0 mg·g?1;当MBC投加量继续增加时,MBC对磷的去除率基本保持不变,而吸附容量持续下降。其原因是:由于当MBC投加量逐渐增加时,MBC对磷的吸附位点随之增加,并且MBC与水体的接触面积也相应增大,磷酸盐更易与吸附位点结合,从而MBC对磷的去除率逐渐提高。然而,当MBC投加量持续增多,对磷的吸附效果趋于稳定,吸附剂提供的吸附位点过剩时,吸附位点与磷发生竞争吸附;另外,MBC粉末投加过量易发生团聚,导致可供吸附的有效位点减少,不利于磷的去除。考虑经济因素与吸附去除效率,本研究后续实验选用0.2 g·L?1的添加量。生物炭已被证实能够改善土壤结构,加强土壤对养分的吸持能力,促进作物根系的生长与延伸,提高土壤养分的有效性[29]。同时,磷酸盐是植物3种主要养分之一,且是主要肥效成份,故利用磷吸附生物炭能够对土壤中氮、磷迁移特征进行调控,降低淋溶流失,增加土壤中的养分。因此,吸附后的MBC具有农肥资源化利用的潜力,对改善土壤理化性质、促进作物生长具有一定的实际意义。2)吸附动力学。在不同温度下对优选制备工艺下制得的MBC进行磷酸盐吸附实验,并对实验结果进行吸附动力学模型拟合(图7)。