 ,中国医学科学院北京协和医学院医药生物技术研究所免疫生物学室,北京 100050
,中国医学科学院北京协和医学院医药生物技术研究所免疫生物学室,北京 100050Progress of SLFN family proteins in tumor and virus infection
Shumin Chen, Ling Ma, Shan Cen ,Author Affiliation: Department of Immunology, Institute of Medicinal Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Union Medical College, Beijing 100050, China
,Author Affiliation: Department of Immunology, Institute of Medicinal Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Union Medical College, Beijing 100050, China通讯作者: 岑山,博士,研究员,研究方向:病毒学。E-mail:shancen@imb.pumc.edu.cn
责任编辑: 谢建平
收稿日期:2019-12-5修回日期:2020-04-28网络出版日期:2020-05-20
| 基金资助: |
Editor:
Received:2019-12-5Revised:2020-04-28Online:2020-05-20
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
陈淑敏,在读博士研究生,专业方向:SLFN蛋白抑制HIV-1机制研究。E-mail:chenshumin1993@163.com。

摘要
Schlafen (SLFN)家族基因是在人类与小鼠中首先被发现的具有调控细胞生长及T细胞分化等诸多生物学功能的重要基因。该家族基因在小鼠、马和人等各个物种中广泛存在并具有较高的同源性。研究表明,SLFN蛋白在抑制细胞增殖、驱动减数分裂、调控造血细胞、下调血小板数量及调节免疫应答等方面均起到重要的作用,同时还可抑制HIV-1和流感等病毒复制。此外,SLFN蛋白还被发现与肿瘤的治疗密切相关,可以作为预测肿瘤发展进程和化疗敏感性的分子标记。本文介绍了SLFN家族蛋白的分类、结构和主要特征、定位与功能,重点综述了其在肿瘤和病毒感染等相关领域的研究进展,以期为SLFN蛋白新功能的探究提供新思路,对蛋白发挥作用的可能机制给予提示,并为各相关领域的研究提供参考。
关键词:
Abstract
Schlafen (SLFN) family genes were initially found in humans and rats to regulate cell growth and T cell differentiation, and exist widely in mice, horses, humans and other species and exhibit high homology. Lines of evidence suggest that SLFN proteins play important roles in inhibiting cell proliferation, promoting meiosis, regulating hematopoietic cells, reducing platelet numbers and the immune response, and also exert antiviral functions against several virus species including HIV-1, influenza virus and others. In addition, SLFN proteins have also been found to be closely related to cancer therapy, and act as a molecular marker to predict tumor development and the sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs. In this review, we discuss the classification, structures, characteristics, location and functions of SLFN family proteins, and focus on progress related to tumor and virus infection, aiming to provide new thoughts on exploration of SLFN protein functions and the underlying mechanisms.
Keywords:
PDF (483KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
陈淑敏, 马铃, 岑山. Schlafen家族蛋白在肿瘤和病毒感染中的研究进展. 遗传[J], 2020, 42(5): 444-451 doi:10.16288/j.yczz.19-311
Shumin Chen.
