 ), 何虎1,2, 侯友1,2, 贾缨琪1, 冯慎行1
), 何虎1,2, 侯友1,2, 贾缨琪1, 冯慎行1 1 内蒙古自治区心理学重点实验室
2 内蒙古师范大学心理学院, 呼和浩特 010022
收稿日期:2018-01-30出版日期:2019-02-25发布日期:2018-12-24通讯作者:李杰E-mail:healthlj2004@163.com基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(31460250);内蒙古自治区高等学校“青年科技英才支持计划”A类基金项目(NJYT-18-A03);内蒙古自然科学基金项目(2018MS03009);教育部人文社科项目(13XJC190001)Categorical perception of color can be instantly influenced by color vision fatigue and semantic satiation
WU Baizhou1, LI Jie1,2( ), HE Hu1,2, HOU You1,2, JIA Yingqi1, FENG Shenxing1
), HE Hu1,2, HOU You1,2, JIA Yingqi1, FENG Shenxing1 1 The Key Laboratory of Psychology, Inner Mongolia Normal University, Hohhot 010022, China
2 College of Psychology, Inner Mongolia Normal University, Hohhot 010022, China
Received:2018-01-30Online:2019-02-25Published:2018-12-24Contact:LI Jie E-mail:healthlj2004@163.com摘要/Abstract
摘要: 颜色范畴知觉究竟是语言的还是知觉的, 或两者交互引起的认知冲突所致仍在探究与争议之中。本研究采用色觉疲劳和语义饱和操作分别独立地改变知觉或语义加工, 观察二者对颜色范畴知觉效应的即时影响, 以期探究语言和知觉对颜色范畴的作用。结果显示, 色觉疲劳操作导致范畴间颜色辨别反应时减少, 颜色范畴效应增强。语义饱和操作导致被饱和颜色词所属的范畴内颜色辨别反应时增加, 颜色范畴效应增强。说明单独改变知觉或语义加工能力均能影响CCP效应, 支持了语言标签对比模型, 即语言与知觉的交互作用引起颜色范畴知觉的观点。
图/表 7
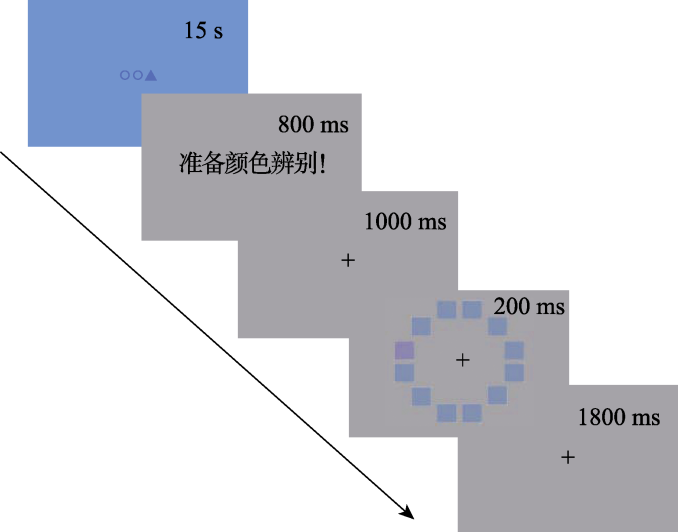
图1疲劳任务实验流程图
 图1疲劳任务实验流程图
图1疲劳任务实验流程图表1不同条件下被试的反应时(M ± SD, ms)
| 范畴 | 左视野(LVF) | 右视野(RVF) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 疲劳 | 无疲劳 | 疲劳 | 无疲劳 | |
| 范畴内(WC) | 328 ± 91 | 315 ± 92 | 308 ± 81 | 305 ± 80 |
| 范畴间(BC) | 285 ± 75 | 297 ± 90 | 269 ± 63 | 290 ± 96 |
表1不同条件下被试的反应时(M ± SD, ms)
| 范畴 | 左视野(LVF) | 右视野(RVF) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 疲劳 | 无疲劳 | 疲劳 | 无疲劳 | |
| 范畴内(WC) | 328 ± 91 | 315 ± 92 | 308 ± 81 | 305 ± 80 |
| 范畴间(BC) | 285 ± 75 | 297 ± 90 | 269 ± 63 | 290 ± 96 |
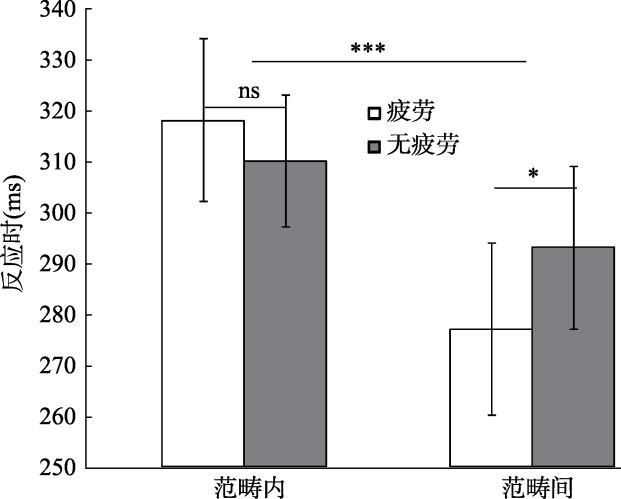
图2不同范畴类型下的疲劳效应 注:***表示p < 0.001, *表示p < 0.05, ns表示p > 0.05, 误差线为标准误, 下同。
 图2不同范畴类型下的疲劳效应 注:***表示p < 0.001, *表示p < 0.05, ns表示p > 0.05, 误差线为标准误, 下同。
图2不同范畴类型下的疲劳效应 注:***表示p < 0.001, *表示p < 0.05, ns表示p > 0.05, 误差线为标准误, 下同。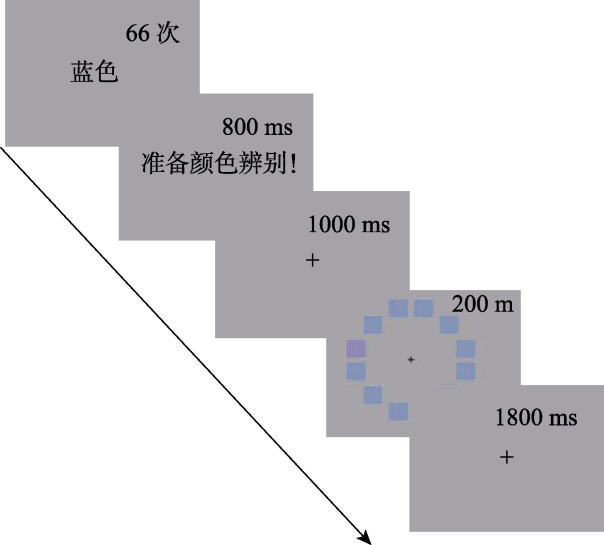
图3语义饱和实验流程
 图3语义饱和实验流程
图3语义饱和实验流程表2不同条件下被试的反应时(M ± SD, ms)
| 范畴 | 左视野(LVF) | 右视野(RVF) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高饱和 | 低饱和 | 高饱和 | 低饱和 | |
| 范畴内(WC) | 289 ± 45 | 290 ± 45 | 281 ± 39 | 280 ± 35 |
| 范畴间(BC) | 267 ± 40 | 270 ± 44 | 255 ± 26 | 256 ± 28 |
表2不同条件下被试的反应时(M ± SD, ms)
| 范畴 | 左视野(LVF) | 右视野(RVF) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高饱和 | 低饱和 | 高饱和 | 低饱和 | |
| 范畴内(WC) | 289 ± 45 | 290 ± 45 | 281 ± 39 | 280 ± 35 |
| 范畴间(BC) | 267 ± 40 | 270 ± 44 | 255 ± 26 | 256 ± 28 |
表3语义饱和任务不同条件下被试的反应时(M ± SD, ms)
| 范畴 | 左视野(LVF) | 右视野(RVF) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高饱和 | 低饱和 | 高饱和 | 低饱和 | |
