 )
) 中国科学院心理研究所, 北京 100101;中国科学院大学心理学系, 北京 100049
收稿日期:2018-02-28出版日期:2019-03-15发布日期:2019-01-22通讯作者:李兴珊E-mail:lixs@psych.ac.cn基金资助:国家自然科学基金委与德国科研基金委联合资助项目(NSFC 61621136008/DFC TRR-169);国国家自然科学基金委项目资助(31571125);国家自然科学基金委项目资助(31771212)Cross-modal integration of audiovisual information in language processing
HAN Haibin, XU Pingping, QU Qingqing, CHENG Xi, LI Xingshan( )
) Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China;University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Received:2018-02-28Online:2019-03-15Published:2019-01-22Contact:LI Xingshan E-mail:lixs@psych.ac.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 日常生活中, 语言的使用往往出现在某个视觉情境里。大量认知科学研究表明, 视觉信息与语言信息加工模块并不是独立工作, 而是存在复杂的交互作用。本文以视觉信息对语言加工的影响为主线, 首先对视觉信息影响言语理解, 言语产生以及言语交流的相关研究进展进行了综述。其次, 重点对视觉信息影响语言加工的机制进行了探讨。最后介绍了关于视觉信息影响语言加工的计算模型, 并对未来的研究方向提出了展望。
图/表 6
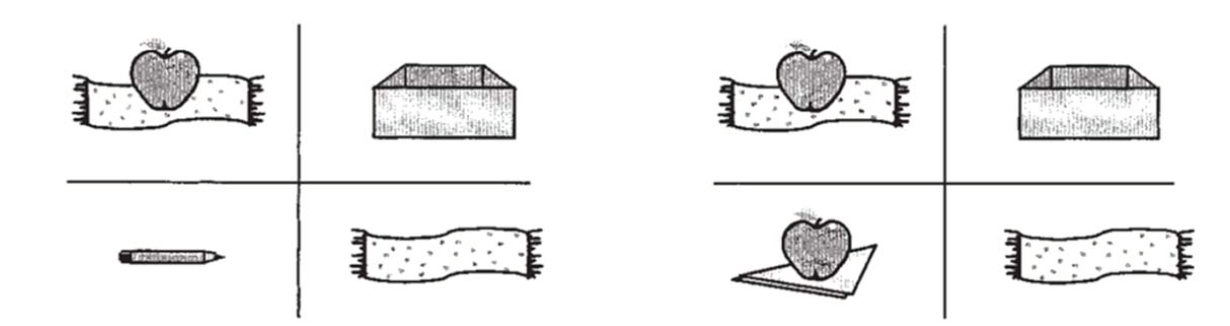
图1Tanenhaus等(1995)使用的视觉刺激。左图为单表征物情境, 右图为双表征物情境, 被试在看图片的同时会听到局部歧义句“Put the apple on the towel in the box”。
 图1Tanenhaus等(1995)使用的视觉刺激。左图为单表征物情境, 右图为双表征物情境, 被试在看图片的同时会听到局部歧义句“Put the apple on the towel in the box”。
图1Tanenhaus等(1995)使用的视觉刺激。左图为单表征物情境, 右图为双表征物情境, 被试在看图片的同时会听到局部歧义句“Put the apple on the towel in the box”。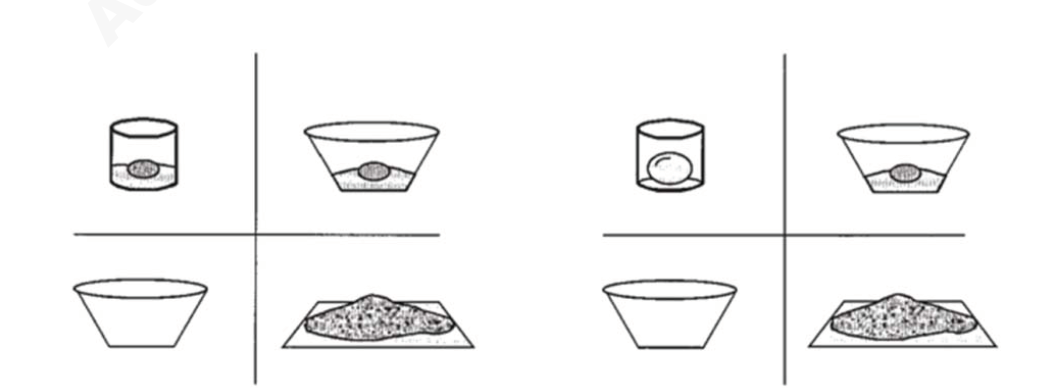
图2Chambers等(2004)使用的视觉刺激示例。左图为包含两个液体鸡蛋的双表征物情境, 右图为只包含一个液体鸡蛋的单表征物情境。
 图2Chambers等(2004)使用的视觉刺激示例。左图为包含两个液体鸡蛋的双表征物情境, 右图为只包含一个液体鸡蛋的单表征物情境。
图2Chambers等(2004)使用的视觉刺激示例。左图为包含两个液体鸡蛋的双表征物情境, 右图为只包含一个液体鸡蛋的单表征物情境。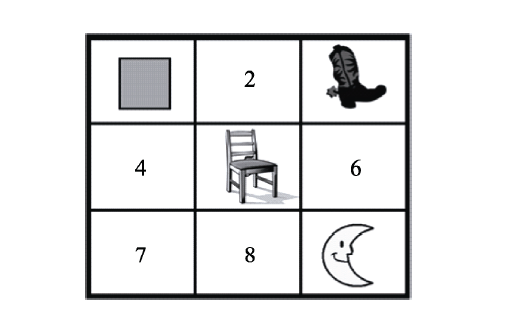
图3Chambers和Juan (2008)的研究使用的视觉刺激示例。从方形到月亮位置标号依次为1~9。
 图3Chambers和Juan (2008)的研究使用的视觉刺激示例。从方形到月亮位置标号依次为1~9。
图3Chambers和Juan (2008)的研究使用的视觉刺激示例。从方形到月亮位置标号依次为1~9。
图4Knoeferle等(2005)使用的视觉刺激示例。共包含三个角色, 其中左侧为海盗, 中间为拿着水桶正在清洗海盗的公主, 右边为拿着画笔正在画公主的击剑者。
 图4Knoeferle等(2005)使用的视觉刺激示例。共包含三个角色, 其中左侧为海盗, 中间为拿着水桶正在清洗海盗的公主, 右边为拿着画笔正在画公主的击剑者。
图4Knoeferle等(2005)使用的视觉刺激示例。共包含三个角色, 其中左侧为海盗, 中间为拿着水桶正在清洗海盗的公主, 右边为拿着画笔正在画公主的击剑者。
图5Altmann和Kamide (2009)使用的视觉刺激示例
 图5Altmann和Kamide (2009)使用的视觉刺激示例
图5Altmann和Kamide (2009)使用的视觉刺激示例
图6模型组成以及模块间的交互作用(McCrae, 2009)。其中句法表征为语言模块, 语义表征为概念结构模块, 视觉背景为视觉感知模块。
 图6模型组成以及模块间的交互作用(McCrae, 2009)。其中句法表征为语言模块, 语义表征为概念结构模块, 视觉背景为视觉感知模块。
图6模型组成以及模块间的交互作用(McCrae, 2009)。其中句法表征为语言模块, 语义表征为概念结构模块, 视觉背景为视觉感知模块。参考文献 89
| [1] | Allopenna P. D., Magnuson J. S., & Tanenhaus M. K . ( 1998). Tracking the time course of spoken word recognition using eye movements: Evidence for continuous mapping models. Journal of Memory and Language, 38( 38), 419-439. |
| [2] | Altmann G. T.M . ( 2004). Language-mediated eye movements in the absence of a visual world: The “blank screen paradigm.” Cognition, 93( 2), 79-87. |
| [3] | Altmann G. T. M., Garnham A., & Dennis Y . ( 1992). Avoiding the garden path: Eye movements in context. Journal of Memory and Language, 31( 5), 685-712. doi: 10.1016/0749-596X(92)90035-VURL |
| [4] | Altmann G. T.M., & Kamide Y. , ( 1999). Incremental interpretation at verbs: Restricting the domain of subsequent reference. Cognition, 73( 3), 247-264. doi: 10.1016/S0010-0277(99)00059-1URLpmid: 10585516 |
| [5] | Altmann G. T.M., & Kamide Y. , ( 2009). Discourse- mediation of the mapping between language and the visual world: Eye movements and mental representation. Cognition, 111( 1), 55-71. |
| [6] | Arias-Trejo N. & Plunkett K., ( 2009). Lexical-semantic priming effects during infancy. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 364( 1536), 3633-3647. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0146URLpmid: 2846315 |
