 ,1, 张清源1,2, 黄剑锋1, 任以胜3
,1, 张清源1,2, 黄剑锋1, 任以胜3A theoretical research and prospect of tourism destination evolution based on a glocalization perspective
LU Lin ,1, ZHANG Qingyuan1,2, HUANG Jianfeng1, REN Yisheng3
,1, ZHANG Qingyuan1,2, HUANG Jianfeng1, REN Yisheng3收稿日期:2020-04-28修回日期:2021-03-13网络出版日期:2021-06-25
| 基金资助: |
Received:2020-04-28Revised:2021-03-13Online:2021-06-25
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
陆林(1962-), 男, 安徽芜湖人, 博士, 教授, 博士生导师, 中国地理学会会员(S110000078M), 主要从事旅游地理教学与科研工作。E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (2310KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
陆林, 张清源, 黄剑锋, 任以胜. 基于全球地方化视角的旅游地演化理论探讨与展望. 地理学报[J], 2021, 76(6): 1504-1520 doi:10.11821/dlxb202106013
LU Lin, ZHANG Qingyuan, HUANG Jianfeng, REN Yisheng.
1 引言
近年来,旅游在转变发展方式、优化经济结构、转换增长动力等方面的作用日益凸显,引导资本、信息、技术、人才、管理等全球性流动要素固着于旅游地空间[1],为全球范围内的制度变革、经济交流和文化变迁创造了条件,为地方空间的能级提升、产业发展和资源活化提供了动能[2]。旅游已经成为建立全球—地方联结和加速全球地方化进程的重要力量[3]。与此同时,全球化和地方化的深刻互动是推进旅游地演化的核心动力。一方面,全球化进程推动了地方社会空间生产方式革新[4]。全球化的国际资本、生产标准和文化偏好异化了旅游地传统的社会生产力和生产关系,重构了旅游地地域组织[5]。另一方面,地方为全球化进程提供了必备的设施空间、劳动力和制度保障[6]。旅游地作为一类特殊的地方空间,在空间尺度上与全球尺度存在巨大的尺度张力,在社会属性上与全球化存在巨大的要素差异,全球化带来的现代性与地方化葆有的制度、文化、社会结构之间的碰撞更加激烈。差异性是旅游地吸引力的核心本质,旅游地的差异性根植于地方性,地方性要素在全球化趋势下的合理利用和有效活化是旅游地发展的关键[7]。因此,全球地方化与旅游地演化之间存在相互促进、对立统一的辩证关系。从方法论层面来看,旅游地演化的已有研究基本遵循实证主义(Positivism)研究范式[8,9,10],对近现代人文地理学的重要研究范式关注不足[11]。结构主义(Structuralism)地理学认为,地方构造性演变的动力来源于所处空间系统的演变。探讨旅游地的演化进程应将其放置在一个由多尺度空间共同构成的复杂系统中[12]。旅游地空间系统内部包含丰富的发展要素,在要素关系上存在差异性和非线性;外部与多等级的空间尺度相联系,在空间结构上存在动态性和不对称性[13]。关于旅游地空间系统的研究不能局限于传统的还原论(Reductionism)思想[14],应运用多学科交叉思维对空间系统的整体性和空间关系的涌现性(Emergence)做出回应[15,16]。全球地方化理论在文化要素层面与人文主义密切相关,在空间尺度层面与结构主义一脉相承,与旅游地演化在时间维度和空间维度具有较好的理论适用性。本文基于文献分析,剖析全球地方化和旅游地演化相互关联的辩证关系和相互促进的科学规律,提出全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的概念框架,从过程、机制和不同尺度空间模式等方面对全球地方化视角下的旅游地演化研究进行展望,构建基于全球地方化视角的旅游地演化研究内容体系。力图为旅游地演化研究提供新的理论视角,为推动中国旅游地理学研究范式转型提供思路,为探索新时代背景下中国旅游地产业优化开发和空间合理布局提供借鉴。
2 研究进展与研究述评
2.1 全球地方化研究进展
全球地方化是一个内涵丰富的学术概念,全球地方化理论的提出弥补了传统全球化理论忽视地方属性和地方要素的缺陷,为研究中国复杂的人地关系提供了新的思路。目前学术界已经围绕全球地方化的概念与理论研究,以及不同领域和不同地域的实践研究开展了丰富的探索。2.1.1 全球地方化的概念与理论研究 全球地方化概念起源于20世纪80年代的日本[17],与全球商业运营中的微市场营销(Micro-marketing)策略密切相关[18]。Robertson最早系统阐述了全球地方化的概念及理论[19],提出全球地方化受到普遍性的特殊化(Universalism of Particularization)和特殊性的普遍化(Particularism of Universalization)双重作用[20],构建了用以描述全球和地方之间多尺度、全要素、连续性的理论框架[21]。该理论有力回应了20世纪70年代以来学界对全球化进程中地方关联的忽视[22],为调节全球化与地方化之间的矛盾创造了可能。在此基础上,众多****从不同角度对全球地方化理论和方法展开讨论。从政治经济发展角度看,全球地方化是“自上而下”和“自下而上”的双向过程,包含社会空间关系的多极化、区域化和地方化,表现为制度管治和经济网络在城市、区域、国家和超国家尺度的尺度重组[23,24,25]。从社会发展角度看,全球地方化体现出一种世界主义思想,表现为一种全球关系在地方的映射,是一个非线性的辩证过程,应考虑普遍性和特殊性、相似性和相异性的关系[26,27,28]。从文化发展角度看,全球地方化表现为全球化异化地方特殊文化的麦当劳化(McDonaldization)现象,全球化在传播、扩散和渗透过程中与地方文化产生的杂合化(Hybridization)现象,以及地方文化对全球化进行负向反馈的地方全球化现象[29,30,31]。这些讨论拓展了全球地方化理论的深度和广度,使其成为研究社会文化变迁和地域空间演化的全新理论视角。
2.1.2 全球地方化在不同领域的研究 目前学界对全球地方化的研究涉及多个领域,体现了该理论在研究对象上的广度。在国际贸易和产业经济领域,****们肯定了地方国际化进程在中国融入国际政治经济体系中发挥的积极作用[32],探讨了全球资本力量与地方制度力量的博弈对全球和地方生产网络的作用[33],考察了全球—地方联结背景下国家和区域产业规模、集聚方式和区位选择等方面的形式和趋势[34,35,36],探索了全球—地方互动背景下企业市场进入、产品研发和技术创新的因素和路径[37,38,39]。在文化领域,全球地方化的影响涉及语言、饮食、体育、动漫、音乐等众多方面[40],民族语言、饮食消费、体育俱乐部、动漫产业和音乐艺术在发展过程中均存在地方化和全球化的相互作用,本土文化和全球文化的交织和融合是不同文化形式形成、传承、创新、活化的重要方式[41,42,43,44,45],文化全球地方化是破除传统文化与现代文化二元对立,以及实现多元文化间认同和共存的有效途径[46]。在旅游领域,****们论证了旅游与全球地方化的辩证关系:一方面,旅游业发展受自上而下的外部力量与自下而上的内部力量共同推动,受全球经济网络和地方社会关系的耦合影响[3, 47-51];另一方面,旅游业是推进全球地方化进程的重要渠道,具有联结全球化外部力量和地方化内部力量的纽带功能[52,53,54,55,56]。全球地方化为开展兼具世界趋势和中国特色的旅游研究提供了理论和思路[57]。