由图7(a)可以看出,MBC在前60 min对磷的吸附速率最快,在反应温度为288、298和308 K时,磷的吸附去除率分别达到61%、73.32%和83.4%,吸附容量分别达到平衡吸附容量的74.35%、77.97%和83.57%。在反应60 min后吸附速率减缓,480 min时吸附反应基本达到平衡,吸附容量分别达到平衡吸附容量的96.78%、98.46%和99.28%。经分析可知:前60 min生物炭吸附位点充足且溶液中磷的浓度较高,MBC表面与溶液中的磷酸盐浓度相差较大,使得吸附推动力也大,因而吸附速率较高;在60~480 min,MBC表面多数活性吸附位点被占据,溶液中剩余磷酸盐的吸附推动力减弱,吸附速率逐渐趋于平缓,吸附容量在480 min时增加至接近吸附平衡容量[30-31]。
吸附动力学模型的拟合结果见表3,准二级动力学模型拟合的R2更接近于1,因此,准二级动力学模型能更好的描述MBC对磷酸盐的吸附行为机理。由此说明MBC对磷的吸附主要由化学吸附控制[3,32]。对比相关文献中制备生物炭材料的吸附容量,负载氧化铁的棉秆生物炭(0.963 mg·g?1)[33]、铈改性水葫芦生物炭(35 mg·g?1)[4]和白果壳遗态Fe/C复合材料(1.62 mg·g?1)[27]等,本研究中的铁改性生物炭吸附性能较优。
由图7(b)和表4可以看出,吸附过程分为3个阶段。在颗粒内扩散模型方程中,吸附平衡量qt与吸附时间t1/2呈线性关系,且没有经过坐标原点,说明颗粒内部扩散是MBC吸附磷酸盐的吸附速率控制步骤,但并不是唯一的吸附机制,还可能涉及边界层和薄膜扩散[34]。
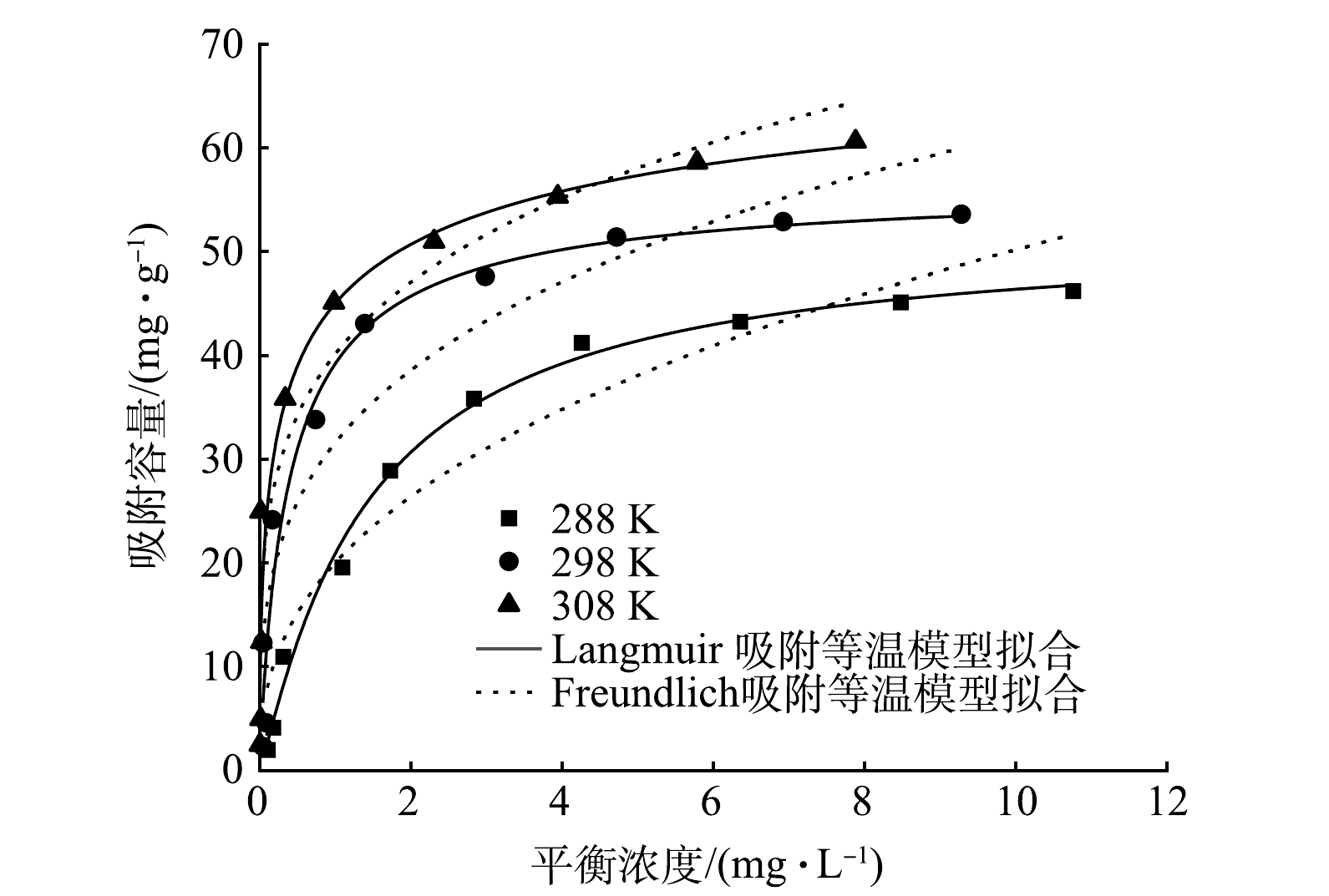
3)吸附等温线。采用Langmuir模型和Freundlich模型对MBC吸附磷的数据进行拟合(图8),拟合参数结果见表5。Langmuir等温吸附模型拟合的R2更接近1,因此,使用Langmuir等温吸附模型描述MBC对磷酸盐的吸附特征更准确,表明MBC对磷酸盐的吸附过程主要为单层吸附[35]。从不同温度下对磷酸盐的吸附量来看,在288、298和308 K时最大吸附量分别为51.82、56.69、76.34 mg·g?1。