全文HTML
--> --> --> 近年来,生活垃圾焚烧处理得到了大力推广和发展,同时也引发了对处理过程中伴随的二次污染及其控制的关注,其中不乏关于垃圾渗滤液处理方式的研究。为得到较好的出水水质,常采用膜技术作为垃圾渗滤液处理流程的末端控制技术,但在该过程中产生的膜浓缩液,含有大量盐分和重金属,可生化性很低,是一种极难处理的高浓度废水[1-2]。目前,国内外关于渗滤液膜浓缩液(简称浓缩液)的处理方法主要有回喷焚烧炉法[3]、回灌填埋场法[4-5]、蒸发法[6-8]、高级氧化法[9-14]等。蒸发处理技术具有占地面积小、产水能力高、可析出盐类晶体的优势,但设备腐蚀和能耗问题导致实际应用中经济效益较差。此外,高级氧化法也存在投资和运行费用较高的问题。回喷法最早在国外得以成功应用,其具有无害化彻底、工艺简单的特点。由于一些发达国家垃圾热值高,渗滤液产量少,可以直接将其回喷焚烧炉处理,但国内垃圾普遍具有热值较低、含水量高的特征,使得回喷法存在一定局限性。根据《关于进一步加强生物质发电项目环境影响评价管理工作的通知》(环发[2008]82号),垃圾焚烧厂产生的渗滤液应优先考虑回喷,浓缩液应焚烧处理。国内的焚烧厂渗滤液产生量约占垃圾总量的15%~30%,通常采用纳滤或反渗透进行深度处理。该过程产生的膜浓缩液约为渗滤液总量的15%~30%,水量较大,仍不宜直接回喷,需要再次减量处理[15]。近年来,一种以物料膜对膜浓缩液进行再浓缩的减量化技术逐渐在国内焚烧厂中使用,能够将回喷量控制在3.5%以下,而理论上回喷比控制在3.96%以内一般不会对焚烧工况造成影响[16]。因此,对于生活垃圾焚烧发电厂而言,浓缩液减量后雾化回喷到炉内焚烧是一种污染物去除效率最高且有效的处理方式。
