全文HTML
--> --> --> 焦化厂、树脂厂、制药厂、塑料厂、合成纤维厂等企业在其生产过程中会排放大量生物降解性差、毒性高的苯酚废水。若不对所排放的苯酚废水进行有效处理而流入自然水体,即使自然水体中含有微量苯酚也可对环境及人体健康造成极大威胁。当水体中苯酚浓度超过10 mg·L?1就会导致鱼类死亡。用其灌溉农田就会使农作物枯死[1]。若人类长期接触含酚废水也会造成皮肤灼伤,甚至引发神经系统疾病及癌症[2]。因此,《污水综合排放标准》(GB 8978-1996)[3]中强制要求将废水排放的苯酚浓度限制在0.5 mg·L?1以下。由于苯环具有高稳定性,难以采用常规生化降解方法来有效处理高浓度苯酚类废水。因此,如何高效,低成本处理苯酚类废水是当今亟待需要解决的问题之一。目前苯酚废水常用处理方法有:萃取法、活性炭吸附法、活性淤泥法及混凝沉淀法等。这些方法处理苯酚废水存在处理效率低,处理不彻底且易形成二次污染等问题,无法满足当今越来越高的环保需求[4]。然而,作为一种新型水处理工艺,电化学高级氧化工艺(electrochemical advanced oxidation process, EAOPs)可解决难生化降解有机废水的处理难题。EAOPs是利用电极直接或间接氧化生成羟基自由基、活性氯等强氧化性物质,甚至直接电子转移来降解废水中的有机物,具有降解效率高、操作条件温和、氧化彻底、自动化程度高等优点[5],现已被广泛用于难生化降解有机废水预处理以及深度处理领域。EAOPs涉及的主要降解方法包括:阳极氧化(anode oxidation, AO),电芬顿技术(electro-fenton, EF),光电芬顿(photoelectro-fenton, PEF),超声电解(sono-electrolysis, SE)等。
采用EAOPs技术处理有机废水需要消耗大量电能,导致废水处理费用高昂。然而,许多企业在其生产过程中不仅排出大量难生化降解有机废水,而且还排出大量低品位热能。如果能利用企业生产过程所排出的废热来处理废水,不仅可大大降低废水处理成本,也可大幅降低企业能源消耗。为此,我们提出了一种“废热治理废水”的创新技术[6-9]。即,通过热分离方法先将热能转换成工作溶液浓差(化学势)能,然后利用逆电渗析反应器(reverse electro-dialysis reactor, REDR)将工作溶液浓差能转换成有机物降解能。由于溶液热分离技术相对较为成熟,并在实践中得到广泛应用[10-12]。而采用REDR将溶液浓差能转换成有机物的降解能的研究却非常少,公开发表的文献极少[13-18]。因此,本研究工作仅对溶液浓差能驱动的REDR处理难生化降解有机废水进行探讨,不涉及低品位热能转换成溶液浓差能过程。
