 ,1,2, 陆林
,1,2, 陆林 ,1, 任以胜3
,1, 任以胜3Evolution and dynamic characteristics of tourism destination complex system from the perspective of nonlinearity: A case study of Shanghai
ZHAO Zan ,1,2, LU Lin
,1,2, LU Lin ,1, REN Yisheng3
,1, REN Yisheng3通讯作者:
收稿日期:2020-03-26修回日期:2021-07-8
| 基金资助: |
Received:2020-03-26Revised:2021-07-8
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
赵赞(1976-), 女, 广西桂林人, 博士, 副教授, 主要从事旅游地理学教学与科研工作。E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (2733KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
赵赞, 陆林, 任以胜. 非线性视角下的上海旅游地复杂系统演化过程及动力学特征. 地理学报, 2021, 76(8): 2032-2047 doi:10.11821/dlxb202108015
ZHAO Zan, LU Lin, REN Yisheng.
1 引言
经济全球化、交通和信息技术变革及互联网的广泛运用,带来了旅游者需求持续增加,旅游业各相关利益主体关系发生本质改变,旅游地发展的复杂性日益增加[1]。传统线性方法对系统各组成部分进行分析,忽略了旅游地的复杂性和动态性[2],已难以适应旅游地发展实践。旅游地是一个复杂的动态系统[2,3],由不同实体(企业、协会等)和资源相互作用并以非平凡和复杂方式满足各类需求,非线性关系、自组织行为、模块化和层次化结构的复杂性是旅游地特征的综合表现[4,5]。由于旅游地系统固有的复杂性,很难对旅游地及其组成部分进行定量分析[6]。对于旅游地系统研究则可能通过记录一些表示系统行为的可观察量,从中得出系统深层结构和动力学特征的暗示[7]。需求在任何企业和行业的生命周期中起着至关重要的作用[8],Butler将接待旅游者的运动(旅游接待人数)视为划分旅游地生命周期的重要指标。旅游者的数量、旅游目的地过夜天数或者花费作为旅游地复杂系统演化的可测变量,被认为是旅游地复杂系统需求方(旅游者)、供应方(旅游地基础设施、旅游企业等)以及一些内部和外部经济因素等诸多组成部分相互作用的结果[9],是旅游地复杂系统行为的重要表征,代表旅游地复杂系统动态演化行为。在目前旅游趋势快速变化时期,运用非线性方法关注以旅游需求为表征的旅游地复杂系统演化阶段“转折点”[10],探究旅游地复杂系统演化过程及动力学特征,使旅游地行动主体充分了解旅游地复杂系统演化的总体趋势方向及阶段性变化时机,对旅游地系统内部及外部环境可能发生的变化做出及时反应,监控管理者决策行为产生的影响,提高旅游地复杂系统演化能力,实现旅游地可持续发展。目前国外****研究主要以混沌理论为主[11],侧重从旅游地相关利益者关系、旅游市场、旅游地活力等方面探讨旅游地复杂系统的复杂性及动态演化特征研究[2, 10, 12-13];国内****主要从一般系统论、自组织理论、耗散结构理论、系统动力学、复杂适应系统理论等诠释旅游地演化的过程和机制,侧重从旅游供求周期振荡性和分布结构的分离[14,15]、系统有序性[16]、空间要素的集聚扩散及极化[17]、系统内外各要素的相互作用及交互关系[18,19],划分旅游地演化过程,探索旅游地系统的整体性、有机性、动态性、非平衡性等特征。在研究方法上,国内外研究以定性分析为主,定量分析较少,不利于探究旅游地系统复杂行为的动态变化过程,揭示旅游地系统演化的本质。国外虽有少数****采用定量研究[10, 12],但涉及旅游地实证研究较少,普适性不强。复杂系统演化的定量研究主要是利用Lyapunov指数、Hurst指数、分形维数、符号离散化等方法对系统可观测变量的时间序列进行非线性分析,并利用熵值测量其系统的复杂度[20]。这些方法通过对复杂系统进化轨迹的时间离散化来测量系统某些动态特性,分析结果主要依赖研究人员的经验和知识,并不总是能够依据完整和严格的定义得到清晰、明确的系统特征。
上海作为中国改革开放和现代化发展的前沿城市,不断发展的国际大都市,在迈向卓越全球城市过程中,对世界著名旅游城市的建设起着示范性作用。本文以上海为案例地,采用水平可视图算法,将旅游需求作为旅游地复杂系统动态行为表征,定量识别旅游地复杂系统演化阶段转折点,明析旅游地复杂系统演化的动力学特征,揭示旅游地复杂系统阶段性进化的“关键要素”,减少旅游地演化分析主观性,充实和完善旅游地发展规律研究理论和实践体系。
2 理论背景与研究方法
2.1 旅游地是一个复杂系统网络
旅游地系统是由广泛参与的当地行动者作为“共同生产者”存在的实体,具有分散结构[21]。当地行动者包括住宿企业、旅游景点、旅游公司、政府机构和旅游办事处以及社区代表。行动者之间复杂、动态的互动关系,容易受到外部冲击影响,其共同目的是为旅游地创造整体旅游产品,为旅游者提供“一篮子”服务。当地行动者的统一协调是旅游地管理的基本要素,治理成效高度影响旅游地发展[22],是旅游地竞争力的根本和可持续发展的保障。行动者之间的连接主要通过不同类型的业务关系(政策、商业、所有权)或者通过个人连接(家庭、友谊、信任)[23]。这些连接增加了旅游业和非旅游业活动中行动者的社会资本[24,25],但很难明确定义旅游地内部关系及连接的强度;连接具有的非线性特征,创造了旅游地复杂系统[12]。旅游地复杂系统是由多个适应性主体相互作用形成的复杂适应系统,包括主体系统、旅游吸引物子系统、旅游服务设施子系统和外部环境系统[18]。不同时空尺度下,旅游地复杂系统通过自组织功能,配备与之相适应的结构(具有模块化和自相似性)进行资源优化配置,适应系统内外环境的变化。旅游地复杂系统可以描述为由一组相互连接、相互作用节点组成的复杂系统网络,当地企业、政府、非政府组织、当地居民等地方行动主体是节点,它们之间的相互作用或关系是链接[2, 4]。节点代表“分散”的资源和服务,是旅游产品的组成部分;链接是“动员”这些资源以创造旅游地的产品[26];网络代表旅游地复杂系统结构,也可以表示复杂系统演化过程和状态(如解释节点为某状态,链路作为转换方式)[12, 27]。旅游地复杂系统网络演化过程,由节点之间链路变化引起,表现为网络中的不连续性[28]。通过对系统可测变量时间序列的相似数据进行分组,分析网络中具有不同结构“社团”;社团表示为网络的模块、类、群组,被定义为网络节点的子集,其连接密度高于网络的其他节点[29]。经济或商业数据的时间序列网络中,属于同一社团的节点代表具有相同经济动力或属于同一商业周期时期;而对于旅游地复杂系统网络,同一社团的节点则代表处于旅游地复杂系统演化的同一阶段[10]。转折点作为网络社团之间的边界节点,起着中介枢纽作用,是旅游地复杂系统可测变量时间序列中的“突破”,即一个旧阶段结束,一个新阶段开始。转折点与社团中众多节点相连,对周围节点行为有较高影响力,是系统动力重构的节点[30],旅游地发展过程的重要时间点。
