全文HTML
--> --> --> 根据活性微生物在污水中的生长条件和生长状态,生物处理技术分为悬浮生长工艺(活性污泥法)和附着生长工艺(生物膜法)[1]。在附着生长处理系统中,微生物(细菌、真菌、藻类、微型动物等)会借助水力动力和自凝聚作用黏附于载体(填料)上,形成微生物及其代谢产物所组成的膜状活性体系生物膜[2]。生物膜特性直接决定水处理效果,研究者们采用各种参数来表征生物膜特性。常采用生物量(MLSS)、活性生物量(MLVSS)表征活性微生物数量。采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)或共焦激光扫描显微镜(CLSM)揭示生物膜结构与形貌[3-4],可以看出,生物膜具有复杂的三维结构,由细胞团簇、孔道和胞外聚合物(EPS)组成。EPS是分布于细胞表面的高分子化合物,由微生物细胞代谢、自溶、脱落及进水基质组成,对维持生物膜结构完整性和代谢产物传质通道的畅通性起着至关重要的作用。根据EPS在生物膜中位置,可分为溶解性EPS(外层,S-EPS)、松散结合型EPS(中层,LB-EPS)和紧密结合型EPS(内层,TB-EPS)[5-6]。一些生化特性指标,如脱氢酶活性(DHA),也常用来表示生物膜微生物活性[7]。
微生物在载体表面快速、稳定地附着是生物膜法成功的基础。影响微生物附着的因素可归纳为微生物特性、载体特性、环境特性3个方面[8],其中生物载体是最基本的、也一直是生物膜领域的研究热点。有研究表明,载体类型[9]、比表面积[10]对附着在载体上的生物膜特性有显著影响。沸石拥有非常高的比表面积(2 000 m2·g?1),但其表面多数微孔环境(1~1.5 nm)难以被微生物利用,生物膜难以更新;高分子有机材料因其优越的物理结构、低廉的成本而广泛应用于污水处理,但表面化学特性(电荷性、生物亲和性等)较差,导致生物膜在形成速度、数量、紧密度等方面存在问题。载体尺寸与孔径大小同样对生物膜的数量、结构和活性有着较大的影响[11]。NGUYEN等[12]以不同尺寸海绵作为载体,在厌氧和好氧下进行挂膜实验,结果表明,中等尺寸(2 cm×2 cm×2 cm)拥有最佳的生物膜量和废水处理效果。AHMAD等[13]同样发现中等尺寸(15 mm)聚氨酯泡沫有利于维持好氧区与厌氧区之间的平衡。
