全文HTML
--> --> --> 近年来,抗生素的广泛使用导致其以不同的方式大量流入环境[1-2],其中包括盐酸土霉素。盐酸土霉素属于一种广谱抗菌素,在养殖业和农业中作为杀虫剂普遍使用,但是其很难被生物体完全吸收,盐酸土霉素的部分代谢产物及大量的残留会进入环境中,危害环境并给人类带来危害风险[3]。目前,针对抗生素的废水处理方法有水解、生物降解、高级氧化法等,其中,水解和生物降解均有耗时长、耗资大等缺点。高级氧化法是目前研究最为广泛一种废水处理方法,包括有芬顿氧化法[4-5]、光催化氧化法[6]和电化学氧化法[7-8]等。高级氧化法主要利用具有强氧化性功能的羟基自由基(·OH)或硫酸根自由基(
1.1. 试剂和仪器
实验试剂:均苯三甲酸(GR,上海化学)、三乙胺(GR,国药控股)、六水合硝酸钴(AR,国药控股)、叔丁醇(CP,国药)、抗坏血酸(AR,国药)、盐酸土霉素(国药);其他试剂均为国药分析纯试剂,实验用水为去离子水。实验仪器:KH-100型Teflon-lined反应釜(北京瑞昌伟业)、pHS-3C型pH计(上海仪电科学)、UV1900型紫外可见分光光度计(上海佑科)、SHA-C型水浴恒温振荡箱(常州澳华)、ZA3300型火焰原子吸收分光光度计(北京日立)。
