 ), 张静3(
), 张静3( ), 平贤洁2
), 平贤洁2 1 绍兴文理学院社会行为与发展科学研究中心
2 绍兴文理学院心理学系, 绍兴 312000
3 杭州电子科技大学心理健康研究所, 杭州 310018
收稿日期:2018-05-11出版日期:2019-01-15发布日期:2018-11-23基金资助:* 国家社科基金青年项目(16CZX015);教育部人文社会科学研究青年基金(17YJCZH243);浙江省大学生科技创新活动计划暨新苗人才计划项目(2017R4280 18)The rubber hand illusion (RHI): The experimental paradigm of sense of ownership and its application
ZHAO Peiqiong1, CHEN Wei1,2( ), ZHANG Jing3(
), ZHANG Jing3( ), PING Xianjie2
), PING Xianjie2 1 Center for Social Behavior and Developmental Science, Shaoxing University, Shaoxing 312000, China
2 Department of Psychology, Shaoxing University, Shaoxing 312000, China
3 Institute of Psychological Health, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018, China
Received:2018-05-11Online:2019-01-15Published:2018-11-23摘要/Abstract
摘要: 橡胶手错觉是一种健康个体将非肉体的假手视为自己真实身体的一部分的体验, 这种错觉可以通过同时轻刷被试面前可见的橡胶手及其不可见的真手而产生.橡胶手错觉已成为一种研究身体拥有感的重要范式, 其产生机制可以分为“自下而上的认知匹配”与“自上而下的认知匹配”两种加工方式.前者涉及视觉与触觉刺激的同步性; 而后者涉及被试心中预存的身体意象与身体图式(包括真假手之间模态特征,位置空间的相似性).综合上述证据, 身体模型假说与个人边缘空间理论进一步为拥有感产生的复杂机制提供了整合两种加工方式的解释.橡胶手错觉范式已经被用于探索精神分裂症患者等特殊被试病理分析,错觉产生和心理特质之间的关系, 以及神经外科和术后恢复上.未来的研究应该更加重视范式本身的拓展, 应用虚拟现实技术来提高身体模态的仿真效果, 利用橡胶手拥有感的易感性作为筛选与预测身体意象障碍疾病的指标.
图/表 4

图1拥有感的研究现状
 图1拥有感的研究现状
图1拥有感的研究现状
图2经典橡胶手错觉实验示意图
 图2经典橡胶手错觉实验示意图
图2经典橡胶手错觉实验示意图
图3虚拟手错觉实验设备与示范
 图3虚拟手错觉实验设备与示范
图3虚拟手错觉实验设备与示范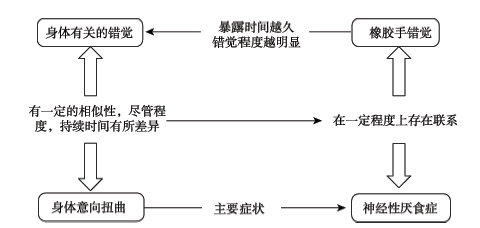
图4橡胶手错觉范式对神经性厌食症的预测
 图4橡胶手错觉范式对神经性厌食症的预测
图4橡胶手错觉范式对神经性厌食症的预测参考文献 95
| 1 | 陈巍, 郭本禹 . (2012). 具身-生成的意识经验: 神经现象学的透视. 华东师范大学学报(教育科学版),30(3), 60-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5560.2012.03.010URL |
| 2 | 张静, 陈巍 . (2016). 身体意象可塑吗?——同步性和距离参照系对身体拥有感的影响. 心理学报,48(8), 933-945. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.00933URL |
| 3 | 周爱保, 朱婧, 夏瑞雪, 李世峰, 徐科明, 张荣华, 蔡美君 . (2013). 我观故我在?——从橡胶手错觉对自我身体所有权的探讨. 心理科学,36(6), 1328-1332. |
| 4 | Abdulkarim Z., &Ehrsson H.H . (2018). Recalibration of hand position sense during unconscious active and passive movement. Experimental Brain Research, 236(2), 551-561. doi: 10.1007/s00221-017-5137-7URL |
| 5 | Aristotle. (1984). On dreams. In Barnes, J. Princeton (Ed.) The complete works of Aristotle. The revised Oxford translation. Volume 1. NJ: Princeton University Press. |
| 6 | Arizono N., Ohmura Y., Yano S ., & Kondo, T. (2016). Functional connectivity analysis of NIRS data under rubber hand illusion to find a biomarker of sense of ownership. Neural Plasticity, 2016,6726238. |
| 7 | Armel K.C., &Ramachandran V.S . (2003). Projecting sensations to external objects: Evidence from skin conductance response. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 270(1523), 1499-1506. |
| 8 | Asai T., Mao Z., Sugimori E., Tanno Y . (2011). Rubber hand illusion, empathy, and schizotypal experiences in terms of self-other representations. Consciousness and Cognition, 20(4), 1744-1750. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2011.02.005URLpmid: 21371911 |
| 9 | Balconi M., & Bortolotti A. (2010). Body and self-awareness: Functional and dysfunctional mechanisms. In M. Balconi (Ed.),Neuropsychology of the Sense of Agency(pp. 173-189). Milano: Springer. doi: 10.1007/978-88-470-1587-6_10URL |
| 10 | Bekrater-Bodmann R., Foell J., Diers M., & Flor H . (2012). The perceptual and neuronal stability of the rubber hand illusion across contexts and over time. Brain Research, 1452, 130-139. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.03.001URLpmid: 22459041 |
| 11 | Botvinick M. . (2004). Probing the neural basis of body ownership. Science, 305 (5685), 782-783. |
| 12 | Botvinick M., & Cohen J. (1998). Rubber hands ‘feel’touch that eyes see. Nature, 391(6669), 756. |
| 13 | Braun N., Debener S., Spychala N., Bongartz E., S?r?s P., Müller H. H. O., & Philipsen A . (2018). The senses of agency and ownership: A review. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 535. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00535URL |
