 )
) 中国人民大学心理学系, 北京 100872
收稿日期:2018-04-10出版日期:2019-02-25发布日期:2018-12-24通讯作者:张清芳E-mail:zhang@ruc.edu.cn基金资助:中国人民大学科学研究基金项目(中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助)(18XNLG28);北京市社科基金重点项目(16YYA006);国家自然科学基金面上项目(31471074)Distinct effects of age of acquisition in Chinese object and action picture naming: An ERP study
LOU Hao, LI Cong, ZHANG Qingfang( )
) Department of Psychology, Renmin University of China, Beijing 100872, China
Received:2018-04-10Online:2019-02-25Published:2018-12-24Contact:ZHANG Qingfang E-mail:zhang@ruc.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 词汇习得年龄指人们最早理解单词意义时的年龄, 已有研究发现早习得词汇的阅读反应时间短于晚习得词汇, 研究者对于词汇习得年龄效应的认知机制存在争论。本研究运用事件相关电位技术, 考察了词汇习得年龄(早与晚)对客体图画和动作图画命名的影响。研究中采用图画命名任务, 要求被试在看到图画后迅速且准确地说出图画名称。结果发现早习得名词的命名快于晚习得名词, 而早习得动词的命名却慢于晚习得动词; 习得年龄对于名词产生的影响发生在图画呈现后的250~300 ms之间, 表现为早习得名词波幅小于晚习得名词, 而习得年龄对于动词产生的影响发生在图画呈现后的200~600 ms之间, 表现为早习得动词波幅大于晚习得动词。这表明名词产生中的习得年龄效应发生在词汇选择阶段, 支持了语义假设的观点; 动词产生过程中的习得年龄效应出现在多个加工阶段, 包括了词汇选择、音韵编码和语音编码阶段, 这与动词语义的多重性及其与动作相关的脑区激活有关, 支持了网络可塑性假说的观点。
图/表 4
表1客体和动作图画早习得词与晚习得词的各项指标均值及其标准差
| 各项指标 | 客体图画 | 动作图画 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早习得词 | 晚习得词 | t | p | 早习得词 | 晚习得词 | t | p | |
| 习得年龄 | 2.58 (0.59) | 4.42 (0.73) | -13.19 | < 0.01 | 2.53 (0.37) | 3.38 (0.25) | -14.15 | < 0.01 |
| 命名一致性(%) | 69.78 (18.36) | 70.24 (0.22) | -0.11 | 0.91 | 71.68 (18.34) | 78.97 (16.37) | -0.95 | 0.35 |
| 熟悉性 | 4.36 (0.47) | 4.38 (0.37) | -0.19 | 0.85 | 3.22 (0.73) | 3.35 (0.88) | -0.24 | 0.81 |
| 具体性 | 3.84 (0.43) | 3.94 (0.42) | -1.19 | 0.24 | 2.01 (0.38) | 1.91 (0.40) | 0.61 | 0.55 |
| 视觉复杂性 | 3.13 (0.94) | 3.27 (0.80) | -0.78 | 0.44 | 3.05 (0.64) | 3.17 (0.58) | -1.04 | 0.30 |
| 表象一致性 | - | - | - | - | 3.84 (0.62) | 3.89 (0.58) | -1.13 | 0.26 |
| 表象变异性 | 3.18 (0.37) | 3.11 (0.35) | 0.96 | 0.34 | - | - | - | - |
| 词频对数 | 3.86 (0.92) | 3.57 (0.72) | 1.66 | 0.11 | 3.63 (0.93) | 3.34 (0.63) | 1.80 | 0.08 |
表1客体和动作图画早习得词与晚习得词的各项指标均值及其标准差
| 各项指标 | 客体图画 | 动作图画 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早习得词 | 晚习得词 | t | p | 早习得词 | 晚习得词 | t | p | |
| 习得年龄 | 2.58 (0.59) | 4.42 (0.73) | -13.19 | < 0.01 | 2.53 (0.37) | 3.38 (0.25) | -14.15 | < 0.01 |
| 命名一致性(%) | 69.78 (18.36) | 70.24 (0.22) | -0.11 | 0.91 | 71.68 (18.34) | 78.97 (16.37) | -0.95 | 0.35 |
| 熟悉性 | 4.36 (0.47) | 4.38 (0.37) | -0.19 | 0.85 | 3.22 (0.73) | 3.35 (0.88) | -0.24 | 0.81 |
| 具体性 | 3.84 (0.43) | 3.94 (0.42) | -1.19 | 0.24 | 2.01 (0.38) | 1.91 (0.40) | 0.61 | 0.55 |
| 视觉复杂性 | 3.13 (0.94) | 3.27 (0.80) | -0.78 | 0.44 | 3.05 (0.64) | 3.17 (0.58) | -1.04 | 0.30 |
| 表象一致性 | - | - | - | - | 3.84 (0.62) | 3.89 (0.58) | -1.13 | 0.26 |
| 表象变异性 | 3.18 (0.37) | 3.11 (0.35) | 0.96 | 0.34 | - | - | - | - |
| 词频对数 | 3.86 (0.92) | 3.57 (0.72) | 1.66 | 0.11 | 3.63 (0.93) | 3.34 (0.63) | 1.80 | 0.08 |
表2以词类、AoA和ROI为自变量在200~600 ms时间窗口(以50 ms为间隔)中方差分析的结果
| 变异来源 | 200~250 ms | 250~300 ms | 300~350 ms | 350~400 ms | 400~450 ms | 450~500 ms | 500~550 ms | 550~600 ms | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | |
