 )
) 北京航空航天大学经济管理学院;复杂系统分析与管理决策教育部重点实验室, 北京100191
收稿日期:2018-06-01出版日期:2019-02-15发布日期:2018-12-25通讯作者:姚唐E-mail:yaot@buaa.edu.cn基金资助:* 国家自然科学基金项目(71702007);国家自然科学基金项目(71572006)How meteorological factors affect consumer behavior? The mechanism of meteo-marketing based on contextual marketing theory
LI Chenxi, YAO Tang( )
) School of Economics and Management, Beihang University;Key Laboratory of Complex System Analysis, Management and Decision (Beihang University), Ministry of Education, Beijing 100191, China
Received:2018-06-01Online:2019-02-15Published:2018-12-25Contact:YAO Tang E-mail:yaot@buaa.edu.cn摘要/Abstract
摘要: 从个体情绪波动到社会经济兴衰, 越来越多的研究开始关注气象因素对人类行为的重要影响。本研究提出大数据时代下, 基于情境营销理论的气象营销新概念。通过识别动态气象环境中对消费者心理和行为有影响的气象因素, 提出和验证“气象因素-消费心理-消费行为”这一逻辑链条的影响机制。研究主要围绕情境营销的气象因素影响、气象因素对消费心理和行为的影响机制、气象因素影响消费者行为机制下的营销策略三个主要问题展开讨论。预期研究成果将进一步延伸和丰富现有情境营销理论, 同时对环境消费心理学也是有益的补充。
图/表 5
表1已有情景营销中气象因素对消费行为和心理影响作用的文献总结
| 研究阶段 | 研究领域 | 研究内容 | 代表性研究 | 研究结论 | 现状及不足 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一阶段 | 情境营销 | 情境营销 有效性 | 情境营销可以增加购买行为, 提高顾客忠诚度 | 二手数据进行相关性分析分析, 没有通过实验说明有效性 | ||
| 情境因素影响 | 地理位置 | 情境因素对消费行为有明显影响, 特别是对移动端消费 | 已探讨的影响因素较集中并有限, 忽略自然环境因素(如气象因素)这一重要情境因素的影响 | |||
| 时间因素 | ||||||
| 拥挤程度 | ||||||
| 第二阶段 | 气象因 素影响 | 天气 情况 | 晴天 | 天气对于消费行为, 股票市场, 日常决策都有影响 | 天气是被探讨最多的气象因素, 但没有通过实验检验因果关系, 明确其影响; 仅考虑了实时天气的影响, 并未探讨动态天气差异/变化的影响 | |
| 雨天 | ||||||
| 阴天 | ||||||
| 其他 因素 | 气温 | 气温对消费者行为也有影响 | 针对其他气象因素影响的研究较少 | |||
| 第三阶段 | 气象因素 影响机制 | 情绪 | 晴天/雨天通过情绪机制对消费者行为产生影响 | 现有研究提出了可能的影响机制, 但并未通过实验对其进行验证; 大多数研究从单一维度对天气情况可能的影响机制进行了分析, 但其他气象因素的综合影响机制仍不明确 | ||
| 计划性偏差 | 购买未来使用的产品时, 气象因素通过计划性偏差影响消费者决策 | |||||
| 风险 | 天气情况会影响消费者风险容忍度 | |||||
表1已有情景营销中气象因素对消费行为和心理影响作用的文献总结
| 研究阶段 | 研究领域 | 研究内容 | 代表性研究 | 研究结论 | 现状及不足 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一阶段 | 情境营销 | 情境营销 有效性 | 情境营销可以增加购买行为, 提高顾客忠诚度 | 二手数据进行相关性分析分析, 没有通过实验说明有效性 | ||
| 情境因素影响 | 地理位置 | 情境因素对消费行为有明显影响, 特别是对移动端消费 | 已探讨的影响因素较集中并有限, 忽略自然环境因素(如气象因素)这一重要情境因素的影响 | |||
| 时间因素 | ||||||
| 拥挤程度 | ||||||