| 14 | Burin D., Garbarini F., Bruno V., Fossataro C., Destefanis C., Berti A., & Pia L . (2017). Movements and body ownership: Evidence from the rubber hand illusion after mechanical limb immobilization. Neuropsychologia, 107, 41-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.11.004URLpmid: 29109038 |
| 15 | Burin D., Livelli A., Garbarini F., Fossataro C., Folegatti A., Gindri P., & Pia L . (2015). Are movements necessary for the sense of body ownership? Evidence from the rubber hand illusion in pure hemiplegic patients. PLoS One, 10(3), e0117155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117155URLpmid: 4361688 |
| 16 | Campos J. L., Richandi G. E. K., Taati B., & Keshavarz B . (2018). The rubber hand illusion in healthy younger and older adults. Multisensory Research, 31(6), 537-555. |
| 17 | Carruthers G. . (2013). Toward a cognitive model of the sense of embodiment in a (rubber) hand. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 20(3-4), 33-60. doi: 10.1179/0308018813Z.00000000036URL |
| 18 | Carruthers G. . (2015). Who am I in out of body experiences? Implications from OBEs for the explanandum of a theory of self-consciousness. Phenomenology and the Cognitive Sciences, 14(1), 183-197. doi: 10.1007/s11097-013-9332-0URL |
| 19 | Cascio C. J., Foss-Feig J. H., Burnette C. P., Heacock J. L., & Cosby A. A . (2012). The rubber hand illusion in children with autism spectrum disorders: Delayed influence of combined tactile and visual input on proprioception. Autism, 16(4), 406-419. doi: 10.1177/1362361311430404URLpmid: 22399451 |
| 20 | Chen W. Y., Huang H. C., Lee Y. T., & Liang C . (2018). Body ownership and the four-hand illusion. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 2153. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19662-xURLpmid: 29391505 |
| 21 | Chen W., Zhang J., Qian Y. Y., & Gao Q. Y . (2017). How disentangled sense of agency and sense of ownership can interact with different emotional events on stress feelings. Psicologia: Reflex?o e Crítica, 30, 17. doi: 10.1186/s41155-017-0071-yURL |
| 22 | Christ O., & Reiner M. (2014). Perspectives and possible applications of the rubber hand and virtual hand illusion in non-invasive rehabilitation: Technological improvements and their consequences. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 44(7), 33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.02.013URLpmid: 24661983 |
| 23 | Costantini M., Robinson J., Migliorati D., Donno B., Ferri F., & Northoff G . (2016). Temporal limits on rubber hand illusion reflect individuals’ temporal resolution in multisensory perception. Cognition, 157, 39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2016.08.010URLpmid: 27592410 |
| 24 | Davies A. M.A., &White R.C . (2013). A sensational illusion: Vision-touch synaesthesia and the rubber hand paradigm. Cortex, 49(3), 806-818. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2012.01.007URLpmid: 22445446 |
| 25 | Davies A. M. A., White R. C., & Davies M . (2013). Spatial limits on the nonvisual self-touch illusion and the visual rubber hand illusion: Subjective experience of the illusion and proprioceptive drift. Consciousness and Cognition, 22(2), 613-636. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2013.03.006URLpmid: 23644413 |
| 26 | de Vignemont F. (2011). Embodiment, ownership and disownership. Consciousness and Cognition, 20(1), 82-93. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2010.09.004 |
| 27 | Della Gatta F., Garbarini F., Puglisi G., Leonetti A., Berti A., & Borroni P . (2016). Decreased motor cortex excitability mirrors own hand disembodiment during the rubber hand illusion. Elife, 5, e14972. doi: 10.7554/eLife.14972URLpmid: 27760692 |