1998年,Schwarz等[1]在研究小鼠(Mus musculus)胸腺发育过程中第一次发现了Schlafen (SLFN)家族基因。“Schlafen”来源于德语,含义为“睡觉”,首次发现的SLFN蛋白为SLFN1,当其在NIH-3T3成纤维细胞中异位表达时观察到G0/G1细胞周期停滞的情况,故而将其命名为Schlafen1。后研究发现,所有SLFN蛋白都含有一个SLFN盒,是SLFN家族蛋白特有的结构域,功能尚不清楚。SLFN基因家族成员在小鼠、马(Equus caballus)和人(Homo sapiens)等多个物种中广泛分布,且具有较高的同源性。研究表明SLFN蛋白不仅在抑制细胞增殖、驱动减数分裂、调控造血细胞、T细胞分化、下调血小板数量及调节免疫应答等方面均起到重要的作用[2,3],还具有抑制HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency virus-1)、流感病毒等病毒复制的活性,并且与肿瘤治疗密切相关[4]。在某些恶性肿瘤中,SLFN蛋白可以抑制癌细胞的锚定生长和侵袭,提高肿瘤细胞对化学疗法的敏感性,预测肿瘤发展进程,并且有望成为新治疗靶标。本文对SLFN家族蛋白的结构和功能特征进行了介绍,并对其细胞生物学功能、与肿瘤和病毒研究领域的相关进展进行了综述,以期为各相关领域的研究提供参考。
1 SLFN家族蛋白分类与结构
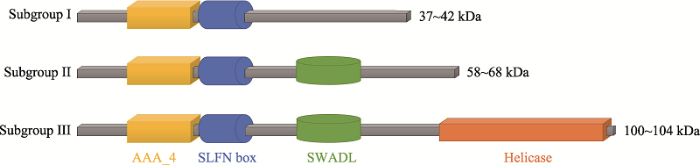
目前已知的小鼠SLFN蛋白包括 SLFN1、2、3、4、5、8、9、10和14,人源SLFN蛋白包括SLFN5、11、12、13和14[5]。根据基因同源性和编码蛋白的大小,SLFN蛋白被分成3组:蛋白分子大小在37~ 42 kDa的SLFN蛋白为Subgroup I,包含SLFN1、2;蛋白分子大小在58~68 kDa的为Subgroup II,包含SLFN3、4、12;蛋白分子大小在100~104 kDa的为Subgroup III,包含SLFN5、8、9、11、13和14[6,7]。与鼠源SLFN不同,人源SLFN中只有SLFN12缺乏解旋酶结构域,是唯一的Subgroup II成员,其余的人源SLFN均属于Subgroup III,C端包含一个解旋酶结构域,其中含有细胞核定位信号[5]。如图1所示,SLFN盒结构域位于SLFN蛋白中AAA_4结构域附近,可能具有参与结合细胞活性相关的GTP/ ATP的功能,从而进一步参与了哺乳动物免疫激活[3,6],SWADL(Ser-Trp-Ala-Asp-Leu)区选择性地表达在SLFN蛋白的Subgroup II和Subgroup III中[6],其功能尚未明确。SLFN蛋白中只有Subgroup III具有C末端的延长结构,与解旋酶超家族I中的解旋酶区同源,这也是SLFN家族蛋白涉及到RNA代谢(RNA metabolism)和RNA结构模型活性(RNA structure-modeling activity)的证据,揭示其可能是解旋酶超家族I[8]中ATP酶新成员。2 SLFN家族蛋白定位与功能
研究发现,通过I型干扰素(interferon,IFN)诱导的鼠源SLFN家族蛋白Subgroup I和II都定位在细胞质,而Subgroup III除SLFN14蛋白外,均包含了核定位序列,主要定位在细胞核中[6]。Subgroup I中SLFN2直接参与了小鼠破骨细胞的细胞发育,当SLFN2基因在小鼠细胞内被敲低后,其破骨细胞数量显著减少,小鼠表现出骨质疏松症相关表型[9]。同时,SLFN2还被发现在调节IFN介导的生物反应中也起关键作用。当细胞中SLFN2基因被定向敲低时,这会导致IFN刺激基因(IFN stimulate gene, ISG)转录上调,并显著增强IFN-α介导的抗病毒细胞免疫反应[10]。实验表明,SLFN2蛋白通过与蛋白磷酸酶6调节亚单位1 (protein phosphatase 6 regulation subunit 1, PPP6R1)相互作用,从而下调IFN-α诱导因子NF-κB (nuclear factor-κ B)的信号转导,进一步降低ISG的细胞表达[11]。与SLFN2类似,鼠源SLFN家族Subgroup II中的SLFN3在T细胞激活的过程中表达也上调。这间接性地说明SLFN家族蛋白主要通过促进T细胞的激活和分化来发挥免疫调节作用[12]。在肠粘膜中,SLFN蛋白在肠粘膜的分化和成熟起到了重要的作用,研究表明位于SLFN3蛋白N端的P-loop结构域对诱导肠的分化至关重要[13,14]。另外,SLFN3的表达导致p27蛋白表达增加,p27是细胞生长的负调节因子[15],这也表明SLFN3可以抑制细胞生长[14]。目前对于Subgroup III的鼠源SLFN蛋白功能所知甚少,然而对于Subgroup III的SLFN蛋白的细胞定位研究发现SLFN9与细胞中的磷酸化形式的RNA聚合酶II和SC-35蛋白呈现共定位,SC-35蛋白是细胞中剪切体的组分,这一现象表明SLFN9在RNA的转录和剪切中起到了一定的作用[3,6]。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1SLFN家族蛋白结构
Fig. 1Structure models of SLFN family proteins
