 ,江苏省农业科学院畜牧研究所,江苏省农业种质资源保护与利用平台,南京 210014
,江苏省农业科学院畜牧研究所,江苏省农业种质资源保护与利用平台,南京 210014Physiology and genetics research progress of teat traits in pigs
Lisheng Zhou, Weimin Zhao, Feng Tu, Yunhe Wu, Shouwen Ren, Xiaomin Fang ,Jiangsu Germplasm Resources Protection and Utilization Platform, Institute of Animal Science, Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Nanjing 210014, China
,Jiangsu Germplasm Resources Protection and Utilization Platform, Institute of Animal Science, Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Nanjing 210014, China通讯作者:
编委: 任军
收稿日期:2018-12-12修回日期:2019-04-22网络出版日期:2019-05-20
| 基金资助: |
Received:2018-12-12Revised:2019-04-22Online:2019-05-20
| Fund supported: |
作者简介 About authors
周李生,博士,助理研究员,研究方向:猪数量性状遗传解析E-mail:

摘要
关键词:
Abstract
Keywords:
PDF (340KB)元数据多维度评价相关文章导出EndNote|Ris|Bibtex收藏本文
本文引用格式
周李生, 赵为民, 涂枫, 吴云鹤, 任守文, 方晓敏. 猪乳头性状生理学和遗传学研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(5): 384-390 doi:10.16288/j.yczz.18-336
Lisheng Zhou, Weimin Zhao, Feng Tu, Yunhe Wu, Shouwen Ren, Xiaomin Fang.
种猪的繁殖性能直接影响养猪生产效益,是品种改良工作中的重要方向,主要包括排卵率、乳头性状、产仔数和断奶活仔数等。其中,乳头性状是衡量母猪哺乳能力的重要指标,具有较多有效乳头数的母猪可以哺乳更多的仔猪,有效乳头数少于产仔数会严重影响仔猪的成活率。同时,乳头数与产仔数也有一定程度的相关性[1],多乳头数和高产仔数的有效结合是实现母猪高繁殖能力的生理基础。
猪乳头数作为具有中等遗传力(约0.3)的数量性状,利用传统育种技术很难在短期内获得较为明显的遗传进展[2]。分子育种技术能够有效克服传统育种的缺点,提高育种效率。然而,猪乳头数在遗传上可能受到多个基因的调控,目前人们对于控制猪乳头数性状的主效基因尚不清晰,也缺乏具有育种价值的分子标记。本文综述了猪乳头在胚胎时期的形成过程、乳头性状表型研究的复杂性以及乳头性状调控基因的遗传定位结果,旨在为今后发掘影响猪乳头性状的因果突变和主效基因,实现猪繁殖性状遗传改良基础理论和技术方法的创新提供参考。
1 猪乳头及乳腺组织在胚胎期的发育
哺乳动物乳头和乳腺在胚胎期的形成和发育过程基本一致,共分为4个阶段[3]:(1)形成乳腺线:在约23天猪胚胎期,由腹部两侧的柱状和多层次外胚层细胞形成乳腺线;(2)形成乳腺原基:在乳腺线形成后的24~36 h内,即26天左右的猪胚胎期,乳腺线逐步特化形成清晰可见的乳腺原基,该过程是决定猪乳头数目的关键发育阶段;(3)形成腺芽:乳腺基板扩增并向下面间质层凹陷为芽状结构形成腺芽;(4)形成原始乳腺导管分支:腺芽上的上皮细胞分化为乳头皮肤,腺芽下的上皮细胞向下分支并伸入到脂肪板中,形成原始乳腺导管分支,组成初级乳腺。至此,乳头及乳腺组织在胚胎期的发育基本完成,它们将在出生后的青春期和妊娠期中进一步发育,最终形成在哺乳期能够产生哺乳功能的组织器官。乳头及乳腺发育是在众多信号通路共同调控下完成的,目前已知的信号通路包括:(1)影响乳腺线特化和乳腺原基大小的Wnt信号通路[4],引发乳腺线的分化并影响乳腺原基的大小,Wnt3、Wnt6和Wnt10b是该过程中的重要候选基因;(2)与Wnt信号通路协同调控乳腺线形成的TBX3信号通路[5,6],Tbx3基因敲除的胚胎无法正常形成腺芽,且Wnt10b和Lef1基因表达也缺失;(3)调控乳腺原基形成的FGF信号通路[7],该通路调控乳腺细胞的形成。对基因敲除小鼠的研究显示,FGF10和FGFR2b基因缺失可导致乳腺原基的形成受阻[6];(4)影响乳腺数量和位置的EGFR家族通路[8],该通路中的Nrg3基因及其受体基因(Erbb2和Erbb4)在乳腺线相应的位置细胞中表达,对乳腺的形成具有重要的调控作用;(5)调节胚胎期乳腺腺泡发育的Notch/RBP-J信号通路[9]。对小鼠乳腺祖细胞的研究发现, Notch/RBP-J信号通路中的RBP-J和Pofut1基因可调节乳腺泡形成;(6)调节胚胎期乳腺腺芽形成和发育的p190- BRhoGAP/IGF通路[10],该通路中IGF-1R基因通过p190-B和IRS蛋白发挥相应的调控作用。上述研究表明:信号通路及其包含的基因间的相互作用,不仅可调控乳头和乳腺的形成数目与功能学发育状态,也可以调控其形态学发生的位置。然而,多数乳头及乳腺在胚胎时期的发育学研究是利用小鼠等小型模式动物完成,目前在猪等大型哺乳动物中的相关研究尚少。
2 猪乳头性状的复杂性
猪乳头性状复杂多样,主要体现在4个方面:乳头数量在不同品种及同一品种的不同个体间存在变异、乳头类型多样、乳头在腹部的分布具有区域性和不对称性。2.1 猪乳头数存在变异
根据《中国畜禽遗传资源志-猪志》和已报道的文献公布的数据(表1),发现猪乳头数存在品种间及品种内的差异,并与其繁殖性能相适应。繁殖性能最强的江海型猪乳头数最多,二花脸猪的乳头数可多达22个。大体型的北方猪种乳头数略多于小体型的南方猪种,繁殖力较弱的滇南小耳猪等南方小型猪的乳头数少至10个。二花脸猪、巴马香猪、五指山猪等品种内的乳头数存在较大变异。大白猪等西方商品猪的乳头数多为12或14个,相对固定。这些数据表明:相对于西方商品猪种,中国地方猪种乳头数的遗传多样性更加丰富;中国地方猪种对乳头数的选育程度较弱,品种内乳头数的一致性不强。Table 1
表1
表1 中西方部分猪种乳头数分布
Table 1
| 猪种 | 产地 | 乳头数(个) |
|---|---|---|
| 中国地方猪种 | ||
| 二花脸猪 | 江苏 | 18~22 |
| 莱芜猪 | 山东 | 14~16 |
| 金华猪 | 浙江 | 14~16 |
| 民猪 | 黑龙江 | 10~19 |
| 河套大耳猪 | 内蒙古 | 14~18 |
| 通城猪 | 湖北 | 12~14 |
| 大花白猪 | 广东 | 12 |
| 荣昌猪 | 重庆 | 12~14 |
| 内江猪 | 四川 | 12~14 |
| 巴马香猪 | 广西 | 10~16 |
| 五指山猪 | 海南 | 10~14 |
| 迪庆藏猪 | 云南 | 10~12 |
| 滇南小耳猪 | 云南 | 10 |
| 西方商品猪种 | ||
| 长白猪 | 丹麦 | 14~16 |
| 大白猪 | 英国 | 14 |
| 巴克夏猪 | 英国 | 14 |
| 杜洛克猪 | 美国 | 12 |
| 皮特兰猪 | 比利时 | 12 |
新窗口打开|下载CSV
2.2 猪乳头存在不同类型
依据猪乳头形态结构的完整程度和生理功能的正常程度,可将其分为正常乳头、翻乳头(又称火山乳头)和副乳头(又称瞎乳头) 3大类型[11]。成年猪的正常乳头凸起完整,乳头体较明显,顶端具有明显开口,具备正常的泌乳和哺乳功能。翻乳头乳头体不明显(不完全翻乳头)或者没有(完全翻乳头),乳头管存在发育缺陷,乳腺与正常乳头的一致,具有泌乳功能,但由于乳头体缺失,导致仔猪吸取乳汁困难,难以实现哺乳功能。副乳头仅在猪体表面上呈现为一个小的凸起,无乳房膨大部,乳腺组织发育不全,基本无泌乳功能。翻乳头和副乳头统称为功能缺陷型乳头,可能是乳头基部结缔组织和乳腺组织在发育的某些阶段受遗传或环境因素的干扰所致。2.3 猪乳头分布具有区域性
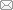
2012年,Nikitin等[12]分析了5个家猪群体(约20 000个体)的乳头表型数据,发现猪乳头在腹部的分布具有一定的规律性。研究发现,猪乳头在腹部的分布可分为10个区域,每个区域包含有1对乳头(图1)。其中,区域1、3、7和8为固定乳头区,即该区域有且仅有1对正常乳头;区域2、4、5、6、9和10为可变乳头区,该区域可能含有1对、1个或者没有乳头。功能缺陷的副乳头大多分布于区域4和5,肛门乳头位于接近尾部的区域9和10,大多功能异常,其他区域的乳头基本为正常乳头。同一区域中2个乳头的乳头类型不一定相同;若某区域仅有1个乳头,则其分布于左侧或右侧的概率基本一致。图1