有关溶液浓差能驱动的REDR处理有机或无机废水的研究,最先是由D'ANGELO[13]在其博士研究工作期间提出的,作者采用REDR对废水中的偶氮染料氧化降解和电镀废水中六价铬的脱毒方面进行了研究[14-17]。ZHOU等[18]采用REDR对废水中氨氮物的降解进行了研究,但仅利用了REDR阳极氧化反应所生产的HClO来降解废水中的氨氮。徐士鸣等[7-9]为了验证REDR阴/阳极氧化降解有机废水的工作机理,分别对REDR阴/阳极独立降解和阴/阳极联合降解偶氮染料(酸性橙Ⅱ)模拟废水进行了实验研究。结果表明,REDR阴/阳极处的还原/氧化反应均能降解废水中的有机物且具有较高的降解率[7]。但也发现采用REDR阴/阳极联合降解有机废水时,其阴/阳极生成物容易相互干扰,从而降低了偶氮染料废水的降解速率[8-9]。
到目前为止,国内外对由溶液浓差能驱动的REDR处理各类有机或无机废水的文献报道极少,尚未发现利用该技术处理苯酚类废水的研究。对于该方式是否可广泛且高效处理各类难生化降解有机废水仍缺乏大量的实验依据。另外,与外电源驱动的EAOPs相比,REDR属于内生电源。工作溶液操作参数及电极液(废水)参数变化对其输出(降解)特性有很大影响。因此,本研究利用溶液浓差能驱动的REDR对有机废水中的苯酚降解情况进行了研究,考察了各操作参数变化对REDR阴/阳极苯酚降解过程的影响规律。其目的是为了拓展REDR在水处理技术中的应用,为后续“废热治理废水”热力循环研究奠定基础。
1)阳极反应[25-27]。阳极有直接和间接两种氧化反应。直接氧化反应机理为[28]:在总膜电势作用下,废水(H2O)流经金属氧化物涂层电极(Ti/IrO2、Ti/RuO2、Ti/PbO2等)表面时发生直接氧化反应而失去电子,产生氢离子(H+)和2种状态的活性氧。其中:一种是废水在阳极上放电并与金属氧化物涂层(MOx)形成吸附的羟基自由基(MOx(·OH));另一种则是吸附的羟基自由基与阳极上现存的氧进行反应,使得羟基自由基上的氧发生转移而形成的更高价的氧化物(MOx+1)。MOx(·OH)和MOx+1均具有强烈的氧化作用,可以氧化降解废水中的有机物。
间接氧化降解反应机理为[29]:在总膜电势作用下,含有氯盐的有机废水流经阳极时,废水中的氯根(Cl?)会失去电子而被氧化成为活性氯(Cl·)。2个Cl·形成的Cl2分子,与水反应生成次氯酸(HClO)和盐酸(HCl)。HClO在水中还会部分电离成H+和ClO?。由于HClO和ClO?也是强氧化剂,也会氧化降解废水中的有机物,且可杀死废水中的各种有害病菌,这对垃圾渗滤液和医院废水的处理尤为重要。
2)阴极反应[30-32]。在总膜电势作用下,阳极产生的2个H+离子(或酸性废水自身电离出的H+离子)会在阴极处获得从阳极放出并经外电路迁移来的2个电子,并与溶解于废水中的O2发生反应,生成过氧化氢(H2O2)。在亚铁离子(Fe2+)的催化作用下,H2O2会被分解成羟基自由基(·OH)和氢氧根(OH?),而Fe2+被氧化成Fe3+,同时,Fe3+又会从阴极获得1个电子被还原成Fe2+。由于·OH具有强氧化作用,因而可以氧化降解废水中的有机物。该反应也称为电芬顿(EF)反应[31-32]。为了有足够多的氧气可参与EF反应,有机废水在进入阴极流道前需要通入空气或氧气,并以气-液两相流动方式流经阴极流道。为了尽可能使空气或氧气与溶液和电极表面接触,REDR阴极多采用多孔介质的气体扩散电极以扩展其反应面积。