| 词类(1, 20) | 8.07** | 0.29 | 3.46? | 0.15 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| AoA (1, 20) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 词类×AoA (1, 20) | 3.54? | 0.15 | 3.42? | 0.15 | 3.20? | 0.14 | 3.38? | 0.14 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 词类×脑区(2, 40) | 34.40** | 0.63 | 28.57** | 0.59 | 18.53** | 0.48 | 13.15** | 0.40 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| AoA×脑区(2, 40) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 词类×AoA×脑区(2, 40) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 词类×半球(2, 40) | — | — | — | — | 2.69? | 0.12 | — | — | 2.53? | 0.11 | — | — | — | — | 2.52? | 0.11 |
| AoA×半球(2, 40) | — | — | — | — | 6.24* | 0.24 | 4.03* | 0.17 | 5.69* | 0.22 | 7.46** | 0.27 | 5.44* | 0.21 | 5.08* | 0.20 |
| 词类×AoA×半球(2, 40) | — | — | 5.35* | 0.21 | 7.95** | 0.28 | 9.46** | 0.32 | 9.81** | 0.33 | 11.83** | 0.37 | 17.52** | 0.47 | 9.67** | 0.33 |
| 词类×脑区×半球(4, 80) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2.35? | 0.11 | 3.14* | 0.14 | 2.07? | 0.09 |
| AoA×脑区×半球(4, 80) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2.87* | 0.13 | — | — | 3.40* | 0.15 |
| 词类×AoA×脑区×半球(4, 80) | 7.16** | 0.26 | 8.89** | 0.31 | 9.78** | 0.33 | 8.36** | 0.29 | 11.38** | 0.36 | 18.53** | 0.48 | 15.71*** | 0.44 | 7.69** | 0.28 |
表2以词类、AoA和ROI为自变量在200~600 ms时间窗口(以50 ms为间隔)中方差分析的结果
| 变异来源 | 200~250 ms | 250~300 ms | 300~350 ms | 350~400 ms | 400~450 ms | 450~500 ms | 500~550 ms | 550~600 ms | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | F | ηp2 | |
| 词类(1, 20) | 8.07** | 0.29 | 3.46? | 0.15 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| AoA (1, 20) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 词类×AoA (1, 20) | 3.54? | 0.15 | 3.42? | 0.15 | 3.20? | 0.14 | 3.38? | 0.14 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 词类×脑区(2, 40) | 34.40** | 0.63 | 28.57** | 0.59 | 18.53** | 0.48 | 13.15** | 0.40 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| AoA×脑区(2, 40) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 词类×AoA×脑区(2, 40) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 词类×半球(2, 40) | — | — | — | — | 2.69? | 0.12 | — | — | 2.53? | 0.11 | — | — | — | — | 2.52? | 0.11 |
| AoA×半球(2, 40) | — | — | — | — | 6.24* | 0.24 | 4.03* | 0.17 | 5.69* | 0.22 | 7.46** | 0.27 | 5.44* | 0.21 | 5.08* | 0.20 |
| 词类×AoA×半球(2, 40) | — | — | 5.35* | 0.21 | 7.95** | 0.28 | 9.46** | 0.32 | 9.81** | 0.33 | 11.83** | 0.37 | 17.52** | 0.47 | 9.67** | 0.33 |
| 词类×脑区×半球(4, 80) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2.35? | 0.11 | 3.14* | 0.14 | 2.07? | 0.09 |
| AoA×脑区×半球(4, 80) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2.87* | 0.13 | — | — | 3.40* | 0.15 |
| 词类×AoA×脑区×半球(4, 80) | 7.16** | 0.26 | 8.89** | 0.31 | 9.78** | 0.33 | 8.36** | 0.29 | 11.38** | 0.36 | 18.53** | 0.48 | 15.71*** | 0.44 | 7.69** | 0.28 |
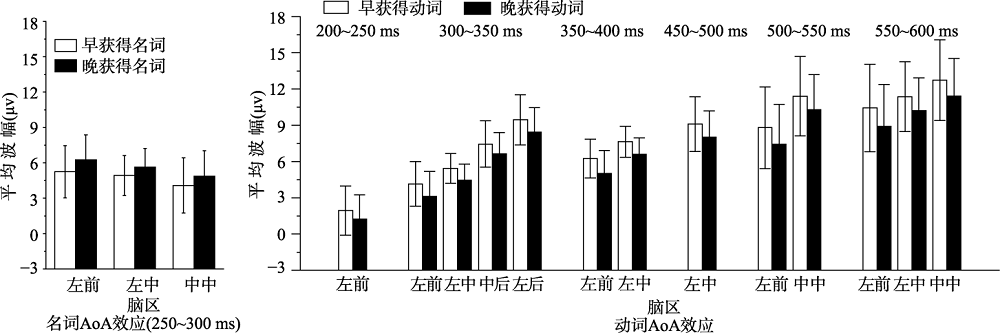
图1名词和动词在不同时间窗口下的AoA效应 注:图中误差棒均为95%CI