在焚烧厂实际工程的运行操作中,浓缩液回喷对于焚烧系统以及烟气、飞灰的二次污染控制均存在潜在风险。目前,国内外文献中涉及浓缩液回喷后物质转化规律及回喷影响的研究较为缺乏,且由于条件限制,难以在焚烧厂实际运行中,对浓缩液回喷后污染物的迁移情况进行研究。因此,本研究通过实验模拟不同的回喷温度,研究了浓缩液回喷所得固相物质的特性和转化规律以及Cl、S等产生腐蚀性气体和物质的主要元素的变化规律,以此分析固相颗粒物对烟气系统负荷的影响及固相物质中腐蚀性成分对焚烧设备的影响,同时为回喷可行性的研究提供参考。
1.1. 实验样品
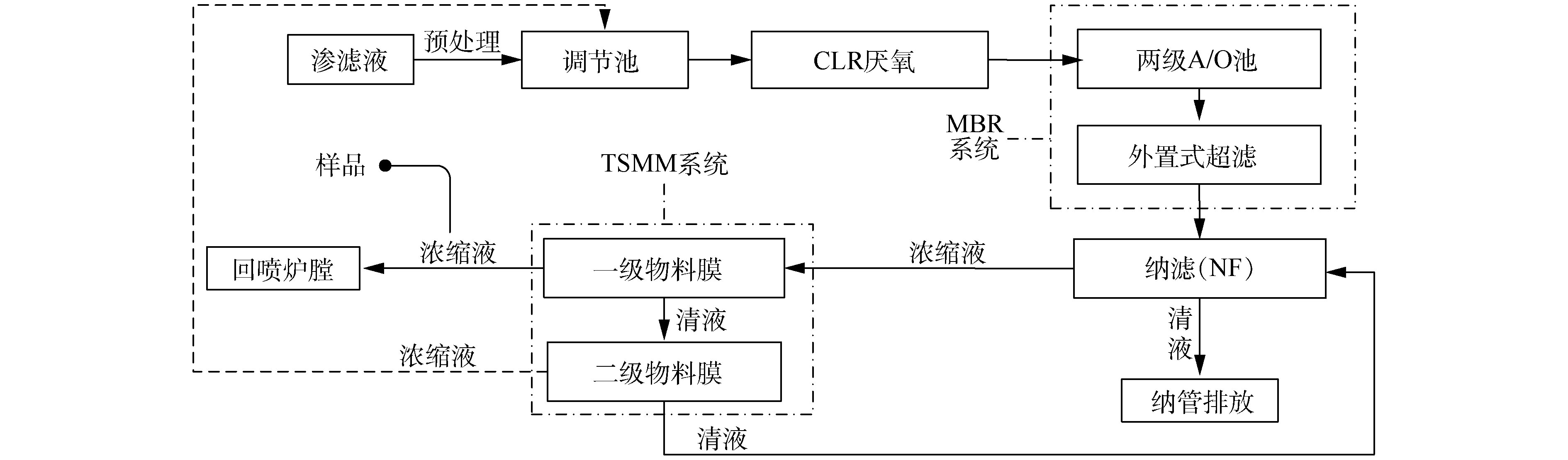
实验样品为一级物料膜浓缩液,来自于上海市某垃圾焚烧发电厂纳滤膜浓缩液的两级物料膜(two stage material membrane,TSMM)处理系统。该厂的渗滤液及浓缩液处理工艺如图1所示。1.2. 实验与分析测试方法
水质特性分析:COD、BOD等常规水质特性均采用国标法测试;重金属和阴离子浓度分别通过塞曼原子吸收分光光度计(Z-5000,日立)和离子色谱仪(IC6000,安徽皖仪)测定。晶体粒径分析:《生活垃圾焚烧污染控制标准》(GB 18485-2014)中对炉膛焚烧温度的指标要求为≥850 ℃,研究过程中调研了多个垃圾焚烧厂亦发现,大部分焚烧厂会在温度达到850 ℃时开始回喷。因此,将100 mL的浓缩液样品在850 ℃的条件下烧干,并采用激光粒度仪检测晶体粒径,采用场发射扫描电镜(日本JSM 5900LV)分析其微观形貌。
晶体主要成分分析:结合各焚烧厂垃圾热值差异和焚烧运行工况波动情况[17],在温度为750、850、900、1 000、1 100 ℃的条件下,将100 mL浓缩液样品在马弗炉中烧干,再用X射线衍射(北京普析XD-2型)分析其组分。工作条件:以CuKα为射线源,管电流40 mA,管电压30 kV,连续扫描,扫描方式θ~2θ,扫描步长0.02(°)·min?1,扫描速度4(°)·min?1。