实际上,REDR阴/阳电极流道内的有机物降解是一个由大分子降解为小分子再逐渐降解为无机物过程。PIMENTEL等[33]采用高效液相色谱法测定了苯酚在电芬顿作用下的降解途径,苯酚经羟基化首先降解成苯醌、对苯二酚、邻苯二酚等中间产物,然后继续降解为顺丁烯二酸、反丁烯二酸、琥珀酸和乙醛酸,再进一步降解为草酸和甲酸,最终降解为水和二氧化碳等无机物。
2.1. REDR
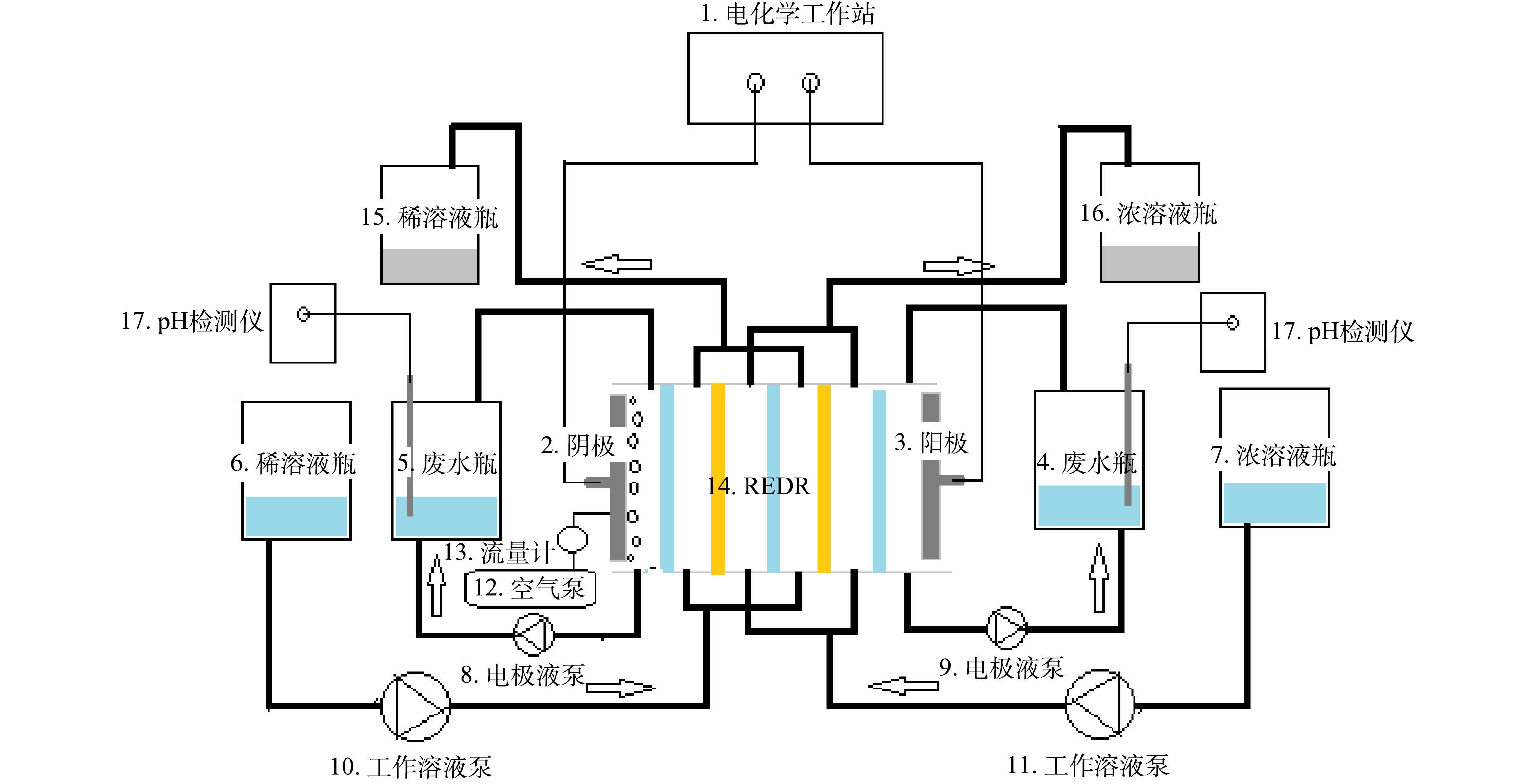
实验中使用的REDR为自制,由日本富士公司生产的40张CEM和41张AEM构成(最外两侧膜采用AEM)。织网隔垫由200 μm的涤纶织网和2张50 μm的TPU热熔胶模压制而成,总厚度仍为200 μm。离子交换膜和织网隔垫外廓尺寸均为20 cm×15 cm。阳极采用1 mm厚的钛镀钌铱板(dimensionally stable anodes,DSA),阴极采用5 mm厚孔隙率为75%的碳毡(气体扩散电极),电极外廓尺寸均为10 cm×10 cm。亚克力材质的外端板外廓尺寸为25 cm×20 cm×30 cm。2.2. 实验系统流程及工作溶液和电极液配制
实验系统采用REDR阴/阳极独立环路降解苯酚方式,其流程如图1所示,其实际照片由图2所示。实验过程为:将配置好的稀/浓工作溶液和模拟苯酚废水分别注入稀/浓溶液瓶(6和7)和模拟废水瓶(4和5)内。开启工作溶液泵(蠕动泵10和11),让稀/浓溶液分别以96 mL·min?1的固定流率(过膜流速为0.2 cm·s?1)流经REDR内部相应流道而产生电势。流经REDR的稀/浓溶液分别存入对应的溶液瓶(15和16)内。启动电极液泵(蠕动泵8和9),作为电极液的模拟苯酚废水分别流经REDR阴/阳电极流道,与电极氧化还原反应产生的强氧化剂作氧化降解反应后流出REDR,并在储存瓶与电极流道之间作循环降解流动,直至达到规定的降解时间。REDR输出电性能参数(电流和电压)由电化学工作站(1)监控。系统中各种检测和运行设备参数如表1所列。工作溶液:NaCl水溶液作为工作溶液,稀/浓溶液摩尔浓度分别为:0.03 mol·kg?1/3 mol·kg?1(浓差比为100)。电极液(模拟废水):由于不含杂质的纯有机废水电导率很低,会使REDR内阻增大而影响REDR电输出特性[18]。而实际有机废水中含有各种金属盐杂质,废水电导率较大。因此,在配制模拟有机废水时,除了在去离子水中添加有机物以外,还要添加少量支撑电解质和EF反应所需的催化剂并调节模拟废水的酸碱度(pH)以适应REDR阴/阳极氧化还原反应的需要。另外,电极液流经电极流道的流速,阴极电极液曝气率,REDR输出电流密度的变化也会对REDR阴/阳极有机废水的降解率产生影响。因此,模拟废水中支撑电解质浓度、pH、电极液流速、阴极电极液曝气率以及REDR输出电流变化对REDR有机废水降解率的影响是本次实验研究工作的内容。实验过程阴/阳电极液配制参数及REDR操作参数变化范围如表2所列。表2中的电流密度是指单位电极投影面积上的电流强度[4]。
