全文HTML
--> --> --> 随着城市化进程的加快,我国城市污水产量不断增加,污泥产量也随之增长。截至2013年底,我国城市污泥年产量达到3.5×107 t (以含水率80%计)[1]。2016年底,全国城市污水排放量达7.1×109 t,污泥产量达4×107 t (以含水率80%计);预计到2020年,我国污泥产量将达到6×107 t[2]。急速增长的污泥产量使污泥的处理处置形势愈发严峻,污泥的减量化也变得十分重要。2015年,我国颁布的《水污染防治行动计划》[3]提出,需要推进污泥处理处置,对污水处理设施产生的污泥需要进行减量化、稳定化、无害化和资源化处理处置。其中,污泥的减量化是其进行后续处理的前提,而污泥调理和脱水是实现其减量化的关键步骤。污泥的调理方法可分为物理法、化学法、生物法[4]。在化学法中,硫酸根自由基(
SUN等[15]研究发现,Fe0在反应中活性较低,因此,采用纳米零价铁包裹在微米级的碳球(Fe0@CS)中,来激活PMS生成
尽管Fe0/Fe3C@CS激发PMS产生自由基在水中有机物的氧化降解方面具有技术优势,但该方法在污泥调理方面的效果尚未得到评价。本研究以污水处理厂回流污泥为研究对象,通过改进的水热法合成Fe0/Fe3C@CS,利用Fe0/Fe3C@CS活化PMS改善污泥的脱水性能,通过单因素变量法确定调理的最佳投药量,分析调理前后污泥脱水性能的差异以及污泥EPS中典型有机物分布和浓度的变化特征。
1.1. 供试污泥样品
污泥为北京某污水处理厂回流活性污泥,处理厂采用AO工艺,日处理水量达1×106 m3。污泥样品自然沉降2 h,弃去上清液,将沉淀的污泥通过孔径为0.18 cm的网筛进行过滤,收集过滤后的污泥置于(4.0±0.5) ℃冰箱保存。为了避免污泥性质的变化,所有实验在5 d内完成。本研究共采集2批污泥样品进行不同阶段实验。相应的污泥基本性质见表1。每次开始实验之前,污泥样品需要自然升至室温。1.2. Fe0/Fe3C@CS材料的制备
