 , 张晓芳, 毕勤胜
, 张晓芳, 毕勤胜江苏大学土木工程与力学学院,江苏镇江 212013
POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE PULSE-SHAPED EXPLOSION AS WELL AS BURSTING OSCILLATIONS INDUCED BY IT1)
WeiMengke, HanXiujing , ZhangXiaofang, BiQinsheng
, ZhangXiaofang, BiQinsheng中图分类号:O322
文献标识码:A
通讯作者:
收稿日期:2018-09-29
网络出版日期:2019-05-18
版权声明:2019力学学报期刊社 所有
基金资助:
展开
摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
-->0
PDF (1282KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章收藏文章
本文引用格式导出EndNoteRisBibtex收藏本文-->
引 言
在非线性振动理论中,Rayleigh型方程是一类重要的非线性模型[1-3]. 它源自于诺贝尔物理学奖得主Lord Rayleigh对芦笛振动的研究.随后,****们发现,船舶非线性侧倾动力学[4]以及输电线的舞动[5]等实际问题可由Rayleigh型方程近似地加以描述.特别地,近年来,各种形式的Rayleigh型方程已被广泛应用于机械以及电子电路等工程技术领域.例如,Felix等[6]以及Warminski和Balthazar[7]利用Rayleigh型方程分别模拟了悬臂梁振子和电机模型,并对频率振幅响应进行了数值模拟;Kumar等[8]利用改进的van der Pol-Duffing-Rayleigh振子研究了人类在刚性地板上行走的侧向行走力;Tabejieu等[9]研究了Rayleigh梁对随机移动载荷的振幅响应及其概率特征.然而,需要指出的是,目前对Rayleigh型方程的研究多为单一尺度;而对于不同尺度耦合下的Rayleigh型模型的动力学特性,相关的研究鲜有报道.与单一尺度下的非线性系统相比,不同尺度耦合作用下的非线性模型往往能够表现出独特的复杂动力学行为[10-13],如簇发振荡,其特征是在每一演化周期中大幅振荡与小幅振荡的交替出现.簇发振荡可以通过实验或数值模拟的方法在自然科学的各种典型系统中发现[14-18],特别地,离散系统[19-20]和非光滑系统[21]中的簇发现象也相继被报道.簇发的动力学机理问题是簇发研究的重要问题之一,通向簇发振荡的多种不同的路径已被揭示.例如,Koper[22]探讨了Shilnikov同宿轨道的失稳导致的簇发振荡;Bi等[23]研究了经由不变环面的破裂诱发的簇发振荡;Curtu[24]揭示了经由奇异Hopf分岔而进入簇发振荡的道路;Canard爆炸[25]、延迟分岔[26-27]等也是诱发簇发振荡的常见机制.文献[2]研究了多频外激励作用下的Rayleigh系统的簇发振荡,其特征在于当慢变量接近临界点时,吸引子附近的轨线会出现急剧的定量转迁,即吸引子的"极速逃逸".基于此,得到了一种通向簇发振荡的新机制.
最近,一种名为"脉冲式爆炸"(pulse-shaped explosion,PSE)[28]的诱发簇发振荡的新机制被提出,其特征为平衡点和极限环表现出了与参数变化相关的脉冲式急剧量变.PSE导致系统轨线急剧跃迁,诱发了典型的簇发振荡.此外,现有研究已经证明了PSE在簇发振荡中起关键性作用.然而,需要指出的是,已报道的PSE及其诱发的簇发振荡模式均较为简单,尤其是PSE包含的尖峰为单向,且在其作用下的簇发振荡中的振荡簇也仅是单向振荡.PSE的不同表现形式以及与此相关的簇发动力学有待进一步探讨.基于此,考虑如下的Rayleigh型方程[7]
\begin{equation}\label{eq1} \ddot {x} + f\left( \dot {x} \right) + [1 - \mu \cos(2\omega t)](x + \gamma x^3) = q\sin (\omega t)\tag{1}\end{equation}
其中,$f\left( \dot {x} \right) = - \alpha \dot {x} + \beta \dot{x}^3$,$\mu \cos (2\omega t)$和$q\sin (\omega)$分别是系统的参数激励和外部激励,且激励频率$\omega$远小于系统的固有频率$\omega _0$,即激励频率和系统的固有频率之间存在量级差异.由此,可以得到频域两尺度耦合的非线性系统.本文旨在探讨频域两尺度下PSE的不同表现形式以及与此相关的簇发动力学.研究表明,不论是平衡点还是极限环,其对应的PSE均可包含正负双向两个不同的尖峰,故得名"正负双向PSE".在正负双向PSE的作用下,系统会迅速远离其先前状态;这导致系统轨线在单个振荡周期内出现了正向和负向的多次跃迁,由此得到了由正负双向PSE所诱发的簇发振荡模式.
1 正负双向PSE
如前所述,本文所关注的情形是"激励频率与系统的固有频率之间存在量级上的差异",因此此时的系统(1)是一个含有两个慢过程(即慢变激励)的快慢系统.由文献[29]所提出的频率转换快慢分析可知,可根据两个慢变激励之间的频率关系将系统(1)转化为仅含一个慢过程的快慢系统.进而,经典的"快慢分析法"[30]可以用于探讨转化后的快慢系统中快子系统的分岔行为,并以此来揭示原系统(1)的簇发动力学.按照上述思路,可视低频的外激励$\sin (\omega t) = \delta$为基准慢变量. 于是,参数激励$\cos (2\omega t)$可以表示为$\cos(2\omega t) = 1 - 2\delta ^2$. 由此可得如下形式的快子系统
\begin{equation}\label{eq2} \ddot {x} + f(\dot {x}) + [1 - \mu (1 - 2\delta ^2)](x+ \gamma x^3) = q\delta\tag{2}\end{equation}
记快子系统的平衡点为$E\left( {x,0} \right)$,其中$x$的取值为方程
\begin{equation}\label{eq3} [1 - \mu (1 - 2\delta ^2)](x + \gamma x^3) - q\delta =0\tag{3}\end{equation}
的实根. 当$\gamma > 0$,$1 - \mu (1 - 2\delta ^2) \ne0$时,方\vspace{2mm}程(3)的判别\vspace{2mm}式$\varDelta =\dfrac{q^2\delta ^2}{4\gamma ^2[1 - \mu (1 - 2\delta ^2)]^2} +\dfrac{1}{27\gamma ^3} > 0$恒成立.
此时,快子系统(2)仅存在一个平衡点. 而当$1 - \mu (1 - 2\delta ^2) =0$,即
\begin{equation}\label{eq4} \delta = \delta _{c\pm } \equiv \pm \sqrt {\frac{\mu -1}{2\mu }}\tag{4}\end{equation}
时,快子系统不存在平衡点.