工作溶液及电极液配制所采用的各种试剂均为天津大茂公司生产,纯度为分析纯级。溶液配制所采用的去离子水为自产。每组实验降解时间设定为80 min,每次实验重复2次。每次实验所配置的稀/浓溶液量各为8 L,配置的用于REDR阴/阳极独立回路降解的模拟苯酚废水各为500 mL。
2.3. 采样与分析方法
在实验过程中,每间隔20 min分别抽取第4、5号废水瓶内的水样,采用4-氨基安替比林显色法检测模拟废水中的苯酚浓度[34]。通过岛津公司生产的UV-1780紫外可见分光光度仪测试样品吸光度,并依据绘制的标准曲线反推其浓度,再按式(1)计算有机物降解率。式中:ηde为苯酚降解率,%;c0为初始时刻模拟废水中的苯酚浓度,mg·L?1; ct为t时刻取样检出的苯酚浓度,mg·L?1。
3.1. 阳极电极液操作参数变化对苯酚降解率的影响
由于REDR属于内生电源,通过外电路连接的阴/阳两极的电化学反应会相互影响。因而在探索阳极电极液操作参数变化对苯酚降解率的影响时,需固定阴极电极液操作参数:Fe2+浓度为1.0 mmol·L?1、pH为3、电极液泵流速为128 mL·min?1、曝气强度为800 mL·min?1、电流密度为20 A·m?2。1)氯盐(Cl?)浓度的影响。由阳极氧化降解反应可知,阳极氧化降解反应有直接和间接2种情况。而间接氧化降解反应完全取决于废水中Cl?离子浓度。为了探究REDR阳极直接和间接氧化降解苯酚效果,通过改变阳极电极液氯盐浓度进行实验研究。电极液中NaCl浓度变化范围见表2。但需要指出的是,由于本实验采用了与前期研究相同结构的REDR[7-9],REDR最外侧膜仍采用允许阴离子通过的AEM。因此,即使在电极液中不添加氯盐,但工作溶液中的部分氯离子也会通过AEM进入到电极液中。因而在此种情况下,阳极氧化反应中仍会有微弱的间接氧化反应存在。在后续的研究中,将用CEM替代AEM作为隔离电极液与工作溶液的外侧封膜。
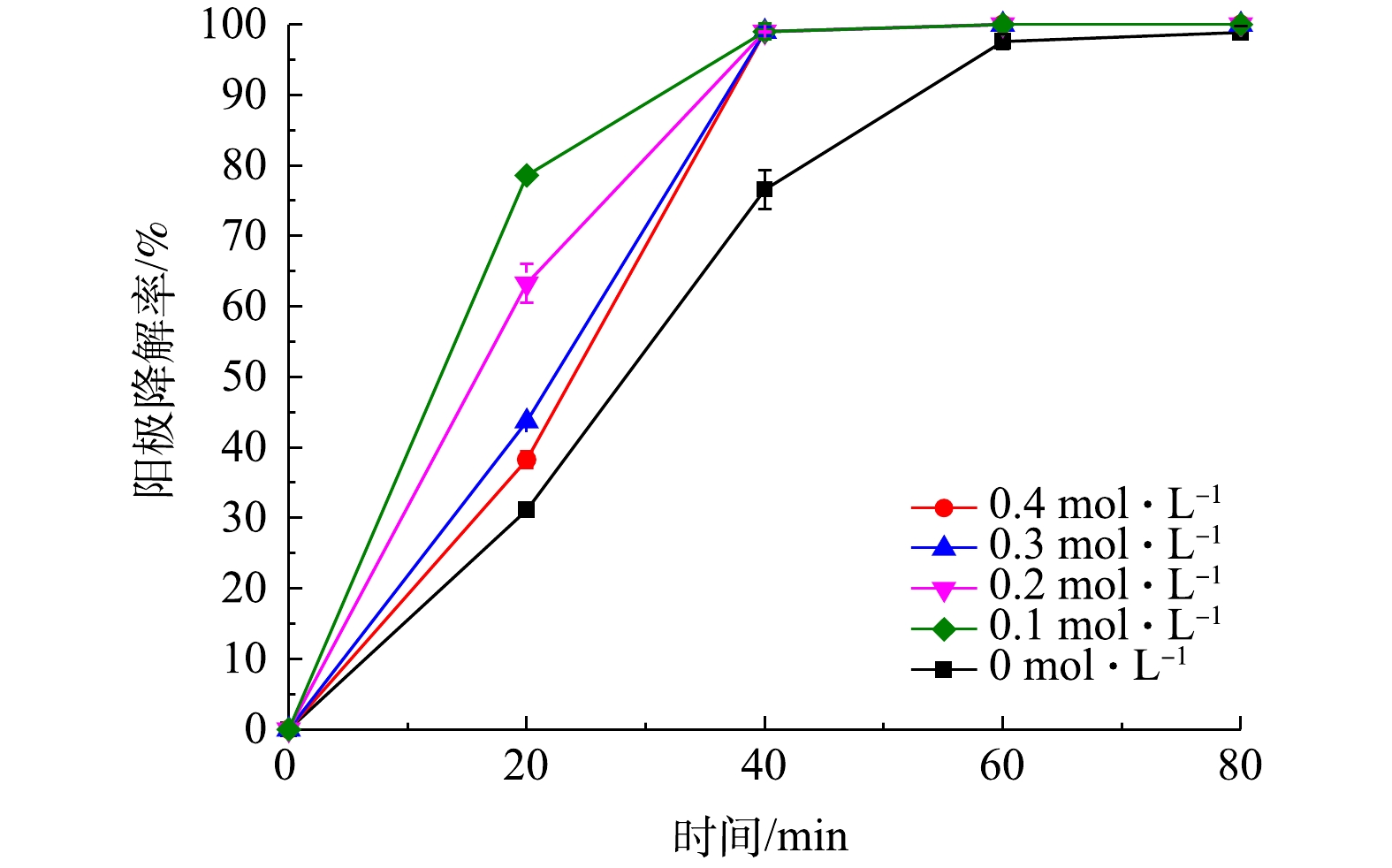
图3为氯盐浓度变化对阳极苯酚降解率随降解时间的影响关系(电极液流率为128 mL·min?1)。由图3可知,无论在电极液中是否添加氯盐,在降解80 min后,阳极回路废水中苯酚降解率均可到达98%以上。但在废水中添加氯盐后,苯酚降解率达到98%时所花费的时间可缩短一半,从而可以降低废水中有机物降解所消耗的能量。但由实验结果也可以看出,废水中的氯盐浓度并非越高越好。当氯盐浓度从0 mol·L?1增加到0.1 mol·L?1时,20 min后苯酚降解率可从31.1%迅速增加到78.6%,降解率增加了153%;但当氯盐浓度增加到0.4 mol·L?1时,苯酚降解率为38.2%,仅增加了23%。在降解40 min后,所有含氯盐的苯酚降解率逐渐趋近于一致。