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图1猪乳头在腹部的分布示意图
根据文献[12]修改绘制。
Fig. 1Teat distribution sketch on pig belly
上述研究表明:猪乳头数的变化主要受可变乳头区影响,在不同的猪种甚至同一品种的不同个体中,可变乳头区中的乳头数变化直接影响总乳头数。由于乳头数的分布具有上述的严格分区特性,故推测在不同区域中,影响其乳头发育的主效基因及因果位点可能不同。因此在遗传学分析中,建议按照分区原则,准确记录猪乳头性状表型数据,以便后续分析。
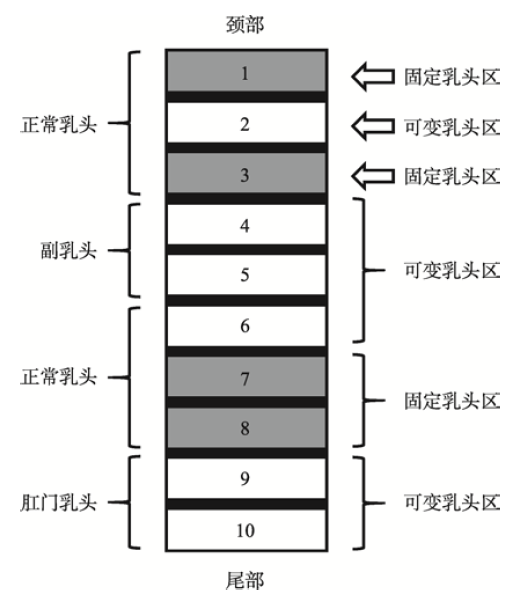
2.4 猪乳头存在波动不对称性现象
大多数情况下,猪左右乳头数及位置分布是对称的(图2A),但也存在左右乳头数不一致和乳头排列不对称的情况,即轴不对称现象[13](图2B)。目前对于该现象的遗传学研究较少,有研究认为是由于非特定的环境因素所导致的随机性“摆动”[14],但该论点尚缺乏有力的证据,需要进一步的深入研究。图2
 新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT
新窗口打开|下载原图ZIP|生成PPT图2猪乳头左右分布情况
Fig. 2Teat distribution at left and right side
3 猪乳头性状的QTL定位
目前,国内外多个研究组对猪乳头性状开展了数量性状位点(quantitative trait locus, QTL)定位研究。据国际猪QTL数据库(3.1 猪乳头数QTL定位
针对乳头数性状的QTL定位研究较多,如:2000年Rohrer等[15]最先报道利用157个微卫星标记在梅山×大白资源群体SSC1、SSC3和SSC10染色体上定位到影响总乳头数的QTL;Geldermann等[16]通过构建梅山×皮特兰×野猪资源家系,在SSC1、SSC2、SSC5、SSC8、SSC10、SSC12和SSCX染色体上定位到影响总乳头数的QTL;Ding等[17]在二花脸×白色杜洛克资源家系中分别定位到影响总乳头数(SSC1、SSC3、SSC4、SSC5、SSC6、SSC7、SSC8和SSC12)、左乳头数(SSC1、SSC3、SSC4、SSC5、SSC6、SSC7、SSC8和SSC12)和右乳头数(SSC1、SSC3、SSC4、SSC5、SSC7和SSC8)的QTL;2014年,Lopes[18]首次报道利用长白猪高密度基因分型芯片数据,通过GWAS分析在SSC4、SSC6、SSC7和SSC12染色体上检测到与总乳头数显著关联位点;2017年Tan等[19]率先使用全基因组测序基因分型技术(genotyping-by-sequencing, GBS),对2936头杜洛克猪群体进行GWAS分析,分别在SSC1、SSC6、SSC7、SSC10、SSC11、SSC12和SSC14染色体上鉴别到显著影响猪乳头数的关联位点。值得肯定的是:随着标记密度和群体规模的提高以及分析手段的不断改进,鉴别到影响猪乳头数QTL的数量与准确性也大大提高。然而,上述研究主要集中在梅山/二花脸猪×西方商品猪构建的资源群体和西方商品猪纯种群体,而对中国地方猪纯种群体和含中国地方猪血缘的培育品种的研究则相对较少。
3.2 猪功能缺陷乳头QTL定位研究
关于功能缺陷乳头的遗传定位研究较少:Demeure等[20]利用梅山×大白/长白群体在SSC7染色体上鉴别到影响功能缺陷乳头的QTL;Sato等[21]在梅山×杜洛克资源群体中SSC2和SSC16染色体上检测到影响功能缺陷乳头的QTL;Jonas等[22]在杜洛克×柏林微型猪资源家系中发现,在SSC3、SSC4、SSC6和SSC11染色体上有影响功能缺陷乳头的QTL。上述研究结果表明:不同实验群体所鉴别的功能缺陷乳头QTL定位结果存在较大的差异,表明其遗传机理比较复杂,可能存在多个遗传位点,需深入研究。4 猪乳头性状候选基因研究
目前,猪乳头性状的候选基因研究主要集中于乳头数和功能缺陷乳头性状。瘦素(protein hormone leptin, LEP)主要由脂肪细胞产生和分泌,主要功能是通过下丘脑产生饱足信号,影响能量摄入来调控体重平衡[23]。然而,Peixoto等[24]对大白×长白×皮特兰F2资源家系的研究发现:LEP基因上的突变C798T与总乳头数(P<0.02)、左乳头数(P<0.03)也存在显著关联,该基因可作为猪乳头数选育的潜在分子标记。Dragos-Wendrich等[25]对大白×梅山F2资源家系QTL定位结果显示,位于SSC10染色体上的AKR1C4基因是总乳头数的位置候选基因,该基因属于醛酮还原酶家族,可通过催化酮甾体和羟基甾体的还原和氧化,将雄激素、雌激素、孕激素和糖皮质激素相互转化为相对更强的对应物,参与生长发育和生殖等多种生理过程[26]。Mart?nez-Giner等[27]在含梅山猪血缘的资源群体中,对AKR1C4基因的全长cDNA测序,发现存在2个与乳头数存在显著关联的SNP(P<0.03),并且AKR1C4基因在仔猪的乳腺组织中高度表达,提示该基因可能在胚胎发育过程中影响乳头的形成。Jin等[28]在大白×韩国地方猪资源家系中鉴别到SSC7染色体上显著影响猪乳头数的QTL,并确定TBC1D21为该QTL最有可能的位置候选基因,同时检测到该基因上存在2个和总乳头数极显著相关的SNPs,分别为g.13,050A>G(P = 6.38E-05)和SNP c.829A>T(P = 1.06E-07)。LEF-1基因是TCF (T-cell specific factor)家族成员之一,在胚胎早期发育过程中调控乳头和乳腺的形态发生。Xu等[29]发现该基因上的2个突变99514A>G和119846C> T在关中黑猪、汉江黑猪、八眉猪和大白猪4个群体中都与总乳头数显著相关(P<0.05)。Duijvesteijn等[30]和Rohrer等[31]研究发现,乳头数和脊椎数的遗传机制存在一定的相关性,VRTN、PROX2、MPP7、ARMC4、MKX和δ-EF1等与脊椎发育相关的基因也是影响乳头数发育的强候选基因。Yang等[32]研究表明,VRTN基因上影响脊椎数的因果突变(g.20311_ 20312ins291)与猪乳头数显著关联。针对功能缺陷乳头,Tetzlaff等[33]在前期QTL定位的基础上[22],发现位置候选基因PTHR1上的突变C1819T与翻乳头性状显著关联。Chomwisarutkun等[34,35]利用基因表达芯片检测成年猪的正常乳头与翻乳头的上皮组织和间充质组织,分别发现62个和24个显著差异表达基因,它们与细胞增殖、器官与组织发育和核酸修饰等代谢过程紧密相关。
到目前为止,还未鉴别到影响猪乳头性状的主效基因和因果突变,可能有以下4点原因:(1)乳头性状复杂多样,在实际研究中对乳头性状的表型区分不够细化,从而造成阴性结果,影响不同乳头性状的因果突变和主效基因不尽相同;(2)前期研究主要集中在纯种猪群或有限世代的资源家系,群体中连锁不平衡(linkage disequilibrium, LD)程度较高,从而无法对鉴别到的QTL进行精细定位和深入解析;(3)定位获得的强关联位点大部分位于基因组上的非编码区域,可能为调控突变,给精确鉴别因果突变和目的基因带来极大的挑战;(4)未探究影响猪乳头数形成的关键组织、细胞及时间节点,无法合理地利用转录组学、蛋白组学等技术手段,无法通过多维组学分析准确锚定目的基因。因此,未来只有利用合适的实验材料、精准的表型记录和更先进的研究策略,才可能为猪乳头性状的遗传机制解析带来新的突破。
5 结语与展望
猪乳头性状是种猪选育中重要的参考指标之一,从遗传水平上解析猪乳头数变异和乳头缺陷发生的机理,能够更有效地开展优良种猪的选育工作。同时,有研究显示人类中也存在多乳头和乳头缺陷等遗传疾病[36,37]。由于猪在生理结构和代谢机制上与人类高度相似,对猪乳头性状的遗传解析有助于其成为人类乳头疾病的模式动物模型,可以在未来的医学研究中发挥一定的作用。然而,国内外科研人员利用不同的品种开展QTL定位并搜寻其主效基因的结果并不理想,仍需要进一步的探索。随着测序技术的发展和测序成本的降低,研究人员可以利用全基因组重测序及基因型填充手段,提高检测标记密度,最大程度地利用实验群体中存在的重组事件,并与其他组学数据(转录组学、蛋白质组学、代谢组学等)整合分析,结合跨物种的保守性进化分析及详细的基因组注释信息,以达到迅速鉴别因果突变和主效基因的目的[38]。因此,今后应在科学细致的表型记录基础上,准确把握猪乳头数胚胎发育时期产生数目差异的关键组织与时间节点,并借鉴QTL解析的最新策略,深入挖掘影响猪乳头数的因果位点和主效基因,为选育含有较多乳头数且乳头无缺陷的种猪提供理论依据。
(责任编委: 任军)
参考文献 原文顺序
文献年度倒序
文中引用次数倒序
被引期刊影响因子
URLPMID:4736284 [本文引用: 1]