晶体元素组成及含量分析:采用SEM/EDS对固相物质进行解析,以分析元素组成和不同温度下的元素变化。电压为20 kV,分辨率为3.0 nm。
2.1. 浓缩液水质特性分析
为了便于对比研究,给后续的固相分析提供参考依据,对浓缩液样品的水质进行了分析,结果如表1所示。由表1可以看出,该物料膜浓缩液呈弱碱性,其COD值相较于纳滤和反渗透浓缩液更高[18-20],这主要是由于物料膜的再浓缩作用导致;B/C值为0.04,远低于污水可生化降解下限值0.3,故可生化性极差,可生化降解的有机物已经在生化处理阶段被大量分解,膜截留下的残余液中主要为腐殖质等极难降解的有机物;金属离子中Ca2+、Mg2+浓度高,说明水的硬度较大;阴离子以Cl?、2.2. 浓缩液烧干后固相物质粒径分析
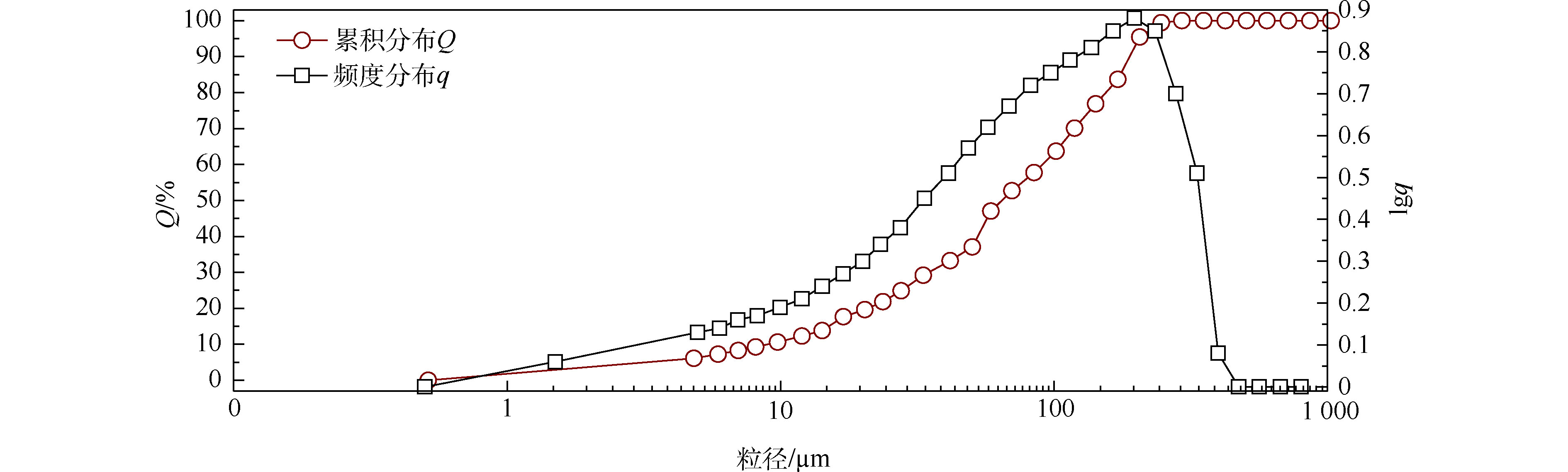
浓缩液样品在850 ℃的条件下烧干后,得到的固相物质为略呈淡黄色的晶体粉末(图2),其粒子尺寸分布如图3所示。由图3可见,模拟回喷温度下烧干浓缩液样品后所形成的固体颗粒粒度的分布形态为单峰分布,最高峰时对应的粒径为197 μm,且137~234 μm的粒径频度最高,对数值均大于0.8。累积分布曲线表明,大多颗粒粒径集中在30~365 μm,约占74.53%,在小于30 μm和大于365 μm区间的颗粒所占百分含量分别为24.89%和0.58%。
