 )
) 1 上海师范大学教育学院
2 上海师范大学商学院
3 上海师范大学音乐学院, 上海 200234
收稿日期:2018-03-02出版日期:2018-11-30发布日期:2018-10-30基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金项目(31470972, 31500876)Effects of lyrics on the processing of musical emotion: Behavioural and ERP study
ZHANG Weixia1, WANG Wanqi2, ZHOU Linshu3, JIANG Cunmei3( )
) 1 Department of Psychology, College of Education, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai 200234, China
2 School of Finance and Business, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai 200234, China
3 Music College, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai 200234, China
Received:2018-03-02Online:2018-11-30Published:2018-10-30摘要/Abstract
摘要: 本研究探讨了歌词对音乐情绪加工的影响。实验1使用情感启动范式, 带有歌词与无歌词音乐片段为启动刺激, 与音乐情绪一致或不一致的面孔图片为目标刺激, 被试任务是既快又准确地判断目标面孔的情绪。结果显示, 无论音乐是否带有歌词, 听者在一致条件下的反应都比不一致条件更快更准确, 这表明听者能加工音乐传达的情绪信息。实验2进一步通过电生理手段探讨歌词影响音乐情绪加工的神经机制。研究结果显示, 尽管听者对带有歌词和无歌词音乐情绪的加工都产生了启动效应, 但是无歌词音乐条件在250~450 ms时间窗口产生了N400效应, 而带有歌词音乐条件在500~700 ms时间窗口诱发了LPC效应, 该结果表明, 歌词影响了大脑加工音乐情绪的时间进程。本研究结果将在一定程度上为音乐与语言关系的探究提供依据。
图/表 4

图1跨通道情感启动范式。启动刺激为带有歌词或无歌词音乐片段, 情绪面孔为目标刺激
 图1跨通道情感启动范式。启动刺激为带有歌词或无歌词音乐片段, 情绪面孔为目标刺激
图1跨通道情感启动范式。启动刺激为带有歌词或无歌词音乐片段, 情绪面孔为目标刺激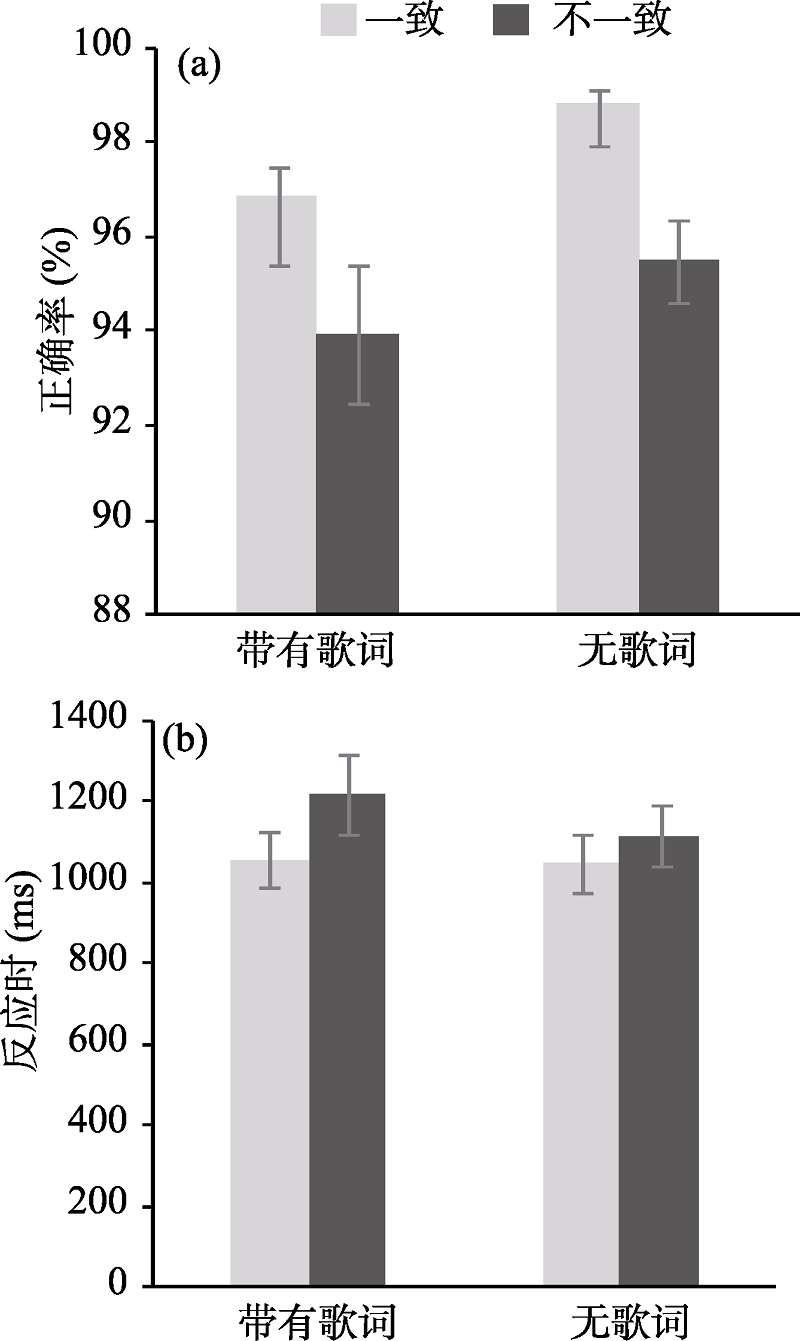
图2每种实验条件下的平均正确率(a)和反应时(b), 误差线为标准误
 图2每种实验条件下的平均正确率(a)和反应时(b), 误差线为标准误
图2每种实验条件下的平均正确率(a)和反应时(b), 误差线为标准误
图3无歌词(a)与带有歌词(b)启动条件下的ERP波形图。浅灰与中灰阴影部分分别表示N400与LPC的时间窗口
 图3无歌词(a)与带有歌词(b)启动条件下的ERP波形图。浅灰与中灰阴影部分分别表示N400与LPC的时间窗口
图3无歌词(a)与带有歌词(b)启动条件下的ERP波形图。浅灰与中灰阴影部分分别表示N400与LPC的时间窗口
图4带有歌词与无歌词在250~450 ms (a)及500~700 ms (b)时间窗内的差异波地形图注:彩图见电子版
 图4带有歌词与无歌词在250~450 ms (a)及500~700 ms (b)时间窗内的差异波地形图注:彩图见电子版
图4带有歌词与无歌词在250~450 ms (a)及500~700 ms (b)时间窗内的差异波地形图注:彩图见电子版参考文献 49
| 1 | Ali S.O., &Peynircio?lu , Z. F . ( 2006). Songs and emotions: Are lyrics and melodies equal partners? Psychology of Music, 34( 4), 511-534. doi: 10.1177/0305735606067168URL |
| 2 | Behrens G.A., &Green , S. B . ( 1993). The ability to identify emotional content of solo improvisations performed vocally and on three different instruments. Psychology of Music, 21( 1), 20-33. doi: 10.1177/030573569302100102URL |
| 3 | Brattico E., Alluri V., Bogert B., Jacobsen T., Vartiainen N., Nieminen S., & Tervaniemi M . ( 2011). A functional MRI study of happy and sad emotions in music with and without lyrics. Frontiers in Psychology, 2, 308. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00308URLpmid: 3227856 |
| 4 | Brown C., &Hagoort P. , ( 1993). The processing nature of the N400: Evidence from masked priming. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 5( 1), 34-44. doi: 10.1162/jocn.1993.5.1.34URLpmid: 23972118 |
| 5 | Daltrozzo J. &Sch?n D. , ( 2009). Conceptual processing in music as revealed by N400 effects on words and musical targets. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21( 10), 1882-1892. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2009.21113URLpmid: 18823240 |