Reproductive traits such as number of stillborn piglets (SB) and number of teats (NT) have been evaluated in many genome-wide association studies (GWAS). Most of these GWAS were performed under the assumption that these traits were normally distributed. However, both SB and NT are discrete (e.g. count) variables. Therefore, it is necessary to test for better fit of other appropriate statistical models based on discrete distributions. In addition, although many GWAS have been performed, the biological meaning of the identified candidate genes, as well as their functional relationships still need to be better understood. Here, we performed and tested a Bayesian treatment of a GWAS model assuming a Poisson distribution for SB and NT in a commercial pig line. To explore the biological role of the genes that underlie SB and NT and identify the most likely candidate genes, we used the most significant single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), to collect related genes and generated gene-transcription factor (TF) networks. Comparisons of the Poisson and Gaussian distributions showed that the Poisson model was appropriate for SB, while the Gaussian was appropriate for NT. The fitted GWAS models indicated 18 and 65 significant SNPs with one and nine quantitative trait locus (QTL) regions within which 18 and 57 related genes were identified for SB and NT, respectively. Based on the related TF, we selected the most representative TF for each trait and constructed a gene-TF network of gene-gene interactions and identified new candidate genes. Our comparative analyses showed that the Poisson model presented the best fit for SB. Thus, to increase the accuracy of GWAS, counting models should be considered for this kind of trait. We identified multiple candidate genes (e.g.PTP4A2, NPHP1,andCYP24A1for SB andYLPM1, SYNDIG1L, TGFB3,andVRTNfor NT) and TF (e.g.NF- BandKLF4for SB andSOX9andELF5for NT), which were consistent with known newborn survival traits (e.g. congenital heart disease in fetuses and kidney diseases and diabetes in the mother) and mammary gland biology (e.g. mammary gland development and body length). The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12711-016-0189-x) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
URLPMID:25817797 [本文引用: 1]

Summary The genetic improvement in pig litter size has been substantial. The number of teats on the sow must thus increase as well to meet the needs of the piglets, because each piglet needs access to its own teat. We applied a genetic heterogeneity model to teat counts in pigs, and estimated a medium heritability for teat counts (0.35), but found a low heritability for residual variance (0.06), indicating that selection for reduced residual variance might have a limited effect. A numerically positive correlation (0.8) was estimated between the breeding values for the mean and the residual variance. However, because of the low heritability of the residual variance, the residual variance will probably increase very slowly with the mean.
URLPMID:18007652 [本文引用: 1]

Mammary glands become functional only in adult life but their development starts in the embryo. Initiation of the epithelial bud and ductal outgrowth are coordinated through short-range signals between epithelium and mesenchyme. Studies of natural and induced mouse mutants in which early mammary development is perturbed have identified genetic networks that regulate specific steps in these processes. Some of these signals contribute to aberrant mammary development in humans and are deregulated in cancer.
URLPMID:17898001 [本文引用: 1]

Transforming -beta (TGF-beta) plays an essential role in and patterning of the mammary gland, and alterations in its have been shown to illicit biphasic effects on and metastasis. We demonstrate in that TGF-beta (Tgfbeta) regulates the expression of a non-canonical member of the wingless-related family, . Loss of expression has been associated with poor prognosis in breast patients; however, data are lacking with regard to a functional role for in . We show that is capable of inhibiting ductal extension and lateral branching in the mammary gland. Furthermore, (-/-) mammary tissue exhibits an accelerated developmental capacity compared with wild-type tissue, marked by larger terminal end buds, rapid ductal elongation, increased lateral branching and increased proliferation. Additionally, dominant-negative interference of TGF-beta impacts not only the expression of , but also the of discoidin domain receptor 1 (), a receptor for and downstream target of implicated in /migration. Lastly, we show that is required for TGF-beta-mediated inhibition of ductal extension in vivo and branching in culture. This study is the first to show a requirement for in normal mammary development and its functional connection to TGF-beta.
URL [本文引用: 1]

Interactions between Wnts, Fgfs and Tbx genes are involved in limb initiation and the same gene families have been implicated in mammary gland development. Here we explore how these genes act together in mammary gland initiation. We compared expression of Tbx3 , the gene associated with the human condition ulnar鈥搈ammary syndrome, expression of the gene encoding the dual-specificity MAPK phosphatase Pyst1 /MKP3, which is an early response to FGFR1 signalling (as judged by sensitivity to the SU5402 inhibitor), and expression of Lef1 , encoding a transcription factor mediating Wnt signalling and the earliest gene so far known to be expressed in mammary gland development. We found that Tbx3 is expressed earlier than Lef1 and that Pyst1 is also expressed early but only transiently. Patterns of expression of Tbx3 , Pyst1 and Lef1 in different glands suggest that the order of mammary gland initiation is 3, 4, 1, 2 and 5. Consistent with expression of Pyst1 in the mammary gland, we detected expression of Fgfr1b , Fgf8 and Fgf9 in both surface ectoderm and mammary bud epithelium, and Fgf4 and Fgf17 in mammary bud epithelium. Beads soaked in FGF-8 applied to the flank of mouse embryos, at a stage just prior to mammary bud initiation, induce expression of Pyst1 and Lef1 and maintain Tbx3 expression in flank tissue surrounding the bead. Grafting beads soaked in the FGFR1 inhibitor, SU5402, abolishes Tbx3 , Pyst1 and Lef1 expression, supporting the idea that FGFR1 signalling is required for early mammary gland initiation. We also showed that blocking Wnt signalling abolishes Tbx3 expression but not Pyst1 expression. These data, taken together with previous findings, suggest a model in which Tbx3 expression is induced and maintained in early gland initiation by both Wnt and Fgf signalling through FGFR1.
URLPMID:16720875 [本文引用: 2]