1.2. 实验方法
1) Co-MOF的制备。量取25 mL去离子水于烧杯中,加入1.45 g Co(NO3)2?6H2O、1.05 g均苯三甲酸和2 mL三乙胺,再将烧杯放置在磁力搅拌器上搅拌15 min,然后将溶液转移到Teflon-lined反应釜中,密封放置在190 ℃的电热鼓风干燥箱中24 h。将反应后所得离心(6 000 r·min?1) 2 min获取沉淀物,用乙醇和去离子水各反复冲洗3次,再60 ℃真空烘干备用。2) Co-MOF降解盐酸土霉素的实验。量取20 mg·L的盐酸土霉素于反应器中,加入一定量的Co-MOF和PS,在恒温震荡箱中反应5 min,特定时间取样,并用紫外分光光度计在353 nm波长处测定吸光度,根据标准曲线计算盐酸土霉素反应后的浓度。实验结束后收集定量的上清液,加入适量硝酸酸化至pH≤2,然后用火焰原子吸收分光光度计测定其中的钴含量。盐酸土霉素的降解率按照式(1)进行计算。
式中:
2.1. Co-MOF表征
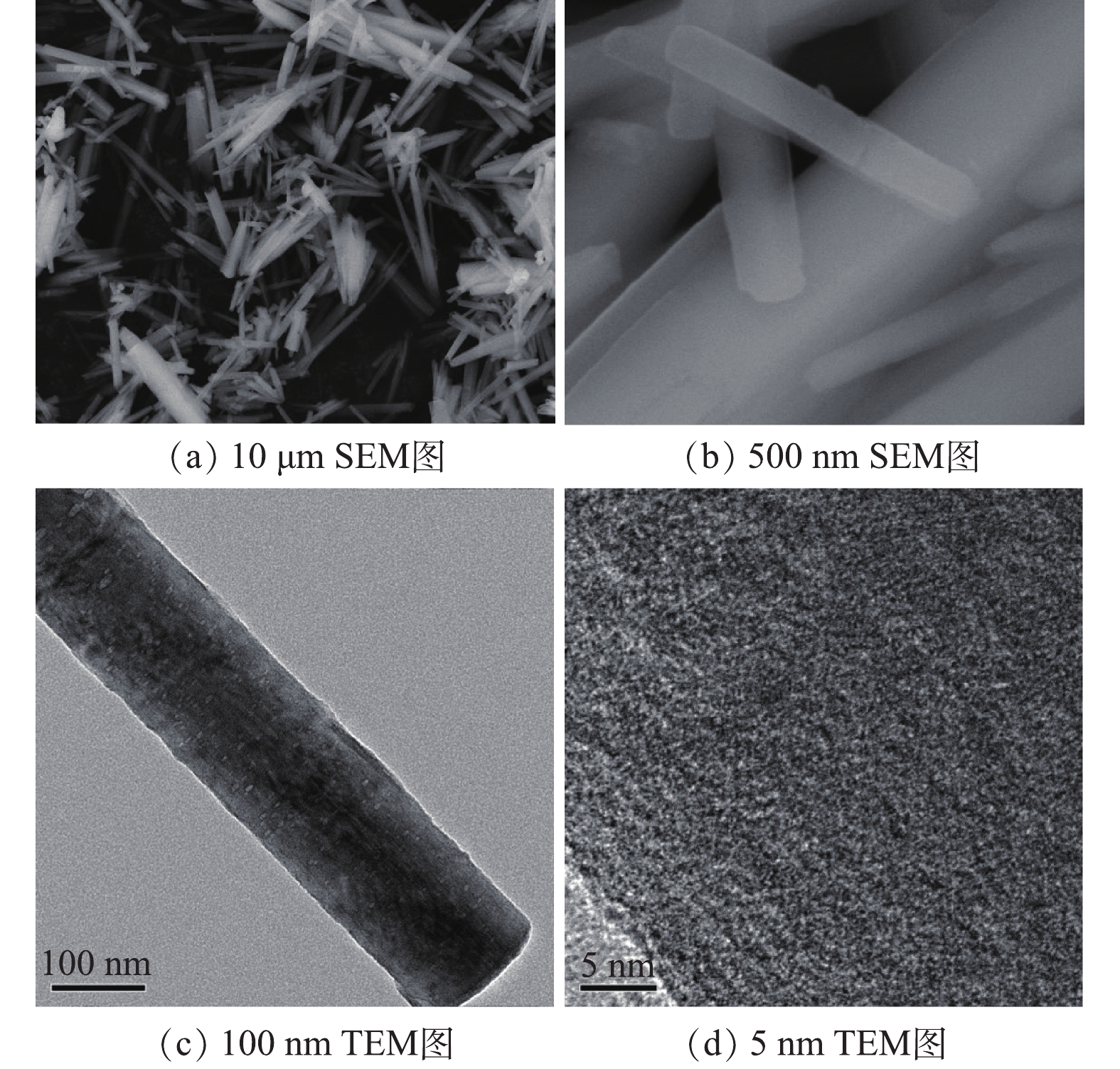
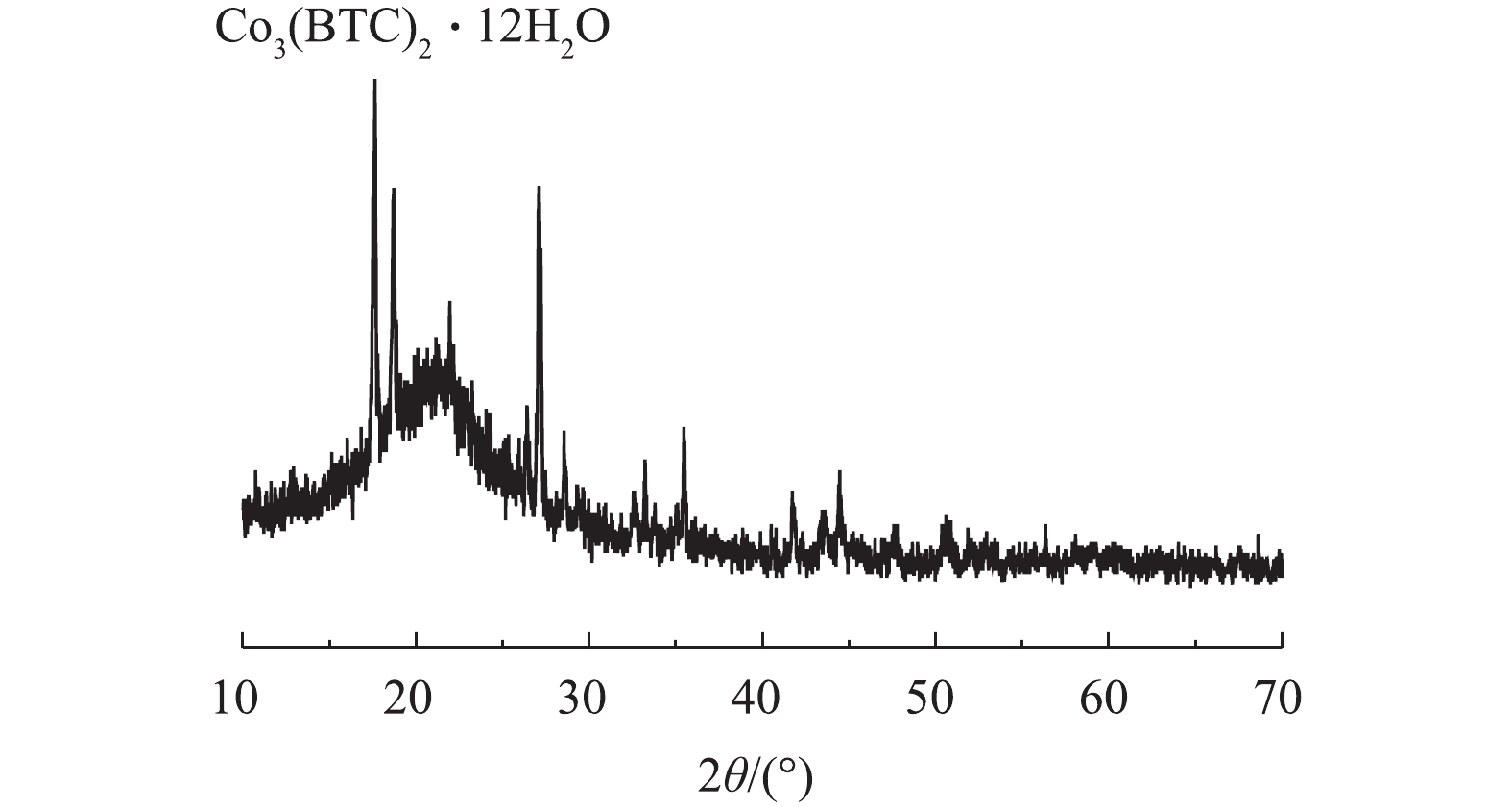
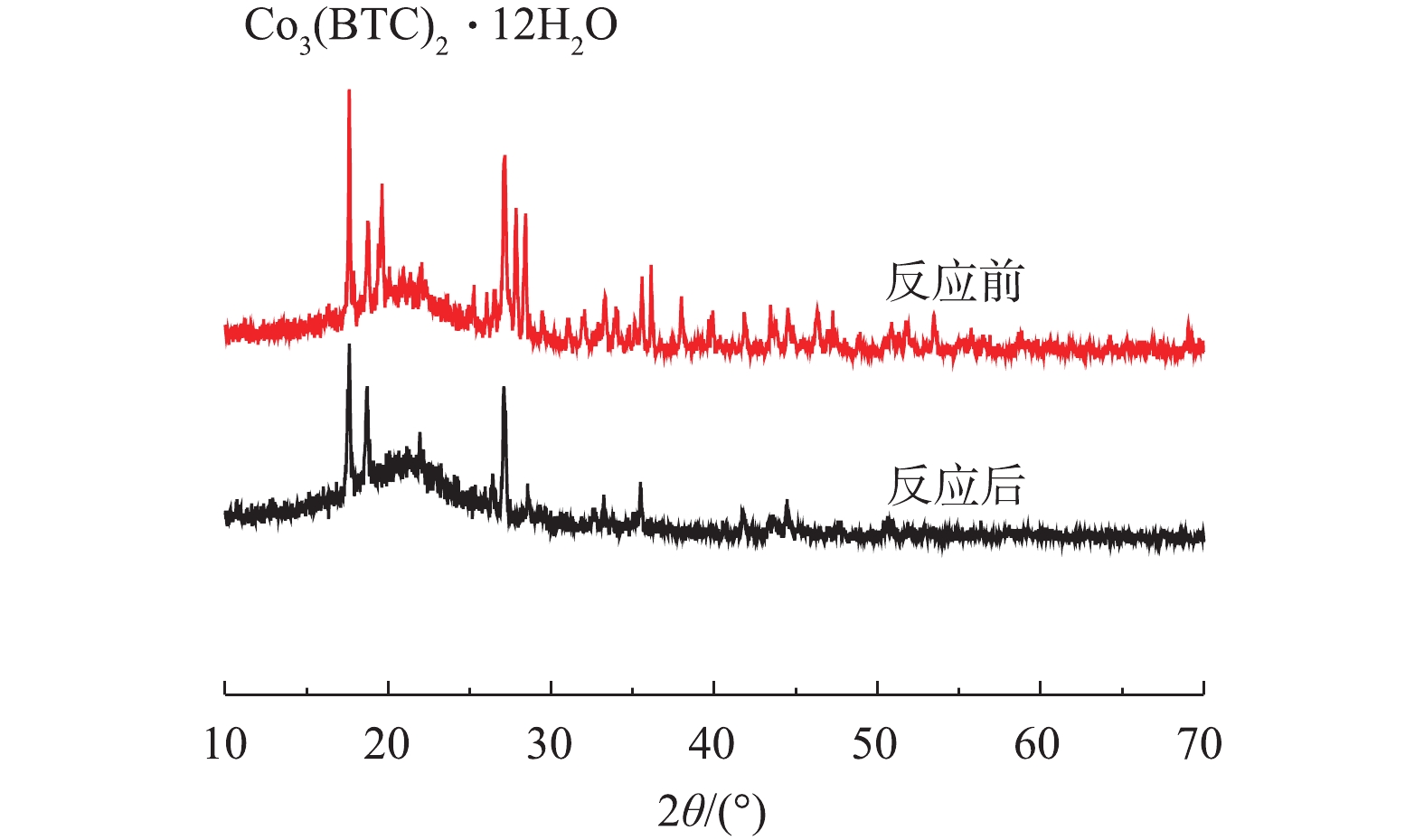