| 28 | Edin B. B., Ascari L., Beccai L., Roccella S., Cabibihan J. -J., & Carrozza M . (2008). Bio-inspired sensorization of a biomechatronic robot hand for the grasp-and-lift task. Brain Research Bulletin, 75(6), 785-795. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2008.01.017URLpmid: 18394525 |
| 29 | Ehrsson H. H., Rosén B., Stockselius A., Ragn? C., K?hler P., & Lundborg G . (2008). Upper limb amputees can be induced to experience a rubber hand as their own. Brain, 131(12), 3443-3452. doi: 10.1093/brain/awn297URLpmid: 2639202 |
| 30 | Ehrsson H. H., Spence C., & Passingham R. E . (2004). That's my hand! Activity in premotor cortex reflects feeling of ownership of a limb. Science, 305(5685), 875-877. |
| 31 | Erro R., Marotta A., Tinazzi M., Frera E., & Fiorio M . (2018). Judging the position of the artificial hand induces a "visual" drift towards the real one during the rubber hand illusion. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 2531. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20551-6URL |
| 32 | Falconer C. J., Rovira A., King J. A., Gilbert P., Antley A., Fearon P., .. Brewin C. R . (2016). Embodying self- compassion within virtual reality and its effects on patients with depression. British Journal of Psychiatry Open, 2(1), 74-80. doi: 10.1192/bjpo.bp.115.002147URLpmid: 4995586 |
| 33 | Fl?gel M., Kalveram K. T., Christ O., & Vogt J . (2016). Application of the rubber hand illusion paradigm: Comparison between upper and lower limbs. Psychological Research, 80(2), 298-306. doi: 10.1007/s00426-015-0650-4URLpmid: 25656162 |
| 34 | Folegatti A., Farnè A., Salemme R., & de Vignemont F . (2012). The rubber hand illusion: Two’s a company, but three’s a crowd. Consciousness and Cognition, 21(2), 799-812. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2012.02.008 |
| 35 | Gallagher S. . (2000). Philosophical conceptions of the self: Implications for cognitive science. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4(1), 14-21. |
| 36 | Germine L., Benson T. L., Cohen F ., & Hooker, C. I. L. (2013). Psychosis-proneness and the rubber hand illusion of body ownership. Psychiatry Research, 207(1-2), 45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2012.11.022URLpmid: 23273611 |
| 37 | Glenberg A. M., Witt J. K., & Metcalfe J . (2013). From the revolution to embodiment 25 years of cognitive psychology. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 8(5), 573-585. doi: 10.1177/1745691613498098URLpmid: 26173215 |
| 38 | Grynberg D., & Pollatos O. (2015). Alexithymia modulates the experience of the rubber hand illusion. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 357. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00357URLpmid: 4471366 |
| 39 | Guterstam A., Abdulkarim Z., & Ehrsson H. H . (2015). Illusory ownership of an invisible body reduces autonomic and subjective social anxiety responses. Scientific Reports, 5(1), 9831-9831. doi: 10.1038/srep09831URLpmid: 4407500 |
| 40 | Guterstam A., Petkova V. I., & Ehrsson H. H . (2011). The illusion of owning a third arm. PLoS One, 6(2), e17208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017208URLpmid: 21383847 |
| 41 | Guterstam A., Zeberg H., ?z?iftci V. M., & Ehrsson H. H . (2016). The magnetic touch illusion: A perceptual correlate of visuo-tactile integration in peripersonal space. Cognition 155, 44-56. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2016.06.004URLpmid: 27348406 |
| 42 | Haans A., IJsselsteijn W. A ., & de Kort, Y. A. (2008). The effect of similarities in skin texture and hand shape on perceived ownership of a fake limb. Body Image, 5(4), 389-394. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2008.04.003URLpmid: 18650135 |
| 43 | Haans A., Kaiser F. G., Bouwhuis D. G., & IJsselsteijn W. A . (2012). Individual differences in the rubber-hand illusion: Predicting self-reports of people’s personal experiences. Acta Psychologica, 141(2), 169-177. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2012.07.016URLpmid: 22964058 |
