全文HTML
--> --> --> 随着我国城市污水处理量的增加,污泥产量也急剧增加[1]。污泥若得不到妥善处置,会给环境带来二次污染。因此,污泥的减量化和资源化利用已成为研究热点[2]。针对剩余污泥单独厌氧消化处理效率低的缺点,水热预处理+厌氧消化的组合工艺,可有效提高污泥水解效率,在国内外污水处理厂已有成功运行的案例[3-5]。如能进一步提高剩余污泥含固率,采用高含固污泥进行水热预处理,则可大幅提高生物质能转化效率并降低整个工艺能耗[6]。水热预处理通过高温将污泥中微生物絮体解体,使得胞内有机物释放至液相,转化为溶解态有机物(dissolved organic matter,DOM),从而提高后续厌氧消化效率[7]。预处理温度和时间是热水解的主要影响因素[8]。程瑶等[9]研究发现,在不同的温度下,对含固率为10%污泥进行水解时,170 ℃、50 min条件下水解效果最佳,污泥中大部分固相有机物水解为溶解态物质转移至液相。污泥固态有机物水解为溶解态有机物的效果通常采用挥发性悬浮固体(volatile suspended solid,VSS)的水解率来表征。王治军等[10]研究发现,在水解过程中,VSS的溶解速度常数与温度的关系符合Arrhenius方程,验证了温度为热水解重要的影响因素。卓杨等[11]在165 ℃、50 min条件下对10%高含固污泥进行热水解得出1 g VSS约产生1.48 g溶解化学需氧量(soluble chemical oxygen demand,SCOD),表明污泥中的固体有机物在此条件下充分溶解。
污泥中有机物类型通常可分为酪氨酸类、色氨酸类、富里酸类、可溶解性微生物产物和腐殖酸类物质5种,不同有机物组分及含量对后续处理效率影响较大[12]。目前的研究多关注污泥热水解过程中溶解性有机物变化,对于水解后溶解性有机物的官能团构成以及组分变化的研究较少。由于污泥热水解属于物化反应,从有机官能团变化的视角分析污泥热水解过程,可为污泥热水解后资源的回收利用提供一定的理论基础。本研究针对含固率为10%的高含固污泥在不同温度下进行水热预处理,分析水热处理前、后污泥溶解性指标的变化;在此基础上,进行傅里叶变换红外光谱和三维荧光光谱分析,进一步探讨热水解对污泥有机物官能团影响和有机物组分变化情况,探究污泥热水解效果和物质转化规律,以期为后续污泥资源化利用提供参考。
1.1. 实验材料
