全文HTML
--> --> --> 2019年末暴发的新型冠状病毒肺炎敲响公共与个人卫生安全的警钟。研究者在新型冠状病毒肺炎患者的粪便样本中分离出活性新型冠状病毒[1]。因此,有必要对公共场所、公共设施及水(包括饮用水、污水及医疗废水等)进行消毒处理,以阻断疫病的进一步传播,保护人员健康并保障水质与水环境安全。常用的消毒工艺有加氯消毒、紫外线消毒、二氧化氯消毒和臭氧消毒等。电解法现场制次氯酸钠消毒属于一种氯消毒方式。该方法安全可靠,已被广泛用于水处理和卫生消毒中。另外,电化学消毒作为一种新型消毒技术,近年来也受到较多关注。该技术已在一些现场应急处理处置中发挥作用。本研究针对电解法制备次氯酸钠与电化学消毒技术,从原理、特点、使用方法和发展前景等方面进行了介绍与分析,为相关消毒技术的实际应用提供参考。
1.1. 次氯酸钠消毒剂现场电解制备原理
次氯酸钠是高效广谱的含氯杀菌消毒剂,在杀灭病菌与病毒中发挥着重要作用。次氯酸钠通过水解生成次氯酸(HClO)和氯离子起到杀菌消毒作用。HClO的作用原理有2个方面:破坏细胞壁、病毒外壳,因其分子小、呈电中性,进入生物体内与菌(病毒)体核酸、蛋白和酶等发生氧化反应,进而杀死病原微生物[2-3];反应产物氯离子通过改变细菌和病毒体的渗透压使其丧失活性最终死亡[3]。国家卫生健康委办公厅和国家中医药管理局办公室联合发布的《新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎诊疗方案(试行第五版)》指出,含氯消毒剂可有效灭活新型冠状病毒[4]。次氯酸钠的获得方式有2种:一是向氯碱厂购买商品次氯酸钠溶液(制备方法为液碱氯化法,是氯碱厂的副产品);二是利用次氯酸钠发生器现场电解制备。商品次氯酸钠易分解,无法长期贮存,需频繁运输,且质量参差不齐[5]。现场电解法制备次氯酸钠具有原料安全、自控程度高、综合运行成本低等优点。相比投加成品次氯酸钠,现场制备次氯酸钠的消毒稳定性更高[6-7]。同时,该方法也避免了使用成品次氯酸钠、液氯和二氧化氯时存在的危险品运输和存储的安全风险等问题。
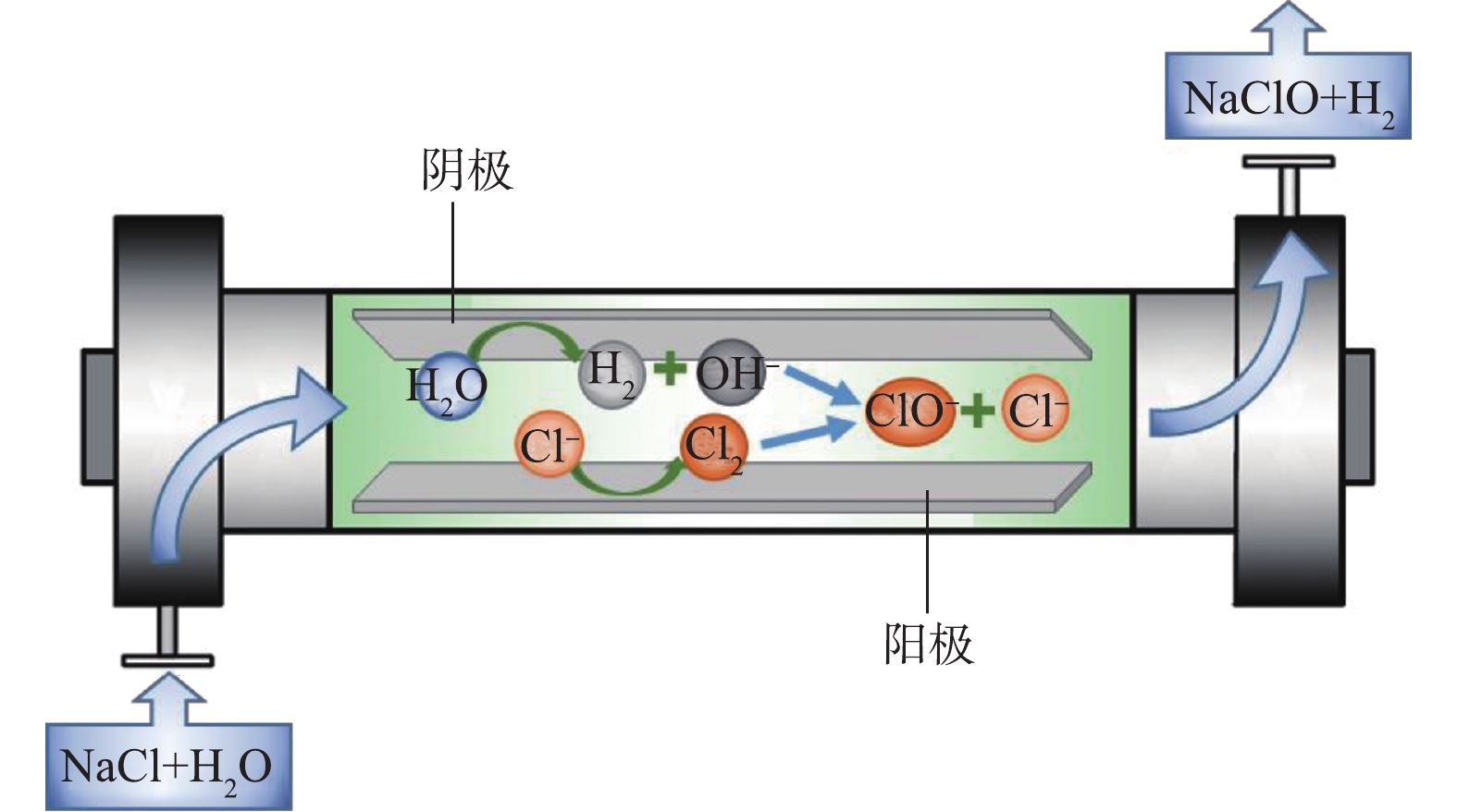
现场次氯酸钠发生器采用氯化钠溶液电解制备次氯酸钠溶液,总化学反应如式(1)所示,电化学反应如式(2)和式(3)所示,化学反应如式(4)所示。其原理见图1。
次氯酸钠的现场制备包括盐水精制、软水处理、盐水电解、次氯酸钠脱气储存等工序,最终制成次氯酸钠液体。电解工序通常在无隔膜电解槽中进行。阳极一般选用表面涂有钌、铱等金属氧化物涂层的钛基体电极,阴极采用耐腐蚀性好的钛或钛合金电极。市面上常见的发生器设备型号中的数字代表每小时产生总有效氯克数(有效氯产率),其中,有效氯是指与每升产生的次氯酸钠溶液所具有的氧化能力相当的氯气质量。该指标可用来定量表示消毒效果。根据法拉第定律,电解槽每通过1 A·h的电量,有效氯的理论生成量为1.323 g。