2.1.3 全球地方化在不同地域的研究 国内外全球地方化的相关研究涵盖了不同类型的地域空间,体现了该理论在研究尺度上的纵深。在区域尺度,区域是国家为缓解地区间差距进行权力和资源再分配的核心尺度[58,59,60],资本对空间的地域化(Territorialization)、去地域化(Deterritorialization)和再地域化(Reterritorialization)是全球地方化的重要表现形式[6,7],沿海地区的去地域化和再地域化为区域经济增长、转型升级和均衡发展创造了有利条件[61,62],全球化与地方化并存的理念强化了区域发展研究中探讨区域内外相互作用的重要性和必要性[63]。在城市尺度,跨国要素与地方制度互动是城市空间转变和全球化空间生产的核心动力[64,65],顺应全球化趋势、发挥本土特色和自身优势是提升城市吸引力和竞争力的重要方式[66,67],提升城市服务业国际化水平、强化城市核心区与周边地区的联系是城市与城市群进入全球平台的重要措施[68,69],基于城市地方性和流动性的重大事件营销是实现全球地方化的有效途径[70,71]。在社区和街区尺度,地方社区和历史街区的绅士化现象是全球化资本逻辑和地方化“领土”逻辑的实践前沿[72,73,74],特殊族裔在地方社区和街区的兴起及其引发的社会经济现象是全球地方化的特殊表现[75,76],民族社区和街区的社会空间演化受到现代性和本土性互动的强烈作用[77,78],地方社区在全球尺度化结构中的位置决定了其地方性表现,旅游引致的全球化力量是地方社区去地方和再地方化的重要驱动力[79,80]。
2.2 研究述评
全球地方化的已有研究目前在理论层面已经形成了完善的概念框架和理论体系,并从实践层面针对不同学科领域和不同地域空间展开了丰富探讨,为中国旅游地演化研究提供了具有创新性的理论视角。但在理论层面,已有研究更多从全球地方化的概念演化及科学内涵展开深入探讨,尚未从全局视角对某一类地域空间研发理论工具和研究分析框架。在实践层面,已有研究更多关注某一具体类型地域空间的全球地方化作用,缺乏针对多尺度、多地域、多类型研究案例的历时性和系统性研究。旅游地演化是国内外旅游地理学的重要研究议题,已有研究对旅游地演化过程中空间系统整体性、动态性、非平衡性特征展开探讨[9,10]。但已有旅游地演化研究基本遵循实证主义研究范式,对现代人文地理学的范式转型和创新关注不足。相关研究多局限于旅游地空间系统内部,未能将旅游地放置在全球—地方的尺度化系统中,立足于全局性视野观照推动旅游地演化的全球化力量。针对旅游地演化研究,亟需跨学科的研究范式在方法论层面进行创新,亟需跨尺度的研究模式在研究对象上进行探索。基于上述认识,开展针对全球地方化与旅游地演化的关联性和系统性研究是本文尝试探讨的科学问题。目前,全球地方化的理论和实证研究多关注地缘政治、国际贸易和城市管治等方面,鲜有针对旅游地的系统性研究。随着资本空间化的深入推进,越来越多以旅游地为代表的地方空间逐渐接驳全球化进程,进入国际格局对话平台。因此,基于全球地方化与旅游地演化双向辩证的互动关系,探索全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的过程与机制,开展全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的不同空间模式研究,在理论和实践层面具有科学性与创新性。
3 理论适用性分析与概念框架
3.1 理论适用性分析
全球地方化理论具有突出的整体性、跨尺度和多要素的特征,能够帮助理解特定地域空间与整体空间系统之间的关系。全球地方化考察全球化和地方化的互动、普遍化和特殊化的融合,重点关注政治、经济、社会过程的全局性效应[81]。旅游是新时期中国社会经济发展的新兴发展要素和新兴发展动能[1],旅游地是旅游发展的核心地域空间,全球化和地方化的深刻互动具有突出的时代性。因此,需要在旅游地演化研究中充分考察全球化和地方化的具体表征,分析全球地方化与旅游地演化的时空共轭性,进而论证全球地方化理论在旅游地演化研究中的适用性。在时间维度上,全球地方化进程与中国的旅游地演化过程具有耦合性。全球地方化概念最早起源于20世纪80年代,在随后的近40年间,全球地方化进程逐渐深入到不同国家的政治、经济、社会和文化等不同层面。中国大众旅游的兴起在时间上与全球地方化趋于同步,旅游地演化是全球地方化过程的重要组成部分,并受到全球地方化的深刻影响。首先,从演化阶段角度,全球地方化理论为旅游地演化研究提供了更为宏大的时空维度,使其与国际时代背景和国家社会经济发展趋势紧密联系,增强了研究的历时性和全面性。其次,从发展要素角度,旅游地空间系统具有复杂的发展要素,全球地方化是外部要素与内部要素的互动过程,为厘清旅游地的要素类型和要素组合方式提供了良好的分析路径。最后,从资本运动规律角度,旅游地演化受到资本力量的强烈驱动,空间生产方式的发展体现了资本三重循环的不同阶段[82],全球地方化蕴含资本循环的发展逻辑,为剖析旅游地演化的递进层次和内在本质创造了条件。
在空间维度上,全球地方化的不同空间尺度与旅游地空间系统具有嵌套性。全球地方化具有鲜明的结构主义思想,关注全球、国家、区域、地方等不同尺度间的相互作用[83]。旅游地系统是一类特殊的人地关系地域系统,具有复杂性、开放性和流动性。因此,首先从空间尺度本体角度,旅游地系统具有不同等级和规模的空间尺度,全球地方化在不同空间尺度上具有差异化的表现形式,二者在空间尺度上具有较好的对应关系。其次,从空间尺度嵌套的角度,不同空间尺度的旅游地在发展要素和驱动力量上具有一定的特殊性与一般性,全球地方化既关注全球化的均衡化趋势,又强调地方化的分异化趋势[84],能够有效揭示旅游地演化过程中的尺度嵌套关系。最后,从空间尺度转化的角度,旅游地系统在演化过程中,能够藉由对权力和资本的控制与吸纳能力,在不同空间尺度发生尺度跃迁和尺度推绎。结构主义强调社会空间的整体性和互动性,全球地方化的结构主义框架具有鲜明的辩证思想,对旅游地空间系统相互渗透、相互转化的演化特征具有较好的适用性。
3.2 概念框架
全球地方化视角下旅游地演化研究具有鲜明的动态性、复杂性和系统性,本文以结构主义研究范式为理论边界,考察旅游地的空间尺度定位和社会空间属性,结合已有研究基础[12, 52],为旅游地演化的过程、机制和不同尺度空间模式研究提供理论工具。全球地方化在空间尺度层面强调尺度的重组与转化,在空间主体层面关注要素的关联与互动。旅游地演化具有突出的阶段性和动态性,受到外部力量和内部力量的共同作用。因此,需要充分考察全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的外在结构和内在机理,分别从空间尺度和空间主体层面构建基于全球地方化视角的旅游地演化概念框架(图1)。图1
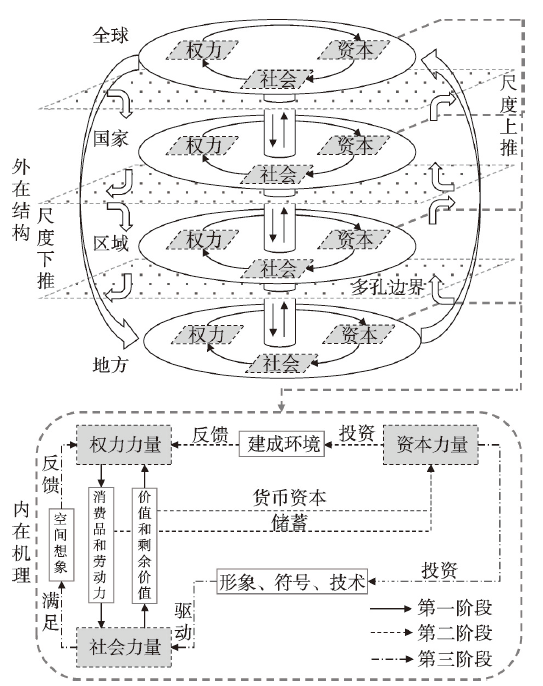 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1基于全球地方化视角的旅游地演化概念框架
Fig.1The conceptual framework of tourism destination evolution based on a glocalization perspective
在外在结构层面,构建多层级、关联性的空间尺度结构体系。在全球地方化的总体视角下,旅游地演化具有多尺度的关联性,是不平衡地理空间结构下多层级空间尺度综合作用的结果。因此,需要以全球、国家、区域、地方等不同空间尺度为框架的结构性基础,充分考察空间尺度的等级性、嵌套性和能动性,从尺度上推和尺度下推两方面建立多尺度旅游地空间系统的联系通道。在尺度上推方面,探寻下级尺度旅游地通过向上级尺度旅游地表达诉求和建立联盟的突破途径,分析旅游地空间对权力控制能力和资本吸纳能力在空间尺度上的跃迁方式,探究地方化力量向全球化力量的上推路径。在尺度下推方面,探寻上级尺度旅游地通过向下级尺度旅游地划定边界和形成管治的固化途径,分析高等级空间尺度遴选特定旅游地区域强化自身发展指向的限定方式,探究全球化力量向地方化力量的下推路径。通过厘清多尺度旅游地空间的尺度上推和尺度下推作用机制,搭建全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的多尺度关联外在结构。