 图1名词和动词在不同时间窗口下的AoA效应 注:图中误差棒均为95%CI
图1名词和动词在不同时间窗口下的AoA效应 注:图中误差棒均为95%CI
图2F5电极点(左前)名词和动词AoA效应 注:彩图见电子版
 图2F5电极点(左前)名词和动词AoA效应 注:彩图见电子版
图2F5电极点(左前)名词和动词AoA效应 注:彩图见电子版参考文献 60
| 1 | Akinina Y. L., Malyutina S., Ivanova M., Iskra E., Mannova E., & Dragoy O . ( 2015). Russian normative data for 375 action pictures and verbs. Behavior Research Methods, 47 (3), 691-707. doi: 10.3758/s13428-014-0492-9URL |
| 2 | Alario F. X., Ferrand L., Laganaro M., New B., Frauenfelder U. H., & Segui J . ( 2004). Predictors of picture naming speed. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, and Computers, 36 (1), 140-155. doi: 10.3758/BF03195559URL |
| 3 | Arévalo A. L., Lu C. C., Huang L. B. Y., Bates E. A., & Dronkers N. F . ( 2011). Action and object processing in brain-injured speakers of Chinese. Neuropsychology, 25 (6), 792-805. doi: 10.1037/a0024272URL |
| 4 | Bai X. J., Wang L. H., Lv Y., & Hu W . ( 2010). An ERP study on age of acquisition effect. Psychological Exploration, 30 (1), 21-26. |
| [ 白学军, 王丽红, 吕勇, 胡伟 . ( 2010). 词汇的获得年龄效应: ERP研究. 心理学探新, 30(1), 21-26.] | |
| 5 | Bakhtiar M., Su I. F., Lee H. K., & Weekes B. S . ( 2016). Neural correlates of age of acquisition on visual word recognition in Persian. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 39, 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroling.2015.12.001URL |
| 6 | Barry C., Johnston R. A., & Wood R. F . ( 2006). Effects of age of acquisition, age, and repetition priming on object naming. Visual Cognition, 13 (7-8), 911-927. doi: 10.1080/13506280544000101URL |
| 7 | Bates E., D'Amico S., Jacobsen T., Székely A., Andonova E., & Devescovi A., … Tzeng O . ( 2003). Timed picture naming in seven languages. Psychonomic Bulletin Review, 10 (2), 344-380. doi: 10.3758/BF03196494URL |
| 8 | Belke E., Brysbaert M., Meyer A. S., & Ghyselinck M . ( 2005). Age of acquisition effects in picture naming: Evidence for a lexical-semantic competition hypothesis. Cognition, 96 (2), B45-B54. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2004.11.006URL |
| 9 | Bonin P., Boyer B., Méot A., Fayol M., & Droit S . ( 2004). Psycholinguistic norms for action photographs in French and their relationships with spoken and written latencies. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, and Computers, 36 (1), 127-139. doi: 10.3758/BF03195558URL |
| 10 | Brown, G. D.A., &Watson, F.L ., ( 1987). First in, first out: Word learning age and spoken word frequency as predictors of word familiarity and word naming latency. Memory and cognition, 15 (3), 208-216. doi: 10.3758/BF03197718URL |
| 11 | Brysbaert M., Van W. I., & De Deyne. S . ( 2000). Age-of-acquisition effects in semantic processing tasks. Acta Psychologica, 104 (2), 215-226. doi: 10.1016/S0001-6918(00)00021-4URL |
| 12 | Carroll, J.B., &White, M.N ., ( 1973). Age-of-acquisition norms for 220 picturable nouns. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 12 (5), 563-576. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5371(73)80036-2URL |