为了揭示快子系统(2)中的正负双向PSE,下面探讨当$1 - \mu (1 -2\delta ^2) \ne 0$时,平衡点$E$的稳定性和分岔行为.将快子系统(2)在平衡点$E$处线性化,可得对应的特征方程
\begin{equation}\label{eq5} F(\lambda ) = \lambda ^2 - \lambda \alpha - \xi =0\tag{5}\end{equation}
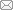
其中,$\xi = [\mu (1 - 2\delta ^2) - 1](1 + 3\gamma x^2)$.当$\alpha < 0$,$\gamma > 0$时,在参数区间$(\delta _{c - } ,\delta_{c + })$之内,特征方程(5)存在异号实根,因此此时系统发散;而在区间$(\delta_{c - } ,\delta _{c + })$之外,特征方程(5)存在实部为负的共轭复根,此时平衡点渐近稳定.当$\alpha =0$时,特征方程(5)存在一对纯虚根,此时快子系统出现了超临界Hopf分岔.如图1所示,当$\alpha$从负值出发穿越0时,平衡点失稳,快子系统表现为由稳定极限环吸引子所构成的单稳态.
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1快子系统(2)的超临界Hopf分岔,其中分岔值是$\alpha = 0$.系统参数分别是$\delta = 0.5$,$\mu = 0.1$,$\beta = 0.05$,$\gamma= 0.1$和$q = 0.5$
-->Fig. 1A supercritical Hopf bifurcation in the fast subsystem (2), where the bifurcation value is $\alpha = 0$. The system parameters are $\delta = 0.5$, $\mu = 0.1$, $\beta = 0.05$, $\gamma = 0.1$ and $q = 0.5$, respectively
-->
基于上述分析,下面探讨快子系统(2)中的正负双向PSE.根据吸引子的类型可将PSE分为两类,即与平衡点和极限环相关的正负双向PSE.首先考虑平衡点的正负双向PSE.
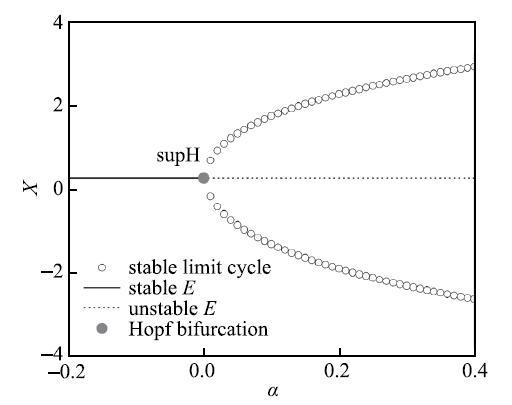
情形1 平衡点的正负双向PSE.为了清晰地展示正负双向PSE现象,固定$q =0.5$,其余参数的选取与文献[2]相同,即$\alpha = - 0.05$,$\beta =0.05$,$\gamma = 0.1$,$\omega = 0.01$.基于上述对系统(2)的稳定性分析,可知参数区间$(\delta _{c - },\delta _{c + })$是系统的不稳定区域,该区间以外的其他区域为稳定区域(见图2(a)上).$\delta _c $曲线随着参数的变化意味着,快子系统轨线在$(\delta,x)$平面内的渐近线的数量变化;特别地,$\delta _c$曲线在折点$F(0,1)$处发生fold分岔,快子系统关于$\delta$的变化规律处于临界情形;图2(a)下$\sim$图2(b)下给出了快子系统其平衡点曲线的演化过程.基于此,可以清晰地解释正负双向PSE的产生机制.图2(a)下给出的是当$\mu = 1.01$时快子系统的平衡点曲线.如图所示,横坐标$\delta $被渐近线$\delta _{c - } $和$\delta _{c +}$分为左、中、右三个区域,其中中间区域为发散区,而左右区域是稳定区;特别地,在$\delta$接近渐近线$\delta _{c\pm }$时,平衡点吸引子发生了"极速逃逸"[2].
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2$\delta _c $曲线图和平衡点的正负双向PSE的产生和演变过程
-->Fig. 2$\delta _c $ curves as well as the generation and evolution of positive and negative PSE of equilibrium point
-->
当$\mu $降至$\mu _c = 1$时,在$(\delta ,\mu)$参数平面内出现了一个fold点.如图2(b)上所示,此时原先的两条渐近线现已经融合为一条.在该渐近线的左右两侧,两条平衡点曲线由平缓变得极其陡峭,分别沿着正负两个方向向无穷远处延伸.当$\mu $不断减小并越过$\mu _c$时,仅存的一条渐近线因fold分岔而消失.此时,两条反向的平衡点曲线合并为一个整体并保留了原先的陡峭性;PSE因而产生.如图2(b)下所示,当慢变量$\delta $接近$\delta _c =0$时,平衡点迅速离开并返回其初始位置,于是发生了PSE.
需要指出的是,文献[28]探讨的平衡点吸引子的PSE仅含有单向的尖峰,其尖峰或是向上或是向下.其原因是,渐近线左右两侧的平衡点曲线具有相同的延伸方向,即平衡点曲线同时向正向或负向延伸.如图2(b)上所示,这里的PSE的产生与两条反向的平衡点曲线有关,这因此使得平衡点曲线在正负两个方向都形成了尖峰.基于上述PSE所具备的特征,不妨将其命名为"正负双向PSE".
随着参数$\mu $的不断减小,正负双向PSE的峰值亦不断减小. 当$\mu$减小至某一临界值时,PSE消失.此时,平衡点曲线中的急剧量变消失(见图2(b)下),通常意义上的平衡点曲线因此而出现.
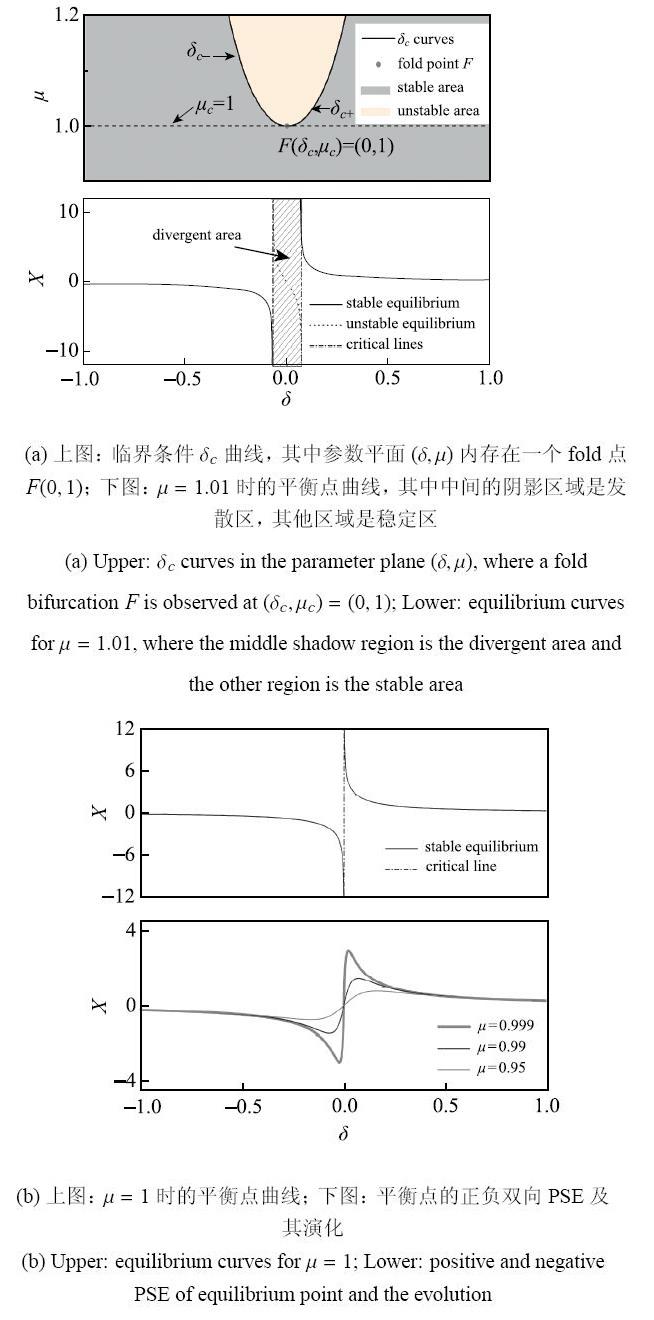
情形2 极限环的正负双向PSE. 当控制参数$\alpha $从$\alpha= - 0.05$越过临界值$\alpha =0$时,快子系统出现了超临界Hopf分岔(见图1). 取$\alpha =0.01$,其他参数的取值与情形1相同,此时,平衡点吸引子失稳,同时产生了一个稳定的极限环.图3给出了平衡点和极限环的演变过程.与平衡点的情形类似,当控制参数$\mu$稍大于1时,如图3(a)所示,系统出现了极限环吸引子的"极速逃逸"行为[2].图3(b)进一步给出了该逃逸行为在$\delta _{c\pm } $附近的相描述.