1.2. 次氯酸钠电解制备过程的安全防护
次氯酸钠发生器的设计与制造须遵循《次氯酸钠发生器》(GB 12176-1990)、《次氯酸钠发生器安全与卫生标准》(GB 28233-2011)和《供配电系统设计规范》(GB 50052-2009)等技术标准及设计规范。使用前,应对操作人员进行严格的技术和安全培训,确保安全生产操作。发生器装配有排氢系统和氢气检测报警系统。工作过程中,应将电解产生的氢气及时排放进大气中,避免爆炸危险。通过风机可将其浓度稀释至1%以下,设备间也能保持通风良好[6]。电解槽电极是现场制备次氯酸钠设备的核心部件,需定期清洗维护,以免电极结垢引起电解槽能耗升高或产能下降[6]。清洗时,应避免损害钛阳极的表面涂层,产生的酸性废水排放前需加碱中和处理。次氯酸钠消毒液应根据使用需要现场制备,并贮存在阴凉干燥处,远离火源,不得与易燃物接触或与还原物质共储共运。消毒液制成后,存放时间不宜超过24 h,在使用前先测定有效氯含量。消毒液外观应清澈透明(无色或浅黄色),无可见杂质和分层沉淀,原液pH为8~10。
1.3. 技术特点及应用现状
电解法次氯酸钠发生器适用于自来水厂、污水处理厂和工业废水的消毒处理工艺。从消毒能力方面考虑,次氯酸钠的消毒效果与液氯相当,且更有利于避免生成消毒副产物[8-9];从安全角度考虑,现场电解法制备次氯酸钠的优势较为突出。发生器的原料为成品氯化钠,其采购质量和运输安全均易得到保障。然而,从自来水厂运营成本来考虑,现场制备次氯酸钠的主要问题是一次性投资高及耗电量较高[6,10]。因此,目前国内大多数以次氯酸钠代替液氯消毒的水厂仍倾向于采用浓度为10%的氯碱厂生产的次氯酸钠溶液进行消毒[10]。与采用商品次氯酸钠溶液相比,采用现场制备系统获得次氯酸钠的方式设备投资较大,但药剂单价低、综合运行成本低,一般在现场运行4~6 a后即可收回投资[10]。以日供水7×105 t的浙江宋六陵水厂为例,次氯酸钠现场生产设备前期投资约6×106元,但是相比采用成品次氯酸钠溶液,消毒成本每年可节约1×106元以上[5]。另外,次氯酸钠发生器可在谷电价时段运行,夜间生产的次氯酸钠贮存后供白天使用,可降低运行成本[7]。国内外有多个大中型水厂采用现场电解制备次氯酸钠的消毒方式。该方式运行稳定可靠、安全环保,将成为水厂供水消毒的重要发展方向[5,7]。次氯酸钠发生器还可用于医院、酒店、饭店及公共设施环境的安全消毒,在预防性消毒、传染病污染的消毒防疫中发挥作用[11-12]。《次氯酸钠发生器安全与卫生标准》(GB 28233-2011)明确规定了次氯酸钠消毒液杀灭微生物的指标:消毒液浓度(以有效氯计)为100 mg·L?1,作用时间为10 min,对大肠杆菌的杀灭对数值≥5;浓度为200 mg·L?1,作用时间为20 min时,对脊髓灰质炎病毒-I型疫苗株的杀灭对数值≥4。