1)扫描电镜(SEM)和透射电镜(TEM)。通过SEM、TEM和EDS对制备的Co-MOF的形貌特征、粒径以及组成成分进行分析,结果见图1。如图1(a)和图1(b)的SEM表征所示,Co-MOF是由棒状晶体组成,每个棒状晶体的长度大约几百微米,宽约为30~100 μm,这与YAGHI等[19]的报道结果相似。如图2所示,Co-MOF含有C、O和Co元素,其中,Co元素的相对峰面积占比较大,这表明Co在Co-MOF结构中的重要性。如图1(c)和图1(d)的TEM表征所示,可见Co-MOF是由棒状晶体组成,并且每个棒状晶体表面平滑、多孔隙,这与PATTERSON等[20]的研究结果类似。2)X射线衍射(XRD)。通过XRD对制备的Co-MOF结构进行分析。如图3所示,在17.5°附近有明显的衍射峰,此峰对应Co3(BTC)2·12H2O的晶面(014),故这表明Co(NO3)2·6H2O和均苯三甲酸发生完美融合,这与以往报道[21-22]中的Co-MOF的XRD图谱相似。
2.2. 不同体系对盐酸土霉素的降解效果
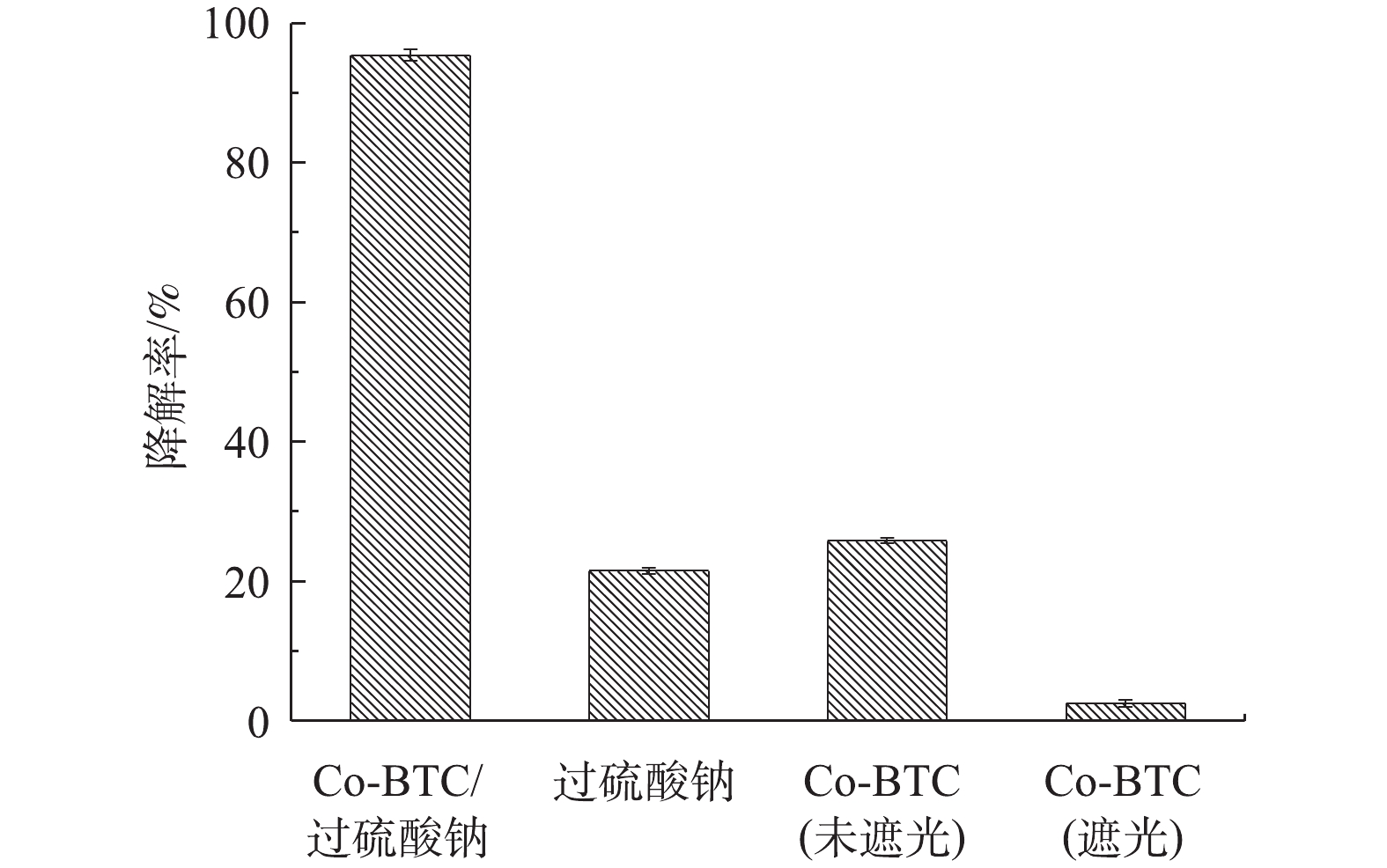