| 44 | Ide M. . (2013). The effect of “anatomical plausibility” of hand angle on the rubber-hand illusion. Perception, 42(1), 103-111. doi: 10.1068/p7322URLpmid: 23678620 |
| 45 | Ide M., & Wada M. (2016). Periodic visuotactile stimulation slowly enhances the rubber hand illusion in individuals with high autistic traits. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 10, 21. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2016.00021URLpmid: 4899459 |
| 46 | Ionta S., Heydrich L., Lenggenhager B., Mouthon M., Fornari E., Chapuis D ., et al. Blanke, O. (2011). Multisensory mechanisms in temporo-parietal cortex support self-location and first-person perspective. Neuron, 70(2), 363-374. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.03.009URLpmid: 21521620 |
| 47 | Jackson S. R., Buxbaum L. J., & Coslett H. B . (2011). Cognitive neuroscience of bodily representations: Psychological processes and neural mechanisms. Cognitive Neuroscience, 2(34), 135-137. doi: 10.1080/17588928.2011.630723URLpmid: 24168527 |
| 48 | Jalal B., Krishnakumar D., & Ramachandran V. S . (2015). “I feel contaminated in my fake hand”: Obsessive- compulsive-disorder like disgust sensations arise from dummy during rubber hand illusion. PLoS One, 10(12), e0139159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139159URLpmid: 4671689 |
| 49 | Jeannerod M. . (2003). The mechanism of self-recognition in humans. Behavioural Brain Research, 142(1-2), 1-15. doi: 10.1016/S0166-4328(02)00384-4URLpmid: 12798261 |
| 50 | Jenkinson P. M., Haggard P., Ferreira N. C., & Fotopoulou A . (2013). Body ownership and attention in the mirror: Insights from somatoparaphrenia and the rubber hand illusion. Neuropsychologia, 51(8), 1453-1462. |
| 51 | Kállai J., Hegedüs G., Feldmann á., Rózsa S., Darnai G., Herold R., .. Szolcsányi T . (2015). Temperament and psychopathological syndromes specific susceptibility for rubber hand illusion. Psychiatry Research, 229(1), 410-419. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2015.05.109URL |
| 52 | Kalckert A., & Ehrsson H. (2017). The onset time of the ownership sensation in the moving rubber hand illusion. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 344. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00344URLpmid: 5345084 |
| 53 | Kalckert A., &Ehrsson H.H . (2014). The moving rubber hand illusion revisited: Comparing movements and visuotactile stimulation to induce illusory ownership. Consciousness and Cognition, 26, 117-132. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2014.02.003URLpmid: 24705182 |
| 54 | Keizer A., Smeets M. A., Postma A., van Elburg A., & Dijkerman H. C . (2014). Does the experience of ownership over a rubber hand change body size perception in anorexia nervosa patients? Neuropsychologia, 62, 26-37. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.07.003URLpmid: 25050852 |
| 55 | Knoblich G., Thornton I., Grosjean M. , & Shiffrar, M.(2006) . Human body perception from the inside out. New York: Oxford University Press. |
| 56 | Lane T., Yeh S.-L., Tseng P., & Chang A.-Y . (2017). Timing disownership experiences in the rubber hand illusion. Cognitive Research, 2(1), 4. doi: 10.1186/s41235-016-0041-4URLpmid: 5281674 |
| 57 | Lee I.-S., & Chae Y. (2016). Neural network underlying recovery from disowned bodily states induced by the rubber hand illusion. Neural Plasticity, 2016, 8307175. doi: 10.1155/2016/8307175URLpmid: 5223049 |
| 58 | Lev-Ari L., Hirschmann S., Dyskin O., Goldman O., & Hirschmann I . (2015). The Rubber Hand Illusion paradigm as a sensory learning process in patients with schizophrenia. European Psychiatry, 30(7), 868-873. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2015.06.008URLpmid: 26443055 |