向模拟废水中添加氯盐:一方面,有助于提高电极液的电导率[18],降低电极室电阻,使得REDR内部电阻损耗减小[4];另一方面,可促使氯离子在阳极处发生析氯反应,这对于增加活性氯浓度具有重要意义。然而随着电极液中Cl?浓度持续增大,高浓度活性氯在体系中会加剧歧化副反应(式(2)),生成氧化电位很低的高氯酸根,进而削弱阳极间接降解废水中苯酚的能力[26]。此外,在阳极电化学反应的作用下,对于某些有机物在降解过程中会因过量Cl?而析出氯气或与氯反应生成具有高毒性、难降解的有机氯。根据PANIZZA等[35]的研究结果,废水中含氯盐条件下2-萘酚降解过程中检测到有少量有机氯化合物生成,但随着降解过程的进行,有机氯化合物逐渐减少至消失。因此,除必须处理高氯盐有机废水外,仅建议向有机废水中添加适量氯盐以提高有机废水的降解率,减少降解时间和水处理能耗。
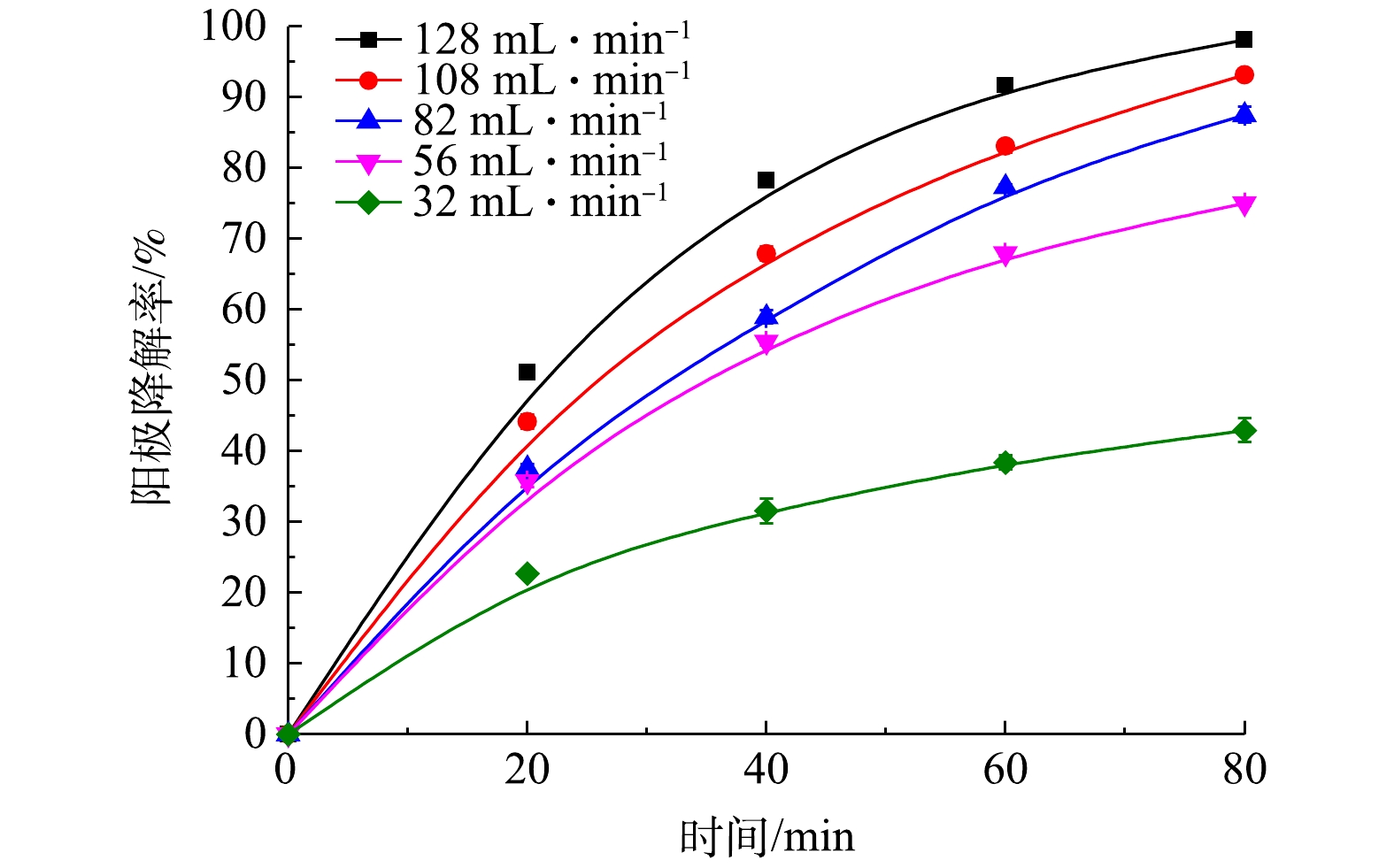
2)电极液流速影响。图4给出了电极液流速变化对阳极环路内模拟苯酚降解率随降解时间的影响关系(电极液氯盐浓度为0.1 mol·L?1)。由图4可见,在降解实验前半阶段(0~40 min)苯酚降解率随电极液流率的增加而迅速提高。当电极液流率由32 mL·min?1增至128 mL·min?1时,降解20 min后废水中的苯酚的降解率由17.1%增加到78.6%,增加了360%。在降解40 min后,苯酚降解率由57.7%增加到98.6%,增加了71%。显然,随着降解时间的延长,电极液流率的变化对废水中苯酚降解率的影响将逐渐减小。当降解时间达到80 min后,在不同的电极液流率条件下,废水中苯酚降解率均趋于一致,达到100%。
实际上有机物氧化降解反应过程是一个传质过程。当电极液流速增大时:一方面降解环路内的有机废水更新率会随之增加,降解反应的电流效率会有所提高;另一方面,电极液流速增大也会改善电极处的浓差极化现象,使得在电极表面上生成的氧化剂从电极表面向主流区的扩散速率增大,废水与电极表面之间的传质系数提高,废水中的有机物降解率有所提升[18]。但是,随着降解时间的延长,废水中有机物浓度逐渐降低,使得氧化剂与有机物之间的反应过程传质驱动力降低,降解反应的电流效率也随之降低。这样就造成无论电极液流率是否变化,当降解时间达到80 min后,废水中的有机物降解率趋于相同。因此,若将苯酚废水目标降解率设定为98%,则可以通过提高电极液流率来缩短降解时间,以降低废水处理时间和能耗。
尽管从电化学反应原理看,当有机废水流经电极时,其流速和有机物降解速率有一个先增加,然后再达到后饱和的过程。但由图4可见,随着模拟废水流率增大,单位时间内苯酚降解率也在增加。其原因可能在于,因驱动模拟废水流动的蠕动泵流量变化为0~128 mL·min?1,当其达到最大流率时电极流道内的最大流速尚未达到其反应饱和时对应的流速所致。
3.2. 阴极电极液操作参数变化对苯酚降解率的影响
在对阴极电极液操作参数变化对苯酚降解率的影响关系研究时,也需要固定阳极电极液操作参数为:氯盐浓度为0.1 mol·L?1、电极液流率为128 mL·min?1、初始pH为10、电流密度为20 A·m?2。1)亚铁离子(Fe2+)浓度的影响。图5给出了亚铁离子(Fe2+)浓度变化对REDR阴极环路模拟苯酚降解率的影响关系(电极液pH为3、曝气强度为800 mL·min?1、电极液流率128 mL·min?1)。由图5可见,Fe2+浓度变化对模拟废水苯酚降解效果起决定性作用。