| 13 | Catling, J.C., &Johnston R.A ., ( 2006). The effects of age of acquisition on an object classification task. Visual Cognition, 13 (7-8), 968-980. doi: 10.1080/13506280544000138URL |
| 14 | Catling, J.C., &Johnston R.A ., ( 2009). The varying effects of age of acquisition. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 62 (1), 50-62. doi: 10.1080/17470210701814352URL |
| 15 | Catling J. C., Dent K., Johnston R. A., & Balding R . ( 2010). Age of acquisition, word frequency, and picture-word interference. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 63 (7), 1304-1317. doi: 10.1080/17470210903380830URL |
| 16 | Chalard, M., &Bonin P ., ( 2006). Age-of-acquisition effects in picture naming: Are they structural and/or semantic in nature? Visual Cognition, 13 (7-8), 864-883. doi: 10.1080/13506280544000084URL |
| 17 | Chen B. G., Dent, K. You, W. P., & Wu G. L . ( 2009). Age of acquisition affects early orthographic processing during Chinese character recognition. Acta Psychologica, 130 (3), 196-203. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2008.12.004URL |
| 18 | Chen B. G., You W. P., & Wang L. X . ( 2006). The research development of the age-of-acquisition effect in lexical processing. Psychological Science, 29 (6), 1515-1517. |
| [ 陈宝国, 尤文平, 王立新 . ( 2006). 词汇习得年龄效应的研究进展. 心理科学, 29(6), 1515-1517.] | |
| 19 | Chen B. G., You W. P., & Zhou H. X . ( 2007). Age of acquisition effects in reading Chinese: Evidence in favor of the semantic hypothesis. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 39, 9-17. |
| [ 陈宝国, 尤文平, 周会霞 . ( 2007). 汉语词汇习得的年龄效应: 语义假设的证据. 心理学报, 39(1), 9-17.] doi: | |
| 20 | Chen B. G., You W. P., Zhang Y. F., & Liu W. H . ( 2010) Acquisition age of effects on the early orthographic processing stage of Chinese character recognition. Psychological Science, 33 (3), 726-728. |
| [ 陈宝国, 尤文平, 张亚峰, 刘文唤 . ( 2010). 汉字早期字形加工阶段的习得年龄效应. 心理科学, 33(3), 726-728.] | |
| 21 | Chen B. G., Zhou H. X., Dunlap S., & Perfetti C. A . ( 2007). Age of acquisition effects in reading Chinese: Evidence in favour of the arbitrary mapping hypothesis. British Journal of Psychology, 98 (3), 499-516. doi: 10.1348/000712606X165484URL |
| 22 | Chen J., Lin S. H., & Zhang J. J . ( 2011). The word AoA effects in Chaoshan-Putonghua bilinguals’ experimental performance. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 43 (2), 111-112. |
| [ 陈俊, 林少惠, 张积家 . ( 2011). 潮汕话-普通话双言者的词汇习得年龄效应. 心理学报, 43(2), 111-112.] doi: | |
| 23 | Chen, Y.X., &Zhu L.Q ., ( 2015). Predictors of action picture naming in Mandarin Chinese. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 47 (1), 11-18. |
| [ 陈永香, 朱莉琪 . ( 2015). 影响动作图片命名的因素. 心理学报, 47(1), 11-18.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2015.00011 | |
| 24 | Cuetos, F., &Alija M . ( 2003). Normative data and naming times for action pictures. Behavior Research Methods Instruments and Computers, 35 (1), 168-177. doi: 10.3758/BF03195508URL |
