3.重庆市三峡水务渝北排水有限责任公司,重庆 401120
1.College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangtze Normal University, Chongqing 408100, China
2.School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu 610500, China
3.Chongqing Three Gorges Water Yubei Drainage Co. Ltd., Chongqing 401120, China
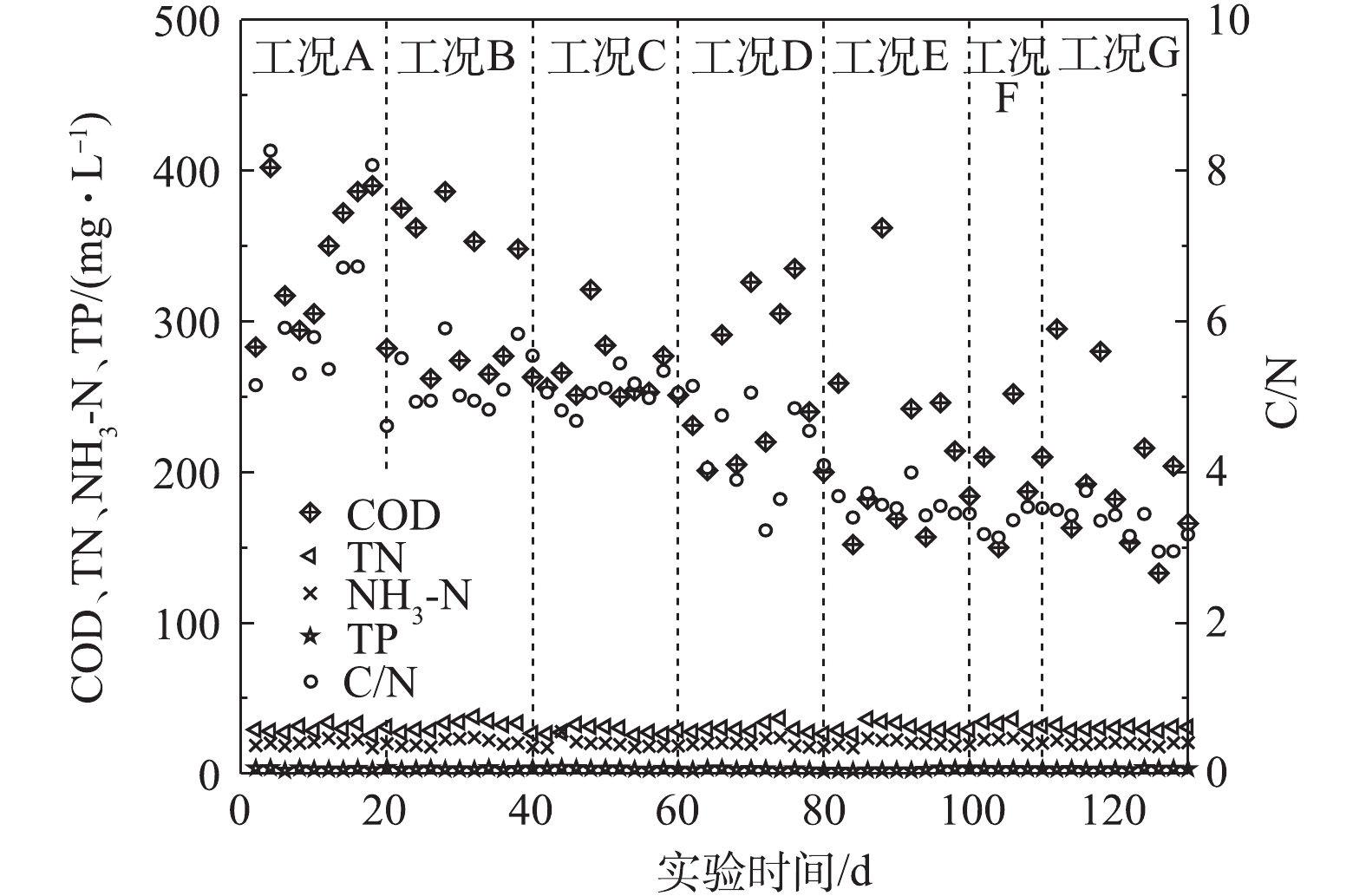
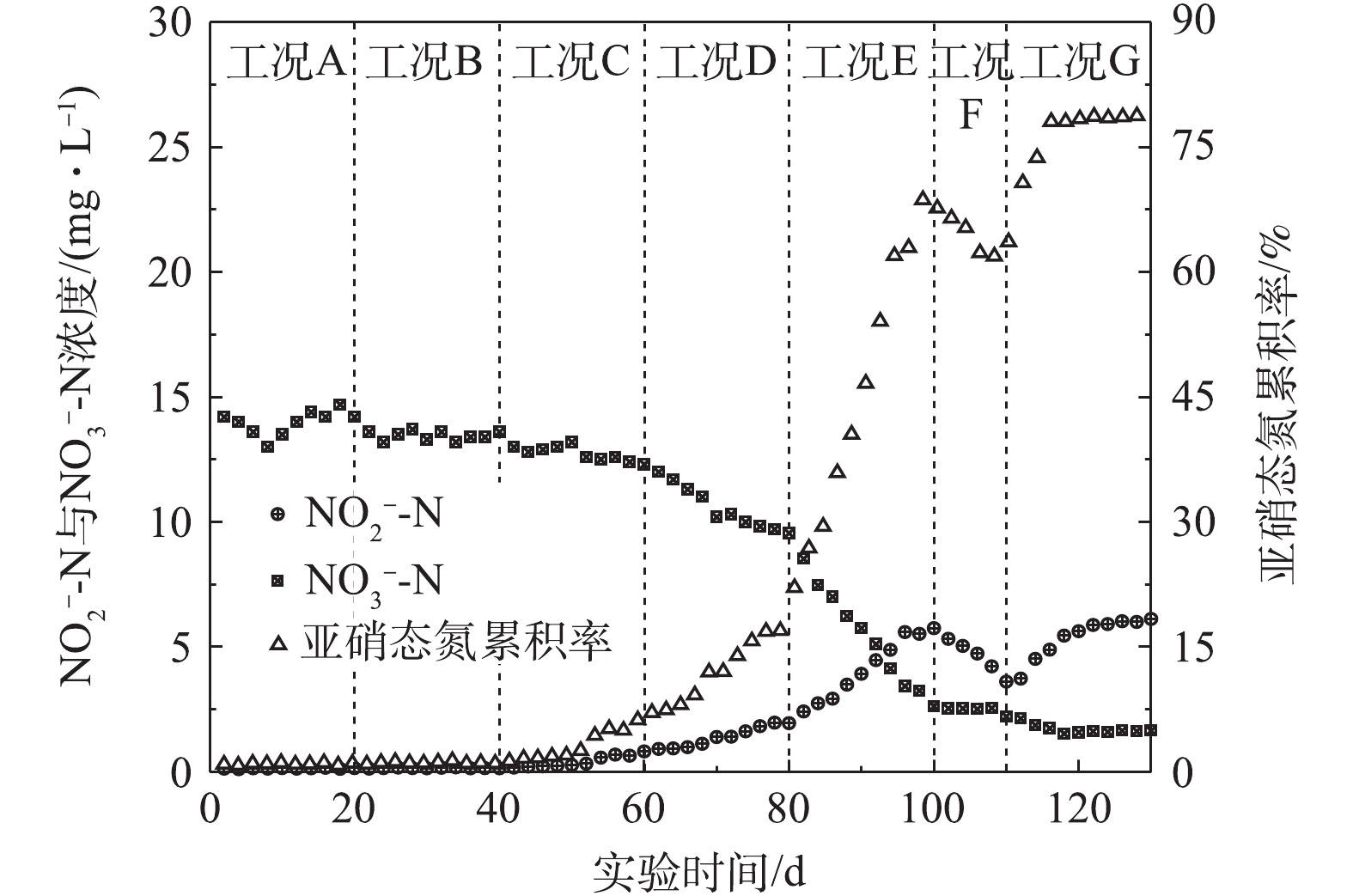
采用好氧/缺氧交替运行模式处理低C/N城市污水,考察了低温环境下启动短程硝化反硝化的可行性,重点研究了好氧池区域Ⅰ、区域Ⅱ、区域Ⅲ溶解氧分布对短程硝化反硝化脱氮效果的影响。结果表明,采用好氧/缺氧交替运行模式,对好氧池溶解氧进行分区优化后,在低温环境下启动短程硝化反硝化具有可行性。在所采用的7种工况中,较为优化的工况是区域Ⅰ、区域Ⅱ、区域Ⅲ,溶解氧分别为0.8~1.2、<0.5、1.2~1.8 mg·L
元左右,有效实现了成本与水质的双赢。以上结果可为短程硝化反硝化工艺的工程推广提供参考。
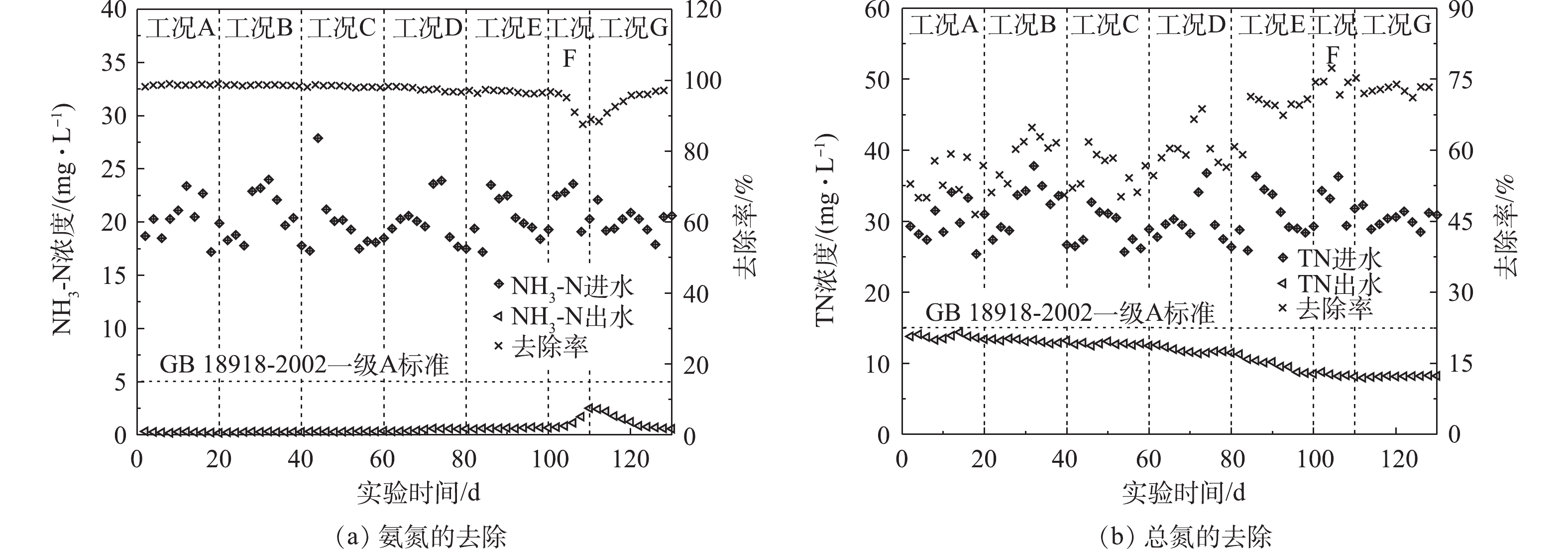
The alternating aerobic/anoxic operation mode was used to treat low C/N urban sewage. The starting up feasibility of the short-cut nitrification and denitrification in low temperature environment and the effect of dissolved oxygen distribution in aerobic zone I, II and III on the nitrogen removal by the short-cut nitrification and denitrification were studied. The results show