在内在机理层面,厘清多类型、交互式的主体力量互动作用机理。聚焦特定尺度的旅游地空间,系统内部多主体互动作用方式的升级推动了旅游地空间系统的演化。因此,需要以权力力量、资本力量和社会力量等为核心,考察主体力量的复杂性、交互性和统一性,厘清旅游地层层叠加、逐步递进的阶段发展规律。在旅游地演化的第一阶段,空间系统主要围绕权力力量和社会力量之间的生产与消费环节,旅游地系统具有鲜明的封闭性和自洽性。在第二阶段,权力力量与资本力量进行合作,全球化外部力量开始对地方化内部力量进行渗透,资本力量利用第一阶段的剩余价值进行建成环境的投资,为旅游地建设必要的基础设施和服务设施,进而对权力力量的发展诉求做出反馈。旅游地系统逐渐开始引入外部发展要素提升系统规模和等级,体现出旅游地演化在空间维度上的扩张。发展至第三阶段,全球化外部力量与地方化内部力量趋于耦合,资本力量对形象、符号和技术等社会性花费进行投入,驱动社会力量的生产和消费升级,满足其更高层次的空间想象,为权力力量的下一轮运动提供基础,体现出旅游地演化在时间维度上的延长。通过分析旅游地空间多类型主体力量的互动逻辑,梳理全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的多主体互动内在机理。
4 全球地方化视角下的旅游地演化研究展望
旅游地演化受到全球化和地方化两种力量的共同作用。识别遴选旅游地演化过程中的全球化和地方化要素,剖析旅游地演化过程中全球化力量和地方化力量在功能上的耦合协调,判别旅游地演化过程中全球地方化力量的作用方式、作用强度,是开展全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的过程、机制和不同尺度空间模式研究中需要解决的科学问题(图2)。图2
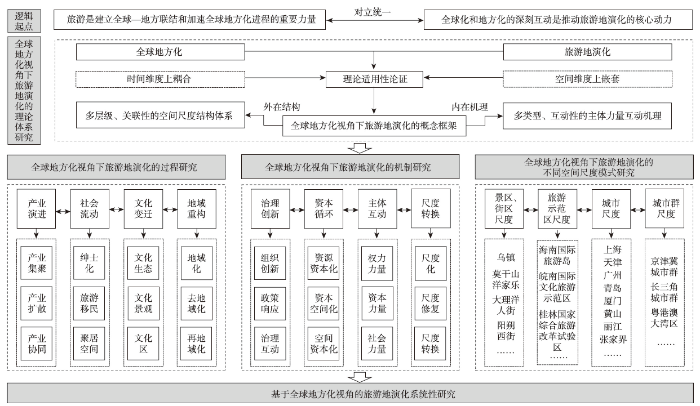 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2基于全球地方化视角的旅游地演化研究内容体系
Fig.2The research content system of tourism destination evolution based on a glocalization perspective
4.1 全球地方化视角下的旅游地演化过程研究
4.1.1 全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的产业演进过程 随着全球化进程推进,全球产业扩充了旅游地系统的空间体量,增加了旅游地空间结构和演化方式的复杂性。在全球地方化视角下,旅游地的地方产业和全球产业在不同阶段呈现不同的响应特征和耦合效应,相关研究可以从以下几个方面进行:① 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的产业集聚过程。分析全球经济要素在旅游地集聚的特征和方式,研究全球地方化视角下旅游引导产业集聚的实现过程,梳理地方产业在旅游地演化发展过程中的集聚作用和实现方式,预测旅游地演化的产业集聚形态及发展趋势。② 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的产业扩散过程。分析全球化产业在旅游地演化过程中产生的全新表现形式和结构形态,透视全球地方化视角下旅游地产业扩散过程中的要素重组和空间创新运动过程,总结全球地方化视角下旅游地产业扩散过程中旅游引导不同区域产业扩散的动态模式。③ 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的产业协同发展过程。运用关联耦合理论研究旅游与文化、体育、教育、医疗、科技等产业的二元或多元协同过程,根据系统耦合理论研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化过程中不同产业协同共构系统的关系和过程,分析全球地方化视角下旅游地演化产业协同发展共构的形式与途径。4.1.2 全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的社会流动过程 社会流动是全球地方化进程的重要表现,在社会流动的时代背景下,要素、人口、劳动力的流动性引发了旅游地演化过程中身份认同、社会分层和空间位移等一系列综合效应,可探究以下几个方面:① 研究全球地方化视角下旅游移民的迁移过程。分析全球化力量和地方化力量不同作用程度下旅游移民的特征差异,探究全球化流动性背景下旅游地移民地方认同的建构过程,研究全球化和地方化互动下旅游移民的地方融入过程。② 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的旅游绅士化过程。分析旅游业发展与城市、乡村旅游地转变为相对富裕和专有区域的耦合过程,探究全球化和地方化互动下旅游业投资、人口结构、基础设施和文化生活方式的转变过程,揭示旅游地绅士化背后蕴含的土地利用方式和空间生产方式的转变过程,探索旅游绅士化背景下区域产业结构的转型模式。③ 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地聚居空间演化过程。探究外来资本和人口流动背景下旅游地聚居空间社会关系的分化和重组过程,探索全球化和中国城乡二元结构背景下旅游地聚居空间的空间分异特征,研究第二居所的休闲、度假、养老、投资等多重功能转型过程,洞悉全球化力量与地方化力量共同作用下旅游地聚居空间的社会效益扩散过程。
4.1.3 全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的文化变迁过程 文化变迁是旅游地系统演化的重要组成部分。在全球化浪潮的冲击下,旅游地地方文化在全球文化的冲击下如何凸显地方特色,是旅游地文化变迁过程中需要着重思考的问题,相关研究可以从以下几个方面展开:① 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地的文化生态转型过程。分析全球化趋势下现代性文化要素对旅游地传统文化生态的作用过程,探究全球化发展的不同阶段旅游地自然环境与文化扩散效应的互动过程,探索全球化导致的旅游地文化转型与生态承载能力之间的辩证关系。② 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地的文化景观变迁过程。研究文化全球化背景下旅游地饮食、民俗、宗教、语言等本土文化景观的演化特征,揭示文学、音乐、书法、美术等艺术景观在旅游地演化过程中的空间分布特征与规律,探索旅游地传统景观向现代景观和后现代景观转变的过程与特征。③ 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地的文化区整合过程。探索全球地方化视角下不同旅游文化区的空间整合过程,剖析全球文化主体和地方文化主体在旅游发展过程中的文化价值观念、生活方式之间的发展与协调过程,探究外来文化与不同地域空间旅游地本土文化的文化整合路径与方式。