Little is known about the regulation of cell fate decisions that lead to the formation of five pairs of mammary placodes in the surface ectoderm of the mouse embryo. We have previously shown that fibroblast growth factor 10 (FGF10) is required for the formation of mammary placodes 1, 2, 3 and 5. Here, we have found that Fgf10 is expressed only in the somites underlying placodes 2 and 3, in gradients across and within these somites. To test whether somitic FGF10 is required for the formation of these two placodes, we analyzed a number of mutants with different perturbations of somitic Fgf10 gradients for the presence of WNT signals and ectodermal multilayering, markers for mammary line and placode formation. The mammary line is displaced dorsally, and formation of placode 3 is impaired in Pax3ILZ/ILZ mutants, which do not form ventral somitic buds. Mammary line formation is impaired and placode 3 is absent in Gli3Xt-J/Xt-J and hypomorphic Fgf10 mutants, in which the somitic Fgf10 gradient is shortened dorsally and less overall Fgf10 is expressed, respectively. Recombinant FGF10 rescued mammogenesis in Fgf10(-/-) and Gli3Xt-J/Xt-J flanks. We correlate increasing levels of somitic FGF10 with progressive maturation of the surface ectoderm, and show that full expression of somitic Fgf10, co-regulated by GLI3, is required for the anteroposterior pattern in which the flank ectoderm acquires a mammary epithelial identity. We propose that the intra-somitic Fgf10 gradient, together with ventral elongation of the somites, determines the correct dorsoventral position of mammary epithelium along the flank.
URLPMID:11782400 [本文引用: 1]

The mouse develops five pairs of mammary glands that arise during mid-gestation from five pairs of placodes of ectodermal origin. We have investigated the molecular mechanisms of mammary placode development using Lef1 as a marker for the epithelial component of the placode, and mice deficient for Fgf10 or Fgfr2b, both of which fail to develop normal mammary glands. Mammary placode induction involves two different signaling pathways, a FGF10/FGFR2b-dependent pathway for placodes 1, 2, 3 and 5 and a FGF10/FGFR2b-independent pathway for placode 4. Our results also suggest that FGF signaling is involved in the maintenance of mammary bud 4, and that Fgf10 deficient epithelium can undergo branching morphogenesis into the mammary fat pad precursor.
URLPMID:16140987 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract The mouse scaramanga (ska) mutation impairs mammary gland development such that both abrogation and stimulation of gland formation occurs. We used positional cloning to narrow the interval containing scaramanga (ska) to a 75.6-kb interval containing the distal part of the Neuregulin3 (Nrg3) gene. Within this region the only sequence difference between ska and wild-type mice is in a microsatellite repeat within intron 7. This alteration correlates with variations in Nrg3 expression profiles both at the whole embryo level and locally in the presumptive mammary region in ska mice. Localized expression of Nrg3 and its receptor, Erbb4, in the presumptive mammary region around the future bud site prior to morphological appearance of buds and the expression of bud epithelial markers further support an inductive role. Finally, Neuregulin3 (Nrg3)-soaked beads can induce expression of the early bud marker Lef1 in mouse embryo explant cultures, and epithelial bud formation can be observed histologically, suggesting that initiation of mammary bud development occurs. Taken together, these results indicate that a Neuregulin signaling pathway is involved in specification of mammary gland morphogenesis and support the long-held view that mesenchymal signal(s) are responsible for mammary gland inductive/initiating events.
URLPMID:16581056 [本文引用: 1]

Mammary alveoli are composed of luminal (secretory) and basal (myoepithelial) cells, which are descendants of a common stem cell. This study addressed the role of RBP-J-dependent Notch signaling in the formation, maintenance and cellular composition of alveoli during pregnancy. For this purpose, the genes encoding RBP-J, the shared transcriptional mediator of Notch receptors, and Pofut1, a fucosyltransferase required for the activity of Notch receptors, were deleted in mammary progenitor cells in the mouse using Cre-mediated recombination. Loss of RBP-J and Pofut1 led to an accumulation of basal cell clusters characterized by the presence of cytokeratins (K5) and K14 and smooth muscle actin (SMA) during pregnancy. Hormonal stimulation of mutant tissue induced the expression of the basal cell transcription factor p63 in luminal cells and excessive proliferation of basal cells. A transient enrichment of K6-positive luminal cells was observed upon hormonal treatment suggesting a temporary arrest at an immature stage prior to transdifferentiation and expansion as basal cells. Despite the extensive proliferation of RBP-J-null basal cells during pregnancy, hormonal withdrawal during involution resulted in complete remodeling and the restoration of normal tissue architecture. We propose that the Notch-RBP-J pathway regulates alveolar development during pregnancy by maintaining luminal cell fate and preventing uncontrolled basal cell proliferation.
URLPMID:17662267 [本文引用: 1]

P190-B RhoGAP (p190-B, also known as ARHGAP5) has been shown to play an essential role in invasion of the terminal end buds (TEBs) into the surrounding fat pad during mammary gland ductal morphogenesis. Here we report that embryos with a homozygous p190-B gene deletion exhibit major defects in embryonic mammary bud development. Overall, p190-B-deficient buds were smaller in size, contained fewer cells, and displayed characteristics of impaired mesenchymal proliferation and differentiation. Consistent with the reported effects of p190-B deletion on IGF-1R signaling, IGF-1R-deficient embryos also displayed a similar small mammary bud phenotype. However, unlike the p190-B-deficient embryos, the IGF-1R-deficient embryos exhibited decreased epithelial proliferation and did not display mesenchymal defects. Because both IGF and p190-B signaling affect IRS-1/2, we examined IRS-1/2 double knockout embryonic mammary buds. These embryos displayed major defects similar to the p190-B-deficient embryos including smaller bud size. Importantly, like the p190-B-deficient buds, proliferation of the IRS-1/2-deficient mesenchyme was impaired. These results indicate that IGF signaling through p190-B and IRS proteins is critical for mammary bud formation and ensuing epithelial鈥搈esenchymal interactions necessary to sustain mammary bud morphogenesis.
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

通过对正常乳头,翻乳头,副乳头及其乳房的组织样本进行解剖学观察,对照,发现正常乳头由乳基,乳头本组成;翻乳头由乳基,不明显的乳头体组成;副乳头只有小突起。对各类乳腺做成切片观察,对照,发现正常乳头和翻乳头均有完整的乳腺,乳管,副乳头的乳腺,乳管不发达,且很稀少。
URLMagsci [本文引用: 1]

通过对正常乳头,翻乳头,副乳头及其乳房的组织样本进行解剖学观察,对照,发现正常乳头由乳基,乳头本组成;翻乳头由乳基,不明显的乳头体组成;副乳头只有小突起。对各类乳腺做成切片观察,对照,发现正常乳头和翻乳头均有完整的乳腺,乳管,副乳头的乳腺,乳管不发达,且很稀少。
URLPMID:23297487 [本文引用: 2]

AbstractIn domestic pig, the number and location of nipples is considered a single quantitative trait, which has a complex spatial structure that includes bilaterality and a linear sequence of repetitive elements. According to this hypothesis, six inadherent biallelic loci are sufficient for a variety of traits observed in domestic pig populations. Verification of representative samplings from five domestic pig populations of different origin (about 20 000 individuals) confirmed the theses of the hypothesis, which allows considering it as a model of the studied bilateral trait. Using the model, the intraclass pheno- and genotypic diversity was examined and the relationship of the trait manifestation asymmetry with heterozygosity of loci that control it was shown.
URLPMID:15241457 [本文引用: 1]

In the framework of Wright's view of evolution, long-separate breeds of domestic animals could establish different adaptive epistatic genetic complexes that could be destroyed in crossbred animals by recombination. The objective of this study was to evaluate heterosis and recombination effects in a crossing experiment involving two distinct European and Asian breeds (Iberian and Jiaxing) in the F1 and two successive backcrosses to the Iberian line. Teat number (TN) was recorded in the right and left sides of piglets and analysed by fitting a mixed linear model including the Dickerson's crossbreeding parameters. TN in pigs is a discontinuous and often canalised trait presenting bilateral symmetry. The minor differences between sides make this trait a good candidate to evaluate fluctuating asymmetry (FA) and developmental instability. For TN, the posterior means and standard deviations (SD) of the heritability and of the relative contribution of common litter environmental effect to variance were 0.248 (0.028) and 0.057 (0.019), respectively. The respective values of the difference between breeds, heterosis and recombination effect were 9.990 (0.411), -0.506 (0.196) and 0.684 (0.232). For FA, the posterior means and SDs of the heritability and of the relative contribution of common litter environmental effect to variance were 0.023 (0.005) and 0.014 (0.005), respectively. Another significant genetic effect was a recombination effect of 0.773 (0.117). These results confirm that the rupture by recombination of coadapted genomes decreases developmental stability in domestic pigs.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:11048919 [本文引用: 1]