that it was feasible to start up the short-cut nitrification and denitrification at low temperature by using the alternating aerobic/anoxic operation mode and partition-optimizing the dissolved oxygen in aerobic tank. Based on the seven different operating conditions, the dissolved oxygen distributions in the more optimal zones I, II and III were 0.8~1.2 mg·L
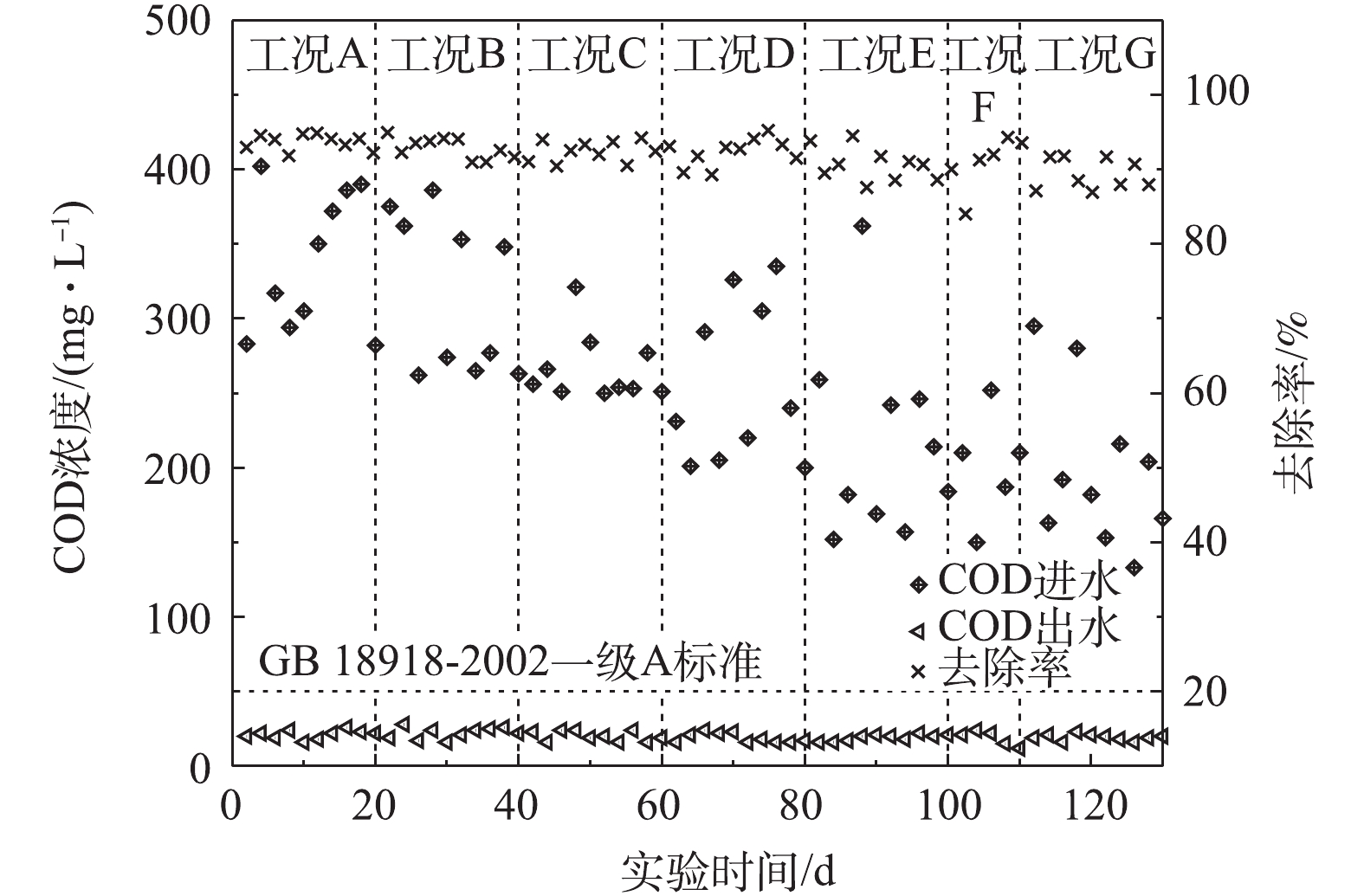
, respectively. Under this operating condition, the accumulation rate of nitrite nitrogen maintained above 78%, the removal rate of total nitrogen in the effluent was about 73%. Compared with that before the start-up of the short-cut nitrification and denitrification, the removal rate increased by 19.4%, the concentration of ammonia nitrogen was lower than 0.60 mg·L
, and the nitrogen index of effluent was significantly better than the emission standard of the first level A of GB 18918-2002. The COD removal rate of the effluent was between 86.9% and 94.9%. The total phosphorus concentration of the effluent was lower than 0.15 mg·L