| [7] | Baumg?rtner C., Beuck N., & Menzel W . ( 2012). An architecture for incremental information fusion of cross- modal representations. IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems, 498-503. doi: 10.1109/MFI.2012.6343045URL |
| [8] | Beauchamp M.S . ( 2016). Chapter 42-Audiovisual speech integration: Neural substrates and behavior. Neurobiology of Language, ( 2011), 515-526. |
| [9] | Binder J. R., Frost J. A., Hammeke T. A., Cox R. W., Rao S. M., & Prieto T . ( 1997). Human brain language areas identified by functional magnetic resonance imaging. The Journal of Neuroscience, 17( 1), 353-362. URLpmid: 8987760 |
| [10] | Bobb S. C., Huettig F., & Mani N . ( 2016). Predicting visual information during sentence processing: Toddlers activate an object’s shape before it is mentioned. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 151, 51-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jecp.2015.11.002URLpmid: 26687440 |
| [11] | Brown-Schmidt S., & Tanenhaus M.K . ( 2008). Real-time investigation of referential domains in unscripted conversation: A targeted language game approach. Cognitive Science, 32(4), 643-684. doi: 10.1080/03640210802066816URLpmid: 2771881 |
| [12] | Bunger A., Skordos D., Trueswell J. C., & Papafragou A . ( 2016). How children and adults encode causative events cross-linguistically: Implications for language production and attention. Language, Cognition and Neuroscience, 31(8), 1015-1037. doi: 10.1080/23273798.2016.1175649URL |
| [13] | Carminati M.N., & Knoeferle P. , ( 2013). Effects of speaker emotional facial expression and listener age on incremental sentence processing. PLoS ONE, 8( 9), e72559. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072559URLpmid: 3765193 |
| [14] | Chambers C.G.,& Juan V.S . ( 2008). Perception and presupposition in real-time language comprehension: Insights from anticipatory processing. Cognition, 108( 1), 26-50. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2007.12.009URLpmid: 18262509 |
| [15] | Chambers C. G., Tanenhaus M. K., Eberhard K. M., Carlson G. N., & Filip H . ( 1998). Words and worlds: The construction of context for definite reference. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society, Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum(pp. 220-225). |
| [16] | Chambers C. G., Tanenhaus M. K., & Magnuson J. S . ( 2004). Actions and affordances in syntactic ambiguity resolution. Journal of Experimental Psychology. Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 30( 3), 687-696. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.30.3.687URLpmid: 15099136 |
| [17] | Chen P-H. & Tsai J-L., ( 2015). The influence of syntactic category and semantic constraints on lexical ambiguity resolution: An eye movement study of processing Chinese homographs. Language and Linguistics, 16(4), 555-586. doi: 10.1177/1606822x15583239URL |
| [18] | Clark H.H., & Wilkes-gibbs D. , ( 1986). Referring as a collaborative process. Cognition, 22( 1), 1-39. doi: 10.1016/0010-0277(86)90010-7URLpmid: 3709088 |
| [19] | Coco M.I., & Keller F. , ( 2009). The impact of visual information on reference assignment in sentence production. Conference of the Cognitive Science Society, 274-279. |
| [20] | Coco M.I., & Keller F. , ( 2012). Scan patterns predict sentence production in the cross-modal processing of visual scenes. Cognitive Science, 36( 7), 1204-1223. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-6709.2012.01246.xURLpmid: 22486717 |
