 ), 侯博文1, 刘文锦2
), 侯博文1, 刘文锦2 1 复旦大学心理学系, 上海 200433
2 美国哥伦比亚大学教师学院, 纽约
收稿日期:2019-06-20出版日期:2020-02-25发布日期:2019-12-24通讯作者:王燕E-mail:yanwang@fudan.edu.cn基金资助:* 教育部人文规划基金项目(18YJAZH095)The influence of parent-child relationship and “good resource” on unmarried males’ unrestricted sociosexual attitudes
WANG Yan1( ), HOU Bowen1, LIU Wenjin2
), HOU Bowen1, LIU Wenjin2 1 Department of Psychology, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Teachers College, Columbia University, New York, USA
Received:2019-06-20Online:2020-02-25Published:2019-12-24Contact:WANG Yan E-mail:yanwang@fudan.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 本研究采用实验启动的方式探讨“好资源”和童年环境对未婚男性性开放态度的影响, 结果发现童年亲子关系(而不是童年经济状况)在资源线索启动和性开放态度之间存在显著调节作用。研究1采用想象启动来控制个体的资源获取状况, 结果发现:童年亲子关系差的个体在“好资源”想象时其性开放态度较“差资源”想象时明显提升。研究2采用图片情境的资源想象方式, 在研究1的基础上进一步把亲子关系细分成亲子沟通、亲子焦虑和亲子回避三个维度, 结果表明:童年亲子回避在男性资源状况启动和性开放态度之间存在显著调节作用, 童年亲子高回避的个体在“好资源”照片情境想象下其性开放态度显著提升, 而童年亲子低回避的个体在“好资源”照片情境想象下其性开放态度明显下降; 此外, 童年亲子回避在性开放态度上的主效应显著, 亲子回避程度高的个体其性开放态度也更高。两个研究共同揭示了“男人有钱就变坏”的情境和群体特殊性。
图/表 3
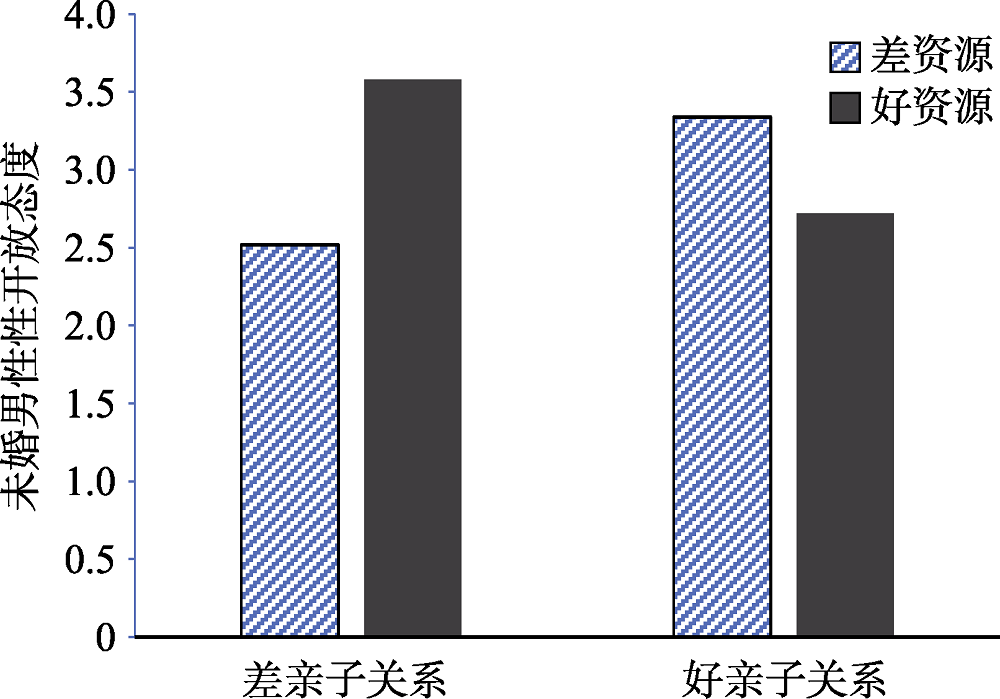
图1童年亲子关系和资源想象在未婚男性性态度上的简单效应分析
 图1童年亲子关系和资源想象在未婚男性性态度上的简单效应分析
图1童年亲子关系和资源想象在未婚男性性态度上的简单效应分析表1亲子亲密关系经历结构量表的因子负荷及公因子方差(n = 62)
| 项目 | 因子负荷 | 公因子方差 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 1.当需要帮助时, 我会向爸爸/妈妈寻求帮助 | 0.92 | -0.12 | 0.10 | 0.88 |
| 2.我常常和爸爸/妈妈商量事情 | 0.88 | -0.12 | 0.28 | 0.87 |
| 3.我认为依靠爸爸/妈妈是一件寻常的事 | 0.88 | -0.16 | 0.04 | 0.81 |
| 4.我经常和爸爸/妈妈讨论我焦虑和担心的事情 | 0.84 | 0.03 | 0.41 | 0.87 |
| 5.当我感到非常沮丧和消沉时, 通常不愿意让爸爸/妈妈知道(r) | 0.12 | -0.07 | 0.92 | 0.86 |
| 6.向爸爸/妈妈坦露心扉会令我感到不舒服(r) | 0.37 | -0.17 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| 7.我担心爸爸/妈妈不会像我关心她那样地关心我 | -0.10 | 0.96 | -0.06 | 0.93 |
| 8.我经常怀疑爸爸/妈妈从来没有真正地关心过我 | -0.19 | 0.92 | -0.01 | 0.89 |
| 9.我担心爸爸/妈妈会抛弃我 | -0.02 | 0.90 | -0.19 | 0.84 |
表1亲子亲密关系经历结构量表的因子负荷及公因子方差(n = 62)
| 项目 | 因子负荷 | 公因子方差 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 1.当需要帮助时, 我会向爸爸/妈妈寻求帮助 | 0.92 | -0.12 | 0.10 | 0.88 |
| 2.我常常和爸爸/妈妈商量事情 | 0.88 | -0.12 | 0.28 | 0.87 |
| 3.我认为依靠爸爸/妈妈是一件寻常的事 | 0.88 | -0.16 | 0.04 | 0.81 |
| 4.我经常和爸爸/妈妈讨论我焦虑和担心的事情 | 0.84 | 0.03 | 0.41 | 0.87 |
| 5.当我感到非常沮丧和消沉时, 通常不愿意让爸爸/妈妈知道(r) | 0.12 | -0.07 | 0.92 | 0.86 |
| 6.向爸爸/妈妈坦露心扉会令我感到不舒服(r) | 0.37 | -0.17 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| 7.我担心爸爸/妈妈不会像我关心她那样地关心我 | -0.10 | 0.96 | -0.06 | 0.93 |
| 8.我经常怀疑爸爸/妈妈从来没有真正地关心过我 | -0.19 | 0.92 | -0.01 | 0.89 |
| 9.我担心爸爸/妈妈会抛弃我 | -0.02 | 0.90 | -0.19 | 0.84 |
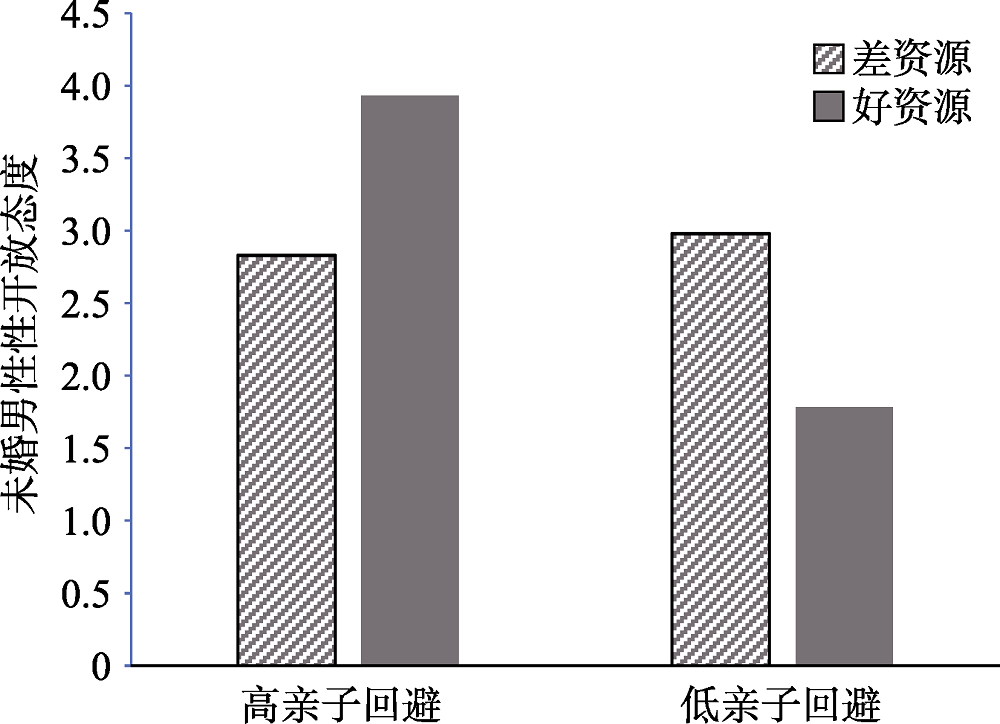
图2童年亲子回避和资源照片场景想象在未婚男性性态度上的简单效应分析
 图2童年亲子回避和资源照片场景想象在未婚男性性态度上的简单效应分析
图2童年亲子回避和资源照片场景想象在未婚男性性态度上的简单效应分析参考文献 51
| [1] | Anderson R. C., & Klofstad C. A . (2012). For love or money? The influence of personal resources and environmental resource pressures on human mate preferences. Ethology, 118(9), 841-849. |