A search for genomic regions affecting birth characters and accretion of weight and backfat was conducted in a Meishan-White Composite reciprocal backcross resource population. Birth traits analyzed (n = 750) were vigor score, number of nipples, and birth weight. Subsequent measures on gilts and barrows (n = 706) analyzed were weaning weight, 8-wk weight, ADG from 8 to 18 wk of age, ADG from 18 to 26 wk of age, 26-wk weight, and backfat over the first rib, last rib, and last lumbar vertebrae at 14 and 26 (n = 599) wk of age. Feed intake and growth of 92 individually penned barrows were also analyzed. A genomic scan was conducted with microsatellite markers spaced at approximately 20-cM intervals, a least squares regression interval analysis was implemented, and significance values were converted to genomewide levels. No associations were detected for traits measured at birth except for number of nipples, where one significant and two suggestive regions were identified on chromosomes (SSC) 10, 1, and 3, respectively. Early growth was affected by a region on SSC 1 as evidenced by associations with weights collected at weaning and 8 wk of age and ADG from 8 to 18 wk of age. Other regions detected for early growth rate were on SSC 2, 12, and X. Chromosomal regions on SSC 6 and 7 affected ADG from 18 to 26 wk of age. All measures of backfat were affected by regions on SSC 1 and X, whereas SSC 7 consistently affected backfat measures recorded at 26 wk of age. Suggestive evidence for QTL affecting backfat at 14 wk of age was also detected on SSC 2, 6, 8, and 9. These results have improved our knowledge about the genetics of growth rate and fat accretion at the molecular level in swine.
URL [本文引用: 1]

Summary Three informative pig F 2 families based on European Wild Boar (W), Meishan (M) and Pietrain (P) crosses have been used for genome-wide linkage and quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis. Altogether 129 microsatellites, 56 type I loci and 46 trait definitions (specific to growth, fattening, fat deposition, muscling, meat quality, stress resistance and body conformation) were included in the study. In the linkage maps of M P, W P and W M families, average spacing of markers were 18.4, 19.7 and 18.8cM, the numbers of informative meioses were 582, 534 and 625, and the total lengths of autosomes measured were 27.3, 26.0 and 26.2Morgan units, respectively. Maternal maps were on average 1.3 times longer than paternal maps. QTLs contributing more than 3% of F 2 phenotypic variance could be identified at p<0.05 chromosome-wide level. Differences in the numbers and positions of QTLs were observed between families. Genome-wide significant QTL effects were mapped for growth and fattening traits on eight chromosomes (1, 2, 4, 13, 14, 17, 18 and X), for fat deposition traits on seven chromosomes (1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7 and X), for muscling traits on 11 chromosomes (1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 12, 14, 15 and X), for meat quality and stress resistance traits on seven chromosomes (2, 3, 6, 13, 16, 18 and X), and QTLs for body-conformation traits were detected on 14 chromosomes. Closely correlated traits showed similar QTL profiles within families. Major QTL effects for meat quality and stress resistance traits were found on SSC6 in the interval RYR1-A1BG in the W脳P and M脳P families, and could be attributed to segregation of the RYR1 allele T derived from Pietrain, whereas no effect in the corresponding SSC6 interval was found in family W M, where Wild Boar and Meishan both contributed the RYR1 allele C. QTL positions were mostly similar in two of the three families for body conformation traits and for growth, fattening, fat deposition and muscling traits, especially on SSC4 (interval SW1073-NGFB ). QTLs with large effects were also mapped on SSC7 in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) (interval CYP21A2-S0102 ) and affected body length, weight of head and many other traits. The identification of DNA variants in genes causative for the QTLs requires further fine mapping of QTL intervals and a positional cloning. However, for these subsequent steps, the genome-wide QTL mapping in F 2 families represents an essential starting point and is therefore significant for animal breeding.
URLPMID:2672953 [本文引用: 1]

Background Teat number is an important fertility trait for pig production, reflecting the mothering ability of sows. It is also a discrete and often canalized trait presenting bilateral symmetry with minor differences between the two sides, providing a potential power to evaluate fluctuating asymmetry and developmental instability. The knowledge of its genetic control is still limited. In this study, a genome-wide scan was performed with 183 microsatellites covering the pig genome to identify quantitative trait loci (QTL) for three traits related to teat number including the total teat number (TTN), the teat number at the left (LTN) and right (RTN) sides in a large scale White Duroc ?? Erhualian resource population. Results A sex-average linkage map with a total length of 2350.3 cM and an average marker interval of 12.84 cM was constructed. Eleven genome-wide significant QTL for TTN were detected on 8 autosomes including pig chromosomes (SSC) 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 12. Six suggestive QTL for this trait were detected on SSC6, 9, 13, 14 and 16. Eight chromosomal regions each on SSC1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 12 showed significant associations with LTN. These regions were also evidenced as significant QTL for RTN except for those on SSC6 and SSC8. The most significant QTL for the 3 traits were all located on SSC7. Erhualian alleles at most of the identified QTL had positive additive effects except for three QTL on SSC1 and SSC7, at which White Duroc alleles increased teat numbers. On SSC1, 6, 9, 13 and 16, significant dominance effects were observed on TTN, and predominant imprinting effect on TTN was only detected on SSC12. Conclusion The results not only confirmed the QTL regions from previous experiments, but also identified five new QTL for the total teat number in swine. Minor differences between the QTL regions responsible for LTN and RTN were validated. Further fine mapping should be focused on consistently identified regions with small confidence intervals, such as those on SSC1, SSC7 and SSC12.
URLPMID:25158056 [本文引用: 1]

Dominance has been suggested as one of the genetic mechanisms explaining heterosis. However, using traditional quantitative genetic methods it is difficult to obtain accurate estimates of dominance effects. With the availability of dense SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) panels, we now have new opportunities for the detection and use of dominance at individual loci. Thus, the aim of this study was to detect additive and dominance effects on number of teats (NT), specifically to investigate the importance of dominance in a Landrace-based population of pigs. In total, 1,550 animals, genotyped for 32,911 SNPs, were used in single SNP analysis. SNPs with a significant genetic effect were tested for their mode of gene action being additive, dominant or a combination. In total, 21 SNPs were associated with NT, located in three regions with additive (SSC6, 7 and 12) and one region with dominant effects (SSC4). Estimates of additive effects ranged from 0.24 to 0.29 teats. The dominance effect of the QTL located on SSC4 was negative (0.26 teats). The additive variance of the four QTLs together explained 7.37% of the total phenotypic variance. The dominance variance of the four QTLs together explained 1.82% of the total phenotypic variance, which corresponds to one-fourth of the variance explained by additive effects. The results suggest that dominance effects play a relevant role in the genetic architecture of NT. The QTL region on SSC7 contains the most promising candidate gene: VRTN. This gene has been suggested to be related to the number of vertebrae, a trait correlated with NT.
URLPMID:5371258 [本文引用: 1]