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3极限环的正负双向PSE产生和演化过程
-->Fig. 3The generation and evolution of positive and negative PSE of limit cycle
-->
当参数$\mu $减小并越过$\mu _c$时,采用与情形1类似的分析,此时不稳定的平衡点发生了正负双向PSE.另一方面,注意到极限环吸引子总是围绕着不稳定的平衡点,并随之同时演化(见图3(b)).因此,在平衡点排斥子发生了正负双向PSE的同时,极限环吸引子也发生了类似的PSE现象(见图3(c)和图3(d)).
特别地,注意到该PSE的产生与两个反方向演化的极限环吸引子有关,且表现出了两个具有不同坐标值的峰值(见图3(d)中的垂线).因此,类似地,我们将极限环的这种急剧转迁现象,命名为"极限环的正负双向PSE".
2 正负双向PSE诱发的簇发动力学
在前一部分中,针对不同类型的吸引子,先后揭示了正负双向PSE的产生机制.接下来,本部分将探讨正负双向PSE下的簇发动力学.2.1 沉寂态和激发态区域
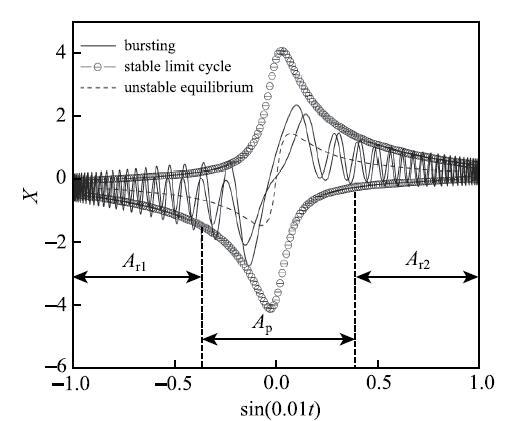
一般来说,簇发振荡的产生与系统在不同的吸引子之间的转迁有关[31-33].然而,本文所涉及的系统并不含有共存的吸引子,而是始终处于单稳态.注意到,正负双向PSE导致系统存在明显的沉寂态与激发态区域;且慢变量$\delta= \sin (\omega t)$中$\omega \ll1$为小量,故在慢变量的驱动下系统可以周期缓慢的通过沉寂态和激发态.系统由沉寂态向激发态的周期转迁形成了簇发振荡.图4展示了$\mu = 0.999$时快子系统中的沉寂态和激发态区域的示意图.如图所示,参数轴$\delta $可分为3个部分:两个沉寂态区域$A_{\rm r1}$和$A_{\rm r2} $,以及由正负双向PSE诱发的激发态区域$A_{\rm p}$.在正负双向PSE发生前后,吸引子保持在原点附近.此时,系统的动力学行为比较平缓,处于沉寂态;而当正负双向PSE发生时,系统产生了急剧量变,因而此时系统处于激发态.
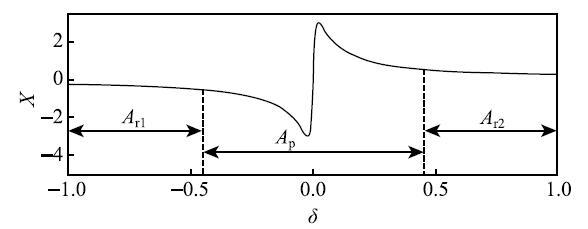 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4快子系统的沉寂态与激发态区域的示意图,其中平衡点曲线与
-->Fig. 4Schematic diagram of the rest areas and active area of the fast subsystem, where the equilibrium curve corresponds to the situation of $\mu = 0.999$ in
-->
2.2 平衡点的正负双向PSE诱发的点--点型簇发振荡
首先,考虑平衡点吸引子的正负双向PSE所诱发的簇发振荡模式.作为一个例子,我们考虑振幅$\mu =0.99$情况下的簇发振荡;其对应的振荡模式由图5给出.此时相应快子系统的平衡点是依照图2(d)的模式而演变的.注意到在一个振荡周期内,振荡波形出现了两个正负双向的振荡簇,即可以观测到两个与准静态过程相交替的大幅振荡(见图5虚线框).为了进一步揭示此类振荡行为的产生机理,现将外激励$\sin (\omega t) =\delta$视为基准的慢变量,并引入相应的转换相图[34-35]及快慢分析.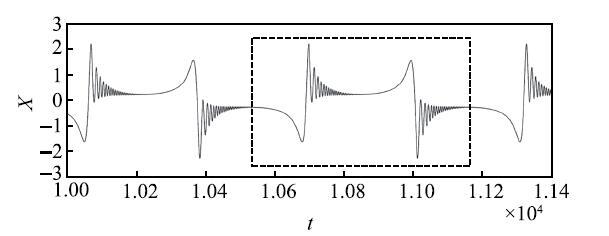 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5平衡点的正负双向PSE诱发的点{--}点型簇发振荡$\alpha = - 0.05$,$\beta = 0.05$,$\gamma = 0.1$,$q = 0.5$,$\omega = 0.01$,$\mu = 0.99$
-->Fig. 5Bursting oscillations of point-point type induced by positive and negative PSE of equilibrium point for $\alpha = - 0.05$, $\beta = 0.05$, $\gamma = 0.1$, $q = 0.5$, $\omega = 0.01$, $\mu = 0.99$
-->
如图6所示,注意到快子系统处于由平衡点吸引子所构成的单稳态,系统轨线无法在不同吸引子间转迁.然而,受稳定的平衡点吸引子的影响,轨线一开始几乎沿着平衡点曲线运动,表现为沉寂态.当慢变量$\sin (\omega t)$进入激发态区域$A_{\rm p}$时,出现了平衡点吸引子的PSE.于是,系统轨线由沉寂态向激发态转迁,正负双向的大振幅振荡由此而产生.当慢变量$\sin (\omega t)$离开激发态区域$A_{\rm p}$,进入沉寂态区域$A_{\rm r1} $或$A_{\rm r2}$时,轨线逐渐地向平衡点收敛,导致大幅振荡结束.