在非线性作用下,旅游地复杂系统可能从完全有序和稳定的阶段发展到高度不稳定和不可预测的混沌阶段[31]。混沌是非线性动力系统中出现的一种确定性、貌似无规则的运动,既不是简单的无序,也不是简单的有序,而是一种无序中的有序,一种高级的有序态[32];具有内在随机性与确定性结构,是有序与无序、稳定性与不稳定性的统一,有序系统演化的新方向。旅游地复杂系统到达有序与混沌相交临界点——任何有新事物涌现的地方——一切都是突显和未定的,Langton称为“混沌边缘”“进化”的开始[33],一个“趋向混沌的转变”“混沌的边界”“混沌的开始”的复杂区域[31],也是最具活力和创新的区域。此时系统原有属性和结构趋于瓦解,随着系统整体“涌现”行为完成,新的属性和结构将产生,旅游地复杂系统向更高级秩序跃升,实现简单到复杂的演化过程。当旅游地复杂系统越过混沌边缘,呈现混沌无序行为,则需通过混沌控制,有效调节导致旅游地复杂系统混沌的主要参量,实现系统从混沌无序向有序态转化。旅游地行动主体应具有足够的动态适应性和主观能动性,采取有效行动决策,避免违背系统自组织趋势,促进系统新的有序和稳定阶段的生成[34]。运用非线性方法研究旅游地系统演化过程及动力学特征,发挥系统自组织功能和适应性主体非线性作用,适应和创造旅游地复杂系统演化有利环境,是旅游地科学预测和调控的前提。
2.2 水平可视图算法
近年来复杂网络理论被引入时间序列分析研究。Lacasa等提出可视图算法(Visibility Graph, VG)将时间序列映射成图,被认为建立起时间序列分析、非线性动力学和图论之间的桥梁[35],受到学术界广泛关注。Luque等在可视图算法基础上提出了一种具有更少统计量的方法——水平可视图算法(Horizontal Visibility Graph, HVG)[36]。2.2.1 原理 水平可视图算法可将任意时间序列转化为全连通网络,网络中心节点对应于时间序列数值特别大的数据,映射后的网络图继承了时间序列的结构、周期性,随机、分形和混沌时间序列映射为具有不同拓扑结构的网络,网络结构的统计特性保留反映了原时间序列的非线性动力学信息[37]。
原理:X={xi}(i =1, 2, …, n)是一个具有n个观察值的时间序列,每个点画垂直柱形条,每个柱形条都链接到所有可以与水平段连接而不与任何其他中间柱形条相交的水平线。如果每个中间值Xk满足条件:
图1
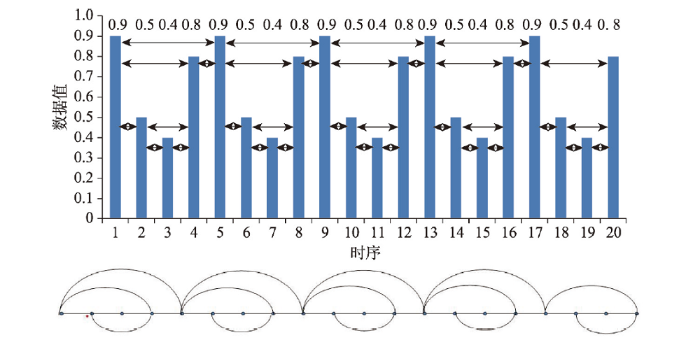 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1水平可视图建网[36]
Fig. 1Horizontal visibility graphs
2.2.2 随机时间序列与混沌时间序列 时间序列结构在映射网络图的拓扑中是守恒的:周期性时间序列映射为正则网络图,度分布服从离散度分布;分形时间序列映射为无标度网络图,度分布服从幂律度分布;随机时间序列和混沌时间序列则都可映射为指数度分布的水平可视图网络,即网络节点度分布遵循指数分布(累加分布在半对数坐标下大致呈直线),网络的度分布为P(k)= e-λk,其中k表示度,λ为率参数。λc = ln(2/3) = 0.405在随机和混沌过程之间起着有效边界的作用,将稳定状态与混沌状态分开:λ<λc表现为混沌过程,系统不稳定且难预测;λ>λc对应相关随机过程,系统稳定、有序且预测性强;λ=λc则对应于不相关随机过程[38]。随机过程和混沌过程具有许多共同特征,它们之间区别非常微小:混沌过程具有有限维吸引子,能够重构吸引子,具有“内在随机性”,时间序列由确定非线性动力系统生成;随机过程产生于无限维吸引子,时间序列是由随机动力系统生成[39]。水平可视图算法在混沌和随机时间序列的检测中具鲁棒性和可靠性,对于混沌与随机时间序列及噪声系统的检测优于其他常用方法[40]。
水平可视图算法计算简单,原理清晰易懂,且考虑所研究现象的非线性特征,在自然、社会和经济系统被广泛应用,如股票市场指数、汇率、宏观经济指数、人类行为、飓风的发生或湍流系统耗散率[41,42,43],也开始有效地应用于旅游地系统的复杂性特征和演化阶段研究[10, 12]。旅游地系统作为具有强大自组织能力和复杂行为的动态经济系统,采用线性指标或方法,假设系统行为的连续性和高预测性,通常与现实相矛盾,甚至破坏系统。目前常用的社会网络分析法,收集和分析数据较为困难,并受到特定方法限制(仅是基于一年的定量和定性分析,创建的仅是特定时间的“快照”),难以提供旅游地复杂系统演化的整个网络动态变化过程[12]。水平可视图算法将表征旅游地复杂系统行为的时间序列映射成水平可视图网络,运用成熟的网络理论描述旅游地复杂系统随时间变化的整体动态演变过程、系统非线性复杂行为及可能存在的优先进化路径,为管理和预测系统行为,以某种方式进行有效干预,提高旅游地复杂系统演化能力提供了可能。
3 数据来源与处理
本文借鉴Baggio[10]和Sainaghi[12]采用月度接待旅游者统计人数作为旅游需求指标,表征旅游地复杂系统动态行为的方法,以上海文旅局官网发布的月度接待旅游者统计人数为研究数据。由于上海文旅局发布的月度接待旅游者统计人数仅包括接待入境旅游者人数和旅行社接待国内游客人数,本文以《上海旅游年鉴》年度接待入境旅游者和国内游客的总人数作为补充和验证。本文收集4组的时间序列为:2004年1月—2018年6月接待入境旅游者人数174个月度统计数据(INT);2008年4月—2018年6月接待国内旅行社旅游者人数122个月度统计数据(DOM);2008年4月—2018年6月接待旅游者人数122个月度统计数据(Month,接待入境旅游者人数和旅行社接待国内游客人数总和);1998—2017年接待旅游者人数20个年度统计数据(Year,接待入境旅游者人数和国内游客人数总和)(图2)。图2
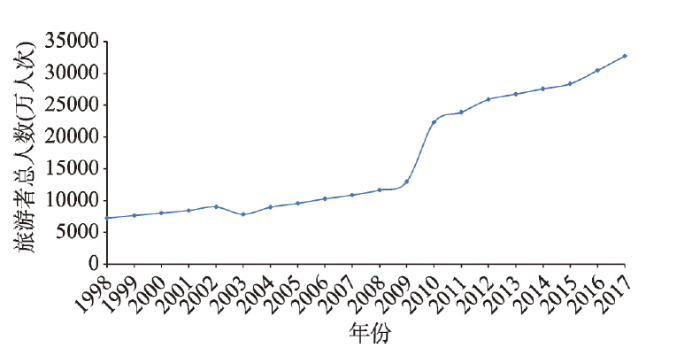 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图21998—2017年上海接待旅游者总人数
注:数据来源《上海旅游年鉴》。
Fig. 2The number of tourists in Shanghai in 1998-2017
本文运用Python、Pajek及Matlab等软件,分析基于水平可视图算法的上海接待旅游者人数4组时间序列网络结构特征。为了更好进行比较分析,本文将上海4组时间序列网络特征与随机序列(Rnd,相关随机过程)、布朗运动时间序列(Fbm,一种白噪声,表示不相关随机过程)、逻辑斯谛方程(Lgst)和洛伦兹方程(Lorenz)两个典型混沌序列进行比较,考察上海旅游地复杂系统演化动态行为的非线性特征。4组比较时间序列的度分布指数,采用十次随机生成结果的平均数,并计算变异系数。
