 )
) 西南大学心理学部, 重庆 400715
收稿日期:2018-01-23出版日期:2019-03-25发布日期:2019-01-22通讯作者:冯廷勇E-mail:fengty0@swu.edu.cn基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金面上项目(31571128)Mindfulness training can improve 3-and 4-year-old children’s attention and executive function
LI Quan, SONG Yanan, LIAN Bin, FENG Tingyong( )
) Faculty of Psychology, Southwest University, Chongqing, 400715, China
Received:2018-01-23Online:2019-03-25Published:2019-01-22Contact:FENG Tingyong E-mail:fengty0@swu.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 正念训练是指个体将注意力集中于当下体验的一种心理干预方法。先前研究表明正念训练可以促进其注意力、执行功能、情绪调节等的发展, 而正念训练对幼儿心理发展的作用机制并不清楚。因此, 为了考察正念训练对3~4岁幼儿注意力和执行功能的影响。采用前后测设计, 对正念组进行每周2次, 每次20~30分钟, 共12次的正念训练; 对照组不进行任何训练。结果发现:(1) 在注意力方面, 正念组与对照组前测差异不显著, 训练后正念组幼儿持续性注意力得分显著高于对照组。(2) 在执行功能方面, 正念组和实验组在抑制控制、认知灵活性以及工作记忆上前测得分差异不显著, 训练后正念组幼儿抑制控制和认知灵活性得分显著优于对照组, 而两组幼儿工作记忆差异不显著。研究表明, 正念训练促进了3~4岁幼儿注意力和执行功能的发展, 且在执行功能方面主要表现为对抑制控制和认知灵活性的提升。
图/表 10
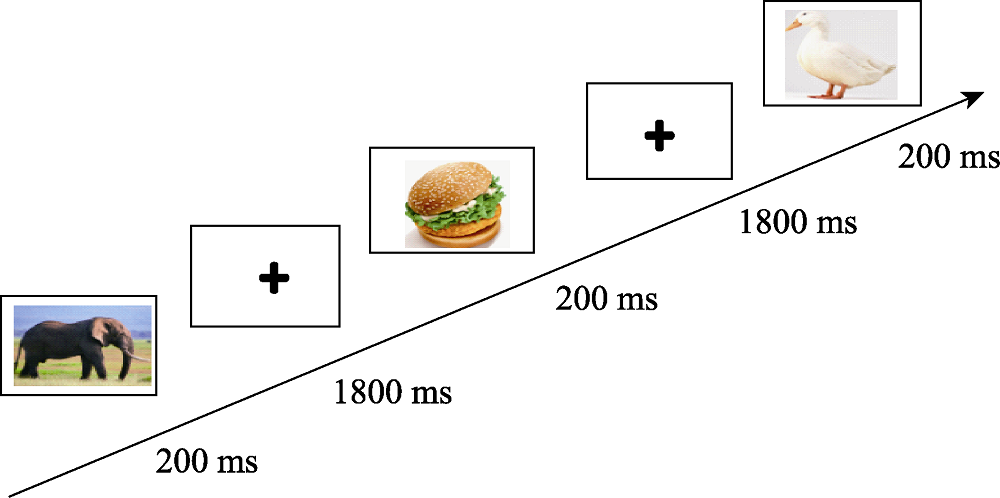
图1持续性注意力实验流程图
 图1持续性注意力实验流程图
图1持续性注意力实验流程图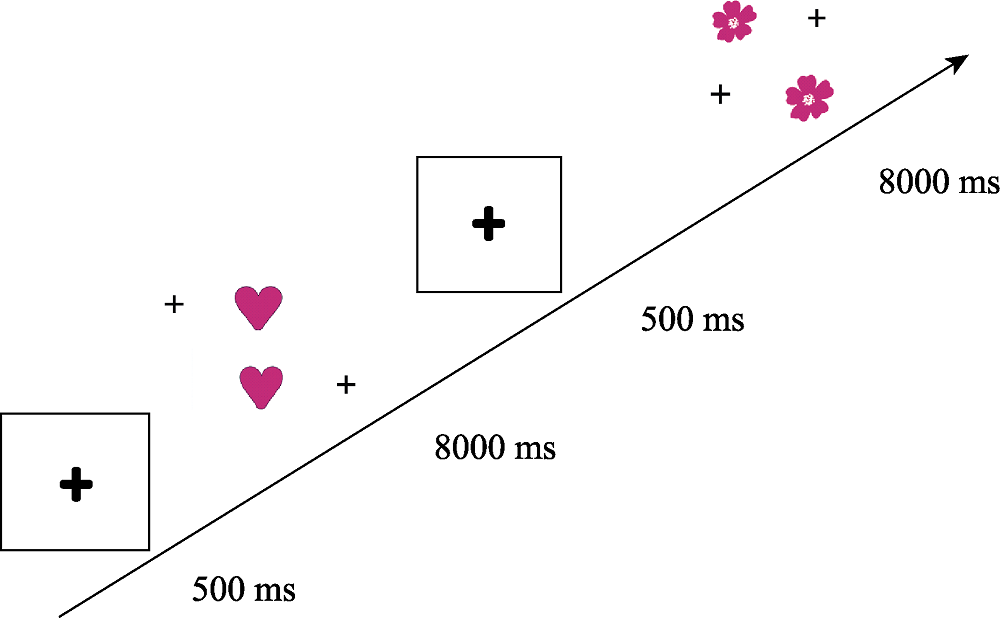
图2抑制控制实验流程图
 图2抑制控制实验流程图
图2抑制控制实验流程图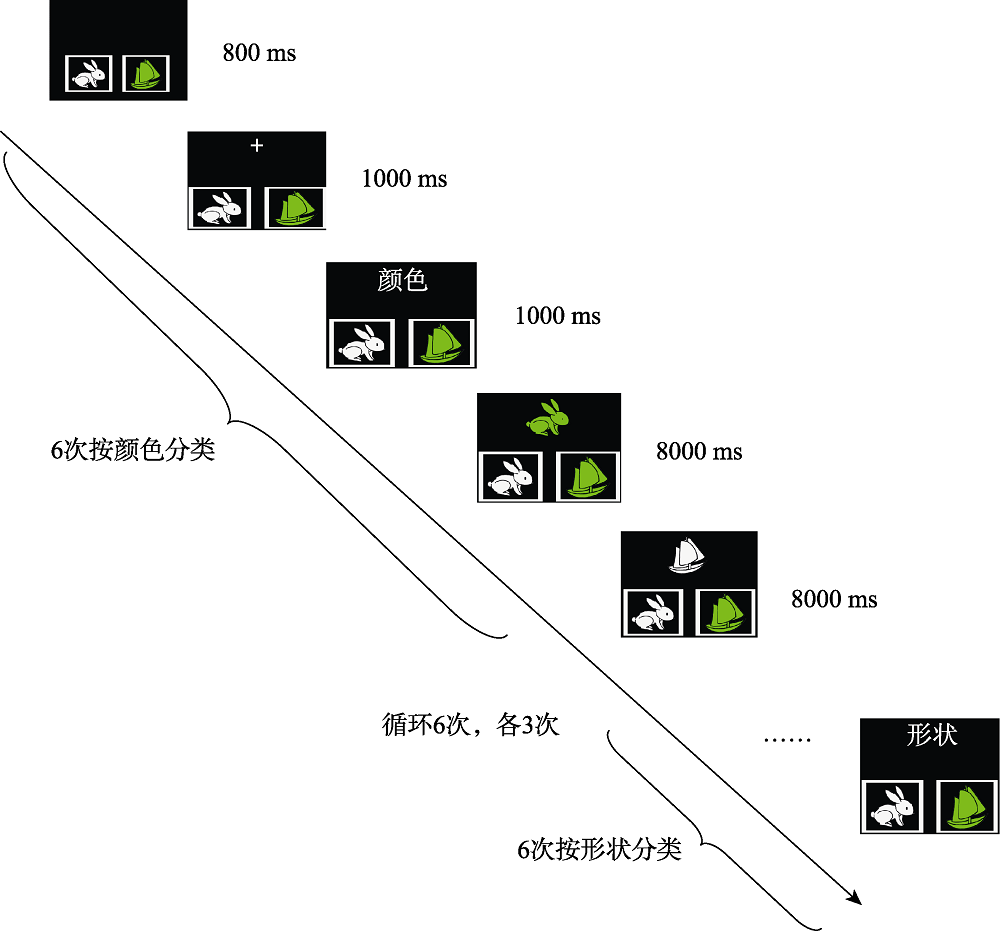
图3认知灵活性实验流程图
 图3认知灵活性实验流程图
图3认知灵活性实验流程图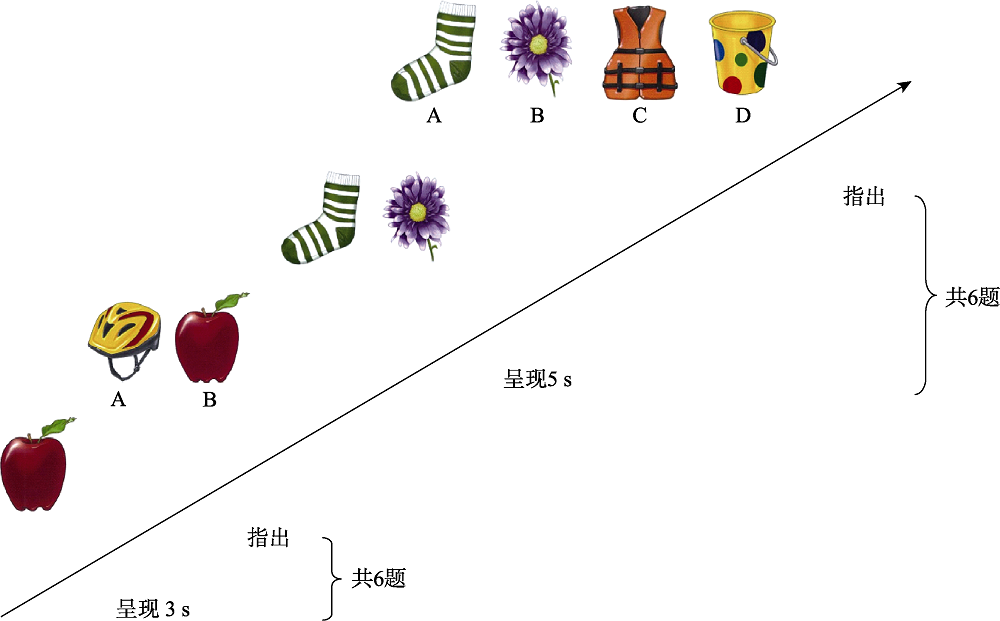
图4工作记忆实验流程图
 图4工作记忆实验流程图
图4工作记忆实验流程图表13~4岁幼儿正念训练课程表
 |
表13~4岁幼儿正念训练课程表
 |
表2正念组与对照组在注意力、执行功能上的发展水平
| 组别 | 注意力 | 抑制控制 | 认知灵活性 | 工作记忆 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 正念组 | 12.04 (7.10) | 21.73 (5.59) | 0.74 (0.16) | 0.92 (0.10) | 0.71 (0.16) | 0.92 (0.08) | 14.00 (5.39) | 18.14 (5.64) |
| 对照组 | 13.42 (8.27) | 18.27 (6.51) | 0.73 (0.17) | 0.74 (0.14) | 0.63 (0.22) | 0.76 (0.18) | 14.38 (4.85) | 16.38 (5.38) |
表2正念组与对照组在注意力、执行功能上的发展水平
| 组别 | 注意力 | 抑制控制 | 认知灵活性 | 工作记忆 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 正念组 | 12.04 (7.10) | 21.73 (5.59) | 0.74 (0.16) | 0.92 (0.10) | 0.71 (0.16) | 0.92 (0.08) | 14.00 (5.39) | 18.14 (5.64) |
| 对照组 | 13.42 (8.27) | 18.27 (6.51) | 0.73 (0.17) | 0.74 (0.14) | 0.63 (0.22) | 0.76 (0.18) | 14.38 (4.85) | 16.38 (5.38) |

图5正念组和对照组前后测注意力得分
 图5正念组和对照组前后测注意力得分
图5正念组和对照组前后测注意力得分
图6正念组和对照组前后测抑制控制得分
 图6正念组和对照组前后测抑制控制得分
图6正念组和对照组前后测抑制控制得分
图7正念组和对照组前后测认知灵活性得分
 图7正念组和对照组前后测认知灵活性得分
图7正念组和对照组前后测认知灵活性得分
图8正念组和对照组前后测工作记忆得分
 图8正念组和对照组前后测工作记忆得分
图8正念组和对照组前后测工作记忆得分参考文献 75
| [1] | Alloway T. P., Gathercole S. E., Adams A-M., Willis C., Eaglen R., &Lamont E . ( 2005). Working memory and phonological awareness as predictors of progress towards early learning goals at school entry. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 23( 3), 417-426. doi: 10.1348/026151005X26804URL |
| [2] | Aron A. R., Robbins T. W., &Poldrack R. A . ( 2014). Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 18( 4), 170-177. |
| [3] | Baddeley A . ( 2013). Working memory and emotion: Ruminations on a theory of depression. Review of General Psychology, 17( 1), 20-27. doi: 10.1037/a0030029URL |