| 59 | Limanowski J., & Blankenburg F. (2016). That’s not quite me: Limb ownership encoding in the brain. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 11(7), 1130-1140. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsv079URLpmid: 4927034 |
| 60 | Lira M., Egito J. H., Dall’Agnol P. A., Amodio D. M., Gon?alves ó. F., & Boggio P. S . (2017). The influence of skin colour on the experience of ownership in the rubber hand illusion. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 15745. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16137-3URLpmid: 29147006 |
| 61 | Lloyd D.M . (2007). Spatial limits on referred touch to an alien limb may reflect boundaries of visuo-tactile peripersonal space surrounding the hand. Brain and Cognition, 64(1), 104-109. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2006.09.013URLpmid: 17118503 |
| 62 | Ma K., & Hommel B. (2013). The virtual-hand illusion: Effects of impact and threat on perceived ownership and affective resonance. Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 604. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00604URLpmid: 24046762 |
| 63 | Ma K., & Hommel B. (2015). Body-ownership for actively operated non-corporeal objects. Consciousness and Cognition, 36, 75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2015.06.003URLpmid: 26094223 |
| 64 | Makin T. R., Holmes N. P., & Ehrsson H. H . (2008). On the other hand: Dummy hands and peripersonal space. Behavioural Brain Research, 191(1), 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.02.041URLpmid: 18423906 |
| 65 | Makin T. R., Holmes N. P., & Zohary E . (2007). Is that near my hand? Multisensory representation of peripersonal space in human intraparietal sulcus. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(4), 731-740. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3653-06.2007URLpmid: 17251412 |
| 66 | Marotta A., Tinazzi M., Cavedini C., Zampini M., & Fiorio M . (2016). Individual differences in the rubber hand illusion are related to sensory suggestibility. PLoS One, 11(12), e0168489. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168489URL |
| 67 | Mirucka B. . (2016). The sense of body ownership in schizophrenia: Research in the rubber hand illusion paradigm. Psychiatria Polska, 50(4), 731-740. doi: 10.12740/PP/44964URLpmid: 27847924 |
| 68 | Ocklenburg S., Peterburs J., Rüther N., & Güntürkün O . (2012). The rubber hand illusion modulates pseudoneglect. Neuroscience Letters, 523(2), 158-161. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.06.068URLpmid: 22771568 |
| 69 | Olivé I., Tempelmann C., Berthoz A., & Heinze H. J . (2015). Increased functional connectivity between superior colliculus and brain regions implicated in bodily self-consciousness during the rubber hand illusion. Human Brain Mapping, 36(2), 717-730. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22659URLpmid: 25346407 |
| 70 | Paladino M.-P., Mazzurega M., Pavani F., & Schubert T. W . (2010). Synchronous multisensory stimulation blurs self-other boundaries. Psychological Science, 21(9), 1202-1207. doi: 10.1177/0956797610379234URLpmid: 20679523 |
| 71 | Palmer C.E., & Tsakiris M. (2018). Going at the heart of social cognition: Is there a role for interoception in self-other distinction? Current Opinion in Psychology, 24, 21-26. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2018.04.008URLpmid: 29704794 |
| 72 | Ramakonar H., Franz E. A., & Lind C. R . (2011). The rubber hand illusion and its application to clinical neuroscience. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, 18(12), 1596-1601. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2011.05.008URLpmid: 22000838 |
| 73 | Pasqualotto A., &Proulx M.J . (2015). Two-dimensional rubber-hand illusion: The Dorian Gray hand illusion. Multisensory Research, 28(1-2), 101-110. doi: 10.1163/22134808-00002473URLpmid: 26152054 |