旅游地复杂系统同一演化阶段的网络节点具有相同动态特征,在网络中表现为同一社团。网络社团结构划分可以采用多种方法,比如频谱划分、层次聚类,但它们通常对特定类型问题表现良好,在一般情况下表现不佳[10]。模块化表现为网络属性,是网络社团划分的主要方法。本文采用Newman和Grivan的模块化算法对上海4组时间序列水平可视图网络划分社团结构,计算网络模块度,进行模块化分析:
式中:eii是模块i中任意两个节点之间网络边缘的分数;ai是源自它链路的总分数,以及连接属于不同节点的节点[44]。模块度Q值是一个归一化数量,其假定值从0到1,其中0表示没有模块,1表示分成完全分离的组。模块化Q值越大,表明网络具有较强的聚类性质,不同模块定义越清晰,复杂网络社区结构越明显[45],旅游地复杂系统演化不同阶段的分离越清晰。该算法根据网络图拓扑结构迭代计算边介数度量值,为最大限度提高模块化程度,社团边界节点被移动到相邻社团[46]。
基于观测值可见性连接的水平可视图时间序列复杂网络,模块间转折点介数高,可见度强,在社团内和社团间比其他节点具有更多链接数量,是网络社团结构的“网络星(Network Stars)”,代表系统随时间变化的规律及发展趋势[47,48]。上海旅游地复杂系统演化具有不可逆性,网络中各节点按时间先后顺序演进,数字代表系统时间序列的具体时间,不同颜色表示不同结构的社团;识别网络社团间转折点,划分上海旅游地复杂系统演化阶段,分析系统复杂的时序演变趋势,从小尺度层面刻画上海旅游地复杂系统阶段性演化的波动结构及特征,能够更好地从网络理论理解旅游地复杂系统演化趋势背后的“力量”,探索影响系统演化趋势的关键要素,揭示旅游地复杂系统长尺度的时序进化规律。
4 结果分析
4.1 上海旅游地复杂系统演化的非线性动力学特征
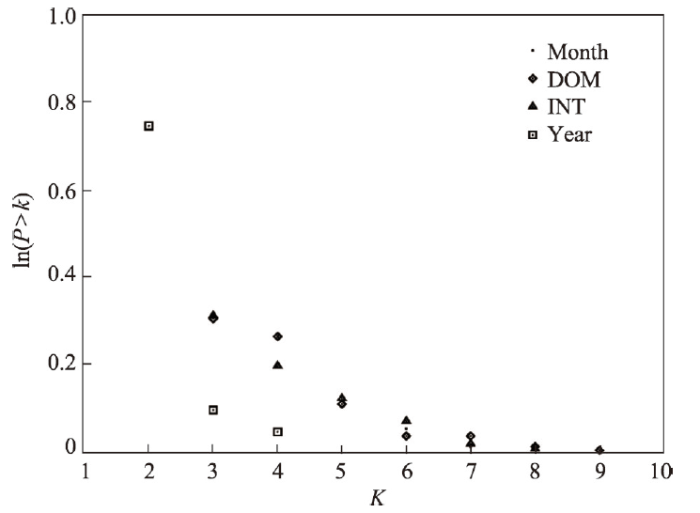
4.1.1 上海旅游地复杂系统演化的复杂网络统计特征 运用水平可视图算法,将上海旅游地复杂系统4组时间序列的观测值映射到复杂网络,提取相关图度分布(图3)。上海旅游地复杂系统4组时间序列相关图的度分布以及结构特征相类似,节点度的累加分布在半对数坐标下都大致呈直线,4组时间序列相关图度分布遵循指数分布形式。为了进一步验证,采用累积概率分布函数对4组时间序列相关图的度分布进行描述(图4),4组时间序列相关图的度分布拟合近似幂律分布函数(相关系数大于0.75),但指数分布函数相关系数更高(近乎为1),表现为指数度分布特征的水平可视图网络,网络度分布表示为图3
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图3Month、INT、DOM和Year时间序列的度分布
Fig. 3Degree distribution for Month, INT, DOM and Year time series
图4
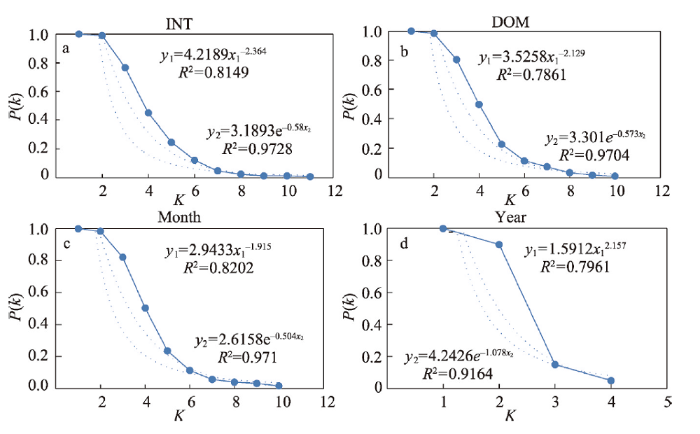 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图4度值累积概率分布图
Fig. 4Cumulative probability distribution value of degree value
对4组时间序列相关图的平均路径长度(L)与聚类系数(C)进行统计(表1),与同等规模(相同节点和边数)随机网络比较,随机网络平均路径长度(Lrond)与聚类系数(Crond)采用十次随机生成结果的平均数并计算变异系数。4组时间序列水平可视图网络都满足小世界网络特征L ≥ Lrond且C ≥ Crond[49],表明上海旅游地复杂系统演化具有小世界特性,近似无标度网络(幂律分布),网络度分布遵循指数分布形式。
Tab. 1
表1
表14组时间序列的小世界特性指标表
Tab. 1
| 时间序列 | L | Lrond (变异系数) | C | Crond (变异系数) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | 5.637 | 3.677(0.015) | 0.588 | 0.030(0.242) |
| Year | 6.289 | 3.159(0.155) | 0.130 | 0.119(0.181) |
| DOM | 6.195 | 3.752(0.021) | 0.594 | 0.031(0.150) |
| INT | 9.390 | 4.035(0.015) | 0.580 | 0.024(0.251) |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
4.1.2 上海旅游地复杂系统演化的非线性动态行为特征 分析上海旅游地复杂系统演化非线性动力学特征,将Month时间序列的网络度分布指数拟合线(斜率)与Rnd、Fbm、Lgst、Lorenz序列进行比较(图5),发现Month与Lgst、Lorenz两个混沌时间序列的度分布指数拟合线特征大致相同,具有混沌时间序列的动态行为特征。
图5
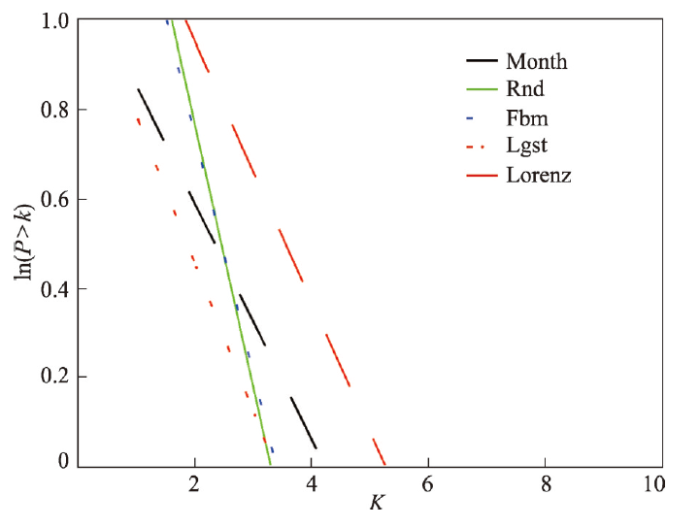 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图5Month、Rnd、Fbm、Lgst和Lorenz度分布指数拟合线比较
Fig. 5Comparison graphs of exponential fitting to the degree distributions for Month, Rnd, Fbm, Lgst and Lorenz
4组时间序列水平可视图网络与4组比较时间序列水平可视图网络度分布指数λ及95%置信区间,并进行显著性检验(表2)。由于年度时间序列数据较少,网络度分布数值较少,度分布指数λ线性拟合优度稍差,显著性稍弱。4组比较时间序列的十次随机生成结果的变异系数不大(表2),表明十次随机生成结果的离散程度较小。从4组时间序列的度分布指数λ的数值来看,Month、INT、DOM水平可视图网络度分布指数λ<λc,Year水平可视图网络度分布指数λ近似λc。Rnd(相关随机序列)和Fbm(不相关随机序列)水平可视图网络度分布指数λ>λc,Lgst和Lorenz(混沌序列)水平可视图网络度分布指数λ<λc。
Tab. 2
表2
表2各组时间序列度分布指数及95%置信区间
Tab. 2
| 时间序列 | λ值 | 置信区间(95%) | 变异系数 | Sig(双侧) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | 0.264 | 0.022 | - | 0.000 |
| Year | 0.409 | 0.529 | - | 0.059 |
| INT | 0.201 | 0.016 | - | 0.000 |
| DOM | 0.298 | 0.021 | - | 0.000 |