在Fe2+浓度从0 mmol·L?1逐渐增加到2.5 mmol·L?1过程中,废水中苯酚降解率呈先升后降趋势。当Fe2+浓度为0 mmol·L?1时,阴极还原反应仅生成H2O2。尽管H2O2也是一种氧化剂,但其25 ℃时的氧化电位仅有1.78 V,远低于相同温度下的自由羟基(·OH) 2.80 V的氧化电位。所以,此时阴极反应的苯酚降解速率较低。但由图5也可看出,即使向模拟苯酚废水中添加少量亚铁离子(0.5 mmol·L?1),苯酚降解速率迅速增加。与不添加亚铁离子的苯酚废水相比,当废水中亚铁离子浓度为0.5 mmol·L?1时,经80 min降解后苯酚降解率由57.3 %升高到89.0%。这说明废水中加入亚铁离子后会产生EF效应,会将阴极还原反应生成的H2O2分解成·OH和OH?1,使得废水中有机物的降解速率提高。
由图5还可见,继续增加亚铁离子浓度到1.0 mmol·L?1,在相同降解时间内苯酚降解率可达到最大。而且与不添加亚铁离子时的情况相比,降解时间越短,降解率的增幅越大。当降解时间达到40 min后,废水中无亚铁离子时的苯酚降解率为38%,而亚铁离子浓度为1.0 mmol·L?1时的苯酚降解率为78.6%,降解率增加了107%。而降解时间达到80 min后,废水中苯酚降解率从57.3 %增至98.1%,降解速率仅增加了71%。这一现象表明,在一定的亚铁离子浓度条件下,增加Fe2+浓度促使反应生成更多的·OH,会提升REDR阴极电芬顿反应的氧化降解能力。然而,继续增加Fe2+浓度使废水中的亚铁离子浓度超过1.0 mmol·L?1,过量铁离子(Fe2+、Fe3+、FeOH+)会与自由基(·OH、HO2·等)发生副反应而影响其降解效果,阴极环路苯酚降解率开始出现下降趋势。因此,当Fe2+浓度为1.0 mmol·L?1时,REDR阴极EF反应降解苯酚的效果最佳,此结论与班福忱等[34]对EF法降解废水中有机物研究所取得的结论一致。
2) pH的影响。由阴极反应可知,EF反应过程需要消耗H+离子,因此,需要在酸性环境条件下进行。对于独立的阴极有机物降解环路,在EF反应过程中废水的pH会升高。为了维持EF反应,必须向废水中不断添加稀硫酸,保证废水中有足够的H+离子浓度以维持EF反应需求。而反映废水中H+离子浓度就是废水的pH。图6给出了苯酚废水pH变化对阴极环路苯酚降解率的影响(Fe2+浓度为1.0 mmol·L?1、曝气强度为800 mL·min?1、电极液流率128 mL·min?1)。由图6可见,在相同的降解时间内,废水的pH由2.0逐渐升高到4.0时,阴极环路模拟苯酚降解率呈先增后降的趋势。当pH低于3.0时,因过量的H+离子会使阴极降解能力减弱,当pH为2.0时,降解80 min后,废水中苯酚降解率仅为38.5%。其原因可能是阴极析氢副反应(式(3))争夺电子所致。因为酸性溶液中电极液pH越低,越易发生析氢反应[36]。