图4为不同催化剂反应体系下盐酸土霉素的降解效果对比。由图4可见,在第1组(未遮光)和第2组(遮光)中,单独的Co-MOF添加对盐酸土霉素的降解率分别为25.8%和3.9%,这是Co-MOF自身的光催化特性导致,如孙登荣等[23]研究MOFs材料的光催化性能时发现,MOFs具有光催化性能。在第3组实验中,单独的PS添加对盐酸土霉素的降解率为21.5%,这是由于PS的热活化反应导致。杨世迎等[24]开展的活化过硫酸盐高级氧化技术的研究结果表明,在热、光、过渡金属等外在条件的催化下,过硫酸盐均能通过吸收能量来使内部构造发生变化。在第4组实验中,Co-MOF/PS对盐酸土霉素的降解率为95.4%。这样的结果与预期一样,表明Co-MOF具有高效活化PS的性能。2.3. 影响Co-MOF降解盐酸土霉素的因素
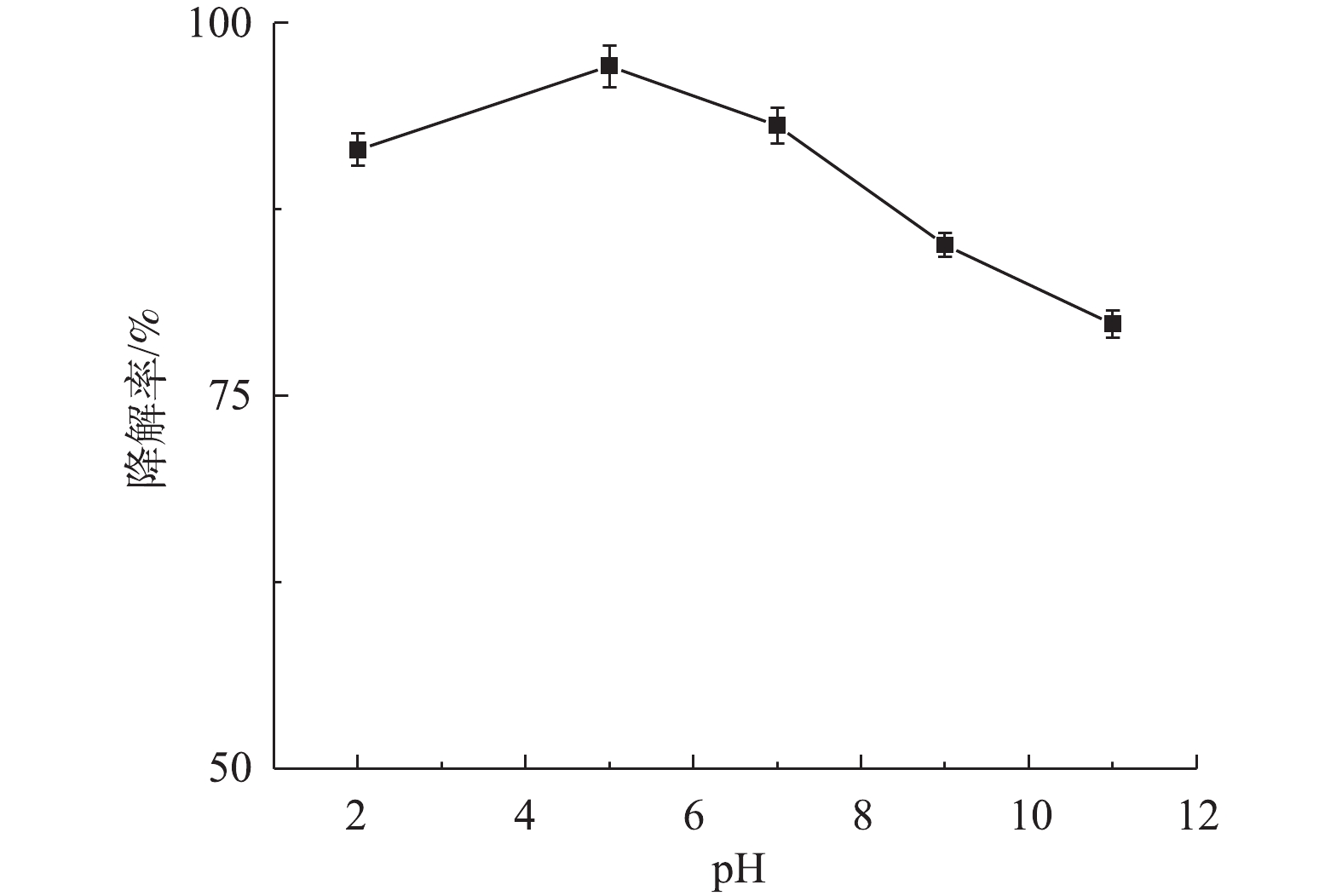
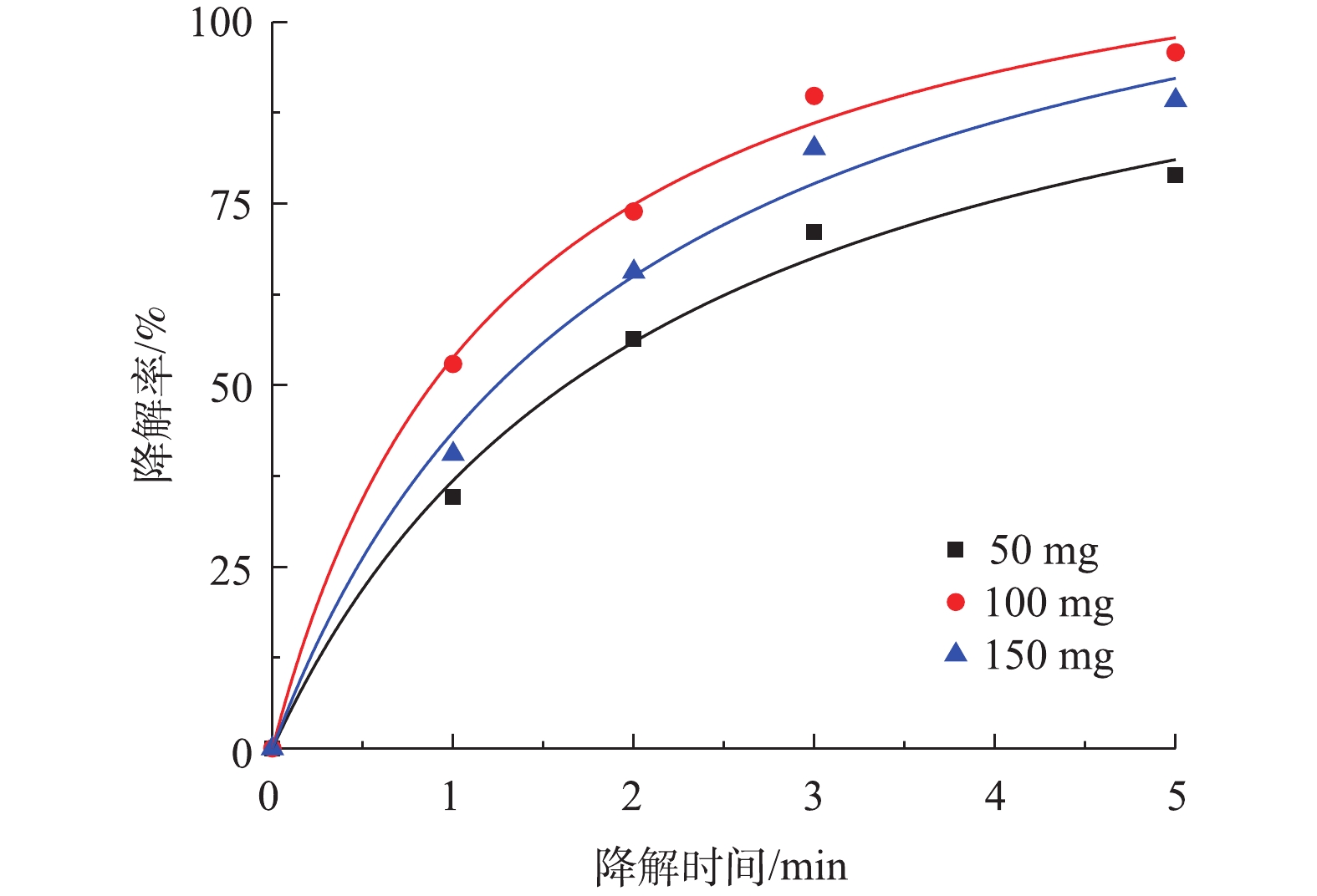
1) pH对盐酸土霉素降解的影响。图5为不同pH对盐酸土霉素降解的影响。如图5所示,盐酸土霉素在pH=2.0~11.0时均有不同程度的降解,其中,当pH=5.0时,对盐酸土霉素的降解率最高为97.1%。当pH=2.0、3.0、9.0和11.0时,对盐酸土霉素的降解率分别为91.5%、93.1%、85.3%和79.8%,这与预估一致,一方面是由于2) PS投加量对盐酸土霉素降解的影响。