| Rnd | 0.589 | 0.051 | 0.245 | - |
| Fbm | 0.533 | 0.124 | 0.327 | - |
| Lgst | 0.331 | 0.044 | 0.236 | - |
| Lorenz | 0.291 | 0.058 | 0.277 | - |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
比较8组时间序列水平可视图网络度分布指数λ及95%置信区间和混沌与随机系统区别阈值λc(图6)。Year度分布指数λ基本与λc持平,Month、INT、DOM 3组月度时间序列与Lgst、Lorenz 2组经典混沌时间序列所处的位置大致相同。4组时间序列中,Year时间序列水平可视图网络度分布指数λ相当接近0.405,处于混沌边缘区域;Year时间序列与3组月度时间序列相比较,网络节点数据较少,对网络度分布形式具有一定影响,分析结论存在一定程度的时间滞后现象,即上海旅游地复杂系统处于混沌的开始——混沌边缘区域,而其它3组时间序列λ值表明上海旅游地复杂系统演化已越过混沌边缘,处于混沌区域。
图6
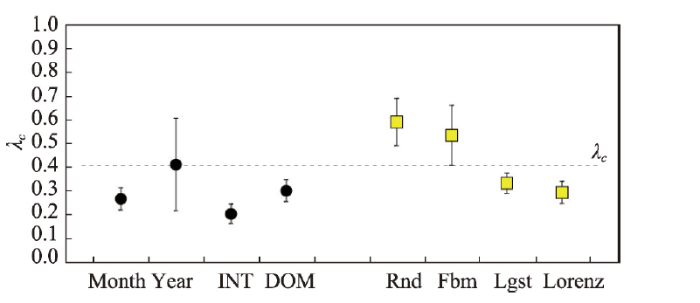 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图6度分布指数
Fig. 6Degree distribution exponents
综合4组时间序列与4组比较时间序列发现,上海旅游地复杂系统的时序演化表征为混沌动态行为特征。系统表现为混沌确定非线性动力系统,在不断运行的均衡过程中,外部环境引入的外部湍流(物流、资金流、人流、信息流及外部环境变化)导致系统熵产生,使系统处于非平衡状态。上海旅游地复杂系统演化处于混沌或混沌边缘,一个快速变化的复杂区域,系统旧的稳定、有序演化阶段已趋于结束,新属性和结构正逐渐涌现,但还处于不稳定的发展状态,有待新演化阶段稳定、高级有序态的生成。
4.2 非线性动力下的上海旅游地复杂系统演化过程
4.2.1 演化过程转折点及演化阶段 Month、Year、INT、DOM 4组时间序列水平可视图网络由有限数量子网络组成(图7),展示了上海旅游地复杂系统演化过程模块化结构及转折点,构建网络的节点被着色进行模块化划分,相同颜色的节点比其它节点更紧密地聚集在一起,形成相互关联的社团结构。Month、Year、INT、DOM 4组时间序列水平可视图网络模块度分别为0.724、0.568、0.757、0.729,表明网络不同社团之间具有良好的分离,上海旅游地复杂系统演化阶段划分较好。图7
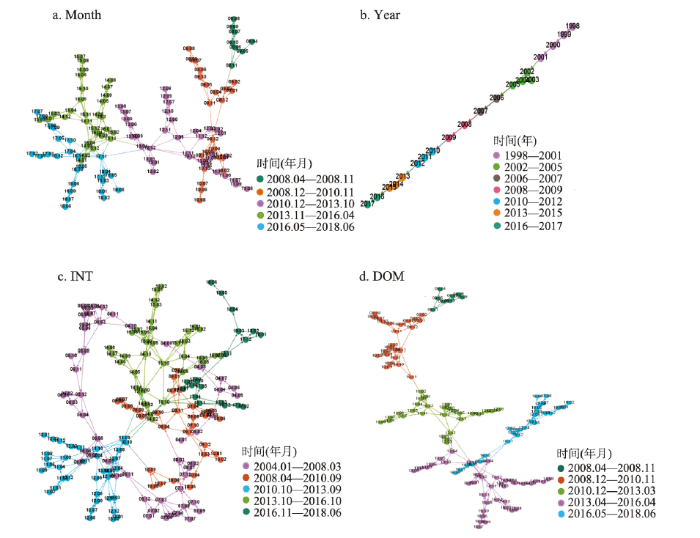 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图7Month、Year、INT、DOM的HVG网络及模块化转折点
Fig. 7HVG network and modularization turning point of Month, Year, INT and DOM
Month、INT、DOM 3组月度时间序列水平可视图网络依据网络模块化时间节点,识别转折点年份相同,为2008年、2010年、2013年和2016年;Year时间序列时间较长,比月度时间序列的转折点增加了2002年和2006年(表3)。6个转折点观测值都位于4组时间序列不同社团周期范围内的较高(低)的峰值处,在结构上与许多其他节点进行交互,对周围节点影响较大。作为社团之间的边界节点,6个转折点的介数高,是网络社团间最短传播路径的必经之处,具有很高的中介中心性,在网络中起到连接器枢纽作用。虽然数据来源有所差异,但4组时间序列水平可视图网络划分具有相似的动态变化特征,即上海旅游地复杂系统演化阶段分析结果一致,可以划分为1998—2002年、2003—2006年、2007—2008年、2009—2010年、2011—2013年、2014—2016年、2017年至今7个演化阶段。
Tab. 3
表3
表3转折点数值和年份
Tab. 3
| 时间序列 | 模块时间节点(年月) | 年份 |
|---|---|---|
| Month | 2008.12,2010.12,2013.11,2016.05 | 2008,2010,2013,2016 |
| Year | 2002,2006,2008,2010,2013,2016 | 2002,2006,2008,2010,2013,2016 |
| INT | 2008.04,2010.10,2013.10,2016.11 | 2008,2010,2013,2016 |
| DOM | 2008.12,2010.12,2013.04,2016.05 | 2008,2010,2013,2016 |
| Month(2013.01—2018.06) | 2013.11,2016.05 | 2013,2016 |
| Year(1998—2013年) | 2002,2006,2008,2010 | 2002,2006,2008,2010 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
进一步验证上海旅游地复杂系统演化过程转折点及动态行为特征,截取Year和Month 2组时间序列前后两段进行分析。Year(1998—2013年)时间序列截取时间从1998—2013年,Month(2013.01—2018.06)时间序列截取时间从2013年1月—2018年6月。Year(1998—2013年)和Month(2013.01—2018.06)2组时间序列水平可视图网络(图8)模块度分别为0.541、0.548,表明识别网络不同社团的分离度比较好。由于网络节点减少,Month(2013.01—2018.06)时间序列比Month时间序列的网络模块度有所降低。Year(1998—2013年)时间序列水平可视图网络转折点为2002年、2006年、2008年和2010年,λ= 0.289;Month(2013.01—2018.06)时间序列水平可视图网络转折点为2013年和2016年,λ = 0.019。Year(1998—2013年)和Month(2013.01—2018.06)2组时间序列与Month、Year、INT、DOM 4组时间序列对上海旅游地复杂系统演化过程转折点及动态行为特征分析相一致(表3)。
图8
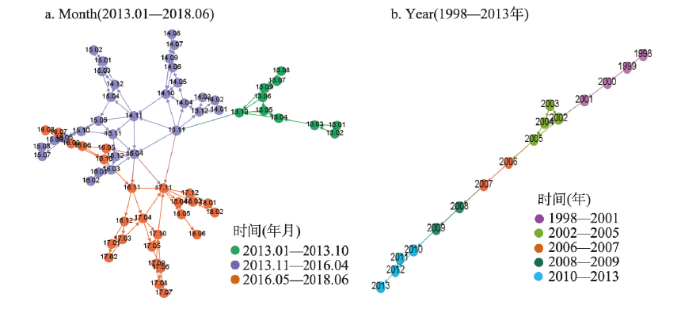 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图8Month(2013.01—2018.06)和Year(1998—2013年)HVG网络及模块化转折点
Fig. 8HVG network and modularization turning point of Month (2013.01-2018.06) and Year (1998-2013)