采用原位水热碳化法合成具有磁性的Fe0/Fe3C@CS材料。将0.02 mol的三聚氰胺和0.02 mol的D-葡萄糖溶解在50 mL超纯水中,然后将0.02 mol的FeCl3·6H2O和0.01 mol的FeCl2·4H2O溶解在上述溶液中,搅拌1 h。搅拌的同时,在40 mL·min?1的氮气流下以0.5 mL·min?1的速率滴加28%的氨水溶液,使溶液pH达到10。然后,将混合溶液转移到120 mL的水热反应釜中,并在180 ℃的烘箱中处理18 h。自然冷却至室温后,将得到的黑色悬浮液过滤并用乙醇/水洗涤3次。然后将沉淀物在80 ℃的烘箱中干燥后在通入N2的管式炉中以550 ℃的温度进一步处理4 h,得到Fe0/Fe3C@CS材料。1.3. Fe0/Fe3C@CS激发PMS调理污泥
取250 mL预处理后的污泥置于250 mL的烧杯中,向污泥中投加一定量的Fe0/Fe3C@CS和PMS。根据WANG等[15]的研究中所选投加比及初步实验,综合考虑污泥的后续处理及经济因素,将Fe0/Fe3C@CS与PMS的投药比设置为1∶12;随后,以300 r·min?1的转速搅拌10 min,然后采集污泥样品,测定污泥CST、真空抽滤后泥饼含水率[17],并测定污泥EPS中多糖、蛋白质、腐殖酸以及典型有机物的组成和含量。污泥EPS采用离心-超声法[18]进行提取。1.4. 污泥理化性质分析
污泥含水率和脱水率采用质量法[19]进行测定;污泥毛细吸水时间(capillary suction time,CST)采用毛细吸水时间测定仪(304M型,Triton Electronics)[20]测定。1.5. 污泥EPS组分分析
PS中多糖(polysaccharide,PS)含量依据硫酸-葱酮法[21]进行测量,蛋白质(protein,PN)和腐殖酸(humic acid,HA)的含量依据Folin-酚法[22]进行测量。EPS中典型有机物采用EEM荧光光谱法,利用分子荧光光谱仪(F-7000,Hitachi,日本)进行测定,发射波长设定为220~600 nm,接收波长为200~400 nm,以5 nm的增量增加。采用荧光区域整合(FRI)技术分析并计算每个EEM区域下的体积积分[23]和荧光响应百分比。2.1. Fe0/Fe3C@CS和PMS投加量的确定