| [2] | Belsky J . (1997). Attachment, mating, and parenting. Human Nature, 8(4), 361-381. |
| [3] | Belsky J . (1999). Modern evolutionary theory and patterns of attachment. In J. Cassidy & P. R. Shaver (Eds.), Handbook of attachment: Theory, research, and clinical applications (pp. 141-161). New York: Guilford Press. |
| [4] | Belsky J . (2010). Childhood experience and the development of reproductive strategies. Psicothema, 22(1), 28-34. |
| [5] | Belsky J., Schlomer G. L., & Ellis B. J . (2012). Beyond cumulative risk: Distinguishing harshness and unpredictability as determinants of parenting and early life history strategy. Developmental Psychology, 48(3), 662-673. |
| [6] | Belsky J., Steinberg L., & Draper P . (1991). Childhood experience, interpersonal development, and reproductive strategy: An evolutionary theory of socialization. Child Development, 62(4), 647-670. |
| [7] | Buss D. M . (1989). Sex differences in human mate preferences: Evolutionary hypotheses tested in 37 cultures. Behavioral & Brain Sciences, 12(1), 1-14. |
| [8] | Buss D. M., & Schmitt D. P . (1993). Sexual strategies theory: An evolutionary perspective on human mating. Psychological Review, 100(2), 204-232. |
| [9] | Buss D. M., & Shackelford T. K . (2008). Attractive women want it all: Good genes, economic investment, parenting proclivities, and emotional commitment. Evolutionary Psychology, 6(1), 134-146. |
| [10] | Caron S. L., & Moskey E. G . (2002). Changes over time in teenage sexual relationships: Comparing the high school class of 1950, 1975, and 2000. Adolescence, 37(147), 515-526. |
| [11] | Chang L., Lu H. J., Lansford J. E., Skinner A. T., Bornstein M. H., Steinberg L., ... Tapanya S . (2019). Environmental harshness and unpredictability, life history, and social and academic behavior of adolescents in nine countries. Developmental Psychology, 55(4), 890-903. |
| [12] | Chang L., Wang Y., Shackelford T. K., & Buss D. M . (2011). Chinese mate preferences: Cultural evolution and continuity across a quarter of a century. Personality & Individual Differences, 50(5), 678-683. |
| [13] | Charnov E. L . (1993). Life history invariants. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. |
| [14] | Chen B.-B . (2017). Insecure attachment, resource control, and unrestricted sociosexuality: From a life history perspective. Personality and Individual Differences, 105, 213-217. |
| [15] | Chen B.-B., & Chang L . (2016). Procrastination as a fast life history strategy. Evolutionary Psychology, 14(1), 1-5. |
| [16] | Chisholm J. S . (1996). The evolutionary ecology of attachment organization. Human Nature, 7(1), 1-37. |