然而,当废水pH超过3.0时,阴极环路苯酚降解率也会迅速降低;当pH为4.0时,经80 min降解后,阴极环路模拟苯酚降解率由最高的98.1%迅速降至15.5%。高的废水pH抑制阴极环路降解效果的主要原因有以下3点:pH越高意味着废水中的H+浓度越低,越不利于EF反应生成H2O2;在酸性环境中,pH越高,EF反应生成的H2O2越易分解成H2O和O2;pH越高,Fe2+离子越易与OH?根结合,生成氢氧化物沉淀而失去催化活性[37]。因此,通过本研究,对于REDR阴极环路降解苯酚时,将pH控制在3.0左右可获得最佳降解效果。
3)电极液流速影响。与阳极氧化降解类似,阴极电极液流速变化也会影响阴极环路内模拟废水中苯酚的降解率,如图7所示(曝气强度为800 mL·min?1、pH为3、Fe2+浓度为0.1 mmol·L?1)。由图7可见,当电极液流速从32 mL·min?1逐渐升高到128 mL·min?1时,阴极环路内模拟废水中苯酚的降解率也随之逐渐增加。其原因与阳极氧化降解过程电极液流率升高导致有机废水降解率增加的原因相同。与之不同的是,在低流率(32 mL·min?1)下,经80 min降解后,阴极环路内废水中苯酚降解率仅为42.9%,而阳极环路苯酚的降解率则可达到与128 mL·min?1大流率下100%的降解率。因此,阴极环路电极液流率对模拟废水有机物降解率的影响更大。因电极液蠕动泵最大流率的限制,没有继续进行更大流率下阴极环路苯酚降解的实验研究。
4)曝气强度的影响。EF反应过程电极液中氧浓度直接影响着EF反应对有机物的降解效果。图8为曝气强度变化对阴极环路模拟苯酚降解率的影响(pH为3、Fe2+浓度为0.1 mmol·L?1,电极液流率128 mL·min?1)。由图8可见,当曝气量从0 mL·min?1逐渐增加到1 000 mL·min?1时,阴极环路苯酚降解率先逐渐增大,后保持不变。当曝气量为0 mL·min?1时,经40 min降解后,废水中的苯酚降解率可以达到17.0%,后续再增加降解时间,苯酚的降解率将不再变化。其原因在于,在模拟废水配制过程中需要通过搅拌器将各种组分溶入去离子水中。敞口长时间搅拌也会使得模拟废水的氧溶解度接近或达到饱和。即使在无曝气条件下,溶解于模拟废水中的氧也会参与阴极的EF反应,直到溶解于模拟废水中的氧被完全耗尽。
然而,曝气强度达到一定值(800 mL·min?1)后再继续增大曝气强度,阴极环路苯酚的降解速率不再升高。其原因在于,当电流密度恒定时,阴极还原反应生成H2O2所需的氧气量也已确定,当实际输入的氧气量超过反应所需的氧气量时,继续增加曝气强度不仅不会增加H2O2生成量,反而会使溶解于废水中的过量O2与Fe2+发生氧化反应,导致溶液中亚铁离子量减少而抑制EF反应。
3.3. 电流密度的影响
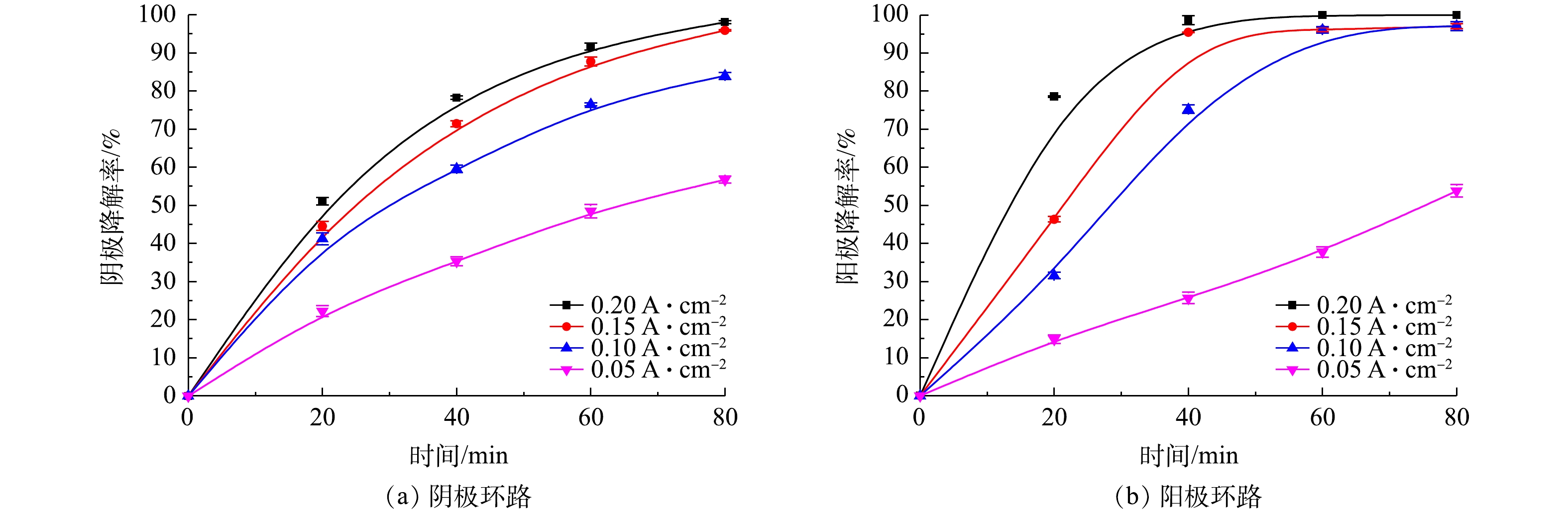