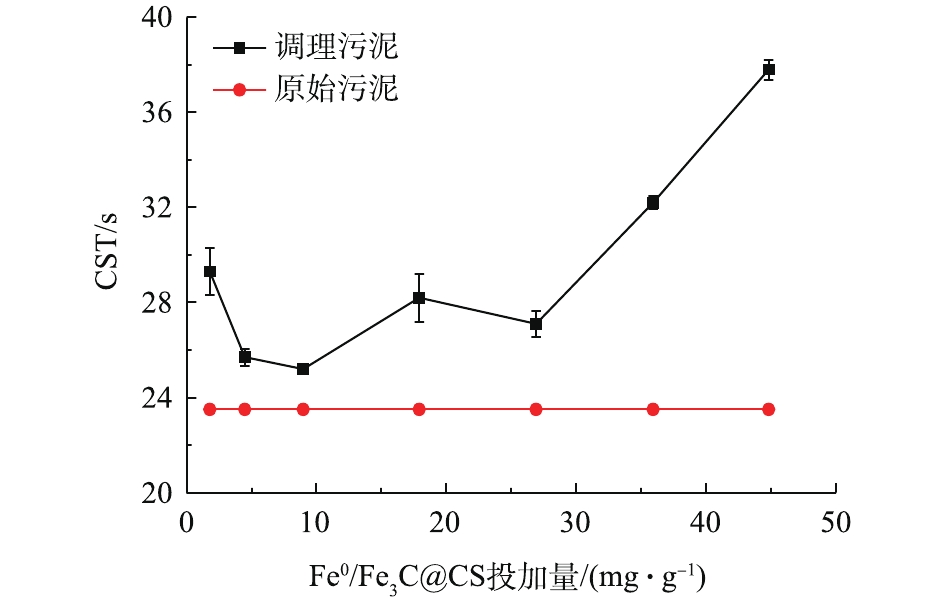
图1为当PMS投加量为0.43 g·g?1(以TSS计)时,不同Fe0/Fe3C@CS投加量对污泥CST值的影响曲线。图1显示,随着投加量的升高,污泥CST值整体上呈现先降低后增加趋势,但均比原泥的CST值高。产生此现象的原因可能是,由于当投加量不断增加时,污泥破解程度增大,一方面污泥絮体过小不利于水分与污泥颗粒分离[24];另一方面污泥破解后孔隙率变小,使得水分难以通过[25],从而降低了污泥的过滤性能,增大了污泥的CST值。当Fe0/Fe3C@CS投加量为8.97 mg·g?1时,污泥CST值达到最低值为25.2 s,但依然比原泥的CST值高1.7 s。当Fe0/Fe3C@CS投加量大于26.9 mg·g?1时,污泥CST值随投加量增加而持续升高。图2为不同投加量对污泥抽滤含水率的影响曲线。由图2可知,调理后污泥的抽滤含水率随Fe0/Fe3C@CS投加量增加均有不同程度的降低,当Fe0/Fe3C@CS的投加量为35.9 mg·g?1(以TSS计)时,污泥的抽滤含水率最低下降至最低值69.45%,这说明此时污泥脱水效果较好。综合图1、图2可知,虽然在重力作用下污泥的CST值升高,过滤性能降低,但在抽滤作用下,负压不仅可以克服由于污泥破解所带来的过滤性能不利的影响,而且可以提升污泥的脱水效果。因此,在后续的污泥调理研究中,确定当PMS投加量为0.43 g·g?1时,Fe0/Fe3C@CS的最优投加量为35.9 mg·g?1。2.2. 调理前后EPS组分的变化
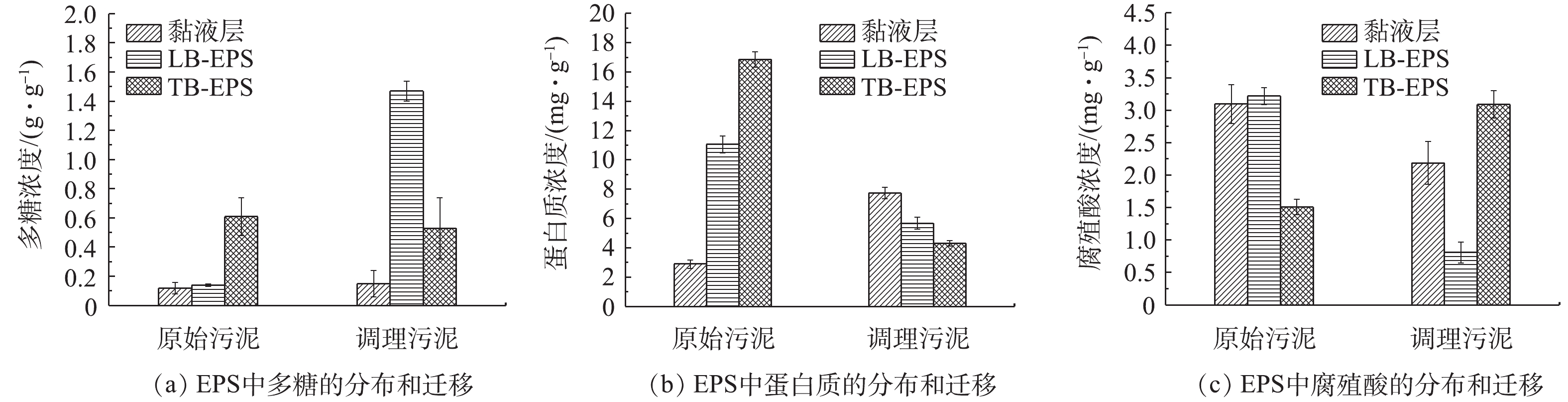