| [17] | DelPriore D. J., & Hill S. E . (2013). The effects of paternal disengagement on women’s sexual decision making: An experimental approach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 105(2), 234-246. |
| [18] | DelPriore D. J., Proffitt L. R., Ellis B. J., & Hill S. E . (2017). The effects of paternal disengagement on women’s perceptions of male mating intent. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 114(2), 286-302. |
| [19] | Draper P., & Harpending H . (1982). Father absence and reproductive strategy: An evolutionary perspective. Journal of Anthropological Research, 38(3), 255-273. |
| [20] | Ellis B. J., & Essex M. J . (2007). Family environments, adrenarche, and sexual maturation: A longitudinal test of a life history model. Child Development, 78(6), 1799-1817. |
| [21] | Fraley R. C., Heffernan M. E., Vicary A. M., & Brumbaugh C. C . (2011). The experiences in close relationships— relationship structures questionnaire: A method for assessing attachment orientations across relationships. Psychological Assessment, 23(3), 615-625. |
| [22] | Giudice M. D., Kaplan H., & Gangestad S. W . (2015). Life history theory and evolutionary psychology. In D. M. Buss (Ed), The handbook of evolutionary psychology (pp. 68-95). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. |
| [23] | Griskevicius V., Delton A. W., Robertson T. E., & Tybur J. M . (2011). Environmental contingency in life history strategies: The influence of mortality and socioeconomic status on reproductive timing. Journal of Personality & Social Psychology, 100(2), 241-54. |
| [24] | Guo W., Tian G . (2019). A study of the influence of family, school, peers and internet on adolescents’ sexual values. Chinese Youth Studies, (5), 57-63. |
| [ 郭未, 田鸽 . (2019). 青春摇曳: 家庭、学校、侪辈及互联网对中学生性价值观的影响. 中国青年研究, (5), 57-63.] | |
| [25] | Hayes A. F., & Rockwood N. J . (2016). Regression-based statistical mediation and moderation analysis in clinical research: Observations, recommendations, and implementation. Behaviour Research & Therapy, 98, 39-57. |
| [26] | Hendrick C., Hendrick S. S., & Reich D. A . (2006). The brief sexual attitudes scale. Journal of Sex Research, 43(1), 76-86. |
| [27] | Jaccard J., Dodge T., & Dittus P . (2003). Maternal discussions about pregnancy and adolescents, attitudes toward pregnancy. Journal of Adolescent Health, 33(2), 84-87. |
| [28] | Jackson J., J. & Kirkpatrick, L. A. ( 2007). The structure and measurement of human mating strategies: Toward a multidimensional model of sociosexuality. Evolution & Human Behavior, 28(6), 382-391. |