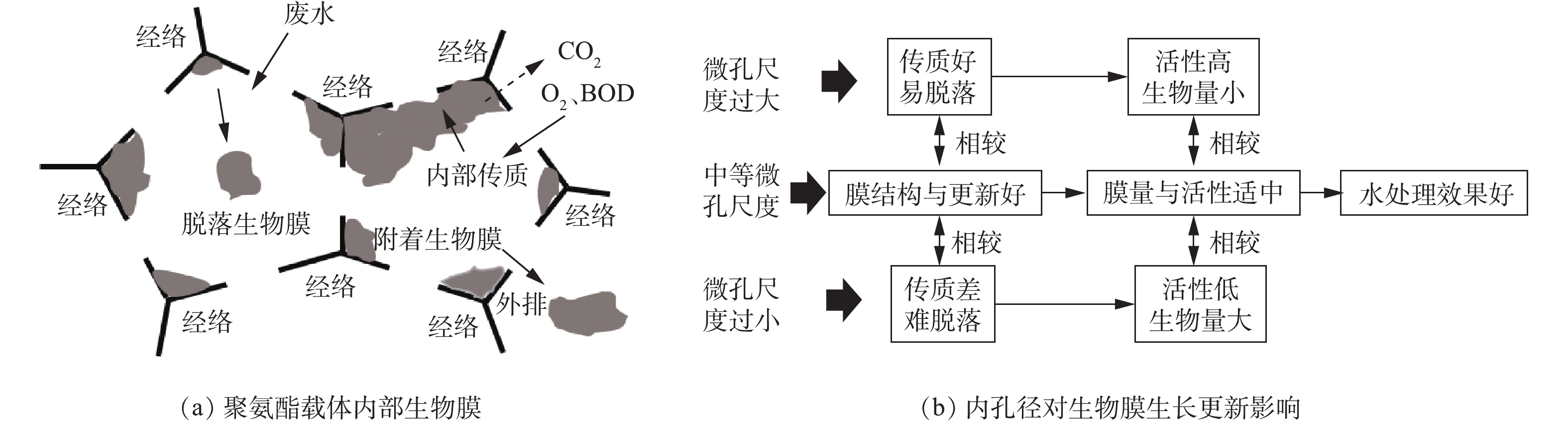
在已有的报道中,对于载体表面物理结构和载体外尺寸研究较多,但对载体内部孔径及其生物膜特性研究很少。微孔孔径小的载体比表面积大,生物膜可附着面积多,但微孔中老化的生物膜难自行从孔隙中排出,会因堵塞而使内比表面积锐减,不能正常发挥应有净化作用[14]。适当扩大载体内部孔径有利于提高生物量与废水处理效率[15],但会增大水力剪切作用造成生物膜脱落,且不利于载体内部厌氧氨氧化反应[16]。因此,载体内部孔径过大、过小均不利生物膜生长与脱落,不利污水处理。载体内理想的微孔孔径不仅可以为生物膜附着和生长提供足够的空间,而且可促进微生物细胞与基质之间物质扩散和氧传递。本研究从生物膜生物量、EPS组分、DHA和生物膜结构等方面,考察了载体微孔孔径对生物膜特性的影响,分析了不同孔径载体废水处理效果,探索了载体内部微孔孔径与生物膜特性的相关性,以期为从内部微孔孔径角度合理选择与研发新型载体提供参考。
1.1. 实验载体和反应器
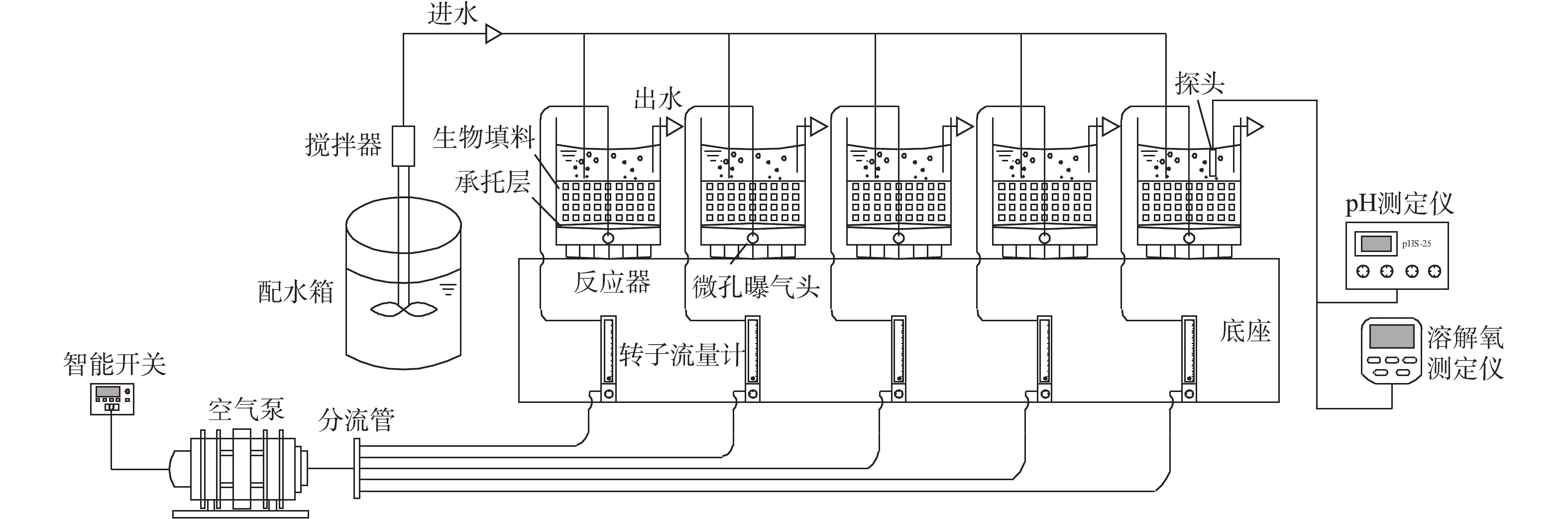
实验载体为购自市场(昆山茂祯电子有限公司)的5种孔径(0.6、1、2、3、4 mm)聚氨酯过滤海绵,加工成约10 mm×10 mm×10 mm的立方体小块(R1、R2、R3、R4、R5)。用0.85%乙醇溶液浸泡1 d,取出用蒸馏水清洗,自然晾干后待用。不同载体性能参数如表1所示。平均孔径反映载体内部微孔孔径特征;孔隙率为材料内部孔隙体积占其总体积的百分率,采用浸泡介质法[15]测定;表观密度为单位体积载体的干质量,采用容重法测定,孔隙率和表观密度反映载体孔径数量和利用率;空隙率为单位体积载体所具有的空隙体积比,采用体积法[17]进行测定;亲水性表征载体的亲水性能,以持水倍率[15]表示。