| 74 | Paton B., Hohwy J., & Enticott P. G . (2012). The rubber hand illusion reveals proprioceptive and sensorimotor differences in autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(9), 1870-1883. doi: 10.1007/s10803-011-1430-7URLpmid: 22189963 |
| 75 | Peled A., Ritsner M., Hirschmann S., Geva A. B., & Modai I . (2000). Touch feel illusion in schizophrenic patients. Biological Psychiatry, 48(11), 1105-1108. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(00)00947-1URL |
| 76 | Reinersmann A., Landwehrt J., Krumova E. K., Peterburs J., Ocklenburg S., Güntürkün O., & Maier C . (2013). The rubber hand illusion in complex regional pain syndrome: Preserved ability to integrate a rubber hand indicates intact multisensory integration. Pain, 154(9), 1519-1527. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.03.039URLpmid: 23706626 |
| 77 | Petkova V.I., &Ehrsson H.H . (2009). When right feels left: Referral of touch and ownership between the hands. PLoS One, 4(9), e6933. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006933URLpmid: 19742313 |
| 78 | Riemer M., Fuchs X., Bublatzky F., Kleinb?hl D., H?lzl R., & Trojan J . (2014). The rubber hand illusion depends on a congruent mapping between real and artificial fingers. Acta Psychologica, 152, 34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2014.07.012URLpmid: 25103418 |
| 79 | Sanchez-Vives M. V., Spanlang B., Frisoli A., Bergamasco M., & Slater M . (2010). Virtual hand illusion induced by visuomotor correlations. PLoS One, 5(4), e10381. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010381URLpmid: 2861624 |
| 80 | Scandola M., Tidoni E., Avesani R., Brunelli G., Aglioti S. M., & Moro V . (2014). Rubber hand illusion induced by touching the face ipsilaterally to a deprived hand: Evidence for plastic “somatotopic” remapping in tetraplegics. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 404. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00404URLpmid: 4050649 |
| 81 | Schütz-Bosbach S., Tausche P., & Weiss C . (2009). Roughness perception during the rubber hand illusion. Brain and Cognition, 70(1), 136-144. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2009.01.006URLpmid: 19231057 |
| 82 | Siedlecka M., Klimza A., ?ukowska M., & Wierzchoń M . (2014). Rubber hand illusion reduces discomfort caused by cold stimulus. PLoS One, 9(10), e109909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109909URLpmid: 4190400 |
| 83 | Siedlecka M., Spycha?a N., ?ukowska M., Wiercioch K., & Wierzchoń M . (2018). Rubber Hand Illusion Increases Pain Caused by Electric Stimuli. The Journal of Pain, 19(1), 35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2017.08.005URLpmid: 28864079 |
| 84 | Smit M., Kooistra D., van der Ham I., & Dijkerman H . (2017). Laterality and body ownership: Effect of handedness on experience of the rubber hand illusion. Laterality: Asymmetries of Body, Brain and Cognition, 22(6), 703-724. doi: 10.1080/1357650X.2016.1273940URLpmid: 28041532 |
| 85 | S?rensen J.B . (2005). The alien-hand experiment. Phenomenology and the Cognitive Sciences, 4(1), 73-90. doi: 10.1007/s11097-005-5854-4 |
| 86 | Suzuki K., Garfinkel S. N., Critchley H. D., & Seth A. K . (2013). Multisensory integration across exteroceptive and interoceptive domains modulates self-experience in the rubber-hand illusion. Neuropsychologia, 51(13), 2909-2917. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2013.08.014URLpmid: 23993906 |
| 87 | Synofzik M., Vosgerau G., & Newen A . (2008). I move, therefore I am: A new theoretical framework to investigate agency and ownership. Consciousness and Cognition, 17(2), 411-424. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2008.03.008URLpmid: 18411059 |