| [21] | Cooper R.M . ( 1974). The control of eye fixation by the meaning of spoken language: A new methodology for the real-time investigation of speech perception, memory, and language processing. Cognitive Psychology, 6( 1), 84-107. |
| [22] | De Groot F., Huettig F & Olivers C. N. L. .,( 2016). Revisiting the looking at nothing phenomenon: Visual and semantic biases in memory search. Visual Cognition, 24, 226-245. doi: 10.1080/13506285.2016.1221013URL |
| [23] | Dilkina K., McClelland J. L., & Plaut D. C . ( 2010). Are there mental lexicons? The role of semantics in lexical decision. Brain Research, 1365, 66-81. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.09.057URLpmid: 20869349 |
| [24] | Elman J.L . ( 1990). Finding structure in time. Cognitive Science, 14( 2), 179-211. |
| [25] | Ferreira F., Foucart A., & Engelhardt P. E . ( 2013). Language processing in the visual world: Effects of preview, visual complexity, and prediction. Journal of Memory and Language, 69(3), 165-182. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2013.06.001URL |
| [26] | Findlay J. M. & Gilchrist I. D.. ,( 2003) . Active vision: The psychology of looking and seeing US: Oxford University Press The psychology of looking and seeing. US: Oxford University Press. |
| [27] | Fodor J.A . ( 1983). The modularity of mind. MIT press Cambridge. |
| [28] | Frazier L. & Rayner K., ( 1982). Making and correcting errors during sentence comprehension: Eye movements in the analysis of structurally ambiguous sentences. Cognitive Psychology, 14(2), 178-210. doi: 10.1016/0010-0285(82)90008-1URL |
| [29] | Garoufi K., Staudte M., Koller A., & Crocker M. W . ( 2016). Exploiting listener gaze to improve situated communication in dynamic virtual environments. Cognitive Science, 40(7), 1671-1703. doi: 10.1111/cogs.12298URLpmid: 26471391 |
| [30] | Gleitman L. R., January D., Nappa R., & Trueswell J. C . ( 2007). On the give and take between event apprehension and utterance formulation. Journal of Memory and Language, 57( 4), 544-569. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2007.01.007URLpmid: 2151743 |
| [31] | Griffin Z.M., & Bock K. ,( 2000). What the eyes say about speaking. Psychological Science, 11( 4), 274-279. doi: 10.1111/1467-9280.00255URLpmid: 11273384 |
| [32] | Grill-Spector K. & Malach R., ( 2004). The human visual cortex. Annual. Review. Neuroscience, 27, 649-677. |
| [33] | Hafri A., Trueswell J. C., & Strickland B . ( 2018). Extraction of event roles from visual scenes is rapid, automatic, and interacts with higher-level visual processing. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society(Vol. 73). |
| [34] | Hagoort P. ( 2005). On Broca, brain, and binding: A new framework. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(9), 416-423. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2005.07.004URL |
| [35] | Hale J. ( 2001). A probabilistic Earley parser as a psycholinguistic model. In Proceedings of the second meeting of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics on Language technologies(pp. 1-8). doi: 10.3115/1073336.1073357URL |
| [36] | Heinrich S. & Wermter S., ( 2018). Interactive natural language acquisition in a multi-modal recurrent neural architecture . Connection Science, 30( 1), 99-133. doi: 10.1080/09540091.2017.1318357URL |
| [37] | Hintz F., Meyer A. S., & Huettig F . ( 2017). Predictors of verb-mediated anticipatory eye movements in the visual world. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 43( 9), 1352-1374. doi: 10.1037/xlm0000388. doi: 10.1037/xlm0000388URLpmid: 28287762 |