浓缩液烧干后的固相粒子粒径分布规律与飞灰[21-26]类似,粒径分布较广,且整体呈正态分布。因此,当浓缩液回喷焚烧炉后,炉内高温使其立即转变为粒径为30~365 μm左右的固体颗粒物。但由于焚烧炉内气流条件复杂,焚烧后残余的细小颗粒在气流的扰动下会不断运动并发生碰撞,有可能聚集形成粒径较大的颗粒,且部分小颗粒附着于较大颗粒表面,在重力场的作用下,共同沉积到底灰或炉渣中。而粒径较小的颗粒通常会随飞灰进入烟气净化系统,由布袋除尘器拦截。由此可见,浓缩液焚烧后形成的固体颗粒物极有可能增加烟气净化系统的处理负荷。因此,若采用回喷法处理膜浓缩液,在计算烟气处理系统的处理负荷时,应充分考虑由膜浓缩液所带来的增量。
2.3. 不同温度浓缩液烧干后固相物质的成分分析
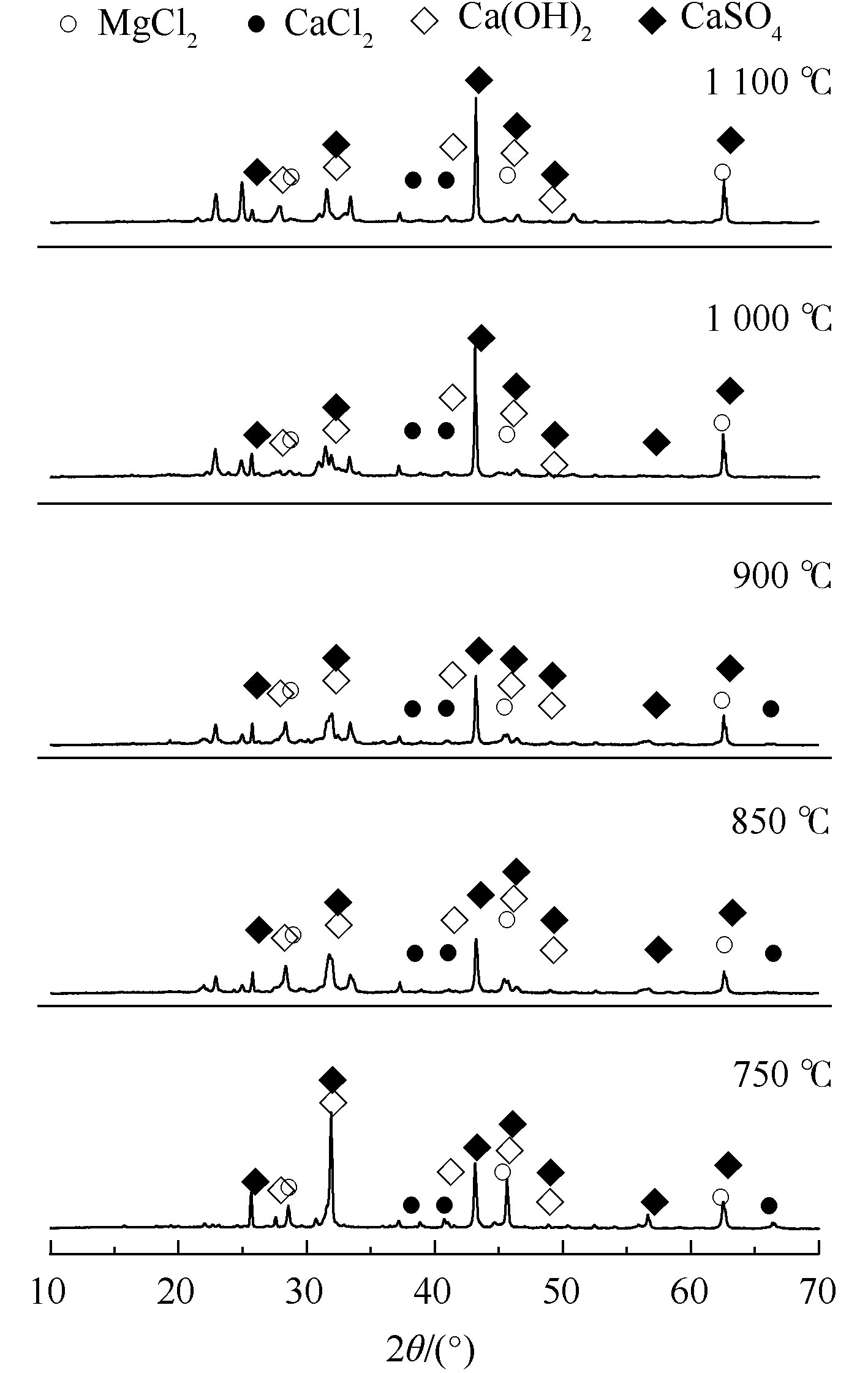
图4为固相物质的XRD分析结果。从图4中可以看出,虽然浓缩液中含有大量Na、K,但经过高温焚烧后,并无稳定的钠盐和钾盐晶体物质存在。这可能是由于晶态钾盐、钠盐经过分解转化过程,成为了非晶态物质,而晶型物质主要是以氯盐和钙盐(CaCl2、MgCl2、CaSO4)为主。随着温度的升高,2θ为43.14°和62.48°所代表的CaSO4的衍射峰强度呈明显增强趋势;2θ为25.66°、31.89°、45.55°代表的CaCl2、Ca(OH)2衍射峰强度有不同程度的减弱。推测其原因是:随温度的升高,CaCl2、Ca(OH)2晶体在高温下熔融,或者转化为非晶态物质,反应方程如式(1)和式(2)所示。
另一方面,高温也促使CaO等非晶体形式与硫化物反应,逐渐转变为热稳定性更好的CaSO4晶体[27],其转化方式如式(3)~式(6)所示。
由此可见,S元素最终以CaSO4的形式被固定,固相物质成分类似于垃圾焚烧的Ca-S型积灰[28];同时,由于CaSO4晶体的熔点高(1 450 ℃),其在实验温度范围内基本可以保持稳定存在。
2.4. 不同温度下浓缩液回喷后固相物质的微观形貌和元素变化分析