The number of teats in pigs is related to a sow’s ability to rear piglets to weaning age. Several studies have identified genes and genomic regions that affect teat number in swine but few common results were reported. The objective of this study was to identify genetic factors that affect teat number in pigs, evaluate the accuracy of genomic prediction, and evaluate the contribution of significant genes and genomic regions to genomic broad-sense heritability and prediction accuracy using 41,108 autosomal single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from genotyping-by-sequencing on 2936 Duroc boars. Narrow-sense heritability and dominance heritability of teat number estimated by genomic restricted maximum likelihood were 0.36502±020.030 and 0.03502±020.019, respectively. The accuracy of genomic predictions, calculated as the average correlation between the genomic best linear unbiased prediction and phenotype in a tenfold validation study, was 0.43702±020.064 for the model with additive and dominance effects and 0.43502±020.064 for the model with additive effects only. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) using three methods of analysis identified 85 significant SNP effects for teat number on chromosomes 1, 6, 7, 10, 11, 12 and 14. The region between 102.9 and 106.002Mb on chromosome 7, which was reported in several studies, had the most significant SNP effects in or near thePTGR2,FAM161B,LIN52,VRTN,FCF1,AREL1andLRRC74Agenes. This region accounted for 10.0% of the genomic additive heritability and 8.0% of the accuracy of prediction. The second most significant chromosome region not reported by previous GWAS was the region between 77.7 and 79.702Mb on chromosome 11, where SNPs in theFGF14gene had the most significant effect and accounted for 5.1% of the genomic additive heritability and 5.2% of the accuracy of prediction. The 85 significant SNPs accounted for 28.502to0228.8% of the genomic additive heritability and 35.802to0236.8% of the accuracy of prediction. The three methods used for the GWAS identified 85 significant SNPs with additive effects on teat number, including SNPs in a previously reported chromosomal region and SNPs in novel chromosomal regions. Most significant SNPs with larger estimated effects also had larger contributions to the total genomic heritability and accuracy of prediction than other SNPs. The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12711-017-0311-8) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
URLPMID:16100052 [本文引用: 1]

Pig chromosome 7 (SSC 7) has been shown to be rich in QTL affecting performance and quality traits. Most studies mapped the QTL close to the swine leukocyte antigens (SLA), which has a large effect on adaptability and natural selection. Previous comparative mapping studies suggested that the 15-cM region limited by markers LRA1 (mapped at 55 cM) and S0102 (mapped at 70 cM) contains hundreds of genes. To decrease the number of candidate genes, we improved the mapping resolution with a genetic chromosome dissection through a backcross recombinant progeny test program between Meishan (MS) and European (EU; i.e., Large White or Landrace) breeds. Three first-generation backcross--(EU x MS) x EU--and two second-generation backcross--([EU x MS] x EU) x EU--sires carrying a recombination in the QTL mapping interval were progeny-tested (i.e., measured for a total of 44 growth, fatness, carcass and meat quality traits). Progeny family size varied from 29 to 119 pigs. Animals were genotyped for markers covering the region of interest. Progeny-test results allowed the QTL interval to be decreased from 15 to 20 cM down to 10 cM, and even less than 6 cM if we assumed that the EU pigs used in this study share only one QTL allele. Except for a putative QTL affecting some carcass composition traits, the SLA is excluded as a candidate region, suggesting that it might be possible to apply a marker-assisted selection strategy for this QTL, while controlling SLA allele diversity. The strong QTL effects remaining in animals with only 12.5% (issued from first-generation backcross boars) and 6.25% (issued from second-generation back-cross boars) Meishan genetic background shows that epistatic interactions are likely to be limited. Finally, the QTL does not have strong effects on meat quality traits.
URLPMID:17032781 [本文引用: 1]

Understanding of the genetic control of female reproductive performance in pigs would offer the opportunity to utilize natural variation and improve selective breeding programs through marker-assisted selection. The Chinese Meishan is one of the most prolific pig breeds known, farrowing 3 to 5 more viable piglets per litter than Western breeds. This difference in prolificacy is attributed to the Meishan's superior prenatal survival. Our study utilized a 3-generation resource population, in which the founder grandparental animals were purebred Meishan and Duroc pigs, in a genome scan for QTL. Grandparent, F1, and F2 animals were genotyped for 180 microsatellite markers. Reproductive traits, including number of corpora lutea (number of animals = 234), number of fetuses per animal (n = 226),
URLPMID:18219525 [本文引用: 2]

The mothering ability of a sow largely depends on the shape and function of the mammary gland. The aim of this study was to identify QTL for the heritable inverted teat defect, a condition characterized by disturbed development of functional teats. A QTL analysis was conducted in a porcine experimental population based on Duroc and Berlin Miniature pigs (DUMI). The significant QTL were confirmed by linkage analysis in commercial pigs according to the affected sib pair design and refined by family-based association test (FBAT). Nonparametric linkage (NPL) analysis revealed five significant and seven suggestive QTL for the inverted teat defect in the porcine experimental population. In commercial dam lines five significant NPL values were detected. QTL regions in overlapping marker intervals or close proximity in both populations were found on SSC3, SSC4, SSC6, and SSC11. SSC6 revealed QTL in both populations at different positions, indicating the segregation of at least two QTL. The results confirm the previously proposed polygenic inheritance of the inverted teat defect and, for the first time, point to genomic regions harboring relevant genes. The investigation revealed variation of the importance of QTL in the various populations due to either differences in allele frequencies and statistical power or differences in the genetic background that modulates the impact of the liability loci on the expression of the disease. The QTL study enabled us to name a number of plausible positional candidate genes. The correspondence of QTL regions for the inverted teat defect and previously mapped QTL for teat number are in line with the etiologic relationship of these traits.
URLPMID:11872322 [本文引用: 1]

The recently discovered protein, leptin, which is secreted by fat cells in response to changes in body weight or energy, has been implicated in regulation of feed intake, energy expenditure and the neuroendocrine axis in rodents and humans. Leptin was first identified as the gene product found deficient in the obese ob/ob mouse. Administration of leptin to ob/ob mice led to improved reproduction as well as reduced feed intake and weight loss. The porcine leptin receptor has been cloned and is a member of the class 1 cytokine family of receptors. Leptin has been implicated in the regulation of immune function and the anorexia associated with disease. The leptin receptor is localized in the brain and pituitary of the pig. The leptin response to acute inflammation is uncoupled from anorexia and is differentially regulated among swine genotypes. In vitro studies demonstrated that the leptin gene is expressed by porcine preadipocytes and leptin gene expression is highly dependent on dexamethasone induced preadipocyte differentiation. Hormonally driven preadipocyte recruitment and subsequent fat cell size may regulate leptin gene expression in the pig. Expression of CCAAT-enhancer binding protein伪 (C/EBP伪) mediates insulin dependent preadipocyte leptin gene expression during lipid accretion. In contrast, insulin independent leptin gene expression may be maintained by C/EBP auto-activation and phosphorylation/dephosphorylation. Adipogenic hormones may increase adipose tissue leptin gene expression in the fetus indirectly by inducing preadipocyte recruitment and subsequent differentiation. Central administration of leptin to pigs suppressed feed intake and stimulated growth hormone (GH) secretion. Serum leptin concentrations increased with age and estradiol-induced leptin mRNA expression in fat was age and weight dependent in prepuberal gilts. This occurred at the time of expected puberty in intact contemporaries and was associated with greater LH secretion. Further work demonstrated that leptin acts directly on pituitary cells to enhance LH and GH secretion, and brain tissue to stimulate gonadotropin releasing hormone secretion. Thus, development of nutritional schemes and (or) gene therapy to manipulate leptin secretion will lead to practical methods of controlling appetite, growth and reproduction in farm animals, thereby increasing efficiency of lean meat production.
URLPMID:17177692 [本文引用: 1]

Summary <p>The associations of leptin ( LEP ) gene polymorphisms C798T, T2411C, T3266G and T3469C with production traits were investigated in a F2 pig population produced by divergent crosses. The statistical model included genotype, sex, batch and genotype by sex interaction as fixed effects and sire as random effect. Polymorphism C798T was associated with variation in total teat number (p02<020.02) and left teat number (p02<020.03), and polymorphism T3469C was associated with weight at 2102days (p02<020.03), 4202days (p02<020.05), 6302days (p02<020.02) and 7702days of age (p02<020.04) as well as feed intake (p02<020.01), average daily gain (p02<020.01), feed conversion (p02<020.01), bacon depth (p02<020.03) and slaughter weight (p02<020.03). Phenotypic associations were also performed by combining T3469C and C798T genotypes. Interaction between C798T genotypes and sex was observed for some traits. LEP genotypes had significant influence on performance traits, and can be considered as potential genetic markers for selection. However, these results have to be validated in commercial herds.</p>
URL [本文引用: 1]