电化学法处理有机废水的过程实际上就是一个电子交换的过程,而电流强度则表征了单位时间电子的交换量。因此,REDR输出电流密度大小直接影响其阴/阳电极环路内苯酚的降解效果。图9给出了REDR输出电流密度变化对阴/阳各环路内模拟苯酚降解率的影响。实验条件为:阳极电极液、氯盐浓度为0.1 mol·L?1、电极液流率为128 mL·min?1、初始pH为10;阴极电极液:pH=3、Fe2+浓度为0.1 mmol·L?1、曝气强度为800 mL·min?1、电极液流率128 mL·min?1。由图9可见,当REDR输出电流密度从5 A·m?2逐渐增加到20 A·m?2时,REDR阴/阳电极各环路内模拟废水中的苯酚降解率均随之而增大,尤其是对阳极环路的苯酚降解率影响更大。其原因在于,随着电流密度的增加,单位时间内REDR阴/阳极反应产生的氧化剂量相应增加,导致单位时间内废水中的有机物降解率提高。当电流密度达到20 A·m?2且降解时间到达80 min时,阴/阳极环路模拟苯酚降解率分别达到98.1%和100%。由图9还可知,尽管REDR输出电流密度增加会使REDR阴/阳电极独立环路苯酚的降解率保持持续增长态势,但增幅却随之减缓。其原因在于,随着电流密度的增大,阴/阳电极流道内质量传输控制会发生变化并有副反应产生[26]。大电流密度情况下,有机物降解过程传输动力学由电荷传输控制转向质量传输控制,电极处的被降解物质逐渐受控于质量传输过程而非电荷变化数目,导致降解过程电流效率降低。另外,过量电子交换也会增加阴极和阳电极的析氢、析氧等副反应发生的概率。然而,对于属于内生电源的REDR装置而言,其电输出特性与RED电堆输出特性相同,输出电压随输出电流几乎呈线性下降关系[38]。因此,即使是在短路条件下,其输出电流也有限[39]。本次实验所用的由40对膜所构成的REDR,当输出电流密度为20 A·m?2时,其端(输出)电压仅有0.76 V。需要注意的是,对于REDR的输出电压是膜电势减去电极氧化还原电势和内阻损耗电势后的电势。因此,REDR输出电压变化仅表示其对应的输出电流变化。当电路短接时,REDR的输出电压为0 V,而输出电流达到最大值。
2)阴极环路苯酚降解率会受Fe2+浓度,pH,电极液流率,曝气强度及电流密度的影响。在实验参数的调整范围内,环路内苯酚废水Fe2+浓度和pH的逐渐增加对废水中苯酚的降解率呈先增后减的趋势;而电极液流率和曝气强度的逐渐增加对废水中苯酚的降解率基本呈升高的趋势,但当曝气强度达到800 mL·min?1后废水中苯酚的降解率达到最大,再继续增加曝气强度苯酚降解率不再变化。
3)电流强度变化对REDR阴/阳极环路苯酚降解率有很大影响。随着电流密度的增加,阴/阳极环路苯酚降解率逐渐升高,而REDR的输出电压随之降低,但REDR的输出电压变化不影响REDR阴/阳极环路内苯酚的降解率。
4)对于在电流密度为20 A·m?2、浓度为50 mg·L?1、总量各为500 mL的模拟苯酚废水,阴/阳电极液流速同为128 mL·min?1时,经80 min处理后,阳极环路废水中氯盐浓度为0.1 mol·L?1,苯酚降解率达到100%;而阴极环路废水中Fe2+浓度为1.0 mmol·L?1、pH为3、曝气强度800 mL·min?1时,苯酚降解率达到98.1%。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 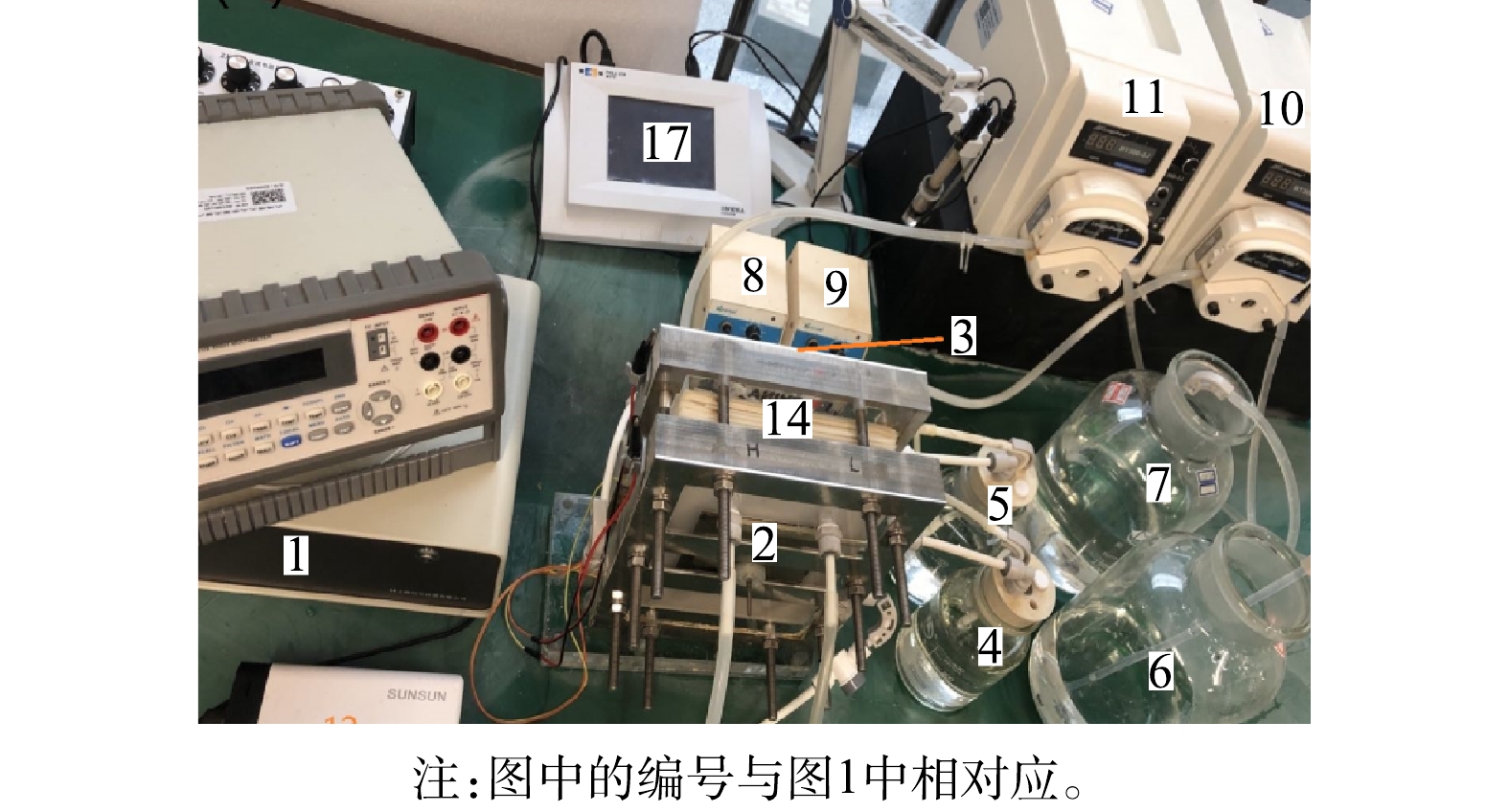




 点击查看大图
点击查看大图