| 一致-范畴内(Y-WC) | 295 ± 49 | 293 ± 49 | 287 ± 40 | 280 ± 36 |
| 不一致-范畴内(N-WC) | 284 ± 43 | 286 ± 46 | 274 ± 39 | 279 ± 37 |
| 范畴间(BC) | 267 ± 40 | 270 ± 44 | 255 ± 25 | 256 ± 28 |
表3语义饱和任务不同条件下被试的反应时(M ± SD, ms)
| 范畴 | 左视野(LVF) | 右视野(RVF) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高饱和 | 低饱和 | 高饱和 | 低饱和 | |
| 一致-范畴内(Y-WC) | 295 ± 49 | 293 ± 49 | 287 ± 40 | 280 ± 36 |
| 不一致-范畴内(N-WC) | 284 ± 43 | 286 ± 46 | 274 ± 39 | 279 ± 37 |
| 范畴间(BC) | 267 ± 40 | 270 ± 44 | 255 ± 25 | 256 ± 28 |
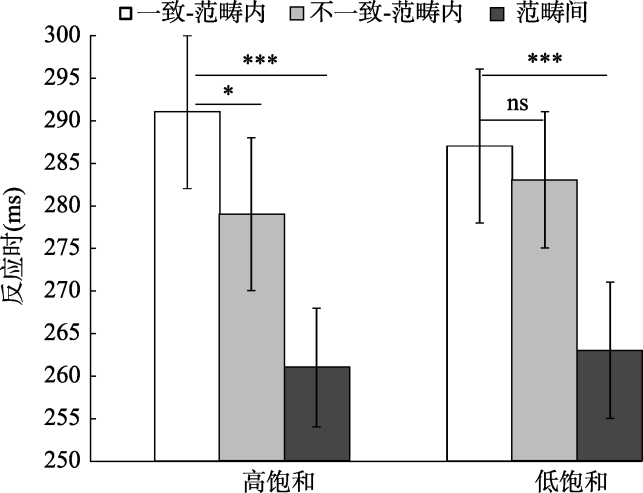
图4不同范畴类型的饱和效应
 图4不同范畴类型的饱和效应
图4不同范畴类型的饱和效应参考文献 28
| 1 | Abbott J. T., Griffiths T. L., & Regier T . ( 2016). Focal colors across languages are representative members of color categories. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113( 40), 11178-11183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1513298113URL |
| 2 | Cheng, C.M., & Lai H.D, . ( 2012). The mechanism underlying Chinese orthographic decomposition. Advances in Psychology, 2( 4), 163-172. |
| [ 郑昭明, 赖惠德 . ( 2012). 汉字的解体及其机制. 心理科学进展, 2( 4), 163-172.] | |
| 3 | Cogan, F.C., & Cogan D.G, . ( 1938). Recovery time from color fatigue in the peripheral visual field. Ophthalmologica, 96( 4-5), 267-276. doi: 10.1159/000299621URL |
| 4 | Franklin A., Drivonikou G. V., Bevis L., Davies I. R. L., Kay P., & Regier T . ( 2008 a). Categorical perception of color is lateralized to the right hemisphere in infants, but to the left hemisphere in adults. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105( 9), 3221-3225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712286105URL |
| 5 | Franklin A., Drivonikou G. V., Clifford A., Kay P., Regier T., & Davies I. R . ( 2008 b). Lateralization of categorical perception of color changes with color term acquisition. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105( 47), 18221-18225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809952105URL |
| 6 | Galmar, B. ( 2012). Verbal satiation of Chinese bisyllabic words: A semantic locus and its time course. Palm.mindmodeling.org. |
| 7 | Gilbert A. L., Regier T., Kay P., & Ivry R. B . ( 2006). Whorf hypothesis is supported in the right visual field but not the left. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103( 2), 489-494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509868103URL |
| 8 | He H., Li J., Zhang Y., & Zhang S . ( 2016). Language affects perception: evidence from Mongolian. Paper presented at the 16th International Conference on the Processing of East Asian Languages, Guangzhou, China. |