| 6 | Darwin C. ( 1871). The descent of man and selection in relation to sex. London, UK: John Murray. |
| 7 | Erickson D.A . ( 2005). Language, ineffability and paradox in music philosophy (Unpublished doctorial dissertation).Simon Fraser University. |
| 8 | Franco F., Chew M., & Swaine J. S . ( 2017). Preschoolers’ attribution of affect to music: A comparison between vocal and instrumental performance. Psychology of Music, 45( 1), 131-149. |
| 9 | Galizio M., &Hendrick , C. ( 1972). Effect of musical accompaniment on attitude: The guitar as a prop for persuasion. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 2( 4), 350-359. doi: 10.1111/j.1559-1816.1972.tb01286.xURL |
| 10 | Goerlich K. S., Witteman J., Aleman A., & Martens S . ( 2011). Hearing feelings: Affective categorization of music and speech in alexithymia, an ERP study. Plos One, 6( 5), e19501. |
| 11 | Goerlich K. S., Witteman J., Schiller N. O., Van -Heuven V. J., Aleman A., & Martens S . ( 2012). The nature of affective priming in music and speech. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 24( 8), 1725-1741. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00213URLpmid: 22360592 |
| 12 | Gong X., Huang Y-X., Wang Y., & Luo Y-J . ( 2011). Revision of the Chinese facial affective picture system. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 25( 1), 40-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6729.2011.01.011URL |
| 13 | [ 龚栩, 黄宇霞, 王妍, 罗跃嘉 . ( 2011). 中国面孔表情图片系统的修订. 中国心理卫生杂志, 25( 1), 40-46.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6729.2011.01.011URL |
| 14 | Hailstone J. C., Omar R., Henley S. M. D., Frost C., Kenward M. G., & Warren J. D . ( 2009). It's not what you play, it's how you play it: Timbre affects perception of emotion in music. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 62( 11), 2141-2155. doi: 10.1080/17470210902765957URLpmid: 2683716 |
| 15 | Herring D. R., Taylor J. H., White K. R., & Crites S. L . ( 2011). Electrophysiological responses to evaluative priming: The LPP is sensitive to incongruity. Emotion, 11( 4), 794-806. doi: 10.1037/a0022804URLpmid: 21517156 |
| 16 | Hu X., Downie J. S., & Ehmann A. F . ( 2009, October). Lyric text mining in music mood classification. Paper presented at the International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference, Kobe, Japan. |
| 17 | Ibá?ez A., Manes F., Escobar J., Trujillo N., Andreucci P., & Hurtado E . ( 2010). Gesture influences the processing of figurative language in non-native speakers: ERP evidence. Neuroscience Letters, 471( 1), 48-52. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.01.009URLpmid: 20079804 |