在人源SLFN蛋白中,除SLFN12未有报道其定位信息外,其余蛋白均被定位于细胞核中[16,17,18]。目前对人源SLFN蛋白的研究表明,各SLFN因子均参与了单核细胞(monocytes)到树突状细胞(dendritic cells, DCs)的分化过程,在单核细胞被诱导分化成为DCs过程中,SLFN13表达被检测到大幅增加,表明其在细胞分化过程中发挥着促分化的功能,而SLFN12的表达水平则明显下调[19],表明它可能在DCs分化过程起负面调节作用,但在T细胞活化的过程中SLFN12蛋白水平上调显著,反映了SLFN家族蛋白在人体免疫细胞分化过程及功能调节中起着重要作用,但其具体机制仍不明确。此外,SLFN13还能靶向剪切哺乳动物tRNA/rRNA,分子结构研究揭示SLFN13 N端结构域具有独特的假二聚U形结构,可以夹住碱基配对的RNA,进一步抑制细胞中的蛋白质的合成[20]。Pisareva等[18]研究发现在兔(Oryctolagus cuniculus)成熟的网状红细胞内,被剪切的SLFN14蛋白可以识别并结合核糖体,并且非特异性地识别并剪切细胞中的rRNA与mRNA,而人源全长的SLFN14蛋白经特定氨基酸突变及剪切后也会显示相同的生物学活性,提示SLFN14在血细胞的功能行使中起着重要的作用。Saes等[21]和Stapley等[22]在大量遗传性血小板减少症患者中发现,正是SLFN14 GTP/ATP结合区的杂合错义突变导致其遗传性血小板致密颗粒数量减少,并伴随大量出血,表明SLFN14在血小板形成过程中发挥着重要作用。临床研究发现,人体内c.2557insC突变后的SLFN14基因可与c.1187delT突变的原钙粘蛋白γ-A4 (protocadherin gamma-A4, PCDHGA4)基因协同作 用,从而导致心房间隔缺损,诱发先天性紫癜性心脏病[23]。而SLFN5、11、13和14也已经被证实均在肿瘤或抗病毒方面有着重要的生物学活性。
3 SLFN家族蛋白在肿瘤中的研究
SLFN家族基因在调控细胞增殖和调节免疫应答等过程中均发挥着重要作用,提示其极有可能参与了肿瘤发生发展过程,促使研究者开展了在肿瘤领域对SLFN各蛋白的功能探索。研究发现,SLFN家族蛋白与肿瘤发生[24,25,26,27,28]、肿瘤锚定[16,27,29]以及肿瘤细胞耐药性[30,31,32,33,34]密切相关,其中与肿瘤细胞增殖调控相关的有SLFN2、3、5、11及12 (表1)。Table 1
表1
表1SLFN在肿瘤研究中的进展
Table 1
| SLFN | 对肿瘤细胞的影响 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| m-SLFN2 | 抑制肿瘤细胞转移;激活c-Jun、NFATc1蛋白表达,诱导破骨细胞癌变;抑制黑色素瘤细胞增殖 | [24,25,29] |
| m-SLFN3 | 抑制CSC增殖分化,提高结肠癌细胞对抗肿瘤药物敏感性 | [30] |
| h-SLFN5 | 抑制黑色素瘤细胞锚定依赖生长;胃癌细胞高表达,可作为胃癌发展过程组织学诊断标志 | [13,26] |
| h-SLFN11 | 靶向剪切胞内ATR/ATM蛋白翻译所需tRNA,提高肿瘤细胞对电离辐射、拓扑异构酶抑制剂 以及DDA敏感性,促进肿瘤细胞周期停滞和凋亡 | [31~35] |
| h-SLFN12 | SLFN12-PDE3A复合物下调胞内Bcl-2和Mcl-1蛋白水平,靶向诱导PDE3A高表达肿瘤细胞凋亡 | [27,28,36,37] |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
SLFN2基因敲除后的肿瘤细胞,其锚定依赖性生长会增加,而锚定依赖性生长是肿瘤生长转移的重要方式,因此SLFN2对肿瘤细胞转移具有负调节作用[29]。SLFN2蛋白具有诱导破骨细胞生成肿瘤的潜力,坏死因子家族成员NF-κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand, RANKL)具有诱导SLFN2的合成的功能,从而进一步通过激活c-Jun (proto-oncogene c-Jun)和活化T-细胞核因子1 (nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1, NFATc1)的表达促进破骨细胞生成[24]。除此之外,SLFN2还可抑制黑色素瘤细胞的增殖[29]。对Elektra小鼠的研究发现,当SLFN2蛋白第135位的异亮氨酸突变为天冬酰胺时,会导致小鼠的免疫反应异常,其由病毒和细菌感染所导致的死亡率明显高于普通小鼠[25]。
SLFN3的异位表达能抑制结肠癌中肿瘤干细胞(cancer stem cells, CSCs)的增殖分化。SLFN3蛋白在FOLFOX化疗方案中耐药的结肠癌HCT-116细胞中过表达时,观察到CSCs细胞中转化生长因子α (transforming growth factor-α, TGF-α) mRNA水平和蛋白水平均有明显下降[30]。此外,SLFN3蛋白的外源表达使CSCs排出的化疗耐药的指示剂减少,并刺激肿瘤细胞凋亡,从而明显提高结肠癌细胞对抗肿瘤药物的敏感性[30]。
SLFN5对恶性黑色素瘤细胞的锚定依赖性生长及侵犯胶原质具有负调节作用。Katsoulidis等[16]在检测恶性黑色素瘤细胞系中mRNA总体水平时发现,与正常黑色素细胞相比,SLFN5基因的mRNA表达被显著抑制,表明在恶性肿瘤细胞锚定表型出现时会选择性抑制SLFN5基因的表达水平。除此之外,SLFN5蛋白在由肠上皮化生症(intestinal metaplasia, IM)发展至胃癌的病人体内表达也有显著增强,通过统计学分析认定,SLFN5有成为胃癌发展过程组织学诊断标志的潜能[26]。