4.2.2 上海旅游地复杂系统演化阶段特征 结合上海旅游地复杂系统7个演化阶段系统特征、转折点触发事件及主导行动者等要素分析系统演化过程,诠释非线性动力下上海旅游地复杂系统演化不同阶段的“关键要素”。上海旅游地复杂系统演化的6个转折点年度里都相应发生较大的重要事件(表4),除2002年底全国爆发“非典”重大公共卫生事件(2002年底是“非典”酝酿期,2003年上海旅游接待人数增长-13.11%,属“断崖下跌”式转折,非增长性突破,转折点定位于2002年)、2006年由多项重要事件产生综合效应外(这两个转折点是由年度时间序列网络产生,模块度相对较低),其他4个演化转折点都由上海发生的旅游重大事件而“触发”。由此推断,系统内外部的重要事件对转折点起到了“触发”作用,对上海旅游地复杂系统演化过程产生重大影响。政府作为重要事件的主要推动者和举办者、旅游地复杂系统的适应性主体,学习创新能力的提升在旅游地复杂系统演化阶段的跃升过程中起到了“推进器”作用。2016年上海迪士尼开业后,上海旅游地复杂系统的主体系统内部关系由“政府主导”向“企业主导、政府引导”转变,旅游企业在上海旅游地复杂系统演化中开始显现主导地位,充分发挥了市场主体和机制作用,成为未来推动上海旅游地复杂系统演替发展的重要力量。应加强旅游地规划和管理,增强旅游企业自主创新及国际影响力,适应新常态下旅游发展趋势,适时创造有利环境,促进上海旅游地复杂系统持续稳定、有序演化发展。
Tab. 4
表4
表4上海旅游地复杂系统演化阶段特征
Tab. 4
| 演化阶段 | 系统特征(产业结构、规模、业态等) | 转折点 重要事件 | 主导行 动者 | 子系统 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1998—2002年 | 旅游业实现“外事接待型”向“经济产业型”转变,成为国民经济新的增长点。以都市旅游观光产品为主,商业、休闲旅游逐步成为都市旅游重要组成部分,会展、工业、农业旅游新兴业态得到一定发展。“非典”疫情爆发后,旅游者人数明显下降。 | 2002年“非典”疫情爆发 | 自然 环境 | 外部 环境 |
| 2003—2006年 | 都市旅游发展格局初步确立,传统观光旅游、工业旅游、农业旅游、休闲度假旅游、会展旅游进一步发展。通过“两节三赛”,创新旅游产品,中国旅游交易会及上海旅游节等节庆活动发展为国际性大型旅游节,上海向国际性大都市迈进,接待旅游者人数呈明显上升态势。 | 2006年举办多项世界国际性活动赛事 | 政府 | 主体 系统 |
| 2007—2008年 | 以“服务奥运”“迎世博”为契机,推动旅游产业集聚,提升旅游自主创新能力,增强旅游国际竞争力。都市旅游成为上海建设大都市的重要途径和形象品牌,节庆会展旅游更趋势国际化;形成国际、国内旅游共同繁荣局面,接待旅游者人数呈显著增长趋势。 | 2008年北京奥运会足球赛事|分会场 | ||
| 2009—2010年 | 世博会的举办,推动上海多中心、多流向、多圈层旅游格局的形成,旅游业成为上海支柱产业。工业旅游、文化旅游等专项产品不断升级,邮轮旅游、农旅等新型旅游业态蓬勃发展,形成一批具有国际影响力的城市旅游品牌,接待旅游者人数都呈迅速大幅增长态势。 | 2010年举办上海世界博览会 | ||
| 2011—2013年 | 以“创新驱动、转型发展”为主旨,大力发展邮轮旅游,邮轮旅游者人数突破百万人大关,成为上海新兴旅游业态的新增长点,出入境旅游者增长120%。注重旅游与相关产业创新融合,智慧旅游、旅游信息服务等旅游公共服务品质日益提升,形成以旅游业为核心、以服务型经济为主的产业结构。 | 2013年举办首届邮轮旅游节,成立中国邮轮旅游发展实验区 | ||
| 2014—2016年 | 以迪士尼开园为契机,大力创新旅游产品,突出上海都市旅游发展核心,形成“旅游+”十大系列产品,实现了从单一观光、休闲向观光、休闲、度假、商务、会议并重的旅游产业发展方式转变和转型升级,逐步形成“大旅游、大产业”的发展格局。 | 2016上海迪士尼开业 | 企业 | |
| 2017年— | 迪士尼溢出带动效应显著,“本土第一、世界精品”的黄浦江旅游休闲区、崇明世界生态岛等由外资、民资及社会资本参与的具有国际性吸引力的重点项目不断涌现;旅游“大旅游、大市场、大产业”产业融合格局基本形成,并由“景区旅游”向“全域旅游”发展格局转变。 | - |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
4.3 上海旅游地复杂系统演化动力行为的影响因素
复杂系统观测变量时间序列的构成是影响系统演化动力行为的重要因素。通过分析接待旅游者人数构成,揭示影响上海旅游地复杂系统演化动力行为的核心要素,达到调控系统演化的目的。采用格兰杰因果关系检验分析旅游地接待旅游者人数时间序列各构成部分对总序列的不同贡献。格兰杰因果关系检验是评估时间序列之间相互作用的常用方法,F值表示时间序列各构成部分与总序列的关系强度(F值越高,关系强度与影响越大,贡献越多)[10],对各构成部分在总序列的贡献大小进行排序。上海接待国际入境旅游者人数所占比例为3.44%,F值为19.44;国内旅游者人数所占比例为94.56%,F值为18.68,表明国际入境旅游和国内旅游对上海旅游地复杂系统演化动力行为的影响相当。根据以上方法,进一步确定上海国际入境旅游主要客源国、国内旅游本地游客和外地游客的F值和λ值(表5),分析贡献程度和发展状态。国际入境旅游方面:美国的度分布指数λ>λc,旅游市场处于有序、稳定的可预测状态;其他8个国家的度分布指数λ<λc,旅游市场原有秩序趋势被打破,处于“无序中的有序”混沌态。国内旅游方面:接待本地游客和外地游客F值相差不大,本地游客λ值接近λc,旅游市场处于原有秩序刚瓦解、新秩序正待生成的混沌边缘;而外地游客λ值小于λc,旅游市场原有秩序已瓦解,处于新秩序还未稳定的混沌复杂区域。因此,国际入境旅游主要客源国及国内旅游外地游客市场处于新秩序尚未稳定的混沌区域,是上海旅游地复杂系统混沌动态行为特征的重要影响因素。应加强管理和引导国际入境旅游和国内外地旅游市场有序、稳定发展,采取相应措施进行混沌控制,促进上海旅游地复杂系统新演化阶段有序态生成。
Tab. 5
表5
表5上海国际入境、国内旅游各构成时间序列Granger F值和度分布指数
Tab. 5
| 构成 | 占比(%) | F值 | λ值 | 置信区间(95%) | sig.(双侧) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 国际 入境 旅游 | 新加坡 | 3.18 | 41.38 | 0.208 | 0.055 | 0.000 |
| 英国 | 2.68 | 23.40 | 0.080 | 0.064 | 0.000 | |
| 德国 | 3.74 | 20.30 | 0.278 | 0.061 | 0.000 | |
| 澳大利亚 | 2.55 | 13.06 | 0.076 | 0.058 | 0.049 | |
| 加拿大 | 2.37 | 11.22 | 0.101 | 0.064 | 0.029 | |