| [38] | Huang Y.T., & Snedeker J. , ( 2009). Semantic meaning and pragmatic interpretation in 5-year-olds: Evidence from real-time spoken language comprehension. Developmental Psychology, 45( 6), 1723-1739. doi: 10.1037/a0016704URLpmid: 19899927 |
| [39] | Huang Y.T., & Snedeker J. , ( 2011). Logic and conversation revisited: Evidence for a division between semantic and pragmatic content in real-time language comprehension. Language and Cognitive Processes, 26( 8), 1161-1172. doi: 10.1080/01690965.2010.508641URL |
| [40] | Huettig F. ( 2015). Four central questions about prediction in language processing. Brain Research, 1626, 118-135. |
| [41] | Huettig F., Gaskell M. G., & Quinlan P. T . ( 2004). How speech processing affects our attention to visually similar objects: Shape competitor effects and the visual world paradigm. In Proceedings of the 26th annual meeting of the Cognitive Science Society (pp. 607-612). |
| [42] | Huettig F., Olivers C. N. L., & Hartsuiker R. J . ( 2011). Looking, language, and memory: Bridging research from the visual world and visual search paradigms. Acta psychologica, 137( 2), 138-150. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2010.07.013URLpmid: 20817134 |
| [43] | Ito A., Pickering M. J., & Corley M . ( 2018). Investigating the time-course of phonological prediction in native and non-native speakers of English: A visual world eye-tracking study. Journal of Memory and Language, 98, 1-11. |
| [44] | Jackendoff R. ( 1983). Semantics and cognition (Vol.8). MIT press. |
| [45] | Johnson E.K., & Huettig F. , ( 2011). Eye movements during language-mediated visual search reveal a strong link between overt visual attention and lexical processing in 36-month-olds. Psychological Research, 75( 1), 35-42. doi: 10.1007/s00426-010-0285-4URLpmid: 20524009 |
| [46] | Johnson E. K., McQueen J. M., & Huettig F . ( 2011). Toddlers’ language-mediated visual search: They need not have the words for it. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 64( 9), 1672-1682. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2011.594165URLpmid: 21812709 |
| [47] | Knoeferle P., Crocker M. W., Scheepers C., & Pickering M. J . ( 2005). The influence of the immediate visual context on incremental thematic role-assignment: Evidence from eye-movements in depicted events. Cognition, 95( 1), 95-127. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2004.03.002URLpmid: 15629475 |
| [48] | Knoeferle P. & Guerra E., ( 2016). Visually situated language comprehension. Language & Linguistics Compass, 10( 2), 66-82. |
| [49] | Knoeferle P. & Kreysa H., ( 2012). Can speaker gaze modulate syntactic structuring and thematic role assignment during spoken sentence comprehension? Frontiers in Psychology, 3, 538. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00538pmid: 3514542 |
| [50] | Kreysa H., Knoeferle P., & Nunneman E. M . ( 2014). Effects of speaker gaze versus depicted actions on visual attention during sentence comprehension. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society( Vol. 36, No. 36). |
| [51] | Kuchenbuch A., Paraskevopoulos E., Herholz S. C., & Pantev C . ( 2014). Audio-tactile integration and the influence of musical training. PloS One, 9( 1), e85743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085743URLpmid: 3897506 |