多糖和蛋白质是污泥EPS中的主要组分[26]。有研究[27]发现,污泥中蛋白质含量影响污泥的絮凝能力。本研究测定了确定当Fe0/Fe3C@CS与PMS的投加量分别为35.9 g·g?1和0.43 g·g?1时,调理前后污泥EPS不同组分中多糖(图3(a))、蛋白质(图3(b))与腐殖酸(图3(c))的含量。如图3(a)所示,污泥胞外聚合物中多糖的总量在调理后增加,调理前,污泥黏液层、LB-EPS、TB-EPS中多糖含量分别为0.12、0.14、0.61 g·g?1;调理后,黏液层和LB-EPS中多糖含量增加。其中,LB-EPS多糖含量增加至1.47 g·g?1,而TB-EPS中的多糖含量略有降低,且在LB-EPS中的迁移转化较明显。多糖总量增加的原因可能是由于污泥中多糖和蛋白质主要以复合物的形式存在[28],而某些氧化过程只作用于蛋白质长链上。由图3(b)可知,经过调理后,污泥EPS中蛋白质总含量从原泥的30.84 mg·g?1降低至17.47 mg·g?1。其中,黏液层中蛋白质含量从2.9 mg·g?1升高至7.75 mg·g?1,LB-EPS、TB-EPS中的蛋白质含量降低。此现象说明,在调理过程中,一部分蛋白质被降解;同时,LB-EPS和TB-EPS中一部分蛋白质被迁移至黏液层。可见,蛋白质的迁移和转化主要发生在TB-EPS,这与KIM等[29]的研究结果一致。产生这一结果的原因可能是由于蛋白质在EPS中逐层迁移。如图3(c)所示,调理后污泥EPS中腐殖酸的总量从7.83 mg·g?1降低至6.09 mg·g?1,而TB-EPS中的含量由1.51 mg·g?1增加至3.09 mg·g?1,黏液层与LB-EPS的腐殖酸含量降低。这说明黏液层和LB-EPS中的腐殖酸被氧化降解,且在LB-EPS中被降解的腐殖酸更多,而TB-EPS中腐殖酸含量的增加可能是由于被EPS包裹着的细胞相中的物质被释放至EPS中[30]。由上述结果可知,Fe0/Fe3C@CS激发PMS对污泥中有机物有一定的降解效果,且对于污泥EPS中多糖、蛋白质、腐殖酸3种不同有机物的释放、降解效果不同。2.3. 调理前后EPS三维荧光光谱分析