实验装置如图1所示,主体由5根材质、尺寸相同柱状有机塑料柱并联构成。反应柱直径为10.20 cm,高度为23.10 cm,有效容积为1.5 L,各反应器中载体的体积填充率均为40%。反应器在室温(20±5) ℃下运行,由空气压缩机供氧,转子流量计控制供气量,维持反应器中DO浓度为2.58~5.24 mg·L?1,使用智能定时器控制曝气时间。
1.2. 实验用水和接种污泥
在自来水中分别添加葡萄糖、氯化铵、磷酸二氢钾,并补充微量元素浓缩液作为微量元素来源[12],配制成人工模拟废水,采用磷酸缓冲溶液维持进水pH为7.5~8.0。模拟废水基本组成如下:(551.19±32.87) mg·L?1 COD、(31.16±4.41) mg·L?1采用接种挂膜法进行挂膜启动,污泥取自马鞍山市某污水厂曝气池,清洗后闷曝48 h,再将污泥(4 000 mg·L?1)投入各反应器中。
1.3. 实验方法
在整个实验期间,采用序批式生物膜法(SBBR)运行,每天运行2个周期,每个周期包括曝气(10 h)、沉淀(1.5 h)、排水与进水(0.5 h)。在挂膜期间,为保持接种污泥量,每周期换水率为50%。15 d后,载体内表面均出现分散的污泥颗粒,反应器换水率调整到100%。1.4. 生物膜特性分析
使用指标MLSS、MLVSS表征生物膜量,EPS表征生物膜化学组成,f、DHA表征生物膜活性;使用SEM观察生物膜微观结构与形貌特征。根据报道的方法[18],在载体挂膜后,将待测样品剪切成2 mm×2 mm×1 mm的小块,浸没于2.5%的戊二醛溶液中,放置于4 ℃冰箱,固定1.5 h;取出后,再采用0.85%的生理盐水轻微漂洗固定样品3次,每次10 min;接着依次利用30%、50%、70%、90%、100%的乙醇溶液对样品进行梯度脱水,脱水时间为15 min,脱水后冷冻干燥;最后,用离子溅射镀膜仪进行喷金处理。处理完成后,采用扫描电镜(SEM,JSM-6490LV,日本)观察拍摄。