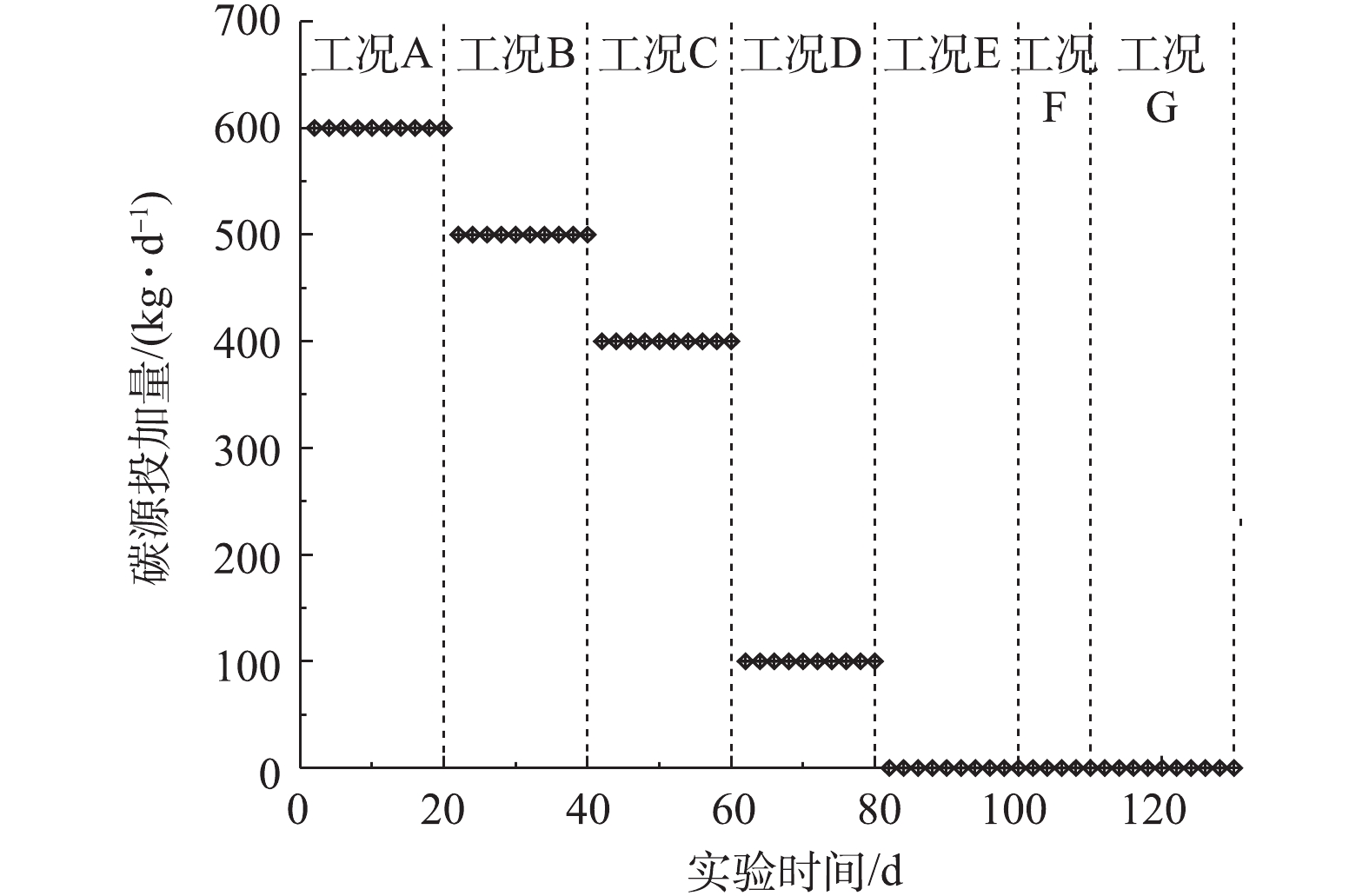
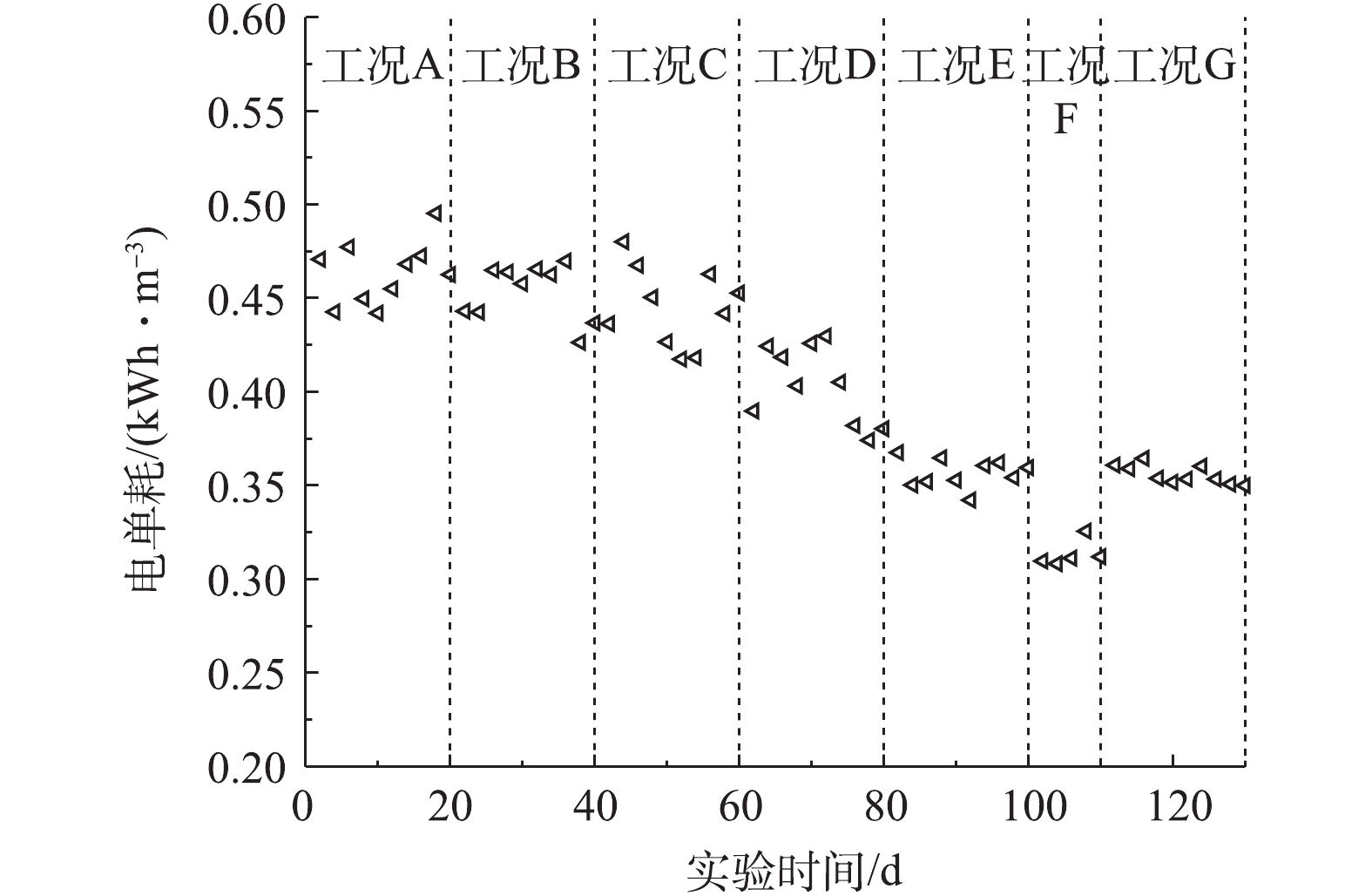
with strong controllability. For the low C/N urban sewage treated by using the short-cut nitrification and denitrification A/O process, it can save more than 970 000 yuan of carbon source investment fund and 420 000 yuan of electricity cost in the whole year, and effectively realize the win-win of cost and water quality. This study provides a case and parameter support for the engineering popularization of the short-cut nitrification and denitrification process.
.
Influent water quality of Xiaojiahe sewage treatment plant
Experimental schematics of biological pool in A/O process
Nitrogen forms and nitrite accumulation rate at the end of aerobic tail
Usage of carbon source
| [1] | WANG F, LIU Y, WANG J H, et al. Influence of growth manner on nitrifying bacterial communities and nitrification kinetics in three lab-scale bioreactors[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2012, 39(4): 595-604. |