平衡吸附量随初始磷质量浓度的升高呈现出先增大后趋于平稳的规律,这与MBC表面可吸附位点数量有关,当溶液中磷酸盐质量浓度较高时,吸附竞争激烈,吸附位点逐渐被占据并趋于饱和。同时,磷的最大吸附容量随反应温度的升高而增大,表明吸附过程为吸热反应过程[36]。
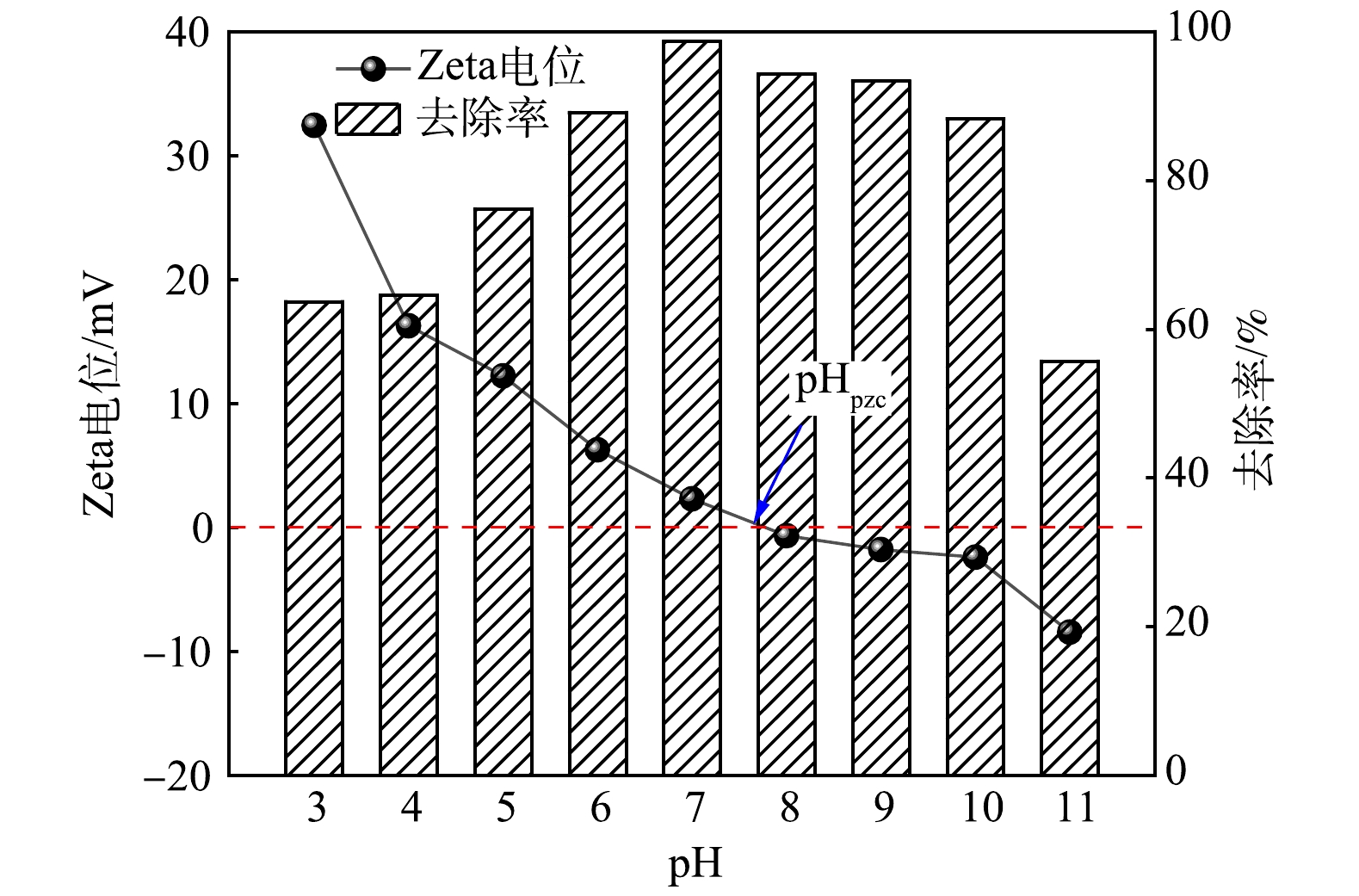
4)溶液pH对吸附除磷效果的影响。溶液pH对生物炭材料吸附除磷效果的影响如图9所示。溶液pH不仅影响污染物在溶液中的存在形式,而且决定着吸附材料表面的电荷分布。调节溶液初始pH为3~11,当pH由3增加至7时,磷去除率由63.7%增加至98.68%,此时,MBC对磷去除率达到峰值;pH继续增加后,MBC对磷的去除率有所降低,当pH=11时,磷的去除率达到最低,仅为55.7%。磷的去除率随pH得变化呈现先升高后降低的趋势,这与施川等[37]的研究结果相似。计算所得MBC的等电位点(pHPZC)为7.74,当pH>7.74时,MBC表面带有负电荷,高pH条件下磷酸盐在溶液中的存在形式为



















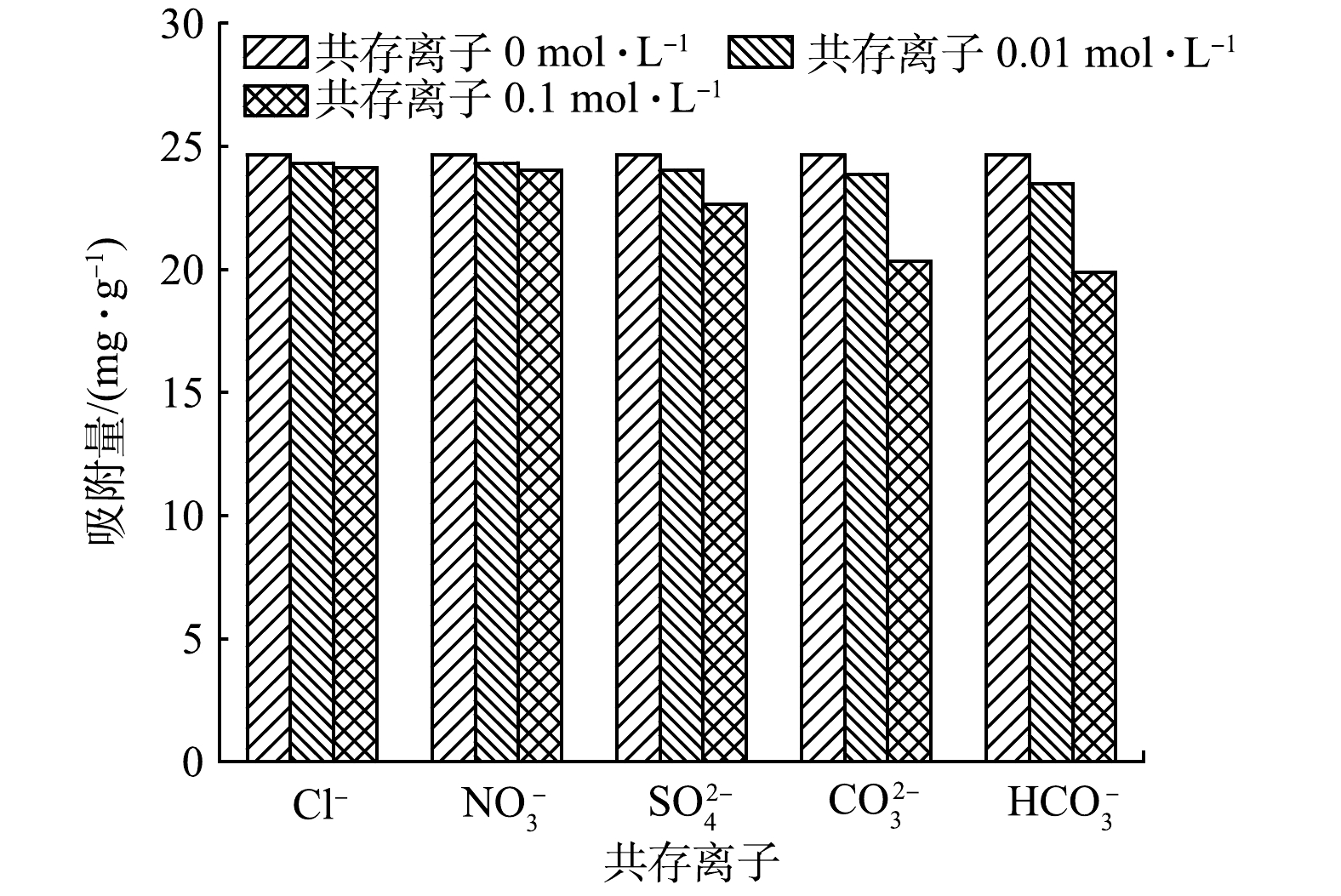