| 88 | Tsakiris M. . (2010). My body in the brain: A neurocognitive model of body-ownership. Neuropsychologia, 48(3), 703-712. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.09.034URLpmid: 19819247 |
| 89 | Tsakiris M., Carpenter L., James D., & Fotopoulou A . (2010). Hands only illusion: Multisensory integration elicits sense of ownership for body parts but not for non-corporeal objects. Experimental Brain Research, 204(3), 343-352. doi: 10.1007/s00221-009-2039-3URLpmid: 19820918 |
| 90 | Tsakiris M., & Haggard P. (2005). The rubber hand illusion revisited: Visuotactile integration and self-attribution. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 31(1), 80-91. |
| 91 | Tsakiris M., Hesse M. D., Boy C., Haggard P., & Fink G. R . (2006). Neural signatures of body ownership: A sensory network for bodily self-consciousness. Cerebral Cortex, 17(10), 2235-2244. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhl131URLpmid: 17138596 |
| 92 | Van der Hoort B., Guterstam A., & Ehrsson H. H . (2011). Being Barbie: The size of one’s own body determines the perceived size of the world. PLoS One, 6(5), e20195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020195URLpmid: 21633503 |
| 93 | Ward J., Mensah A., & Jünemann K . (2015). The rubber hand illusion depends on the tactile congruency of the observed and felt touch. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 41(5), 1203-1208. doi: 10.1037/xhp0000088URLpmid: 26191614 |
| 94 | Zeller D., Gross C., Bartsch A., Johansen-Berg H., & Classen J . (2011). Ventral premotor cortex may be required for dynamic changes in the feeling of limb ownership: A lesion study. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(13), 4852-4857. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5154-10.2011URLpmid: 21451023 |
| 95 | Zeller D., Litvak V., Friston K. J., & Classen J . (2015). Sensory processing and the rubber hand illusion—an evoked potentials study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 27(3), 573-582. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00705URLpmid: 25170795 |
相关文章 15
| [1] | 杨伟平, 李胜楠, 李子默, 郭敖, 任艳娜. 老年人视听觉整合的影响因素及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(5): 790-799. |
| [2] | 张静, 陈巍. 身体拥有感及其可塑性:基于内外感受研究的视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(2): 305-315. |
| [3] | 王爱君, 黄杰, 陆菲菲, 何嘉滢, 唐晓雨, 张明. 多感觉整合中的声音诱发闪光错觉效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(10): 1662-1677. |
| [4] | 张家鑫, 海拉干, 李会杰. 空间导航的测量及其在认知老化中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(12): 2019-2033. |
| [5] | 毛天欣, 熊晓, 李静华, 姚颖, 杨健, 李笑然, 周国富. 光照的警觉性作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(7): 1213-1222. |
| [6] | 张静, 陈巍. 基于自我错觉的最小自我研究:具身建构论的立场[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(7): 1244-1252. |
| [7] | 田昊月, 李力红, 徐 喆, 李飞, 金丹, 安灿翎. 最小自我中的施动感[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(5): 872-885. |
| [8] | 林弋琪, 王希, 彭凯平, 倪士光. 虚拟现实技术与自闭症谱系障碍治疗:科技新希望[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(3): 518-526. |
| [9] | 彭姓, 常若松, 任桂琴, 王爱君, 唐晓雨. 外源性注意与多感觉整合的交互关系[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(12): 2129-2140. |
| [10] | 罗霄骁, 康冠兰, 周晓林. McGurk效应的影响因素与神经基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(11): 1935-1951. |
| [11] | 陈静, 孙伟, 翟广涛, 李黎. 分离光流信息与形状信息对个体朝向目标行进的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(suppl.): 30-30. |
| [12] | 李明英, 吴惠宁, 蒯曙光, 张畅芯. 虚拟现实技术在执行功能评估中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(6): 933-942. |
| [13] | 周爱保;张彦驰;刘沛汝;尹玉龙;张 奋. 我是谁?——人际间多感觉刺激下的识脸错觉[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(2): 159-167. |
| [14] | 王广新;李立. 焦虑障碍的虚拟现实暴露疗法研究述评[J]. 心理科学进展, 2012, 20(8): 1277-1286. |
| [15] | 袁祥勇;黄希庭. 多感觉整合的时间再校准[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(5): 692-700. |
PDF全文下载地址:
http://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlkxjz/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=4565