Barretina等[31]在建立肿瘤细胞系百科全书(cancer cell line encyclopedia, CCLE)过程中,结合24种具有代表性的抗肿瘤药物的药理学特点,预测了947个人类肿瘤细胞系的基因对这24种药物的敏感性,发现SLFN11表达与肿瘤细胞对拓扑异构酶抑制剂的敏感性密切相关。研究推断SLFN11具有预测肿瘤细胞对DNA损伤药物(DNA damage agent, DDA)类化疗药物敏感性的能力[32]。对具有高和低内源性SLFN11蛋白表达的细胞进行siRNA介导的沉默,分析发现SLFN11促进肿瘤细胞在DDA类药物作用下的细胞周期停滞,进而引起细胞死亡。能够将肿瘤细胞对DDA类药物的敏感性提高5倍,但并不影响肿瘤细胞对微管蛋白或蛋白酶抑制剂等的反应[32]。此外,SLFN11基因的表达水平或许还可预测经含顺铂方案治疗的卵巢癌病人的总生存时间。在统计诸多经过含顺铂方案治疗的卵巢癌病人的芯片数据后发现SLFN11高表达者平均总生存时间显著高于低表达者[32]。Kaur等[33]和Marzi等[34]的研究进一步证实了SLFN11会通过影响CD47的信号传导途径,提升肿瘤细胞对电离辐射及拓扑异构酶抑制剂的敏感性,增强以茚并异喹啉等药物对肿瘤细胞的抑制。近期Malone等[35]研究发现了SLFN11提高肿瘤细胞对DDA敏感性的潜在机制,SLFN11具有tRNA核酸内切酶活性,靶向剪切用于济失调毛细血管扩张突变(ataxia telangiectasia mutated,ATM)及ATR (ATM- and Rad3-related)丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶蛋白翻译的tRNA,从而在细胞应答过程中增强细胞受损情况下的细胞周期停滞和凋亡。
SLFN12在前列腺癌细胞的分化及化合物靶向诱导肿瘤细胞死亡的过程中也具有着重要作用。Kovalenko等[27]发现,SLFN12蛋白在前列腺上皮细胞中的过表达可以显著降低细胞内前列腺特异性抗原(prostate- specific antigen,PSA)基因的mRNA水平,并明显增强二肽基肽酶4 (dipeptidyl peptidase-4, DPP4)基因的转录,而这两种蛋白已确定是前列腺 癌的标志性蛋白[36],表明SLFN12很有可能参与 了前列腺癌细胞的分化过程。Wu等[28]研究表明,某些特定化合物,如6-[4-(二乙氨基)-3-硝基苯 基]-5-甲基-4,5-二氢哒嗪-3-酮(6-(4-(diethylamino)- 3-nitrophenyl)-5-methyl-4,5-dihydropyridazin-3(2H)- one, DNMDP),可以诱导肿瘤细胞中SLFN12与磷酸二酯酶3A (phosphodiesterase 3A, PDE3A)蛋白复合物的形成。SLFN12-PDE3A蛋白复合物在肿瘤细胞凋亡过程中起到重要的调节功能,可下调胞内B淋巴细胞瘤-2 (B-cell lymphoma-2, Bcl-2)和髓细胞白血病-1 (myeloid cell leukemia-1, Mcl-1)蛋白水平,触发细胞凋亡[37]。利用此调节机制研发PDE3A高表达的肿瘤细胞的靶向治疗药物,对未来研究癌症靶向治疗提供了有利方向。
4 SLFN家族蛋白在病毒中的研究
除了在肿瘤细胞中发挥着重要的生物学功能,近年研究发现SLFN11、12、13和14蛋白具有抑制多种病毒复制尤其是抑制流感病毒和HIV-1的功能(表2)。Table 2
表2
表2SLFN在病毒感染研究中的进展
Table 2
| SLFN | 对病毒的影响 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| h-SLFN11 | 识别HIV-1密码子偏好性,抑制HIV-1病毒复制; 下调宿主细胞tRNA丰度,选择性抑制单正链RNA病毒(WNV、DENV和ZIKV等)复制 | [17,38,39] |
| h-SLFN12 | 抑制HIV-1、EIAV、HERV-K、MLV及PFV等逆转录病毒复制 | [40] |
| h-SLFN13 | 选择性地剪切病毒RNA,抑制HIV-1;抑制ZIKV病毒复制 | [20] |
| h-SLFN14 | 增强IFN抗病毒活性,抑制流感病毒复制;抑制HIV病毒复制 | [41] |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2012年,Li等[17]研究发现SLFN11可以特异性抑制HIV-1的复制,推测其可通过识别HIV-1的密码子的偏好性而抑制HIV-1蛋白的表达。Lin等[38]发现马SLFN11蛋白也会以相同的密码子识别机制来降低同为慢病毒属的EIAV (equine infectious anemia virus)在细胞内的mRNA水平,从而抑制EIAV的复制。由于SLFN11可以由IFN-α诱导产生,因此推定SLFN11是继APOBEC3G (apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing enzyme catalytic polypeptide-like protein 3G),TRIM5 (tripartite motif-containing protein 5),BST2 (bone marrow stromal antigen 2),SAMHD1 (deoxynucleoside triphosphate triphosphohydrolase SAMHD1)后新发现的宿主限制因子。Valdez等[39]进一步研究发现,SLFN11对RNA病毒的抑制有选择性,SLFN11通过调节胞内宿主tRNA丰度从而抑制单正链RNA病毒(如WNV/west nile virus、DENV/dengue virus、ZIKV/zika virus等)的蛋白合成,但对单负链RNA病毒(如VSV/vesicular stomatitis virus、RVFV/rift valley fever virus等)的感染性并无影响。对后期SLFN11抗病毒机制的深度探究有关键性提示作用。