Summary Linkage and QTL maps of chromosome 10 (SSC10) were constructed by genotyping six microsatellite markers in three F families based on Wild Boar (W), Meishan (M) and Pietrain (P) crosses. The linkage maps were similar for the families and in agreement with the published maps. Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs) were found in the M65×65P and W65×65M families, but not in the W65×65P family. In both these families, QTLs for the number of teats were mapped on distal SSC10. Further, QTLs in the W65×65M family affect the weight of head, live weight and carcass weight traits and were mapped proximally on SSC10 near . The QTLs on SSC10 explained up to 6.5% of F phenotypic variance. QTL effects for some traits were overdominant. Except for the weight of head, Wild Boar alleles slightly increased weight traits and, unexpectedly, markedly increased teat numbers in comparison with Meishan alleles. In the M65×65P family, however, teat number was increased by Meishan alleles. Zusammenfassung Kopplungskarten für Chromosom 10 (SSC10), die durch Analyse von sechs Mikrosatelliten-Markern in drei Familien aus Kreuzungen von Wildschwein (W), Meishan (M) und Pietrain (P) erstellt wurden, zeigten eine gute 05bereinstimmung zwischen den Familien sowie mit Literaturergebnissen. Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs) konnten in den Familien M65×65P und W65×65M nachgewiesen werden, nicht jedoch in der Familie W65×65P. In beiden Familien lie08en sich QTLs auf die Zitzenzahl mit 01hnlichen Kartierungsprofilen feststellen. Weitere QTLs in der Familie W65×65M beeinflussten das Kopfgewicht sowie Kriterien von Lebend- und Schlachtgewichten; sie wurden proximal auf SSC10 nahe dem Locus kartiert. Die beobachteten QTLs erkl01ren bis zu 6,5% der ph01notypischen Varianz in der F-Generation. Einige Merkmale wurden durch überdominante QTL-Effekte beeinflusst. Mit Ausnahme des Kopfgewichtes führten die Wildschwein-Allele im Vergleich zu Meishan-Allelen zu etwas h02heren Gewichtsmerkmalen und signifikant vermehrter Zitzenzahl. Demgegenüber wurde in der Familie M65×65P die Zitzenzahl durch Meishan-Allele vergr0208ert.
URL [本文引用: 1]
URLPMID:1586007 [本文引用: 1]

Background The rate of pubertal development and weaning to estrus interval are correlated and affect reproductive efficiency of swine. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) for age of puberty, nipple number and ovulation rate have been identified in Meishan crosses on pig chromosome 10q (SSC10) near the telomere, which is homologous to human chromosome 10p15 and contains an aldo-keto reductase (AKR) gene cluster with at least six family members. AKRs are tissue-specific hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases that interconvert weak steroid hormones to their more potent counterparts and regulate processes involved in development, homeostasis and reproduction. Because of their location in the swine genome and their implication in reproductive physiology, this gene cluster was characterized and evaluated for effects on reproductive traits in swine. Results Screening the porcine CHORI-242 BAC library with a full-length AKR1C4 cDNA identified 7 positive clones and sample sequencing of 5 BAC clones revealed 5 distinct AKR1C genes (AKR1CL2 and AKR1C1 through 4), which mapped to 126???128 cM on SSC10. Using the IMpRH7000rad and IMNpRH212000rad radiation hybrid panels, these 5 genes mapped between microsatellite markers SWR67 and SW2067. Comparison of sequence data with the porcine BAC fingerprint map show that the cluster of genes resides in a 300 kb region. Twelve SNPs were genotyped in gilts observed for age at first estrus and ovulation rate from the F8 and F10 generations of one-quarter Meishan descendants of the USMARC resource population. Age at puberty, nipple number and ovulation rate data were analyzed for association with genotypes by MTDFREML using an animal model. One SNP, a phenylalanine to isoleucine substitution in AKR1C2, was associated with age of puberty (p = 0.07) and possibly ovulation rate (p = 0.102). Two SNP in AKR1C4 were significantly associated with nipple number (p ??? 0.03) and another possibly associated with age at puberty (p = 0.09). Conclusion AKR1C genotypes were associated with nipple number as well as possible effects on age at puberty and ovulation rate. The estimated effects of AKR1C genotypes on these traits suggest that the SNPs are in incomplete linkage disequilibrium with the causal mutations that affect reproductive traits in swine. Further investigations are necessary to identify these mutations and understand how these AKR1C genes affect these important reproductive traits. The nucleotide sequence data reported have been submitted to GenBank and assigned accession numbers [GenBank:DQ474064???DQ474068, GenBank:DQ494488???DQ494490 and GenBank:DQ487182???DQ487184].
URLPMID:4093071 [本文引用: 1]

Based on a quantitative traits locus (QTL) study using a F-2 intercross between Landrace and Korean native pigs, a significant QTL affecting teat numbers in SSC7 was identified. The strong positional candidate gene, TBC1D21, was selected due to its biological function for epithelial mesenchymal cell development. Sequence analysis revealed six single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the TBC1D21 gene. Among these, two SNP markers, one silent mutation (SNP01) for g.13,050A>G and one missense mutation (SNP04) for c.829A>T (S277C), were genotyped and they showed significant associations with teat number traits (p value = 6.38E-05 for SNP01 and p value = 1.06E-07 for SNP04 with total teat numbers). Further functional validation of these SNPs could give valuable information for understanding the teat number variation in pigs.
URLPMID:4150191 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Lymphoid enhancer binding factor 1 (LEF-1) is a member of the T-cell specific factor (TCF) family, which plays a key role in the development of breast endothelial cells. Moreover, LEF-1 gene has been identified as a candidate gene for teat number trait. In the present study, we detected two novel mutations (NC_010450.3:g. 99514A>G, 119846C>T) by DNA sequencing and polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism in exon 4 and intron 9 of LEF-1 in Guanzhong Black, Hanjiang Black, Bamei and Large White pigs. Furthermore, we analyzed the association between the genetic variations with teat number trait in these breeds. The 99514A>G mutation showed an extremely significant statistical relevance between different genotypes and teat number trait in Guanzhong (pT mutation suggested significant association in Guanzhong Black pigs (p = 0.042) and Large White pigs (p = 0.003). The individuals with "AG" or "GG" genotype displayed more teat numbers than those with "AA"; the individuals with "TC" or "CC" genotype showed more teat numbers than those with "TT". Our findings suggested that the 99514A>G and 119846C>T mutations of LEF-1 affected porcine teat number trait and could be used in breeding strategies to accelerate porcine teat number trait improvement of indigenous pigs breeds through molecular marker assisted selection.
URLPMID:4094776 [本文引用: 1]

Background The change from juvenile to mature phase in woody plants is often accompanied by a gradual loss of rooting ability, as well as by reduced microRNA (miR) 156 and increased miR172 expression. Results We characterized the population of miRNAs of Eucalyptus grandis and compared the gradual reduction in miR156 and increase in miR172 expression during development to the loss of rooting ability. Forty known and eight novel miRNAs were discovered and their predicted targets are listed. The expression pattern of nine miRNAs was determined during adventitious root formation in juvenile and mature cuttings. While the expression levels of miR156 and miR172 were inverse in juvenile and mature tissues, no mutual relationship was found between high miR156 expression and rooting ability, or high miR172 expression and loss of rooting ability. This is shown both in E. grandis and in E. brachyphylla, in which explants that underwent rejuvenation in tissue culture conditions were also examined. Conclusions It is suggested that in these Eucalyptus species, there is no correlation between the switch of miR156 with miR172 expression in the stems and the loss of rooting ability.
URLPMID:5240374 [本文引用: 1]