4.1.4 全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的地域重构过程 旅游地是以旅游业发展为主体的地域空间,空间系统受外来资本力量的强烈影响。在全球地方化视角下,地域重构是构建相对稳定的旅游地发展空间和克服地域空间组织矛盾的重要环节。旅游地演化的地域重构主要体现为地域化、去地域化和再地域化过程:① 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的地域化过程。探究资本、权力、技术、管理、服务等全球化力量在旅游地的介入方式与特点,探索全球化力量和要素在旅游地的作用过程与发展特征,分析全球化力量与要素在旅游地的固着过程,研究具备不同空间属性的旅游地系统对全球化力量的空间响应过程。② 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的去地域化过程。分析权力与资本等全球化力量对旅游地内部自然、经济、政治、文化、社会等方面的作用过程与特点,探究全球化力量影响下的旅游地空间结构和社会组织的异化过程,总结具有高度全球化特征旅游地的发展路径和演化规律。③ 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的再地域化过程。探索全球化背景下旅游地本土力量的活化与复兴过程,探讨全球化力量与地方化力量互动下旅游地空间系统的结构演替过程,剖析全球地方化对促进旅游地资金流动和资本积累发挥的关键作用,讨论全球地方化作用下生产与消费模型升级对旅游地空间生产和空间修复的推动作用。
4.2 全球地方化视角下的旅游地演化机制研究
4.2.1 全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的治理创新机制 伴随全球化的日益深入,旅游地的社会政治过程正在由垂直化的统治走向多元化的治理,地方化要素的有效参与成为旅游地治理创新机制的重要组成部分。面临旅游地演化的全新发展趋势,可以从组织创新、政策响应和治理互动等层面展开思考:① 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的组织创新机制。自组织与差异化结构是治理的基础,在全球地方化进程下,旅游地的多元组织架构正在发挥日益重要的作用。因此,探究旅游地演化的治理创新机制,需要辨析旅游地在全球地方化进程下形成的全新组织形态,探索新的规则体系下各级行政组织与空间组织目标实现的途径和方式。② 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地对治理政策的响应机制。探索全球地方化视角下旅游地在治理实践过程中探索出的创新政策与国家及区域发展战略的内在联系,研究全球地方化影响下国家政策与地方治理的协调关系,总结旅游地应对全球化竞争开展的相关政策配套措施的实施程度与实际效果。③ 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地发展与治理创新的互动机制。研究“自上而下”全球治理与“自下而上”地方治理在旅游地演化过程中的互动机制,探索全球化治理标准与旅游地治理实践的反馈、修正的互动关系,透视旅游地发展与治理创新的动态协调机制。4.2.2 全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的资本循环机制 资本的积累和循环是旅游地发展演化的重要动力,旅游业作为资本积累的新型发展方式,对于旅游地的资本积累和城市发展具有重要影响。在全球化力量的影响下,生产技术在全球迅速扩张,资本的流通和循环不断加速,对旅游地的资本循环研究提出新的要求:① 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的资源资本化机制。分析资本循环初级阶段旅游地人文资源、自然资源进入商品流通环节的转换机制,探寻旅游地在自洽、封闭系统条件下“剩余价值”在地方社会空间的循环渠道,探索全球化资本逻辑和地方化“领土”逻辑共同支配下旅游地“土地—劳动力—资本”三位一体关系的形成机制。② 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的资本空间化机制。分析资本循环第二阶段旅游地资本运作与旅游地生产关系和生产方式的适配机制,探寻全球化资本在旅游地空间生产过程中的空间流动轨迹,探究全球化资本力量对旅游地地方空间的重塑和重组机制,揭示全球化资本逻辑对旅游地不平衡地理空间格局的塑造机制。③ 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的空间资本化机制。研究资本循环第三阶段旅游地空间的空间资本价值增值机制,探寻旅游地地方资本在全球资本影响下的扩张路径和增长模式,探究旅游地地方空间资本与全球化流动资本的互动机制,探索旅游地空间资本集聚效应下空间正义的反馈机制。
4.2.3 全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的主体互动机制 全球地方化视野下旅游地演化包含多元利益主体的参与,旅游地为利益主体互动提供了场所空间,利益主体作为旅游地发展演化的主要参与者,对旅游地的演化路径和方向、要素注入和地方属性的构建有重要影响。基于全球地方化视角,分析多元利益主体在旅游地演化过程中相互作用:① 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化过程中权力力量的作用机制。分析全球地方化视角下各级政府对旅游地生产要素的调动和运营机制,探索政府引导下旅游地生产力和生产方式的转型机制,剖析政府引导下旅游地全球化和地方化发展要素的整合机制,探究政府引导下旅游地发展要素对权力力量的响应机制。② 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化过程中资本力量的作用机制。分析全球地方化视角下以跨国企业为代表的海外资本对地方资本运营方式的转变机制,剖析外来资本对旅游地的要素整合、产品开发的影响与作用机制,探索旅游地演化过程中资本力量与权力力量的协同作用机制,探究海外资本注入后旅游地本土资源与资本要素的耦合机制。③ 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化过程中社会力量的作用机制。分析全球地方化视角下旅游地社会力量的空间涌现机制,探索旅游地演化过程中社会力量对权力力量和资本力量的反馈机制,探究全球化价值观念影响下社会主体行为意向的转变机制,研究社会精英群体、旅游者和旅游地居民等社会力量主体的行为互动机制。
4.2.4 全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的尺度重组机制 旅游地演化的尺度重组是全球生产方式转变与旅游地地域重构动态作用的结果,是旅游地为提高经济竞争力利用不同空间尺度对空间生产策略的调整。全球地方化视角下,旅游作为一种全新的权力表现形式和资本积累方式,持续推动权力和资本在不同旅游地尺度间的重组和推绎,为相关研究提出了新的要求:① 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的尺度化机制。研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化过程中“领土”边界的社会生产机制,探究不同全球化和地方化力量组合下旅游地权力层级的确立机制,探索全球化和地方化深刻互动下旅游地知识权力和活动性质的范围。② 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的尺度修复机制。研究全球化力量对地方化力量的驱动与调节机制,分析全球化发展趋势下上级空间尺度对下级空间尺度的资源配置与优化机制,分析国家和区域尺度基于自身发展逻辑对旅游地发展路径和尺度结构的固化与塑造机制。③ 研究全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的尺度转换机制。探讨全球化和地方化共同驱动下旅游地空间尺度转换的路径形成机制,研究全球化力量和地方化力量共同作用下同等级空间尺度旅游地的尺度互动机制,探究旅游地发展演化过程中空间系统内部的资源调节和尺度重构机制,分析资本全球化背景下地方政府、企业为应对全球变化而采取的尺度转换策略。