| 第二阶段 | 气象因 素影响 | 天气 情况 | 晴天 | 天气对于消费行为, 股票市场, 日常决策都有影响 | 天气是被探讨最多的气象因素, 但没有通过实验检验因果关系, 明确其影响; 仅考虑了实时天气的影响, 并未探讨动态天气差异/变化的影响 | |
| 雨天 | ||||||
| 阴天 | ||||||
| 其他 因素 | 气温 | 气温对消费者行为也有影响 | 针对其他气象因素影响的研究较少 | |||
| 第三阶段 | 气象因素 影响机制 | 情绪 | 晴天/雨天通过情绪机制对消费者行为产生影响 | 现有研究提出了可能的影响机制, 但并未通过实验对其进行验证; 大多数研究从单一维度对天气情况可能的影响机制进行了分析, 但其他气象因素的综合影响机制仍不明确 | ||
| 计划性偏差 | 购买未来使用的产品时, 气象因素通过计划性偏差影响消费者决策 | |||||
| 风险 | 天气情况会影响消费者风险容忍度 | |||||
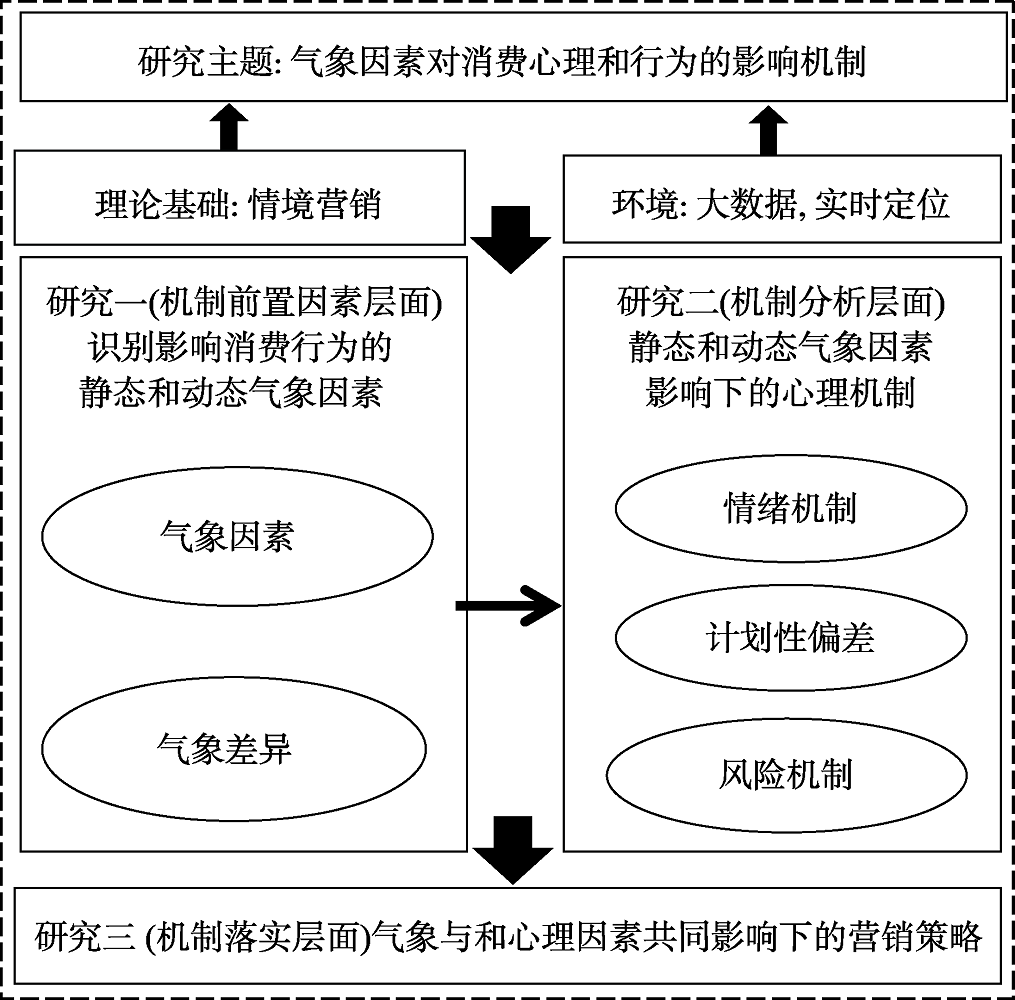
图1本研究整体框架图
 图1本研究整体框架图
图1本研究整体框架图
图2研究一: 静态和动态气象因素对消费行为影响
 图2研究一: 静态和动态气象因素对消费行为影响
图2研究一: 静态和动态气象因素对消费行为影响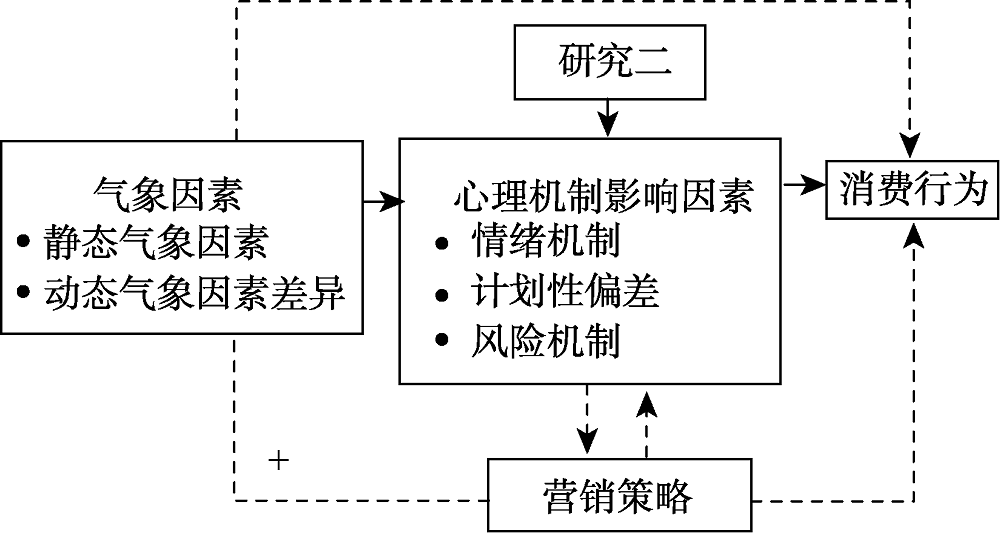
图3研究二: 气象因素对消费行为影响的心理机制
 图3研究二: 气象因素对消费行为影响的心理机制
图3研究二: 气象因素对消费行为影响的心理机制
图4研究三: 气象因素影响消费者心理和行为机制下的营销策略
 图4研究三: 气象因素影响消费者心理和行为机制下的营销策略
图4研究三: 气象因素影响消费者心理和行为机制下的营销策略参考文献 37
| 1 | 林玉莲, 胡正凡 . ( 2000). 环境心理学, 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社. |
| 2 | 吕晓峰 . ( 2013). 环境心理学的理论审视. 长春: 吉林大学. |
| 3 | 王琰, 陈浩 . ( 2017). 人以天地之气生:气象对人类心理与行为的影响.心理科学进展, 25( 6), 1077-1092. |
| 4 | 俞国良, 王青兰, 杨志良 . ( 2000). 环境心理学. 北京: 人民教育出版社. |
| 5 | 张学珉 . ( 1994). 环境心理学与当代环境保护.环境保护, ( 10), 39-40. |
| 6 | Andrews M., Luo X., Fang Z., & Ghose A . ( 2015). Mobile ad effectiveness: Hyper-contextual targeting with crowdedness.Marketing Science, 35( 2), 218-233. |
| 7 | Bargh J.A., & Chartrand, T.L . ( 1999). The unbearable automaticity of being.American Psychologist, 54( 7), 462-479. |
| 8 | Bassi A., Colacito R., & Fulghieri P . ( 2013). ’O sole mio: An experimental analysis of weather and risk attitudes in financial decisions.The Review of Financial Studies, 26( 7), 1824-1852. |
| 9 | Buchheim L. & Kolaska, T. ( 2016). Weather and the psychology of purchasing outdoor movie tickets.Management Science, 63( 11), 3531-3997. |
| 10 | Busse M. R., Pope D. G., Pope J. C., & Silva-Risso J . ( 2015). The psychological effect of weather on car purchases.The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 130( 1), 371-414. |
| 11 | Conlin M., O'Donoghue T., & Vogelsang T. J . ( 2007). Projection bias in catalog orders.American Economic Review, 97( 4), 1217-1249. |
