 ), 张文洁, 李亚蕾, 范伟
), 张文洁, 李亚蕾, 范伟 湖南师范大学教育科学学院, 认知与人类行为湖南省重点实验室, 长沙 410081
收稿日期:2017-08-22出版日期:2018-09-15发布日期:2018-07-27基金资助:国家自然科学基金(31671134, 31500883);国家社会科学基金重大项目(17ZDA326);湖南省自然科学基金(2018JJ3341, 2018JJ2254, 2015JJ2097);湖南省社会科学成果评审委员会重点课题(XSP17ZDI019, XSP18ZDI036);湖南省哲学社会科学基金青年资助项目(16YBQ047);湖南省教科规划青年资助项目(XJK016QXL002);湖南省教育厅科学研究一般项目(17C1013);湖南省博物馆新馆儿童教育合作项目(20131231)Influence of time stress on mood-congruent false memories
ZHONG Yiping( ), ZHANG Wenjie, LI Yalei, FAN Wei
), ZHANG Wenjie, LI Yalei, FAN Wei Cognition and Human Behavior Key Laboratory of Hunan Province, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410081, China
Received:2017-08-22Online:2018-09-15Published:2018-07-27摘要/Abstract
摘要: 考察时间压力下不同类型的情绪刺激和情绪状态对错误记忆的影响, 并进一步探讨时间压力对心境一致性错误记忆的影响。实验1采用经典的DRM范式, 记录被试对情绪关键诱饵的错误再认数。结果发现时间压力增强了被试对负性关键诱饵的错误再认。实验2先在测试阶段启动被试的情绪, 再记录关键诱饵的错误再认数。结果发现, 在时间压力下, 正性情绪组的被试有更多的错误记忆。实验3采用带有情绪效价的DRM词表, 并在测试阶段启动被试的正负情绪, 然后再记录情绪关键诱饵的错误再认数。结果发现, 压力组和控制组被试都表现出了明显的心境一致性错误记忆。研究结果表明, 时间压力对错误记忆具有增强作用, 尤其对负性心境一致性错误记忆具有更为明显的增强作用, 但个体的负性情绪会削弱在时间压力下错误记忆的产生。这些结果进一步发展了激活监控理论和情感信息等价假设理论。
图/表 8
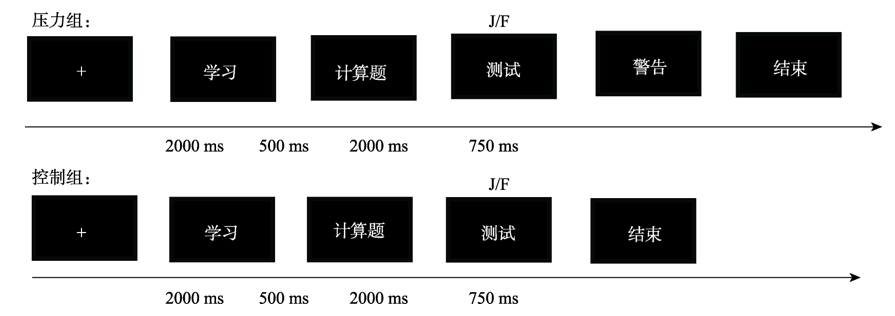
图1压力组和控制组实验流程图
 图1压力组和控制组实验流程图
图1压力组和控制组实验流程图表1两组被试对情绪关键诱饵词的错误再认数(M ± SD)
| 组别 | 正性词 | 中性词 | 负性词 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 压力组 | 4.37 ± 1.51 | 4.58 ± 1.71 | 5.58 ± 1.23 |
| 控制组 | 4.35 ± 1.56 | 4.32 ± 1.21 | 4.60 ± 1.59 |
表1两组被试对情绪关键诱饵词的错误再认数(M ± SD)
| 组别 | 正性词 | 中性词 | 负性词 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 压力组 | 4.37 ± 1.51 | 4.58 ± 1.71 | 5.58 ± 1.23 |
| 控制组 | 4.35 ± 1.56 | 4.32 ± 1.21 | 4.60 ± 1.59 |

图2时间压力和情绪刺激对错误记忆的影响
 图2时间压力和情绪刺激对错误记忆的影响
图2时间压力和情绪刺激对错误记忆的影响表2三种情绪效价在愉悦度和哀伤度量表的得分(M ± SD)
| 维度 | 组别 | N | 前测 | 后测 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 愉悦度 | 正性情绪 | 52 | 23.19 ± 0.29 | 25.85 ± 0.33 |
| 中性组 | 56 | 22.46 ± 0.28 | 23.16 ± 0.32 | |
| 负性情绪 | 53 | 22.90 ± 0.29 | 21.04 ± 0.32 | |
| 哀伤度 | 正性情绪 | 52 | 22.77 ± 0.39 | 20.21 ± 0.36 |
| 中性组 | 56 | 23.29 ± 0.37 | 23.20 ± 0.35 | |
| 负性情绪 | 53 | 23.23 ± 0.39 | 26.04 ± 0.36 |
表2三种情绪效价在愉悦度和哀伤度量表的得分(M ± SD)
| 维度 | 组别 | N | 前测 | 后测 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 愉悦度 | 正性情绪 | 52 | 23.19 ± 0.29 | 25.85 ± 0.33 |
| 中性组 | 56 | 22.46 ± 0.28 | 23.16 ± 0.32 | |
| 负性情绪 | 53 | 22.90 ± 0.29 | 21.04 ± 0.32 | |
| 哀伤度 | 正性情绪 | 52 | 22.77 ± 0.39 | 20.21 ± 0.36 |
| 中性组 | 56 | 23.29 ± 0.37 | 23.20 ± 0.35 | |
| 负性情绪 | 53 | 23.23 ± 0.39 | 26.04 ± 0.36 |
表3六种条件下关键诱饵词的错误再认数(M ± SD)
| 组别 | 正性情绪 | 中性组 | 负性情绪 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 压力组 | 5.96 ± 1.55 | 5.34 ± 1.05 | 4.60 ± 1.31 |
| 控制组 | 5.14 ± 1.54 | 4.56 ± 1.12 | 5.04 ± 1.88 |
表3六种条件下关键诱饵词的错误再认数(M ± SD)