4.3 全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的不同尺度空间模式研究
尺度是地理学研究的核心问题之一。在人文地理学以及旅游地理学中,通常认为尺度具有等级化和交互性特征,跨尺度交互常常发生在低等级尺度与高等级尺度的边界上[85]。尺度像一枚变焦镜头,聚焦不同尺度往往会呈现出地方空间差异化的发展过程、格局与机制。旅游地是具有不同相互包含、相互嵌套的空间尺度构成的地域空间系统。因此,全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的不同尺度空间模式应当关注旅游地要素结构特点,寻求不同尺度旅游地空间的全球地方化差异与侧重点,针对中国不同空间尺度、不同地域特色、不同文化背景、不同发展路径的旅游地展开系统性研究。在此基础上,以“点面结合”的方式遴选不同尺度、不同类型旅游地的典型代表,以此为窥见旅游地空间系统发展演化规律的研究窗口,对开展全球地方化视角下的旅游地演化研究具有实践意义。4.3.1 景区、街区尺度典型模式研究 景区、街区是旅游活动和社会互动的基本单元,是中国传统景观与传统文化根植的基本载体,也是全球化逻辑与本土化逻辑张力最显著的地方空间,为观照旅游地演化的主体互动和文化变迁提供了合适的研究案例。景观与文化等旅游吸引物是景区、街区尺度旅游地的核心发展要素,地方化力量在其旅游地演化过程中发挥着主导作用。因此,相关研究应聚焦于景观、文化、地方行动者等充分体现地方性特征的要素关系和互动机制上,并考察全球化发展逻辑下旅游地地方化力量的崛起路径。在今后的研究中可以重点关注浙江乌镇、莫干山洋家乐、云南大理洋人街、广西阳朔西街等具有典型地方文化特色和全球化力量介入较为深入的景区和街区,探讨小微尺度旅游地发展过程中的全球—地方的动态作用过程及作用特征,探究权力、资本与社会多主体互动的作用机制。
4.3.2 旅游示范区尺度的典型模式研究 旅游示范区是新时代中国旅游改革探索和创新发展的关键阵地,是响应国家区域发展战略举措的先行区,是具备明显核心—边缘结构的地域空间类型,是开展全域旅游的先行区,为探讨旅游地演化中的地域重构和尺度重组提供了绝佳的研究土壤。旅游地地域重构和尺度重组的核心是生产方式和流动性的革新,遵循全球化的发展逻辑。因此,相关研究应重点关注企业、交通等区域发展要素对全球化进程的推进作用,考察地方化特性为示范区带来的独特演化模式。在今后的研究中可以选取海南国际旅游岛、皖南国际文化旅游示范区和桂林国家综合旅游改革试验区等争创建设为“世界一流旅游目的地”的区域①(① 详见《国务院关于推进海南国际旅游岛建设发展的若干意见》《皖南国际文化旅游示范区建设发展规划纲要》。),剖析区域尺度旅游地的政策体制演替和市场经济发展特征,探究全球地方化视角下区域尺度旅游地的市场资源的配置与体制机制创新演化过程,探索旅游引导下的产业结构和区域经济发展新模式。
4.3.3 城市尺度典型模式研究 城市是社会经济效应最凸显、人地作用关系最复杂的地域类型,是旅游与资本、人流、信息、技术、管理等发展要素相互作用最剧烈的空间载体,为探明旅游地演化的产业演进和社会流动提供了良好的研究场域。城市是兼具全球化与地方化的旅游地类型,二者之间的作用强度取决于城市的产业结构与文化底质。因此,相关研究可以聚焦以绅士化、城市更新为代表的全球化力量与地方化力量的博弈过程。今后的研究可以重点关注上海、天津、广州、青岛、厦门等中国较早接触西方现代化文明的城市,以及黄山、丽江、张家界等开发较早且十分典型的旅游城市,探究旅游目的地城市演化过程中产业结构、地方发展要素、地方特征属性的发展与变迁问题,探索旅游引导下全球化力量在城市空间作用的一般特征和一般规律。
4.3.4 城市群尺度的典型模式研究 上升至城市群尺度,应重点关注旅游地演化在全球经济竞争和国家—区域尺度重构中发挥的作用,以及与后者之间的关系。城市群建设是目前中国的核心战略,是联结全球化力量与地方化力量最为关键的途径。城市群是中国参与国际竞争和发展社会经济的基本单元和主要平台[86],具有显著的要素集聚和要素扩散功能。城市群空间不仅是国家权力和全球化力量最直接作用的区域,也富集了大量优秀的地域文化和旅游地创新要素和创新模式,为探究旅游地演化的治理创新和资本循环提供了研究对象。因此,城市群不仅是推动新时代中国社会生产力和生产方式革新的“新国家空间”[5, 59],也是从根本上转变中国旅游地演化方式的功能地域母体。在今后的研究中,可以将京津冀、长三角、粤港澳大湾区等城市群作为重点关注对象,刻画旅游引导下的“新国家空间”的形成过程,探索城市群尺度旅游地演化与中央—地方的“集权”“分权”制度变迁的内在关联,深化理解城市群一体化发展在旅游地高水平演进过程中发挥的引领作用。
5 结论与讨论
5.1 结论
本文基于全球地方化的结构主义地理学研究视角,通过分析已有研究成果,对旅游地演化进行理论探讨和展望,得出以下结论:(1)全球地方化理论在旅游地演化研究方面具有适用性,从外在结构和内在机理层面为旅游地演化提供了科学的概念框架,响应了旅游地演化研究的新时代要求。全球地方化进程在时间维度和空间维度上与旅游地演化具有良好的耦合性和嵌套性,能够有效解释旅游地演化过程中涌现出的复杂现象。因此,需要充分考察全球地方化视角下旅游地演化的外在结构和内在机理,建构基于全球地方化视角的旅游地演化研究分析框架,为该领域的动态性和系统性研究提供方法论支撑。
(2)通过全球地方化理论,旅游地演化的过程与机制研究与中国社会经济发展的诸多问题建立了联系,拓宽了传统旅游地演化命题研究的思路。在过程研究中,全球地方化视角下的旅游地演化涵盖了产业演进、社会流动、文化变迁和地域重构等诸多方面;在机制研究中,全球地方化视角下的旅游地演化与政策创新、资本循环、主体互动和尺度重组等密切关联。因此,全球地方化理论对旅游地演化的不同阶段、不同层面和不同力量给予了充分关注,为该领域的多学科交叉研究提供了认识论基础。
(3)多尺度、多地域、多类型的空间模式研究是开展全球地方化视角下旅游地演化研究的具体路径,为中国旅游地演化的系统性研究提供了实践方案。中国幅员辽阔,空间差异显著,不同空间尺度、不同地域特色、不同文化背景的旅游地共同组成了旅游地空间系统,旅游地空间系统在地域上的复杂性和在结构上的非线性决定了其演化路径和方式的多样性。因此,运用全球地方化的整体性、动态性和综合性思维,能够充分比较不同旅游地之间发展要素及组合方式的差异性,为构建全方位和多梯度的旅游地演化研究体系提供保障。
5.2 讨论
在人地关系地域系统的宏观视域下[87],旅游地是一类特殊的区域和地方人地系统[88]。中国旅游地演化在时间维度上与改革开放以来的社会经济发展趋于同步,在空间维度上受城镇化转型背景下城乡结构和要素流动的显著影响。全球地方化的理论视角为探究旅游地演化的过程与机制构建了一个“自上而下”和“自下而上”双向互动的尺度框架,强调了旅游地人地系统和全球人地系统的有机联系,在一定程度上兼顾了旅游地接入外部空间系统的“流量变化”和旅游地内部要素循环发展的“存量积累”[89]。因此,全球地方化视角下旅游地演化研究既契合旅游人地关系本体论、认识论和方法论层面的理论内涵[88],也为开展旅游地演化的全局性和系统性研究提供了可能。从旅游地理学研究范式转型的角度来看[90],全球地方化蕴含深刻的“对立统一”思想,揭示了旅游地演化过程中静态与动态、宏观与微观、普遍与特殊的辩证关系[91]。纵观西方近现代人文地理学思想史,如果说20世纪50年代兴起的“计量革命”将人文地理学研究由经验化推向了科学化[92,93],那么20世纪70年代后涌现出的人文主义、结构主义、女性主义、后现代主义等研究范式[11, 94],则为人文地理学迈向交叉性和综合性研究创造了条件[95,96]。从西方经验中不难看出,研究范式的转型总是与社会发展主要矛盾转化和生产力进步密切相关[97,98],当前中国社会经济快速发展导致了纷繁复杂的旅游地理现象涌现,为研究范式转型和创新提出了新的时代要求。40年间,中国旅游地理学经历了从经验主义向实证主义的发展历程,重视多种研究范式兼容并蓄、融入地理学学术主流,已经成为中国旅游地理学界正在积极探索的方向[99,100]。鉴于此,本文初步对全球地方化视角下的旅游地演化展开理论探讨与展望,以期为优化和完善中国旅游地理学的学术体系抛砖引玉。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/0042098993466URL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.02.013 [本文引用: 2]