| [4] | Biegel G. M., Brown K. W., Shapiro S. L., &Schubert C. M . ( 2009). Mindfulness-based stress reduction for the treatment of adolescent psychiatric outpatients: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Consulting & Clinical Psychology, 77( 5), 855-866. doi: 10.1037/a0016241URLpmid: 19803566 |
| [5] | Bishop S. R., Lau M., Shapiro S., Carlson L., Anderson N. D., Carmody J., … Devins G. M . ( 2004). Mindfulness: A proposed operational definition. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 11( 3), 230-241. doi: 10.1093/clipsy/bph077URL |
| [6] | Black D. S., Sussman S., Johnson C. A., &Milam J ., ( 2012). Testing the indirect effect of trait mindfulness on adolescent cigarette smoking through negative affect and perceived stress mediators. Journal of Substance Use, 17( 5-6), 417-429. doi: 10.3109/14659891.2011.587092URLpmid: 3705933 |
| [7] | Borders A., Earleywine M., &Jajodia A . ( 2010). Could mindfulness decrease anger, hostility, and aggression by decreasing rumination? Aggressive Behavior, 36( 1), 28-44. doi: 10.1002/ab.20327URLpmid: 19851983 |
| [8] | Breckenridge K . ( 2007). The structure and function of attention in typical and atypical development (Unpublished PhD Dissertation). University ofLondon. |
| [9] | Breckenridge K., Braddick O., &Atkinson J . ( 2013). The organization of attention in typical development: A new preschool attention test battery. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 31( 3), 271-288. doi: 10.1111/bjdp.12004URLpmid: 23901842 |
| [10] | Brooker J. E., Webber L., Julian J., Shawyer F., Graham A. L., Chan J., &Meadows G . ( 2014). Mindfulness-based training shows promise in assisting staff to reduce their use of restrictive interventions in residential services. Mindfulness, 5( 5), 598-603. doi: 10.1007/s12671-014-0306-2URL |
| [11] | Brown K.W., &Ryan R.M . ( 2003). The benefits of being present: Mindfulness and its role in psychological well- being. Journal of Personality Social Psychology, 84( 4), 822-848. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.84.4.822URLpmid: 12703651 |
| [12] | Brown R.P., &Pinel E.C . ( 2003). Stigma on my mind: Individual differences in the experience of stereotype threat. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 39( 6), 626-633. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1031(03)00039-8URL |
| [13] | Cameron C. E., Brock L. L., Hatfield B. E., Cottone E. A., Rubinstein E., Locasale-crouch J., &Grissmer D. W . ( 2015). Visuomotor integration and inhibitory control compensate for each other in school readiness. Developmental Psychology, 51( 11), 1529-1543. doi: 10.1037/a0039740URLpmid: 26436872 |
| [14] | Davidson M. C., Amso D., Anderson L. C., &Diamond A . ( 2006). Development of cognitive control and executive functions from 4 to 13 years: Evidence from manipulations of memory, inhibition, and task switching. Neuropsychologia, 44( 11), 2037-2078. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.02.006URLpmid: 1513793 |