由图6可知,当PS添加量为从50 mg增加到100 mg时,对盐酸土霉素的降解率从78.9%上升到95.8%,这表明盐酸土霉素的降解率随着PS投加量的增加而变大。而PS投加量达到150 mg时,对盐酸土霉素的降解率下降,原因是由于过多的PS会使
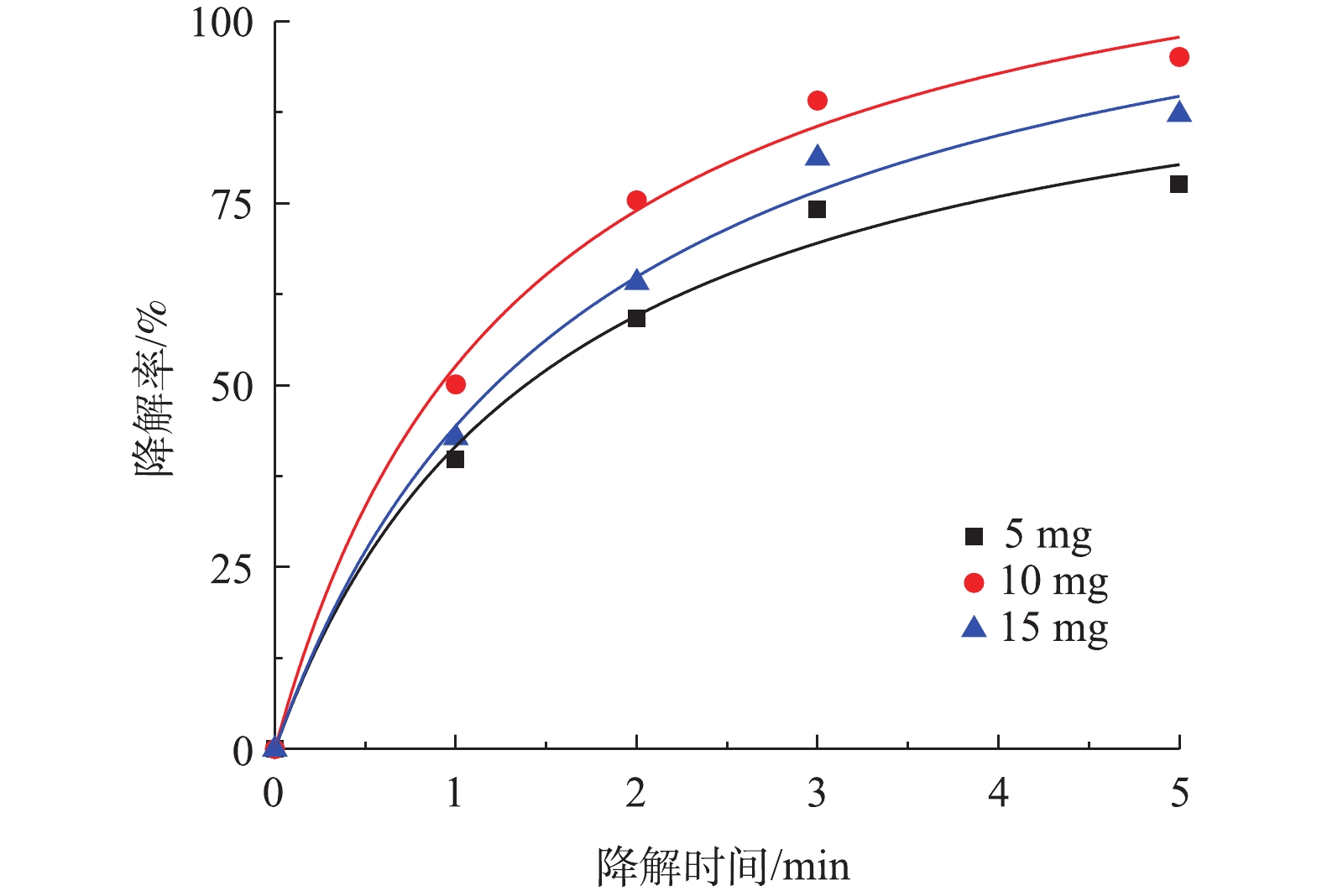
3) Co-MOF投加量对盐酸土霉素降解的影响。由图7可知,5 mg Co-MOF添加量对盐酸土霉素的降解率为77.6%,10 mg Co-MOF添加量对盐酸土霉素的降解率为95.1%,而15 mg Co-MOF添加量对盐酸土霉素的降解率为87.2%,这表明随着Co-MOF投加量的增加,盐酸土霉素去除率呈现先增后减的趋势。造成这种情况的原因是:一方面是由于过多的
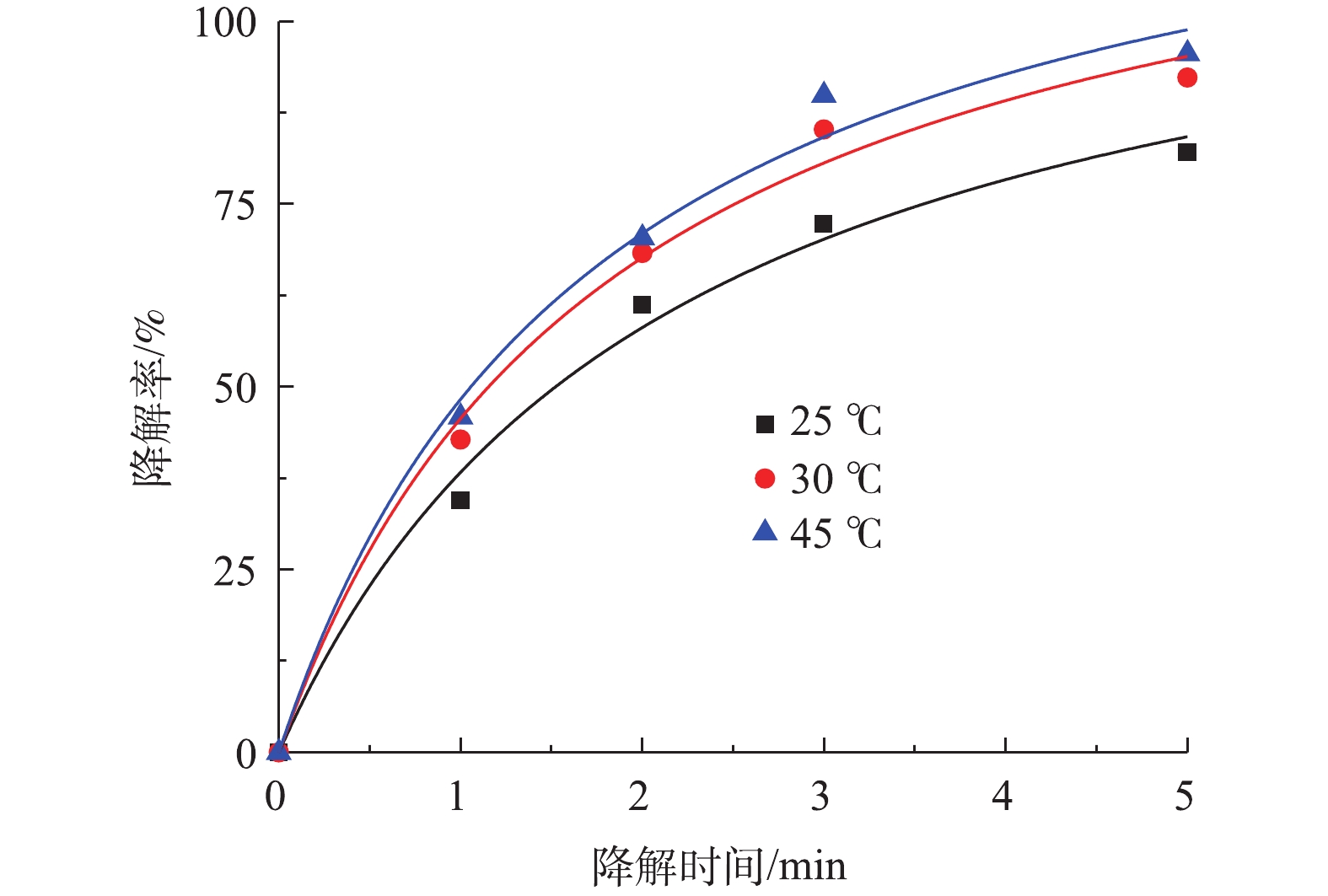
4)温度对盐酸土霉素降解的影响。图8为不同反应温度对盐酸土霉素降解的影响。如图8所示,在25 ℃时,对盐酸土霉素的降解率有82.1%;在30 ℃时,对盐酸土霉素的降解率上升到92.3%;而当45 ℃时,对盐酸土霉素的降解率高达95.6%。这表明随着反应温度的升高,对盐酸土霉素的降解率也随之增大。在Co-MOF/PS体系中,