Tourism area life cycle (TALC) is the theory to describe tourism destination evolution path, which is the most important part of tourism theory system and the most primary tool in regional tourism sustainable development planning. To further develop our existing knowledge on tourism areas evolution, some divergence and confusion on the TALC theory and its basis need to be clarified. Reviewing the domestic and international main literatures, the controversy and achievement about the basic theory are summarized elaborately. First, according to the study of the origination and development of the TALC theory of Butler and the analyzing the key concept, the article concludes that the TALC theory emphasizes the evolution of tourism region system rather than tourism product, though the theory can also be an appropriate tool for analyzing the development of tourism product. Summarizing the discussion about stages division in TALC theory, researching advantages and disadvantages of different way of stages demarcation and considering the practical value of the TALC theory, the article suggests that the evolution path of tourism region should be divided to eight stages. Which are exploration, involvement, development, consolidation, stagnation, reorientation, decline or rejuvenation, and exit stage. Beside the classical six stages in Butler TALC theory, the reorientation stage and exit stage are absolutely necessary in guiding the development of tourism area. Management decision and new investment will determine the tourism area’s evolutionary routine in reorientation stage, if the reorientation effort comes to nothing, the tourism system continues to decline, then the tourism area is doomed to enter exit stage, which means industry transformation. Experience tells us that the industry transformation is very hard for developed tourism area, very few companies want to set new branches in the decline tourism area for lacking of human resource, while a large number of people cannot find a new job after unemployed in tourism industry, there is a great possibility of big recession of whole region in exit stage. Therefore, the eight-stage TALC theory will be a more powerful tool for region development management and planning. Second, summarizing the two hot issues about TALC from 1980 to 2016, the majority literatures focus on the different characters of stages which based on specific area development data, another is the mechanism of the tourism area's evolution and four kinds of influence factors, which are macro-environment, demand, competitors and tourism area’s conditional combination. Which offers a more powerful thrust to regional tourism development planning. At last, proposing the future research prospects on TALC theory in new environment. More studies will focus on the development quality of the human-earth system in different stages instead of the shape of evolution routine of tourism area, reveal the mechanism of tourism industry decline and alternative counterplan of industry transformation in different stages, and rethink about the tourism industrial status in region economic system.