| [15] | Deikman A . ( 2000). A functional approach to mysticism. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 7( 11-12), 75-92. doi: 10.1253/jcj.64.901URL |
| [16] | Deikman A.J . ( 1963). Experimental meditation. Journal of Nervous & Mental Disease. 136( 4), 329-343. |
| [17] | Deloache J. S., Eisenberg N., &Siegler R. S . ( 2010). How children develop (3rd edition). New York:Worth. |
| [18] | Eldar S., Ricon T., &Bar-haim Y . ( 2008). Plasticity in attention: Implications for stress response in children. Behaviour Research & Therapy, 46( 4), 450-461. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2008.01.012URLpmid: 18313034 |
| [19] | Flook L., Goldberg S. B., Pinger L., &Davidson R. J . ( 2015). Promoting prosocial behavior and self-regulatory skills in preschool children through a mindfulness-based kindness curriculum. Developmental Psychology, 51( 1), 44-51. doi: 10.1037/a0038256URLpmid: 4485612 |
| [20] | Friese M., Ostafin B., &Loschelder D . ( 2017). Mindfulness as an intervention to improve self-control. Handbook of self-control in health and well-being(pp.431-445). New York, NY: Routledge. |
| [21] | Good D. J., Lyddy C. J., Glomb T. M., Bono J. E., Brown K. W., &Duffy M. K . ( 2015). Contemplating mindfulness at work: An integrative review. Journal of Management, 42( 1), 114-142. doi: 10.1177/0149206315617003URL |
| [22] | Huang Y., Li, X D., Wang Y . ( 2002). A follow-up study of sensory integrative dysfunction in children. China Journal Peditrics, 40( 5), 260-262. |
| [ 黄悦勤, 李旭东, 王玉凤 . ( 2002). 儿童感觉统合失调的随访研究. 中华儿科杂志, 40( 5), 260-262.] doi: 10.3760/j.issn:0578-1310.2002.05.002URL | |
| [23] | Ivanovski B., &Malhi G.S . ( 2007). The psychological and neurophysiological concomitants of mindfulness forms of meditation. Acta Neuropsychiatrica, 19( 2), 76-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5215.2007.00175.xURLpmid: 26952819 |
| [24] | Josefsson T., Lindwall M., &Broberg A. G . ( 2014). The effects of a short-term mindfulness based intervention on self-reported mindfulness, decentering, executive attention, psychological health, and coping style: Examining unique mindfulness effects and mediators. Mindfulness, 5( 1), 18-35. doi: 10.1007/s12671-012-0142-1URL |
| [25] | Kabat-Zinn J . ( 1994). Wherever you go, there you are: mindfulness meditation in everyday life. New York:Hyperion. |
| [26] | Kabat-Zinn J . ( 2003). Mindfulness-based interventions in context: Past, present, and future. Clinical Psychology- Science and Practice, 10( 2), 144-156. doi: 10.1093/clipsy.bpg016URL |
| [27] | Kabat-Zinn J . ( 2005). Bringing mindfulness to medicine: An interview with Jon Kabat-Zinn, PhD. interview by karolyn gazella. Advances in Mind-body Medicine, 21( 2):22-27. doi: 10.1017/S0007114512006071URLpmid: 16170903 |