生物膜MLVSS、MLSS采用重量法[19]测定,将MLVSS与MLSS的比值记作f。EPS采用加热法进行分层提取[20],其中PN和PS分别采用改进的Lowry法[21]和苯酚-硫酸法[22],将两者之和作为EPS总量。对载体成熟生物膜EPS进行分层分质分析,外层S、中层LB、内层TB中的EPS量分别以S-EPS、LB-EPS、TB-EPS表示;各层蛋白质和多糖分别以S-PN、LB-PN、TB-PN和S-PS、LB-PS、TB-PS表示;总蛋白质、多糖、EPS分别以Tol-PN、Tol-PS、Tol-EPS表示。
DHA采用改进的TTC法[7]测定。在测定样品加入所有试剂后,不直接进行水浴,而是先放入4 ℃冰箱低温冷藏24 h,再进行水浴与萃取,可使TTC扩散到整个生物膜层厚度,提高TPF萃取量。
1.5. 废水理化特性分析
COD、1.6. 数据处理与分析
采用Excel对测量数据统计,平行样取均值;采用Origin与CAD完成相关图表制作;采用SPSS19软件进行载体内微孔孔径与生物膜特性、水处理效果相关性分析。2.1. 微孔孔径对生物膜特性的影响
微生物在载体表面形成生物膜是一个不断更新的动态过程,大量游离细菌逐渐固定在载体上,并不断地固着繁殖、累积、老化、脱落,使生物膜不断地维持与环境相符的数量和活性[23]。本研究中的反应器共运行75 d,除去15 d接种期外,根据生物膜量与活性的变化规律,分为3个时期[24]:挂膜增殖期(0~15 d)、稳定增殖期(15~45 d)和成熟稳定期(45~60 d)。不同反应器内载体生物膜量的变化情况如图2所示。挂膜增殖期,丰富的营养物质使各微孔载体微生物迅速增殖,载体上生物膜量逐渐累积且变幅较大,微孔孔径对生物膜量与f的影响并不显著,小孔径载体(R1~R3)生物膜的MLVSS、MVSS略优于大孔径载体(R4、R5)。