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2015.03.007 [本文引用: 1]

Because of quantitative revolution, geography evolved from a discipline of spatial description into a science of distributions. Accordingly, qualitative methods were replaced by the integrated methods of quantitative analysis and qualitative analysis. One of the important approaches to spatial analysis is to characterize geographical distributions. Geographical distributions fall into spatial distributions and size distributions, both of which can be divided into simple distributions and complex distributions. A simple distribution has a characteristic scale (represented by a characteristic length), while a complex distribution has no characteristic scale but bears a property of scaling invariance (represented by a scaling exponent). The key step of studying a simple distribution is to find its characteristic scale, while the basic way of research for a complex distribution is to make a scaling analysis. For simple distributions, traditional methods based on advanced mathematics are effective, but for complex distributions, the old-fashioned mathematical tools are ineffective. However, due to the lack of understanding of characteristic scale and scaling, geographers often failed to distinguish between simple distributions and complex distributions. As a result, many complex systems such as cities and systems of cities were mistaken for simple systems. Consequently, geography did not succeed in theorization in the 1960s-1970s after quantification in the 1950s-1960s. Geographical distributions can be mathematically abstracted as probability distributions. For a simple distribution, its characteristic scale can be determined. A typical characteristic scale is a mean (average value). Based on means, we can compute a variance and a covariance. Thus we have a clear probability structure comprising means, variances, and covariances, which explain the pattern of the geographical system and predict its process of evolution. In the case of a complex distribution, an effective mean cannot be determined, and thus little is known about its probability structure. In this situation, characteristic scale analysis should be substituted with scaling analysis. Quantitative methods of scaling analysis have emerged from interdisciplinary studies. A new integrated theory based on concepts from fractals, allometry, and complex network has been developing for geographical modeling and analysis.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s11442-016-1322-8URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/13216597.1994.9751780URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1068/d170557URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/0955757042000203632URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1177/0011392105048291URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/1467-9558.00185URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1177/0011392104039311URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/00343400701543272URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.techfore.2011.10.008URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2307/143650URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.02.012 [本文引用: 1]

<p>The global-local relationship generated in the process of innovation and transnational innovative mechanism has become a new topic of regional development. The research on the impact of globalizing forces on the innovation of host countries is mainly based on the perspective of technology spillover and the impact on the evolution of economic and innovation consequence of host countries has attracted great attention during the last two decades. Few literatures, however, have focused on the impact on the process of innovation,which is more significant for developing host countries to achieve technical transition and value upgrading in global production network. Based on a case study of Guangzhou, this article begs the question of what effect the technology spillover of transnational enterprises has on the process of innovation of China, especially on indigenous manufacturing firms, which play a key role in industrialization and face increasingly urgent environmental regulation and the demand of technical transition in China. Fieldwork is carried out to obtain R&D behavior’s characteristics of indigenous manufacturing firms using semi-structured questionnaire through face-to-face interviews with owners or responsible persons of the firms selected by convenient and snowball sampling. Location of the samples covers major manufacturing area in Guangzhou. The results show that since the 1990s, the indigenous firms have gradually increased R&D input, established independent R&D institutions as well as actively promoted R&D internationalization. Meanwhile, the R&D behavior of technology import and external cooperation are relatively weak. These changes indicate the indigenous manufacturing firms have experienced a R&D mode transition from highly dependent on introducing technology from developed Countries to the internalization and internationalization of R&D behavior dominated by self-dependent innovation. Promoting the motivation of self-dependent innovation of indigenous enterprises underlies the evolution of R&D behavior under the circumstance of integrating multinational innovation network. The study further investigates what impacts the technical spillover from foreign investments have on the evolution of R&D mode of indigenous manufacturing firms and its mechanism by building an ordinal polytomous logistic regression model. In the model, the effect of technical relation, productive cooperation and labor turnover between translational and indigenous manufacturing enterprises have been examined. The results show that technical spillover from foreign investments has a significant impact on the transition of R&D mode of local enterprises. Both of the decreased technical gaps and the free flow of labor force between international and local enterprises have significantly promoted the motivation of independent R&D behavior of local enterprises. More closely embedded in global production networks also has a positive effect. However, international technology procurement has a significant negative effect on self-dependent innovation of indigenous manufacturing firms. The results of this paper can help to enrich the understanding of the evolution of local innovation process and its mechanism under the background of globalization, and provide inspiration for the policy-making of regional innovation system integrated global forces.</p>
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.05.010 [本文引用: 1]

Export growth is a key driver for China's economic development. The entry of new export firms is an important indicator of export growth. The New Trade Theory believes that knowledge spillover brought about by agglomeration externalities is a crucial factor affecting the exporting decision making of firms. Global and local knowledge spillovers encourage firms to acquire necessary export knowledge and thus reduce their difficulty of entering export markets. Theories of evolutionary economic geography emphasize that cognitive proximity is the prerequisite for the validity of export spillovers. Global and local export experience and product proximity are the main contents of export spillovers. This study used China Customs Trade Data from 2002 to 2011 to analyze the impact of export spillovers on the entry of new firms into the export market. The results show that export spillovers can significantly increase the probability of new exporters entering the export market. Private firms are more likely to enter markets with stronger spillovers. Besides, export spillovers have a stronger role in promoting the entry of follower firms, especially domestic firms. State-owned collective enterprises emphasize the overflow of overall export experience, and private companies place more emphasis on product knowledge spillovers. Local spillovers are beneficial for the expansion of new exporting firms to new destination countries, while global spillovers are useful for new exporters expanding into new product areas. This study improved the research on the spatial dynamics of export firms, expanded the spatial dimension in which export spillovers affect export decisions, and helped deepen the understanding of China's trade market.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1163/15692090260449995URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1111/bjos.2004.55.issue-4URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/0160-7383(95)00064-XURL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1177/107808749703300204URL
DOI:10.1016/S0160-7383(02)00049-XURL
DOI:10.1111/j.1467-8306.2005.00462.xURL
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/146166800110070478URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1080/14616680500291147URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.annals.2004.10.012PMID:32572282 [本文引用: 1]

In tourism studies globalization and localization are often conceived of as a binary opposition. The ethnography of an Indonesian group of tour guides presented here illustrates how the global and the local are intimately intertwined through what has been described as the process of "glocalization". The guides studied are remarkable front-runners of glocalization. They fully participate in global popular culture and use new technologies in their private lives. While guiding, however, they skillfully represent the glocalized life around them as a distinctive "local", adapted to the tastes of different groups of international tourists. It is concluded that tourism offers excellent opportunities to study glocalization, but that more grounded research is needed.Copyright ? 2005 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
DOI:10.1016/j.annals.2006.10.006URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/03085149500000015URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.03.005 [本文引用: 1]

The state space has undergone significant transformations in China since 2000, changing from urban entrepreneurialism to regionalization. In this context, enclave economy is emerging and developing in various regions, and has been studied by researchers in a range of fields. However, most of the existing studies focus on the microscopic mechanisms and modes, without more detailed analyses of the macroscopic and structural factors behind this phenomenon. Apparently, this approach is problematic because enclave economy is not only a grassroots strategy, but also an integral part of the spatial strategies at the national scale in recent years. Therefore, based on the theories of state spatial restructuring, this article analyzes how enclave economy is produced and what governance structures are formed in this process. It suggests that enclave economy is driven by the crisis of capital accumulation and the tendency of reterritorialization. In this context, it originates from bottom-up institutional experiments, and then becomes a flexible yet inadequate strategy of regionalization. Following this, due to the consistency between enclave economy and the evolution of state spatial selectivity, it is then integrated into China's state spatial strategies that focus on the competitiveness of city-regions. Moreover, the governance structure of enclave economy includes inter-scalar, inter-territorial, and government-market relations, which are contingent, complex, and relatively fragile. In sum, this practice should be viewed as an emerging experiment in the state spatial restructuring, whose effects and consequences remain to be seen.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.12.006 [本文引用: 1]

Space-based cooperation is an important form of interurban cooperation and a multidimensional sociospatial process concerning reterritorialization, network building, and rescaling. Based on the case study of the Shenzhen-Shanwei Special Cooperation Zone and considering three sociospatial dimensions including territory, network, and scale, the production and restructuring of interurban cooperative space is analyzed. This research suggests that the reterritorialization involved both capital and regulatory power; the network that link actors together serves as tools for political mobilization and information sharing; the key factor for rescaling is the mobilization of actors at higher scales. Common interests of relevant actors are fundamental factors of space-based interurban cooperation. Specifically, the actors at higher scales tend to embed their own interests into the political strategies crossing scales. Moreover, a complex interaction is found among the three sociospatial dimensions, with four major types of combination including identical, parallel, substitution, and realization, which could be of significance in future studies aiming to further examining the production of multidimensional space.