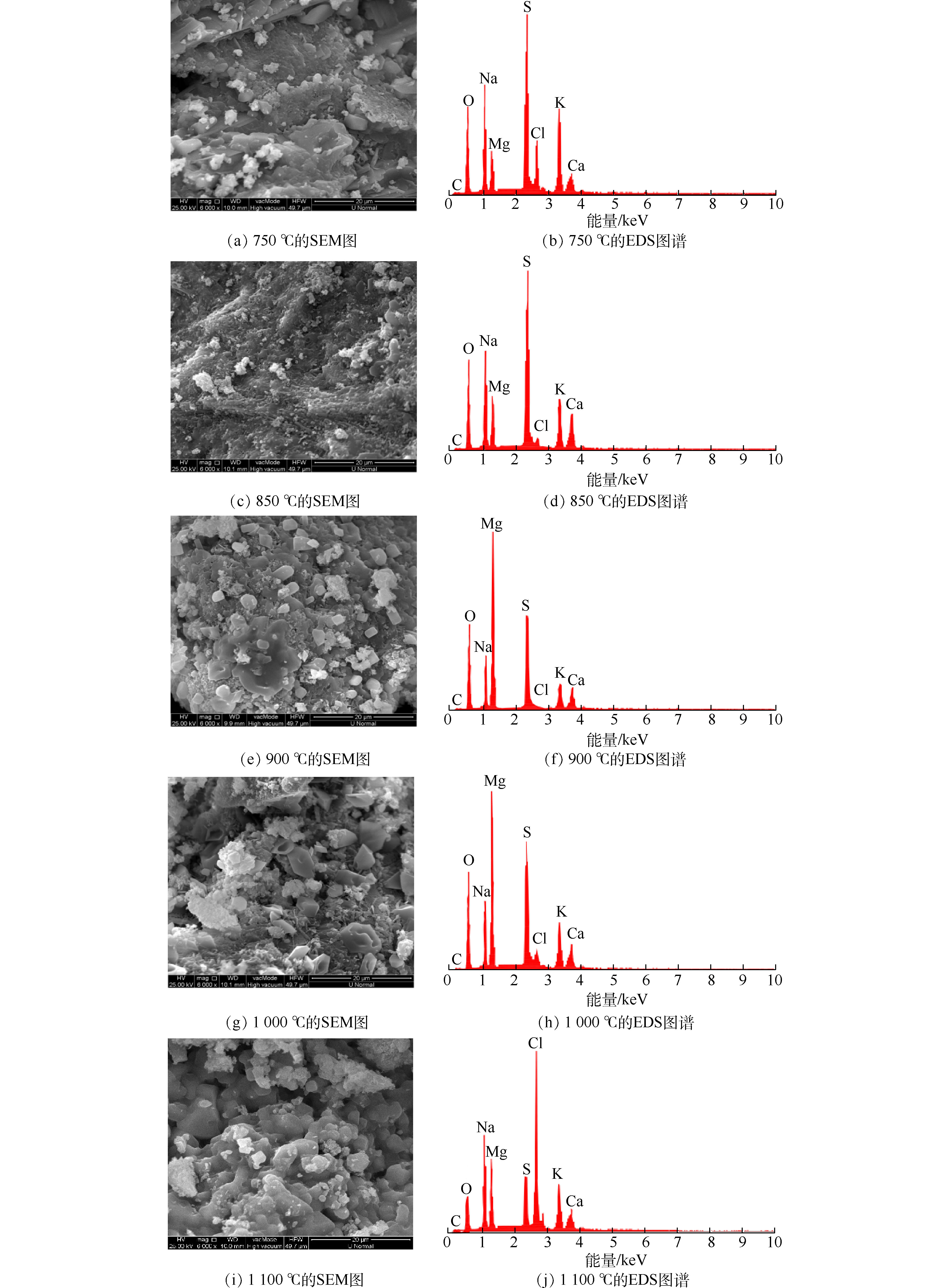
图5为固相物质的SEM及EDS图谱。由SEM图可以看出,晶体粉末的颗粒粒径大小不均,主要由形状不规则的聚合体、块状体及少部分团絮集合体组成。在大颗粒上附着有较小的颗粒物,且在850 ℃及以下温度条件下烧干的晶体颗粒间结构更为致密,孔隙率更小,呈现出类似焚烧炉受热面积灰烧结结构的形态。随温度增高,以900 ℃温度条件为界限,颗粒粒径增大,颗粒间隙增大,颗粒性更为明显,且有明显的颗粒团聚(图5(e))。这可能是由于高温烧结作用使得小颗粒表面熔融、结合而形成了大颗粒。根据SHIN等[29]的研究,当大于某一临界直径时,温度越高、颗粒粒径越大,其团聚效果越好。而在实际运行中,常采用吹灰的手段缓解积灰情况[30]。吹灰的主要清除对象为较为松散的积灰颗粒,对于结构致密是颗粒则难以发挥作用。因此,保持浓缩液回喷过程中合理的温度条件(900 ℃及以上),能有效减轻黏结性积灰程度,避免固相物质的产生造成受热面腐蚀加剧。表2给出了固相物质的元素种类与原子百分比结果,图6为元素含量比值变化,据此可分析在不同温度条件下浓缩液回喷后所得固相物质的元素变化情况。固相物质中主要含有C、O、Na、Mg、S、Cl、K、Ca等元素,也含有少量的重金属物质。随着温度的升高,C、Na、K、Cl原子百分比呈先减少后增加的趋势,O、Mg、Ca的原子百分比呈先增加后减少的趋势,且均以900 ℃左右作为变化的转折点。S元素的原子百分比在温度达到850 ℃时有较大幅度增加,然后无明显变化。O元素和Cl元素的含量主要在750~850 ℃左右发生大幅度的变化,其原因是升温过程中金属氧化物的形成和氯化物的分解。