Melissa等[40]在筛查干扰素刺激因子的抗病毒活性的实验中发现人源SLFN12蛋白同样也对HIV-1、EIAV有显著的抑制作用,除此以外,SLFN12也对HERV-K (human endogenous retrovirus-K)、MLV (murine leukemia virus)及PFV (prototype foamy virus)等逆转录病毒有极强的抑制作用。本研究团队也有类似的发现,微量的SLFN12蛋白表达即可显著抑制HIV-1病毒感染性达一百多倍(结果未发表),但其具体的分子机制尚不清楚。
SLFN13作为一种新发现的tRNA / rRNA的核糖核酸内切酶,其核糖核酸内切酶的能力与其抗HIV-1病毒的水平呈正相关。现有研究者推测,SLFN13有可能是在胞浆当中,利用其N端结构域中U型枕样累二聚体折叠结构识别tRNA / rRNA分子碱基配对的RNA结构,选择性地剪切病毒RNA使其丧失翻译能力,从而达到抑制病毒复制的目的。除此以外,SLFN13对黄病毒属的ZIKV也有一定程度的抑制功能[20]。
Rak-Kyun等[41]在探究SLFN14抗病毒能力时发现,SLFN14可强烈抑制流感病毒的复制并增强IFN的抗病毒活性,Toll样受体3 (Toll-like receptor 3, TLR3)激动剂可调控鼠源SLFN14蛋白的内源表达。本研究团队发现人源SLFN14蛋白具有较好的抑制HIV-1病毒的活性,可有效抑制病毒转录从而下调其mRNA水平(结果未发表),但具体机制尚不清楚。
5 结语与展望
近年来,随着对SLFN家族蛋白的研究不断深入,关于SLFN家族蛋白的功能探索取得了一定的进展。现研究表明,SLFN家族蛋白在调节免疫应答、调控细胞周期方面发挥着重要的作用,其中的某些蛋白与肿瘤敏感性和耐药性均相关,在肿瘤发展的不同阶段有差别表达,对肿瘤细胞的锚定生长起重要作用,SLFN家族蛋白在肿瘤细胞内的生物学功能为肿瘤的检测和治疗提供了新的方法和思路。此外,SLFN家族中诸多蛋白对逆转录病毒初步呈现出较为广泛的抑制作用,参与人体抗病毒天然免疫,显著降低HIV-1及流感病毒的RNA水平和复制能力,对病毒感染和复制过程有着重要的调控作用。当然,目前对SLFN家族蛋白的功能研究仍处于初期阶段,仍有诸多问题亟待解决。如:(1) SLFN家族蛋白在抑制肿瘤发生发展及病毒复制的详细功能机制仍需进一步探究。尽管目前发现SLFN5蛋白可作为胃癌发展过程组织学诊断标志、SLFN11可增强抗肿瘤药物治疗效果,但其具体功能机制仍未可知,限制了其在疾病临床治疗中的应用。(2) SLFN蛋白结构亦需深入分析。SLFN蛋白在多个物种中广泛分布,且有较高的同源性,但其蛋白结构域及功能探究仍处于起始阶段,SLFN家族蛋白的详细结构特征和功能机制不明确,大大限制了其临床应用,目前SLFN13蛋白晶体结构已被解析,对SLFN家族蛋白的后续研究和应用提供了研究参考,对于SLFN家族蛋白进行进一步地深入研究具有重要意义。
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
DOI:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80663-9URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1093/intimm/dxh155URL [本文引用: 3]
DOI:10.1038/nrurol.2012.188URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.gene.2009.07.006URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.03.032URL [本文引用: 5]
DOI:10.1074/jbc.M500435200URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-31428-zURL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1189/jlb.0609410URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2012.07.004URL [本文引用: 1]

BACKGROUND: Understanding gut development may illuminate the adaptive response to massive small-bowel resection and facilitate enteral nutrition. We reported that Schlafen-3 (Slfn3) mediates differentiation in vitro in rat intestinal epithelial. We hypothesized that Slfn3 is involved in intestinal development in vivo.