| [28] | Kabat-Zinn J . ( 2005). Bringing mindfulness to medicine: An interview with Jon Kabat-Zinn, PhD. Interview by Karolyn Gazella. Advances in Mind-body Medicine, 21( 2), 22. doi: 10.1017/S0007114512006071URLpmid: 16170903 |
| [29] | Klingberg T., Fernell E., Olesen P. J., Johnson M., Gustafsson P., Dahlström K., &Westerberg H . ( 2005). Computerized training of working memory in children with ADHD-A randomized, controlled trial. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 44( 2), 177-186. |
| [30] | Lee J.K., &Orsillo S.M . ( 2014). Investigating cognitive flexibility as a potential mechanism of mindfulness in generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 45( 1), 208-216. doi: 10.1016/j.jbtep.2013.10.008URLpmid: 24239587 |
| [31] | Lenroot R.K., &Giedd J.N . ( 2006). Brain development in children and adolescents: Insights from anatomical magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 30( 6), 718-729. |
| [32] | Lenroot R. K., Schmitt J. E., Ordaz S. J., Wallace G. L., Neale M. C., Lerch J. P., Giedd J. N . ( 2009). Differences in genetic and environmental influences on the human cerebral cortex associated with development during childhood and adolescence. Human Brain Mapping, 30( 1), 163-174. |
| [33] | Lutz A., Slagter H. A., Dunne J. D., &Davidson R. J . ( 2008). Attention regulation and monitoring in meditation. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 12( 4), 163-169. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2008.01.005URLpmid: 2693206 |
| [34] | Modesto-Lowe V., Farahmand P., Chaplin M., &Sarro L . ( 2015). Does mindfulness meditation improve attention in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder?. World Journal of Psychiatry, 5( 4), 397-403. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v5.i4.397URLpmid: 26740931 |
| [35] | Moore A., &Malinowski P. ( 2009). Meditation, mindfulness and cognitive flexibility. Consciousness & Cognition, 18( 1), 176-186. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2008.12.008URLpmid: 19181542 |
| [36] | Moore B.A . ( 2013). Propensity for experiencing flow: The roles of cognitive flexibility and mindfulness . Humanistic Psychologist, 41( 4), 319-332. doi: 10.1080/08873267.2013.820954URL |
| [37] | Mrazek M. D., Franklin M. S., Phillips D. T., Baird B., &Schooler J. W . ( 2013). Mindfulness training improves working memory capacity and GRE performance while reducing mind wandering. Psychological Science, 24( 5), 776-781. doi: 10.1177/0956797612459659URLpmid: 23538911 |
| [38] | Mrazek M. D., Smallwood J., &Schooler J. W . ( 2012). Mindfulness and mind-wandering: Finding convergence through opposing constructs. Emotion, 12( 3), 442-448. doi: 10.1037/a0026678URLpmid: 22309719 |