| [52] | Lee R., Chambers C. G., Huettig F., & Ganea P. A . ( 2017). Children’s semantic and world knowledge overrides fictional information during anticipatory linguistic processing. In The 39th Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society (CogSci 2017) |
| [53] | Leonard M.K., & Chang E.F . ( 2014). Dynamic speech representations in the human temporal lobe. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 18(9), 472-479. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2014.05.001URLpmid: 24906217 |
| [54] | Linzen T., & Jaeger T.F . ( 2016). Uncertainty and expectation in sentence processing: Evidence from subcategorization distributions. Cognitive Science, 40(6), 1382-1411. doi: 10.1111/cogs.12274URLpmid: 26286681 |
| [55] | MacDonald M.C . ( 1993). The interaction of lexical and syntactic ambiguity. Journal of Memory and Language, 32( 5), 692-715. doi: 10.1006/jmla.1993.1035URL |
| [56] | MacDonald M. C., Pearlmutter N. J., & Seidenberg M. S . ( 1994). Lexical nature of syntactic ambiguity resolution. Psychological Review, 101( 4), 676-703. doi: 10.1037//0033-295X.101.4.676URLpmid: 7984711 |
| [57] | Mani N., Johnson E., McQueen J. M., & Huettig F . ( 2013). How yellow is your banana? Toddlers’ language-mediated visual search in referent-present tasks. Developmental Psychology, 49( 6), 1036-1044. doi: 10.1037/a0029382URLpmid: 22845828 |
| [58] | Mani N. & Schneider S., ( 2013). Speaker identity supports phonetic category learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 39( 3), 623-629. doi: 10.1037/a0030402URLpmid: 23148468 |
| [59] | Marslen-Wilson W.D . ( 1975). Sentence perception as an interactive parallel process. Science, 189( 4198), 226-228. doi: 10.1126/science.189.4198.226URLpmid: 17733889 |
| [60] | McClelland J. L., Mirman D., Bolger D. J., & Khaitan P . ( 2014). Interactive activation and mutual constraint satisfaction in perception and cognition. Cognitive Science, 38( 6), 1139-1189. doi: 10.1111/cogs.12146URLpmid: 25098813 |
| [61] | McCrae P. ( 2009). A model for the cross-modal influence of visual context upon language processing. International Conference Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing (RANLP 09, Borovets, Bulgaria), 230-235. |
| [62] | McGurk H. & MacDonald J., ( 1976). Hearing lips and seeing voices. Nature, 264( 5588), 746-748. doi: 10.1038/264746a0URLpmid: 1012311 |
| [63] | Melissa K., Snedeker J., & Schulz L . ( 2017). Linking language and events: Spatiotemporal cues drive children’s expectations about the meanings of novel transitive verbs. Language Learning and Development, 13( 1), 1-23. doi: 10.1080/15475441.2016.1171771URL |
| [64] | Milburn E., Warren T., & Dickey M. W . ( 2015). World knowledge affects prediction as quickly as selectional restrictions: Evidence from the visual world paradigm. Language, Cognition and Neuroscience, 31( 4), 536-548. doi: 10.1080/23273798.2015.1117117URLpmid: 27148555 |
| [65] | Ng H. G., Anton P., Brügger M., Churamani N., Flie?wasser E., Hummel T., .. Wermter S . ( 2017). Hey Robot, Why don't you talk to me. IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN). IEEE, Lisbon, Portugal. doi: 10.1109/ROMAN.2017.8172383URL |
| [66] | Noh Y. & Lee M., ( 2017). The impact of inhibitory controls on anticipatory sentence processing in L2. Journal of Cognitive Science, 18( 1), 21-41. |