而在生物膜成熟稳定后,小孔径载体的生物膜量显著大于大孔径载体,其结果为R1((27.02±1.06) mg·cm?3)>R2((25.85±2.30) mg·cm?3)>R3((23.94±1.72) mg·cm?3)>R4((21.47±1.37) mg·cm?3)>R5((19.60±2.83) mg·cm?3)。这是因为小孔径的聚氨酯海绵拥有更高的内部比表面积,其为微生物提供更多的可附着、生长空间。尽管小孔不利于载体孔径深度方向的传质(载体中心区域几乎见不到生物膜),但内部也不易受到水力剪切作用的干扰,且小孔径载体外层区域依然可附着较为可观的生物量。大孔径载体的高空隙率会产生更为剧烈的水力剪切作用和其他物理化学作用,从而加速生物膜解吸脱落速率,在一定程度上限制了生物膜量的增长[25]。
R1~R5对应的f分别为0.898±0.006、0.913±0.007、0.914±0.003、0.923±0.008、0.932±0.006,其随载体内微孔孔径的增大而增大。这是因为小孔容易截留、累积污水中的无机物杂质,且不易于大孔径载体生物膜的脱落与更新,因此,f会低于大孔径载体。
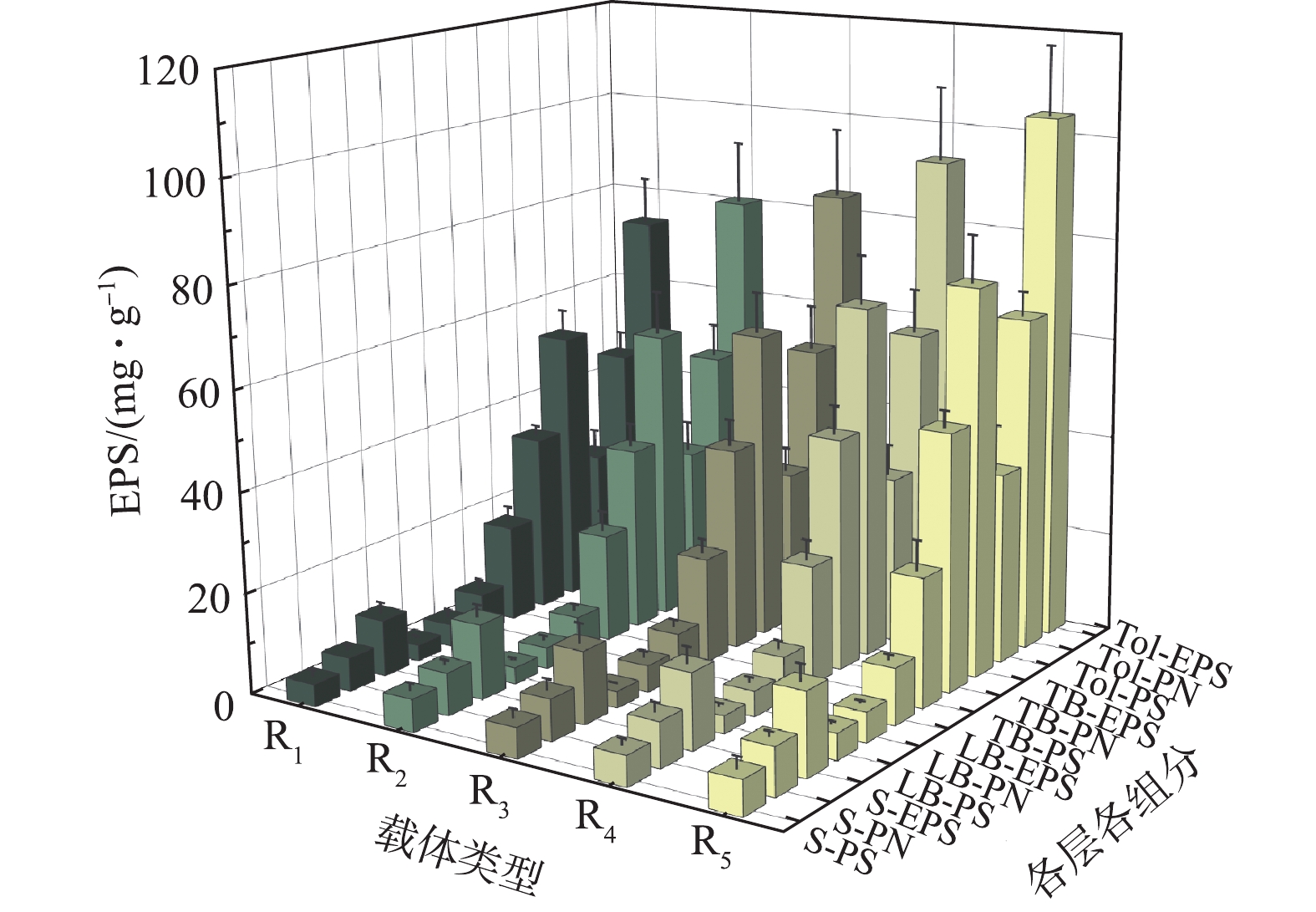
不同微孔孔径对生物膜EPS的影响如图3所示。从EPS分层看,TB层>S层>LB层,TB层EPS占总量的72.13%~74.68%,与细胞紧密结合的TB-EPS是EPS的主要组成部分,受内层分泌TB-EPS的挤压,分布于生物膜外层S-EPS、中层LB-EPS结构疏松、流动性较强,含量较低[26];从组分看,各层蛋白质含量高于多糖,PN/PS为1.30~1.99,这说明蛋白质为EPS主要组分[21,26]。生物膜EPS在各层各组分的分布具有相似的规律,说明载体微孔孔径大小对EPS各组分在各污泥层的分布规律影响较小。
从微孔孔径上看,EPS各组分含量随孔径的增大而递增,R1~R5的Tol-EPS分别为(73.19±9.17)、(80.48±12.19)、(84.11±13.29)、(93.28±14.52)、(104.07±13.56) mg·g?1,主要体现在TB-EPS的增长。