| [39] | Ma C. ( 2013). Comparative study of the executive function training and mindfulness training on the promation of the chilfren's attention (Unpublished Master's thesis). Neimeng Normal University. |
| [ 马超 . ( 2013). 执行功能训练和正念训练对促进小学儿童注意力的比较研究(硕士论文). 内蒙古师范大学.] | |
| [40] | Mao B, B. ( 2009). The investigation and training on 4~6 years old children's sensory integration ability (Unpublished Master's thesis). Shanxi Normal University. |
| [ 毛斌斌 . ( 2009). 4~6岁幼儿感觉统合能力的调查与训练(硕士论文). 山西师范大学.] | |
| [41] | Oh S., &Lewis C. ( 2008). Korean preschoolers’ advanced inhibitory control and its relation to other executive skills and mental state understanding. Child Development, 79( 1), 80-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2007.01112.xURLpmid: 18269510 |
| [42] | Pascual-Leone A., Amedi A., Fregni F., &Merabet L. B . ( 2005). The plastic human brain cortex. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 28( 28), 377-401. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.27.070203.144216URLpmid: 16022601 |
| [43] | Pan X,X., Ma H,W . ( 2009). The application of continuous performance task in diagnosis and treatment of ADHD. International Journal of Pediatrics, 36( 1), 100-102. |
| [ 潘学霞, 麻宏伟 . ( 2009). 持续性操作测验在注意缺陷障碍诊断及治疗中的应用. 国际儿科学杂志, 36( 1), 100-102.] doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4408.2009.01.034URL | |
| [44] | , Purser R.E., &Milillo J. ( 2015). Mindfulness Revisited: A Buddhist-Based Conceptualization. Journal of Management Inquiry, 24( 1), 3-24. |
| [45] | Razza R. A., Bergen-Cico D., &Raymond K . ( 2015). Enhancing preschoolers’ self-regulation via mindful yoga. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 24( 2), 372-385. doi: 10.1007/s10826-013-9847-6URL |
| [46] | Reznick J. S., Morrow J. D., Goldman B. D., &Snyder J . ( 2004). The onset of working memory in infants. Infancy, 6( 1), 145-154. doi: 10.1207/s15327078in0601_7URL |
| [47] | Robins C. J., Keng S-L., Ekblad A. G., &Brantley J. G . ( 2012). Effects of mindfulness-based stress reduction on emotional experience and expression: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 68( 1), 117-131. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20857URLpmid: 22144347 |
| [48] | Riggs N. R., Black D. S., &Ritt-Olson A . ( 2015). Associations between dispositional mindfulness and executive function in early adolescence. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 24( 9), 2745-2751. doi: 10.1007/s10826-014-0077-3URL |
| [49] | Rueda M. R., Checa P., &Cómbita L. M . ( 2012). Enhanced efficiency of the executive attention network after training in preschool children: Immediate changes and effects after two months. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 2( 4), S192-S204. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2011.09.004URLpmid: 22682908 |