| 18 | Imbir K. K., Spustek T., & ?ygierewicz J . ( 2016). Effects of valence and origin of emotions in word processing evidenced by event related potential correlates in a lexical decision task. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 271. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00271URLpmid: 26973569 |
| 19 | Jackendoff R.. , ( 2009). Parallels and nonparallels between language and music. Music Perception, 26( 3), 195-204. doi: 10.1525/mp.2009.26.3.195URL |
| 20 | Jankélévitch V. , & Abbate, C. ( 2003) . Music and the ineffable. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. |
| 21 | Jarymowicz M.T., &Imbir , K. K . ( 2015). Toward a human emotions taxonomy (based on their automatic vs. reflective origin). Emotion Review, 7( 2), 183-188. doi: 10.1177/1754073914555923URL |
| 22 | Juottonen K., Revonsuo A., & Lang H . ( 1996). Dissimilar age influences on two ERP waveforms (LPC and N400) reflecting semantic context effect. Cognitive Brain Research, 4( 2), 99-107. doi: 10.1016/0926-6410(96)00022-5URLpmid: 8883923 |
| 23 | Kamiyama K. S., Abla D., Iwanaga K., & Okanoya K . ( 2013). Interaction between musical emotion and facial expression as measured by event-related potentials. Neuropsychologia, 51( 3), 500-505. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.11.031URLpmid: 23220447 |
| 24 | Koelsch S., Kasper E., Sammler D., Schulze K., Gunter T., & Friederici A. D . ( 2004). Music, language and meaning: Brain signatures of semantic processing. Nature Neuroscience, 7( 3), 302-307. doi: 10.1038/nn1197URLpmid: 14983184 |
| 25 | Kutas M., &Federmeier , K. D . ( 2000). Electrophysiology reveals semantic memory use in language comprehension. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4( 12), 463-470. doi: 10.1016/S1364-6613(00)01560-6URLpmid: 11115760 |
| 26 | Kutas M., &Federmeier , K. D . ( 2011). Thirty years and counting: Finding meaning in the N400 component of the event related brain potential (ERP). Annual Review of Psychology, 62( 1), 621-647. |
| 27 | Kutas M., &Hillyard , S. A . ( 1980). Reading between the lines: Event-related brain potentials during natural sentence processing. Brain and Language, 11( 2), 354-373. doi: 10.1016/0093-934X(80)90133-9URLpmid: 7470854 |
| 28 | Laurier C., Grivolla J., & Herrera P . ( 2008, May). Multimodal music mood classification using audio and lyrics. Paper presented at the Seventh International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Copenhagen, Denmark. |
| 29 | Levman, B. G . ( 1992). The genesis of music and language. Ethnomusicology, 36( 2), 147-170. doi: 10.2307/851912URL |
| 30 | Mithen, S. J . ( 2006). The singing Neanderthals: The origins of music, language, mind and body. Cambridge Archaeological Journal, 59( 2), 54. |
| 31 | Mori K., &Iwanaga M. , ( 2013). Pleasure generated by sadness: Effect of sad lyrics on the emotions induced by happy music. Psychology of Music, 42( 5), 643-652. |