| 法国 | 2.66 | 10.65 | 0.028 | 0.059 | 0.010 | |
| 韩国 | 9.12 | 7.73 | 0.063 | 0.055 | 0.032 | |
| 日本 | 15.12 | 6.93 | 0.132 | 0.064 | 0.019 | |
| 美国 | 9.94 | 3.74 | 0.438 | 0.057 | 0.010 | |
| 国内 旅游 | 国内本地游客 | 42.34 | 19.69 | 0.409 | 0.205 | 0.059 |
| 国内外地游客 | 57.66 | 20.43 | 0.109 | 0.150 | 0.037 | |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
5 结论与讨论
5.1 结论
以非线性为视角,采用水平可视图算法,将旅游需求作为旅游地复杂系统动态行为表征,把接待旅游者人数的时间序列映射为复杂网络,探究上海旅游地复杂系统演化的动力学特征,分析上海旅游地复杂系统演化过程,结论如下:(1)旅游地复杂系统演化具有小世界和近似无标度网络特性,表征为复杂的混沌动态行为特征,是一个混沌确定非线性动力系统。上海旅游地复杂系统的4组时间序列水平可视图网络λ值小于或接近λc,表明上海旅游地复杂系统演化处于非平衡态下的混沌或混沌边缘的复杂区域,系统旧的有序、稳定演化阶段已趋于结束,新的属性和结构逐渐涌现,有待新演化阶段稳定、高级有序态的生成。
(2)旅游地复杂系统遵循“有序—混沌(边缘)—涌现—新有序”,从低级有序向高级有序演化跃升的过程。上海旅游地复杂系统演化过程的6个转折点,社团结构的网络星,网络结构的连接器枢纽,代表系统随时间变化的规律和趋势,揭示了外部环境和主体系统主导下的重要事件是旅游地复杂系统由低级有序向高级有序演进的“关键要素”。政府作为旅游地复杂系统重要的适应性主体,学习创新能力的提升对系统阶段性演进起到了“推进器”作用。旅游企业作为市场机制主体,在系统演化中开始显现主导地位,成为未来推动上海旅游地复杂系统演替发展的主导力量。
(3)上海国际入境旅游主要客源国(日、韩、新、德、英、法、加、澳)和国内旅游外地游客市场处于不稳定的混沌区域,是影响上海旅游地复杂系统混沌动态行为特征的重要因素。上海应加强管理和引导国际入境旅游和国内外地旅游市场有序、稳定发展,采取相应措施进行混沌控制,促进上海旅游地复杂系统新演化阶段有序态的生成。
5.2 讨论
如何定量精准地刻画与研判旅游地演化是旅游地理学长期探索亟待突破的研究议题[17,18]。本文运用水平可视图算法将表征旅游地复杂系统动态行为的时间序列映射为复杂网络,使系统科学、非线性动力学和和网络科学相结合,采用成熟复杂网络分析法诠释旅游地复杂系统随时间变化的演化规律,尝试搭建网络科学与旅游地生命周期理论之间的桥梁,为旅游地演化研究提供一种新的分析框架。水平可视图算法重在关注旅游地阶段性演进中系统复杂的非线性动态行为特征,能够从长尺度探索旅游地复杂系统演化趋势分期规律,在小尺度刻画系统时序上的阶段性演进和波动性成长过程,准确客观判别系统不同演化阶段的发展特征。该算法对于在时序演化中探究系统阶段性演进的“关键要素”和“关键力量”,甚至对预测未来趋势提供了可能性;也为经典的旅游地演化理论更加精准有效地协助管理者在旅游地采取适应性管理与调控提供了方法技术支持。值得注意的是水平可视图算法较传统旅游地生命周期理论,识别旅游地复杂系统演化过程转折点较为“敏感”和“细粒度”[12]。除了与非线性时间序列包含的复杂性和非线性微观细节信息有关之外[50,51],这也与1998年以来上海游客量总体上呈高增长趋势,即水平可视图网络具有较强活力有关。但正如Baggio所述这种局限性并没有降低实证研究结论的价值,水平可视图算法可能具有较广的运用前景[10]。未来可以尝试基于复杂网络科学与地理信息科学集成的方法,从时间序列上深入探索旅游地复杂系统时空演化过程及动力学特征。另外,本文使用游客量的单一数据且国内散客月度统计数据缺失都会导致研究结论的局限与偏颇。未来可探索挖掘不同的时间序列和多元类型的综合数据以验证本文研究结论,推动旅游演化的复杂网络科学研究。
上海城市旅游发展长期以来具有独霸性的产业特征[52,53]。但作为中国最大的综合性大都市,其旅游演化过程与机理极为错综复杂,导致传统的定量或定性研究方法难以从全局性和整体性上进行有效地分析与探索。本研究通过复杂网络科学的技术方法寻求研究突破,首次对上海旅游发展在长尺度上的演化及小尺度上的阶段性演进的过程进行细致刻画,揭示了综合大都市旅游业发展从无到有、从弱到强、从低级到高级的复杂演化规律。研究显示上海的旅游地复杂系统演化表征为混沌动态行为特征,这与意大利米兰案例的研究发现相一致[10],但与意大利特兰托和博尔扎诺的研究发现“系统很复杂,但远离混沌阈值”有明显差异[12]。作为世界知名的国际性大都市,上海和米兰的旅游地系统更为庞大和复杂,包含了商务、观光度假、会展事件以及医疗、探亲等多种旅游子系统。但城市旅游地复杂系统的混沌态是否与城市首位度相关,以及受到都市系统哪些具体因素作用影响则需要进一步探索与验证。
致谢
中山大学地理科学与规划学院张海洲博士研究生在文章修改过程中提供了帮助,在此表示感谢!参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.1080/14616688.2012.675581URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3727/108354208784548797URL [本文引用: 4]
DOI:10.1016/j.tourman.2013.08.004URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.annals.2010.02.008URL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1146/annurev.anthro.32.061002.093440URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1147/sj.423.0462URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2307/1883410URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/per.2003.8.issue-3URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.tourman.2015.10.008URL [本文引用: 10]
DOI:10.1016/j.tourman.2014.09.011URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.tourman.2017.07.004URL [本文引用: 9]