实验污泥取自西安市某污水处理厂(A2/O工艺)剩余污泥。将剩余污泥用筛(1.0 mm)过滤后,投加絮凝剂(PAM)沉降脱水,用自来水将含固率调至10%作为污泥热水解预处理的实验用泥。1.2. 实验装置
热水解实验使用热水解预处理实验装置,高压反应釜(KCF-5型,北京世纪森朗有限责任公司)有效容积为5 L,工作温度 < 350 ℃,工作压力 < 10 MPa。实验针对高含固污泥(10%含固率)采用不同预处理温度(分别为140、170、200、230和260 ℃)进行热水解预处理,反应釜投加1.2 L实验污泥,在设定温度下热水解30 min,待热水解反应结束后停止加热,当反应釜自然冷却至室温,再取出水解污泥并置于4 ℃冰箱保存待分析。1.3. 实验分析指标及测定方法
热水解实验过程中测定的样品指标主要分为2类:总指标和溶解态指标。总指标测定的预处理方法:取5 mL左右热水解后污泥(简称水解液)置于超声波细胞破碎仪(JY-92II型,上海比郎仪器制造有限公司)中,待测样品在超声波细胞破碎仪中充分破碎后置于冰箱待用。溶解态指标测定的预处理方法:取经热水解后污泥约80 mL于100 mL离心管,置于离心机(5804R型,德国Eppendorf公司)中离心(10 000 r·min?1,10 min)后,取上清液经快速定性滤纸过滤后置于冰箱待用。COD采用重铬酸钾法[13]测定;蛋白质采用Folin-酚试剂法测定,以牛血清蛋白作为标准样品[14];碳水化合物采用苯酚-硫酸法测定,以葡萄糖为标准样品[15];SS、VSS采用称重法测定氨氮采用纳氏试剂分光光度法测定;TN采用碱性过硫酸钾氧化-紫外分光光度法测定;TP采用过硫酸钾氧化-钼酸铵分光光度法[13]测定。
傅里叶红外光谱[16]可探究上清液中官能团存在形式,三维荧光光谱[17]则可探究溶解有机物组分处理前后变化情况。傅里叶红外光谱仪(Nicolet6700,深圳市瑞盛科技有限公司)采用溴化钾压片法检测,首先将热水解预处理过后的污泥水解上清液进行冷冻干燥预处理,再用溴化钾作为稀释剂稀释样品(待测样品1 mg,溴化钾150 mg),充分研磨后压成薄片[18]待测;三维荧光分光光度计(F-7000,日立高新技术公司),将各个热水解处理温度水样稀释相应的倍数后使用比色皿进行测试。
2.1. 水解温度对污泥特性的影响