| 32 | Morton J. BJ..,& Trehub S. E., (2007). Children's judgements of emotion in song. Psychology of Music, 35( 4), 629-639. doi: 10.1177/0305735607076445URL |
| 33 | Perlovsky L. ( 2010). Musical emotions: Functions, origins, evolution. Physics of Life Reviews, 7( 1), 2-27. doi: 10.1016/j.plrev.2009.11.001URLpmid: 20374916 |
| 34 | Rohaut B.., &Naccache L. ,( 2017). Disentangling conscious from unconscious cognitive processing with event-related EEG potentials. Revue Neurologique, 173( 7-8), 521-528. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2017.08.001URLpmid: 28843414 |
| 35 | Serafine M. L., Davidson J., Crowder R. G., & Repp B. H . ( 1986). On the nature of melody-text integration in memory for songs. Journal of Memory and Language, 25( 2), 123-135. doi: 10.1016/0749-596X(86)90025-2URL |
| 36 | Schirmer A., Kotz S. A., & Friederici A. D . ( 2002). Sex differentiates the role of emotional prosody during word processing. Cognitive Brain Research, 14( 2), 228-233. doi: 10.1016/S0926-6410(02)00108-8URLpmid: 12067695 |
| 37 | Sousou S.D . ( 1997). Effects of melody and lyrics on mood and memory. Perceptual & Motor Skills, 85( 1), 31-40. doi: 10.2466/pms.1997.85.1.31URLpmid: 9293553 |
| 38 | Steinbeis N.., &Koelsch , S. ( 2011). Affective priming effects of musical sounds on the processing of word meaning. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 23( 3), 604-621. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2009.21383URLpmid: 19925192 |
| 39 | Stratton V.N., &Zalanowski , A. H . ( 1994). Affective impact of music vs. lyrics. Empirical Studies of the Arts, 12( 2), 173-184. doi: 10.2190/35T0-U4DT-N09Q-LQHWURL |
| 40 | Thompson W. F., Marin M. M., & Stewart L . ( 2012). Reduced sensitivity to emotional prosody in congenital amusia rekindles the musical protolanguage hypothesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109( 46), 19027-19032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1210344109URL |
| 41 | Wang Y., &Qin Z. , (2016). Affective priming by simple geometric shapes: Evidence from event-related brain potentials. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 917. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00917URLpmid: 4911398 |
| 42 | Werheid K., Alpay G., Jentzsch I., & Sommer W . ( 2005). Priming emotional facial expressions as evidenced by event-related brain potentials. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 55( 2), 209-219. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2004.07.006URLpmid: 15649552 |
| 43 | Yu R. Y. ( 2000). An introduction to modern western music philosophy. Changsha, China: Hunan Education Press. |
| 44 | [ 于润洋 . ( 2000). 现代西方音乐哲学导论. 长沙: 湖南教育出版社.] |