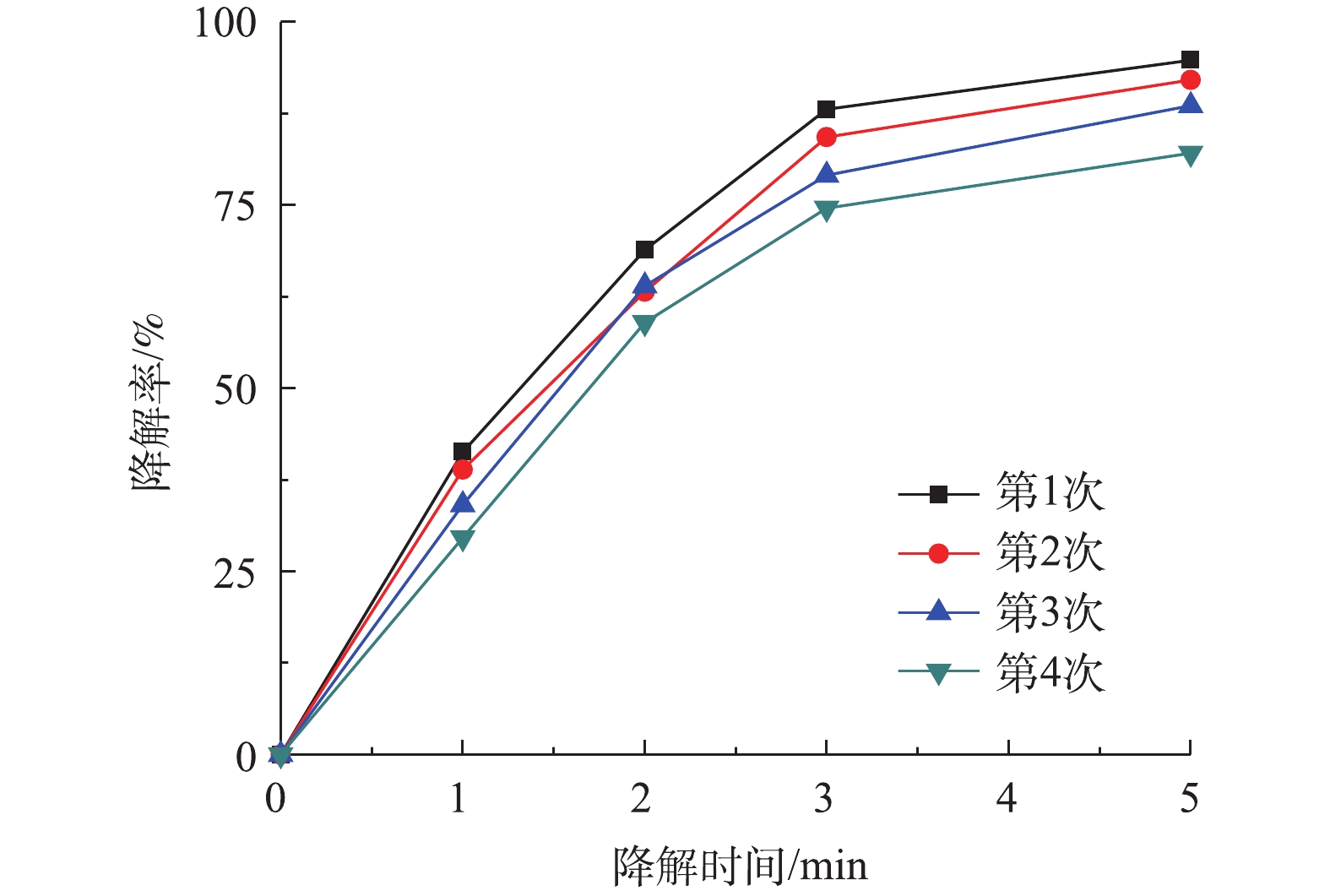
2.4. 重复利用Co-MOF对盐酸土霉素降解率的影响
催化剂的稳定性是检验催化剂性能的重要指标,图9为Co-MOF重复利用对降解盐酸土霉素的影响。如图9所示,Co-MOF第4次运行后,对盐酸土霉素的降解率下降为82.1%,这表明Co-MOF具备较高的稳定性。其中,导致盐酸土霉素降解率降低的原因是:一方面由于Co-MOF活化PS降解盐酸土霉素时,长时间浸泡导致Co(Ⅱ)的活性位点损失;另一方面是由于Co2+随着多次循环出现微量损失(式(6))。第4次运行结束后收集定量的上清液,经检测显示钴含量为1×10?4 mg·L?1,而国标(GB 25467-2010)中的钴排放标准为总钴含量≤1 mg·L?1,故本次研究中Co-MOF的使用不会对环境造成二次污染。2.5. 反应机理
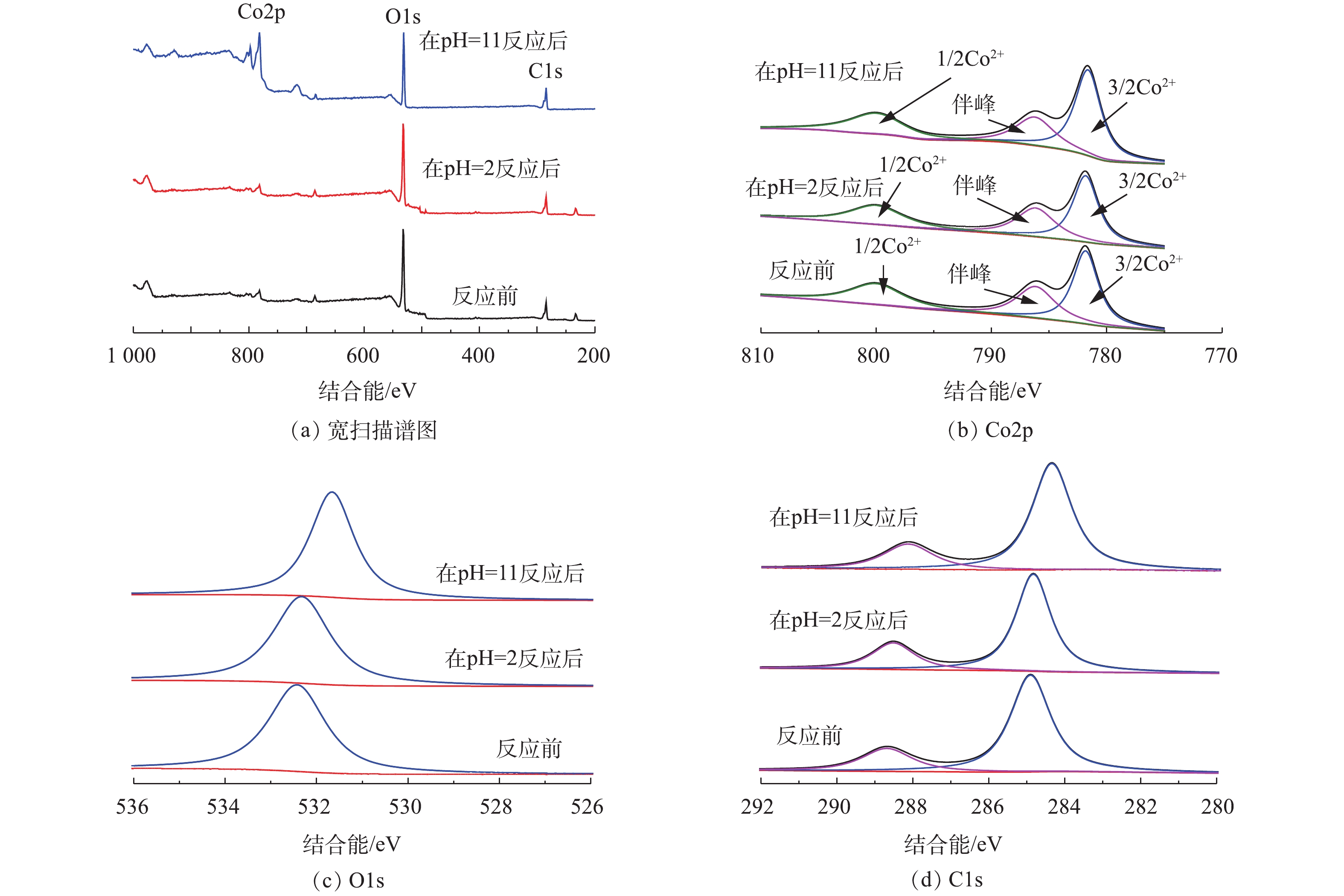