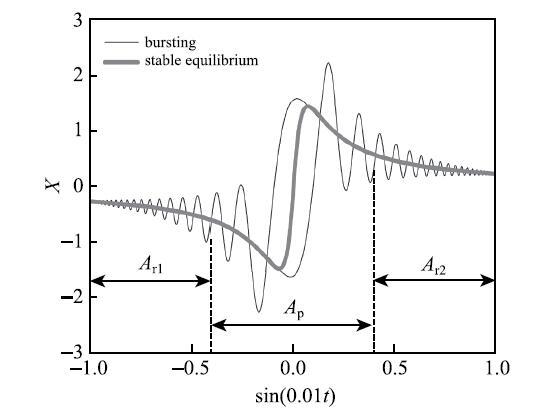 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6与
-->Fig. 6Fast-slow analysis of the bursting oscillations in
-->
上述分析表明,随着慢变量缓慢地穿越对应于不同动力学特性的区域时,轨线因平衡点的正负双向PSE而在沉寂态与激发态之间互相转迁,由此形成了图5所示的簇发振荡模式.注意到这里的沉寂态与激发态均与平衡点相关,因此图5所示的簇发振荡属于"点--点"型.
2.3 极限环的正负双向PSE诱发的环--环型簇发振荡
图7为极限环的正负双向PSE相关的环--环型簇发振荡模式.与平衡点的情形类似,极限环的正负双向PSE也导致了具有不同动力学特性的参数区域的存在,即参数轴$\delta$也可划分为沉寂态区域$A_{\rm r1} $和$A_{\rm r2}$以及激发态区域$A_{\rm p}$.与此相对应,当慢变量缓慢地穿越这些区域时,轨线因极限环的正负双向PSE而发生急剧转迁(见图8).这正是图7所示的簇发振荡其大幅振荡产生和消失的原因.注意到此时系统的沉寂态和激发态都与极限环相关,因此图7为代表的簇发振荡属于"环--环"型.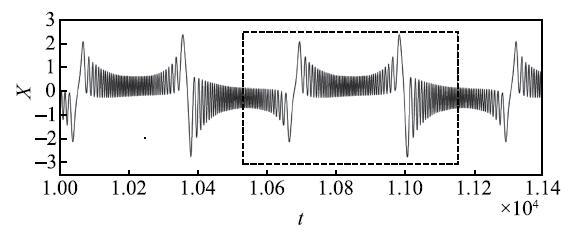 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图7极限环的正负双向PSE诱发的环--环型簇发振荡$\alpha = 0.01$,$\beta= 0.05$,$\gamma = 0.1$,$q = 0.5$,$\omega =0.01$,$\mu = 0.99$
-->Fig. 7Bursting oscillations of cycle-cycle type induced by positive and negative PSE of limit cycle for$\alpha = 0.01$, $\beta = 0.05$, $\gamma = 0.1$, $q = 0.5$, $\omega = 0.01$, $\mu = 0.99$
-->
 显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
显示原图|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图8与
-->Fig. 8Fast-slow analysis of the bursting oscillations in
-->
3 结 论
簇发振荡是快--慢子系统耦合作用下产生的小幅振荡与大幅振荡交替演变的复杂动力学行为;探讨簇发振荡各种可能的诱发机制一直是簇发研究的重要问题之一.本文以频域两尺度下的一类Rayleigh型方程为例,探讨了PSE的新型表现形式,即包含了正负双向两个不同的尖峰,故称之为正负双向PSE.正负双向PSE的急剧量变行为,致使系统表现出明显的沉寂态和激发态.在慢变量的调节作用下,系统在沉寂态与激发态之间周期转迁,从而诱发了两类典型的簇发振荡模式,即"点--点"型和"环--环"型簇发振荡.需要指出的是,进一步的分析表明,正负双向PSE的峰值会随着参数的变化而减小;特别地,当峰值减小至某一临界值时,簇发振荡会消失.然而,如何计算与簇发产生相关的"临界峰值",需进一步探讨.The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
| [1] | . In this work, we investigate the following Rayleigh type equation: x ″ ( t ) + f ( x ′ ( t ) ) + g ( t , x ( t ) ) = e ( t ) . Some criteria for guaranteeing the existence of asymptotically stable (in the sense of Lyapunov) periodic solutions of this equation is presented by using Mawhin’s continuation theorem, Floquet theory, Lyapunov stability theory and some analysis techniques. Moreover, an example is provided to illustrate the validity of our results. |
| [2] | . The purpose of this paper is to report a novel route to mixed-mode oscillations (MMOs), i.e., the mechanism which we call speed escape of attractors, based on a Rayleigh equation with multiple-frequen |
| [3] | . http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11071-010-9679-5 |
| [4] | . In the framework of a general roll-damping model, we study the influence of different damping models on the nonlinear roll dynamics of ships through a detailed Melnikov analysis. We introduce the concept of the Melnikov equivalent damping and use phase-plane concepts to obtain simple expressions for what we call the Melnikov damping coefficients. We also study the sensitivity of these coefficients to parameter variations. As an application, we consider the equivalence of the linear-plus-cubic and linear-plus-quadratic damping models, and we derive a condition under which the two models yields the same Melnikov predictions. The free- and forced-oscillation behaviors of the models satisfying this condition are also compared. |
| [5] | . http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/004579499400630L |
| [6] | . An analytical and numerical investigation into the dynamic interaction between a cantilever beam with nonlinear damping and stiffness behavior, modeled by the Duffing-Rayleigh equation, and a non-ideal motor that is connected to the end of the beam, is presented. Non-stationary and steady-state responses in the resonance region as well as the passage through resonance behavior when the frequency of the excitation is varied are analyzed. The influences of nonlinear stiffness, nonlinear damping and the extent of the unbalance in the motor are examined. It is found that in this situation so-called Sommerfeld effects may be observed; the increase required by a source operating near the resonance results in a small change in the frequency, but there is a large increase in the amplitude of the resultant vibration and the jump phenomenon occurs. |
| [7] | . |
| [8] | . The paper proposes a single degree of freedom oscillator in order to accurately represent the lateral force acting on a rigid floor due to human walking. As a pedestrian produces itself the energy required to maintain its motion, it can be modelled as a self-sustained oscillator that is able to produce: (i) self-sustained motion; (ii) a lateral periodic force signal; and (iii) a stable limit cycle. The proposed oscillator is a modification of hybrid Van der Pol-Duffing-Rayleigh oscillator, by introducing an additional nonlinear hardening term. Stability analysis of the proposed oscillator has been performed by using the energy balance method and the Lindstedt-Poincare perturbation technique. Model parameters were identified from the experimental force signals of ten pedestrians using the least squares identification technique. The experimental and the model generated lateral forces show a good agreement. |