5)共存离子对吸附除磷效果的影响。不同浓度梯度共存离子(Cl?、














2)吸附动力学模型和颗粒内扩散模型的拟合结果表明,准二级动力学模型能更好的描述MBC对磷酸盐的吸附行为机理,吸附机制包括表面吸附、外部膜扩散和颗粒内扩散。等温吸附模型拟合结果表明,Langmuir等温吸附模型对MBC对磷酸盐的吸附特征描述较符合,MBC对磷酸盐的吸附过程主要为单层吸附机制。
3)改性后生物炭材料的亲水性和极性得到提高,总比表面积、微孔比表面积和微孔孔容大幅增加;改性后生物炭材料表面负载了Fe3O4和α-Fe2O3晶体且存在大量羟基等官能团,可促进磷的去除。MBC受溶液pH和共存离子的影响较小,对污水水质、pH具有较宽的适应范围,对磷酸根离子具有较强的选择吸附性。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 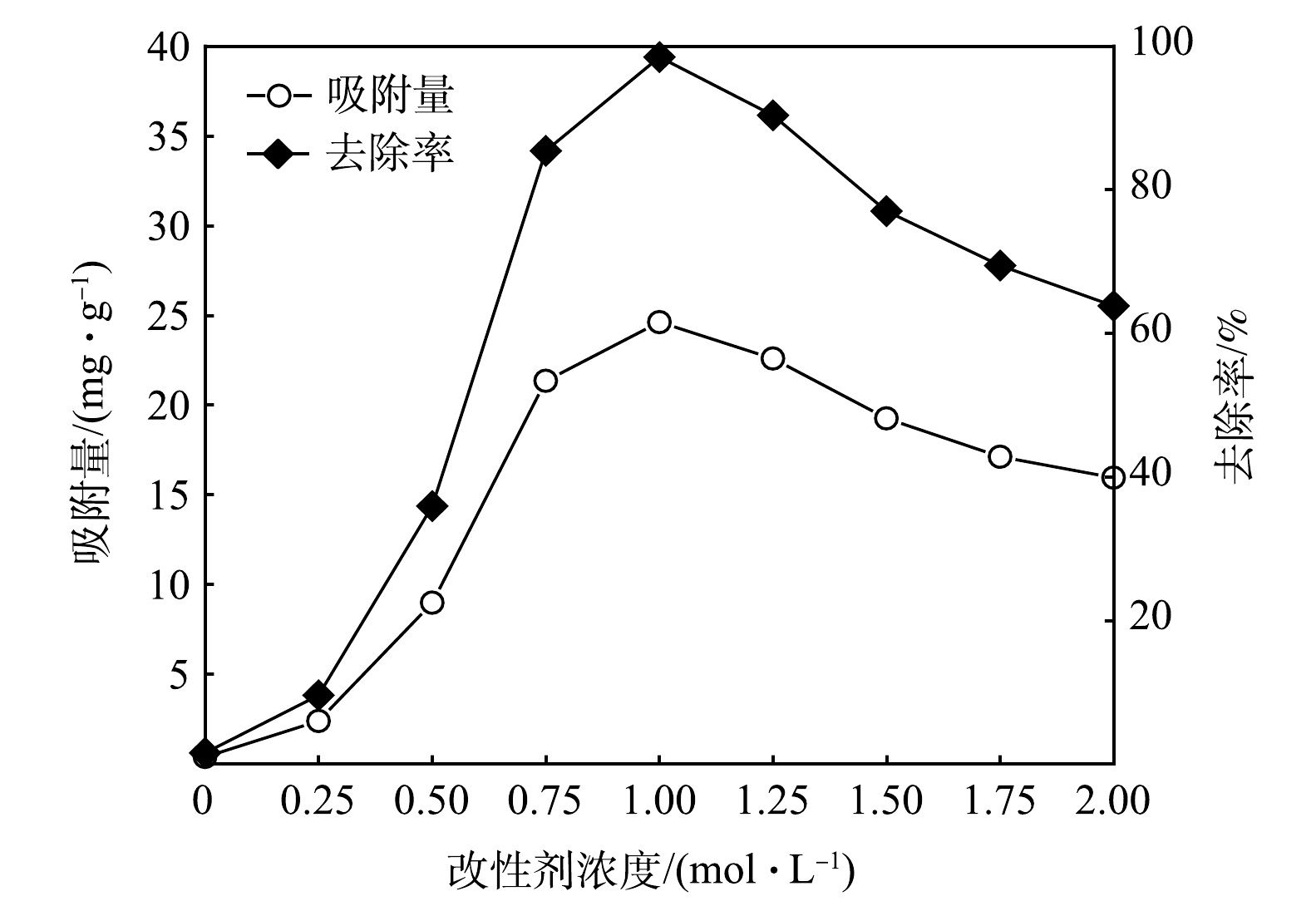
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图