微生物生长条件的差异会影响其生长速率进而影响EPS的产量[27],大孔有利于废水流通于载体内表面,从而提高了废水与载体内微孔的接触频率,使营养物质、DO的传输速率更高,促进了微生物的生长代谢速度,故可分泌更多的EPS。此外,大孔径内更为剧烈的水力条件会也促进具有保护细胞免受外界影响、维持生物膜稳定作用的EPS分泌[28]。
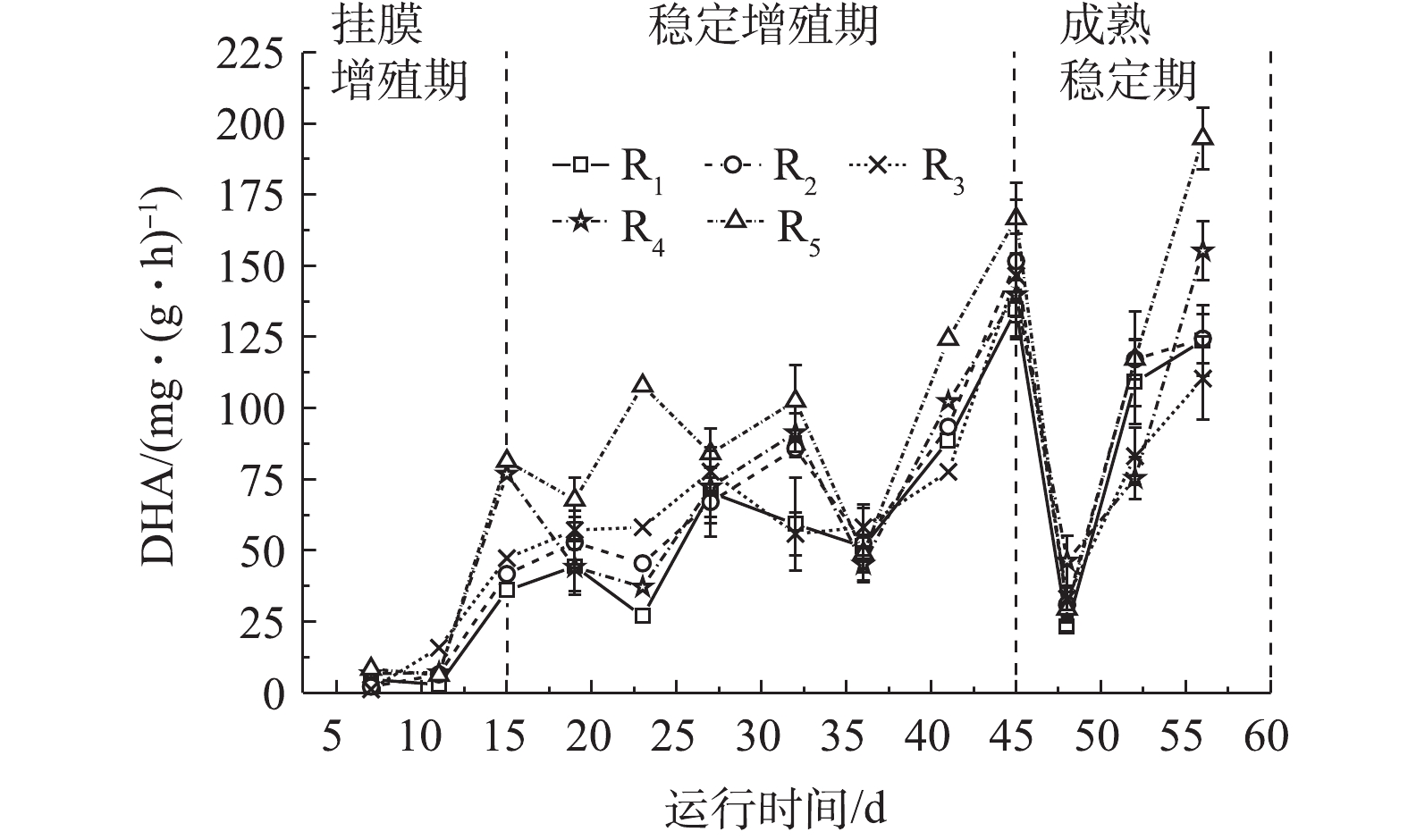
脱氢酶是微生物细胞所产生参与污染物氧化分解的氧化还原酶,能一定程度上反映微生物对有机物的降解能力[29]。在实验中,不同微孔孔径载体生物膜脱氢酶活性如图4所示。由图4可知,各微孔载体生物膜DHA变化与生物量变化吻合。在挂膜增殖期,游离微生物逐渐固定于载体上,不断吸收营养物质而大量增殖,代谢活动剧烈,DHA从1.28~8.42 mg·(g·h)?1迅速上升至36.02~76.86 mg·(g·h)?1;在稳定增殖期,DHA在26.88~124.31 mg·(g·h)?1波动,这是因为微生物由物化依附载体向生化黏附载体过渡,迅速增殖的微生物受水力剪切等环境作用,不断脱落与更新,导致DHA有较大波动变化。成熟期生物膜逐渐成熟稳定,DHA较高,且趋于稳定。
在生物膜成熟稳定后,R1~R5的DHA分别为(116.48±13.68)、(120.80±12.65)、(96.80±13.29)、(125.30±8.75)、(156.02±16.56) mg·(g·h)?1。小孔径聚氨酯载体拥有更高的生物量,高生物膜量会堵塞污泥内部的通道和空穴,进而抑制营养物质和氧的传质,使生物膜活性降低[30],大孔径载体传质快,代谢旺盛,生物膜脱落与更新更为频繁,有助于脱氢酶活性的提高,因此微孔孔径小的载体生物膜DHA值低于微孔孔径大的载体生物膜。