| 45 | Zhang Q., Kong L., & Jiang Y . ( 2012). The interaction of arousal and valence in affective priming: Behavioral and electrophysiological evidence. Brain Research, 1474, 60-72. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.07.023URLpmid: 3694405 |
| 46 | Zhang Q., Li X. H., Gold B. T., & Jiang Y . ( 2010). Neural correlates of cross-domain affective priming. Brain Research, 1329, 142-151. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.03.021URLpmid: 2857548 |
| 47 | Zhang Q. , & Wang, C. Z.( 1992) . Foundation in musical aesthetics. Beijing, China: People's Education Press. |
| 48 | [ 张前, 王次炤 . ( 1992). 音乐美学基础. 北京: 人民音乐出版社.] |
| 49 | Zhang Q., Lawson A., Guo C. Y., & Jiang Y . ( 2006). Electrophysiological correlates of visual affective priming. Brain Research Bulletin, 71( 1-3), 316-323. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2006.09.023URLpmid: 1783676 |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 骆方, 姜力铭, 田雪涛, 肖梦格, 马彦珍, 张生. 小学生羞怯特质预测及语言风格模型构建[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(2): 155-169. |
| [2] | 吴翰林, 于宙, 王雪娇, 张清芳. 语言能力的老化机制:语言特异性与非特异性因素的共同作用[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(5): 541-561. |
| [3] | 赵鑫,李红利,金戈,李世峰,周爱保,梁文佳,郭红霞,蔡亚亚. 语音记忆和中央执行功能在不同年级儿童解码和语言理解中的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(4): 469-484. |
| [4] | 吴建设,常嘉宝,邱寅晨,Joseph Dien. 汉语复合词视觉识别的时间进程:基于同形语素的行为与ERP证据[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(2): 113-127. |
| [5] | 王汉林,蒋泽亮,冯晓慧,鲁忠义. 道德概念的空间形象性:语言因素和具身因素的共同作用[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(2): 128-138. |
| [6] | 杨群,张启睿,冯意然,张积家. 语言和文化影响颜色认知:直接语言效应抑或间接语言效应?[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(5): 543-556. |
| [7] | 吴柏周,李杰,何虎,侯友,贾缨琪,冯慎行. 色觉疲劳、语义饱和对颜色范畴知觉的即时影响[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(2): 196-206. |
| [8] | 汪新筱, 江珊, 张积家. 空间语言标记影响亲属关系的容器隐喻 *[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(9): 953-964. |
| [9] | 张积家, 陈栩茜, 尤宁, 王斌. 颜色词的语用关系影响颜色认知[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(4): 390-399. |
| [10] | 赵庆柏;柯娓;童彪;周治金; 周宗奎. 网络语言的创造性加工过程:新颖N400与LPC[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(2): 143-154. |
| [11] | 刘世雄, 毕晓培, 贺凯彬. 网络语言文案对广告注意和感知的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(12): 1590-1603. |
| [12] | 刘聪;焦鲁;孙逊;王瑞明. 语言转换对非熟练双语者不同认知控制成分的即时影响[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(5): 472-481. |
| [13] | 李恒;曹宇. 第二语言水平对双语者语言抑制能力的影响 ——来自英语–汉语单通道双语者和英语–美国手语双通道双语者的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(4): 343-351. |
| [14] | 孟迎芳;林无忌;林静远;蔡超群. 双语即时切换下非目标语言语音和语义的激活状态[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(2): 121-129. |
| [15] | 李利;张扬;李璇;郭红婷;伍丽梅;王瑞明. 三语者语义通达中的跨语言重复启动效应[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(11): 1401-1409. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4321