| 12 | Cunningham, M. R . ( 1979). Weather, mood, and helping behavior: Quasi experiments with the sunshine Samaritan.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 37( 11), 1947-1956. |
| 13 | Denissen, J. J. A, Butalid L, Penke L, & Van Aken, M. A. G . ( 2008). The effects of weather on daily mood: A multilevel approach.Emotion, 8( 5), 662-667. |
| 14 | Feng C., Li J., Sun W. J., Zhang Y., & Wang Q. Y . ( 2016). Impact of ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) exposure on the risk of influenza-like-illness: A time-series analysis in Beijing, China.Environmental Health, 15( 1), 17-29. doi: 10.1186/s12940-016-0115-2URL |
| 15 | Ghose A., Goldfarb A., & Han S. P . ( 2012). How is the mobile internet different? Search costs and local activities.Information Systems Research, 24( 3), 613-631. |
| 16 | Guven C. & Hoxha, I. ( 2015). Rain or shine: Happiness and risk-taking.The Quarterly Review of Economics and Finance, 57, 1-10. |
| 17 | Hsiang S. M., Burke M., & Miguel E . ( 2013). Quantifying the influence of climate on human conflict.Science, 341( 6151), 1-21. |
| 18 | Kenny D. & Marshall, J.F . ( 2000). Contextual marketing.Harvard Business Review, 78( 6), 119-125. |
| 19 | Lambert G. W., Reid C., Kaye D., Jennings G. L., & Esler M. D . ( 2002). Effect of sunlight and season on serotonin turnover in the brain.The Lancet, 360( 9348), 1840-1842. |
| 20 | Li C. X., Luo X. M., Zhang C., & Wang X. Y . ( 2017). Sunny, rainy, and cloudy with a chance of mobile promotion effectiveness.Marketing Science, 36( 5), 762-779. |
| 21 | Lohse G. L., Bellman S., & Johnson E. J . ( 2000). Consumer buying behavior on the Internet: Findings from panel data.Journal of Interactive Marketing, 14( 1), 15-29. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6653(200024)14:1<15::AID-DIR2>3.0.CO;2-CURL |
| 22 | Loughran T. & Schultz, P. ( 2004). Weather, stock returns, and the impact of localized trading behavior.Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 39( 2), 343-364. |