S元素的含量在固相物质中逐渐占据较大比重,说明S在升温过程中与其他物质发生反应,产生相变,转化为了固态物质。Ca/S的比例随着温度的升高略减小,整体趋势较为平稳(图6)。其原因在于,S元素逐渐以CaSO4的形式被固定,并且在1 100 ℃时以该物相稳定存在,这与图4中形成了CaSO4晶相的结果相吻合。而部分Ca以氢氧化物形式分解,导致了Ca/S的比例略有减小。综合上结果可知,浓缩液中的SO42?在焚烧炉内可能转化为硫化物和硫酸盐等,但最终大部分与Ca2+、Mg2+结合形成较为稳定的化合物,经烟气系统拦截或沉积到炉渣,由此带来的腐蚀影响是较小的。另外,垃圾焚烧产生的SO2、SO3、H2S等腐蚀性气体和复合硫酸盐均会造成腐蚀[31-32]。浓缩液回喷主要造成的是硫氧化物和极少量复合硫酸盐的腐蚀,复合硫酸盐的产生和腐蚀机理如式(7)~式(11)所示。
随着温度的升高,Ca/Cl、K/Cl、Na/Cl、Mg/Cl的变化规律为先增大后减小。其原因如下:750~900 ℃,K、Na的含氯化合物逐渐挥发,同时Cl元素还会以Cl2和HCl的形式排放,故Cl元素较高的挥发速率导致了Ca/Cl、K/Cl、Na/Cl和Mg/Cl比值逐渐增加;900~1 100 ℃,熔融态的金属氯化物均大量挥发,故比值逐渐减小。固相物质中的Cl元素含量最终表现为减少的状态,说明Cl从固态化合物中释放,形成HCl、Cl2或熔融态的金属氯化物。由于HCl、CI2均是高温腐蚀的主要因素,因此,这一定程度上加大了腐蚀防护的难度[33-35],同时导致了烟气中酸性气体的增多。
炉内腐蚀主要由含Cl、S的物质导致,尤其以Cl腐蚀影响最为严重。一方面,S元素在固相物质中累积,但因为复合硫酸盐在低于850 ℃的高温下便会熔融分解,不会带来长时间的炉内腐蚀;另一方面,氯元素从固相物质中释放,易转化为HCl和Cl2等气体进而加剧了腐蚀,且氯化物在靠近金属壁面处气化还易发生类似于活化氧化的气态氯腐蚀,气态氯具备穿透金属壁面保护膜的能力[36]。