1) Co-MOF降解盐酸土霉素反应前后的XPS表征。通过XPS对Co-MOF降解盐酸土霉素反应前后的组分变化进行分析。图10为Co-MOF反应前后的XPS图谱。如图10(a)所示,Co-MOF材料的宽扫描光电子能谱呈现Co2p、O1s和C1s 3个光谱图。在Co2p核心级XPS光谱中(图10(b)),反应前的Co2p1/2和Co2p3/2的结合能对应781.4 eV和800.4 eV;在786.2 eV的峰值是由辅峰造成的,由Co的sp3杂化所形成。有研究[30]表明,在低结合能一侧的781.4 eV若是归属于Co(Ⅱ),就表明Co在材料中的主要存在状态是Co(Ⅱ)氧化态,其在pH=2时没明显变化,而在pH=11时Co2p1/2对应的强度明显增强,这表明Co-MOF在酸性条件下更稳定。由图10(a)可知,在pH=11时反应后的Co2p的峰值有所升高,这是由于碱性条件下Co3+被还原为Co2+所致(式(7))。图10(c)显示的是O1s的光谱,反应前和当体系的pH=2反应后的结合能峰均为532.4 eV,表明CO-MOF中的羧基没有受到损坏,结合C1s的XPS光谱中(图10(d))的数据,其结合能没有发生明显的变化。综上所述,Co-MOF具有良好的稳定性。2) Co-MOF降解盐酸土霉素反应前后的XRD表征。如图11所示,在Co-MOF降解盐酸土霉素反应完成后,XRD图谱中Co3(BTC)2·12H2O对应的峰强度降低,这表明Co-MOF材料在降解盐酸土霉素的过程中有损失。