METHODS: We removed fetal intestines, liver, and lungs on day 20 of gestation, at birth, and on postnatal days 1 and 5. Expression of Slfn3, markers of intestinal differentiation, and Slfn5, to address specificity, were determined by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction.
RESULTS: Villin expression increased on days 1 and 5 (8.7 +/- .6 and 5.4 +/- .4, respectively; P < .01). Intestinal Slfn3 expression was increased substantially after birth (2.1- +/- .5-fold) and on days 1 and 5 (P < .02). Slfn3 was higher after birth in liver and lung but decreased sharply thereafter. Slfn5 expression was mostly unchanged.
CONCLUSIONS: The data suggest that the developmental/maturation effects we observed correlate with Slfn3 but not Slfn5 and are more relevant to the intestines. A better understanding of how Slfn3 promotes intestinal differentiation could help promote intestinal maturation, improving outcomes in children or adults with short-gut syndrome. Published by Elsevier Inc.
DOI:10.1152/ajpgi.90726.2008URL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1074/jbc.M110.151076URL [本文引用: 3]
DOI:10.1038/nature11433URL [本文引用: 2]

In mammals, one of the most pronounced consequences of viral infection is the induction of type I interferons, cytokines with potent antiviral activity. Schlafen (Slfn) genes are a subset of interferon-stimulated early response genes (ISGs) that are also induced directly by pathogens via the interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) pathway(1). However, many ISGs are of unknown or incompletely understood function. Here we show that human SLFN11 potently and specifically abrogates the production of retroviruses such as human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1). Our study revealed that SLFN11 has no effect on the early steps of the retroviral infection cycle, including reverse transcription, integration and transcription. Rather, SLFN11 acts at the late stage of virus production by selectively inhibiting the expression of viral proteins in a codon-usage-dependent manner. We further find that SLFN11 binds transfer RNA, and counteracts changes in the tRNA pool elicited by the presence of HIV. Our studies identified a novel antiviral mechanism within the innate immune response, in which SLFN11 selectively inhibits viral protein synthesis in HIV-infected cells by means of codon-bias discrimination.