| [9] | . We consider the problem of the nonlinear response of a Rayleigh beam to the passage of a train of forces moving with stochastic velocity. The Fourier transform and the theory of residues is used to estimate the mean-square amplitude of the beam, while the stochastic averaging method gives the stationary probability density function of the oscillations amplitude. The analysis shows that the effect of the load random velocities is highly nonlinear, leading to a nonmonotonic behavior of the mean amplitude versus the intensity of the stochastic term and of the load weight. The analytic approach is also checked with numerical simulations. The effect of loads number on the system response is numerically investigated. |
| [10] | . 应用小波多尺度分解算法进行噪声减缩,从混沌背景中分离周期信号、噪声及其他混沌信号.小波多尺度分解算法能够区分不同尺度的信号是利用小波变换在时、频两域具有突出信号特征的能力以及小波变换是一线性变换的特点.提出的方法仅利用信号的尺度特性,克服了先前的噪声减缩要知道产生混沌信号的数学模型,并且要求叠加在混沌背景中的其他信号的幅度相对混沌背景信号的幅度很小的假定.给出了从Lorenz混沌背景中提取正弦信号、白噪声和Chua's电路产生的混沌信号的计算机模拟结果. . 应用小波多尺度分解算法进行噪声减缩,从混沌背景中分离周期信号、噪声及其他混沌信号.小波多尺度分解算法能够区分不同尺度的信号是利用小波变换在时、频两域具有突出信号特征的能力以及小波变换是一线性变换的特点.提出的方法仅利用信号的尺度特性,克服了先前的噪声减缩要知道产生混沌信号的数学模型,并且要求叠加在混沌背景中的其他信号的幅度相对混沌背景信号的幅度很小的假定.给出了从Lorenz混沌背景中提取正弦信号、白噪声和Chua's电路产生的混沌信号的计算机模拟结果. |
| [11] | . <p>鼓泡流化床因其较高的传热特性以及较好的相间接触已经被广泛应用于工业生产中,而对鼓泡流态化气固流动特性的充分认知是鼓泡流化床设计的关键.在鼓泡流化床中,气泡相和乳化相的同时存在使得床中呈现非均匀流动结构,而这种非均匀结构给鼓泡流化床的数值模拟造成了很大的误差.基于此,以气泡作为介尺度结构,建立了多尺度曳力消耗能量最小的稳定性条件,构建了适用于鼓泡流化床的多尺度气固相间曳力模型.结合双流体模型,对A类和B类颗粒的鼓泡流化床中气固流动特性进行了模拟研究,分析了气泡速度、气泡直径等参数的变化规律.研究表明,与传统的曳力模型相比,考虑气泡影响的多尺度气固相间曳力模型给出的曳力系数与颗粒浓度的关系是一条分布带,建立了控制体内曳力系数与局部结构参数之间的关系.通过模拟得到的颗粒浓度和速度与实验的比较可以发现,考虑气泡影响的多尺度曳力模型可以更好地再现实验结果.通过A类和B类颗粒的鼓泡床模拟研究发现,A类颗粒的鼓泡床模拟受多尺度曳力模型的影响更为显著.</p> . <p>鼓泡流化床因其较高的传热特性以及较好的相间接触已经被广泛应用于工业生产中,而对鼓泡流态化气固流动特性的充分认知是鼓泡流化床设计的关键.在鼓泡流化床中,气泡相和乳化相的同时存在使得床中呈现非均匀流动结构,而这种非均匀结构给鼓泡流化床的数值模拟造成了很大的误差.基于此,以气泡作为介尺度结构,建立了多尺度曳力消耗能量最小的稳定性条件,构建了适用于鼓泡流化床的多尺度气固相间曳力模型.结合双流体模型,对A类和B类颗粒的鼓泡流化床中气固流动特性进行了模拟研究,分析了气泡速度、气泡直径等参数的变化规律.研究表明,与传统的曳力模型相比,考虑气泡影响的多尺度气固相间曳力模型给出的曳力系数与颗粒浓度的关系是一条分布带,建立了控制体内曳力系数与局部结构参数之间的关系.通过模拟得到的颗粒浓度和速度与实验的比较可以发现,考虑气泡影响的多尺度曳力模型可以更好地再现实验结果.通过A类和B类颗粒的鼓泡床模拟研究发现,A类颗粒的鼓泡床模拟受多尺度曳力模型的影响更为显著.</p> |
| [12] | . 利用槽道湍流直接数值模拟的数据库和离散正交子波,对近壁湍流的多尺度输运特性进行了研究.通过在流向和展向分别进行子波多尺度分解,得到了近壁区湍动能在流向和展向多尺度传输的不同性质,发现流向传输以能量的反传为主,而在展向能量存在明显的正传,并且当过滤尺度较大时以正传为主.近壁湍流能量传输的各向异性为进一步构造各向异性大涡模拟亚格子模式提供了必要的参考. . 利用槽道湍流直接数值模拟的数据库和离散正交子波,对近壁湍流的多尺度输运特性进行了研究.通过在流向和展向分别进行子波多尺度分解,得到了近壁区湍动能在流向和展向多尺度传输的不同性质,发现流向传输以能量的反传为主,而在展向能量存在明显的正传,并且当过滤尺度较大时以正传为主.近壁湍流能量传输的各向异性为进一步构造各向异性大涡模拟亚格子模式提供了必要的参考. |
| [13] | . Computational modeling and imaging in biology and medicine are gaining more and more interest with the discovery of in-depth structural and functional knowledge at all space and time scales (molecule to proteins, cells to organs and organisms). The recursion between description levels for highly dynamical, interacting and complex systems, i.e the integrative approach, is a very challenging topic where formal models, observational tools and experimental investigations have to be closely designed, coupled and confronted together. Imaging techniques play a major role in this interdisciplinary attempt to elucidate this biocomplexity: they convey relevant information about the underlying mechanisms, depict the conformations and anatomical topologies and draw the biophysical laws they may follow. Furthermore, the basic image analysis tools (from calibration to segmentation, motion estimation and registration up to pattern recognition) are generic enough to be of value whatever the objects under consideration. The same comments apply when Computer Graphics or Virtual Reality techniques are concerned. This paper will survey the recent contributions dealing with both models, imaging data and processing frames. Examples ranging over different scales, from macro to nano, will be given in order to enhance the mutual benefits and perspectives that can be expected from this coupling. |
| [14] | . It is difficult to design electronic nonlinear devices capable of reproducing complex oscillations because of the lack of general constructive rules, and because of stability problems related to the dynamical robustness of the circuits. This is particularly true for current analog electronic circuits that implement mathematical models of bursting and spiking neurons. Here we describe a novel, four-dimensional and dynamically robust nonlinear analog electronic circuit that is intrinsic excitable, and that displays frequency adaptation bursting and spiking oscillations. Despite differences from the classical Hodgkin–Huxley (HH) neuron model, its bifurcation sequences and dynamical properties are preserved, validating the circuit as a neuron model. The circuit's performance is based on a nonlinear interaction of fast–slow circuit blocks that can be clearly dissected, elucidating burst's starting, sustaining and stopping mechanisms, which may also operate in real neurons. Our analog circuit unit is easily linked and may be useful in building networks that perform in real-time. |