| 组别 | 正性情绪 | 中性组 | 负性情绪 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 压力组 | 5.96 ± 1.55 | 5.34 ± 1.05 | 4.60 ± 1.31 |
| 控制组 | 5.14 ± 1.54 | 4.56 ± 1.12 | 5.04 ± 1.88 |
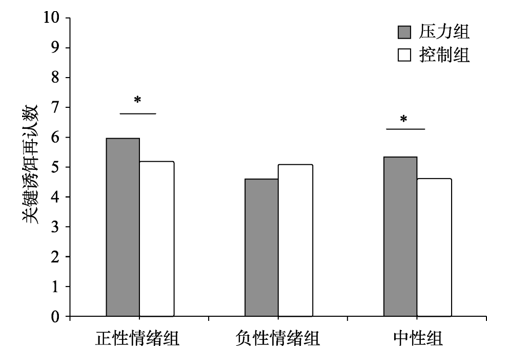
图3时间压力和情绪对关键诱饵错误再认数的影响
 图3时间压力和情绪对关键诱饵错误再认数的影响
图3时间压力和情绪对关键诱饵错误再认数的影响表4两种条件下正负关键诱饵词的错误再认数(M ± SD)
| 组别 | 正性心境 一致 | 负性心境 一致 | 正性心境 不一致 | 负性心境 不一致 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 压力组 | 6.26 ± 1.13 | 6.94 ± 0.96 | 3.90 ± 1.04 | 3.68 ± 0.79 |
| 控制组 | 5.77 ± 1.20 | 5.71 ± 1.32 | 4.03 ± 0.95 | 3.84 ± 0.97 |
表4两种条件下正负关键诱饵词的错误再认数(M ± SD)
| 组别 | 正性心境 一致 | 负性心境 一致 | 正性心境 不一致 | 负性心境 不一致 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 压力组 | 6.26 ± 1.13 | 6.94 ± 0.96 | 3.90 ± 1.04 | 3.68 ± 0.79 |
| 控制组 | 5.77 ± 1.20 | 5.71 ± 1.32 | 4.03 ± 0.95 | 3.84 ± 0.97 |
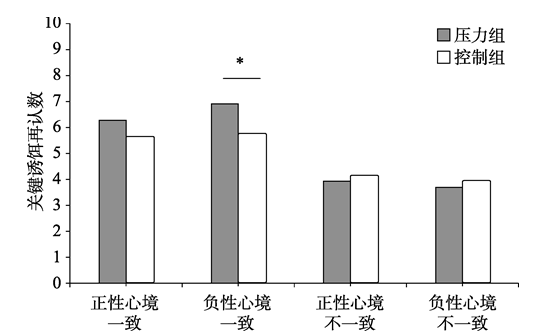
图4压力组和控制组在不同心境类型下的关键诱饵错误再认数
 图4压力组和控制组在不同心境类型下的关键诱饵错误再认数
图4压力组和控制组在不同心境类型下的关键诱饵错误再认数参考文献 46
| 1 | Benjamin, A. S . ( 2001). On the dual effects of repetition on false recognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning Memory and Cognition, 27( 4), 941-947. doi: 10.1037//0278-7393.27.4.941URLpmid: 11486927 |
| 2 | Bland C. E., Howe M. L., & Knott L . ( 2016). Discrete emotion-congruent false memories in the DRM paradigm. Emotion, 16( 5), 611-619. doi: 10.1037/emo0000153URLpmid: 26765099 |
| 3 | Bower, G. H . ( 1981). Mood and memory. American psychologist, 36( 2), 129-148. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.36.2.129URL |
| 4 | Brainerd, C E., Holliday, R E., Reyna, V F., Yang Y., & Toglia, M P . ( 2010). Developmental reversals in false memory: Effects of emotional valence and arousal. Journal of experimental child psychology, 107( 2), 137-154. doi: 10.1016/j.jecp.2010.04.013URLpmid: 2904859 |
| 5 | Brainerd C. J., Stein L. M., Silveira, R A., Rohenkohl G., & Reyna V. F . ( 2008). How does negative emotion cause false memories? Psychological Science, 19( 9), 919-925. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02177.xURLpmid: 18947358 |
| 6 | Carneiro P., Fernandez A., Diez E., Garcia-Marques L., Ramos T., & Ferreira M. B . ( 2012). “Identify-to-reject”: A specific strategy to avoid false memories in the DRM paradigm. Memory & Cognition, 40( 2), 252-265. |
| 7 | Chepenik L. G., Cornew L. A., & Farah M. J . ( 2007). The influence of sad mood on cognition. Emotion, 7( 4), 802-811. doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.7.4.802URLpmid: 18039049 |
| 8 | Corson, Y., & Verrier , N. (2007). Emotions and false memories: valence or arousal? Psychological Science, 18( 3), 208-211. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2007.01874.xURL |