| [2] | 张周, 赵明星, 阮文权, 等. 短程硝化反硝化工艺处理低C/N餐厨废水[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(9): 4165-4170. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150912 |
| [3] | KATSOGIANNIS A N, KORNAROS M, LYBERATOS G. Enhanced nitrogen removal in SBRs bypassing nitrate generation accomplished by multiple aerobic/anoxic phase pairs[J]. Water Science & Technology , 2003, 47(11): 53-59. |
| [4] | ZHU G B, PENG Y Z, GUO J H. Biological nitrogen removal with nitrification and denitrification via nitrite pathway[J]. Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2006, 73(1): 15-26. |
| [5] | 郭建华, 彭永臻, 黄惠珺, 等. 好氧曝气时间实时控制实现短程硝化[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 49(12): 1997-2000. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0054.2009.12.021 |
| [6] | GAO C D, FAN S X, JIAO E L, et al. Operation and optimization of an alternating oxic-anoxic shortcut nitrification-denitrification system[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 1030-1032: 387-390. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1030-1032.387 |
| [7] | 常赜, 孙宁, 李召旭, 等. 硫化物抑制亚硝酸氧化菌推动短程硝化反硝化生物脱氮技术[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(5): 1416-1423. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201710144 |
| [8] | 高春娣, 赵楠, 安冉, 等. FNA对短程硝化污泥菌群结构的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(5): 1977-1984. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.05.022 |
| [9] | JENNI S, VLAEMINCK S E, MORGENROTH E, et al. Successful application of nitritation/anammox to wastewater with elevated organic carbon to ammonia ratios[J]. Water Research, 2014, 49(2): 316-326. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.073 |
| [10] | ZHU G B, PENG Y Z, LI B K, et al. Biological removal of nitrogen from wastewater[J]. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2008, 192: 159-195. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-71724-1_5 |
| [11] | KORNAROS M, DOKIANAKIS S N, LYBERATOS G. Partial nitrification/denitrification can be attributed to the slow response of nitrite oxidizing bacteria to periodic anoxic disturbances[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(19): 7245-7253. |