热水解预处理可以促使污泥中固体有机物的水解,使得溶解态有机物增加。SCOD浓度是污泥破碎程度的重要指标,SCOD浓度越高,污泥水解破胞效果越好,碳水化合物和蛋白质是污泥细胞的主要组成部分,易于微生物利用[19]。高含固污泥在不同温度热水解前后特性变化见表1。由表1可知,在预处理时间为30 min时,随着温度的增加,热水解后污泥的SCOD、溶解性蛋白质和溶解性碳水化合物浓度均呈现先略微增加后稍有降低的趋势。在170 ℃时,3个指标均达到最大值。当温度从140 ℃升至170 ℃时,COD的水解率由38.26%升高到43.59%;200 ℃以上COD溶出效果与170 ℃相差并不大。溶解性蛋白质在170 ℃达到最大值20.56 g·L?1;随着温度的升高溶解性蛋白质浓度降低。溶解性碳水化合物在140 ℃和170 ℃时浓度基本相同为9 g·L?1左右;当热水解温度高于170 ℃时,随着温度的提高溶解性碳水化合物快速降低。170 ℃为热水解最佳温度,污泥中蛋白质和碳水化合物均达到水解阈值。
从各物质水解率进行分析可知,与未预处理污泥相比,170 ℃时,COD的水解率为43.59%,和蛋白质水解率44.41%接近。这是因为蛋白质为SCOD的主要贡献者;同时,碳水化合物的水解率为61.78%。这一实验结论与DONOSO-BRAVO等[20]的研究结果一致。溶解性TN随处理温度的升高相差并不大,各个处理温度浓度基本为4 g·L?1左右;随着处理温度的升高,SS浓度降低,在260 ℃时,达到最小值50.78 g·L?1;VSS随着处理温度的升高,呈现出先增高再减小的趋势,在170 ℃浓度达到最大值40.2 g·L?1。
2.2. 污泥水解上清液红外光谱分析
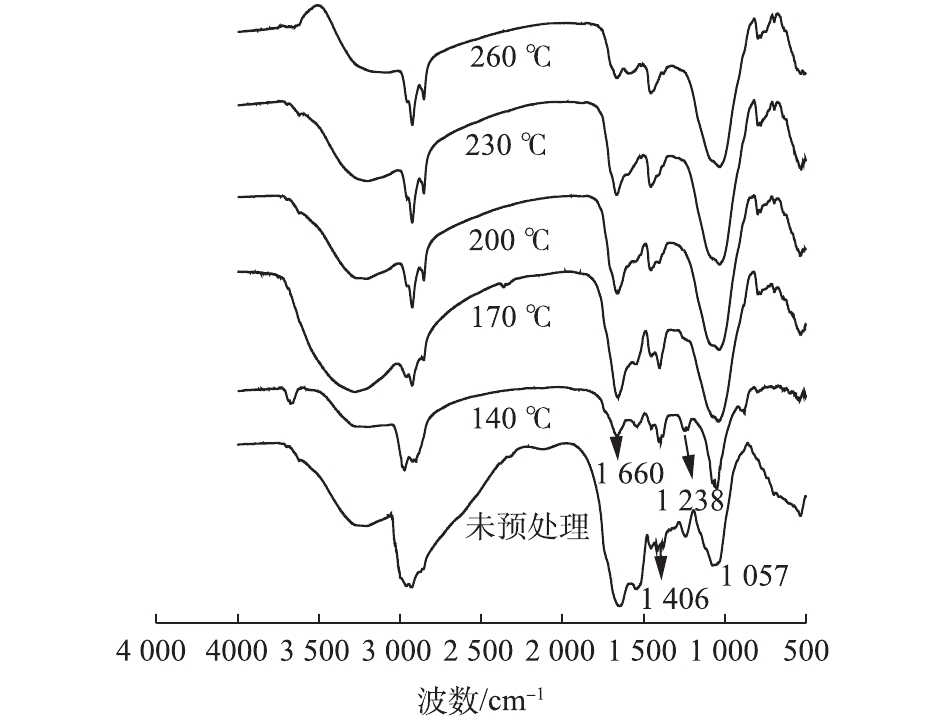
由图1可以看出,未处理污泥上清液与通过水热预处理污泥水解上清液相比,性质发生了较大变化。可以看出,在3 050~3 600 cm?1和1 300~1 480 cm?1区域内,170 ℃的荧光峰强度明显强于其他温度和未预处理污泥。傅里叶红外光谱振动频率所对应的各个基团[21-22]如表2所示。可以看出,3 050~3 600 cm?1区域吸收峰为糖类O—H伸缩振动;1 300~1 480 cm?1区域吸收峰为糖类CH3、CH2和CH变角振动。这表明170 ℃热水解高含固污泥,细胞中大量碳水化合物溶出并被水解为二糖和单糖;当预处理温度为140 ℃时,O—H振动峰强弱于170 ℃,表明污泥中的多糖还未完全水解;当热水解温度高于170 ℃后,O—H伸缩振动的峰强随温度升高而降低,170 ℃达到碳水化合物水解阈值;再升高温度水解液中的碳水化合物浓度会变低。这一结果与前面分析出的碳水化合物随热水解温度升高降低的趋势相符合。1 400~1 700 cm?1的吸收峰主要表现为蛋白质吸收峰[23]。其中,1 600~1 660 cm?1吸收峰为氨基酸