| 9 | Dou, G. ( 2014). The aging effect on false memories in the DRM paradigm (Unpublished Doctoral Dissertations), East China Normal University, Shanghai. |
| 10 | [ 窦刚 . ( 2014). DRM范式下错误记忆的老化效应研究. (博士论文), 华东师范大学, 上海.] |
| 11 | Du,J. Z., & Gao, Y. C . ( 2008). The effects of emotional state on false memory, psychological science, 31( 3), 571-574. |
| 12 | [ 杜建政, 高妍春 . ( 2008). 情绪对错误记忆的影响. 心理科学, 31( 3), 571-574. ] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6981.2008.03.013URL |
| 13 | Frenda S. J., Berkowitz S. R., Loftus E. F., & Fenn K. M . ( 2016). Sleep deprivation and false confessions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113( 8), 2047-2050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1521518113URLpmid: 26858426 |
| 14 | Howe M. L., & Malone c . ( 2011). Mood-congruent true and false memory: Effects of depression. Memory, 19(2), 192-201. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2010.544073URLpmid: 21294037 |
| 15 | Howe, M. L . ( 2007). Children's emotional false memories. Psychological Science, 18( 10), 856-860. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2007.01991.xURLpmid: 17894601 |
| 16 | Huang, Y. X., & Luo, Y. J . ( 2009). Can negative stimuli always have the processing superiority?Acta Psychologica Sinica, 41( 9), 822-831. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2009.00822URL |
| 17 | [ 黄宇霞, 罗跃嘉 . ( 2009). 负性情绪刺激是否总是优先得到加工: ERP研究. 心理学报, 41( 9), 822-831.] |
| 18 | Jiang J., Scolaro A. J., Bailey K., & Chen A . ( 2011). The effect of music-induced mood on attentional networks. International Journal of Psychology, 46( 3), 214-222. doi: 10.1080/00207594.2010.541255URLpmid: 22044234 |
| 19 | Lin Q., Zheng X., &Wang Y. F . ( 2008). Revision of the positive affect and negative affect scale. Chinese Journal of Applied Psychology. 14( 3), 249-254. |
| 20 | [ 邱林, 郑雪, & 王雁飞 . ( 2008). 积极情感消极情感量表(PANAS)的修订. 应用心理学, 14( 3), 249-254.] |
| 21 | Otgaar H., Howe M. L., & Muris P . ( 2017). Maltreatment increases spontaneous false memories but decreases suggestion-induced false memories in children. Developmental Psychology, 35( 3), 376-391. doi: 10.1111/bjdp.2017.35.issue-3URL |
| 22 | Roediger, H. L., & Mcdermott, K. B . ( 1995). Creating false memories: Remembering words not presented in lists. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory and Cognition, 21( 4), 803-814. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.21.4.803URL |
| 23 | Schwarz, N., &Clore, G. L . ( 1983). Mood, misattribution, and judgement of well-being: Informative and directive functions of affective states. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 45( 3), 513-523. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.45.3.513URL |