在多元混合腐蚀气氛中,腐蚀过程十分复杂,这些因素均加大了防腐难度。因此,在回喷浓缩液的情况下,炉内防腐蚀材料的选择上应当更有针对性,注重对Cl腐蚀的防护;另外,大部分元素含量变化拐点所处的900 ℃是浓缩液回喷的关键温度,结合SEM-EDS分析结果,最佳的回喷温度应控制在900 ℃左右,以使腐蚀作用的影响最小化。
此外,本研究仍存在需要改进之处和进一步的探索。实际上,浓缩液回喷到焚烧炉的环境和过程十分复杂,受到浓缩液喷入状态、与垃圾协同作用等因素的影响。下一步可对回喷后的烟气、飞灰等进行收集分析,以期提高实验数据的支撑力度,为工程实践提供科学参考。
2)浓缩液烧干后得到的固体颗粒成分以氯盐、钙盐(CaCl2、MgCl2、CaSO4)为主,因为高温下钠盐、钾盐不能稳定存在。XRD结果表明,CaSO4结晶度明显增强,原因是部分含Ca晶体物质经历高温熔融、反应转化等过程,最终成为热稳定性更好的CaSO4。
3)SEM结果表明,以900 ℃为界限,固相物质微观形态有明显差异,其随温度升高,由较为致密的烧结结构转变为颗粒性更明显,孔隙率更大的形态。保持浓缩液回喷过程中合理的温度条件(900 ℃),能有效减轻所产生的固相物质粘结性积灰程度,避免对受热面腐蚀产生促进作用。
4)炉内腐蚀主要由含Cl、S的物质导致,尤其以Cl腐蚀影响最为严重,因此,在回喷浓缩液的情况下,炉内防腐蚀材料的选择上应当更有针对性,注重对Cl腐蚀的防护;为使腐蚀作用的影响最小化,最佳的回喷温度应控制在900 ℃左右。
参考文献

 下载:
下载: 

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图