| 9 | Holmes A., Franklin A., Clifford A., & Davies I . ( 2009). Neurophysiological evidence for categorical perception of color. Brain Cognition, 69( 2), 426-434. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2008.09.003URL |
| 10 | Hu Z., Hanley J. R., Zhang R., Liu Q., & Roberson D . ( 2014). A conflict-based model of color categorical perception: Evidence from a priming study. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 21( 5), 1214-1223. |
| 11 | Lewis, M.B., & Ellis H.D, . ( 2000). Satiation in name and face recognition. Memory & Cognition, 28( 5), 783-788. |
| 12 | Li F. M. (1995). Handbook of ophthalmology. People's Medical Publishing House. |
| [ 李凤鸣 . (1995). 眼科全书. 人民卫生出版社.] | |
| 13 | Liu Q., Chen A-T., Wang Q., Zhou L., & Sun H-J ., ( 2008). An evidence for the effect of categorical perception on color perception. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 40( 1), 8-13. |
| [ 刘强, 陈安涛, 王琪, 周柳, 孙弘进 . ( 2008). 知觉加工中存在颜色类别知觉效应的证据. 心理学报, 40( 1), 8-13.] | |
| 14 | Liu Q., Li H., Campos J. L., Teeter C., Tao W., Zhang Q., & Sun H-J . ( 2010). Language suppression effects on the categorical perception of colour as evidenced through ERPs. Biological Psychology, 85( 1), 45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2010.05.001URL |
| 15 | Liu Q., Li H., Campos J. L., Wang Q., Zhang Y., Qiu J., Zhang Q., & Sun H. J . ( 2009). The N2pc component in ERP and the lateralization effect of language on color perception. Neuroscience Letters, 454( 1), 58-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.02.045URL |
| 16 | Mo L., Xu G., Kay P., & Tan L-H . ( 2011). Electrophysiological evidence for the left-lateralized effect of language on preattentive categorical perception of color. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108( 34), 14026-14030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111860108URL |
| 17 | Roberson D., & Hanley, J. R .( 2010). Relatively speaking: An account of the relationship between language and thought in the color domain In B C Malt & P Wolff (Eds), Words and the mind: How words capture human experience (pp 183-198) New York, NY: Oxford University Press. |
| 18 | Skelton A. E., Catchpole G., Abbott J. T., Bosten J. M., & Franklin A . ( 2017). Biological origins of color categorization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114( 21), 5545-5550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1612881114URL |
| 19 | Tajima C. I., Tajima S., Koida K., Komatsu H., Aihara K., & Suzuki H . ( 2016). Population code dynamics in categorical perception. Scientific Reports, 6, 22536. doi: 10.1038/srep22536URL |