| [29] | James J., Ellis B. J., Schlomer G. L., & Garber J . (2012). Sex-specific pathways to early puberty, sexual debut, and sexual risk taking: Tests of an integrated evolutionary- developmental model. Developmental Psychology, 48(3), 687-702. |
| [30] | Johnson K. A., & Tyler K. A . (2007). Adolescent sexual onset: An intergenerational analysis. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 36(7), 939-949. |
| [31] | Kinsman S. B., Romer D., Furstenberg F. F., & Schwarz D. F . (1996). Early initiation of sexual activity: The role of peer norms. Journal of Adolescent Health, 18(2), 134-134. |
| [32] | Kirkpatrick L. A., & Davis K. E . (1994). Attachment style, gender, and relationship stability: A longitudinal analysis. Journal of Personality & Social Psychology, 66(3), 502-512. |
| [33] | Lenciauskiene I., & Zaborskis A . (2008). The effects of family structure, parent-child relationship and parental monitoring on early sexual behaviour among adolescents in nine European countries. Scandinavian Journal of Public Health, 36(6), 607-618. |
| [34] | Li N.-P . (2007). Mate preference necessities in long- and short-term mating: People prioritize in themselves what their mates prioritize in them. Acta Psychologica Sinica(心理学报), 39(3), 528-535. |
| [35] | Li Y. M., Li J., Chan D. K.-S., & Zhang B . (2016). When love meets money: Priming the possession of money influences mating strategies. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 387. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00387. |
| [36] | Lou C. H., Cheng Y., Gao E., Zuo X. Y., Emerson M. R., & Zabin L. S . (2012). Media’s contribution to sexual knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors for adolescents and young adults in three Asian cities. Journal of Adolescent Health, 50(3), 26-36. |
| [37] | Lu H. J., Zhu X. Q., & Chang L . (2015). Good genes, good providers, and good fathers: Economic development involved in how women select a mate. Evolutionary Behavioral Science, 9(4), 215-228. |
| [38] | Nettle D., Coall D. A., & Dickins T. E . (2010). Early-life conditions and age at first pregnancy in British women. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 278(1712), 1721-1727. |
| [39] | Roff D. A . (2002). Life history evolution. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer. |
| [40] | Romo L. F., Lefkowitz E. S., Sigman M., & Au T. K . (2002). A longitudinal study of maternal messages about dating and sexuality and their influence on Latino adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health, 31(1), 59-69. |
| [41] | Schachner D. A., & Shaver P. R . (2002). Attachment style and human mate poaching. New Review of Social Psychology, 1, 122-129. |
| [42] | Schachner D. A., & Shaver P. R . (2004). Attachment dimensions and sexual motives. Personal Relationships, 11(2), 179-195. |