| [67] | Nozari N., Trueswell J. C., & Thompson-Schill S. L . ( 2016). The interplay of local attraction, context and domain-general cognitive control in activation and suppression of semantic distractors during sentence comprehension. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 23( 6), 1942-1953. doi: 10.3758/s13423-016-1068-8URLpmid: 27230894 |
| [68] | Ostarek M. & Hüettig F., ( 2017). Spoken words can make the invisible visible - Testing the involvement of low- level visual representations in spoken word processing. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 43( 3), 499-508. doi: 10.1037/xhp0000313URLpmid: 28080110 |
| [69] | Peeters D., Snijders T. M., Hagoort P., & ?zyürek A . ( 2017). Linking language to the visual world: Neural correlates of comprehending verbal reference to objects through pointing and visual cues. Neuropsychologia, 95, 21-29. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2016.12.004URLpmid: 27939189 |
| [70] | Pickering M. J., Garrod S., & McElree B . ( 2004). Interactions of language and vision restrict "visual world" interpretations. |
| [71] | Pluciennicka E., Coello Y., & Kalénine S . ( 2016). Development of implicit processing of thematic and functional similarity relations during manipulable artifact object identification: Evidence from eye-tracking in the Visual World Paradigm. Cognitive Development, 38, 75-88. |
| [72] | Pozzan L., & Trueswell J.C . ( 2016). Second language processing and revision of garden-path sentences: A visual word study. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 19( 3), 636-643. doi: 10.1017/S1366728915000838URLpmid: 27212888 |
| [73] | Eggermont J. J. (2017). Hearing loss: Causes, prevention, and treatment. Academic Press. |
| [74] | Richardson D.C., & Spivey M.J . ( 2000). Representation, space and Hollywood Squares: Looking at things that aren’t there anymore. Cognition, 76( 3), 269-295. doi: 10.1016/S0010-0277(00)00084-6URLpmid: 10913578 |
| [75] | Rossion B. & Pourtois G., ( 2004). Revisiting Snodgrass and Vanderwart’s object pictorial set: The role of surface detail in basic-level object recognition. Perception, 33( 2), 217-236. doi: 10.1068/p5117URLpmid: 15109163 |
| [76] | Salverda A.P., & Tanenhaus M.K . ( 2010). Tracking the time course of orthographic information in spoken-word recognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology. Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 36( 5), 1108-1117. doi: 10.1037/a0019901URLpmid: 20804288 |
| [77] | Smith A. C., Monaghan P., & Huettig F . ( 2017). The multimodal nature of spoken word processing in the visual world: Testing the predictions of alternative models of multimodal integration. Journal of Memory and Language, 93, 276-303. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2016.08.005URL |
| [78] | Smith A. C., Monaghan P., & Huettig F . ( 2014). Modelling language-Vision interactions in the hub and spoke framework. Computational Models of Cognitive Processes, 3-16. doi: 10.1142/9789814458849_0001URL |
| [79] | Smith A. C., Monaghan P., & Huettig F . ( 2014). A comprehensive model of spoken word recognition must be multimodal: Evidence from studies of language-mediated visual attention. In 36th Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society (CogSci 2014). Cognitive Science Society. |
| [80] | Snedeker J., & Trueswell J.C . ( 2004). The developing constraints on parsing decisions: The role of lexical-biases and referential scenes in child and adult sentence processing. Cognitive Psychology, 49( 3), 238-299. doi: 10.1016/j.cogpsych.2004.03.001URLpmid: 15342261 |