| [15] | . Recent advances in the experimental and theoretical study of dynamics of neuronal electrical firing activities are reviewed. Firstly, some experimental phenomena of neuronal irregular firing patterns, especially chaotic and stochastic firing patterns, are presented, and practical nonlinear time analysis methods are introduced to distinguish deterministic and stochastic mechanism in time series. Secondly, the dynamics of electrical firing activities in a single neuron is concerned, namely, fast鈥搒low dynamics analysis for classification and mechanism of various bursting patterns, one- or two-parameter bifurcation analysis for transitions of firing patterns, and stochastic dynamics of firing activities (stochastic and coherence resonances, integer multiple and other firing patterns induced by noise, etc.). Thirdly, different types of synchronization of coupled neurons with electrical and chemical synapses are discussed. As noise and time delay are inevitable in nervous systems, it is found that noise and time delay may induce or enhance synchronization and change firing patterns of coupled neurons. Noise-induced resonance and spatiotemporal patterns in coupled neuronal networks are also demonstrated. Finally, some prospects are presented for future research. In consequence, the idea and methods of nonlinear dynamics are of great significance in exploration of dynamic processes and physiological functions of nervous systems. |
| [16] | . Delayed feedbacks are quite common in many physical and biological systems and in particular many physiological systems. Delay can cause a stable system to become unstable and vice versa. One of the well-studied non-biological chemical oscillators is the Belousov-Zhabotinskii (BZ) reaction. This gives relaxation oscillations for a considerable period of time under batch conditions. This paper deals with the effect of perturbing the limit cycle oscillation of BZ reaction by employing a delayed electrical feedback to the system under batch conditions. The parameters chosen to study are external resistance and delay. For various resistances and delays the system was electrically perturbed and found to exhibit various complex mixed mode oscillations. The dynamic features are accounted for by the Oregonator model, with time delay incorporated in one of the variables. |
| [17] | . Abstract Bursting, an important communication activity in biological neurons and endocrine cells, has been widely found in fast-slow dynamical systems. In this paper, a modified second-order generalized memristor, memristive diode bridge cascaded with LC network, is presented and its fingerprints of the pinched hysteresis loops are analyzed. By replacing the parallel resistor with the modified generalized memristor, a novel memristive Wien-bridge oscillator is constructed and its mathematical model is established, from which the dynamical behaviors of symmetric chaotic and periodic bursting oscillations are observed and the corresponding bifurcation mechanisms are explained. Based on a hardware realization circuit, experimental observations are performed, which verify the numerical simulations. |
| [18] | . This paper presents stability and bifurcations of two synaptically coupled identical Hindmarsh–Rose neurons with one time delay. The parameters we choose contribute to the single neuron exhibiting exc |
| [19] | . <p>簇发振荡是多时间尺度系统复杂动力学行为的典型代表,簇发振荡的动力学机制与分类问题是簇发研究的重要问题之一,但当前****们所揭示的簇发振荡的结构大多较为简单.研究以非自治离散Duffing系统为例,探讨具有复杂分岔结构的新型簇发振荡模式,并将其分为两大类,一类经由Fold分岔所诱发的对称式簇发,另一类经由延迟倍周期分岔所诱发的非对称式簇发.快子系统的分岔表现为典型的含有两个Fold分岔点的S形不动点曲线,其上、下稳定支可经由倍周期(即Flip)分岔通向混沌.当非自治项(即慢变量)穿越Fold分岔点时,系统的轨线可以向上、下稳定支的各种吸引子(例如,周期轨道和混沌)进行转迁,因此得到了经由Fold分岔所诱发的各种对称式簇发;而当非自治项无法穿越Fold分岔点,但可以穿越Flip分岔点时,系统产生了延迟Flip分岔现象.基于此,得到了经由延迟Flip分岔所诱发的各种非对称簇发.特别地,文中所报道的簇发振荡模式展现出复杂的反向Flip分岔结构.研究结果表明,这与非自治项缓慢地反向穿越快子系统的Flip分岔点有关.研究结果丰富了离散系统簇发的动力学机理和分类.</p> . <p>簇发振荡是多时间尺度系统复杂动力学行为的典型代表,簇发振荡的动力学机制与分类问题是簇发研究的重要问题之一,但当前****们所揭示的簇发振荡的结构大多较为简单.研究以非自治离散Duffing系统为例,探讨具有复杂分岔结构的新型簇发振荡模式,并将其分为两大类,一类经由Fold分岔所诱发的对称式簇发,另一类经由延迟倍周期分岔所诱发的非对称式簇发.快子系统的分岔表现为典型的含有两个Fold分岔点的S形不动点曲线,其上、下稳定支可经由倍周期(即Flip)分岔通向混沌.当非自治项(即慢变量)穿越Fold分岔点时,系统的轨线可以向上、下稳定支的各种吸引子(例如,周期轨道和混沌)进行转迁,因此得到了经由Fold分岔所诱发的各种对称式簇发;而当非自治项无法穿越Fold分岔点,但可以穿越Flip分岔点时,系统产生了延迟Flip分岔现象.基于此,得到了经由延迟Flip分岔所诱发的各种非对称簇发.特别地,文中所报道的簇发振荡模式展现出复杂的反向Flip分岔结构.研究结果表明,这与非自治项缓慢地反向穿越快子系统的Flip分岔点有关.研究结果丰富了离散系统簇发的动力学机理和分类.</p> |
| [20] | . 多时间尺度问题具有广泛的工程与科学研究背景,慢变参数则是多时间尺度问题的典型标志之一.然而现有文献所报道的慢变参数问题,其展现出的振荡形式及内部分岔结构,大多较为单一,此外少有文献涉及到混沌激变的现象.本文以含慢变周期激励的达芬映射为例,探讨了一类具有复杂分岔结构的张弛振荡.快子系统的分岔表现为S形不动点曲线,其上、下稳定支可经由倍周期分岔通向混沌.而在一定的参数条件下,存在着导致混沌吸引子突然消失的一对临界参数值.当分岔参数达到此临界值时,混沌吸引子可能与不稳定不动点相接触,也可能与之相距一定距离.对快子系统吸引域分布的模拟,表明存在着导致边界激变(boundary crisis)的临界值,在这些值附近,经由延迟倍周期分岔演化而来的混沌吸引子可与2n(n=0,1,2,...)周期轨道乃至混沌吸引子共存.当慢变量周期地穿过临界点后,双稳态的消失导致原本处于混沌轨道的轨线对称地向此前共存的吸引子转迁,从而使系统出现了不同吸引子之间的滞后行为,由此产生了由边界激变所诱发的多种对称式张弛振荡.本文的结果丰富了对离散系统的多时间尺度动力学机理的认识. . 多时间尺度问题具有广泛的工程与科学研究背景,慢变参数则是多时间尺度问题的典型标志之一.然而现有文献所报道的慢变参数问题,其展现出的振荡形式及内部分岔结构,大多较为单一,此外少有文献涉及到混沌激变的现象.本文以含慢变周期激励的达芬映射为例,探讨了一类具有复杂分岔结构的张弛振荡.快子系统的分岔表现为S形不动点曲线,其上、下稳定支可经由倍周期分岔通向混沌.而在一定的参数条件下,存在着导致混沌吸引子突然消失的一对临界参数值.当分岔参数达到此临界值时,混沌吸引子可能与不稳定不动点相接触,也可能与之相距一定距离.对快子系统吸引域分布的模拟,表明存在着导致边界激变(boundary crisis)的临界值,在这些值附近,经由延迟倍周期分岔演化而来的混沌吸引子可与2n(n=0,1,2,...)周期轨道乃至混沌吸引子共存.当慢变量周期地穿过临界点后,双稳态的消失导致原本处于混沌轨道的轨线对称地向此前共存的吸引子转迁,从而使系统出现了不同吸引子之间的滞后行为,由此产生了由边界激变所诱发的多种对称式张弛振荡.本文的结果丰富了对离散系统的多时间尺度动力学机理的认识. |