Number of functional teats is an important trait in commercial swine production. As litter size increases, the number of teats must also increase to supply nutrition to all piglets. Therefore, a genome-wide association analysis was conducted to identify genomic regions that affect this trait in a commercial swine population. Genotypic data from the Illumina Porcine SNP60v1 BeadChip were available for 2951 animals with total teat number (TTN) records. A subset of these animals (n02=021828) had number of teats on each side recorded. From this information, the following traits were derived: number of teats on the left (LTN) and right side (RTN), maximum number of teats on a side (MAX), difference between LTN and RTN (L026102R) and absolute value of L026102R (DIF). Bayes C option of GENSEL (version 4.61) and 1-Mb windows were implemented. Identified regions that explained more than 1.5% of the genomic variation were tested in a larger group of animals (n02=025453) to estimate additive genetic effects. Marker heritabilities were highest for TTN (0.233), intermediate for individual side counts (0.08802to020.115) and virtually nil for difference traits (0.002 for L026102R and 0.006 for DIF). Each copy of theVRTNmutant allele increased teat count by 0.35 (TTN), 0.16 (LTN and RTN) and 0.19 (MAX). 15, 18, 13 and 18 one-Mb windows were detected that explained more than 1.0% of the genomic variation for TTN, LTN, RTN, and MAX, respectively. These regions cumulatively accounted for over 50% of the genomic variation of LTN, RTN and MAX, but only 30% of that of TTN.Sus scrofachromosome SSC10:5202Mb was associated with all four count traits, while SSC10:60 and SSC14:5402Mb were associated with three count traits. Thirty-three SNPs accounted for nearly 39% of the additive genetic variation in the validation dataset. No effect of piglet sex or percentage of males in litter was detected, but birth weight was positively correlated with TTN. Teat number is a heritable trait and use of genetic markers would expedite selection progress. Exploiting genetic variation associated with teat counts on each side would enhance selection focused on total teat counts. These results confirm QTL on SSC4, seven and ten and identify a novel QTL on SSC14. The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12711-016-0282-1) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
URLPMID:26781738 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Vertnin (VRTN) variants have been associated with the number of thoracic vertebrae in European pigs, but the association has not been evidenced in Chinese indigenous pigs. In this study, we first performed a genome-wide association study in Chinese Erhualian pigs using one VRTN candidate causative mutation and the Illumina Porcine 60K SNP Beadchips. The VRTN mutation is significantly associated with thoracic vertebral number in this population. We further show that the VRTN mutation has pleiotropic and desirable effects on teat number and carcass (body) length across four diverse populations, including Erhualian, White Duroc rhualian F2 population, Duroc and Landrace pigs. No association was observed between VRTN genotype and growth and fatness traits in these populations. Therefore, testing for the VRTN mutation in pig breeding schemes would not only increase the number of vertebrae and nipples, but also enlarge body size without undesirable effects on growth and fatness traits, consequently improving pork production. Further, by using whole-genome sequence data, we show that the VRTN mutation was possibly introgressed from Chinese pigs into European pigs. Our results provide another example showing that introgressed Chinese genes greatly contributed to the development and production of modern European pig breeds.
URLPMID:19646152 [本文引用: 1]

Summary Parathyroid hormone-like hormone gene ( PTHLH ) and its receptor, parathyroid hormone/ parathyroid hormone-like hormone receptor 1 ( PTHR1 ), play a role in epithelial mesenchymal interactions during growth and differentiation of different tissues and anatomic structures, including teats. Therefore, PTHLH and PTHR1 were evaluated as functional candidate genes for their effects on number and shape of teats in pigs. In particular, focus was on the occurrence and number of inverted teats, the most frequent and economically relevant teat developmental defect in pigs. For this purpose, association and linkage of the PTHLH gene and the PTHR1 gene with inverted teat defect and the total number of teats and inverted teats were studied in an experimental Duroc and Berlin Miniature pig (DUMI) population. Polymorphism C1819T of PTHR1 was significantly associated with inverted teat phenotype (p02=020.014), total number of teats (p02=020.047) and was close to significance with the number of inverted teats (p02=020.078). Polymorphism C375T of PTHLH was close to significance with the inverted teat phenotype (p02=020.122) and showed no significant association with the total number of teats (p02=020.621) and the number of inverted teats (p02=020.256) in the DUMI population. Association analyses were also performed for combined effects of PTHLH and PTHR1 in order to address potential interaction, however, revealed no indication of effects of interaction. The function, position and the association shown here promote PTHR1 as a candidate gene for number of teats and in particular for affection by and number of inverted teats.
URLPMID:21856889 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract The inverted teat defect is characterized by the failure of teats to protrude from the udder surface and has a negative effect on the economic efficiency of pig production. The inverted teat defect is influenced by genetic factors, but the number and identity of relevant genes are unknown. In this study, we compared the mRNA expression of teat tissues from unaffected pigs and affected pigs by using microarrays. Simultaneously, 24,123 probe sets were screened, of which some 15,000 had present calls and were analyzed for differential expression between mesenchymal and epithelial tissue of 3 categories of teats (i.e., normal teats of unaffected and affected animals, and inverted teats of the latter). Differential expression was more pronounced in epithelial than in mesenchymal tissue, and the comparisons among the 3 categories of teats showed that local processes at the side of the affected area as well as processes taking place at the level of the organ contribute to the development of inverted teats. Genes related to biofunctions of cell maintenance, proliferation, differentiation, and replacement; organismal, organ, and tissue development; genetic information and nucleic acid processing; and cell-to-cell signaling and interaction were differentially expressed, depending on the teat phenotype and the status of the animal as affected or unaffected. In particular, genes encoding members of canonical pathways of growth factor signaling were highlighted. Complementary to previous real-time quantitative reverse-transcription PCR experiments showing upregulation of growth factors (epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, vascular endothelial growth factor) and their receptors in the inverted teat, here it is shown that the abundance of transcripts encoding subordinated proteins (acid phosphatase 1, soluble; activating transcription factor 2; casein kinase 2, 伪 1 polypeptide; casein kinase 2, prime polypeptide; actinin, 2; and Homo sapiens growth factor receptor-bound protein 2) within the growth factor signaling pathways are also affected. Tuning of the expression of genes of these pathways balances the differentiation and proliferation of epithelial and mesenchymal teat tissue and finally affects the shape and structure of the teats.
URLPMID:22690698 [本文引用: 1]

The inverted teat defect is the most common disorder of the mammary complex in pigs. It is characterized by the failure of teats to protrude from the udder surface, preventing normal milk flow and thus limiting the rearing capacity and increasing the risk of mastitis. The inverted teat defect is a liability trait with a complex mode of inheritance. We previously identified QTL for inverted teats. As a complementary approach that integrates map-based efforts to identify candidate genes for the inverted teat defect with function-driven expression analysis, application-specific microarrays were constructed that cover 1525 transcripts mapping in QTL regions on pig chromosomes 2, 3, 4, 6 and 11. About 950 transcripts were expressed in epithelial and mesenchymal teat tissue. The expression of three categories of teats was compared: normal teats of both non-affected and affected animals and inverted teats of affected animals. In epithelium and mesenchyme, 62 and 24 genes respectively were significantly differentially expressed (DE). The majority of biofunctions to which a significant number of DE genes were assigned are related to the following: (1) cell maintenance, proliferation, differentiation and replacement; (2) organismal, organ and tissue development; or (3) genetic information and nucleic acid processing. Moreover, the DE genes belong almost exclusively to canonical pathways related to signaling rather than metabolic pathways. This is in line with findings obtained by genome-wide catalogue microarrays. This study adds another piece to the puzzle of the etiology of inverted teats by indicating that causal genetic variation leading to the disorder is likely among the genes encoding for members of the signaling cascades of growth factors.
URLPMID:27117240 [本文引用: 1]

Ectopic breast tissue, which includes both supernumerary breast and aberrant breast tissue, is the most common congenital breast abnormality. Ectopic breast cancers are rare neoplasm, that occur in 0.3-0.6% of all cases of breast cancer. We retrospectively report, accounting a large series of breast abnormalities diagnosed and treated, our clinical experience on the management of the ectopic breast cancer. In two decades, we observed, out of a total of 12,177 subjects undergone to a breast visit, 327 (2.7%) patients with ectopic breast tissue. All patients were classified, in eight classes, according to Kajava classification and assessed by physician examination, ultrasounds, and when appropriate further integrated with fine needle aspiration cytology and mammography. All specimens were submitted to the anatomo-pathologist. The most frequent benign histological diagnosis was fibrocystic disease. A rare granulosa cell tumor was also found in the right anterior thoracic wall. Four malignancies were also diagnosed in four women, an infiltrating lobular cancer in a patient class I, an infiltrating apocrine carcinoma, an infiltrating ductal cancer, and an infiltrating ductal cancer with tubular pattern, occurred in three patients belonging to class IV. Only one recurrence was observed. We recommended an earlier surgical approach for patients with lesions from class I to IV.
URLPMID:26542818 [本文引用: 1]

Abstract Polymastia, or the presence of supranumerary breasts, occurs in 2-6% of the female population, the spectrum of the disorder ranging between a small mole and a fully functional ectopic breast. They are often asymptomatic but require treatment when symptomatic or if they harbour malignancy. We present a case of a 41-year-old woman with an accessory breast in the left inframammary fold, which increased in size over the decade following her first pregnancy, to reach a size almost three times that of her right breast. Preoperative fine-needle aspiration and ultrasound was suggestive of accessory breast tissue, distinct from the left breast. Intraoperatively, a 14脳10脳8 cm accessory breast was found in the inframammary fold, distinct from the left breast and having an accessory nipple areola complex as well. A simple mastectomy was performed with trimming and rotation of the inframammary flap. The patient was happy with the cosmetic outcome. This article also reviews the literature and covers classification of polymastia, diagnostic complexities and challenges associated with surgery. 2015 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
URL [本文引用: 1]