| 25 | Damian, M.F., &Martin R.C . ( 1999). Semantic and phonological codes interact in single word production. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 25 (2), 345-361. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.25.2.345URL |
| 26 | Dell’Acqua R., Sessa P., Peressotti F., Mulatti C., Navarrete E., & Grainger J . ( 2010). ERP evidence for ultra-fast semantic processing in the picture-word interference paradigm. Frontiers in Psychology, 1, 177. |
| 27 | Druks J., Masterson J., Kopelman M., Claire L., Rose A., & Ray G . ( 2006). Is action naming better preserved (than object naming) in Alzheimer’s disease and why should we ask? Brain and Language, 98 (3), 332-340. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2006.06.003URL |
| 28 | Ellis, A.W., & Lambon Ralph M.A . ( 2000). Age of acquisition effects in adult lexical processing reflect loss of plasticity in maturing system: Insights from connectionist networks. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition, 26 (5), 1103-1123. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.26.5.1103URL |
| 29 | Fang, J.M., & Zhang Z . ( 1998). Comparative study on cognitive processing of Chinese characters between hearing-impaired and normal children. Chinese Journal of Special Education,(4), 19-21. |
| [ 方俊明, 张朝 . ( 1998). 聋人与听力正常人汉字加工认知途径的比较研究. 中国特殊教育, (4), 19-22.] | |
| 30 | Gentner, D . ( 1982). Why nouns are learned before verbs: Linguistic relativity versus natural partitioning. Language, 2, 301-334. |
| 31 | Gerhand, S., &Barry C . ( 1999). Age of acquisition, word frequency, and the role of phonology in the lexical decision task. Memory and Cognition, 27 (4), 592-602. doi: 10.3758/BF03211553URL |
| 32 | Holmes, S.J., &Ellis A.W . ( 2006). Age of acquisition and typicality effects in three object processing tasks. Visual Cognition, 13 (7-8), 884-910. doi: 10.1080/13506280544000093URL |
| 33 | Indefrey, P . ( 2011). The spatial and temporal signatures of word production components: A critical update. Frontiers in Psychology, 2, 255-275. |
| 34 | Indefrey P., &Levelt W. J. M . ( 2004). The spatial and temporal signatures of word production components. Cognition. 92 (1-2), 101-144. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2002.06.001URL |
| 35 | Johnston, R.A., &Barry, C . ( 2006). Age of acquisition and lexical processing. Visual Cognition, 13 (7-8), 789-845. doi: 10.1080/13506280544000066URL |
| 36 | Laganaro, M., &Perret C . ( 2011). Comparing electrophysiological correlates of word production in immediate and delayed naming through the analysis of word age of acquisition effects. Brain Topography, 24 (1), 19-29. doi: 10.1007/s10548-010-0162-xURL |
| 37 | Laganaro M., Valente A., & Perret C . ( 2012). Time course of word production in fast and slow speakers: A high density ERP topographic study. Neuroimage, 59 (4), 3881-3888. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.082URL |