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.09.001 [本文引用: 1]

Time-space compression in the context of globalization leads to declining costs of communication and transportation and increasing transnational activities. The emergence of multi-national firms and international organizations, in accordance with increasing boundary-crossing activities, has simultaneously weaken the power of state on economic, political, and cultural processes within its territory. Under such circumstances, some researchers assert globalization as "the end of geography", which sounds like an argument of hyper-globalist. In light of scale construction, human geographers are engaged in reconstructing the global scale and relating it to other scales. It turns out that space matters in the process of globalization. Two key points emerge: (1) Scale construction is not necessarily with hierarchical structures. Relation-based scales provide a better model for globalization, which is featured with horizontal communication rather than vertical regulation. (2) Global shifting exhibits trends both towards globalization and localization simultaneously, much of which appears to be global-local nexus rather than simplex globalizing process. These findings introduce new perspectives into globalization research in human geography: framework based on relational network makes it possible to conduct a trans-territorial analysis and to depict a big picture of the reshaping pattern of global economic landscape. On the other hand, in light of localized globalization, researchers set out to refer regional development to global-local interactions other than local embeddedness and endogenous factors, which offers insight into urban and regional governance in the context of globalization.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.2747/0272-3638.30.2.162URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/00420980500120881URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2017.07.002 [本文引用: 1]

Against the context of high-speed economic growth in China, the number of South Koreans who have expatriated to China soared over the last two decades. This increase has made China the third largest destination for South Korean Transmigrants among all nations, following only USA and Japan. The South Korean transmigrants mainly lived in major metropolises such as Beijing, Guangzhou and Shanghai. With the population growth of South Korean transmigrants in Chinese cities, now many South Korean enclaves have established and attracted attention both in China and abroad. However, compared to the foreign enclaves in Beijing and Shanghai coming from immigration policy and specific districts such as the economic and technological development zone, and embassy District, Yuanjing Road in Guangzhou got rid of the mark of impoverished urban village (Tangxia village) in Baiyun district, and transformed into a South Korean enclave mainly resided by South Korean traders. Based on the theory of production of space, this research sheds light upon the Yuanjing Road, taking it as a case to examine the production of space of this South Korean enclave, and first-hand data were gathered from questionnaires and interviews in February, May,October 2015 and September 2016. In the context of commodity chains and regional divisions of labor in an age of globalization, and transnational entrepreneurialism booming in Guangzhou, the local government took advantage of the situation that some South Korean traders have assembled in Yuanjing Road, and then put forward the construction of a Korean town at Yuanjing Road. Also, the local government, associating with investors, reconstructed the material space of the Yuanjing Road. At the same time, the South Korean traders strengthened their living and working foundation in the Yuanjing Road through three factors: the location advantage (next to some wholesale trade markets), social network connected to transnational trade chain, and Korean ethnic economy. Therefore, the South Korean traders succeed in occupying the space of the Yuanjing Road, and in redeveloping the social relations there. In summary, this study found that the Yuanjing Road’s transformation from an urban village to a South Korean enclave is a joint product of the local government, investors, and South Korean traders. As the result of production of space, the Yuanjing Road has become the place of transnational trade chain between China and South Korea, also the living space of diversify groups including the South Korean transmigrants, villagers, and migrant populations. The production of space of South Korean enclave in the Yuanjing Road, gives us a valuable lesson of the urban villages’ reconstruction in China, and also introduced ideas for immigration management to Guangzhou.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.geoforum.2006.09.010URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.08.012 [本文引用: 1]

Trade-environment relationship is one of the major manifestations of the coupled human-environment system, exhibiting significant complexity and uncertainty. Studies on the environmental effects of trade (EET) seek to explore the complementary or competing relationship between free trade and environment conservation, and give birth to a series of theories and hypotheses. Since globalization has witnessed increasing global-local interactions, this article outlines a framework of global connection, national power, and regional development to review existing studies on EET. It highlights how the process (flows) and the outcome (stocks) of trade work together to generate EET. Based on neo-classical international trade theory, this study identifies three types of stocks, namely location, growth, and regulation. In contrast, the integration of international trade and investment indicates the importance of intra-industry trade. This study shows that existing literature on EET is primarily based on the global and national scale, showing a "top-down" trend, where the role of environmental regulation stands at the center. However, these studies failed to incorporate the localized factors and neglected the interaction between trade policy and environmental regulation. They are also confined to the "north-south" trade and cease to follow the changing geography of trade. Accordingly, this article argues that EET studies should pay closer attention to regional development from a "glocalization" perspective to: (1) consider the expanding trade-induced regional inequality; (2) adapt to the coexistence of intra-and inter-industry trade; and (3) produce a proper scale for the coordination between trade policy and environmental regulation.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.03.002 [本文引用: 1]

The elimination of geography at Harvard University is a big event in the history of geography, which contributed to a key question whether geography is a vulnerable discipline. The elimination of geography at Harvard has a significant influence in the history of geographic thought. This article takes the elimination of geography at Harvard as a typical case and attempts to reveal the truth and the influences of the event based on the analysis of the stories in some references. The present essay is not just a case study of an important event in the history of American geography, but an opportunity for reflection and an invitation to learn from history and to apply these lessons to the present. The article argues that there were six reasons for the elimination of geography at Harvard, including the prevailing atmosphere of science, the arrogance of the university management, infighting between natural sciences and humanistic studies, the political factor of excluding communist influences, discrimination against homosexuals, university financial constraints, and the background of the particular period. The vulnerability of geography is actually a matter of identity, and is how to position the subject. It depends on how geography deals with its own relationship with other disciplines, society, the government, and management, which involves the scientific, social, and political nature of geography. As an independent interdisciplinary field with a long history, geography is closely related to other sciences, society, and politics. This is both a vulnerability and an advantage. The identity of other disciplines and societal issues are important to geography. Geography should adapt and change.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.01.001 [本文引用: 1]

Spatial differentiation of natural and human factors in the land surface system of the Earth is the main concern of Geography. Given the complexity of the land surface system, different research methods should be applied to different issues concerning the system. Based on past geographical research, four paradigms were generalized, including geographical empirical paradigm, geographical positivist paradigm, geographical system science paradigm, and geographical big data paradigm. Appropriate paradigms should be employed for different scientific questions, and multiple paradigms should be applied to some complicated questions.
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