| [21] | . 旨在揭示含双频周期激励的不同尺度Filippov系统的非光滑簇发振荡模式及分岔机制.以Duffing和Van der Pol耦合振子作为动力系统模型,引入周期变化的双频激励项,当两激励频率与固有频率存在量级差时,将两周期激励项表示为可以作为一慢变参数的单一周期激励项的代数表达式,给出了当保持外部激励频率不变,改变参数激励频率的情况下,快子系统随慢变参数变化的平衡曲线及因系统出现的fold分岔或Hopf分岔导致的系统分岔行为的演化机制.结合转换相图和由Hopf分岔产生稳定极限环的演化过程,得到了由慢变参数确定的同宿分岔、多滑分岔的临界情形及因慢变参数改变而出现的混合振荡模式,并详细阐述了系统的簇发振荡机制和非光滑动力学行为特性.通过对比两种不同情形下的平衡曲线及分岔图,指出虽然系统有相似的平衡曲线结构,却因参数激励频率取值的不同,致使平衡曲线发生了更多的曲折,对应的极值点的个数也有所改变,并通过数值模拟,对结果进行了验证. . 旨在揭示含双频周期激励的不同尺度Filippov系统的非光滑簇发振荡模式及分岔机制.以Duffing和Van der Pol耦合振子作为动力系统模型,引入周期变化的双频激励项,当两激励频率与固有频率存在量级差时,将两周期激励项表示为可以作为一慢变参数的单一周期激励项的代数表达式,给出了当保持外部激励频率不变,改变参数激励频率的情况下,快子系统随慢变参数变化的平衡曲线及因系统出现的fold分岔或Hopf分岔导致的系统分岔行为的演化机制.结合转换相图和由Hopf分岔产生稳定极限环的演化过程,得到了由慢变参数确定的同宿分岔、多滑分岔的临界情形及因慢变参数改变而出现的混合振荡模式,并详细阐述了系统的簇发振荡机制和非光滑动力学行为特性.通过对比两种不同情形下的平衡曲线及分岔图,指出虽然系统有相似的平衡曲线结构,却因参数激励频率取值的不同,致使平衡曲线发生了更多的曲折,对应的极值点的个数也有所改变,并通过数值模拟,对结果进行了验证. |
| [22] | . The bifurcation structure of a three-variable Van der Pol-Duffing-type model is studied in some detail, with special attention to the mixed-mode solutions, a type of complex periodic behavior frequently encountered in oscillating chemical reactions. The mixed-mode oscillations in the model occur close to two Hopf bifurcations, which are arranged with the saddle-node bifurcations in a so-called cross-shaped phase diagram, a bifurcation diagram also typical for chemical reactions. The mixed-mode oscillations are shown to lie on isolated bifurcation curves, which are all born in a single codimension-two bifurcation known as the neutrally twisted homoclinic orbit or inclination switch. With the introduction of an additional slow time scale, the same model can exhibit more complex mixed-mode oscillations and torus bifurcations. |
| [23] | . 分析了耦合vain der Pol振子参数共振条件下的复杂动力学行为.基于平均方程,得到了参数平面上的转迁集,这些转迁集将参数平面划分为不同的区域,在各个不同的区域对应于系 统不同的解.随着参数的变化,从平衡点分岔出两类不同的周期解,根据不同的分岔特性,这两类周期解失稳后,将产生概周期解或3-D环面解,它们都会随参数 的变化进一步导致混沌.发现在系统的混沌区域中,其混沌吸引子随参数的变化会突然发生变化,分解为两个对称的混沌吸引子.值得注意的是,系统首先是由于 2-D环面解破裂产生混沌,该混沌吸引子破裂后演变为新的混沌吸引子,却由倒倍周期分岔走向3-D环面解,也即存在两条通向混沌的道路:倍周期分岔和环面 破裂,而这两种道路产生的混沌吸引子在一定参数条件下会相互转换. . 分析了耦合vain der Pol振子参数共振条件下的复杂动力学行为.基于平均方程,得到了参数平面上的转迁集,这些转迁集将参数平面划分为不同的区域,在各个不同的区域对应于系 统不同的解.随着参数的变化,从平衡点分岔出两类不同的周期解,根据不同的分岔特性,这两类周期解失稳后,将产生概周期解或3-D环面解,它们都会随参数 的变化进一步导致混沌.发现在系统的混沌区域中,其混沌吸引子随参数的变化会突然发生变化,分解为两个对称的混沌吸引子.值得注意的是,系统首先是由于 2-D环面解破裂产生混沌,该混沌吸引子破裂后演变为新的混沌吸引子,却由倒倍周期分岔走向3-D环面解,也即存在两条通向混沌的道路:倍周期分岔和环面 破裂,而这两种道路产生的混沌吸引子在一定参数条件下会相互转换. |
| [24] | . http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0167278909003959 |
| [25] | . Chaotically spiking attractors in semiconductor lasers with optoelectronic feedback have been recently observed to be the result of canard phenomena in three-dimensional phase space (incomplete homoclinic scenarios). Since light-emitting diodes display the same dynamics and are much more easily controllable, we use one of these systems to complete the attractor analysis demonstrating experimentally and theoretically the occurrence of complex sequences of periodic mixed-mode oscillations. In particular, we investigate the transition between periodic and chaotic mixed-mode states and analyze the effects of the unavoidable experimental noise on these transitions. |
| [26] | The dynamics of a typical Belousov-Zhabotinsky (BZ) reaction with two time scales and low perturbation frequency is investigated in this paper. For specific parameters, the typical phenomenon called as double-Hopf bursting is observed, and the corresponding generation mechanism is presented based on the slow-fast dynamical analysis method. With the decrease of the amplitude of external excitation, the double-Hopf bursting evolves into a single-Hopf one. Furthermore, periodic bifurcation delay behaviors are found when the time-varying parameter slowly passes through the critical point of Hopf bifurcation, which results into spiking state (SP) delay behaviors. The detailed delay phenomena as well as their mechanisms are exhibited by theoretical analysis and numerical simulation. |
| [27] | . This paper investigates the generation of some novel bursting patterns in active control oscillator with multiple time delays. We present the bursting patterns, including symmetric codimension one and |
| [28] | . |
| [29] | . We present a general method for analyzing mixed-mode oscillations (MMOs) in parametrically and externally excited systems with two low excitation frequencies (PEESTLEFs) for the case of arbitrary m:n relation between the slow frequencies of excitations. The validity of the approach has been demonstrated using the equations of Duffing and van der Pol, separately. Our study shows that, by introducing a slow variable and finding the relation between the slow variable and the slow excitations, PEESTLEFs can be transformed into a fast-slow form with a single slow variable and therefore MMOs observed in PEESTLEFs can be understood by the classical machinery of fast subsystem analysis of the transformed fast-slow system. |
| [30] | |
| [31] | . |