| 38 | Levelt W. J.M., Roelofs A., & Meyer A. S . 1999). A theory of lexical access in speech production. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 22 (1), 1-75. |
| 39 | Li C., Zhang Q. F., & Huang R . ( 2017). The opposite effects of age of acquisition in object and action pictures naming. Psychological Exploration, 37 (3), 220-225. |
| [ 李丛, 张清芳, 黄韧 . ( 2017). 词汇获得年龄在物体和动作图画命名中的不同作用. 心理学探新, 37(3), 220-225.] | |
| 40 | Liu Y. Y., Hao M. L., Li P., & Shu H . ( 2011). Timed picture naming norms for Mandarin Chinese. Plos One, 6 (1), e16505. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016505URL |
| 41 | Masterson, J., &Druks, J . ( 1998). Description of a set of 164 nouns and 102 verbs matched for printed word frequency, familiarity and age of- acquisition. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 11, 331-354. |
| 42 | Mätzig S., Druks J., Masterson J., & Vigliocco G . ( 2009). Noun and verb differences in picture naming: Past studies and new evidence. Cortex, 45 (6), 738-758. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2008.10.003URL |
| 43 | &Mobaghan, J., Ellis, A.W . ( 2002). Age of acquisition and the completeness of phonological representations. Reading and Writing, 15 (7-8), 759-788. doi: 10.1023/A:1020958722472URL |
| 44 | Morrison, C.M., &Gibbons, Z.C . ( 2006). Lexical determinants of semantic processing speed. Visual Cognition, 13 (7-8), 949-967. doi: 10.1080/13506280544000129URL |
| 45 | Perret C., Bonin P., & Laganaro M . ( 2014). Exploring the multiple-level hypothesis of AoA effects in spoken and written object naming using a topographic ERP analysis. Brain and Language, 135, 20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2014.04.006URL |
| 46 | Pulvermüller F . ( 1999). Words in the brain's language. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 22 (2), 253-279. doi: 10.1017/S0140525X9900182XURL |
| 47 | Schuhmann T., Schiller N. O., Goebel R., & Sack A. T . ( 2009). The temporal characteristics of functional activation in broca's area during overt picture naming. Cortex, 45 (9), 1111-1116. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2008.10.013URL |
| 48 | Schwitter V., Boyer B., Méot A., Bonin P., & Laganaro M . ( 2004). French normative data and naming times for action pictures. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, and Computers, 36 (3), 564-576. doi: 10.3758/BF03195603URL |
| 49 | Shao Z. S., Roelofs A., & Meyer A. S . ( 2013). Predicting naming latencies for action pictures: Dutch norms. Behavior Research Methods, 46 (1), 274-283. |
| 50 | Starreveld, P.A., & La Heij, W . ( 1995). Semantic interference, orthographic facilitation, and their interaction in naming tasks. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 21 (3), 686-698. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.21.3.686URL |