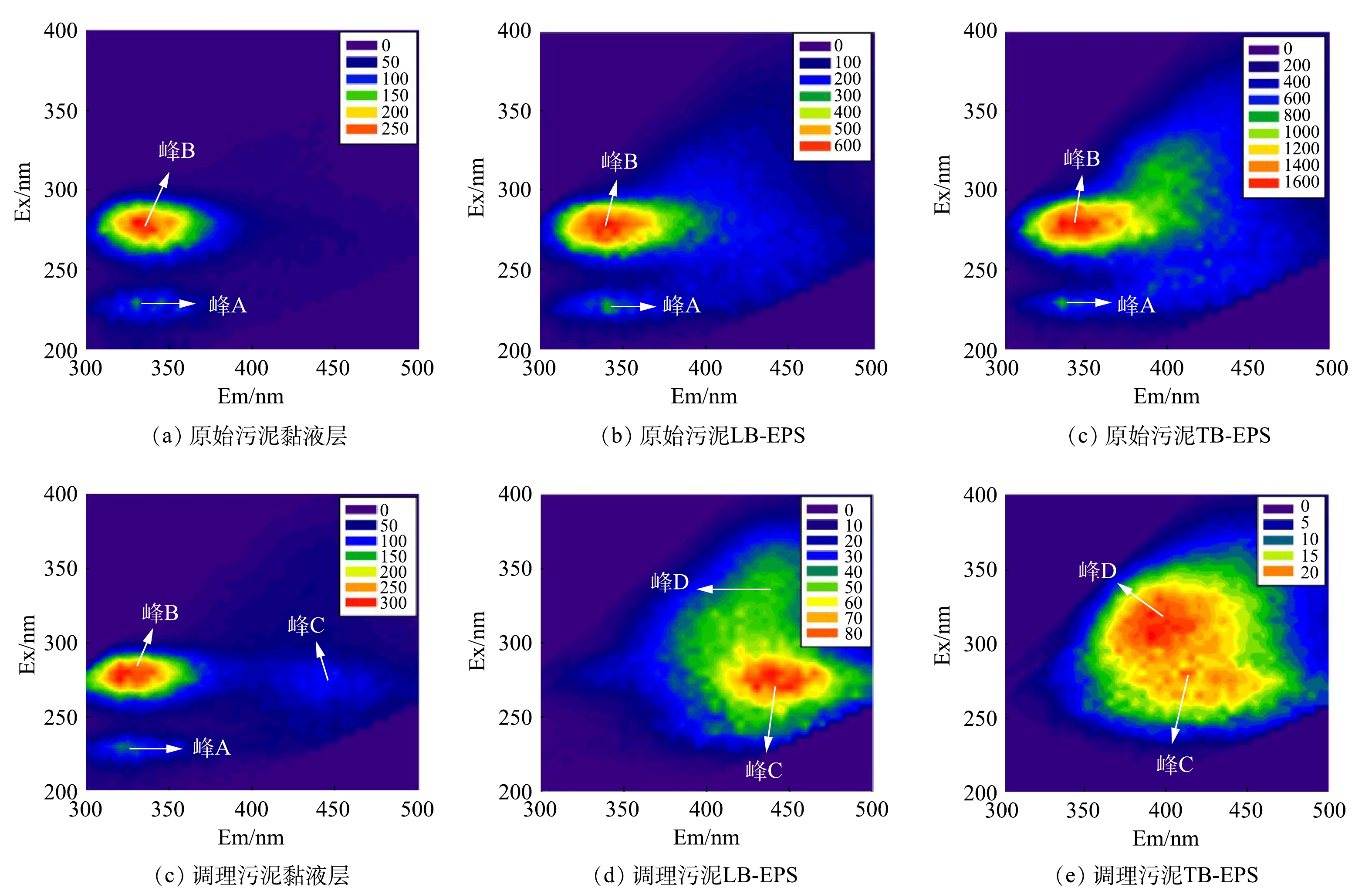
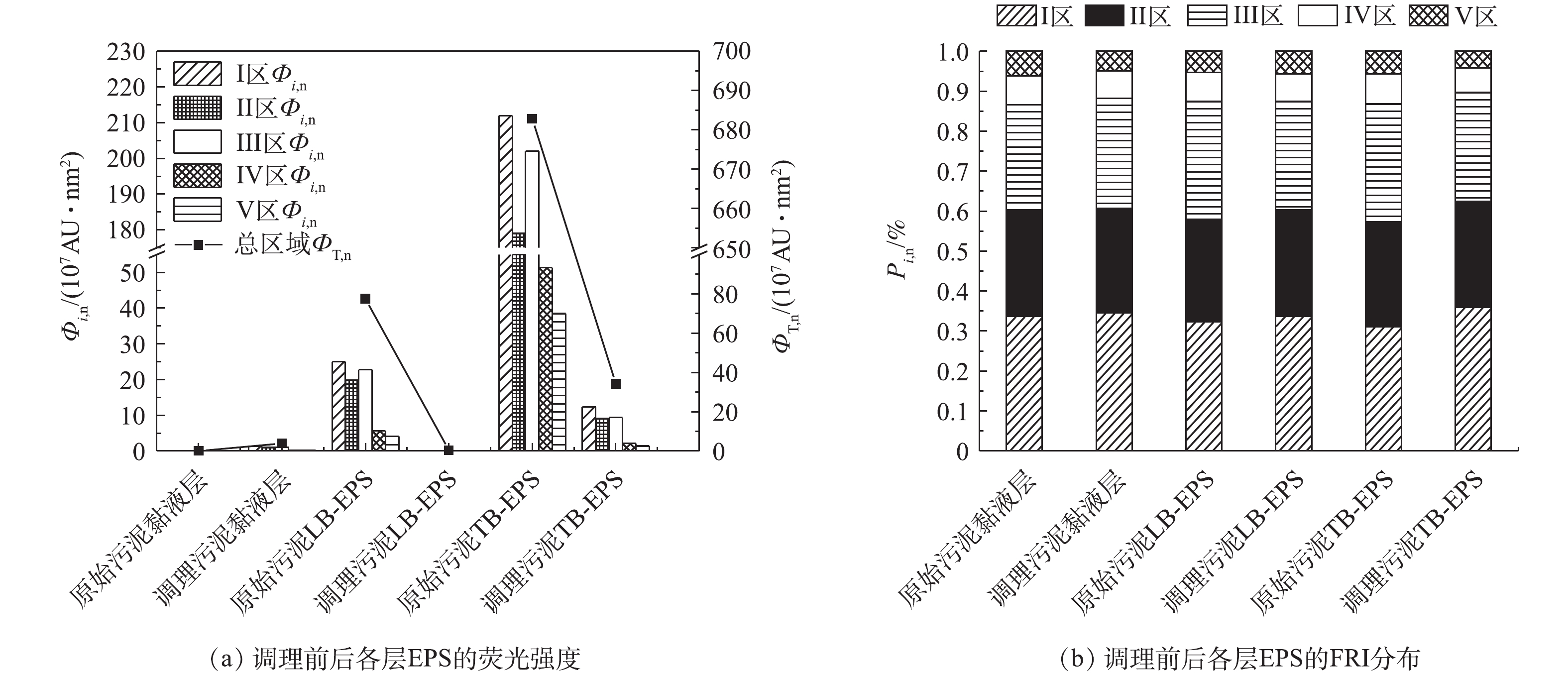
对调理前后污泥各层EPS进行三维荧光光谱扫描,经过标准化处理,得到谱图(图4)。由图4(a)~图4(c)可知,调理前污泥EPS各层中均含有酪氨酸和微生物副产物2种物质,而且TB-EPS的浓度最高。调理后污泥EPS中有机物种类增加,主要含有微生物副产物、酪氨酸和腐殖酸类物质。其中,酪氨酸和微生物副产物主要存在于黏液层。由图4(d)~图4(f)可知,调理后污泥黏液层中的酪氨酸和微生物副产物的浓度升高,这可能是由于内层EPS中的有机物被迁移或转化;此外,调理后的黏液层中还出现了腐殖酸类物质。调理后LB-EPS与TB-EPS中的典型有机物浓度明显降低,这与LI等[31]的研究结果一致。污泥LB-EPS与TB-EPS在调理前后的典型有机物浓度变化类似调理后代表酪氨酸的峰A与代表微生物副产物的峰B消失,同时出现了代表腐殖酸类物质的峰C与峰D。此现象说明酪氨酸和微生物副产物在调理过程中被降解为其他类型的中间产物,或者迁移至黏液层。ZHEN等[32]的研究发现,污泥EPS中酪氨酸浓度增加会导致污泥脱水性变差,可见污泥调理可改善脱水性。腐殖酸类物质的出现可能来自污泥内部细胞相的破解和释放。而EPS各层中腐殖酸浓度变化与图3结果不同的原因可能是由于腐殖酸的检测方法不同所导致的。采用FRI方法对EEMs谱图进行分区整合后得到荧光强度及其占比,结果如图5所示。由图5(a)可知,原始污泥各层EPS的EEM谱图的总区域标准体积ΦT,n由小到大依次为黏液层、LB-EPS、TB-EPS。可见,污泥EPS中各层典型有机物分布浓度由外层至内层逐渐增加。调理后污泥EPS中总区域标准体积由760.26×107 AU·nm2减少至38.43×107 AU·nm2,总体荧光强度呈下降趋势。其中,LB-EPS和TB-EPS中各物质的荧光强度降低,而黏液层的荧光强度略有升高。