DOI:10.1016/j.tourman.2012.04.009URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2012.09.1066 [本文引用: 2]

By constructing the basic mode of tourism spatial evolution, this article analyzes the evolution progress of Guilin-Lijiang River-Yangshuo tourism destination system. The evolution progress of tourism destination system is divided into 3 stages (the embryonic stage, the polarization stage and the optimization stage), which shows different characteristics (homogeneous development, polarization development, proliferation development) respectively, and tends to plate development stage. Before 1978, the tourism destination was in the stage of homogeneous development when the destination system was in the embryonic statement. The original landscape provided a good foundation for tourism development, but during this period, tourism space structure was in the low homogeneous disordered state, and the scenic spots have not been effectively developed. The following 20 years has experienced the polarization process, which can be divided into the early polarization evolution marked by the formation of the tourism growth pole of Guilin City and late polarization evolution stage marked by the formation of Guilin City-Lijiang River-Yangshuo tourism destination system. In the early polarization evolution stage, with the driving of tourism demand, Guilin City had a rapid development as the tourism growth pole, and provided a good infrastructure and service facilities for the tourism of Lijiang River. It played a role of the organization for the regional tourist development. During the late polarization evolution stage, Yangshuo County had a good development as the new growth pole, Guilin City further strengthened tourism function, Lijiang River was developed as tourism corridor. Guilin City-Lijiang River-Yangshuo tourism spatial system was formed basically. During the 11th Five-Year Plan, the tourism destination was in the proliferation stage. The tourism impact diffused at this stage and pushed the transformational development of the tourism destination. Meanwhile, the shape of regional tourism plate was initially formed. Travel city and scenic sites were increasingly interconnected, and a more coordinated Guilin City-Lijiang River-Yangshuo tourism system promoted the formation and development of a higher level of tourism spatial system, which can be called the tourism spatial system, or North Guangxi tourism board. This article analyzed the dynamic mechanism of the evolution and considered that there were varies leading dynamic mechanisms at different times. In the homogeneous development stage, the tourism resources endowment had played a decisive role. The dominating dynamic factor in the development stage of polarization was affected by circulation accumulation, and different types of demand had become the main power for construction. In the proliferation stage, the pursuit of overall efficiency has become the dominant force.