我国已生产出具有自主知识产权的高端大型发生器,并应用在次氯酸钠现场制备中。次氯酸钠发生系统发展初期存在的阳极防腐能力差、可控硅电源能耗大、自动化控制欠佳等限制性问题现已逐步解决[13]。研制出电流效率高、耐久性好、产率高的电解设备是未来次氯酸钠发生器研发领域的重点方向。次氯酸钠发生系统的发展将呈现高度集成化、智能化、高效化的趋势,并进一步降低单位有效产氯能耗[13-14]。
2.1. 电化学消毒原理
电化学消毒水处理指经由通电装置来消灭水中(包括饮用水、污水和工业废水等)微生物的过程,对大多数微生物(如病毒、细菌、真菌和藻类等)都有良好的消毒效果 [15-17]。电化学消毒的机理包括物理和化学等多种作用机制和反应过程[18](见图2)。电化学消毒原理包括电场直接破坏及电极表面吸附、电催化析氯和电产氧化活性物种3个方面。1)电场直接破坏及电极表面吸附。电场可破坏细菌细胞膜,使之分解或者膨胀破裂(电穿孔现象),从而导致细菌死亡;或细菌吸附于电极表面,发生直接电子传递,其细胞内辅酶CoA被氧化,导致细胞呼吸系统失调而死亡。另外,电场驱动下的细胞电泳等会影响细菌代谢功能,对杀菌作用亦有贡献[19]。
2)电催化析氯。当水中存在氯离子时,氯离子在阳极表面可被氧化生成氯气,氯气进而与水反应生成次氯酸(盐),消毒机制与前述次氯酸钠消毒相似,同样具有广谱的消毒作用[20]。
3)电产氧化活性物种。水分子、溶解氧等在电化学体系中会发生一系列反应,生成·OH、H2O2和O3等活性氧化物种。这些强氧化性物种可使微生物快速被氧化破坏而死亡。氧化活性物种的生成效率与电极材料催化活性、电解液组分和操作条件(曝气)[21-23]等密切相关。
2.2. 电化学消毒过程的主要影响因素
在电化学消毒过程中,电极材料、氯离子浓度、电流密度、处理时间、电解液(电导率、pH)、反应器结构、水动力条件及循环方式等都会影响电化学消毒效率。电极材料的电势窗、析氯性能、产自由基能力等为选择电极时需要重点考虑的因素。目前,成熟稳定的阳极材料主要为涂有贵金属(钌、铂、铱和钽中之一种或多种)氧化物的钛电极,阴极材料主要有钛、不锈钢和石墨。氯离子浓度的提高可增加水中活性氯含量;电流密度的提高可促进电化学反应及活性物种生成,提高杀菌效率,但过高也会加剧水解副反应,降低电流效率;从能耗角度考虑,电流密度大小还应与反应时间统筹考虑[24-27]。酸性环境(pH < 6)有利于提高HClO浓度,而通常HClO杀菌效力是ClO?的80~100倍[28]。反应器结构、电极形状和排布、电极间距等会影响电场强度、传质效率、水力流态和一次性投资费用。循环流电化学消毒相比单向流更适用于氯离子含量较低的二次水箱水的消毒,且低流量下(6 L·min?1,二次水箱蓄水量为10 m3)细菌的灭活效果比高流量下(14 L·min?1)的略好[29]。2.3. 电化学消毒技术的特点及应用现状