| 23 | Luo X. & Seyedian, M. ( 2003). Contextual marketing and customer-orientation strategy for e-commerce: An empirical analysis.International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 8( 2), 95-118. |
| 24 | Marshall, J. ( 2014). How Verizon plans to fix mobile advertising. The Wall Street Journal, ( May 23). |
| 25 | Nguyen Y. & Noussair, C.N . ( 2014). Risk aversion and emotions.Pacific Economic Review, 19( 3), 296-312. |
| 26 | Page, L. A., & Howard, L.M . ( 2010). The impact of climate change on mental health (but will mental health be discussed at Copenhagen)?.Psychological Medicine, 40(2), 177-180. |
| 27 | Persson M., Sundell A., & Öhrvall R . ( 2014). Does election day weather affect voter turnout? Evidence from Swedish elections.Electoral Studies, 33, 335-342. |
| 28 | Reser, J. P., & Swim, J.K . ( 2011). Adapting to and coping with the threat and impacts of climate change.American Psychologist, 66( 4), 277-289. |
| 29 | Rind, B. ( 1996). Effect of beliefs about weather conditions on tipping.Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 26( 2), 137-147. |
| 30 | Schwarz N. & Clore, G.L . ( 1983). Mood, misattribution, and judgments of well-being: Informative and directive functions of affective states.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 45( 3), 513-523. |
| 31 | Simonsohn, U. ( 2010). Weather to go to college.The Economic Journal, 120( 543), 270-280. |
| 32 | Steele, A. T . ( 1951). Weather's effect on the sales of a department store.Journal of Marketing, 15( 4), 436-443. |
| 33 | Stokols D., Misra S., Runnerstrom M. G., & Hipp J. A . ( 2009). Psychology in an age of ecological crisis: From personal angst to collective action.American Psychologist, 64( 3), 181-193. |
| 34 | Suddath C . ( 2014). The weather channel’s secret: Less weather, more clickbait.Business Week.(October 9). |
| 35 | Winter, D. D. N . ( 2000). Some big ideas for some big problems.American Psychologist, 55( 5), 516-522. |
| 36 | Zivin J. S. G., Hsiang S. M., & Neidell M. J . ( 2015). Temperature and human capital in the short- and long-run. National Bureau of Economic Research. |