| [32] | . By introducing subcircuit module and taking suitable values for the parameters as well as the characteristics of the nonlinear resistance, a four-dimensional generalized Hartley model whose fast subsystem has multiple balances is established. Based on the multiple balances as well as stabilities of the fast subsystem, bifurcation sets are derived, which divide the parameter space into different regions. In each region, nonlinear dynamical behaviors as well as the bifurcation patterns corresponding to different critical conditions are obtained. Two typical cases with different bifurcations are investigated, in which two different bursting oscillations with multiple balances of the fast subsystem involved are presented. Combining with the bifurcation analysis of the fast subsystem, the mechanism of the alternation between quiescent state and the spiking state is explored, which reveals that multiple balances of the fast subsystem not only may cause multiple quiescent states and spiking states to involve a periodic burster simultaneously, but also may lead to the multiplicity of patterns of bursting oscillations. . By introducing subcircuit module and taking suitable values for the parameters as well as the characteristics of the nonlinear resistance, a four-dimensional generalized Hartley model whose fast subsystem has multiple balances is established. Based on the multiple balances as well as stabilities of the fast subsystem, bifurcation sets are derived, which divide the parameter space into different regions. In each region, nonlinear dynamical behaviors as well as the bifurcation patterns corresponding to different critical conditions are obtained. Two typical cases with different bifurcations are investigated, in which two different bursting oscillations with multiple balances of the fast subsystem involved are presented. Combining with the bifurcation analysis of the fast subsystem, the mechanism of the alternation between quiescent state and the spiking state is explored, which reveals that multiple balances of the fast subsystem not only may cause multiple quiescent states and spiking states to involve a periodic burster simultaneously, but also may lead to the multiplicity of patterns of bursting oscillations. |
| [33] | . Classification of the dynamical mechanisms that support bistability between bursting oscillations and silence has not yet been clarified in detail. The purpose of this paper is to demonstrate that the coexistence of a stable equilibrium point with a state of continuous bursting can occur in a slightly modified, biophysical model that describe the dynamics of pancreatic beta-cells. To realize this form of coexistence, we have introduced an additional voltage-dependent potassium current that is activated in the region around the original, unstable equilibrium point. It is interesting to note that this modification also leads the model to display a blue-sky catastrophe in the transition region between chaotic and bursting states. |
| [34] | . 不同尺度耦合系统存在的复杂振荡及其分岔机理一直是当前国内外研究的热点课题之一. 目前相关工作大都是针对单频周期激励频域两尺度系统,而对于含有两个或两个以上周期激励系统尺度效应的研究则相对较少. 为深入揭示多频激励系统的不同尺度效应,本文以修正的四维蔡氏电路为例,通过引入两个频率不同的周期电流源,建立了双频1:2周期激励两尺度动力学模型. 当两激励频率之间存在严格共振关系,且周期激励频率远小于系统的固有频率时,可以将两周期激励项转换为单一周期激励项的函数形式. 将该单一周期激励项视为慢变参数,给出了不同激励幅值下快子系统随慢变参数变化的平衡曲线及其分岔行为的演化过程,重点考察了3种较为典型的不同外激励幅值下系统的簇发振荡行为. 结合转换相图,揭示了各种簇发振荡的产生机理. 系统的轨线会随慢变参数的变化,沿相应的稳定平衡曲线运动,而fold分岔会导致轨迹在不同稳定平衡曲线上的跳跃,产生相应的激发态. 激发态可以用从分岔点向相应稳定平衡曲线的暂态过程来近似,其振荡幅值的变化和振荡频率也可用相应平衡点特征值的实部和虚部来描述,并进一步指出随着外激励幅值的改变,导致系统参与簇发振荡的平衡曲线分岔点越多,其相应簇发振荡吸引子的结构也越复杂. . 不同尺度耦合系统存在的复杂振荡及其分岔机理一直是当前国内外研究的热点课题之一. 目前相关工作大都是针对单频周期激励频域两尺度系统,而对于含有两个或两个以上周期激励系统尺度效应的研究则相对较少. 为深入揭示多频激励系统的不同尺度效应,本文以修正的四维蔡氏电路为例,通过引入两个频率不同的周期电流源,建立了双频1:2周期激励两尺度动力学模型. 当两激励频率之间存在严格共振关系,且周期激励频率远小于系统的固有频率时,可以将两周期激励项转换为单一周期激励项的函数形式. 将该单一周期激励项视为慢变参数,给出了不同激励幅值下快子系统随慢变参数变化的平衡曲线及其分岔行为的演化过程,重点考察了3种较为典型的不同外激励幅值下系统的簇发振荡行为. 结合转换相图,揭示了各种簇发振荡的产生机理. 系统的轨线会随慢变参数的变化,沿相应的稳定平衡曲线运动,而fold分岔会导致轨迹在不同稳定平衡曲线上的跳跃,产生相应的激发态. 激发态可以用从分岔点向相应稳定平衡曲线的暂态过程来近似,其振荡幅值的变化和振荡频率也可用相应平衡点特征值的实部和虚部来描述,并进一步指出随着外激励幅值的改变,导致系统参与簇发振荡的平衡曲线分岔点越多,其相应簇发振荡吸引子的结构也越复杂. |
| [35] | . In this paper, we investigate the emergence of bursting dynamics with complex waveforms and their relation to periodic behavior in typical Van der pol-Duffing equation with fifth order polynomial stiffness nonlinearity, when the external force changes slowly with the variation of time. We exploit bifurcation characteristics of the fast subsystem using the slowly changing periodic excitation as a bifurcation parameter to show how the bursting oscillations are created in this model. We also identify that some regimes of bursting patterns are related to codimension two bifurcation type over a wide range of parameters. A subsequent two-parameter continuation reveals a transition in the bursting behavior from fold/fold hysteresis cycle to sup-Hopf/sup-Hopf or limit point cycle/sub-Hopf bursting type. Furthermore, the effects of external forcing item on bursting oscillations are investigated. For instance, the time interval between two adjacent spikes of bursting oscillations is dependent on the forcing frequency. Some numerical simulations are included to illustrate the validity of our study. |