不同载体在成熟稳定期的生物膜微观结构表征结果如图5所示。聚氨酯载体内孔骨架较为光滑,孔径分布均匀、立体多层(图5(a)),骨架结构为微生物生长提供了丰富的附着空间,错综的孔径结构也能为内部生物膜提供良好的隐蔽环境,减少水力剪切力对生物膜的冲刷。不同结构载体上微生物的黏附会形成不同形貌生物膜,继而影响生物膜的生长发育,这些形貌差异是由载体与载体、载体与水流之间摩擦作用产生的剧烈水力条件所造成[31]。小孔径载体(R1、R2)内生物膜(图5(b)、图5(c))结构松散,细菌群落生长较慢,可见较多的丝状菌。由于适度的水力剪切作用刺激微生物EPS的分泌,中等孔径载体(R3、R4)生物膜具有多孔性和致密性(图5(d)、图5(e)),载体与细菌菌落具有较强的黏结作用,球形菌、丝状菌多呈菌落形式均匀分布于EPS基质中,形成非常致密、较均匀的网状结构。大孔径载体(R5)生物膜为抵御更为强烈的水力剪切力,分泌大量的黏性聚合物(EPS)使生物膜致密且粗糙,表面拥有丰富的孔洞结构(图5(f))。但细菌群落不多见,可能是较大的剪切作用将细菌从载体表面剥离,阻碍了细菌群落的生长。
2.2. 微孔孔径对废水处理效果的影响
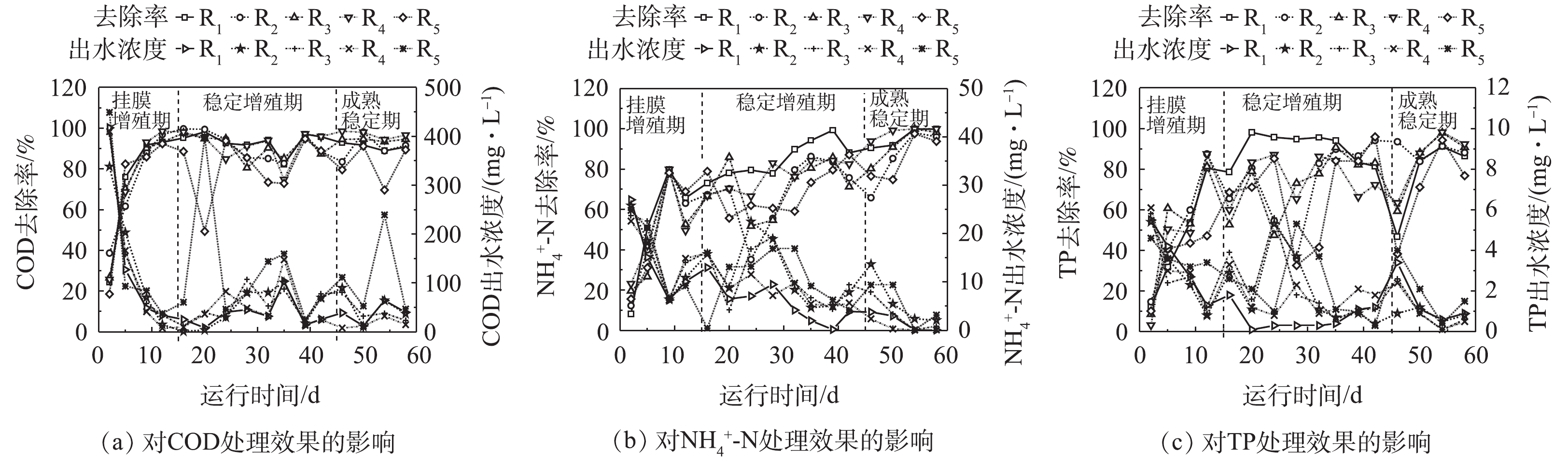
各微孔孔径载体反应器污染物出水浓度、去除效果如图6所示。生物膜在挂膜增殖初期,由于生物膜累积较薄,未形成良好的好氧、厌氧区域[32],对含C有机物、N、P元素的吸附、降解与转化能力较弱。随后微生物迅速繁殖,COD、2.3. 载体微孔孔径与生物膜特性间的相关性
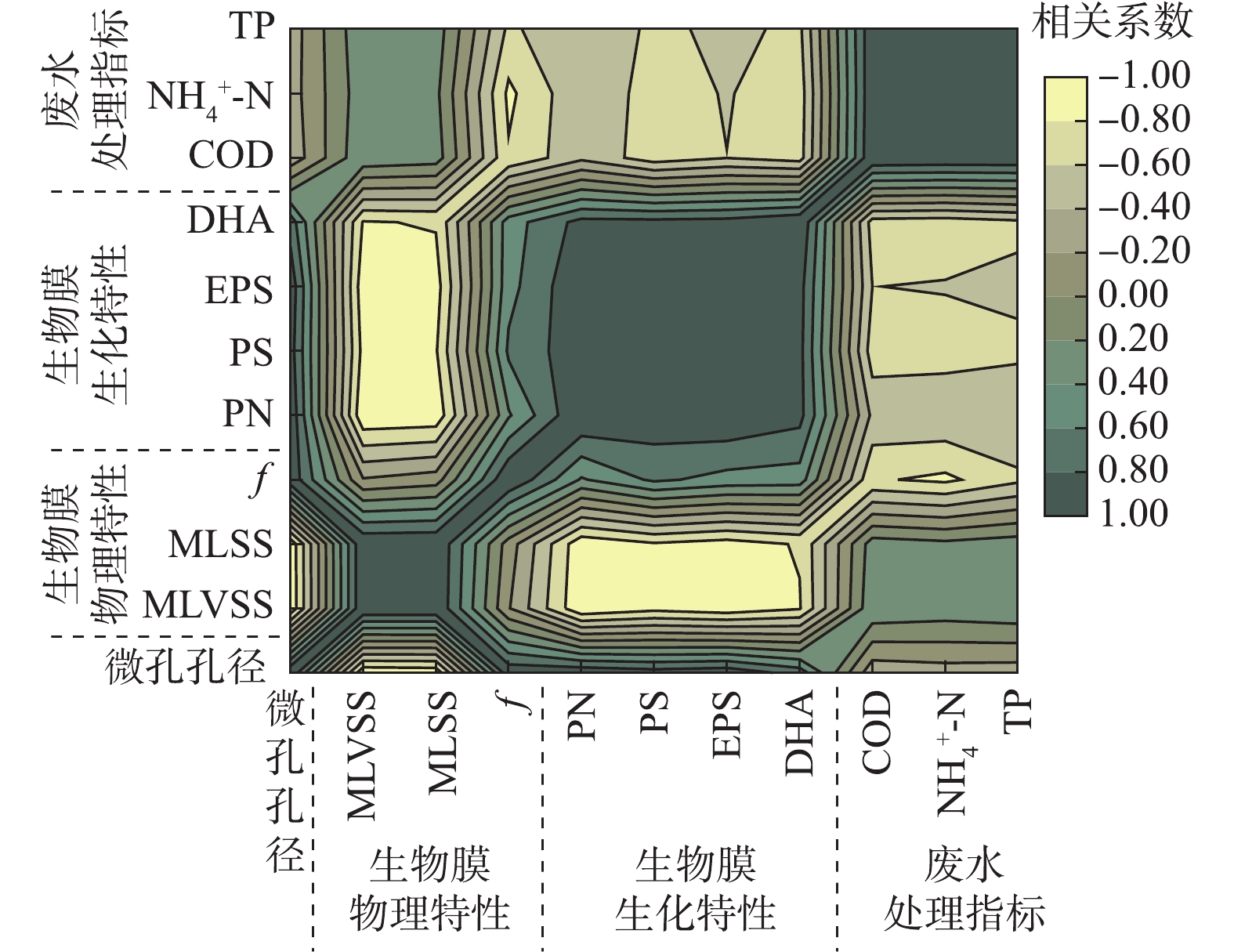
图7为生物载体内微孔孔径、生物膜特性以及废水处理效果间的相关系数矩阵图,可根据颜色深浅直接看出不同参数之间相关性的正负与强弱。载体微孔孔径与MLVSS、MLSS的相关系数分别为?0.963(P<0.01)、?0.949(P<0.05),呈显著负相关。载体微孔孔径与生物膜f (相关系数=0.945,P<0.05)、DHA(0.717)呈正相关性,两者表征微生物活性具有同向性。载体微孔孔径与PN、PS、EPS之间的相关系数分别达到0.964 (P<0.01)、0.893 (P<0.05)、0.940 (P<0.05),均呈显著正相关。大孔径载体生物膜为了抵御强烈的水力冲击等外部环境影响,微生物会分泌更多的黏性EPS。此外,PN、PS与EPS相关系数分别为0.979、0.987,说明胞外聚合物组分之间相互影响。