此外,调理后EEM谱图的总区域标准体积ΦT,n最小的EPS分层由黏液层变为LB-EPS,其总荧光强度为0.344 2×107 AU·nm2。因此,可以推测EPS中的典型有机物在调理过程中被降解和转化,调理后污泥中的部分典型有机物从LB-EPS、TB-EPS迁移至黏液层,且调理过程对LB-EPS的有机物的迁移和转化影响最大。YANG等[33]的研究证明,LB-EPS的含量与束缚水含量呈正比关系;WU等[34]也发现,污泥的CST值和LB-EPS的含量呈显著正相关,因此LB-EPS含量的降低可以提高污泥的脱水性能。
Pi,n为相应区域荧光强度的占比,其变化趋势如图5(b)所示。可以看出,各层EPS中酪氨酸(Ⅰ区)在调理后的荧光强度占比增加,而色氨酸(Ⅱ区)的荧光强度占比在调理前后基本不变。富里酸类物质(Ⅲ区)荧光强度在黏液层中的占比降低,在LB-EPS和TB-EPS中的占比增加。各层的微生物副产物(Ⅳ区)荧光强度占比在调理后均降低,可见污泥调理可将EPS中的微生物副产物降解或转化。此外,腐殖酸类物质(Ⅴ区)在LB-EPS的占比增加,在黏液层和TB-EPS的占比降低。
2) Fe0/Fe3C@CS激发PMS调理过程对污泥中有机物有一定的降解和释放效果,对于污泥EPS中多糖、蛋白质、腐殖酸3种有机物的释放、降解效果不同。多糖和腐殖酸在LB-EPS中的迁移活动最为活跃,理过程可以释放TB-EPS中的多糖和蛋白质,且LB-EPS中的多糖更易被降解,而对于腐殖酸则是从被EPS包裹的细胞内释放至TB-EPS,同时LB-EPS与黏液层中的腐殖酸得到降解。
3)调理后污泥EPS中典型有机物种类增加,黏液层中的酪氨酸和微生物副产物的浓度升高,而LB-EPS和TB-EPS中的酪氨酸和微生物副产物的浓度降低,腐殖酸浓度增加。且调理过程对细胞有一定的破解作用,细胞相中部分腐殖酸类物质被释放至EPS中。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 


 点击查看大图
点击查看大图