| 24 | Storbeck, J., & Clore, G. L . ( 2005). With sadness comes accuracy; with happiness, false memory: mood and the false memory effect. Psychological Science, 16( 10), 785-791. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2005.01615.xURLpmid: 16181441 |
| 25 | Stadler M A, Roediger H L, McDermott K B . ( 1999). Norms for word lists that create false memories. Memory & cognition, 27( 3), 494-500. doi: 10.3758/BF03211543URLpmid: 10355238 |
| 26 | Van, D. I . ( 2013). Mood and the DRM paradigm: An investigation of the effects of valence and arousal on false memory. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 66( 6), 1060-1081. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2012.727837URL |
| 27 | Wang, D. W . ( 2007). The experimental research on time pressure affecting decision (Unpublished Doctoral Dissertations), East China Normal University, Shanghai. |
| 28 | [ 王大伟 . ( 2007). 决策制定过程中时间压力效应的实验研究. (博士论文), 华东师范大学, 上海.] |
| 29 | Wang, D. W., & Hu, Y. ( 2008). The experimental research on time pressure affecting decision. Chinese Economy Management Science Magazine, ( 3), 26-29. |
| 30 | [ 王大伟, 胡瑜 . ( 2008). 决策制定过程中时间压力效应的实验研究. 中国经济与管理科学, ( 3), 26-29.] doi: 10.7666/d.y1073781URL |
| 31 | Wang H. B., Zhang D. R., & Yu Y. Q . ( 2009). Time dependence of enhancement effects in emotional memory. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 41( 10), 932-938. |
| 32 | [ 王海宝, 张达人,& 余永强 . ( 2009). 情绪记忆增强效应的时间依赖性. 心理学报, 41( 10), 932-938.] |
| 33 | Wang, Z. H., & Jiang, C. H . ( 2008). Theory Models of Emotional Memory. Journal of Northwest Normal University (Social Sciences), 45( 4), 112-117. |
| 34 | [ 王振宏, 蒋长好 . ( 2008). 情绪记忆的理论模型. 西北师范大学学报(社会科学版), 45( 4), 112-117.] |
| 35 | Zhang, L. ( 2013). The Effects of Emotions on Associatively false memory (Unpublished master’s thesis). Capital Normal University, Beijing. |
| 36 | [ 张兰 . ( 2013). 情绪对关联性错误记忆的影响: 一个ERP研究. (硕士论文), 首都师范大学, 北京.] |
| 37 | Zhang, W. W . ( 2013). The effect of warning cues on mood- congruent false memory in DRM paradigm (Unpublished Master Theses). Southwest University, Chongqing. |
| 38 | [ 张蔚蔚 . ( 2013). DRM范式下预警对心境一致性错误记忆的影响. (硕士论文). 西南大学, 重庆.] |
| 39 | Zhang W. W., Gao F., Jiang J., Zhang J. Y., & Zhang Q. L . ( 2012). The cognitive mechanism of mood-congruent false memory in DRM paradigm. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 44( 12), 1596-1606. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2012.01596URL |
| 40 | [ 张蔚蔚, 高飞, 蒋军, 张继元, 张庆林 . ( 2012). DRM范式下心境一致性错误记忆的认知机制. 心理学报, 44( 12), 1596-1606. ] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2012.01596URL |