| [50] | Rueda M. R., Rothbart M. K., Mccandliss B. D., Saccomanno L., &Posner M. I . ( 2005). Training, maturation, and genetic influences on the development of executive attention. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102( 41), 14931-14936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506897102URLpmid: 16192352 |
| [51] | Ruff H. A., Capozzoli M., &Weissberg R . ( 1998). Age, individuality, and context as factors in sustained visual attention during the preschool years. Developmental Psychology, 34( 3), 454-464. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.34.3.454URLpmid: 9597356 |
| [52] | Roth R. M., Randolph J. J., Koven NS., &Isquith PK . ( 2006). Neural substrates of executive functions: Insights from functional neuroimaging. In J. R. Dupri (Ed.), Focus on neuropsychology research( pp.1-36). NY: Nova Science Publishers. |
| [53] | Salamé P., &Baddeley A.D . ( 1982). Disruption of short-term memory by unattended speech: Implications for the structure of working memory. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 21( 2), 150-164. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5371(82)90521-7URL |
| [54] | Semple R. J., Lee J., Rosa D., &Miller L. F . ( 2010). A randomized trial of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for children: Promoting mindful attention to enhance social-emotional resiliency in children. Journal of Child & Family Studies, 19( 2), 218-229. doi: 10.1007/s10826-009-9301-yURL |
| [55] | Shapiro S. L., Carlson L. E., Astin J. A., &Freedman B . ( 2010). Mechanisms of mindfulness. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 62( 3), 373-386. |
| [56] | Smallwood J., &Schooler J.W . ( 2015). The science of mind wandering: Empirically navigating the stream of consciousness. Annual Review of Psychology, 66( 1), 487-518. |
| [57] | Tang Y-Y., Tang Y., Tang R., &Lewis-peacock J. A . ( 2017). Brief mental training reorganizes large-scale brain networks. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 11, 6. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2017.00006. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2017.00006URLpmid: 5328965 |
| [58] | Tang Y. Y., Yang L., Leve L. D., &Harold G. T . ( 2012). Improving executive function and its neurobiological mechanisms through a mindfulness-based intervention: Advances within the field of developmental neuroscience. Child Development Perspectives, 6( 4), 361-366. |
| [59] | Ying H.K., &Wang C. K.J . ( 2012). Relationships between mindfulness, flow dispositions and mental skills adoption: A cluster analytic approach. Psychology of Sport & Exercise, 9( 4), 393-411. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2007.07.001URL |
| [60] | Thurman S.K., &Torsney B.M . ( 2014). Meditation, mindfulness and executive functions in children and adolescents. In N. N. Singh (Ed.), Psychology of meditation( pp. 187-207). New York, NY: Nova Science Publishers. |