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201606012 [本文引用: 3]

According to the complex adaptive system theory, the tourism destination can be regarded as a complex adaptive system which is composed of multiple adaptive agent interactions based on the complex adaptive system theory, and it consists of agent system, tourist attraction subsystem, tourist service facility subsystem and external environment system. This article, taking southern Anhui as a test case, discusses the spatial evolution. Some conclusions can be drawn as follows. (1) The period 1979-1990 was a formation stage of spatial aggregation, during which the tourist attraction was gradually exploited and aggregated. Additionally, the scenic area of Mounts Huangshan and Jiuhuashan became the core attraction, and the agglomeration around the area began to appear. (2) The period 1991-2000 was a growth stage of spatial aggregation, during which the scenic area of Mounts Huangshan and Jiuhuashan expanded and the tourism facility improved, so the spatial aggregation began to grow. At the same time, the scenic area of Xidi and Hongcun developed quickly, thus a new spatial aggregation emerged. (3) Since 2001, we have entered a blowout-development stage of spatial agglomeration. As the adaptive agent of system, government, enterprise, resident, non-governmental organizations and tourists, they achieved nonlinear interactions with the environment system and each other, which formed new tourist elements of the diversification of tourist demand, diverse tourist attraction and rapid development of expressway and others. The combination of new elements and traditional elements gave birth to diverse tourist product, such as cultural tourism, holiday tourism, rural tourism. It improves spatial evolution of the area of southern Anhui. In the future, the diversification of tourism demand will promote the diversification and global use of tourism resource. The main development will be focused on leisure vacation travel with culture, ecology, rural characteristics. Meanwhile, the construction of high-speed transport network, including railway and highway, will strengthen the communication between southern Anhui and the Yangtze River Delta. As a result, the area of southern Anhui will be taken into the tourism development of the Yangtze River Delta region, and also become an important part of the Yangtze River Delta by global tourism.
[本文引用: 3]
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201810009 [本文引用: 1]

Severe crisis such as architectural landscape destruction, cultural gene loss, settlement space conflict and ecological environment deterioration have aroused widespread concern on transformation of traditional villages' human settlement. Based on complex adaptive system theory, this paper analyzes the systematic characteristics of human settlement from the perspectives of the systematic basic features, structural composition and adaptive mechanism. Composed of natural ecology, social culture, regional space and multi-agent systems, the rural human settlement environment system is a huge open complex system. Compromising multiple objectives, multiple subjects and multiple sub-systems, the system is compatible with complex adaptive system features. With the case of Zhangguying village human settlement evolution studied, the conclusions are shown as follows: (1) At the wavering stage (1978-1988), the villagers' self-organizing development was the leading force of the human settlement evolution. The subject adaptive behavior and the effect of human settlement were both limited. The human settlement evolution of Zhangguying village was still on the accumulative stage of quantitative change. (2) At the transitional stage (1989-2001), strong government intervention was the leading force. This intervention resulted in the complexity of interest relation, high speed transformation of flow elements and uncertainty of systematic evolution. The human settlement evolution of Zhangguying village was on the key stage of qualitative change. (3) At the revulsion stage (2002-till now), interaction of multiple subjects has been the leading force. The intensity and complexity between subjects or between subjects and environment have both increased. Continuous tourism input has led to the dramatic change of the human settlement environment. The transformation of human settlement has been realized. The structure and level of the system have undergone a qualitative leap. In order to promote the orderly development of the traditional villages' human settlement, the paper constructs systematic regulation mechanism from the perspectives of promoting self-adaptive capacity, emphasizing self-organizing reaction, optimizing dominant regulation and introducing social governance. Using complex adaptive system theory to study science of human settlements is still at a groping stage, and it needs to be further improved, which provides innovation space for future research.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/S0261-5177(01)00010-3URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.3727/108354213X13645733247657URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.ijhm.2013.11.004URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.annals.2010.11.015URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1108/IJCHM-05-2014-0236URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.annals.2010.08.008URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1093/jeg/lbm023URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1137/070710111URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.physa.2014.05.058URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1108/09596111111153501URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1073/pnas.0709247105PMID:18362361 [本文引用: 1]

In this work we present a simple and fast computational method, the visibility algorithm, that converts a time series into a graph. The constructed graph inherits several properties of the series in its structure. Thereby, periodic series convert into regular graphs, and random series do so into random graphs. Moreover, fractal series convert into scale-free networks, enhancing the fact that power law degree distributions are related to fractality, something highly discussed recently. Some remarkable examples and analytical tools are outlined to test the method's reliability. Many different measures, recently developed in the complex network theory, could by means of this new approach characterize time series from a new point of view.
URL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.physa.2013.05.012URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.physa.2018.01.010URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1038/30918URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.physa.2016.06.028URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.tust.2019.03.019URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2016.12.013 [本文引用: 1]

On the basis of the geostatistical method and the Origin technology, the article sets up a mathematical model of spatial distribution of and a space-time process model of “city size-tourism growth-city level” on the basis of “revelation and verification of regularity”. A range of basic data of the year 1995-2014 about the urban system in Yangtze River Delta were collected to explore the spatial relations between city size and tourism growth, and the evolution mechanism. The research results showed that: 1) Since 20 years ago, the mathematical and spatial distributions of city size, tourism growth and city level have been demonstrated as three parts in the shape of pyramid, meaning that the higher city level, the less number of city distribution. And this feature is especially applicable to some big cities with flourishing economy and prosperous tourism. 2) In the ternary spatial relations, three stages during 1995-2009 behaved as the line “A” relations of the evolution model, and this feature is very typical like “A” line in the model. In 2010-2014, the relations graph was in the shape of an oval, indicating that tourism growth forced the expansion of city size. In order to achieve tourism economic benefits, cities has realized by way of increased infrastructure. This is also the embodiment of the economic development cycle feedback model. 3) Based on the distribution of cities in 4 basic quadrants, Quarter I is for cities have highest level. With the expansion of city size and the growing tourism, Quarter IV is related to Quarters II and III. 4) The pattern and evolution about the relationship between city size and tourism growth, is a system within three factors. The higher city level, the government has greater efforts with policy system, power allocation, financial support and resources allocation to accelerate the expansion of cities, and then city size effect has been obvious. The analysis of driving factors shows that support policies adopted by governments, city size and rapid tourism growth have jointly contributed to the evolution of the ternary relations.
[本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