| 41 | Zhou, C., & Nie, J. ( 2009). An empirical research on the Dual- processing mechanism of false recognition. Psychological Science, 32(2), 334-337. doi: 10.1360/972009-782URL |
| 42 | [ 周楚, 聂晶 . ( 2009). 错误再认的双加工机制——兼作信号检测论的分析. 心理科学, 32( 2), 334-337.] |
| 43 | Zhou, C., & Yang, Z. L . ( 2008). The effects of warning and presentation duration on false recognition and false recall. Psychological Science, 31( 3), 546-552. doi: 10.1115/DSCC2008-2103URL |
| 44 | [ 周楚, 杨治良 . ( 2008). 预警和呈现时间对错误再认和错误回忆的影响. 心理科学, 31( 3), 546-552.] |
| 45 | Zhou, T. M . ( 2012). Review of emotion theories in the evolutionary psychology. Journal of Shenyang Normal University (Social Scicence Edition), 36( 6), 132-134. |
| 46 | [ 周铁民 . ( 2012). 进化心理学情绪观述评. 沈阳师范大学学报(社会科学版), 36( 6), 132-134.] |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 程瑞, 卢克龙, 郝宁. 愤怒情绪对恶意创造力的影响及调节策略[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(8): 847-860. |
| [2] | 宋琪, 陈扬. 需求和接受的授权型领导匹配对下属工作结果的影响:情绪耗竭的中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(8): 890-903. |
| [3] | 熊承清, 许佳颖, 马丹阳, 刘永芳. 囚徒困境博弈中对手面部表情对合作行为的影响及其作用机制[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(8): 919-932. |
| [4] | 袁加锦, 张祎程, 陈圣栋, 罗利, 茹怡珊. 中国情绪调节词语库的初步编制与试用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 445-455. |
| [5] | 宋锡妍, 程亚华, 谢周秀甜, 龚楠焰, 刘雷. 愤怒情绪对延迟折扣的影响:确定感和控制感的中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 456-468. |
| [6] | 莫李澄, 郭田友, 张岳瑶, 徐锋, 张丹丹. 激活右腹外侧前额叶提高抑郁症患者对社会疼痛的情绪调节能力:一项TMS研究[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 494-504. |
| [7] | 杨伟文, 李超平. 资质过剩感对个体绩效的作用效果及机制:基于情绪-认知加工系统与文化情境的元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 527-554. |
| [8] | 侯娟, 朱英格, 方晓义. 手机成瘾与抑郁:社交焦虑和负性情绪信息注意偏向的多重中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(4): 362-373. |
| [9] | 刘宇平, 李姗珊, 何赟, 王豆豆, 杨波. 消除威胁或无能狂怒?自恋对暴力犯攻击的影响机制[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(3): 244-258. |
| [10] | 雷震, 毕蓉, 莫李澄, 于文汶, 张丹丹. 外显和内隐情绪韵律加工的脑机制:近红外成像研究[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(1): 15-25. |
| [11] | 黄月胜, 张豹, 范兴华, 黄杰. 无关工作记忆表征的负性情绪信息能否捕获视觉注意?一项眼动研究[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(1): 26-37. |
| [12] | 苗晓燕, 孙欣, 匡仪, 汪祚军. 共患难, 更同盟:共同经历相同负性情绪事件促进合作行为[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(1): 81-94. |
| [13] | 华艳, 李明霞, 王巧婷, 冯彩霞, 张晶. 左侧眶额皮层在自动情绪调节下注意选择中的作用:来自经颅直流电刺激的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(9): 1048-1056. |
| [14] | 李树文, 罗瑾琏. 领导-下属情绪评价能力一致与员工建言:内部人身份感知与性别相似性的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(9): 1121-1131. |
| [15] | 张琪, 邓娜丽, 姜秀敏, 李卫君. 自我相关性影响情绪词汇加工的时间进程[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(8): 946-957. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4250