| [61] | Van de Weijer-Bergsma E., Formsma A. R., de Bruin E. I., &Bögels S. M . ( 2012). The effectiveness of mindfulness training on behavioral problems and attentional functioning in adolescents with ADHD. Journal of Child & Family Studies, 21( 5), 775-787. doi: 10.1007/s10826-011-9531-7URLpmid: 22993482 |
| [62] | Wang Y., Xin T-T., Liu, X-H. Zhang Y., Lu H-H., &Zhai Y-B . ( 2012). Mindfulness can reduce automatic responding: Evidences from stroop task and prospective memory task. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 44( 9), 1180-1188 |
| [ 王岩, 辛婷婷, 刘兴华, 张韵, 卢焕华, 翟彦斌 . ( 2012). 正念训练的去自动化效应: Stroop和前瞻记忆任务证据. 心理学报, 44( 9), 1180-1188. ] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2012.01180URL | |
| [63] | Wechsler D .( 2003). Wechsler intelligence scale for children- Fourth Edition (WISC-IV). San Antonio:The Psychological Corporation. |
| [64] | Westbrook C., Creswell J. D., Tabibnia G., Julson E., Kober H., &Tindle H. A . ( 2013). Mindful attention reduces neural and self-reported cue-induced craving in smokers. Social Cognitive & Affective Neuroscience, 8( 1), 73-84. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsr076URLpmid: 22114078 |
| [65] | Wood A.G., Smith E. ( 2008). Executive functions and the frontal lobes: A lifespan perspective (pp. 203-216). Philadelphia, PA: Taylor &Francis. |
| [66] | Wu J,J.., &Zheng R,C. ( 2008). The review of mental awareness intervention. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 22( 2), 148-151. |
| [ 吴九君, 郑日昌 . ( 2008). 心智觉知干预述评. 中国心理卫生杂志, 22( 2), 148-151.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6729.2008.02.023URL | |
| [67] | Yang L,Z., Song, H. ( 2003). Development on preschool children's self-control ability. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 4( 1), 51-56. |
| [ 杨丽珠, 宋辉 . ( 2003). 幼儿自我控制能力发展的研究. 心理与行为研究, 4( 1), 51-56.] | |
| [68] | Zeidan F., Gordon N. S., Merchant J., &Goolkasian P . ( 2010). The effects of brief mindfulness meditation training on experimentally induced pain. Journal of Pain, 11( 3), 199-209. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2009.07.015URLpmid: 19853530 |
| [69] | Zeidan F., Johnson S. K., Diamond B. J., David Z., &Goolkasian P . ( 2010). Mindfulness meditation improves cognition: Evidence of brief mental training. Consciousness and Cognition, 19( 2), 597-605. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2010.03.014URLpmid: 20363650 |
| [70] | Zelazo P.D . ( 2006). The dimensional change card sort (DCCS): A method of assessing executive function in children. Nature Protocol, 1( 1), 297-301. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.46URLpmid: 1740624817406248 |
| [71] | Zelazo P. D., Anderson J. E., Richler J., Wallner-allen K., Beaumont J. L., &Weintraub S . ( 2013). II. NIH toolbox cognition battery (CB): Measuring executive function and attention. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 78( 4), 16-33. |