| 51 | Starreveld, P.A., & La Heij, W . ( 1996). The locus of orthographic-phonological facilitation: Reply to Roelofs, Meyer, and Levelt (1996). Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 22 (1), 252-255. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.22.1.252URL |
| 52 | Tardif, T . ( 1996). Nouns are not always learned before verbs: Evidence from Mandarin speakers' early vocabularies. Developmental Psychology, 32 (3), 492-504. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.32.3.492URL |
| 53 | Warrington, E.K., &McCarthy R.A . ( 1987). Categories of knowledge: Further fractionations and attempted integration. Brain, 110 (5), 1273-1296. doi: 10.1093/brain/110.5.1273URL |
| 54 | Weekes, B . ( 2011). Age of acquisition effects on Chinese character recognition: Evidence from EEG. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, 23 (23), 67-68. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.09.173URL |
| 55 | Weekes B. S., Shu H., Hao M. L., Liu Y. Y., & Tan L. H . ( 2007). Predictors of timed picture naming in Chinese. Behavior Research Methods, 39 (2), 335-342. doi: 10.3758/BF03193165URL |
| 56 | Zevin, J.D., &Seidenberg M.S . ( 2002). Age of acquisition effects in word reading and other tasks. Journal of Memory and Language, 47 (1), 1-29. doi: 10.1006/jmla.2001.2834URL |
| 57 | Zhang J. J., Chen S. Q., Zhang G. Y., & Dai D. H . ( 2012). Age of acquisition effects in deaf college students. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 44 (11), 1421-1433. |
| [ 张积家, 陈穗清, 张广岩, 戴东红 . ( 2012). 聋大学生的词汇习得年龄效应. 心理学报, 44(11), 1421-1433.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2012.01421 | |
| 58 | Zhang Z. J., You W. P., & Chen B. G . ( 2011). Age-of- acquisition effects of Chinese character: Test of phonological completeness hypothesis. Psychological Development and Education, 27 (6), 577-583. |
| [ 张振军, 丁国盛, 陈宝国 . ( 2011). 汉字习得的年龄效应: 语音完整性假设的检验. 心理发展与教育, 27(6), 577-583. ] | |
| 59 | Zhu X. D., Damian M. F., & Zhang Q. F . ( 2015). Seriality of semantic and phonological processes during overt speech in Mandarin as revealed by event-related brain potentials. Brain and Language, 144, 16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2015.03.007URL |
| 60 | Zhu X. B., Zhang Q. F., & Damian M. F . ( 2016). Additivity of semantic and phonological effects: Evidence from speech production in Mandarin. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 69 (11), 2285-2304. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2015.1129427URL |
相关文章 5
| [1] | 张清芳, 钱宗愉, 朱雪冰. 汉语口语词汇产生中的多重音韵激活:单词翻译任务的ERP研究[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(1): 1-14. |
| [2] | 张清芳, 王雪娇. 汉语口语词汇产生的音韵编码单元:内隐启动范式的ERP研究[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(4): 414-425. |
| [3] | 张积家;陈穗清;张广岩;戴东红. 聋大学生的词汇习得年龄效应[J]. 心理学报, 2012, 44(11): 1421-1433. |
| [4] | 陈俊,林少惠,张积家. 潮汕话-普通话双言者的词汇习得年龄效应[J]. 心理学报, 2011, 43(02): 111-122. |
| [5] | 张清芳,杨玉芳. 影响图画命名时间的因素[J]. 心理学报, 2003, 35(04): 447-454. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4378