| [81] | Staub A., Abbott M., & Bogartz R. S . ( 2012). Linguistically guided anticipatory eye movements in scene viewing. Visual Cognition, 20( 8), 922-946. doi: 10.1080/13506285.2012.715599URL |
| [82] | Staub A. & Clifton Jr C. , ( 2006). Syntactic prediction in language comprehension: Evidence from either..or. Journal of Experimental Psychology. Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 32( 2), 425-436. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.32.2.425URLpmid: 1479855 |
| [83] | Tanenhaus M.K., & Brown-Schmidt S. , ( 2008). Language processing in the natural world. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 363( 1493), 1105-1122. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2007.2162URLpmid: 2606799 |
| [84] | Tanenhaus M. K., Spivey-Knowlton M. J., Eberhard K. M., & Sedivy J. C . ( 1995). Integration of visual and linguistic information in spoken language comprehension. Science, 268( 5217), 1632-1634. |
| [85] | Vaidyanathan P., Prud’hommeaux E., Alm C. O., Pelz J. B., & Haake A. R . ( 2015). Alignment of eye movements and spoken language for semantic image understanding. Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computational Semantics, 76-81. |
| [86] | van Bergen G., & Flecken M. , ( 2017). Putting things in new places: Linguistic experience modulates the predictive power of placement verb semantics. Journal of Memory and Language, 92, 26-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2016.05.003URL |
| [87] | Venhuizen N. J., Brouwer H., & Crocker M . ( 2016). When the food arrives before the menu: Modeling event-driven surprisal in language comprehension. In Abstract Presented at Events in Language and Cognition, Pre-CUNY Workshop on Event Structure (Gainesville, FL). |
| [88] | Yeung H.H., & Nazzi T. , ( 2014). Object labeling influences infant phonetic learning and generalization. Cognition, 132( 2), 151-163. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2014.04.001URLpmid: 24809743 |
| [89] | Yeung H.H., & Werker J.F . ( 2009). Learning words’ sounds before learning how words sound: 9-month-olds use distinct objects as cues to categorize speech information. Cognition, 113( 2), 234-243. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2009.08.010URLpmid: 19765698 |
相关文章 13
| [1] | 隋雪, 史汉文, 李雨桐. 语言加工过程中的观点采择及其认知机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(6): 990-999. |
| [2] | 方岚, 郑苑仪, 金晗, 李晓庆, 杨玉芳, 王瑞明. 口语句子的韵律边界:窥探言语理解的秘窗[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 425-437. |
| [3] | 南 云. 音乐学习对语言加工的促进作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(11): 1844-1853. |
| [4] | 伍丽梅;伍国华;陈卓铭. 双语者言语产生中语码切换代价 ——从孤立词汇到句子语境[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(1): 37-48. |
| [5] | 郑媛媛;李晓庆. 主语优先现象及其认知机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(12): 1749-1758. |
| [6] | 黎樱;杨东;张庆林. 语言加工性别差异的神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(11): 1625-1634. |
| [7] | 张烨; 张庆林. 识别电位认知功能探析[J]. 心理科学进展, 2010, 18(1): 28-33. |
| [8] | 方杰;李小健. 复合词在言语产生的词汇通达中的表征[J]. 心理科学进展, 2009, 17(6): 1116-1123. |
| [9] | 方杰;李小健. 言语产生的同音词表征:模型争论与再思[J]. 心理科学进展, 2009, 17(5): 909-916. |
| [10] | 李利;莫雷;王瑞明;潘敬儿. 双语言语产生中的词汇提取机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2006, 14(5): 648-653. |
| [11] | 杨锦陈,杨玉芳. 言语产生中的韵律生成[J]. 心理科学进展, 2004, 12(4): 481-488. |
| [12] | 张清芳,杨玉芳. 言语产生中的词汇通达理论[J]. 心理科学进展, 2003, 11(1): 6-11. |
| [13] | 何华;张武田. 右半球语言功能研究概述[J]. 心理科学进展, 2000, 8(2): 61-66. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4620