| [72] | Zelazo P.D., &Lyons K.E . ( 2012). The potential benefits of mindfulness training in early childhood: A Developmental social cognitive neuroscience perspective. Child Development Perspectives, 6( 2), 154-160. |
| [73] | Zelazo P. D., Müller U., Frye D., Marcovitch S., Argitis G., Boseovski J., Sutherland A . ( 2003). The development of executive function in early childhood. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 68( 3), 48-64. |
| [74] | Zheng, X,X., Li, Y.Q. . ( 1991). The manual of children's sensory development chechlist implementation. Taipei: The special education center of Taipei city normal college. |
| [ 郑信雄, 李月卿 . ( 1991). 儿童感觉发展检核表实施手册. 台北:台北市立师范学院特殊教育中心. ] | |
| [75] | Zoogman S., Goldberg S. B., Hoyt W. T., &Miller L . ( 2015). Mindfulness interventions with youth: A meta-analysis. Mindfulness, 6( 2), 290-302. doi: 10.1007/s12671-013-0260-4URL |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 盖笑松, 许洁, 闫艳, 王元, 谢笑春. 体感游戏促进儿童的执行功能:运动强度和认知参与的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 505-514. |
| [2] | 赵鑫, 李红利, 金戈, 李世峰, 周爱保, 梁文佳, 郭红霞, 蔡亚亚. 语音记忆和中央执行功能在不同年级儿童解码和语言理解中的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(4): 469-484. |
| [3] | 王元, 李柯, 盖笑松, 曹逸飞. 基于即时反馈的反应抑制训练对青少年和成人执行功能的训练效应和迁移效应[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(10): 1212-1223. |
| [4] | 王婷,植凤英,陆禹同,张积家. 侗歌经验对侗族中学生执行功能的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(9): 1040-1056. |
| [5] | 邢淑芬, 李倩倩, 高鑫, 马园园, 傅锐. 不同睡眠时间参数对学前儿童执行功能的差异化影响[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(11): 1269-1281. |
| [6] | 邢强, 孙海龙, 占丹玲, 胡婧, 刘凯. 执行功能对言语顿悟问题解决的影响: 基于行为与ERPs的研究[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(7): 909-919. |
| [7] | 杨海波;赵欣;汪洋;张磊;王瑞萌; 张毅;王力. PTSD青少年执行功能缺陷的情绪特异性[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(5): 643-652. |
| [8] | 王婷, 王丹, 张积家, 崔健爱. “各说各话”的语言经验 对景颇族大学生执行功能的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(11): 1392-1403. |
| [9] | 吴彦文, 游旭群. 颜色字词的识别真的无需注意力资源的参与?——来自Stroop范式的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(10): 1267-1276. |
| [10] | 王岩;辛婷婷;刘兴华;张韵;卢焕华;翟彦斌. 正念训练的去自动化效应:Stroop和前瞻记忆任务证据[J]. 心理学报, 2012, 44(9): 1180-1188. |
| [11] | 陈爱国,殷恒婵,颜军,杨钰. 不同强度短时有氧运动对执行功能的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(09): 1055-1062. |
| [12] | 吴文婕, 张莉,冯廷勇,李红. 热执行功能对儿童标准窗口任务测试的影响 [J]. 心理学报, 2008, 40(03): 319-326. |
| [13] | 李一员,吴睿明,胡兴旺,李红,P ,D ,Zelaz. 聋童执行功能发展:聋童与正常儿童的比较 [J]. 心理学报, 2006, 38(03): 356-364. |
| [14] | 廖渝,吴睿明,Philip ,David ,Zelazo,李红,张婷,张莉,高山,李小晶. 意外地点任务中不同测试问题及意图理解与执行功能的关系[J]. 心理学报, 2006, 38(02): 207-215. |
| [15] | 张婷,吴睿明,李红,Philip ,David ,Zelazo,张莉,廖渝,李小晶 . 不同维度的执行功能与早期心理理论的关系[J]. 心理学报, 2006, 38(01): 56-62. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4405