| 20 | Tian, X., & Huber D.E, . ( 2010). Testing an associative account of semantic satiation. Cognitive Psychology, 60( 4), 267-290. doi: 10.1016/j.cogpsych.2010.01.003URL |
| 21 | Winawer J., Witthoft N., Frank M. C., Wu L., Wade A. R., & Boroditsky L . ( 2007). Russian blues reveal effects of language on color discrimination. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104( 19), 7780-7785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701644104URL |
| 22 | Witzel, C., & Gegenfurtner K.R, . ( 2016). Categorical perception for red and brown. Journal of Experimental Psychology Human Perception & Performance, 42( 4), 540-570. |
| 23 | Yang J., Kanazawa S., Yamaguchi M. K., & Kuriki I . ( 2016). Cortical response to categorical color perception in infants investigated by near-infrared spectroscopy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113( 9), 2370-2375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1512044113URL |
| 24 | Yuan J., Carr S., Ding G., Fu S., & Zhang J. X . ( 2016). An associative account of orthographic satiation in Chinese characters. Reading and Writing, 30( 3), 631-651. |
| 25 | Zhang J. J., Fang Y. H., & Xie S. S . ( 2013). Interactive theory of color cognition and its evidence. Advances in Psychological Science, 20( 7), 949-962. |
| [ 张积家, 方燕红, 谢书书 . ( 2012). 颜色词与颜色认知的关系:相互作用理论及其证据. 心理科学进展, 20( 7), 949-962.] | |
| 26 | Zhang J. J., Liu X., & Wang Y . ( 2014). On the semantic satiation of Chinese-English bilinguals. Foreign Language Teaching and Research (bimonthly), 46( 3), 423-435. |
| [ 张积家, 刘翔, 王悦 . ( 2014). 汉英双语者语义饱和效应研究. 外语教学与研究, 46( 3), 423-434.] | |
| 27 | Zhong W., Li Y., Huang Y., Li H., & Mo L . ( 2017). Is the lateralized categorical perception of color a situational effect of language on color perception?. Cognitive Science, 42( 3), 1-15. |
| 28 | Zhong W., Li Y., Xu G., Qin K., & Mo L . ( 2014). Short-term trained lexical categories cause a shift of color categorical perception from right hemisphere to left hemisphere. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 46( 4), 450-458. |
| [ 钟伟芳, 李悠, 徐贵平, 秦凯鑫, 莫雷 . ( 2014). 短期习得的语言范畴使成人大脑右半球颜色范畴知觉转为左半球颜色范畴知觉. 心理学报, 46( 4), 450-458.] |
相关文章 3
| [1] | 谢书书, 张积家, 朱君. 颜色范畴知觉效应发生在大脑两半球:来自纳西族和汉族的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(11): 1229-1243. |
| [2] | 李杰, 何虎, 吴柏周, 侯友, 曹亢, 阿如罕. 不同熟练度双语者的颜色范畴知觉效应:来自行为和ERP的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(11): 1259-1268. |
| [3] | 钟伟芳;李悠;徐贵平;秦凯鑫;莫雷. 短期习得的语言范畴使成人大脑右半球颜色范畴知觉转为左半球颜色范畴知觉[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(4): 450-458. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4383