电化学消毒技术主要特点包括4个方面:1)可杀死多种有害微生物,反应速率快,电产活性氯和H2O2具有持续消毒能力;2)无需或仅需投加少量药剂、设备紧凑占地少、自控程度高;3)可结合其他电化学处理过程(电絮凝、电气浮及电催化氧化还原等)进行一体化设计[30-31],实现水中污染物的同步去除;4)电化学法消毒过程中消毒副产物三氯甲烷的量低于加氯消毒过程[32]。目前,电化学消毒相关研究主要集中在饮用水、污水处理厂二沉池出水、再生水、医院污水、生物性污染废水、海水养殖场养殖水和厕所废水等水源的消毒处理,研究层次还停留在实验探究或示范工程阶段[33-39]。HUO等[40]将CuO纳米线负载于三维泡沫铜电极上,建立了一种新型纳米线电穿孔消毒体系;在外接电压1 V、接触时间7 s时,纳米线尖端附近产生的强电场可将水中细菌全部杀灭,且无消毒副产物生成;该技术可为偏远地区居民提供可靠的安全饮用水消毒保障技术,具有良好的应用前景。周键等[36]采用电化学方法消毒处理医院污水,用Ti/SnO2-Sb2O3/β-PbO2作阳极,碳纤维为阴极;在电流密度为80 A·m?2,不需要额外添加电解质的情况下,消毒12 min后,出水的粪大肠菌群数小于500 cfu·L?1,符合污水综合排放一级标准(GB 8978-1996)。徐文英等[34]采用阳极为形稳电极、阴极为不锈钢板的电化学装置对德国Wiesbaden污水处理厂的二沉池出水进行消毒,发现电压为3~15 V、处理时间为6.5~37.5 s条件下,细菌去除率达到82.61%~99.16%,平均能耗仅为0.11 kWh·m?3。该研究表明,电化学消毒是一种低能耗、无污染、高效率的污水消毒方法。CID等[41]报道了一种自给式生态厕所的尿液废水经生化预处理和电化学氧化消毒后作为冲洗水回用的水循环模式;该技术现已在一些没有条件使用抽水马桶的发展中国家、灾害安置区、学校和景区等地得到开发和应用实践。
由于电化学消毒技术具有安全高效、方便灵活、环境友好的特点,可利用在无集中供水地区的安全终端饮用水供应、小规模应急消毒保障、生态设施中水回用等特定应用场景[42-43],发展前景广阔。然而,该技术的大规模工程化应用仍存在一些限制因素:1)消毒机理和适用条件尚不十分明确,关键消毒物种的调控规律仍有待深入研究;2)当前主流的高效稳定阳极仍为贵金属涂层钛电极,一次性投入成本较高;3)运行过程中可能存在阴极结垢、电解水副反应和水质变化引起的电流效率下降等问题。为解决电化学消毒技术的应用问题,还依赖于材料、电子和电化学反应控制理论与技术等领域的不断发展进步[44]。
电化学消毒灭菌水处理技术作为一种新型技术,具有安全高效、方便灵活、环境友好等特点,正受到越来越多的关注。电化学消毒在无集中供水地区的安全终端饮用水供应、小规模应急消毒处理、生态设施中水回用等需求场景上具有广阔的应用前景。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 
 点击查看大图
点击查看大图