DOI:10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00302URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1016/j.rinim.2015.10.001URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1038/s41467-018-03544-xURL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1111/hae.2019.25.issue-1URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1080/09537104.2019.1648781URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1007/s11596-018-1974-2URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.08.019URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1038/ni0410-281URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1007/s00535-016-1202-4URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1016/j.jss.2014.03.069URL [本文引用: 3]

Background: Schlafen proteins have previously been linked to leukocyte and intestinal epithelial differentiation. We hypothesized that Schlafen 12 (SLFN12) overexpression in human prostate epithelial cells would modulate expression of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4), markers of prostatic epithelial differentiation.
Materials and methods: Differentiation of the human prostate cancer cell lines LNCaP and PC-3 was compared after infection with an adenoviral vector coding for SLFN12 (Ad-SLFN12) or green fluorescent protein (GFP) only expressing virus (control). Transcript levels of SLFN12, PSA, and DPP4 were evaluated by real-time reverse transcription PCR and protein levels by Western blotting. Because mixed lineage kinase (MLK) and one of its downstream effectors (extracellular signal-regulated kinases [ERK]) have previously been implicated in some aspects of prostate epithelial differentiation, we conducted further studies in which LNCaP cells were cotreated with dimethyl sulfoxide (control), PD98059 (ERK inhibitor), or MLK inhibitor during transfection with Ad-SLFN12 for 72 h.
Results: Treatment of LNCaP or PC-3 cells with Ad-SLFN12 reduced PSA expression by 56.6 +/- 4.6% (P < 0.05) but increased DPP4 transcript level by 4.8 +/- 1.0 fold (P < 0.05) versus Ad-GFP-treated controls. Further studies in LNCaP cells showed that Ad-SLFN12 overexpression increased the ratio of the mature E-cadherin protein to its precursor protein. Furthermore, SLFN12 overexpression promoted DPP4 expression either when MLK or ERK was blocked. ERK inhibition did not reverse SLFN12- induced changes in PSA, E-cadherin, or DPP4.
Conclusions: SLFN12 may regulate differentiation in prostate epithelial cells, at least in part independently of ERK or MLK. Understanding how SLFN12 influences prostatic epithelial differentiation may ultimately identify targets to influence the phenotype of prostatic malignancy. (C) 2014 Elsevier Inc.
DOI:10.1074/jbc.RA119.011191URL [本文引用: 2]
DOI:10.1074/jbc.M109.030445URL [本文引用: 3]
DOI:10.1152/ajpgi.00403.2010URL [本文引用: 3]
DOI:10.1038/nature11003URL [本文引用: 2]

The systematic translation of cancer genomic data into knowledge of tumour biology and therapeutic possibilities remains challenging. Such efforts should be greatly aided by robust preclinical model systems that reflect the genomic diversity of human cancers and for which detailed genetic and pharmacological annotation is available(1). Here we describe the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE): a compilation of gene expression, chromosomal copy number and massively parallel sequencing data from947 human cancer cell lines. When coupled with pharmacological profiles for 24 anticancer drugs across 479 of the cell lines, this collection allowed identification of genetic, lineage, and gene-expression-based predictors of drug sensitivity. In addition to known predictors, we found that plasma cell lineage correlated with sensitivity to IGF1 receptor inhibitors; AHR expression was associated with MEK inhibitor efficacy in NRAS-mutant lines; and SLFN11 expression predicted sensitivity to topoisomerase inhibitors. Together, our results indicate that large, annotated cell-line collections may help to enable preclinical stratification schemata for anticancer agents. The generation of genetic predictions of drug response in the preclinical setting and their incorporation into cancer clinical trial design could speed the emergence of 'personalized' therapeutic regimens(2).
[本文引用: 4]
DOI:10.3389/fonc.2019.00994URL [本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 2]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.molcel.2019.06.040URL [本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
[本文引用: 1]