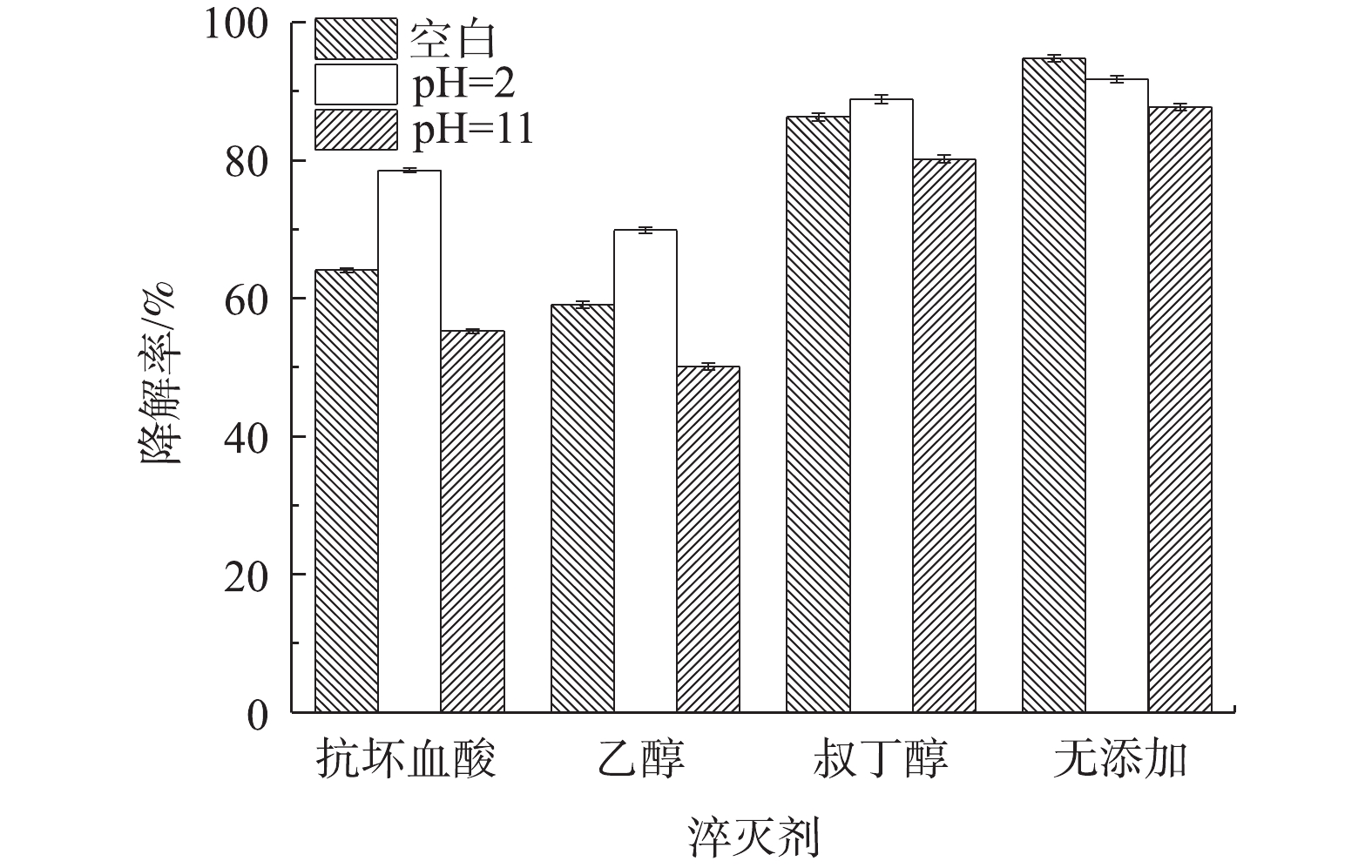
3)自由基淬灭剂对Co-MOF降解盐酸土霉素的影响。为了确定Co-MOF活化PS所产生的自由基种类,采用自由基捕获实验以验证活化体系中可能存在的自由基。众所周知,抗坏血酸和乙醇均为·OH和
2) Co-MOF投加量、PS投加量和温度对Co-MOF降解盐酸土霉素有较大的影响,pH对降解盐酸土霉素的影响不大。其中,当pH=5、温度30 ℃、Co-MOF浓度为200 mg·L?1、PS浓度为2 000 mg·L?1时,Co-MOF/PS对盐酸土霉素的降解率可达到最高。
3)重复利用Co-MOF降解盐酸土霉素结果表明,Co-MOF具有可重复利用性能。Co-MOF反应前后的XRD和XPS数据表明,Co-MOF具有良好的稳定性。自由基捕获结果表明,在该降解反应过程中,
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 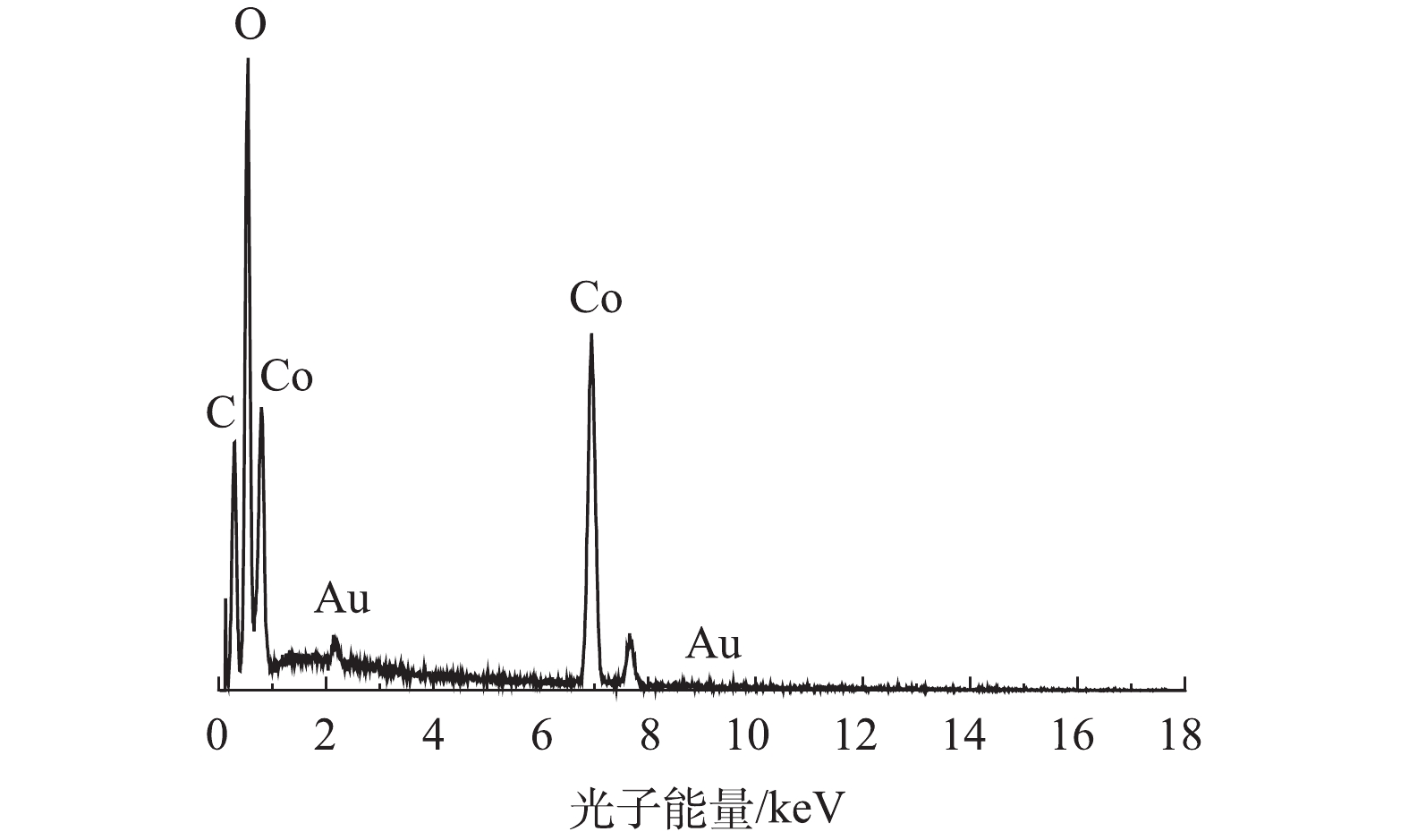
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图