从废水处理效果来看,载体微孔孔径与污染物去除率之间相关性均不显著,其与COD、
中等微孔孔径(2 mm、3 mm)载体不仅能维持适量的微生物量,还能保持良好的生物膜结构与活性,为生物膜反应器提供良好的长期运行条件与处理效果(图8)。因此,通过选择适宜的载体微孔孔径来控制生物膜特性,可保证优异的生物量、活性和更新状况,是使生物膜反应器在长期运行中保持高效处理效果的关键性因素。
2)微孔孔径大小与MLVSS (相关系数=?0.949,P<0.05)和MLSS (相关系数=?0.963,P<0.01)呈显著负相关,MLSS、MLVSS均随着载体微孔孔径的增大而减小。
3)载体微孔孔径与PN (相关系数=0.964,P<0.01)、PS (相关系数=0.893,P<0.05)、EPS (相关系数=0.940,P<0.05)、f (相关系数=0.945,P<0.05)呈显著正相关。由于水力剪切、营养物质传输等作用,微孔孔径大的R3~R5载体上的生物膜具有更高的生物活性(DHA、f ),有利于胞外聚合物的分泌与积累,主要体现在TB-EPS层的显著增长。但载体内微孔孔径大小对EPS各组分在各污泥层的分布规律影响较小。
4)在生物膜挂膜增殖的前中期,高生物量使小孔径载体拥有更为优异的废水处理效果。但在生物膜成熟稳定后,中等孔径R3 (2 mm)、R4 (3 mm)载体表现出最为优异的生物膜特性与污染物去除效果,对COD、
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 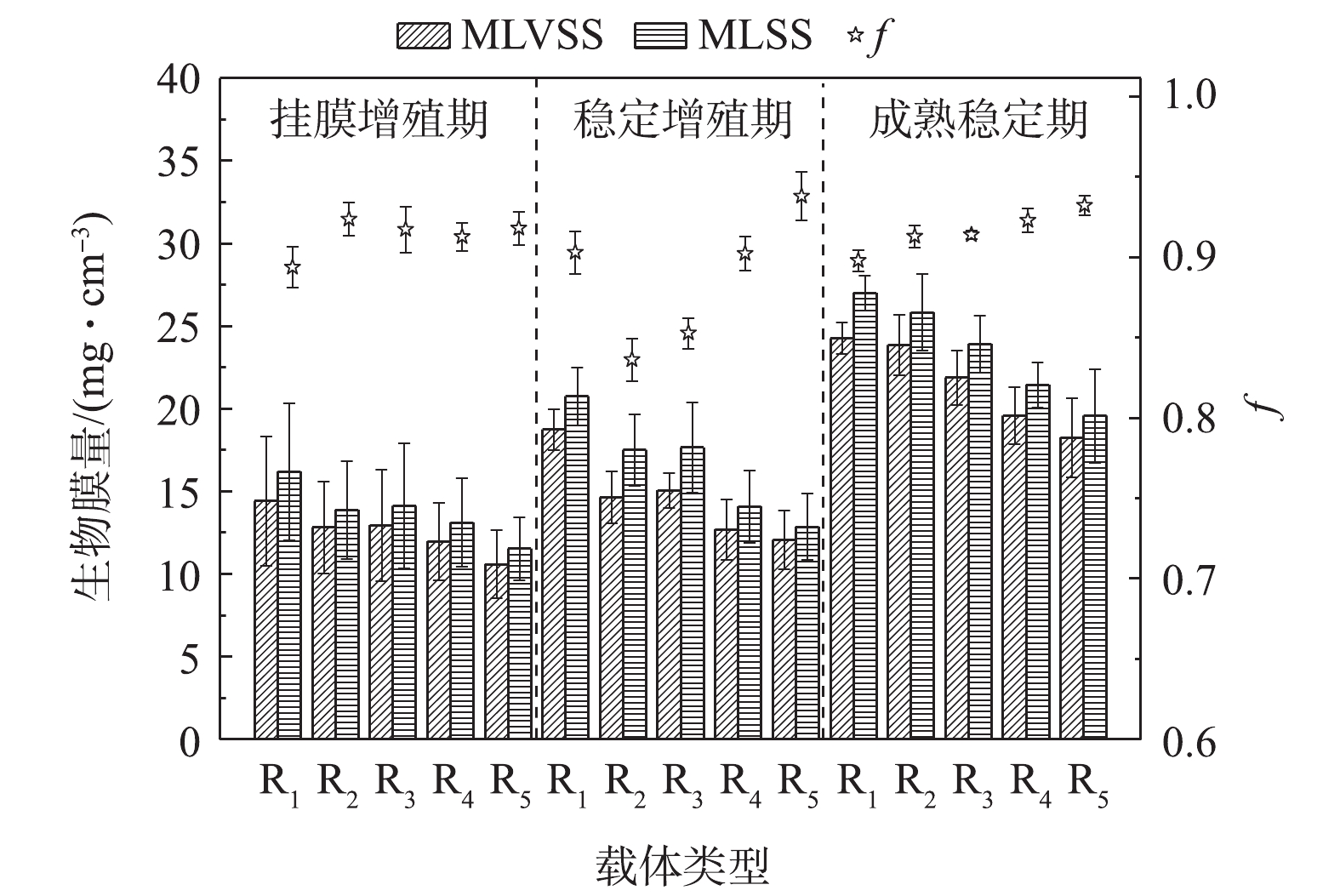

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图