2.3. 污泥水解上清液三维荧光分析
为了后续对污泥水解液的资源化利用,需了解热水解上清液中DOM组成性质以及不同预处理温度热水解液的变化。本研究采用三维荧光光谱对污泥热水解上清液进行分析,研究不同温度热水解液中溶解有机物的组成。由于不同温度处理后水解液中DOM三维荧光光谱强度差别过大,所以分别对水解上清液进行不同倍数的稀释后再进行测定。不同温度处理后的水解上清液荧光光谱见图2。三维荧光光谱可分为五个区域:区域I(Ex=200~250 nm,Em=260~320 nm)主要是由酪氨酸等蛋白质类物质组成;区域II(Ex=200~250 nm,Em=320~380 nm)则与色氨酸有关;区域III(Ex=200~250 nm,Em>380 nm)由类富里酸类物质组成;区域IV(Ex=250~450 nm,Em=260~380 nm)由微生物的代谢产物构成,如蛋白质、色素、小分子有机酸、辅酶等;区域V(Ex=250~450 nm,Em>380 nm)则由可见光区类富里酸类、腐殖酸类及多环芳香烃等大分子有机物构成[12]。由图2(a)可知,未处理的高含固污泥DOM中主要成分为色氨酸类物质和可溶解性微生物代谢产物,经过热水解预处理后,水解上清液DOM的性质发生了较大变化。由图2(b)和图2(c)可知,当预处理温度为140 ℃和170 ℃,热水解上清液中的DOM中可溶解性微生物代谢产物浓度明显升高;而当预处理温度高于170 ℃时(图2(d)、图2(e)、图2(f)),则会产生大量的腐殖酸类物质。为了更准确的分析预处理温度对水解上清液中DOM的影响,对三维荧光图谱使用积分区域法(fluorescence regional integration,FRI)进行三维荧光数据解析[24]。该方法计算的是某一区域有机化合物含量的相对值,不同的稀释倍数并不会影响三维荧光的分析结果。FRI方法中不同荧光区域[25]分别代表5类有机物:酪氨酸类、色氨酸类、富里酸类、可溶解性微生物产物和腐殖酸类物质[26]。依据FRI算法,计算出DOM三维荧光光谱的5个荧光区域积分标准体积,见图3。各个区域的积分标准体积可以间接的表征各个区域所代表有机物质的相对含量。