| 37 | Zubcsek P. P., Katona Z., & Sarvary M . ( 2015). Social and location effects in mobile advertising.Advances in Consumer Research, 43, 117-212. |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 陈坤瑜, 王琦, 王霞, 邢采. 体验型消费和实物型消费的差异:研究方法及效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(6): 1111-1121. |
| [2] | 张燚, 龚政, 丁润, 范秀成. 消费者厌腻感的生成机理、诱发因素及缓解策略[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(5): 936-950. |
| [3] | 谢志鹏, 肖婷婷, 秦环宇. 文字的“偷心术”:营销中的字体效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(2): 365-380. |
| [4] | 晋向东, 范秀成, 朱华伟, 袁靖波. 传统媒体上强势品牌广告竞争溢出效应的作用机制及分布规律[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(12): 1989-1999. |
| [5] | 谢志鹏, 赵晶, 汪涛. 消费者一定偏爱“笑脸”吗?产品外观中的表情元素对消费者的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(8): 1256-1272. |
| [6] | 魏华, 汪涛, 毛磊, 冯文婷, 熊莎莎. 叠音品牌名称对消费者知觉和态度的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7): 1071-1082. |
| [7] | 柳武妹, 马增光, 叶富荣. 营销领域中包装元素对消费者的影响及其内在作用机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(6): 1015-1028. |
| [8] | 武丽慧. 自我建构对口碑两极分化产品偏好的影响及作用机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(4): 535-548. |
| [9] | 余樱, 景奉杰, 杨艳. 怎样花钱更幸福?购买类型对幸福感的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(12): 2133-2140. |
| [10] | 杜伟强. 厌恶情绪与消费者行为[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(11): 1929-1938. |
| [11] | 王财玉, 郑晓旭, 余秋婷, 雷雳. 绿色消费的困境:身份建构抑或环境关心?[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(8): 1507-1520. |
| [12] | 戚海峰, 于辉, 向伟林, 孙韵益, 徐昌皓. 绿色消费情境下消费者为什么会言行不一?[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(7): 1307-1319. |
| [13] | 衡书鹏, 赵换方, 孙丽君, 周宗奎. 虚拟销售代理的拟人效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(5): 884-904. |
| [14] | 骆紫薇, 吕林祥. 善因营销对消费者态度的影响及其理论解释[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(4): 737-747. |
| [15] | 王艳芝, 姚唐, 卢宏亮. 结伴购物情境下消费者冲动购买行为发生机理[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(11): 1915-1927. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4585