| [43] | Schaffer W. M . (1983). The application of optimal control theory to the general life history problem. The American Naturalist, 121(3), 418-431. |
| [44] | Sefcek J. A., Brumbach B. H., Vasquez G., & Miller G. F . (2006). The evolutionary psychology of human mate choice: How ecology, genes, fertility, and fashion influence mating strategies. International Journal of Sexual Health, 18(2-3), 125-182. |
| [45] | Sheppard P., Pearce M. S., & Sear R . (2015). How does childhood socioeconomic hardship affect reproductive strategy? Pathways of development. American Journal of Human Biology, 28(3), 356-363. |
| [46] | Trivers R. L . (1972). Parental investment and sexual selection. In B. G. Campbell (Ed), Sexual selection and the descent of man, 1871-1971, (pp. 136-179). Transaction Publishers, New Jersey |
| [47] | van Oosten J. M. F., Peter J., & Boot I . (2015). Exploring associations between exposure to sexy online self-presentations and adolescents' sexual attitudes and behavior. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 44(5), 1078-1091. |
| [48] | Wang Y., Hou B., Li X. Y., Li X. X., & Jiao L . (2017). The influence of different sex ratios and resource-gaining capability on male’s mating selection. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 49(9), 1195-1205. |
| [ 王燕, 侯博文, 李歆瑶, 李晓煦, 焦璐 . (2017). 不同性别比和资源获取能力对未婚男性择偶标准的影响. 心理学报, 49(9), 1195-1205.] | |
| [49] | Wang Y., Lin Z. C., Hou B. W., & Sun S. J . (2017). The intrinsic mechanism of life history trade-offs: The mediating role of control striving. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 49(6), 783-793. |
| [ 王燕, 林镇超, 侯博文, 孙时进 . (2017). 生命史权衡的内在机制: 动机控制策略的中介作用. 心理学报, 49(6), 783-793.] | |
| [50] | Wang Y., Qu Y., Hou B., & Tian Q . (2019). What makes her a material girl? The influence of childhood economic background and sex ratio on female preference for male resource availability. Evolutionary Psychology, 17(1), 1-10. |
| [51] | Yong J. C., & Li N. P . (2012). Cash in hand, want better looking mate: Significant resource cues raise men’s mating standards. Personality & Individual Differences, 53(1), 55-58. |
相关文章 4
| [1] | 罗一君, 牛更枫, 陈红. 生命早期环境不可预测性对过度进食的影响:基于生命史理论[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(10): 1224-1236. |
| [2] | 王燕, 侯博文, 李歆瑶, 李晓煦, 焦璐. 不同性别比和资源获取能力 对未婚男性择偶标准的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(9): 1195-1205. |
| [3] | 王 燕, 林镇超, 侯博文, 孙时进. 生命史权衡的内在机制:动机控制策略的中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(6): 783-793. |
| [4] | 汪佳瑛; 陈斌斌. 童年压力及死亡威胁启动对择偶要求的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(7): 857-866. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4633