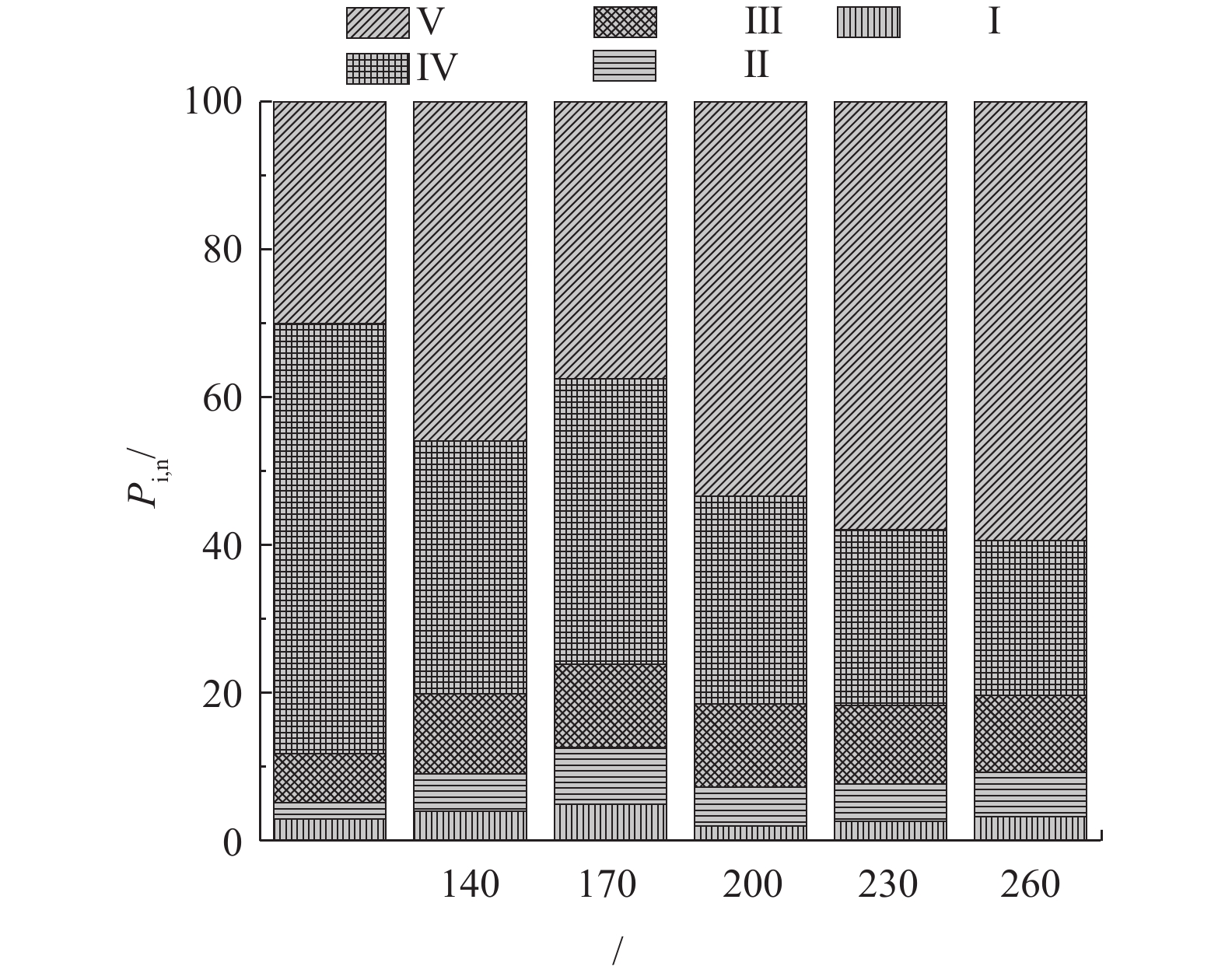
在图3中,纵坐标为某一荧光区域积分标准体积占总积分标准体积比例。由图3可知,未处理的高含固污泥DOM中,IV微生物代谢产物和V腐殖酸类占主要成分,分别占58.14%和30.59%。经热水解后由于微生物絮体破碎、胞外聚合物打开,污泥中的蛋白质和碳水化合物溶解至液相中。其中的部分大分子有机物还会进一步发生水解作用,生成多肽、二肽以及氨基酸等,部分氨基酸也可能会进一步水解为低分子有机酸、氨以及二氧化碳[27-28]。
针对5类物质热水解前、后DOM组分变化可知,I酪氨酸类所占比例较小,约为2.01%~4.90%。II色氨酸类属易生物降解物质,水解后含量较原污泥略微升高,170 ℃时,色氨酸类所占比例最高为7.71%,随着预处理温度的升高,其占比略微减小为5.04%~6.07%。III富里酸类物质在不同处理温度下含量相差不大,约为10.35%~11.24%。IV微生物代谢产物易于被微生物利用,随着温度的升高呈现先增加再减少的趋势,在170 ℃所占比例最大为38.68%,在200、230和260 ℃时所占比例分别为28.10%、23.77%和21.00%,主要是由于温度升高部分蛋白质类物质变性[29]。V腐殖酸类物质不利于微生物的利用,170 ℃所占比例最少为37.47%。这是由于富里酸类大分子、腐殖酸类大分子有机物会分解成不具有荧光特性的小分子物质。170 ℃水热预处理后水解上清液中的可生物降解物质所占比例最高,生物难降解物质所占比例最少;同时,相比其他处理温度170 ℃蛋白质和糖类的水解率最高,所以170 ℃更有利于后续污泥水解液的回收利用。
2)在水热预处理温度为170 ℃时,大分子有机物分解为小分子有机物,高含固污泥中多糖分解为二糖和单糖,含有大量O—H键。
3)高含固污泥经水解后,DOM中可被生物利用的微生物代谢产物所占比例随水热预处理温度的升高先增大再减小,在170 ℃时所占比例达到最大;并且,该温度下难被生物利用的腐殖酸类物质所占比例最小。综合考虑,170 ℃为最佳水热预处理温度,更有利于后续污泥的资源化利用。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 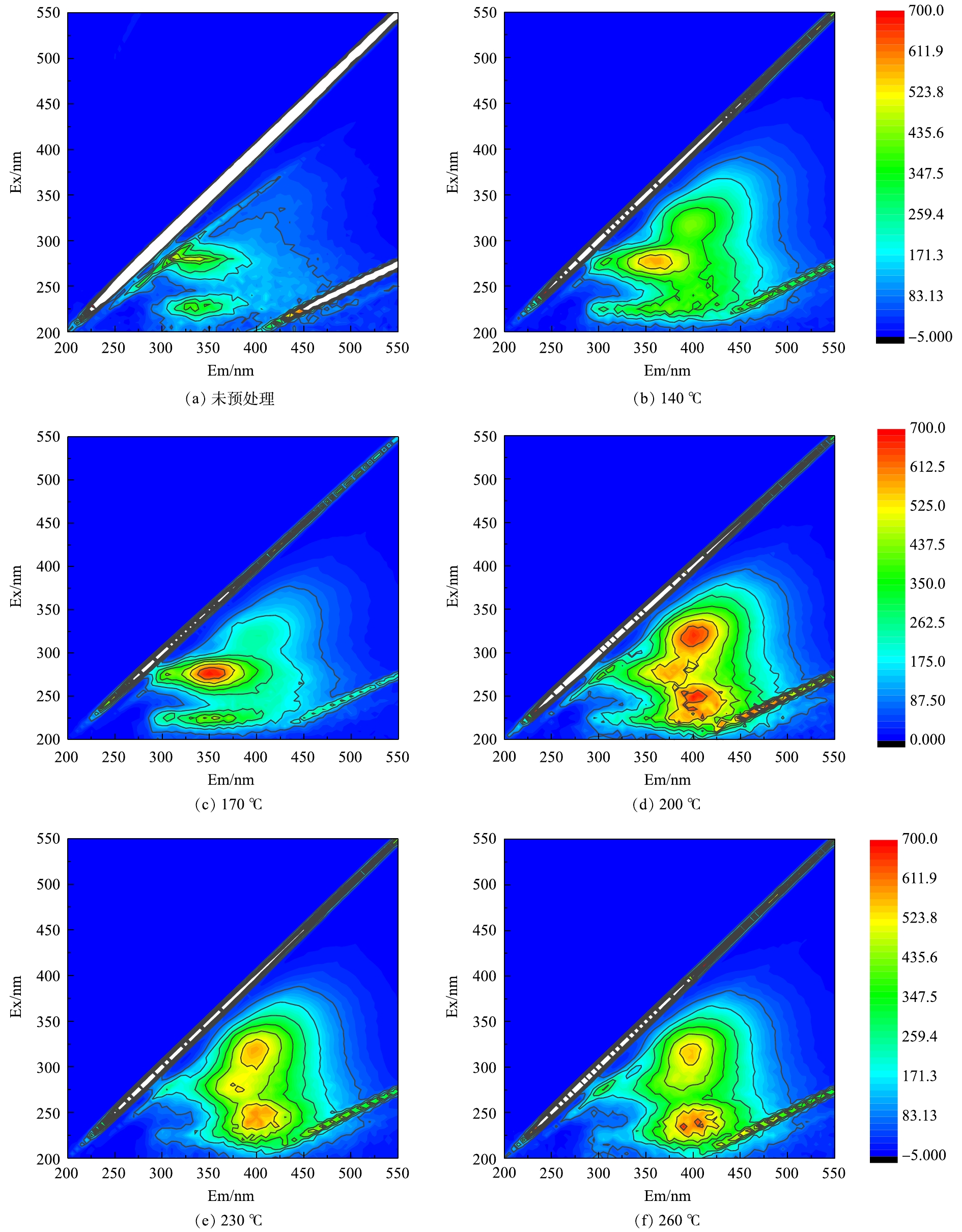






 点击查看大图
点击查看大图