| [12] | TOBINO T, CHEN J X, SAWAI O, et al. Inline thickener-MBR as a compact, energy efficient organic carbon removal and sludge production devise for municipal wastewater treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2016, 107: 177-184. doi: 10.1016/j.cep.2015.11.010 |
| [13] | VERSTRAETE W, PHILIPS S. Nitrification-denitrification processes and technologies in new contexts[J]. Environmental Pollution, 1998, 102(1): 717-726. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(98)80104-8 |
| [14] | 高大文, 彭永臻, 王淑莹. 交替好氧/缺氧短程硝化反硝化生物脱氮Ⅰ. 方法实现与控制[J]. 环境科学学报, 2004, 24(5): 761-768. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2004.05.002 |
| [15] | 曾薇, 张悦, 李磊, 等. 生活污水常温处理系统中AOB与NOB竞争优势的调控[J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(5): 1430-1436. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.05.030 |
| [16] | MA B, BAO P, WEI Y, et al. Suppressing nitrite-oxidizing bacteria growth to achieve nitrogen removal from domestic wastewater via anammox using intermittent aeration with low dissolved oxygen[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 13048. doi: 10.1038/srep13048 |
| [17] | 李思敏, 杜国帅, 唐锋兵. 多点进水改良型复合A2/O处理低C/N污水[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(10): 3805-3811. |
| [18] | 刘春, 王聪聪, 陈晓轩, 等. 微气泡曝气生物膜反应器处理低C/N比废水脱氮过程[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(2): 754-760. |
| [19] | CHEN Y Z, LI B K, YE L, et al. The combined effects of cod/n ratio and nitrate recycling ratio on nitrogen and phosphorus removal in anaerobic/anoxic/aerobic (A2/O)-biological aerated filter (BAF) systems[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 93(10): 235-242. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2014.10.005 |
| [20] | PELAZ L, GOMEZ A, LETONA A, et al. Nitrogen removal in domestic wastewater. Effect of nitrate recycling and COD/N ratio[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 212: 8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.08.052 |
| [21] | 高春娣, 李浩, 焦二龙, 等. 交替好氧缺氧短程硝化及其特性[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2015, 41(1): 116-122. |
| [22] | 徐浩, 李捷, 罗凡, 等. 低C/N比城市污水短程硝化特性及微生物种群分布[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(3): 1477-1481. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201511206 |
| [23] | 张功良, 李冬, 张肖静, 等. 低温低氨氮SBR短程硝化稳定性试验研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(3): 610-616. |
| [24] | 吴春雷, 荣懿, 刘晓鹏, 等. 基于分区供氧与溶解氧调控的低C/N比污水短程硝化反硝化[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(5): 314-320. |
| [25] | 吴朕君, 穆剑楠, 单润涛, 等. 基于DO和ORP的短程硝化SBR控制方法研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2019, 45(7): 114-118. |
| [26] | 邱春生, 聂海伦, 孙力平, 等. 不同碳源条件下聚磷菌代谢特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2014, 8(6): 2191-2197. |
| [27] | SHISKOWSKI D M, MAVINIC D S. Biological treatment of a high ammonia leachate: Influence of external carbon during initial startup[J]. Water Research, 1998, 32(8): 2533-2541. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00465-X |
| [28] | 楚想想, 罗丽, 王晓昌, 等. 我国城镇污水处理厂的能耗现状分析[J]. 中国给水排水, 2018, 34(7): 70-74. |

 下载:
下载: 

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图